Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Microglial Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 2 Deficiency Accelerates Seizure Development via Increasing AMPAR-Mediated Neuronal Excitability
- First Published: 14 July 2025
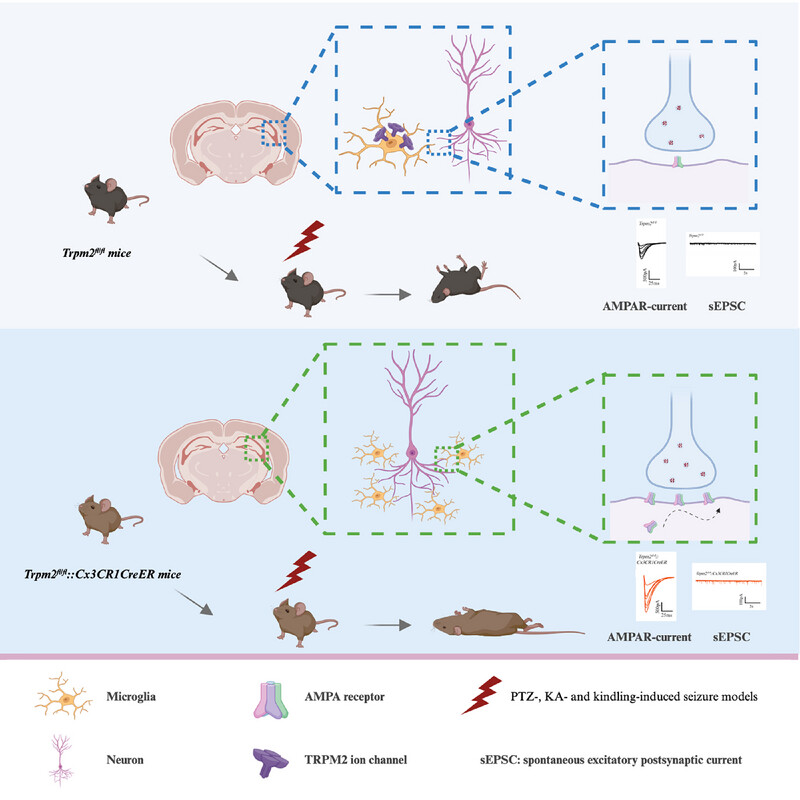
The deficiency of transient receptor potential melastatin type 2 (TRPM2) channel as a calcium permeable nonselective cation channel, accelerates seizure development in various mouse seizure models including PTZ-, KA-, and kindling-induced models, but does not affect seizure susceptibility in initial acute seizure. Interestingly, the deficiency of TRPM2 in microglia, but not CaMKIIα+ or PV+ neurons, is mainly responsible for seizure development. Moreover, microglial TRPM2 deficiency increases the excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons via enhancing the AMPAR-mediated excitatory synaptic transmission but does not influence the expression of inflammation cytokines.
REVIEW
Improvement of the Anticancer Efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade: Advances in Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
