Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
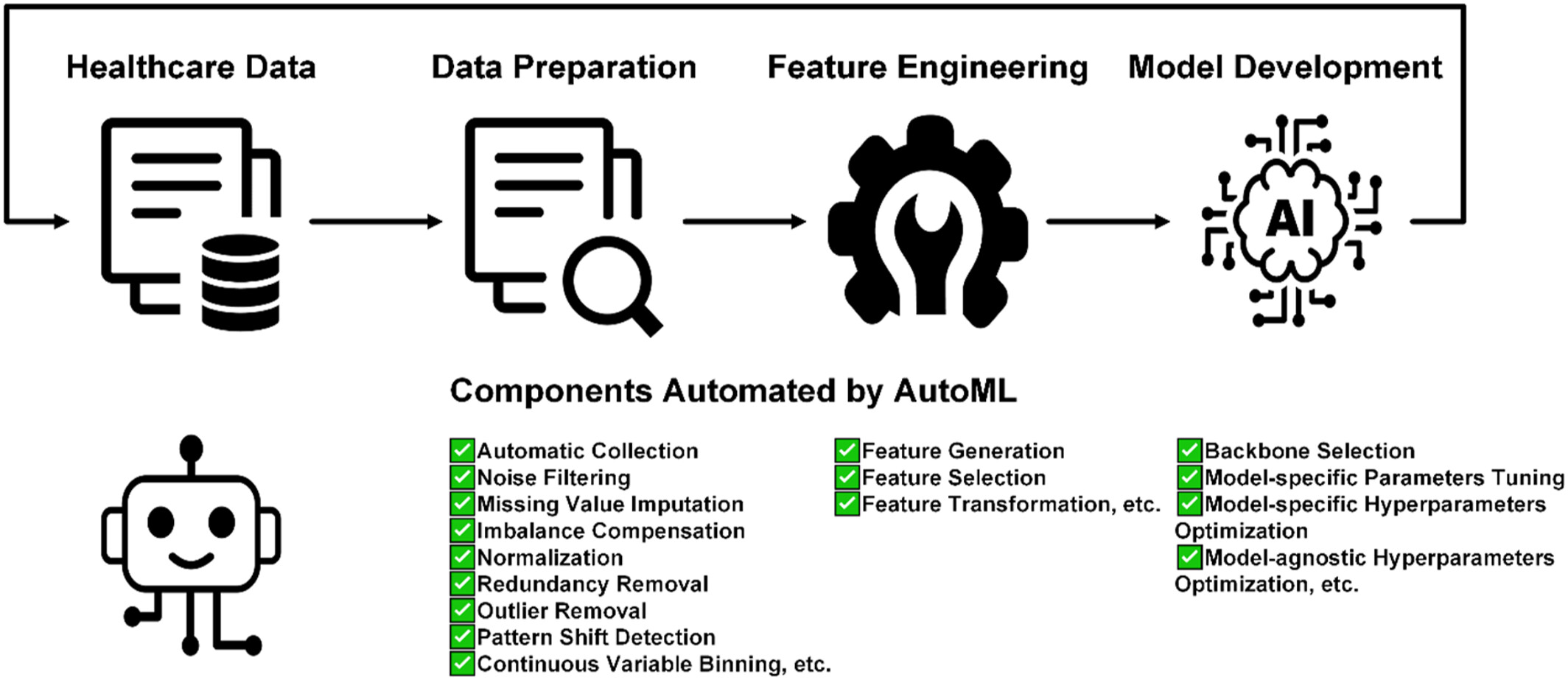
Automated machine learning with interpretation: A systematic review of methodologies and applications in healthcare
- Pages: 205-237
- First Published: 27 August 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Comprehensive analyses of nuclear mitochondria-related genes in the molecular features, immune infiltration, and drug sensitivity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 238-253
- First Published: 04 September 2024
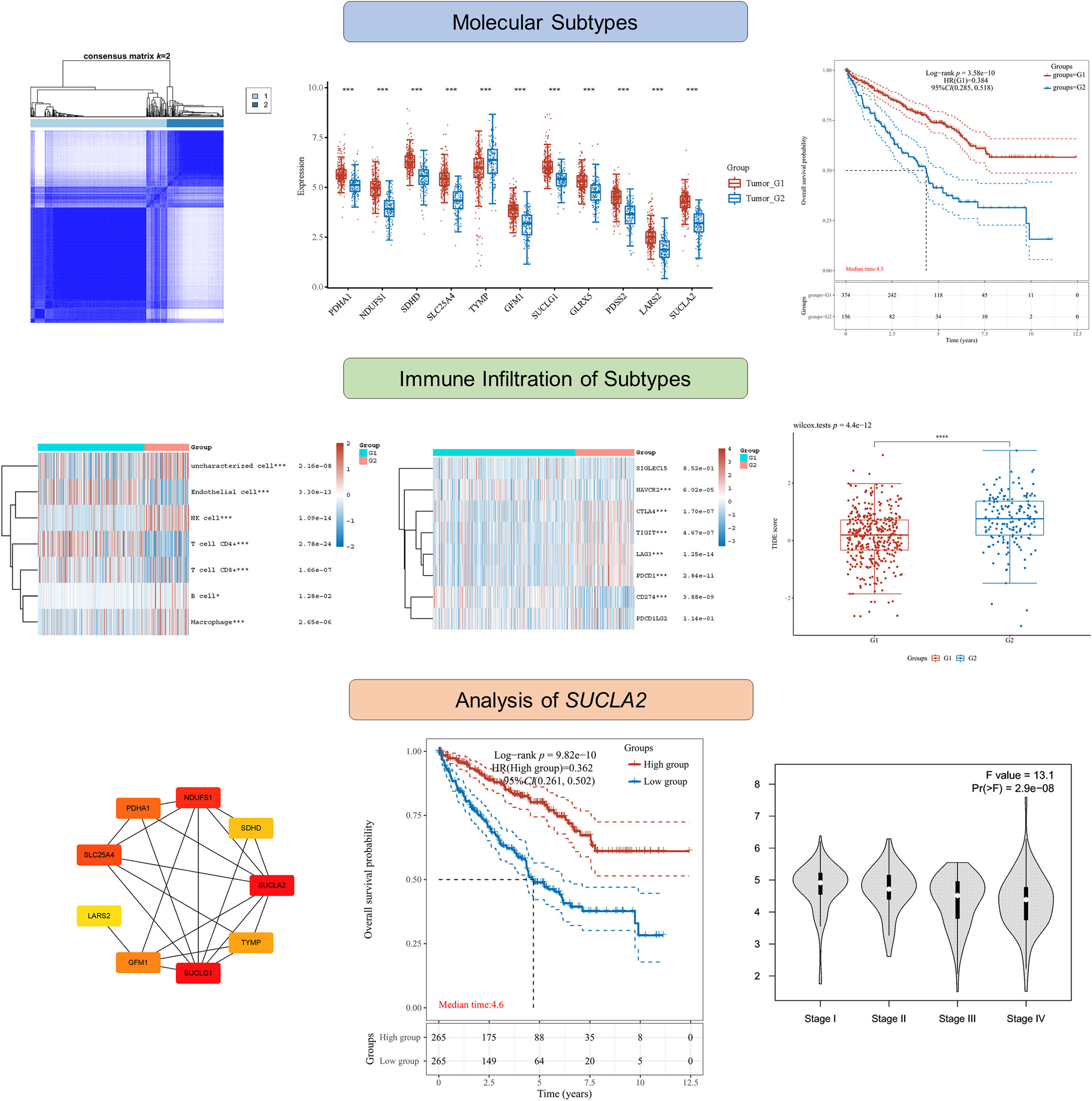
Our work revealed that molecular subtypes based on nuclear mitochondria-related genes (MTRGs) in Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) were related to patient prognosis and immune infiltration