Edited by: Professor Stephen Ackland
Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology provides a multidisciplinary oncology forum, facilitating collaboration and exchanging information on all aspects of cancer medicine, cancer treatment, and cancer care across the Asia-Pacific region.
This clinical oncology journal is ideally positioned to receive articles that deal with diversity in cancer behavior, management and outcome related to ethnic, cultural, economic and other differences between populations. We publish Original Articles, Review Articles, Letters to the Editor, Case Reports, Editorials, and Guidelines.
Journal Metrics
- 3.9CiteScore
- 1.6Journal Impact Factor
- 8%Acceptance rate
- 57 days Submission to first decision
Articles
Understanding and Addressing Clinical Variation in Rectal Cancer Care: Application of an Analytic Framework
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
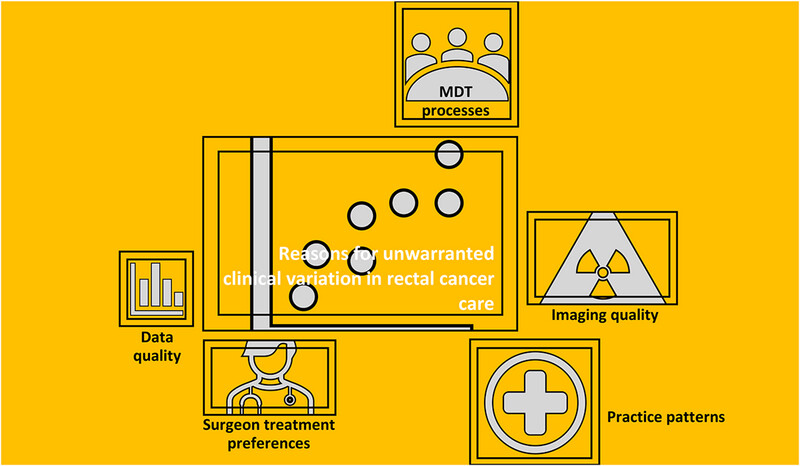
There is substantial clinical variation in the use of neoadjuvant radiotherapy for high-risk rectal cancer, ranging from 25% to 59% in New South Wales, Australia. Assessed against an empirically based analytic framework, the reasons for this clinical variation were largely unwarranted and related to MDT processes, imaging quality, workforce/practice patterns, surgeon treatment preferences, and data quality.
The Current Status of Circulating Tumor DNA Utilization in Australasia: A Survey of Thoracic Oncology Group Australasia Members
- 16 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
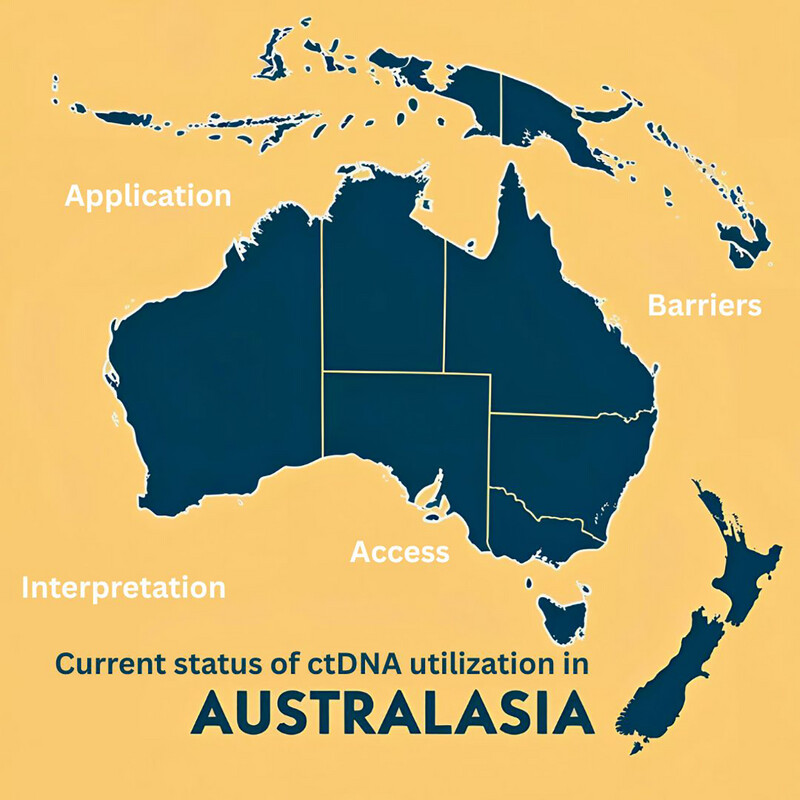
This study explores the current status, utilization, and barriers to circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) testing in thoracic oncology across Australia and New Zealand. While clinicians recognize the potential of ctDNA for guiding targeted therapy and monitoring disease, real-world access remains inconsistent due to funding, availability, and infrastructure gaps.
