Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases
- First Published: 31 July 2023
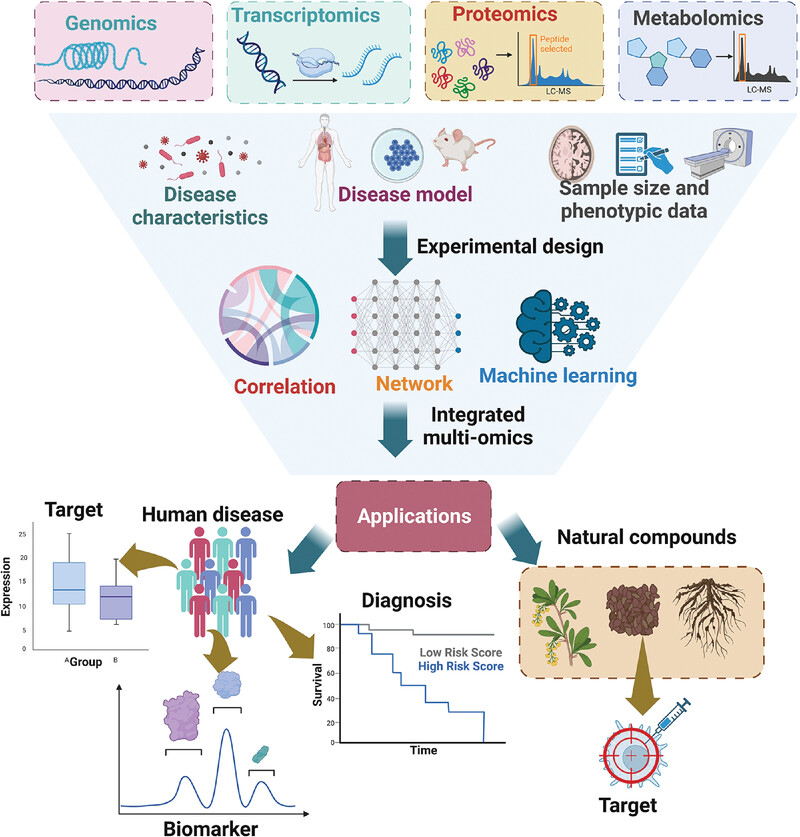
Multi-omics contains genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, etc. And the experimental design considers the disease characteristics, disease model, sample size and phenotypic data. After the data integration by the approach of correlation, network and machining learning, the multi-omics can be applied in diagnosis, biomarkers, targets of human disease and target discovery of natural compound.
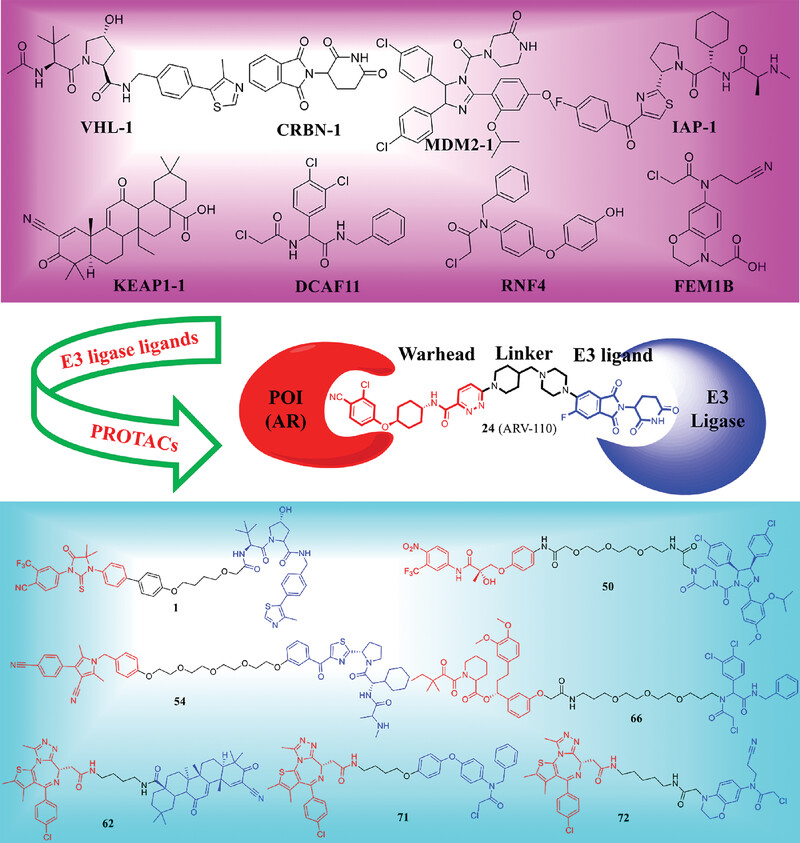
PROTACs: A novel strategy for cancer drug discovery and development
- First Published: 29 May 2023
Organoids: The current status and biomedical applications
- First Published: 17 May 2023
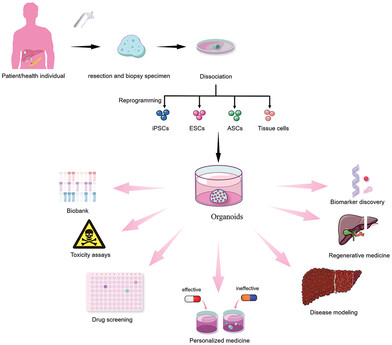
Organoids can be generated by inducing and culturing pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs), adult stem cells (ASCs), and tumor cells from healthy donors or patients. The potential biomedical applications for organoids include disease modeling, drug screening, toxicity assays, personalized medicine, biobank, biomarker discovery, and regenerative medicine.
Protein posttranslational modifications in health and diseases: Functions, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic implications
- First Published: 02 May 2023