- First Published: 15 July 2025
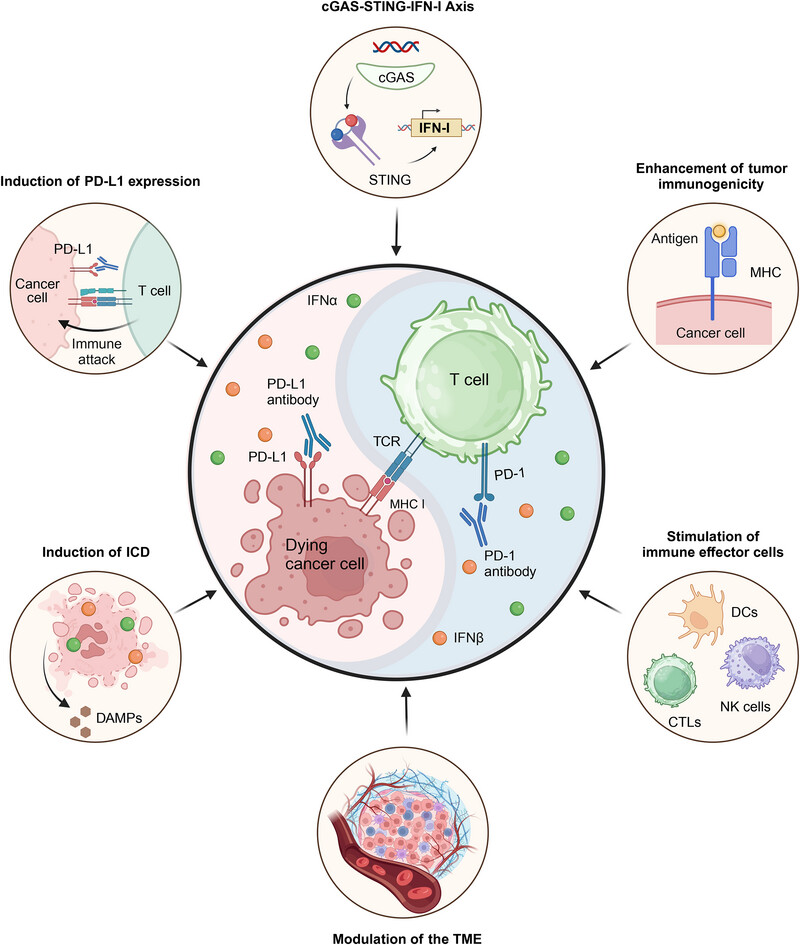
Mechanisms of alleviating resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade by IFN-α and IFN-β. In these mechanisms, the “yin-yang balance” is disrupted, thus preventing T cells from attacking cancer cells. Restoring this balance may improve the efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy and reinvigorate T cells and other immune cells to target and destroy cancer cells.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Long-Term High-Fat Diet Affected Bone Marrow Microenvironment During Aging at Single-Cell Resolution
- First Published: 21 July 2025
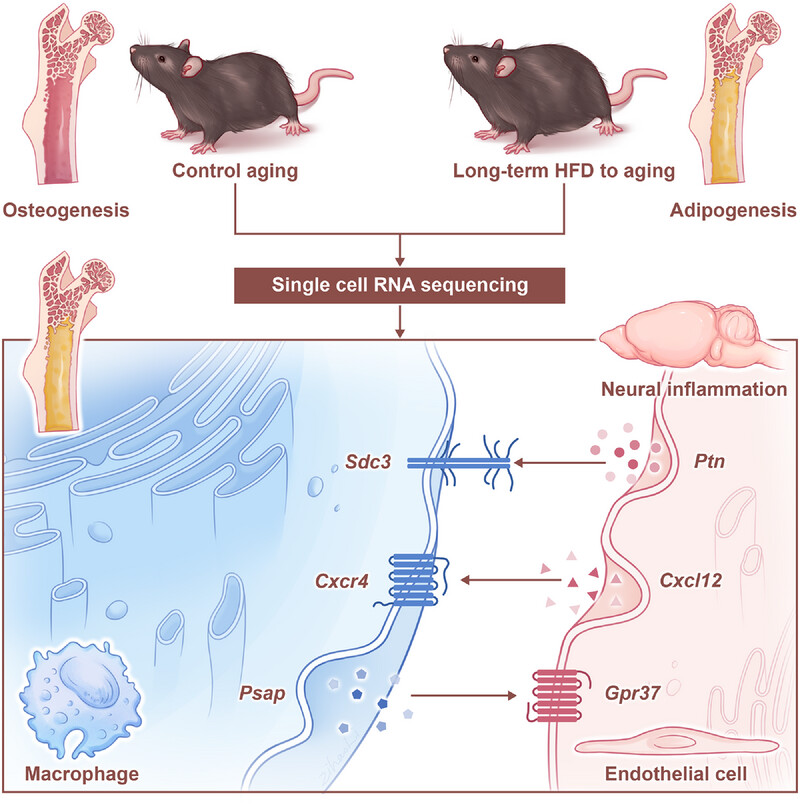
High-fat diet (HFD) promotes obesity and degenerative diseases. We established a long-term HFD to aging (LHA) mouse model, finding it induces a bone marrow shift from osteogenesis to adipogenesis and abnormal immune cell metabolic adaptations. Signaling axes were identified through single-cell RNA sequencing as potential bone marrow-brain crosstalk pathways, providing insights for treating related diseases.
