Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
LINC00922: A Critical Oncogenic Long Non-Coding RNA Involved in Cancer Progression, Chemotherapy Resistance, and microRNA Regulation
- Pages: 65-79
- First Published: 13 June 2025
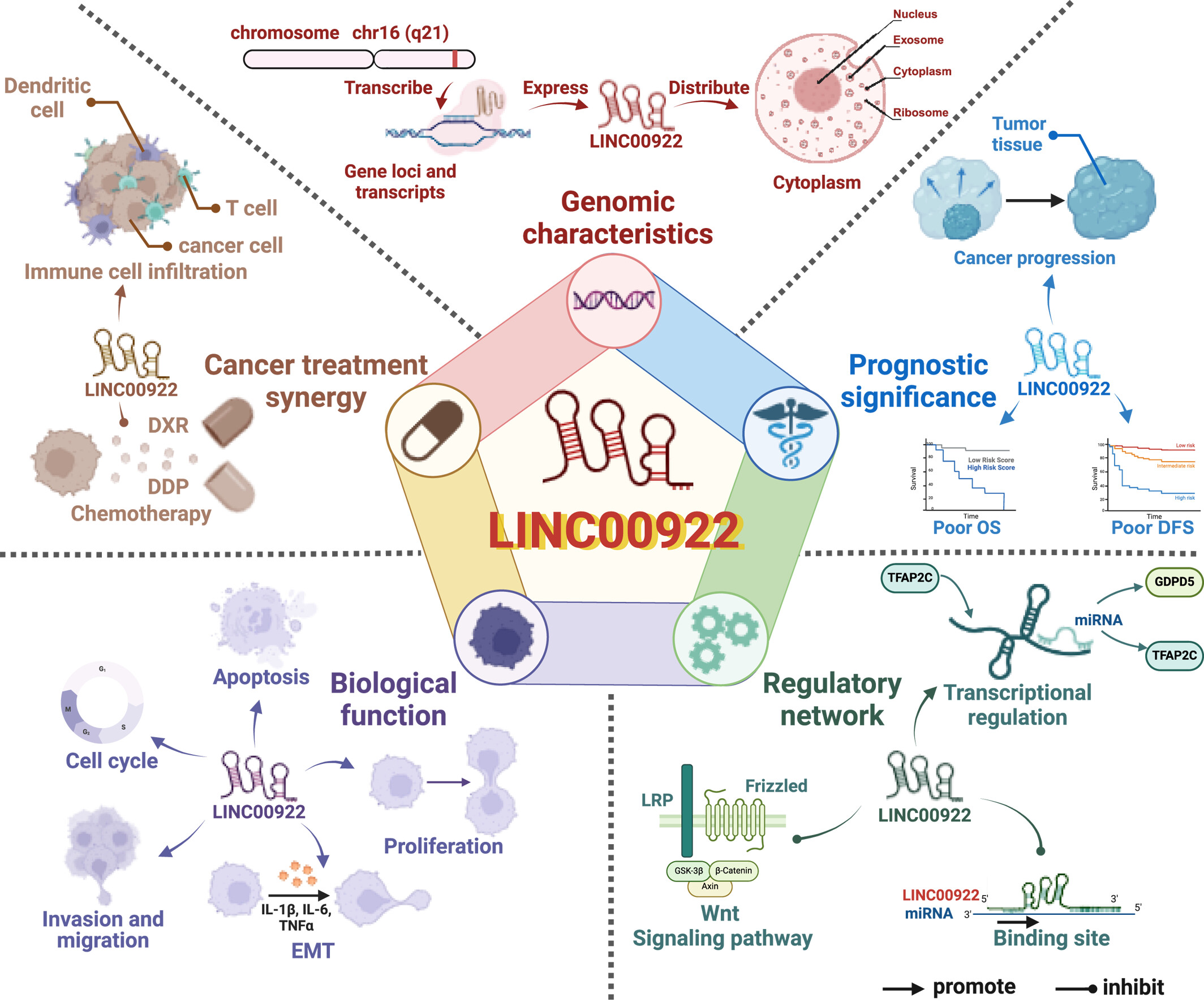
LINC00922 is located at 16q21 and is primarily expressed in the cytoplasm. It has been implicated in promoting tumor progression, contributing to poor overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in patients. LINC00922 drives cancer progression through a complex network of gene interactions, enhances chemotherapy resistance in cancer cells, and facilitates immune cell infiltration within the tumor microenvironment.