Development and Real‐World Evaluation of a Statewide Mainstream Model of Germline Genetic Testing for BRCA1/2 and Mismatch Repair Gene Variants (Lynch Syndrome)
- 9 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
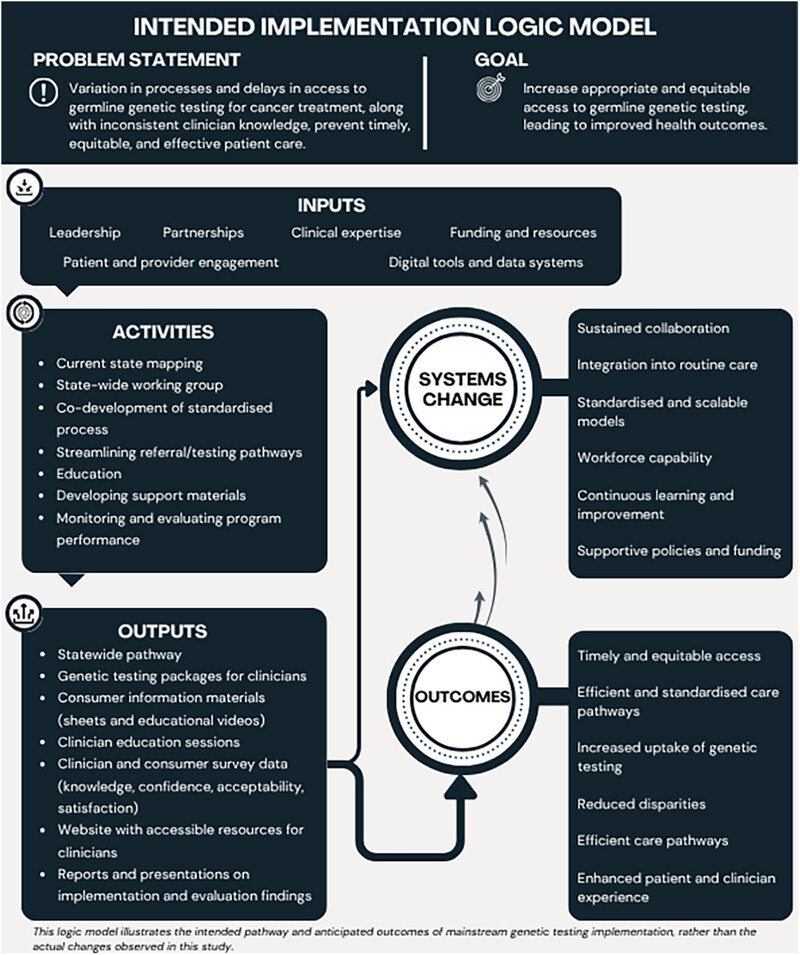
This translational quality improvement study evaluated a statewide pathway for mainstream genetic testing in South Australia. Adoption of mainstream BRCA1/2 testing increased significantly, but not MMR testing. Findings highlight the need for tailored, context-specific strategies to integrate genetic testing into routine care across diverse cancer types and clinical environments.
Implementing Teletrials to Improve Equity of Access for Regional Patients With Cancer: Report From the Victorian Teletrial Collaborative
- 6 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
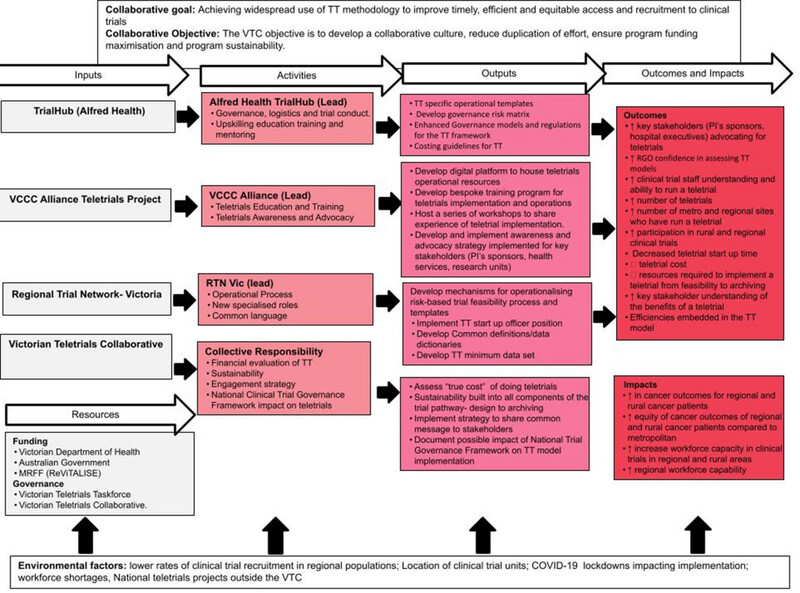
This paper summarizes the efforts of the Victorian Teletrials Collaborative to overcome barriers to using telehealth to conduct clinical trials. The collaborative has produced tools and suggestions for health services and clinicians for the implementation of teletrials to enable improved access to clinical trials for disadvantaged populations.
