Editors-in-Chief: Xueqing Yu, Yeguang Chen & Liming Liang
Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Tsinghua University Press
Medicine Advances is an open access general medical journal with a focus on new technologies, new methods and new products in the full life cycle of diseases. This includes development and progression, screening and early warning, diagnosis and classification, treatment and intervention, and prognosis. The journal also covers exploration and innovation in interdisciplinary medical research, including but not limited to new drug development and artificial intelligence applications.
Journal Metrics
- 83%Acceptance rate
- 35 days Submission to first decision
Editor's Choice: Volume 2, Issue 4
Articles
Performance of ResNet‐18 and InceptionResNetV2 in Automated Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy
- 15 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
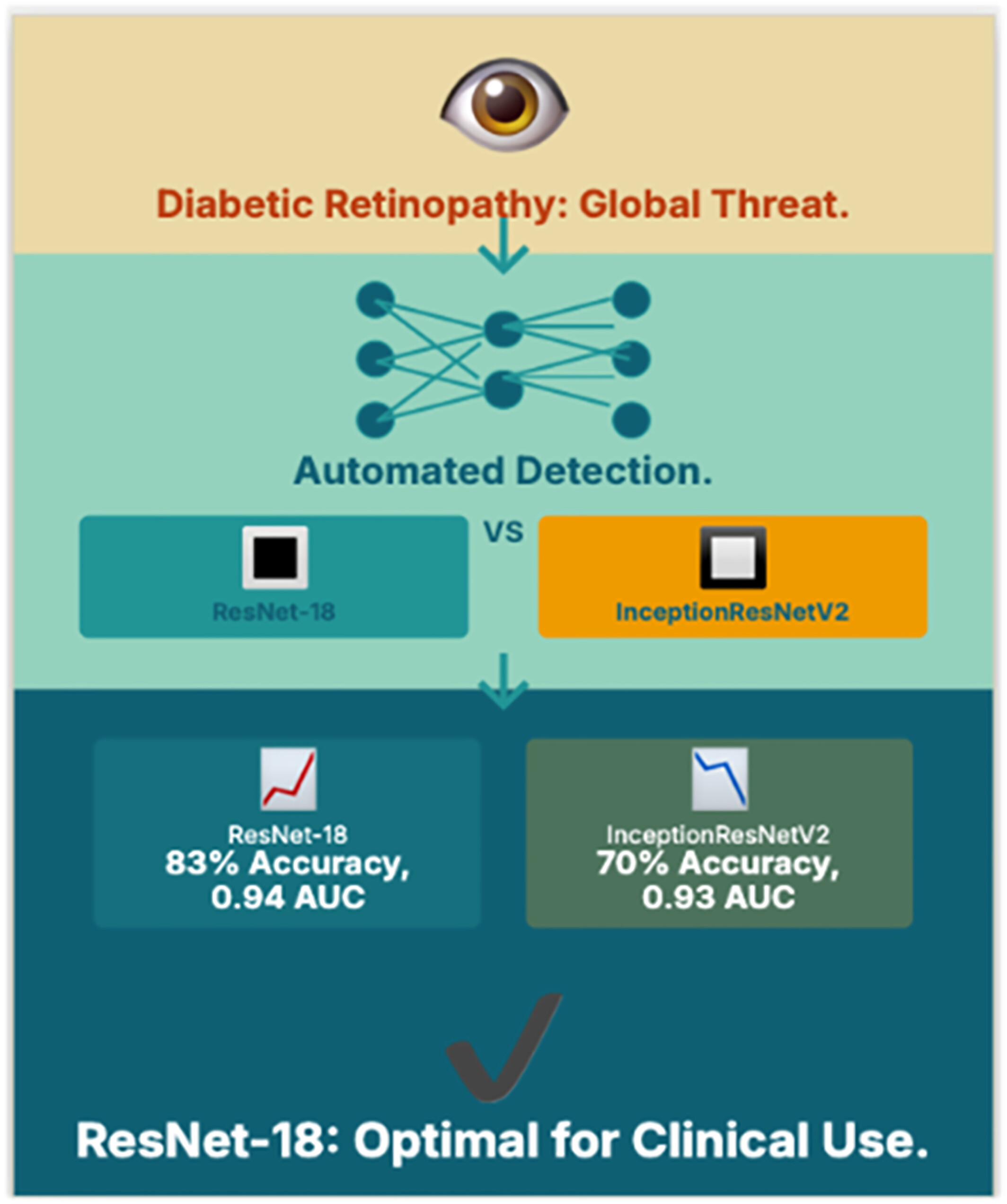
This study compares ResNet-18 and InceptionResNetV2 for automated diabetic retinopathy (DR) classification using retinal fundus images. ResNet-18 achieved a test accuracy of 83% and an AUC of 94.6%, demonstrating robust generalization across all DR stages. In contrast, InceptionResNetV2 attained 70.4% test accuracy and an AUC of 93.05%, with high precision in detecting “No DR” cases but signs of overfitting in “Mild” and “Proliferative DR” classifications, making ResNet-18 a more reliable candidate for clinical deployment.
