Editors-in-Chief: Robin Ali, Michael Karin and Kang Zhang
© Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA)
MedComm – Future Medicine publishes the latest advances in biomedical research and healthcare delivery to address unmet medical needs and transform future medical therapies.
We're a multidisciplinary journal our content includes the development of ground-breaking technologies and therapies, interdisciplinary approaches, application of big data and AI in healthcare delivery, and precision medicine for early detection and outcome prediction for major diseases.
Journal Metrics
- 2.1CiteScore
- 50%Acceptance rate
- 35 days Submission to first decision
MedComm – Future Medicine is a new open access journal showcasing the latest and most impactful biomedical research.
- We publish high-quality, impactful research in medicine and biology on the basis of novelty, timeliness and significance to human health and diseases.
- We are a multidisciplinary journal with special interest in multiomics, bioinformatics, medical artificial intelligence, stem cell and regenerative medicine, gene editing and therapy.
- We cover the latest advances in biomedical research that address unmet, urgent medical needs which will transform patient care.
- Read more to learn about the journal.
- Take advantage of the article publication charges that are currently waived and submit your manuscripts to MedComm – Future Medicine.
MedComm – Future Medicine is now indexed by DOAJ and Scopus.
Articles
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Aging: Future Therapies and Precision Medicine Approaches
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
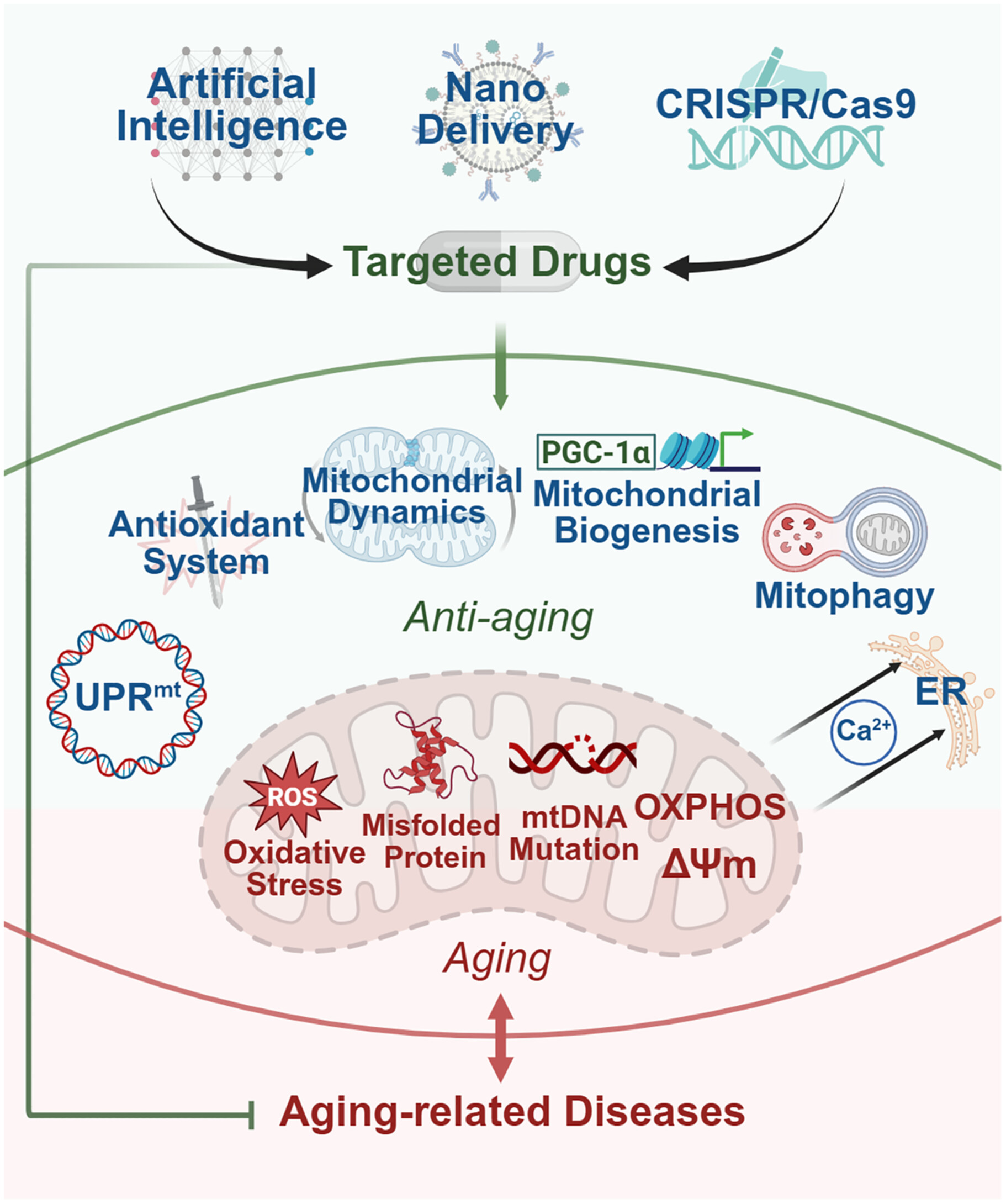