levels. Moreover, a critical nuclear MTRG, succinate-CoA ligase ADP-forming subunit beta (SUCLA2), was identified, which potentially represented an important risk factor in ccRCC. In brief, this study provided new insights and guidance for the clinical diagnosis of ccRCC.
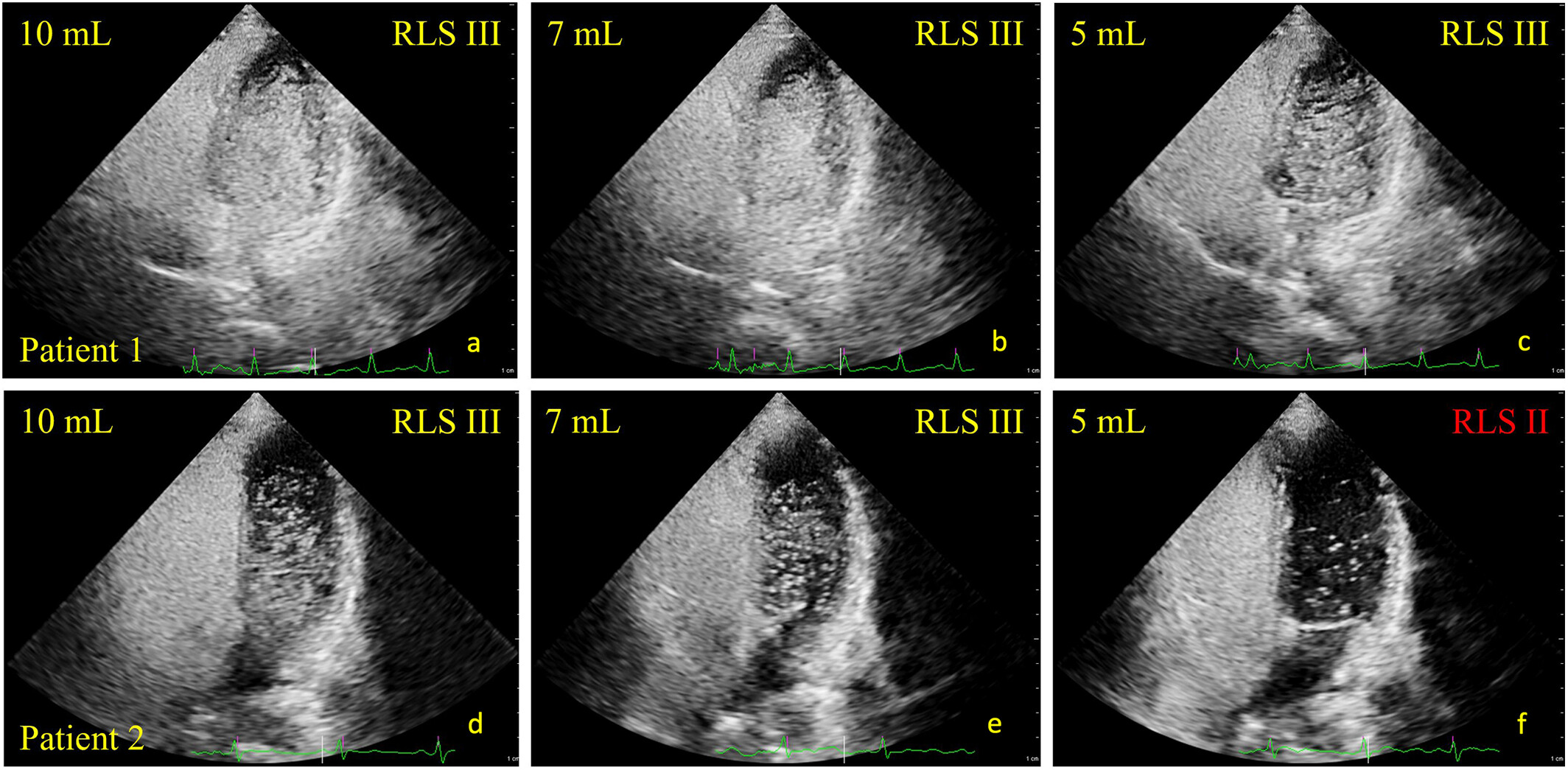
Optimizing agitated saline volume for contrast echocardiography: Balancing diagnostic performance and operator fatigue
- Pages: 254-261
- First Published: 21 August 2024
Internal drivers of the global pandemic of the Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2
- Pages: 262-273
- First Published: 27 August 2024
This study forecasts the transmissibility of specific amino acid mutations that have emerged in the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Through