Psychosocial Challenges After Treatment for Colorectal and Anal Cancer: A Descriptive Study
- 13 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
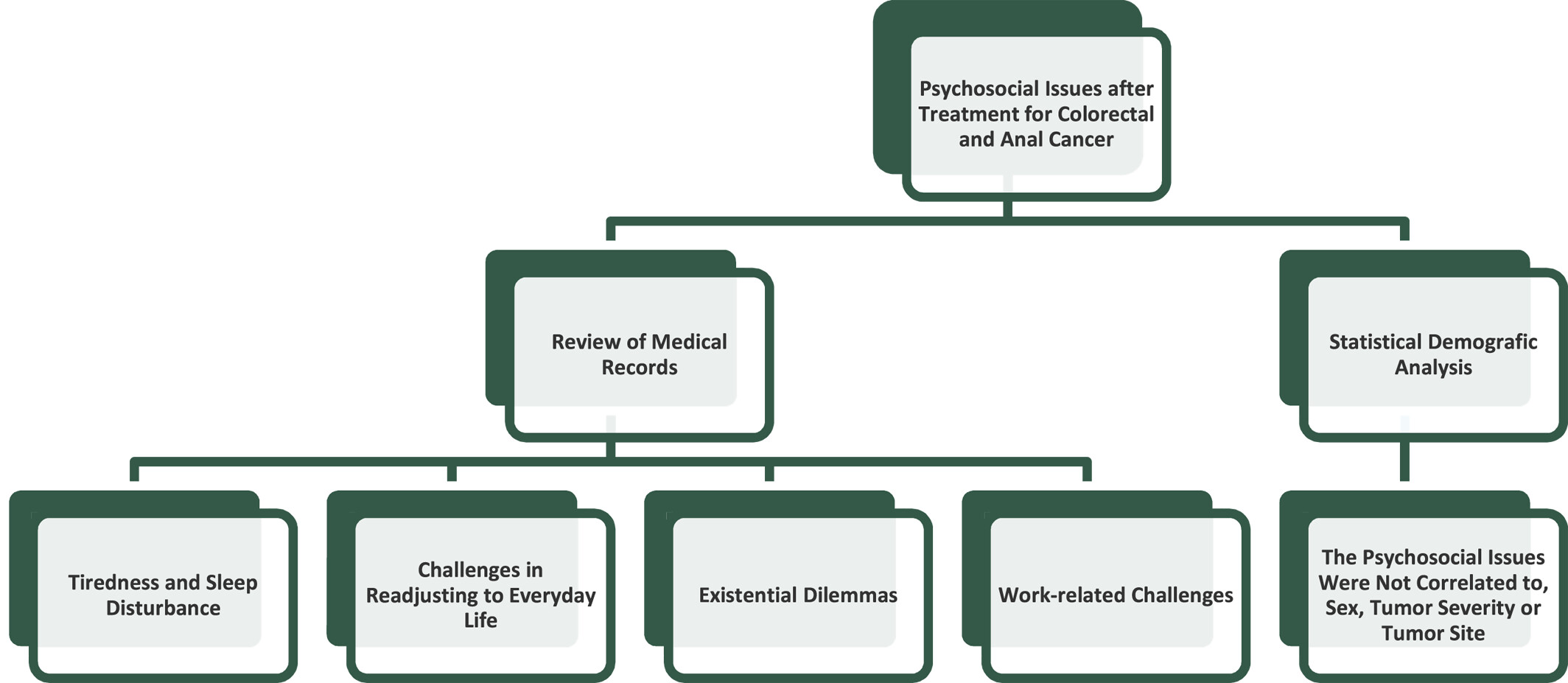
After treatment for colorectal and anal cancer a lot of patients experience psychological distress. This prospective single center observational study aimed to identify these psychosocial problems and examine if patients experiencing psychosocial issues could be correlated to age, gender, or tumor stadium.