Combining Intramuscular and Intranasal Immunization With the MF59-Adjuvanted Respiratory Syncytial Virus Pre-Fusion Protein Subunit Vaccine Induces Potent Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice
- First Published: 15 July 2025
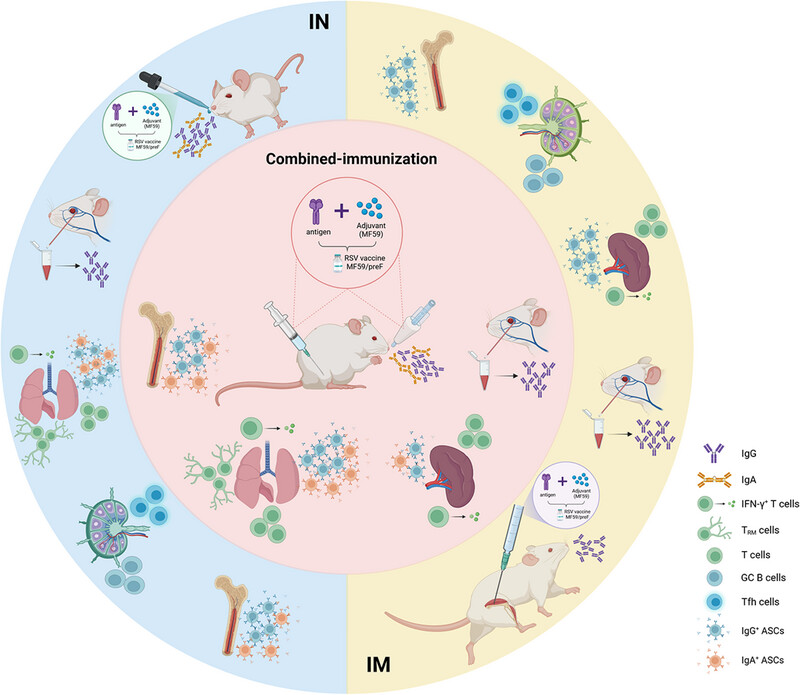
In our study, we formulated a protein-based vaccine known as MF59/preF, which contains RSV pre-fusion (preF) protein antigen in combination with an MF59-like oil-in-water adjuvant. Three-dose intramuscular (IM) administration of this vaccine induced robust humoral and cellular immunity against RSV F protein in systemic immune organs rather than at local sites. Intranasal (IN) immunization with MF59/preF demonstrated superior mucosal immunity, characterized by elevated levels of secretory IgA antibodies and an increased frequency of tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells locally. We then optimized the MF59/preF vaccine by combining IM and IN immunization, which induced stronger systemic and mucosal immunity.
HIGHLIGHT
SARS-CoV-2 Spike S2 Refolding: Structural Insights and Inhibition Strategies Against Emerging Variants
- First Published: 15 July 2025
REVIEW
Extracellular Matrix Signaling Cues: Biological Functions, Diseases, and Therapeutic Targets
- First Published: 17 July 2025
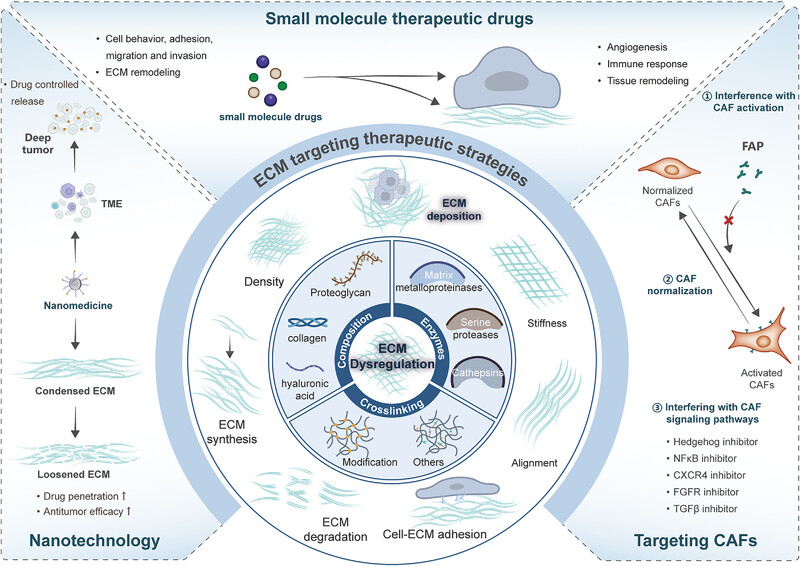
Targeting ECM dysregulation: therapeutic strategies for disease intervention. Dysregulated ECM composition and biomechanics contribute to disease pathogenesis in cancer and fibrotic disorders. Physical modulation: Nanomedicine-based strategies tune ECM physical properties (e.g., density, stiffness) to enhance drug penetration and therapeutic efficacy in the TME. Molecular targeting: Small-molecule drugs selectively modify ECM components to induce angiogenesis, immune response, and tissue remodeling. Cellular reprogramming: Pharmacological intervention of CAF signaling pathways promotes functional normalization, thereby restoring ECM homeostasis.