Mitochondria play a critical role in aging and aging-related diseases. This review systematically explores the mechanisms underlying mitochondrial deterioration during aging and highlights innovative therapeutic strategies for these mitochondrial problems. On this basis, it is expected that more targeted and efficient antiaging treatment strategies will be developed in the future to achieve precision and efficiency in the treatment of aging-related diseases.
Recent Progress in Gene Delivery Systems Based on Gemini‐Surfactant
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
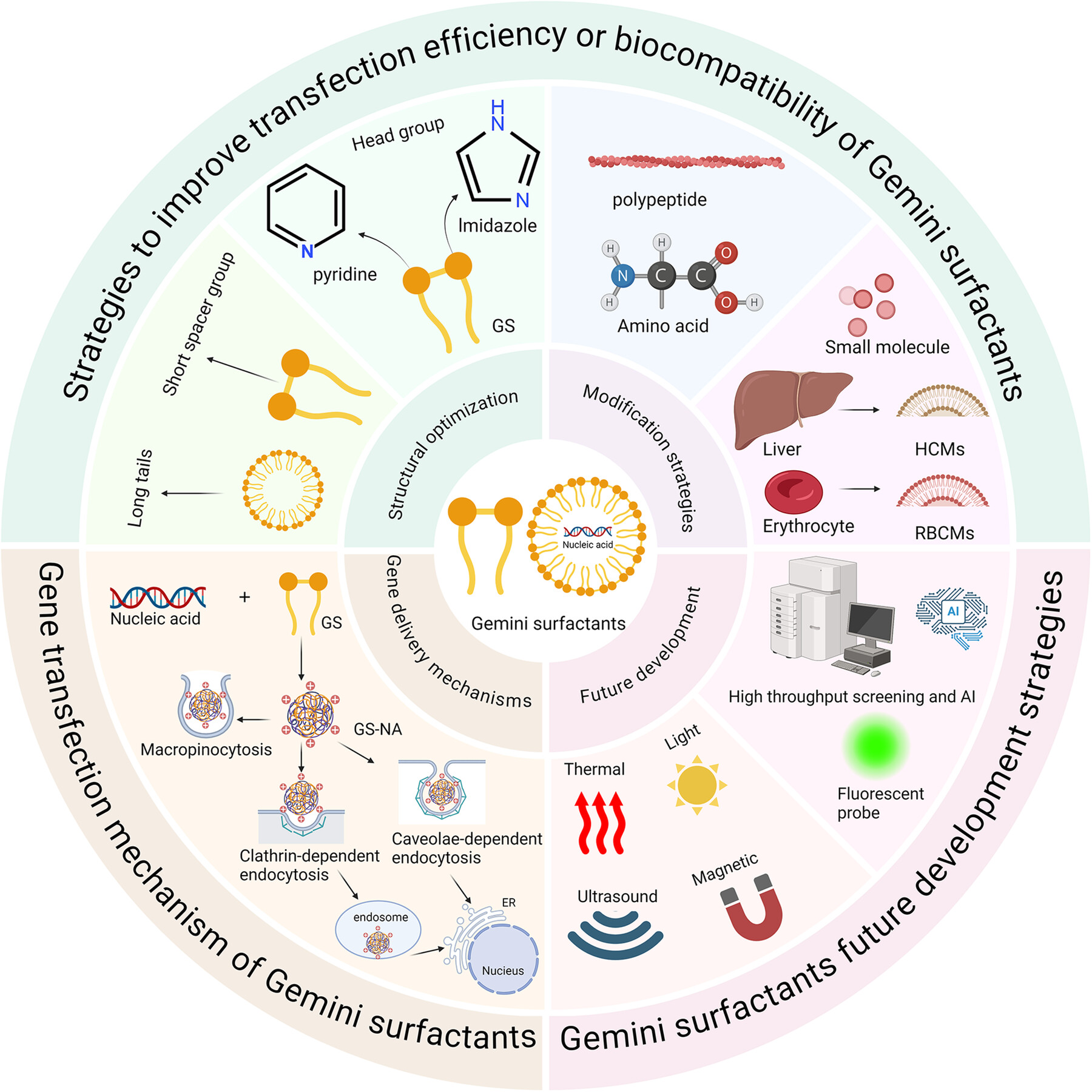
Gene delivery is a key area in biomedicine, where nucleic acids are delivered into cells to treat diseases by modulating genes. The low micelle concentration, effective nucleic acid complexation, and low immunogenicity make Gemini surfactants promising gene delivery vectors. This paper summarizes strategies to improve the transfection efficiency or biocompatibility of Gemini surfactant vectors and explores their delivery mechanisms, thereby offering new insights into the field's development.