Natural Peptides Versus Semaglutide: A Safer Approach to Obesity Management
- 5 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
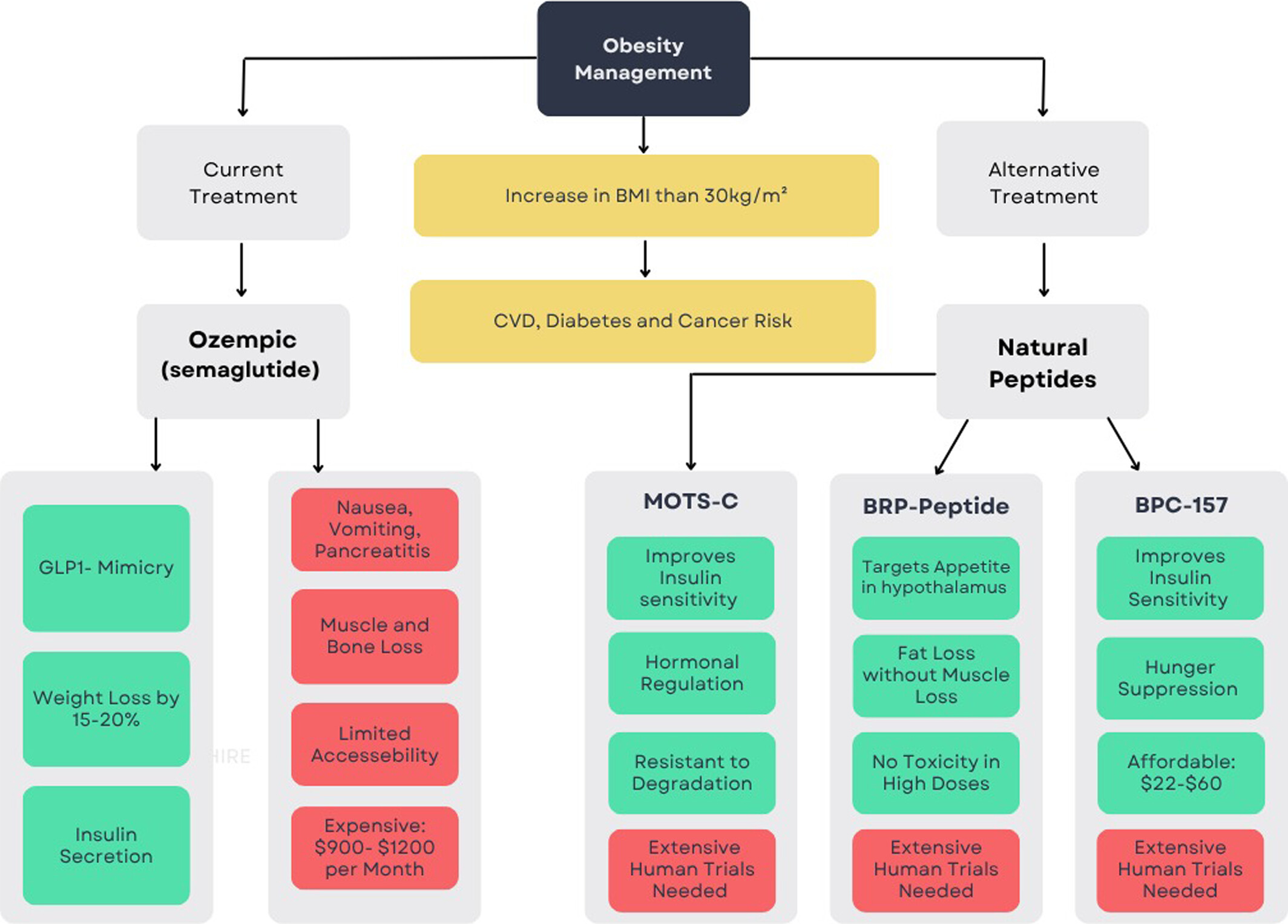
This paper highlights that while semaglutide is effective for weight loss, it is associated with significant side effects, high cost, and muscle loss. In contrast, natural peptides such as BRP, BPC-157, and MOTS-c demonstrate promising anti-obesity effects with fewer adverse outcomes, improved safety profiles, and potential affordability making them attractive candidates for future therapeutic development.