Astrocyte in Neurological Disease: Pathogenesis and Therapy
- First Published: 17 July 2025
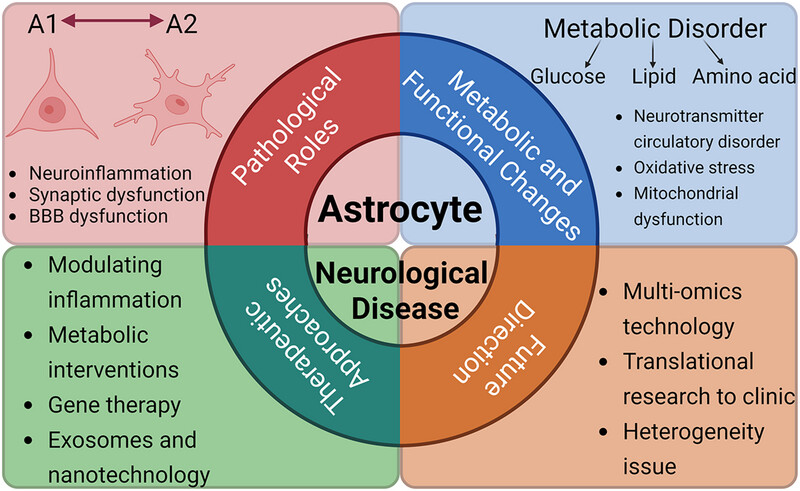
This review provides comprehensive overview of astrocytes in neurological disorders. Astrocytes contribute to neurological disorders via A1/A2 polarization, inducing neuroinflammation, synaptic, and BBB dysfunction. Metabolic disturbances in glucose, lipid, and amino acid pathways leading to oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Therapeutic targets include inflammation modulation, gene therapy, and nanotechnology. Future directions include multi-omics integration, clinical translation, and resolving astrocyte heterogeneity.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Association Between Preoperative Cognitive Performance and Postoperative Delirium in Older Patients: Results From a Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study, and a Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 17 July 2025
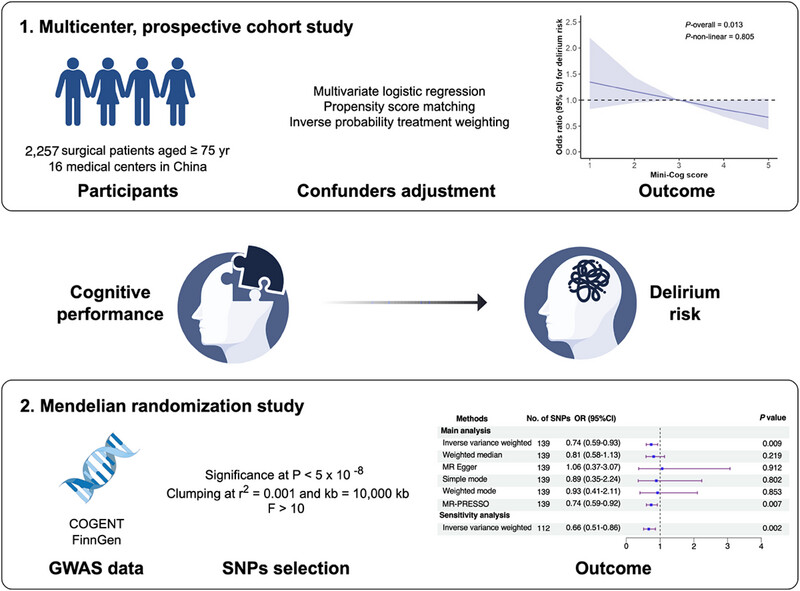
We analyzed population-based data from multicenter cohorts and found a nearly linear negative correlation between preoperative cognitive performance and postoperative delirium risk. In addition, our Mendelian randomization study provides genetic evidence supporting a causal relationship between cognitive performance and delirium risk.
