Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Biomarkers of ageing: Current state-of-art, challenges, and opportunities
- First Published: 18 June 2023
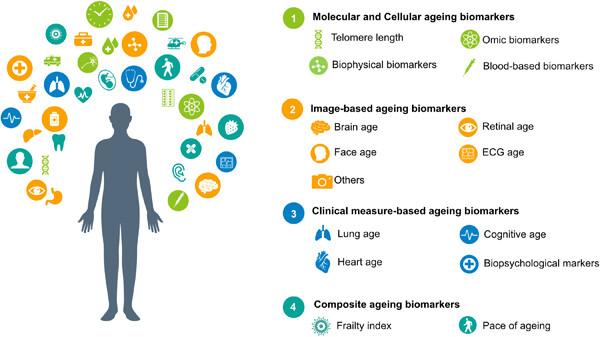
Increasing studies have captured the heterogeneity of the ageing process and introduced the concept of “biological age”. This review provides a comprehensive summary of currently identified ageing biomarkers in humans, spanning from molecular changes and imaging characteristics to clinical phenotypes with a contemporary perspective.
Accelerating the integration of ChatGPT and other large-scale AI models into biomedical research and healthcare
- First Published: 17 May 2023
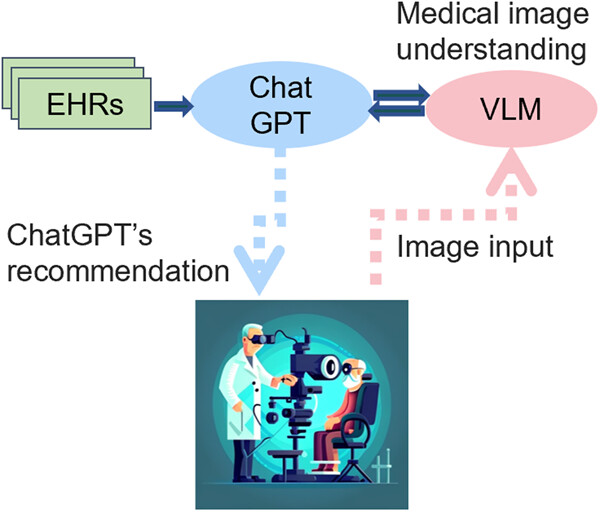
This review provides an overview of large-scale AI models, including language models (e.g., ChatGPT), vision-language models, and language-conditioned multiagent models, and discusses their potential applications in medicine, as well as their limitations and future trends. We also propose how large-scale AI models can be integrated into various scenarios of clinical applications.
Recent advances of Transformers in medical image analysis: A comprehensive review
- First Published: 24 March 2023
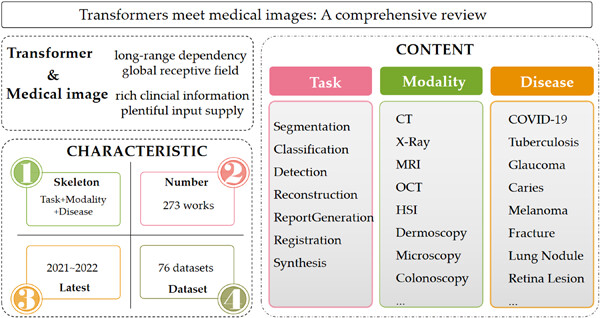
With the development of medical image analysis, many successful cases have shown the clinical potential of Transformer. Thus, this paper collected 273 latest (2021–2022) works that based their frameworks on Transformer. To facilitate the readers, 76 public medical image datasets have also been listed. Considering the diversity of these 273 works, we organize this paper as the following sequences: task-modality-disease.
Antiangiogenic therapy for ocular diseases: Current status and challenges
- First Published: 08 February 2023
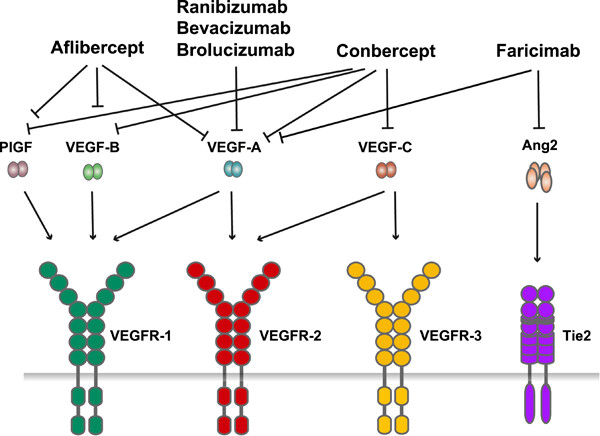
VEGF-A is a key factor mediating ocular neovascularization through their receptors. VEGF-A inhibitors are standard therapies for the treatment of ocular neovascular diseases, including ranibizumab, bevacizumab, aflibercept, conbercept, and faricimab. Although anti-VEGF therapy has achieved great success, many challenges and unmet needs exist. This perspective discusses the status of currently available anti-VEGF drugs, the evolving anti-VEGF formulations, and emerging antiangiogenic therapeutics for ocular neovascular diseases.