predictive modeling, we identify mutations with high transmission potential. Subsequently, we assess these mutations for conservation and their impact on protein structure and function, isolating those that pose significant risk. Based on the intrinsic properties of these high-risk mutations, we delineate the underlying drivers that have facilitated the global spread of the Omicron variants.
Toward bridging gaps in patient navigation: A study on the adoption of artificial intelligence technologies
- Pages: 274-283
- First Published: 11 September 2024
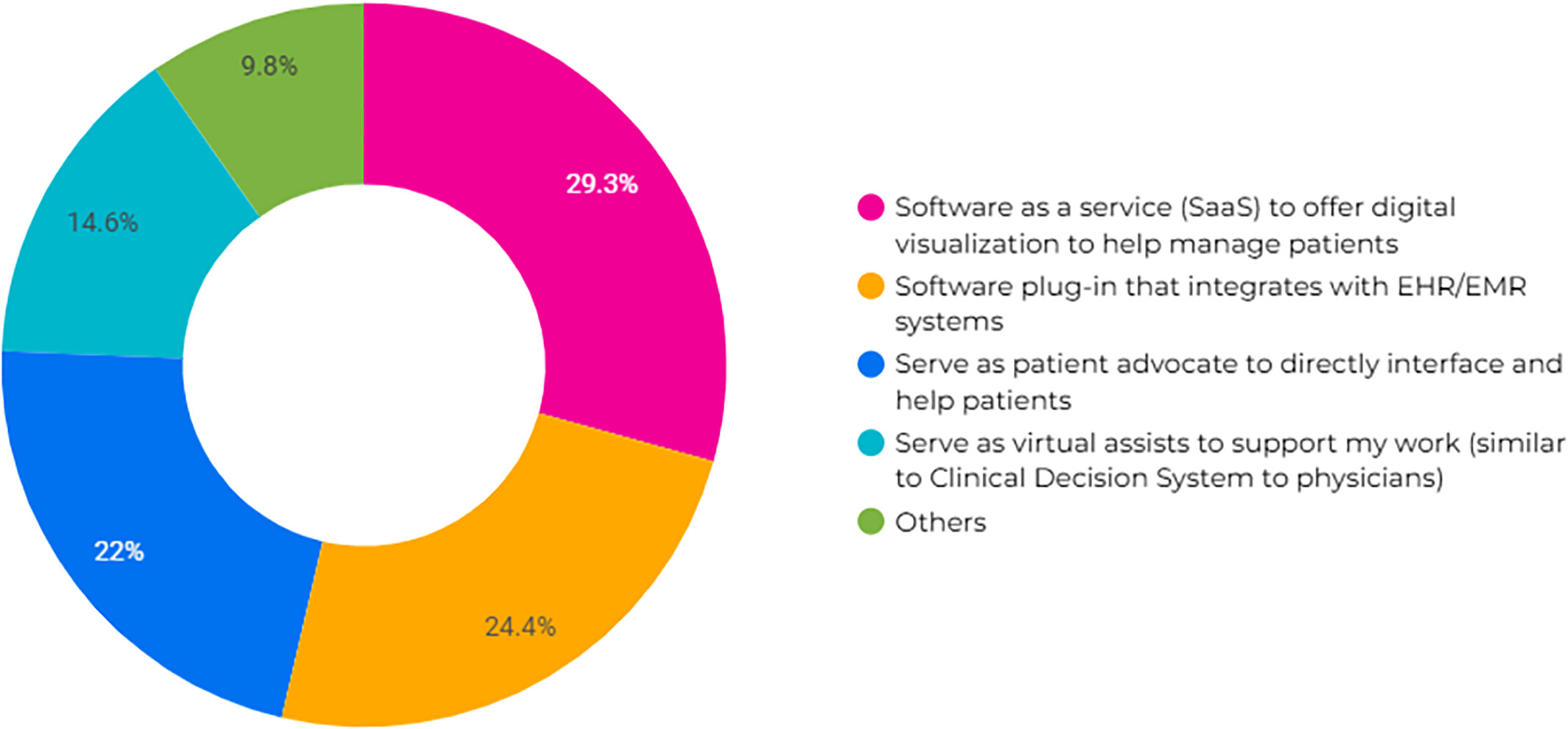
This study investigates the escalated challenges confronting patient navigators following the COVID-19 pandemic and assesses the potential of AI-enhanced tools to alleviate