Optimizing Digital Mental Health Interventions for Breast Cancer Survivors: Insights and Future Directions
- 1 July 2025
Long‐term Longitudinal Observation of Lenvatinib‐associated Adverse Events in Patients With Unresectable Radioiodine‐refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
- 30 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
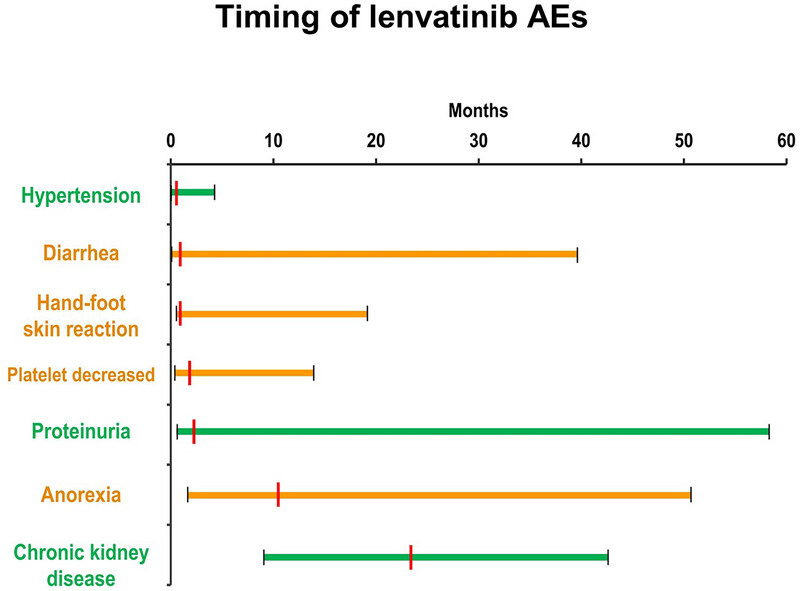
We longitudinally assessed long-term adverse events (AEs) in patients with advanced differentiated thyroid cancer who received lenvatinib. Notable intolerable grade 2 and grade 3 AEs were developed in the following order: hypertension, diarrhea, hand-foot skin reaction, platelet decrease, proteinuria, anorexia, and chronic kidney disease. After 2 years of administration, the decrease in renal function became remarkable. Green, VEGF-associated AEs; orange, other AEs.
A Multicenter Real‐World Study of Outcomes in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B‐Cell Lymphoma Treated with a Polatuzumab Vedotin‐Based Regimen in a Compassionate Use Program in Malaysia
- 27 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
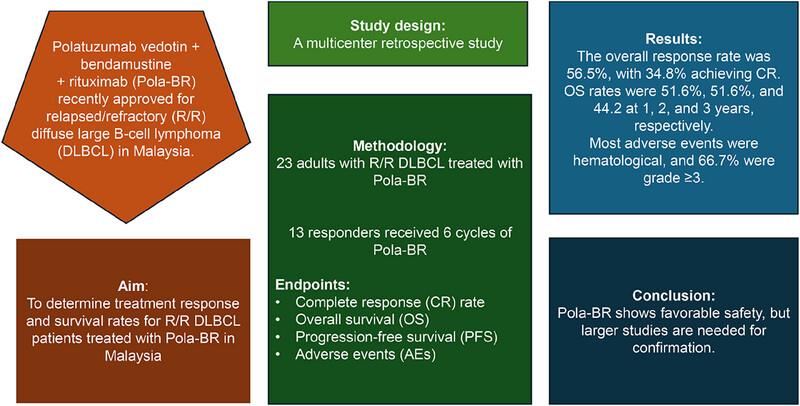
A multicenter retrospective study in Malaysia evaluated the effectiveness of Pola-BR for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Among 23 patients, the overall response rate was 56.5%, with 34.8% achieving a complete response. The 1-, 2-, and 3-year overall survival rates were 51.6%, 51.6%, and 44.2%, respectively, with a median OS of 27 months. Bulky disease was a significant hazard for progression, and 66.7% of adverse events were grade ≥ 3, predominantly hematological.