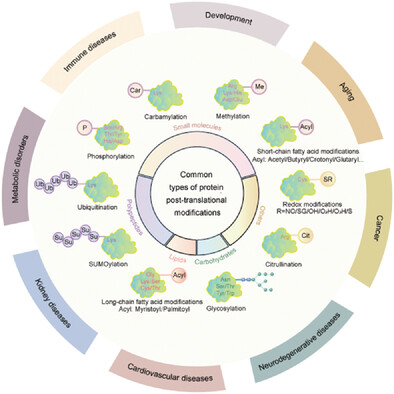
The reversible and irreversible protein posttranslational modifications, such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, SUMOylation, and redox modifications, are essential regulators in organisms and cells. This work systematically summarizes the features, regulatory mechanisms, substrates, functions, and related treatments of protein modifications and will deepen the understanding of protein modifications in health and diseases.
Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics in health and disease
- First Published: 04 November 2023
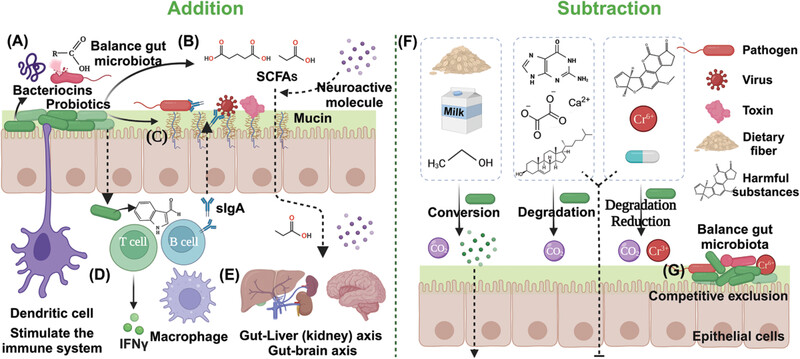
Extensive research and clinical evidence have demonstrated the mechanisms and effectiveness of probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics in restoring gut microbiota homeostasis and treating a variety of diseases. Prebiotics can promote the growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria, while probiotics produce postbiotics through “addition” to regulate the gut microbiota, and “subtraction” to remove harmful metabolites and exogenous substances to reduce their impact on the body, thereby alleviating or treating diseases. Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics may represent the next generation of medicines, with the potential to revolutionize the way we treat and manage disease.