these issues. It uncovers significant gaps in technological support for navigators, who are essential in managing diverse barriers faced by patients. The findings highlight the potential of tailored AI interventions that could significantly boost the capabilities and effectiveness of patient navigators, thereby supporting the long-term sustainability of this service and overall healthcare systems.
Artificial intelligence in orthopaedic education: A comparative analysis of ChatGPT and Bing AI's Orthopaedic In-Training Examination performance
- Pages: 284-290
- First Published: 15 September 2024
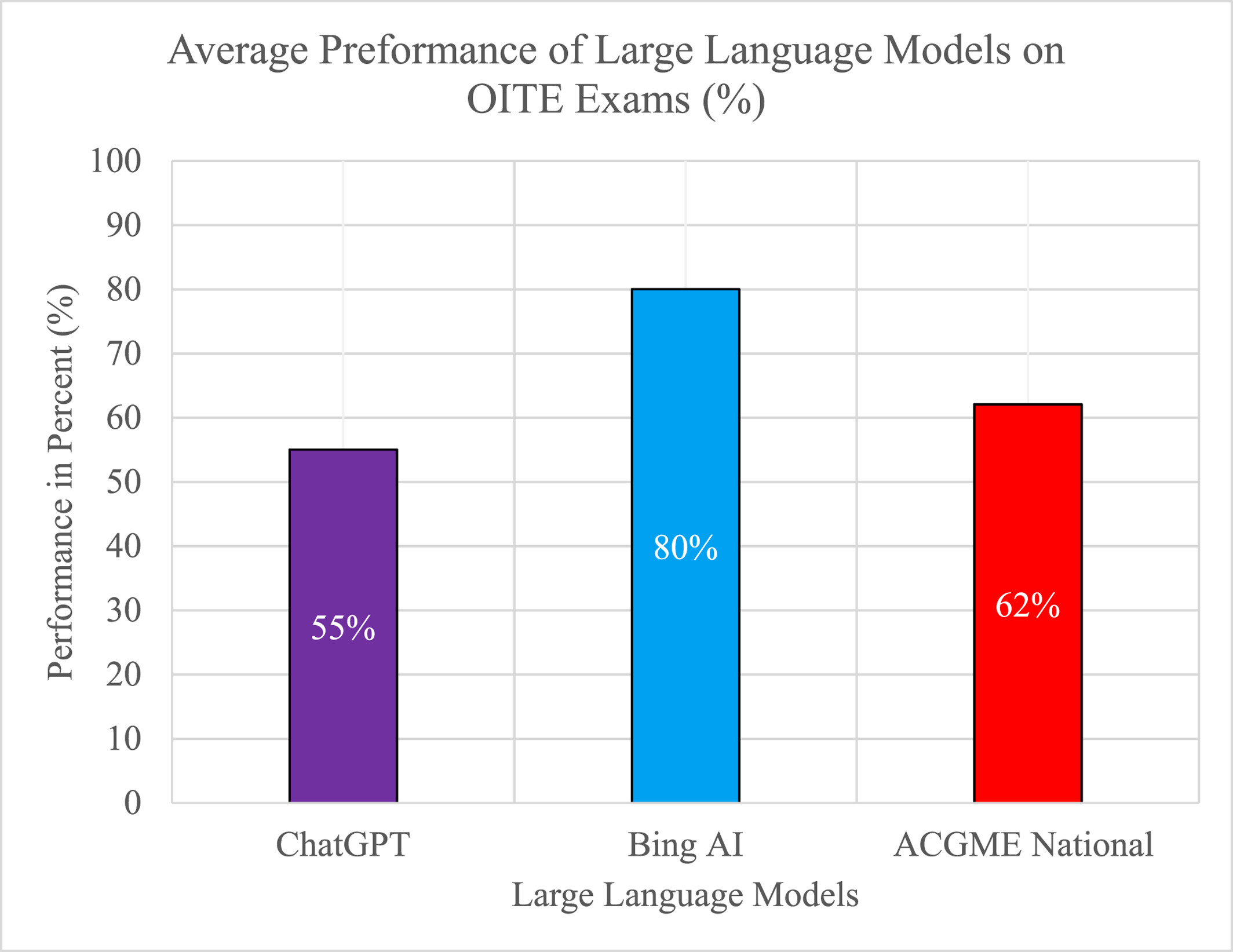
This article provides a comparison between large language models differing in their online web search capability and their performance on the