Case Report: Abemaciclib‐Induced Chronic Renal Failure
- 112-115
- 19 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
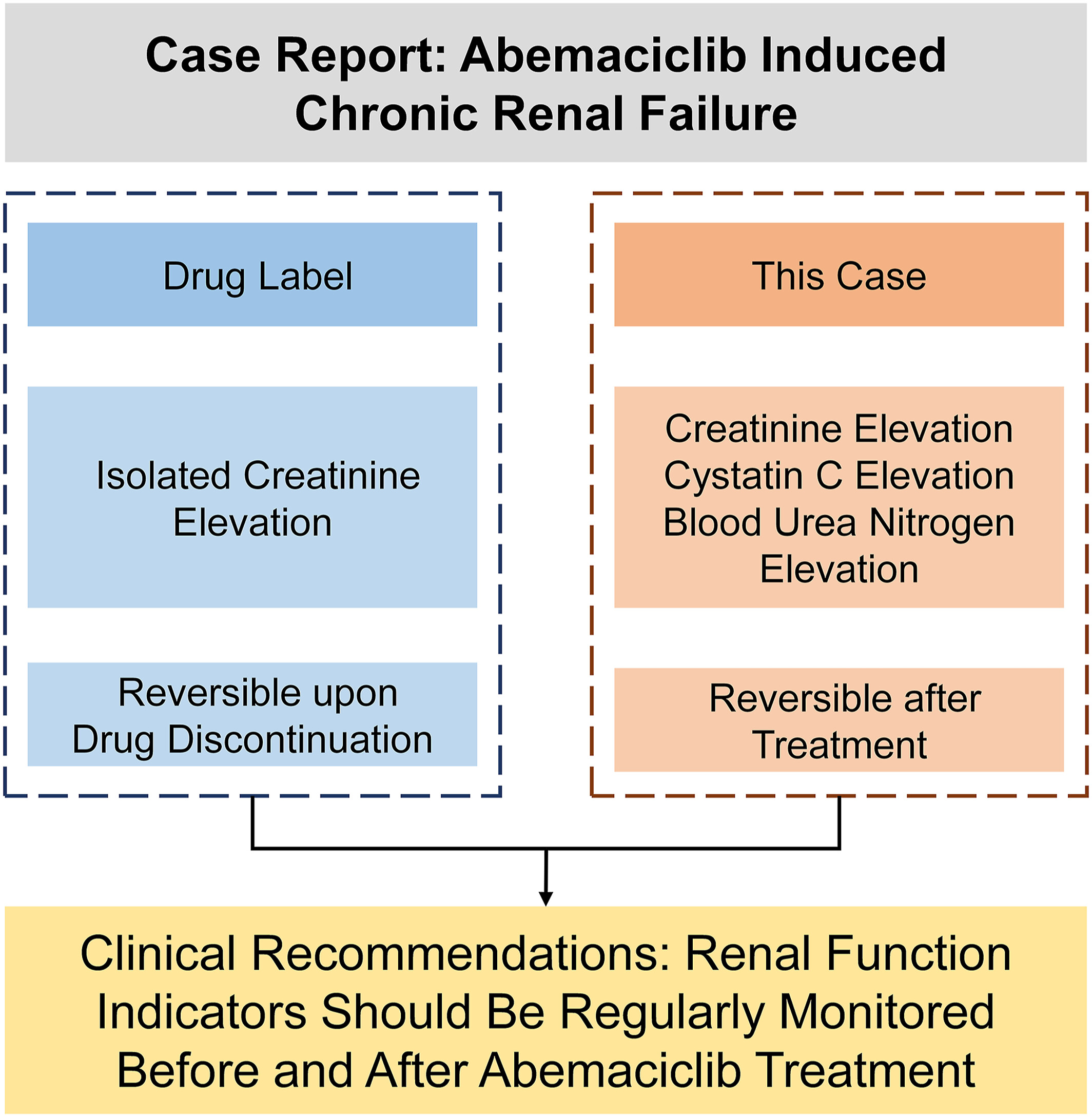
This article reports a case of chronic kidney injury caused by Abemaciclib, which suggests that long-term use of Abemaciclib may lead to kidney damage, potentially progressing to chronic renal failure. It is essential to regularly monitor kidney function indicators before and after treatment. Literature suggests that Abemaciclib may have a dual impact on the kidneys, and regular monitoring of kidney function indicators should be conducted before and after treatment.