Nanopore sequencing technology and its applications
- First Published: 10 July 2023
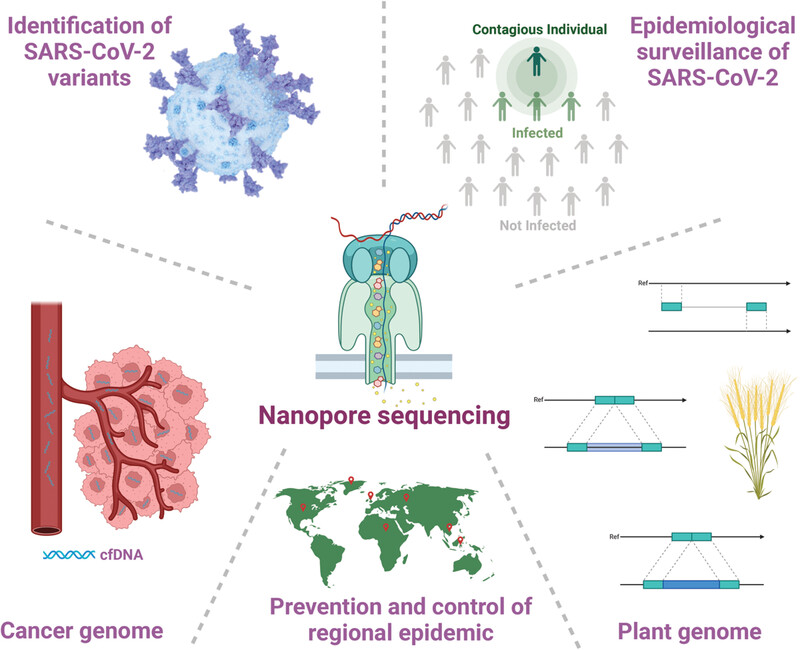
Nanopore sequencing has been instrumental in managing the COVID-19 pandemic. This review aims to increase public understanding of its role in identifying SARS-CoV-2 variants and tracking changes in regional epidemiology. Additionally, the review explores the use of nanopore sequencing in detecting other microbial outbreaks, as well as its applications in cancer and plant genomics.
Metabolic reprogramming in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutics
- First Published: 27 March 2023
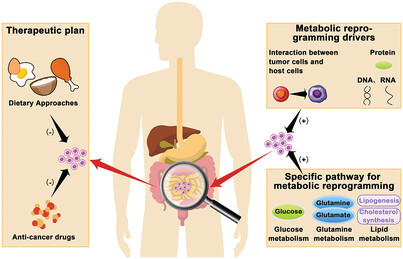
This article presented the metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells to adapt to their microenvironment distinct from normal cells. And this study reviewed the driving factors of metabolic reprogramming, the specific metabolic pathway changes affected, and the related treatment options, in order to provide some suggestions for future tumor treatment.
Vascular calcification: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 03 January 2023
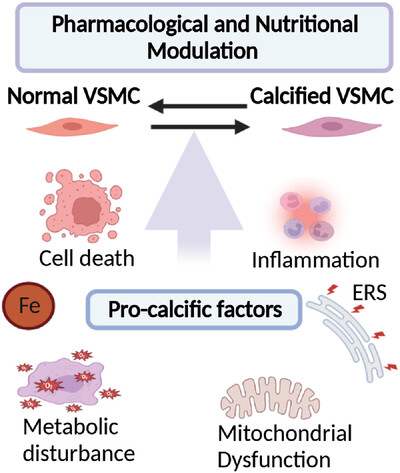
Vascular calcification is caused by the imbalance of vascular microenvironment. The pro-calcific factors include chronic inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, iron homeostasis, programed cell death, and other cellular metabolic dynamics. However, the pharmacological and nutritional modulations, such as CCBs, ACEI/ARB, and vitamins, may provide potential therapeutic strategies on vascular calcification.