Orthopaedic In-Training Examination. Bing AI GPT 4.0 scored higher compared to previous ChatGPT 3.5, and higher than the average performance of orthopaedic residents in national accredited programs. Generative AI can provide a logical context across answer responses through its in-depth information searches and citation of resources.
Prognostic significance of ratio of positive lymph nodes in patients with operable major salivary ductal carcinoma
- Pages: 291-301
- First Published: 16 September 2024
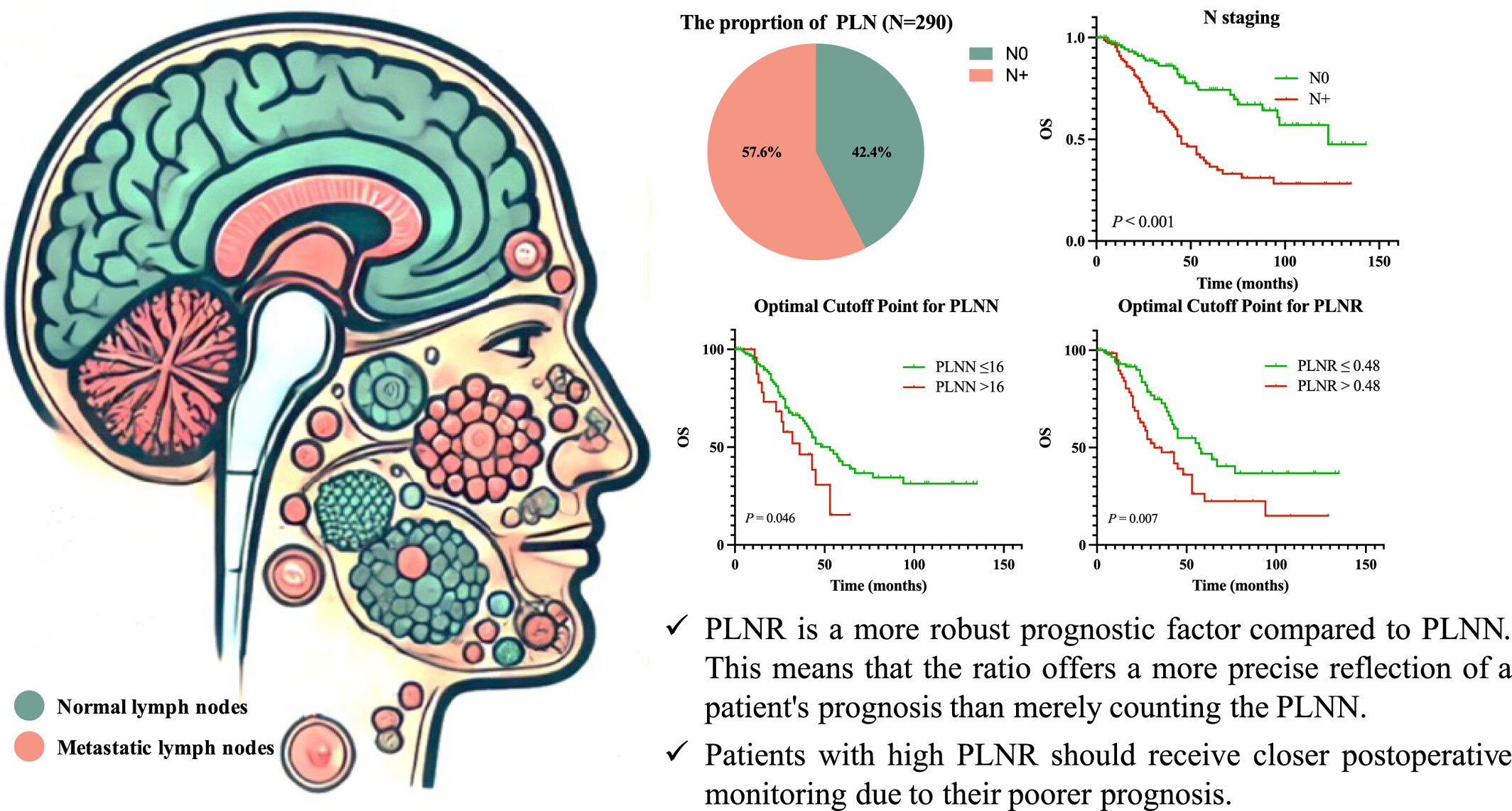
Advanced T stage, submandibular gland location, and unpaired lesions were associated with lymph node involvement. The prognosis of SDC patients with PLNR ≤ 0.48 was better than that of SDC patients with PLNR > 0.48. PLNR can reflect both