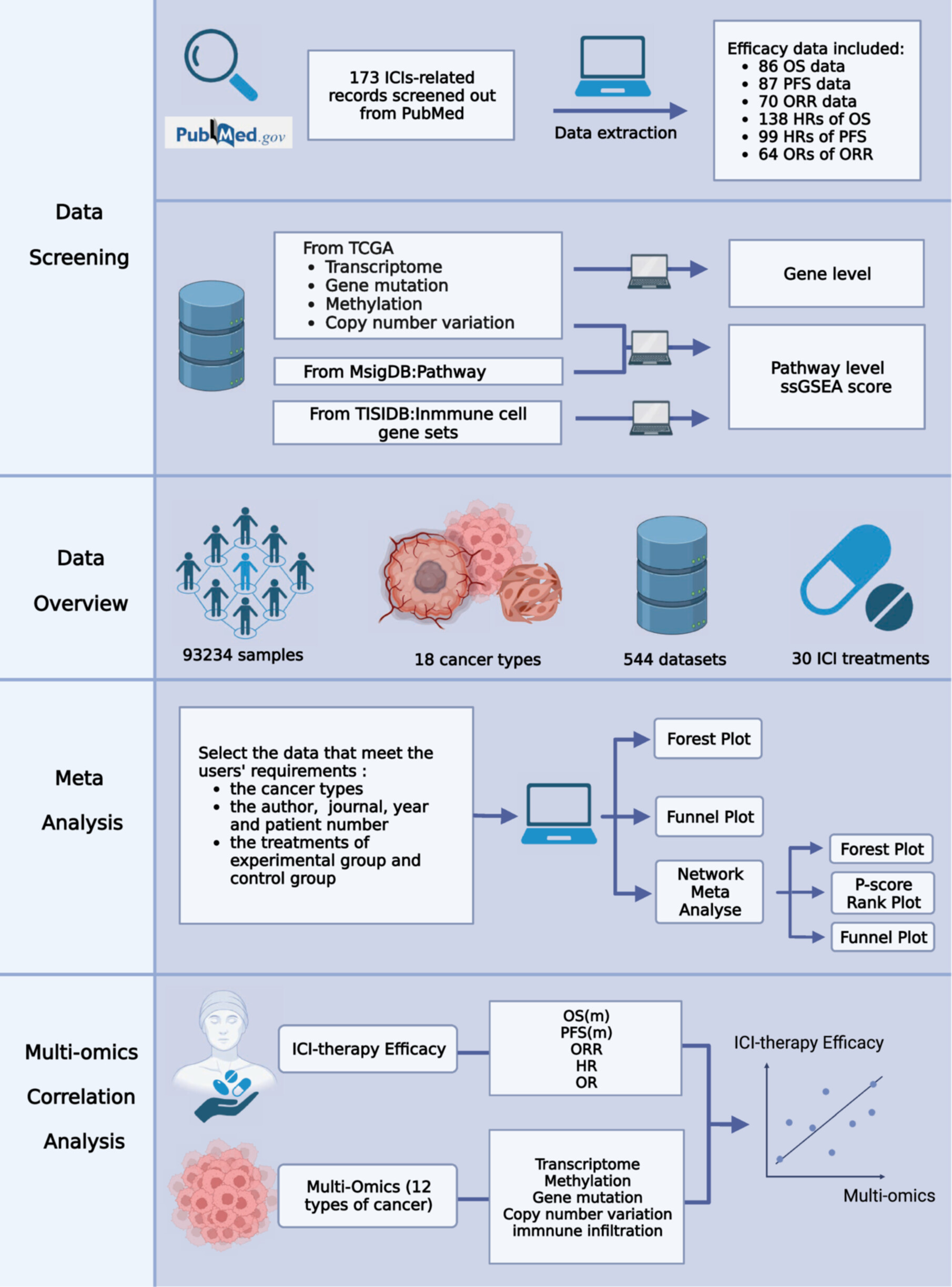
ImmunoCheckDB: A Comprehensive Platform for Evaluating Cancer Immunotherapy Biomarkers Through Meta‐Analyses and Multiomic Profiling
- 19 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
Accelerating the integration of ChatGPT and other large‐scale AI models into biomedical research and healthcare
- 17 May 2023
Graphical Abstract
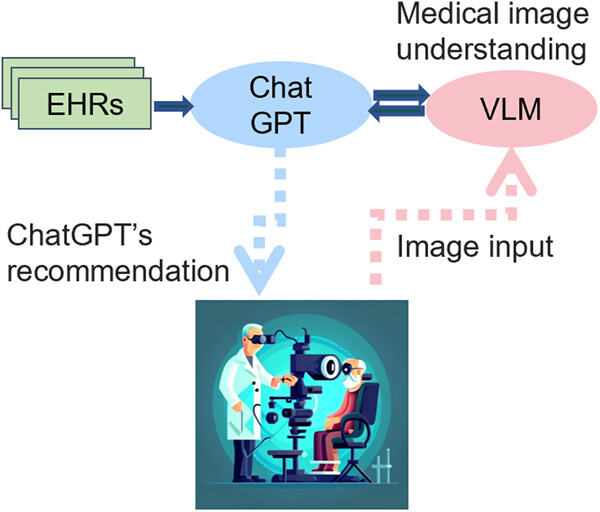
This review provides an overview of large-scale AI models, including language models (e.g., ChatGPT), vision-language models, and language-conditioned multiagent models, and discusses their potential applications in medicine, as well as their limitations and future trends. We also propose how large-scale AI models can be integrated into various scenarios of clinical applications.