VDDB: A comprehensive resource and machine learning tool for antiviral drug discovery
- First Published: 30 January 2023
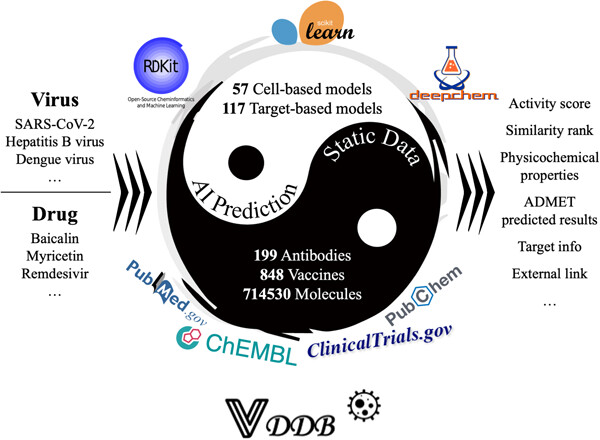
VDDB highlights 848 clinical vaccines and 199 clinical antibodies, as well as over 710,000 small molecules targeting 39 medically important viruses including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. VDDB also integrates 57 cell infection- and 117 target-based associated high-accuracy machine learning models to support various antiviral identification-related tasks, such as compound activity prediction, virtual screening, drug repositioning, and target fishing.
Anti-HIV drugs reduce risk of prediabetes and progression to type 2 diabetes in HIV-infected patients
- First Published: 03 April 2023
AlphaMissense, a groundbreaking advancement in artificial intelligence for predicting the effects of missense variants
- First Published: 05 January 2024
Ferredoxin 1, the key regulator of cuproptosis, was associated with prognosis and immune cell infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- First Published: 07 March 2023
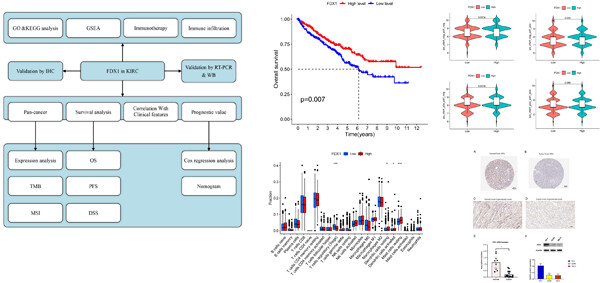
Ferredoxin 1 (FDX1) is a key gene in the process of Cuproptosis, and its expression level reflects the role of copper death in cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) to a certain extent. For the first time, we used a combination of bioinformatics and experimental validation to explore the role of FDX1 in ccRCC prognosis, immunotherapy, and immune cell infiltration.
PM2.5 air pollutant drives the initiate of lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 13 July 2023
Advancing systemic disease diagnosis through ophthalmic image-based artificial intelligence
- First Published: 13 March 2024
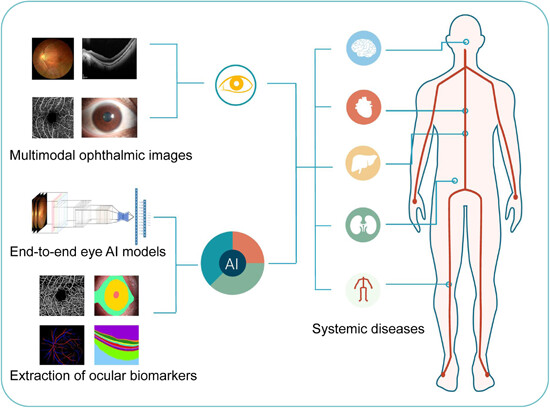
The structural imaging of the eye across various modalities, combined with artificial intelligences end-to-end models and feature extraction of ocular biomarkers, provides valuable insights into systemic diseases and their ophthalmic implications. This integrative approach significantly enhances the early detection of diseases, thereby improving patient care.