the effect of lymph node dissection and the number of positive lymph nodes, and its prognostic value for major SDC exceeds the number of positive lymph node number. Patients with high PLNR should be followed closely after surgery.
Surgical management and histopathological patterns of periampullary cancers in Sudanese patients: A single-center prospective study
- Pages: 302-311
- First Published: 16 August 2024
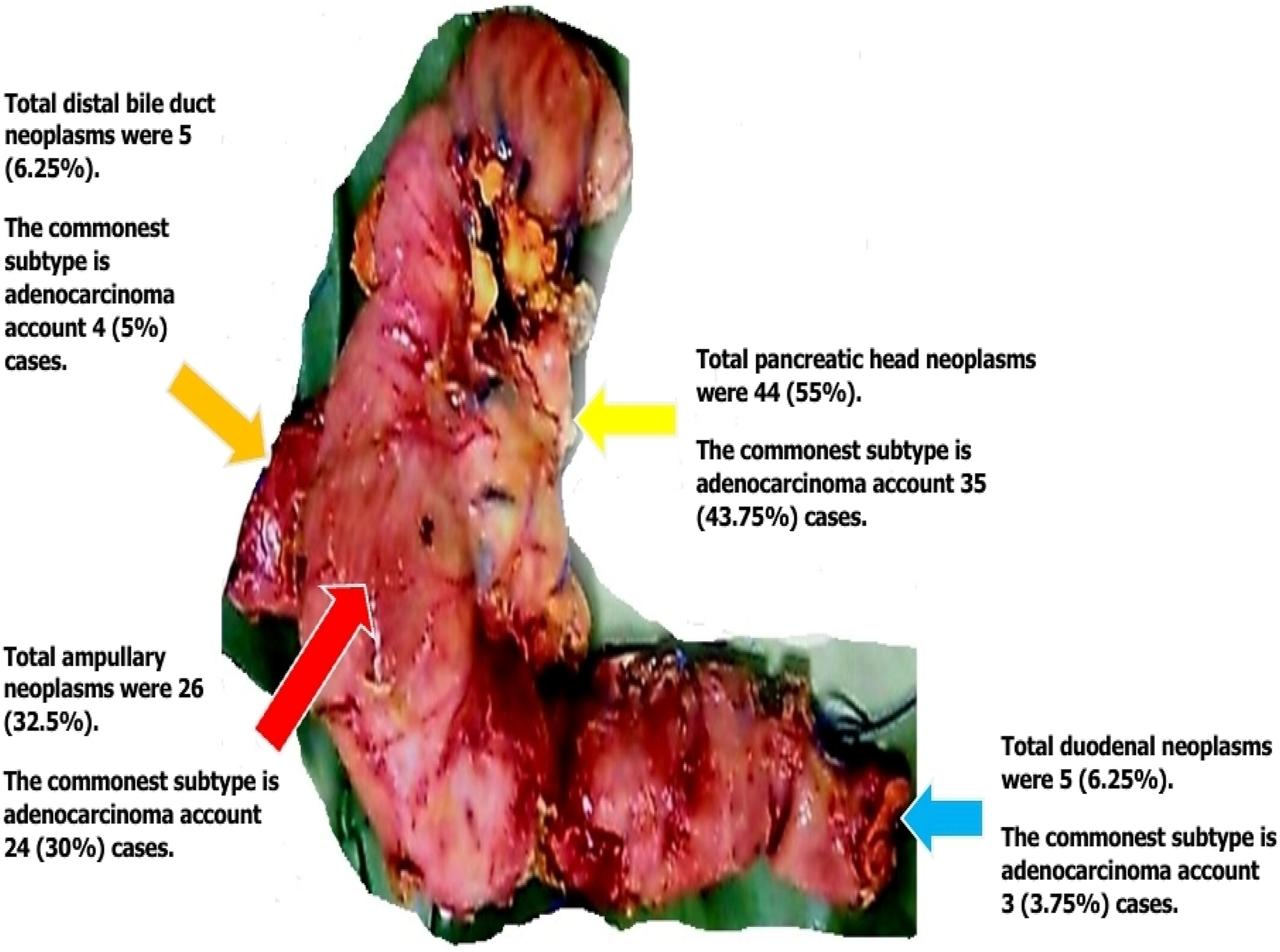
This prospective study showed that updated knowledge regarding the management modalities of PAC is a prerequisite for accurate histopathological assessment and good surgical outcomes. Furthermore, histopathological analysis helps clinicians to select effective postoperative therapies for greater improvement in survival outcomes.