Role of next‐generation sequencing in revolutionizing healthcare for cancer management
- 23 November 2024
Graphical Abstract
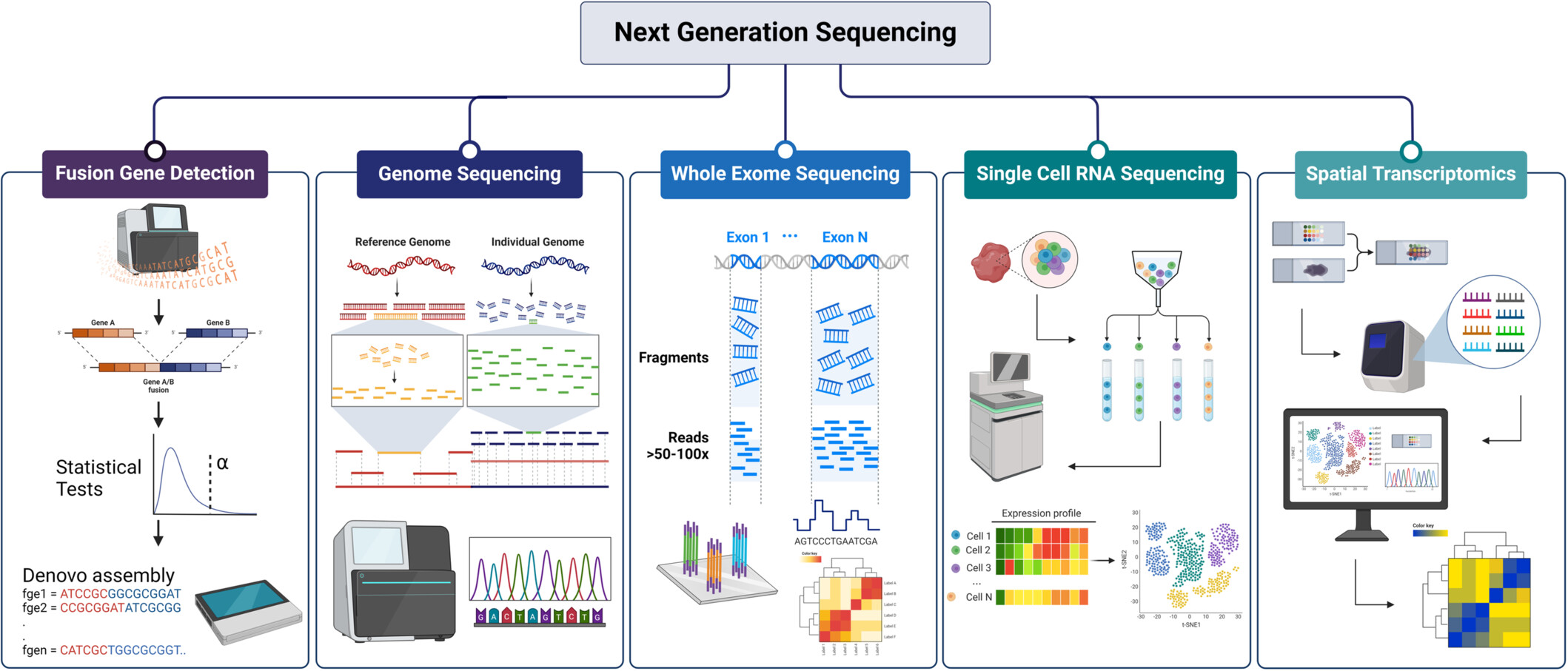
The advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized genome analysis, allowing for high-throughput sequencing and in-depth genomic insights. Contemporary NGS techniques, including fusion gene detection, whole genome sequencing, and spatial transcriptomics, play crucial roles in disease diagnosis, therapeutic development, evolutionary research, and agricultural advancements. NGS technologies continue to drive genomic research forward, deepening our understanding of disease mechanisms and paving the way for innovative treatments.