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Associations Between Lipids and Lipid-Lowering Drug Target Genes and Osteomyelitis: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis
- Pages: 80-87
- First Published: 09 April 2025
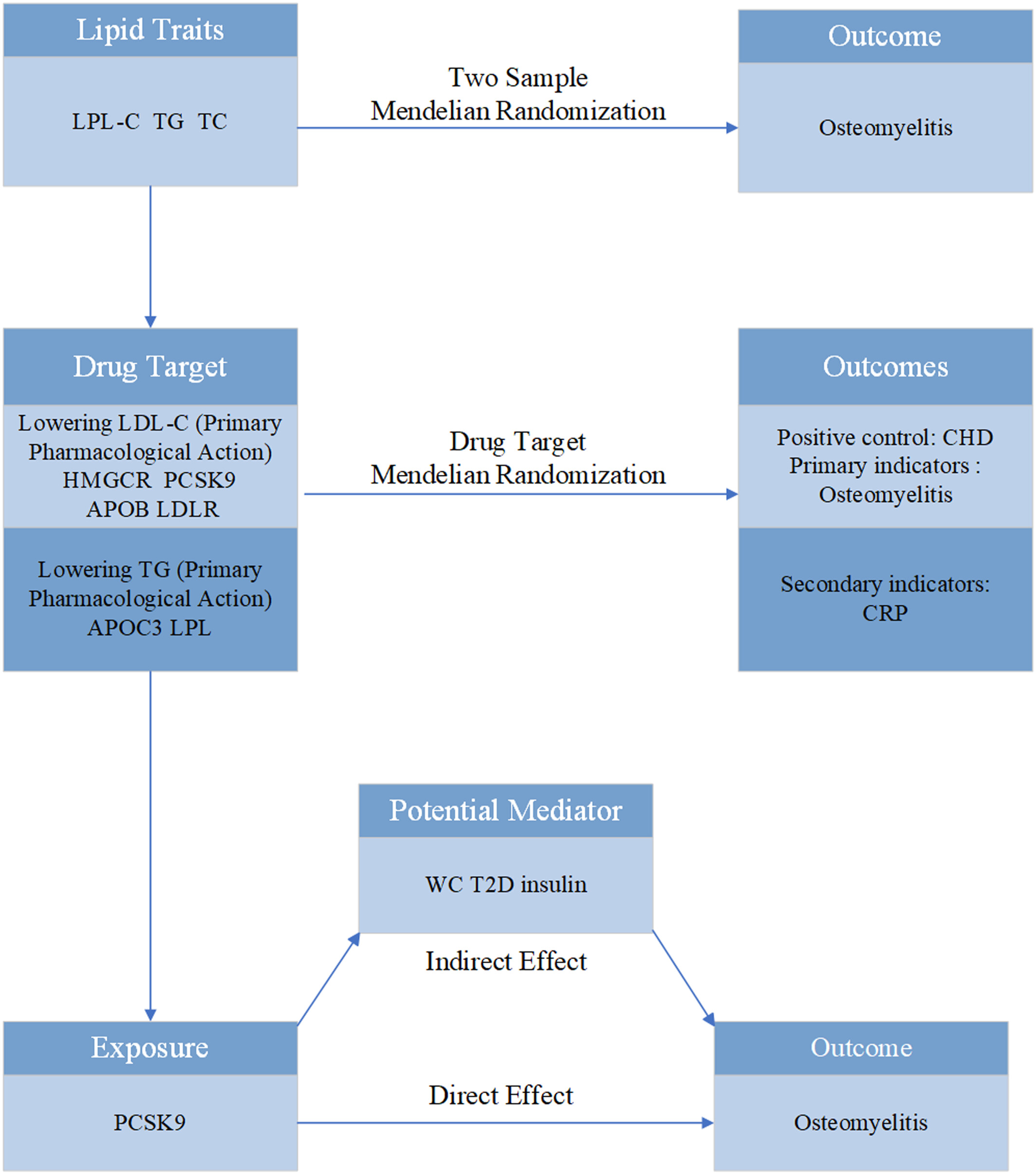
In this study, we identified several SNPs in PCSK9 as genetic tools to comprehensively assess the influential role of PCSK9 in CHD, CRP, and osteomyelitis. PCSK9 is associated with a lower risk of osteomyelitis, and PCSK9 is also associated with a reduction in CRP concentrations. Our study supports the notion that WC may be a potential mediator between osteomyelitis and PCSK9.