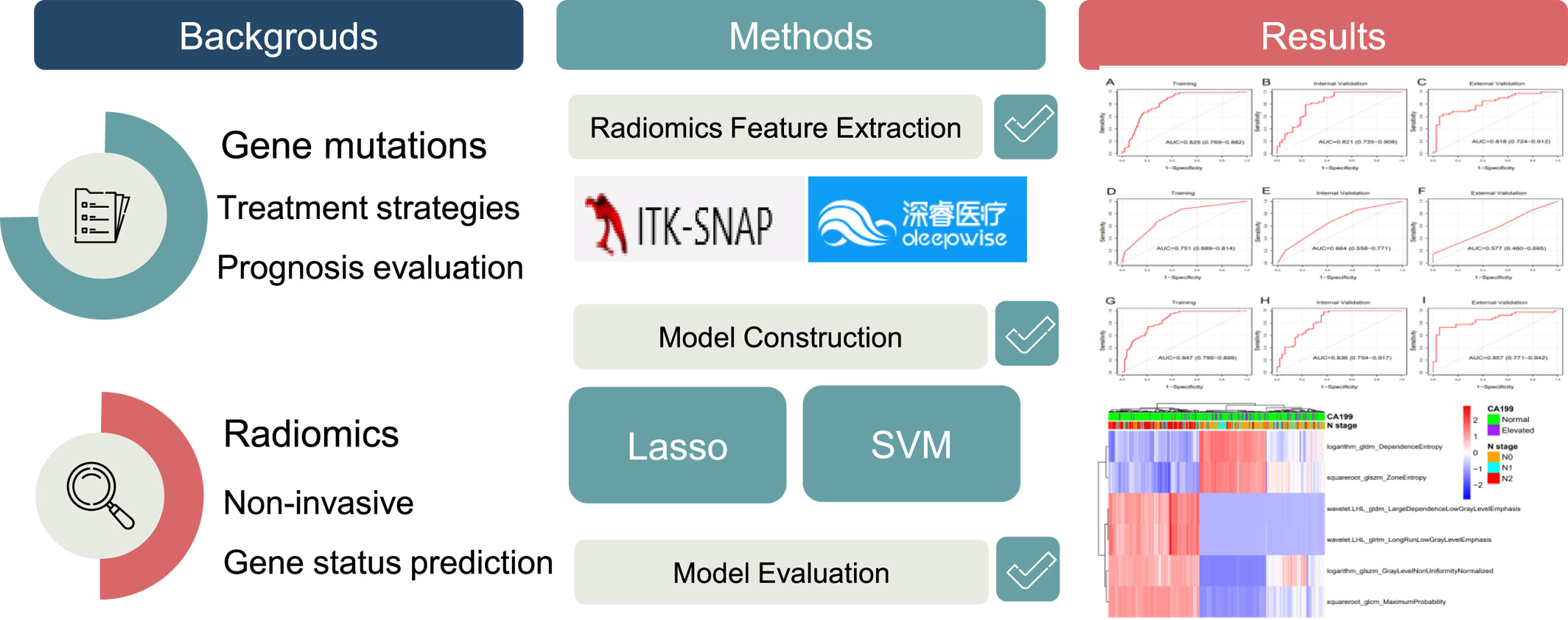
Radiomics‐Based CT Prediction of KRAS/NRAS/BRAF Mutation Status in Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Study
- 18 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
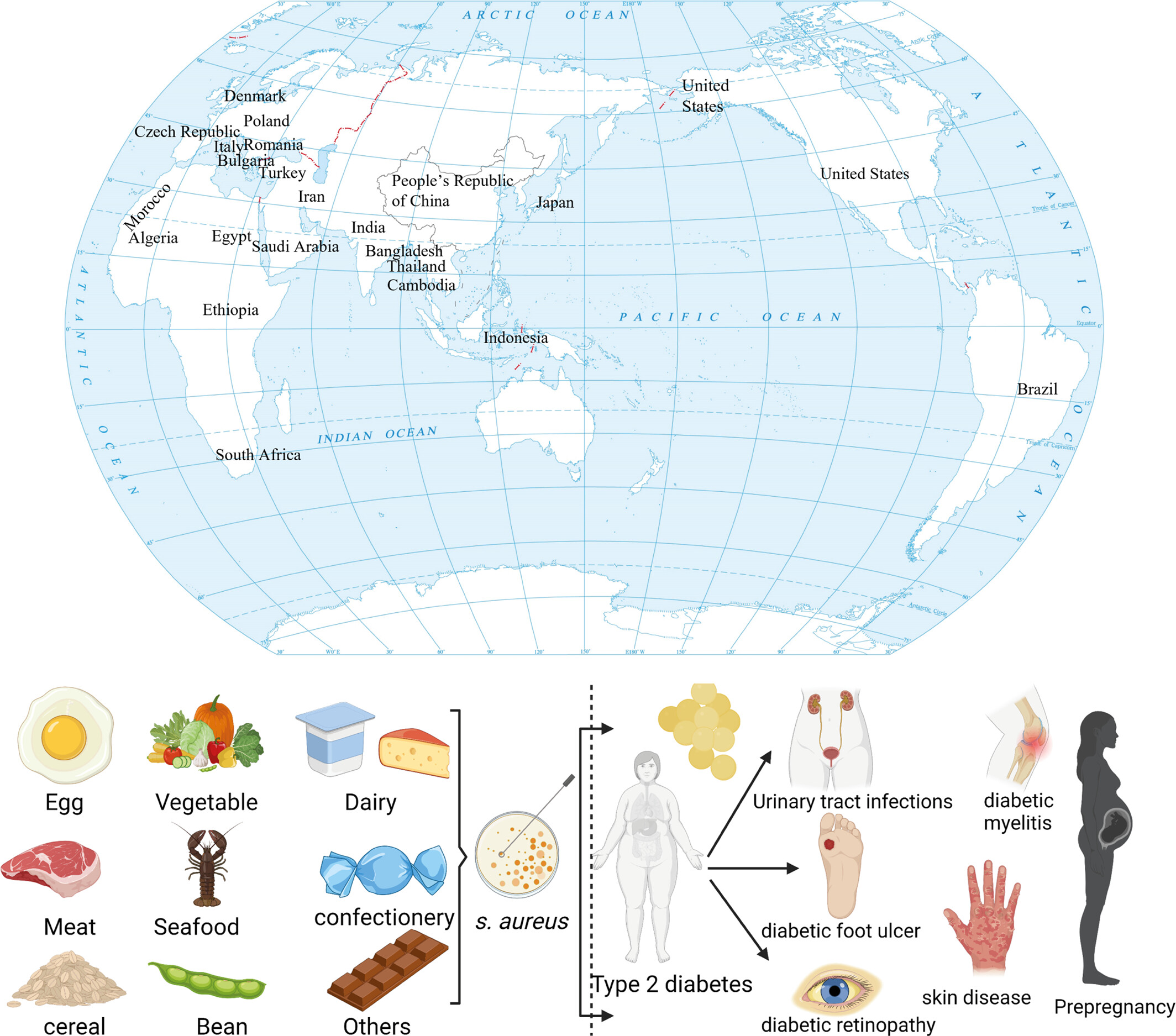
Global prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus in food products and its relationship with the occurrence and development of diabetes mellitus