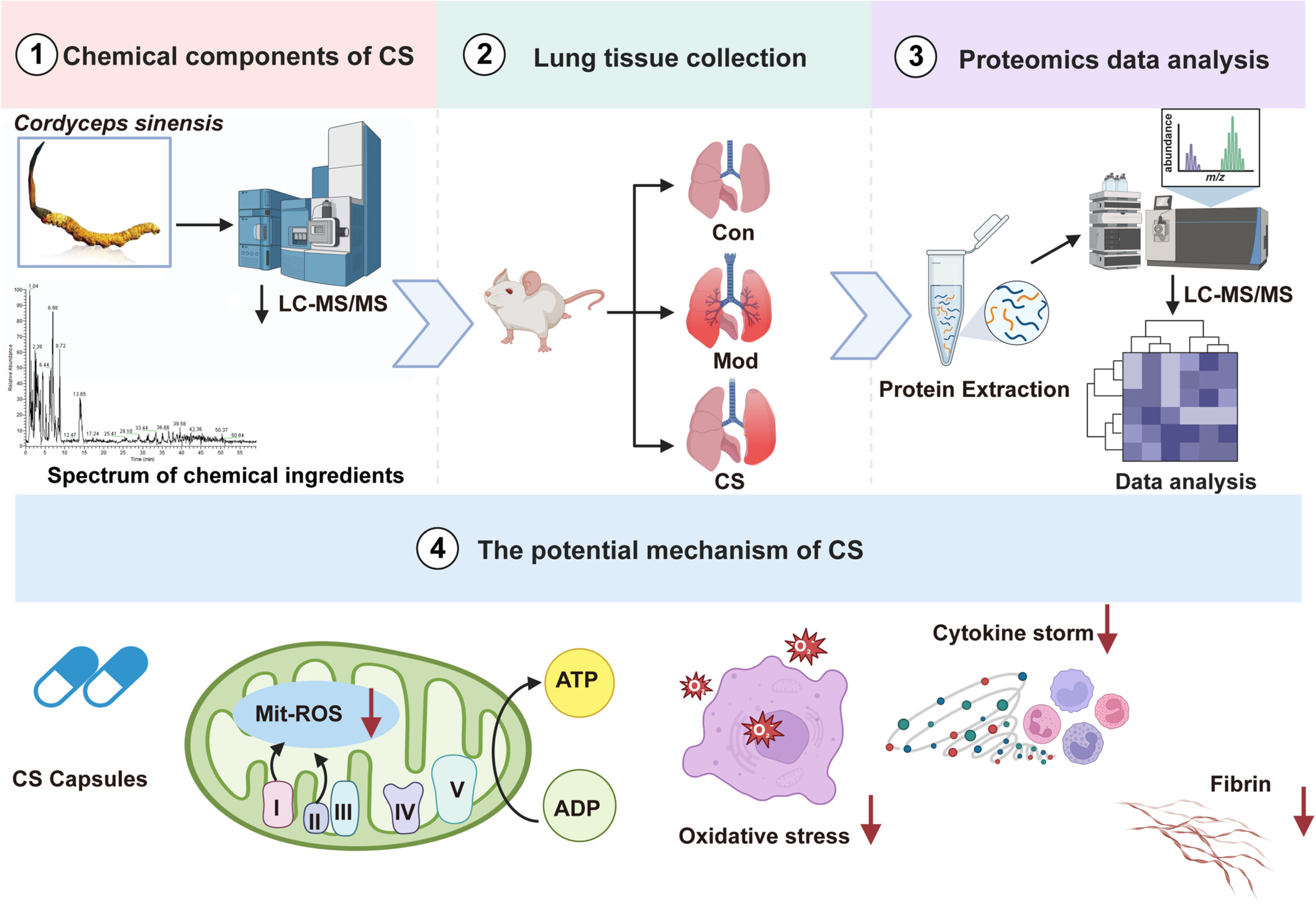
Cordyceps sinensis ameliorates idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in mice via inhibiting mitochondrion-mediated oxidative stress
- 19 July 2024
Graphical Abstract
Long COVID across SARS‐CoV‐2 variants: Clinical features, pathogenesis, and future directions
- 4 December 2024
Graphical Abstract
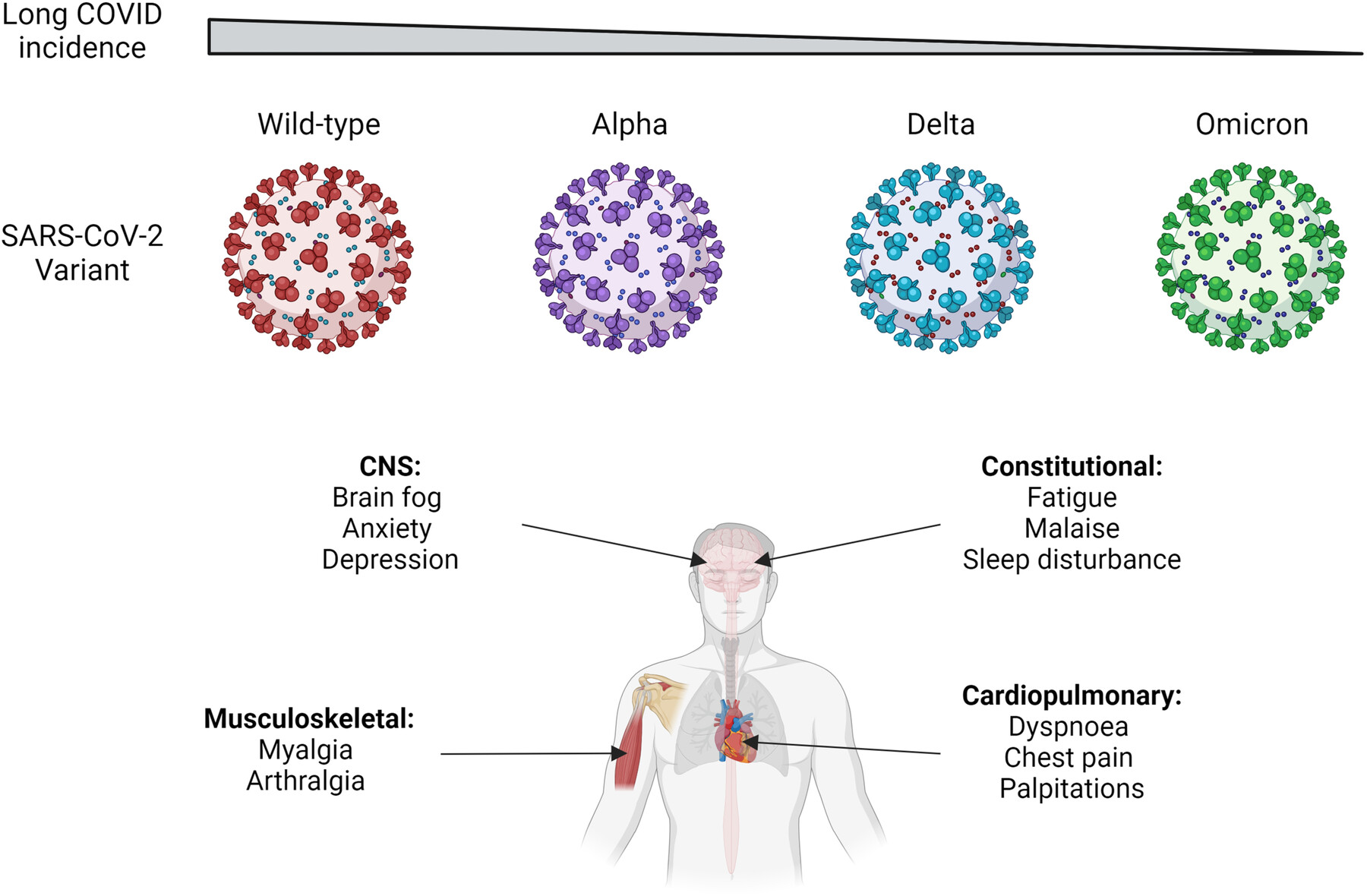
Long coronavirus disease (COVID) affects various body systems resulting in heterogeneous symptomatology, which could be due to increased immunity through vaccination or multiple exposures to the virus. Current data indicate that the incidence of long COVID from the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 wild-type variant to Omicron may be decreasing.