Anticipating On-Target and Off-Target Effects of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Via a Feedforward Neural Network Model
- Pages: 88-96
- First Published: 12 June 2025
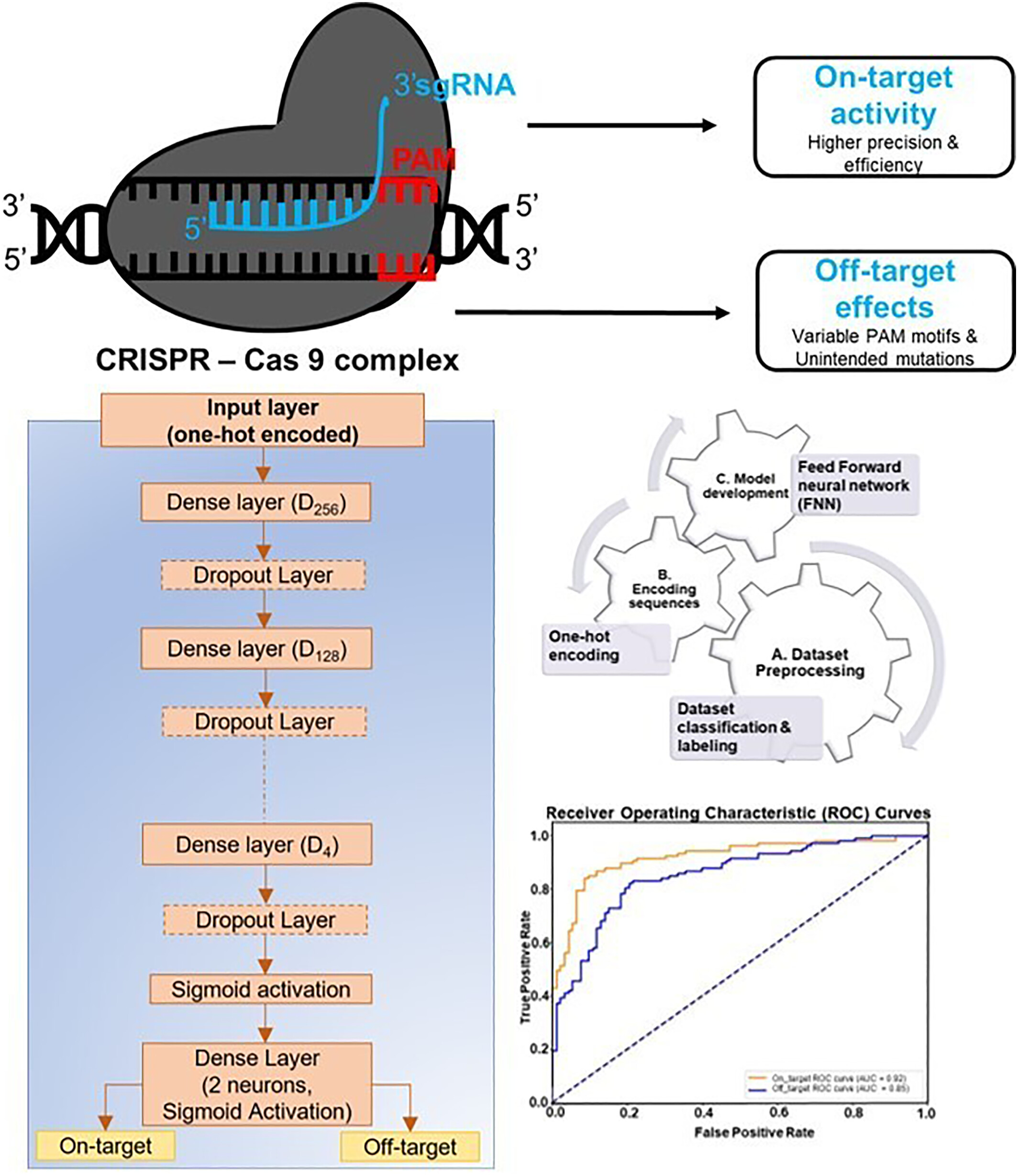
The CRISPR-Cas9 system enables targeted genome editing with high precision but is challenged by unintended off-target effects. In this study, a feedforward neural network (FNN) model was developed to predict on-target and off-target events using SITE-Seq dataset. Our model achieved best accuracy, offering a unified approach to assess editing outcomes in a single predictive framework.