CASE REPORT
Anti-synthetase syndrome complicated by multifocal tuberculosis: A thought-provoking differential diagnosis with tumors
- Pages: 312-317
- First Published: 15 September 2024
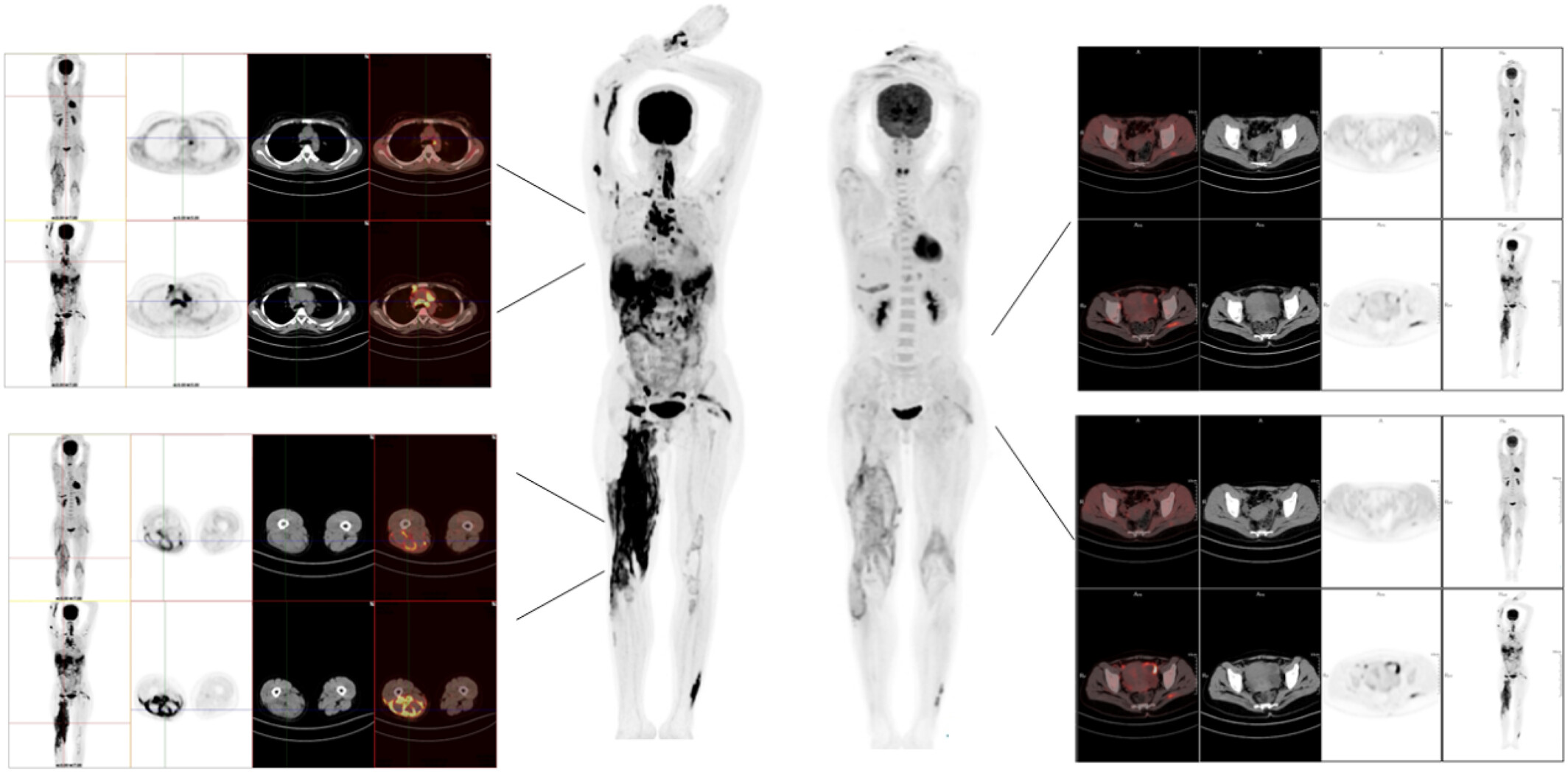
A 31-year-old woman with anti-synthetase syndrome developed abdominal and subcutaneous lumps during immunosuppressive treatment, with elevated tumor markers suggesting malignancy. Pathological examination revealed Mycobacterium tuberculosis, leading to a revised diagnosis of multifocal extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Targeted therapy improved her condition. This case underscores the necessity of thorough pathological evaluations and broad differential diagnosis in patients with overlapping infectious and autoimmune symptoms.