Deep learning methods for protein structure prediction
- 23 September 2024
Graphical Abstract
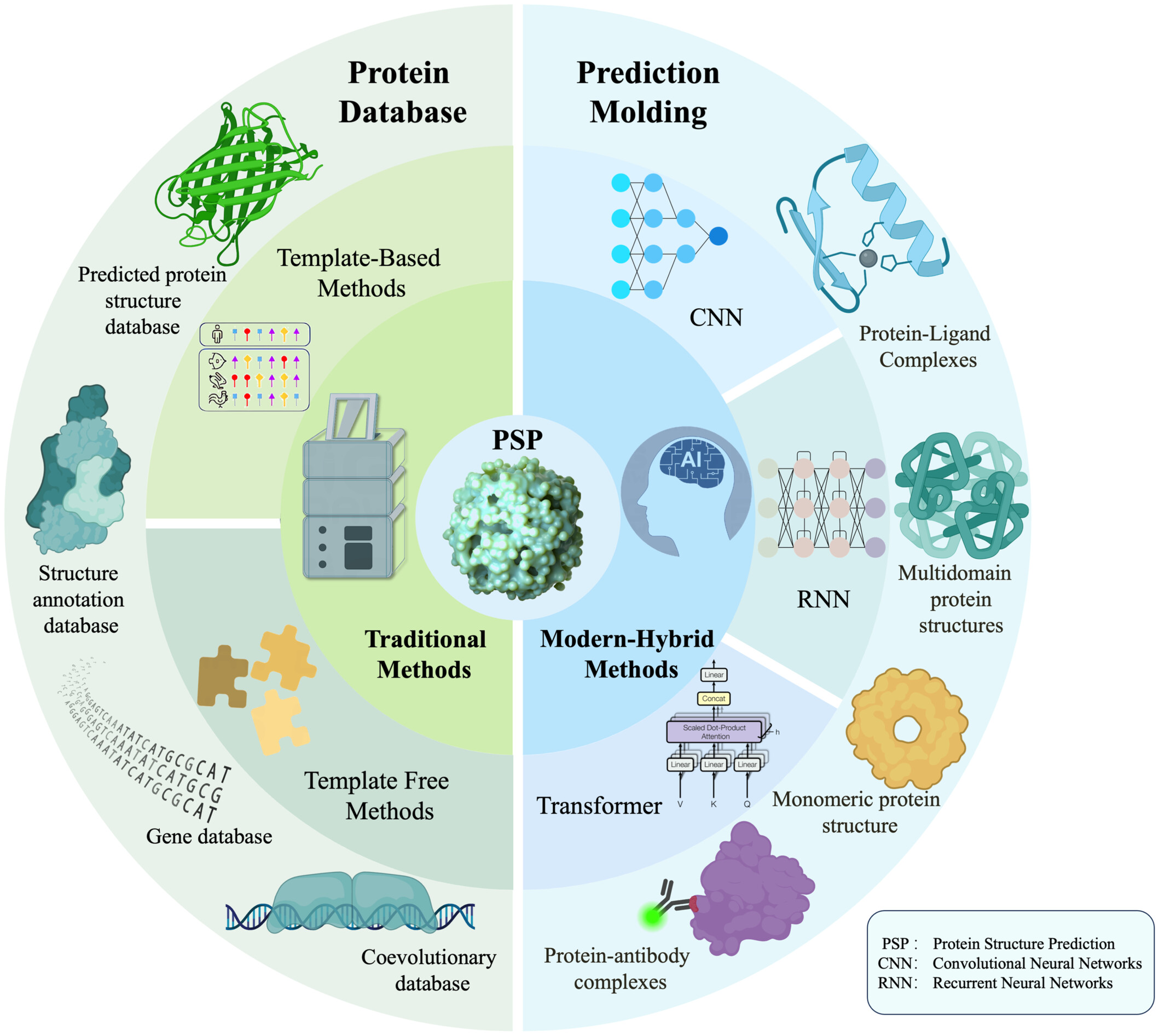
This review provides an overview of traditional and modern methods for protein structure prediction and their characteristics and introduces the groundbreaking network features of the AlphaFold family model. We summarize the applications of different bioinformatics databases and various models based on deep learning architectures (convolutional neural network, recurrent neural network, Transformer, etc.) in this field, which may provide directions for future development of predictive models such as prediction of the structure of large protein complexes and integration of protein language models.
Latest news
Recent issues
- Volume 4, Issue 3September 2025
- Volume 4, Issue 2June 2025
- Volume 4, Issue 1March 2025
- Volume 3, Issue 4December 2024





.png)