Oncolytic viral therapy as promising immunotherapy against glioma
- First Published: 16 October 2023
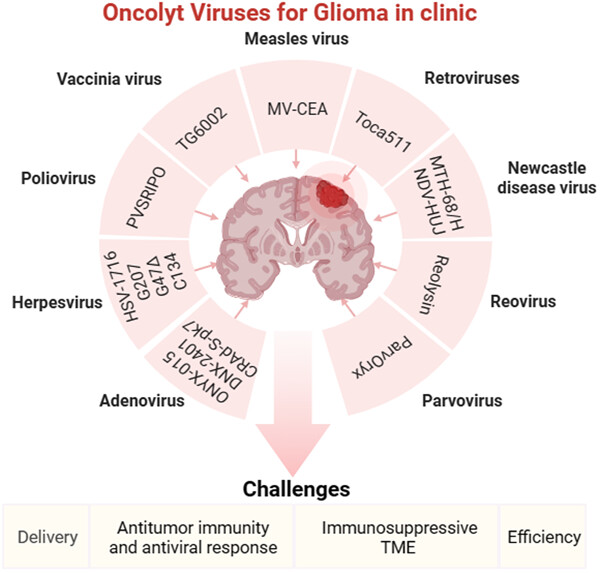
Multiple preclinical experiments and clinical trials have shown that oncolytic viruses (OVs) exhibit good antitumor activity in treating gliomas. This article summarizes the crucial clinical progress of various OVs in the treatment of glioma, the challenges faced by OVs in the treatment of glioma, and looks forward to the future development prospects of OVs.
A multiparameter radiomic model for accurate prognostic prediction of glioma
- First Published: 24 April 2023
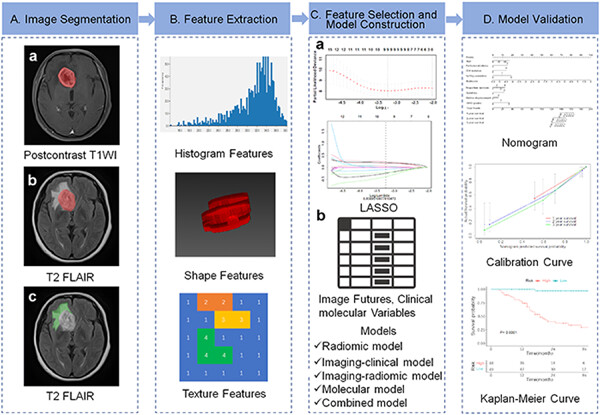
The combined model based on Radscore, conventional image features, and clinical molecular characteristics had better performance in predicting progression-free survival than other models based on uniparameter or biparameter, which could be informative for individualized treatments. The predictive factors in the combined model include age, peritumoral edema, proportion necrosis, Satellites, Midline Displacement, WHO grades, IDH mutation, 1p/19q co-deletion, and Radscore.
Direct cellular targets and anticancer mechanisms of the natural product oridonin
- First Published: 24 February 2023
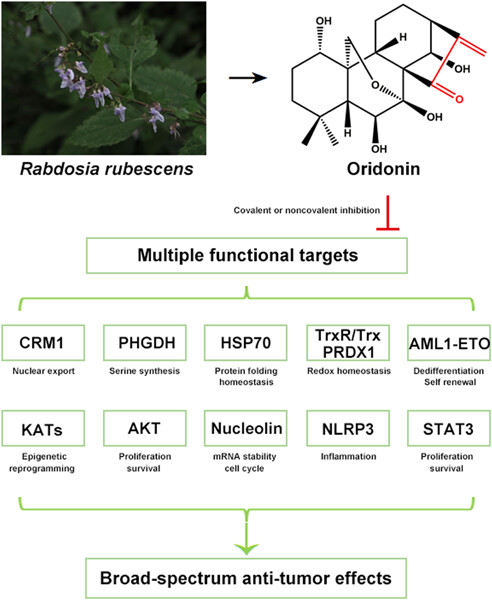
Oridonin, a natural diterpenoid, exhibits broad-spectrum anticancer effects by targeting multiple oncogenic proteins mainly via Michael addition between its unsaturated ketone and the cysteines in the target proteins. Thus, oridonin and its derivatives hold the potential to be developed as multitargeting anticancer drugs.