Post-translational modifications of histones: Mechanisms, biological functions, and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 20 May 2023
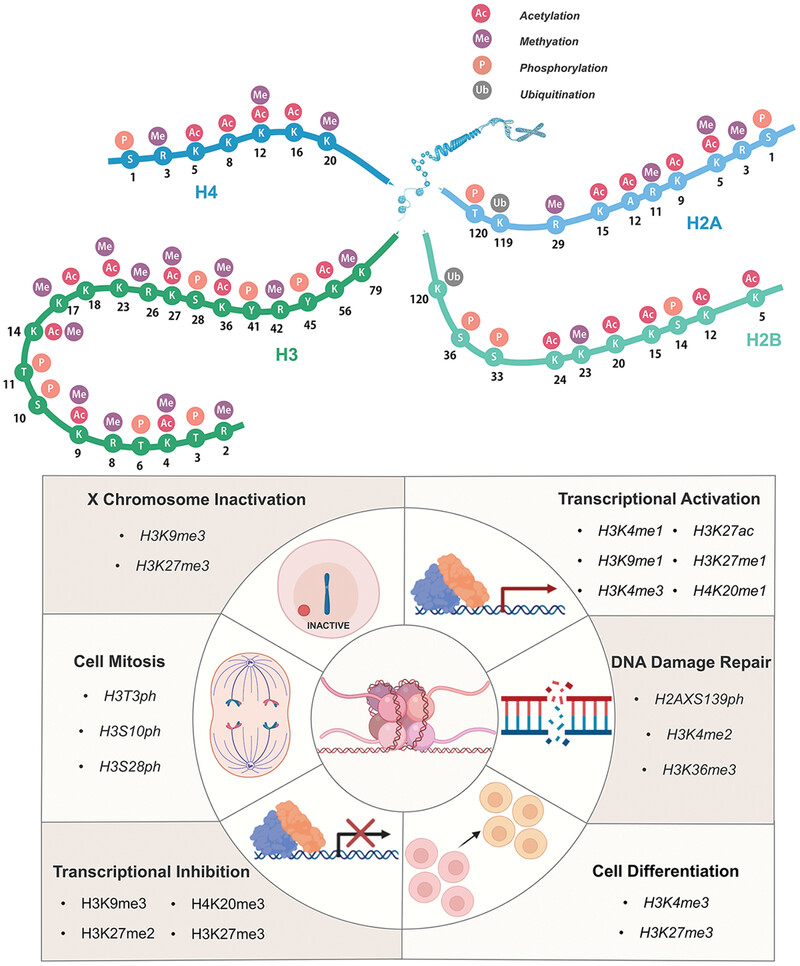
Histone tails are subject to a variety of post-translational modifications. We have introduced histone acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, malonylation, crotonylation, propionylation, butyrylation, and so forth. They participate in many life activities through different related histone sites.
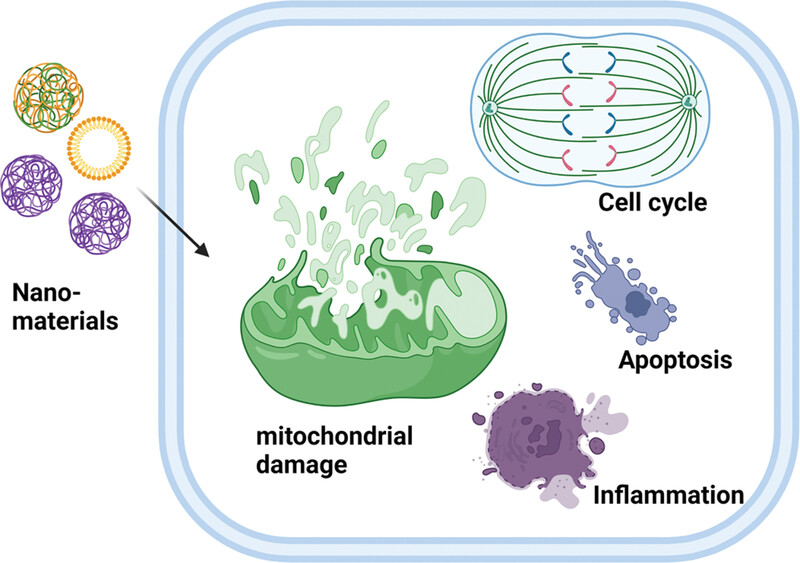
Nanoparticles-induced potential toxicity on human health: Applications, toxicity mechanisms, and evaluation models
- First Published: 14 July 2023
Application of stem cells in regeneration medicine
- First Published: 17 June 2023
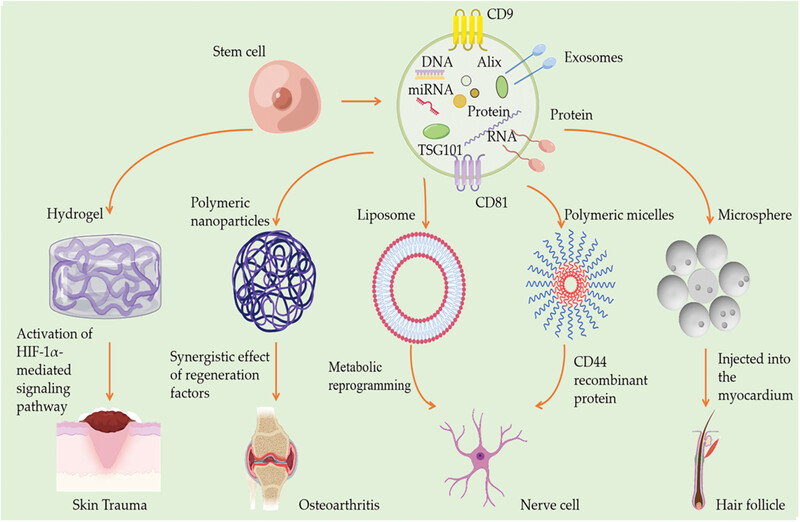
Regeneration is a complex process affected by many elements independent or combined, including inflammation, proliferation, and tissue remodeling. Stem cells is a class of primitive cells with the potentiality of differentiation, regenerate with self-replication, multidirectional differentiation, and immunomodulatory functions. Stem cells and their cytokines not only inextricably linked to the regeneration of ectodermal and skin tissues, but also can be used for the treatment of a variety of chronic wounds. Stem cells can produce exosomes in a paracrine manner. Stem cell exosomes play an important role in tissue regeneration, repair, and accelerated wound healing, the biological properties of which are similar with stem cells, while stem cell exosomes are safer and more effective. Skin and bone tissues are critical