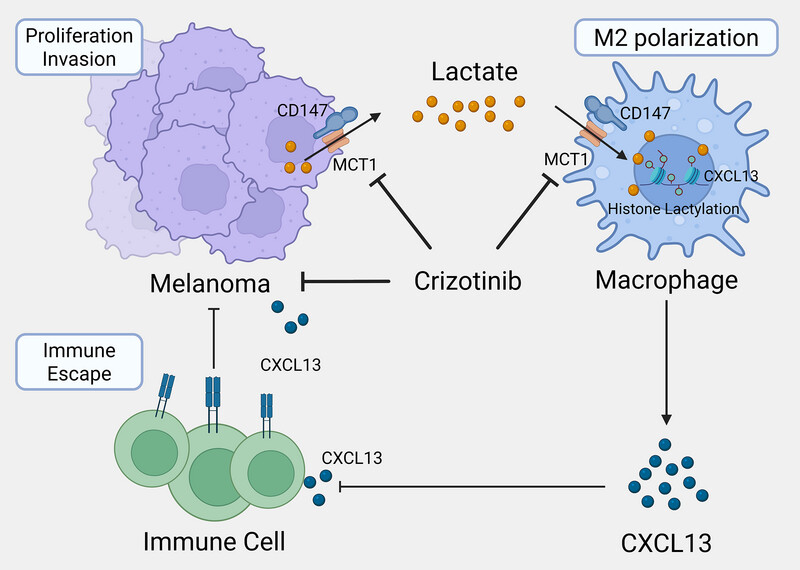
Crizotinib: A Novel Strategy to Reverse Immunosuppression in Melanoma by Targeting Lactate Transport
- First Published: 21 July 2025
Short-Term Results of the SONCAR Study: Optimized Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Patients
- First Published: 23 July 2025
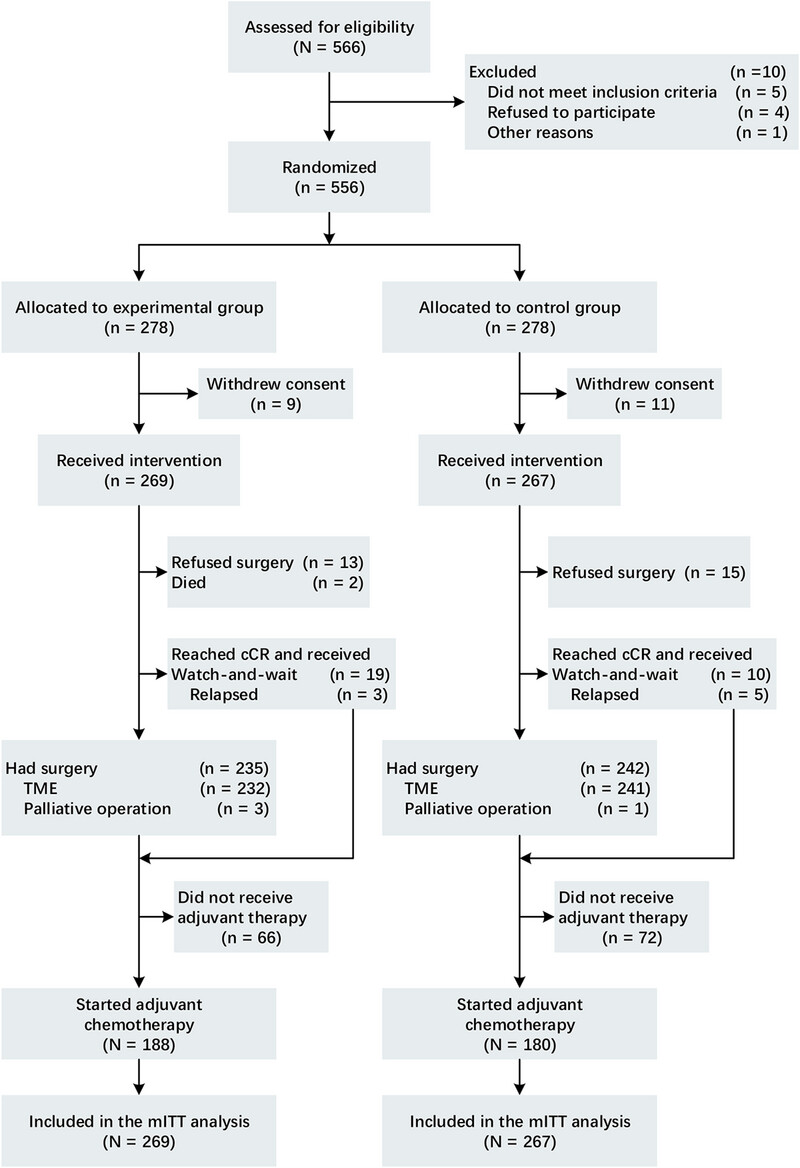
This study investigates whether adding four cycles of CapOX to standard neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy improves overall survival in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. The results show that this combination significantly increases complete tumor response rates, particularly for tumors close to the anal verge, with manageable toxicity.
A Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Gamma Inhibitor Enhances Anti-Programmed Death-1/Programmed Death Ligand-1 Antitumor Effects by Remodeling the Tumor Immune Microenvironment of Ovarian Cancer
- First Published: 23 July 2025
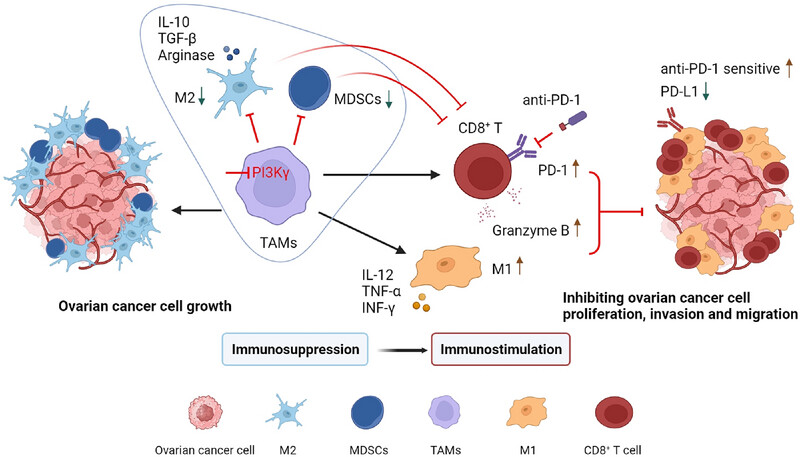
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma (PI3Kγ) inhibitor can sensitize the anti-programmed death-1/programmed death ligand-1 (anti-PD-1/PD-L1) response in ovarian cancer by modulating the PI3Kγ-AKT-NF-κB pathway to remodel tumor immune microenvironment as an activated status, along with downregulating the expression of PD-L1.