Relationships Between Serum Vitamin D, Inflammatory Markers, and Outcomes in Non-Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Pages: 97-106
- First Published: 12 June 2025
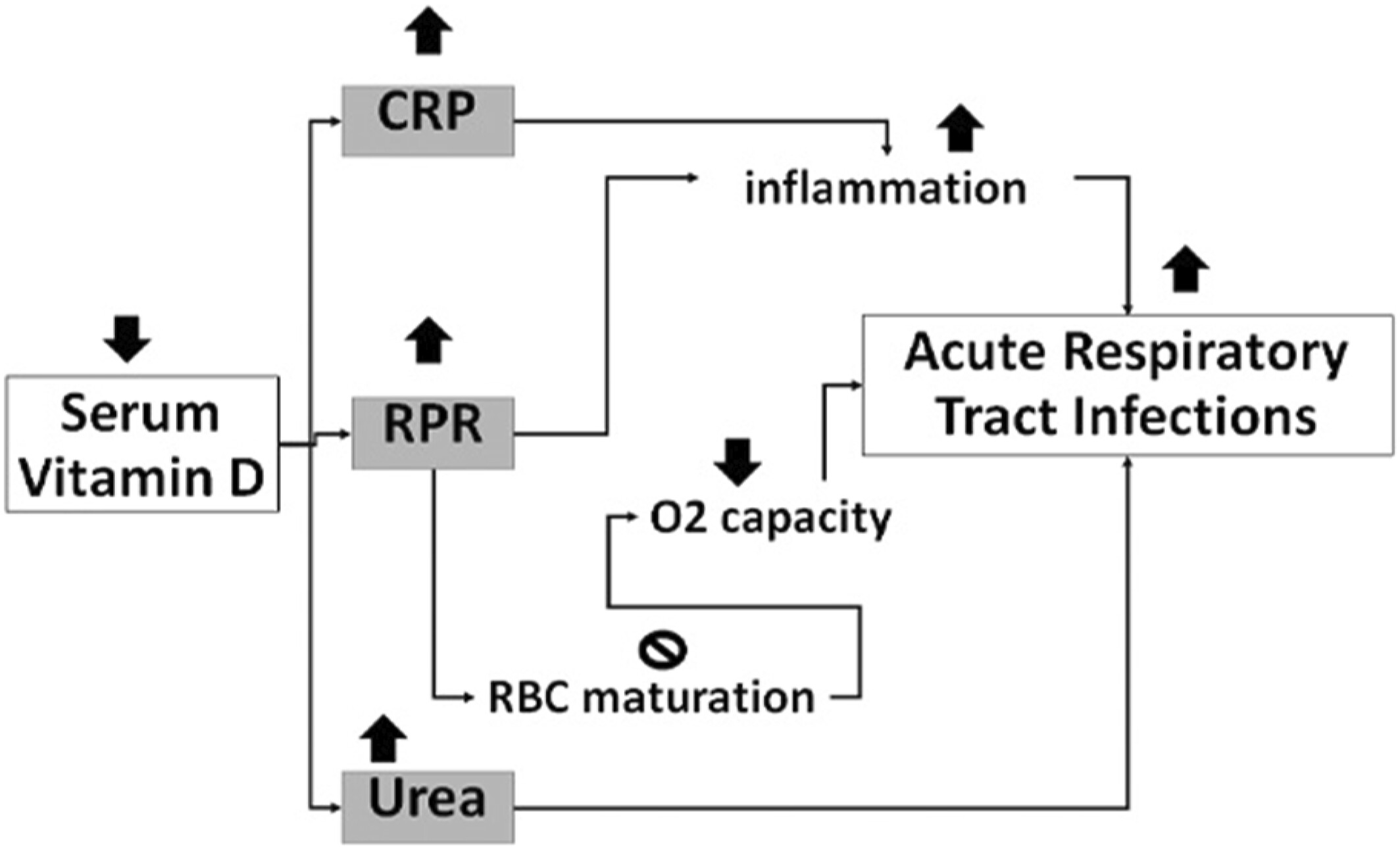
Serum urea levels have been identified as a significant predictor of in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients, whereas vitamin D deficiency correlates with elevated inflammatory markers such as CRP and RPR. To better understand these associations and their implications for clinical