organs in the body, which are essential for sustaining life activities. The weak repairing ability leads a pronounced impact on the quality of life of patients, which could be alleviated by stem cell exosomes treatment. However, there are obstacles that stem cells and stem cells exosomes trough skin for improved bioavailability. This paper summarizes the applications and mechanisms of stem cells and stem cells exosomes for skin and bone healing. We also propose new ways of utilizing stem cells and their exosomes through different nanoformulations, liposomes and nanoliposomes, polymer micelles, microspheres, hydrogels, and scaffold microneedles, to improve their use in tissue healing and regeneration.
Dietary patterns and cardiometabolic health: Clinical evidence and mechanism
- First Published: 05 February 2023
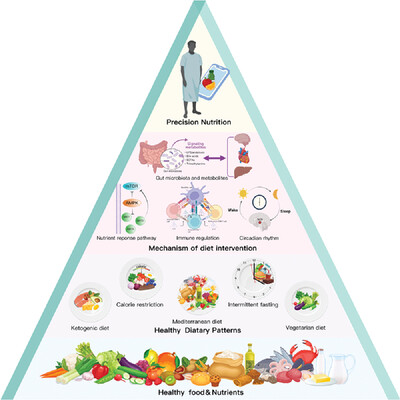
The research process for analyzing nutrition and cardiometabolic health is shown in a bottom–up manner. Phase 1: identification of essential nutrients and healthy foods, such as vegetables and fruits, whole grains, and plant-based oils (tier 4). Phase 2: establishment and development of different types of dietary patterns, such as vegetarian diets, Mediterranean diets, ketogenic diets, calorie restriction, and intermittent fasting (tier 3). Phase 3: exploration of the molecular mechanisms of dietary interventions, including nutrient response pathways, immune regulation, the role of gut microbiota and metabolites, and circadian rhythms (tier 2). Phase 4: providing personalized dietary strategies to cardiometabolic disease patients based on diet–genetic interactions (tier 1).