- 53-78
- 21 March 2023
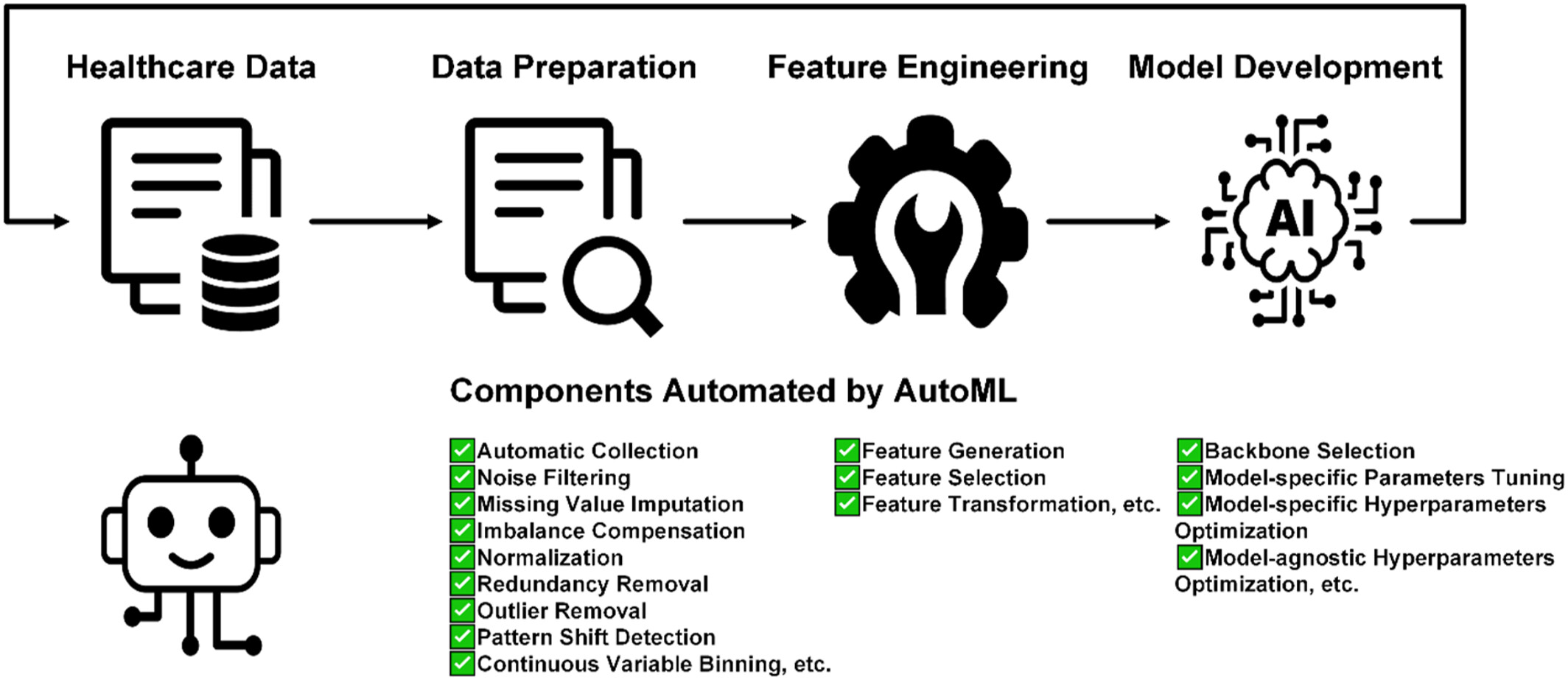
Automated machine learning with interpretation: A systematic review of methodologies and applications in healthcare
- 205-237
- 27 August 2024
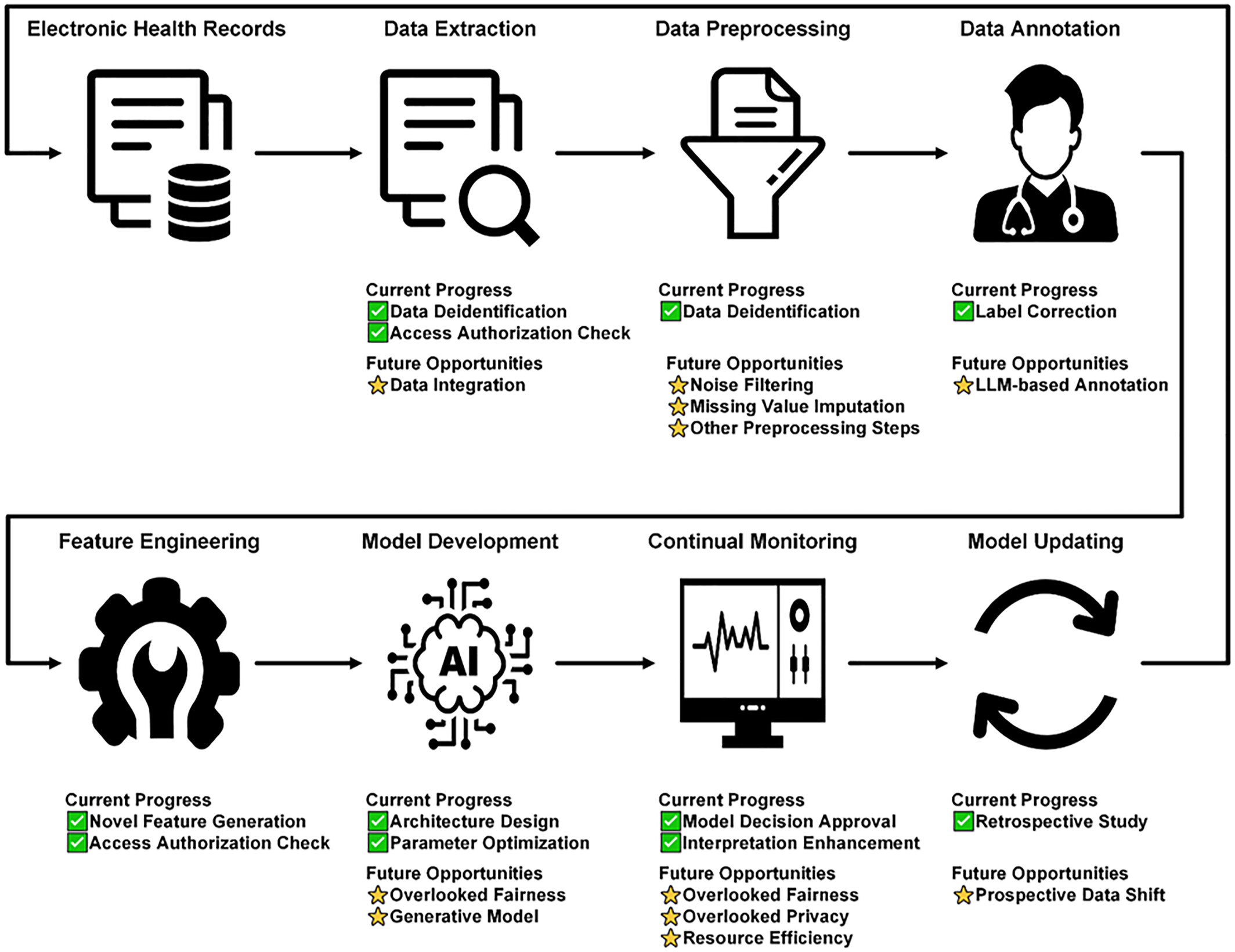
Human‐in‐the‐loop machine learning for healthcare: Current progress and future opportunities in electronic health records