outcomes, further large-scale studies are warranted, emphasizing the potential utility of serum urea and vitamin D levels in the risk assessment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
CASE REPORT
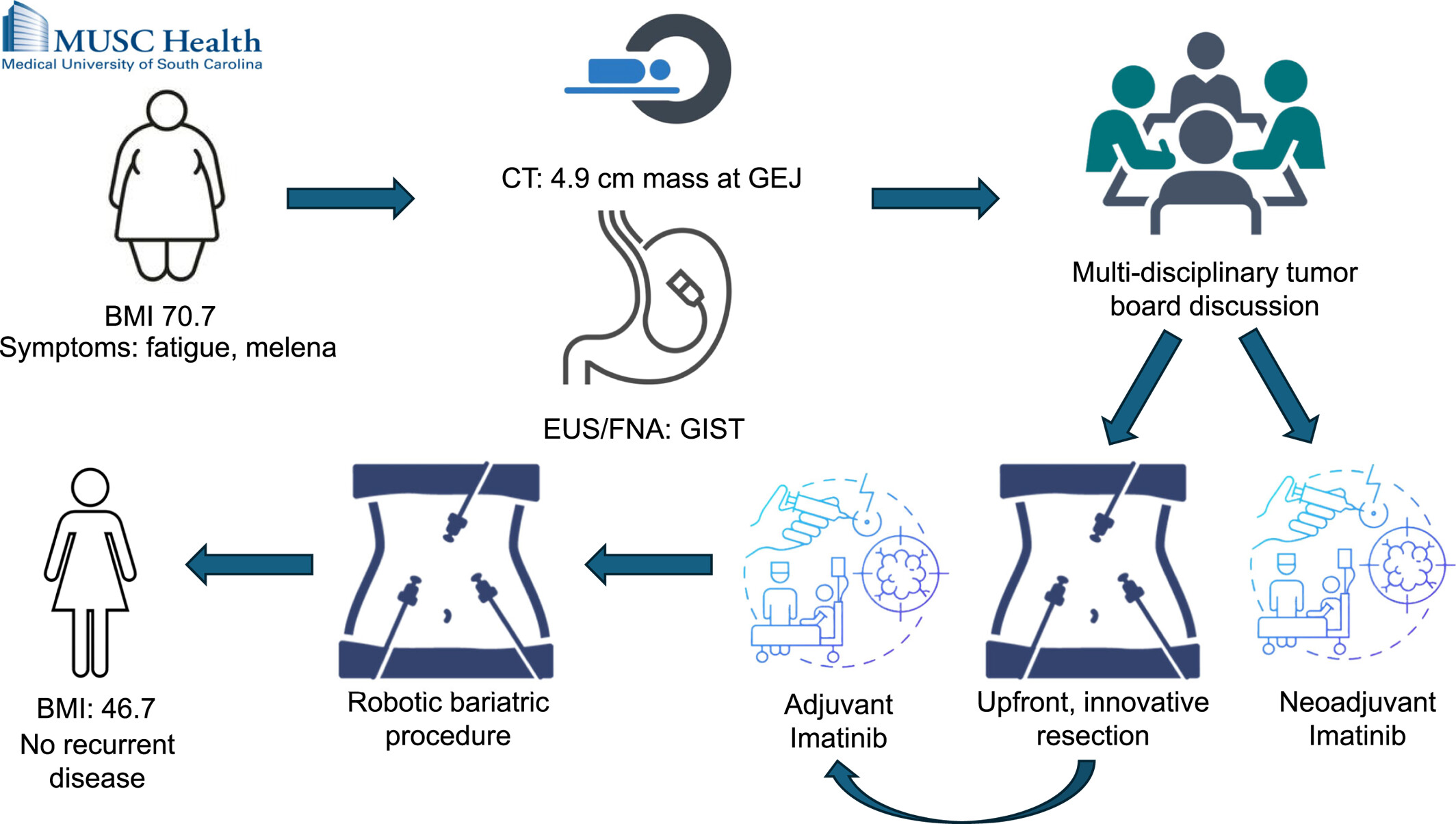
Surgical Management of a High-Grade Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor in a Morbidly Obese Patient: A Case Study
- Pages: 107-111
- First Published: 24 April 2025
Case Report: Abemaciclib-Induced Chronic Renal Failure
- Pages: 112-115
- First Published: 19 June 2025