REVIEW
Mitochondria as Regulators of Nonapoptotic Cell Death in Cancer
- First Published: 23 July 2025
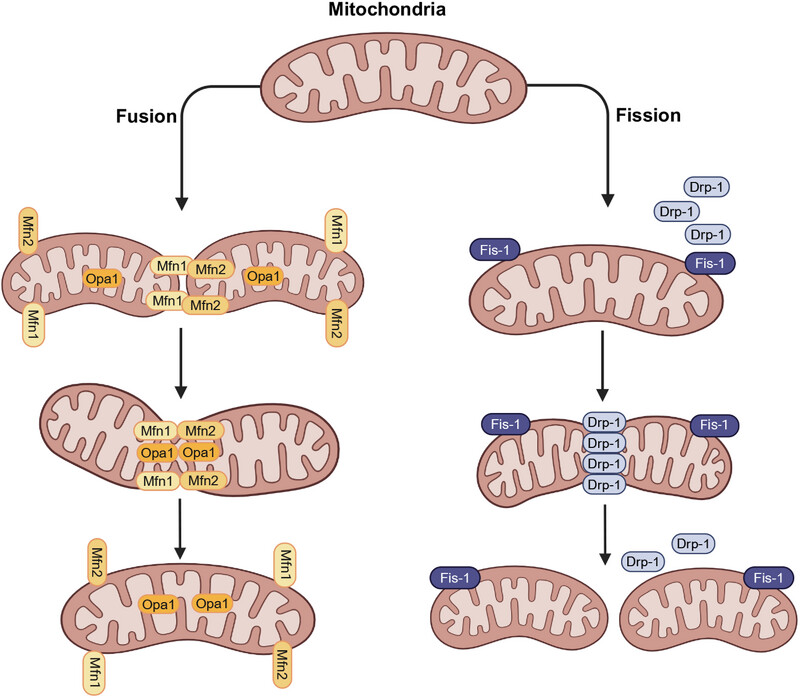
Mitochondrial fission and fusion are key processes in maintaining cellular health. Fission is driven by proteins like, Fis-1, which recruits DRP-1, to facilitate the division of mitochondria. Fusion, however, is mediated by mitofusion 1(MFN1), mitofusion 2(MFN2), and optic atrophy 1 (OPA1), which work together to merge mitochondria, allowing functional maintenance. These opposing but complementary processes are crucial for cellular adaptation and energy regulation.
Peptide Drug: Design and Clinical Applications
- First Published: 25 July 2025
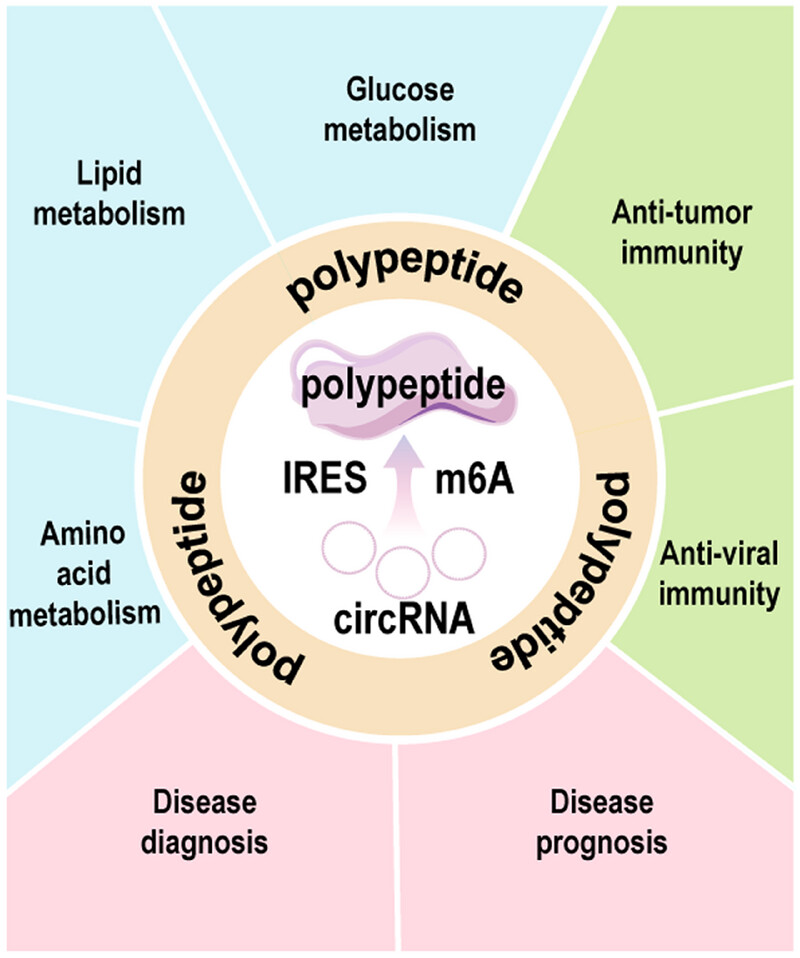
The diagram illustrates the role of poly peptides in various biological processes. It highlights their involvement in glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism, as well as in antitumor and antiviral immunity. Additionally, poly peptides are linked to disease diagnosis and prognosis, emphasizing their significance in healthcare.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Prognostic Value of Coronary Angiography-Derived Index of Microvascular Resistance in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- First Published: 25 July 2025
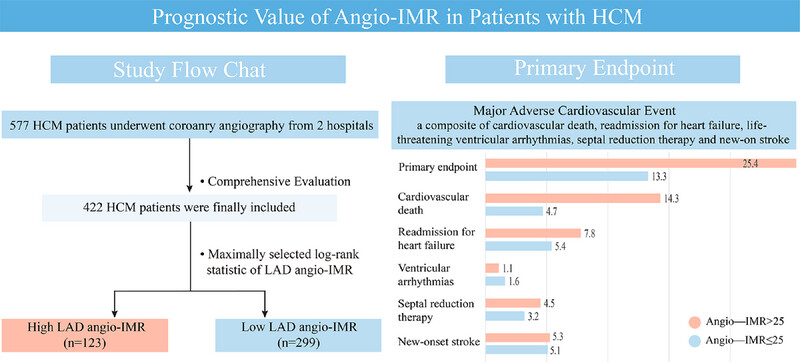