COMMENTARY
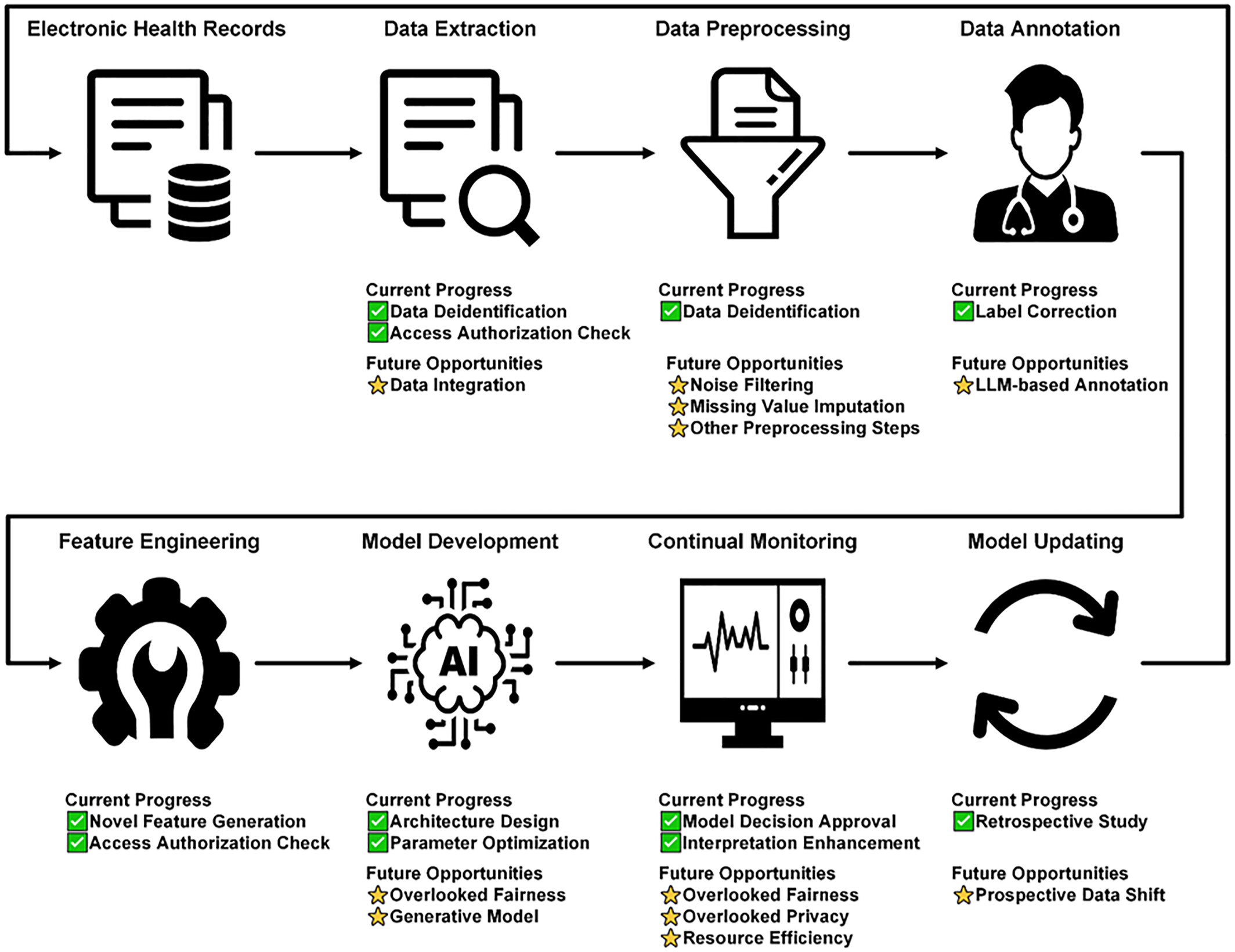
Human-in-the-loop machine learning for healthcare: Current progress and future opportunities in electronic health records
- Pages: 318-322
- First Published: 23 August 2024