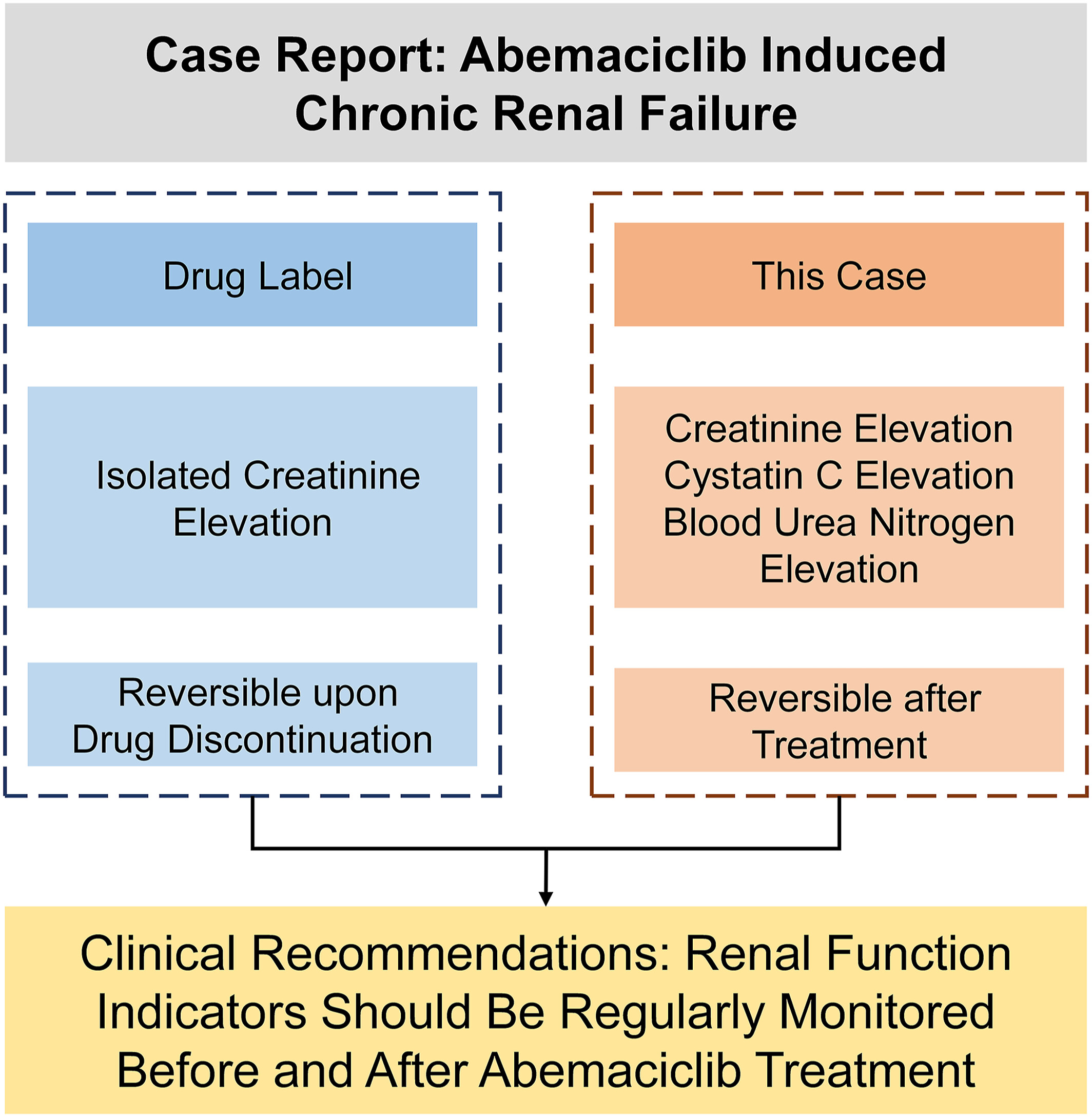
This article reports a case of chronic kidney injury caused by Abemaciclib, which suggests that long-term use of Abemaciclib may lead to kidney damage, potentially progressing to chronic renal failure. It is essential to regularly monitor kidney function indicators before and after treatment. Literature suggests that Abemaciclib may have a dual impact on the kidneys, and regular monitoring of kidney function indicators should be conducted before and after treatment.