- 318-322
- 23 August 2024
Graphical Abstract
Expert consensus on treatment for stage III non‐small cell lung cancer
- 3-13
- 24 March 2023
Clinical decision making: Evolving from the hypothetico‐deductive model to knowledge‐enhanced machine learning
- 375-379
- 16 December 2024
Graphical Abstract
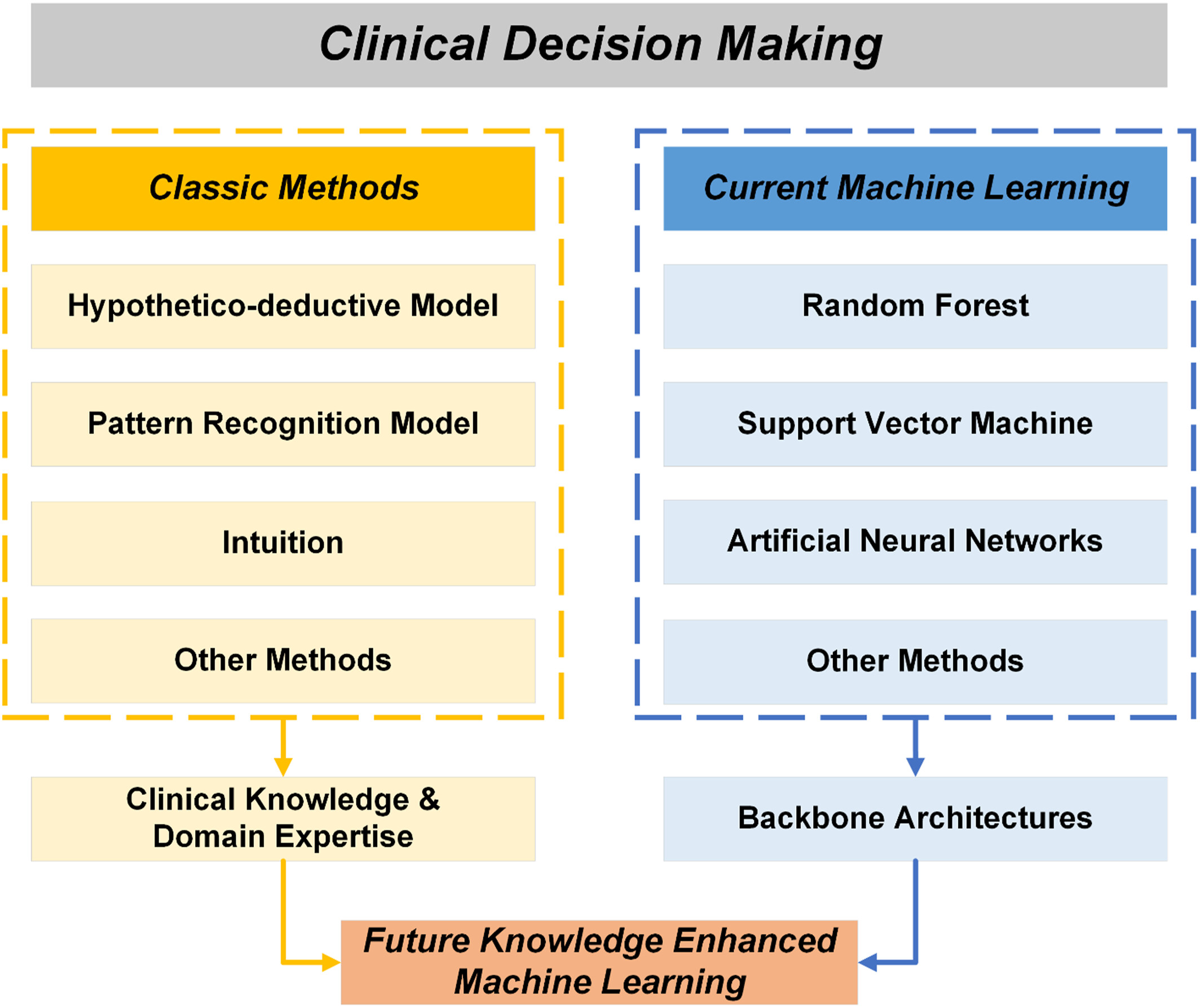
Knowledge-enhanced machine learning can be conceptualized as a fusion of clinical knowledge and domain expertise extracted from traditional clinical decision making methods alongside powerful machine learning architectures. Knowledge-enhanced machine learning significantly improves current machine learning methods in terms of interpretability, generalizability, accuracy, and equity.