Effectiveness and safety of four different beta-blockers in patients with chronic heart failure
- First Published: 06 January 2023
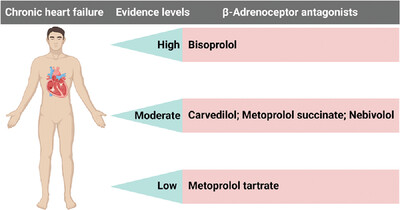
In this study, we evaluated the effectiveness and safety of bisoprolol, metoprolol, carvedilol, and nebivolol in the treatment of chronic heart failure. The results demonstrated that bisoprolol improved the prognosis of chronic heart failure in comparison with carvedilol, and carvedilol exerted similar effects as metoprolol succinate and nebivolol and better effect than metoprolol tartrate (evidence levels: bisoprolol > carvedilol = metoprolol succinate = nebivolol > metoprolol tartrate; “ > ” means “prior to”).
Hot and cold tumors: Immunological features and the therapeutic strategies
- First Published: 26 August 2023
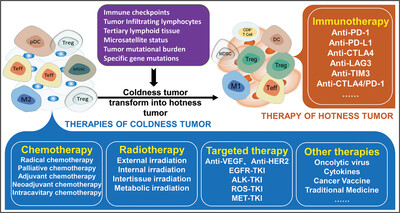
The characteristics of coldness and hotness tumors are determined by the information of cancer cells and tumor microenvironments, which significantly affects cancer patients’ clinical efficacy. Different therapeutic strategies for cold and hot tumors based on clinical efficacy were analyzed through clinical drug targets, tumor microenvironments, and tumor stages. Coldness tumors can transform into hotness tumors through chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and other therapies.
Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in cancer
- First Published: 22 May 2023
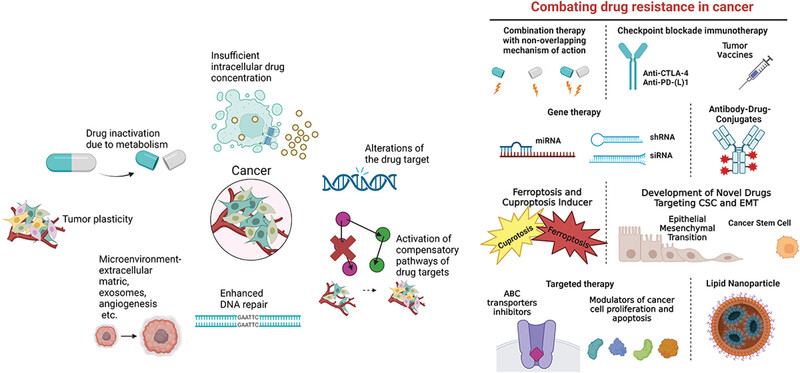
The reduced responsiveness of cancer cells can be associated with various mechanisms, including drug inactivation, reduced intracellular drug accumulation by reduced uptake or increased efflux, drug target alteration, activation of compensatory pathways for cell survival, regulation of DNA repair and cell death, tumor plasticity, and the regulation from tumor microenvironments. Various targeting strategies against different resistance mechanisms have been developed. The purpose of overcoming the drug resistance of cancer cells is to optimize the sensitivity of the therapy. This can be achieved by polytherapy using the combination of at least two drugs; immunotherapy using checkpoint inhibitors or monoclonal antibodies; antibody-drug conjugates improving the selectivity of cancer treatment; gene technology modifying the epigenetic sequence; targeted therapy targeting the overexpression of drug efflux transporter or vital proteins for the cancer cell apoptosis; and nanoparticle delivery system improving the efficacy of the drug and reducing the side effect.