PERSPECTIVE
Xanomeline-Trospium Chloride (Cobenfy): A New Era in Managing Schizophrenia—Comparative Effectiveness and Economic Challenges
- Pages: 116-121
- First Published: 14 May 2025
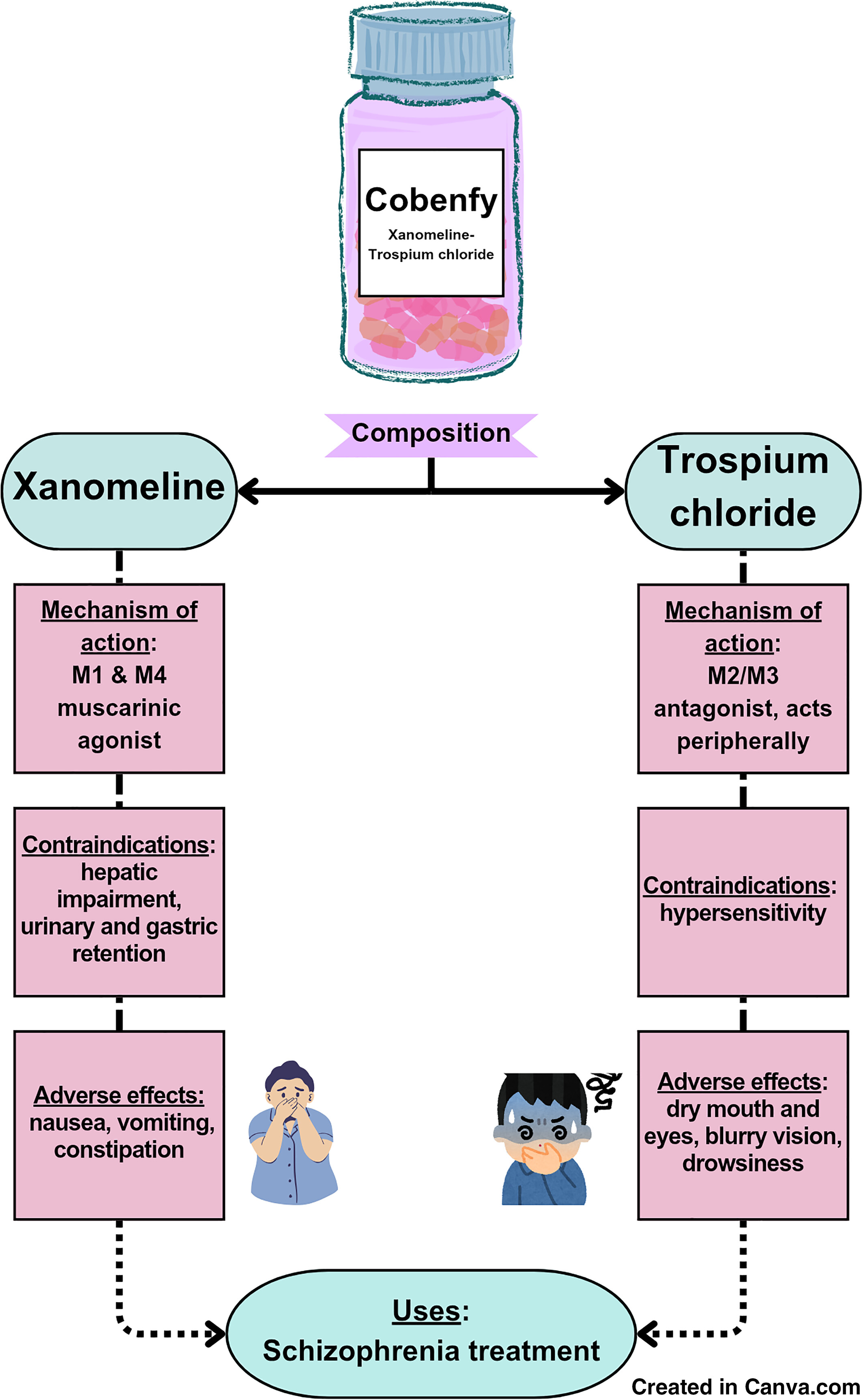
Xanomeline-trospium chloride (cobenfy) is a muscarinic agonist used to treat hallucinations and psychotic illnesses such as Alzheimer's and Schizophrenia. It has been constructed for patients who are unable to tolerate dopamine-targeting therapies and a comparison is drawn against other similar drugs with variables like cost, mechanism of action, efficacy and contraindications taken into account. Specifically effective for schizophrenia, it is safer with fewer side effects and efficient with stronger success rates, offering pharmacists and physicians an alternative to mainstream antipsychotic drugs.