With an angio-IMR threshold of over 25, nearly one-third of HCM patients demonstrated CMD in the LAD. Patients with LAD angio-IMR > 25 exhibited a higher incidence of MACE compared to those with LAD angio-IMR ≤ 25 (cumulative incidence, 25.4% vs. 13.3%, p = 0.035). In HCM patients who underwent coronary angiography without stenting, angio-IMR could be used as an additional risk stratification and precise assessment tool.
REVIEW
Macrophages: Subtypes, Distribution, Polarization, Immunomodulatory Functions, and Therapeutics
- First Published: 25 July 2025
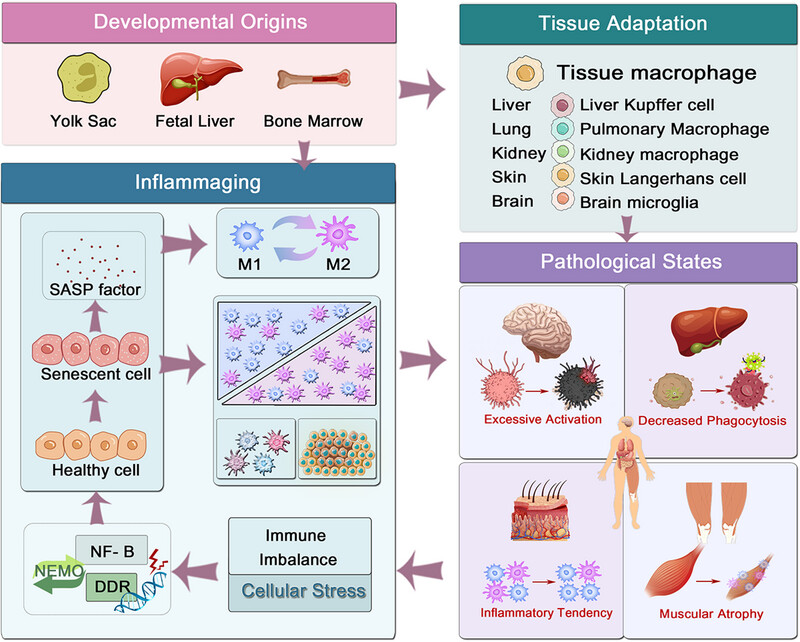
Macrophages originate from the yolk sac, fetal liver, and bone marrow, differentiating into two main subtypes: M1-like (proinflammatory) and M2-like (anti-inflammatory). These subtypes exhibit high plasticity, allowing them to transform in response to environmental cues or therapeutic interventions. In various chronic inflammatory conditions, such as aging and cancer, the polarization and functions of macrophages in various tissues (including liver, lung, kidney, skin, and brain) undergo significant alterations. They enter an imbalanced state, characterized by excessive M1-like activation, weakened phagocytosis, aggravated inflammation, and muscle atrophy. Senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factors further exacerbate these changes, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue dysfunction.
HIGHLIGHT
Metabolic and Epigenetic Control of CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion: The Acetate-to-Citrate Switch
- First Published: 25 July 2025