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Enhancing Heart Health: Expanding the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Disease
- Pages: 122-126
- First Published: 04 June 2025
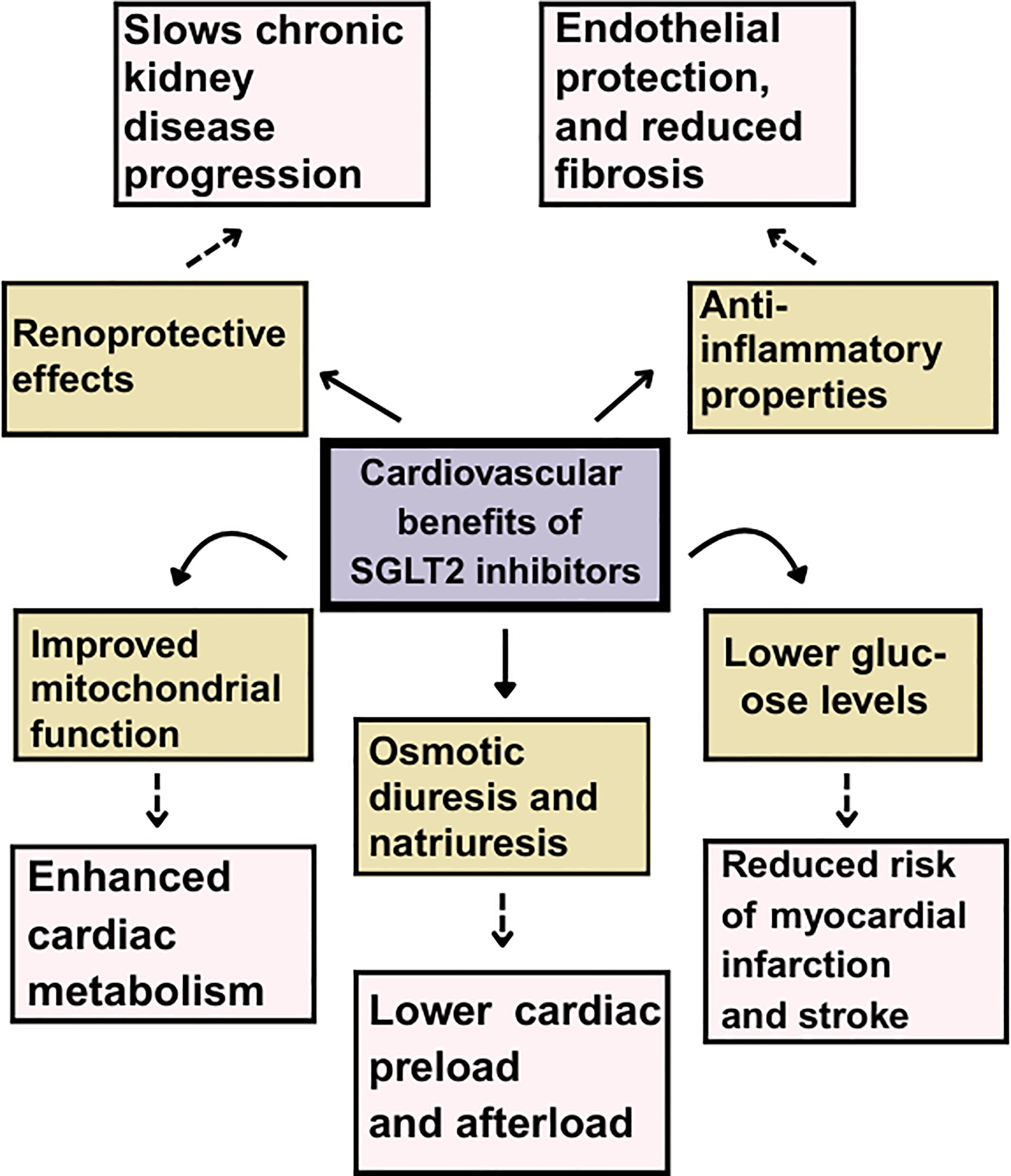
SGLT2 inhibitors offer multifaceted cardiovascular benefits, including improved cardiac metabolism, reduced preload and afterload, and decreased myocardial infarction risk. These effects are driven by renoprotection, anti-inflammatory properties, improved mitochondrial function, osmotic diuresis, and glycemic control. Together, these mechanisms support the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in reducing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.