Prognostic Impact of Synchronous and Metachronous Second Primary Cancers in Laryngeal Cancer Patients Treated With Radiotherapy: Variable With Time‐Varying Effects and Cox Proportional Hazard Analyses
- 22 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
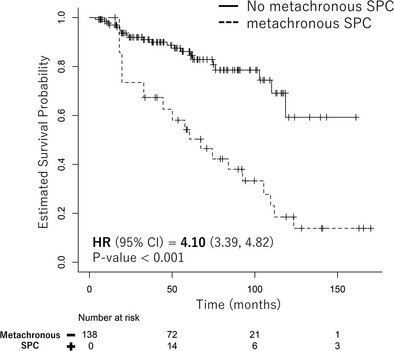
We retrospectively analyzed 138 patients with laryngeal cancer who received radiotherapy. Synchronous second primary cancer was a significant prognostic factor of poor outcomes (hazard ratio [HR], 4.42) on time-independent multivariate analysis, and metachronous second primary cancer was a significant prognostic factor of poor outcomes (HR, 4.55) in the time-dependent Cox proportional hazards model. Reliable initial examinations and close follow-up are important.
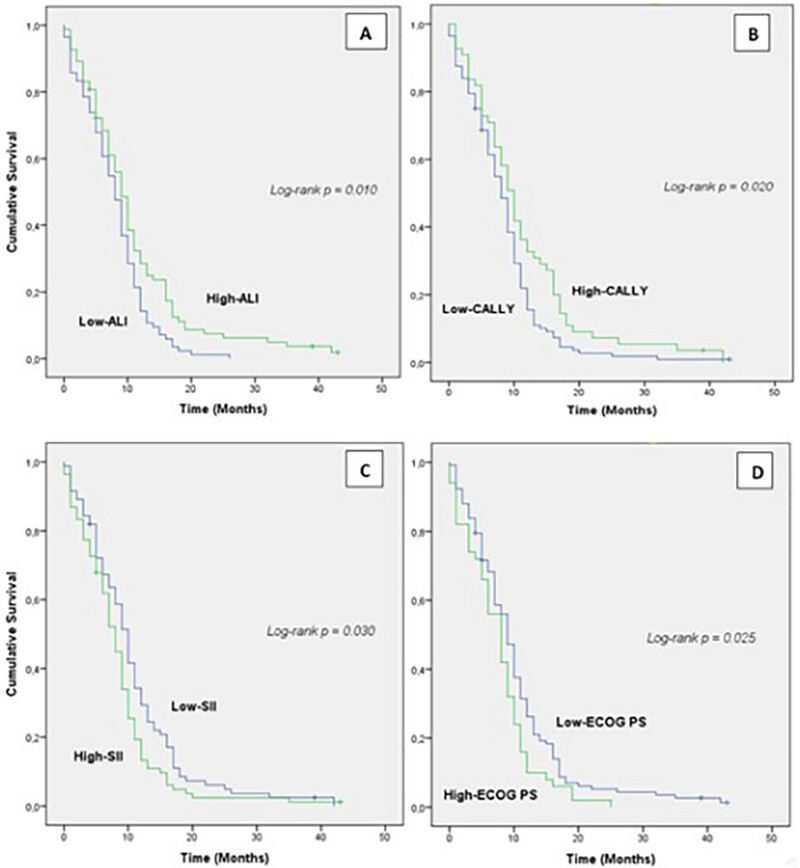
Inflammation‐Based Prognostication in Extensive‐Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer in the First‐Line Setting: The Advanced Lung Inflammation Index and the Others
- 18 June 2025
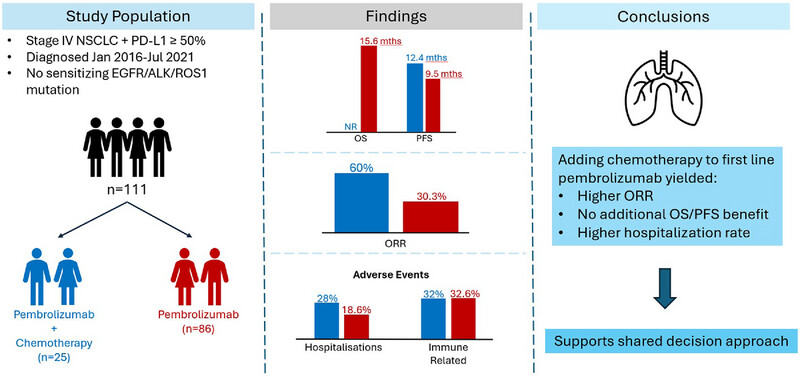
Real‐World Survival Outcomes of Patients With High PD‐L1 Advanced NSCLC Who Received Chemoimmunotherapy Versus Immunotherapy
- 17 June 2025
Overdiagnosis and overtreatment of ground‐glass nodule‐like lung cancer
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 108-114
- 4 January 2024
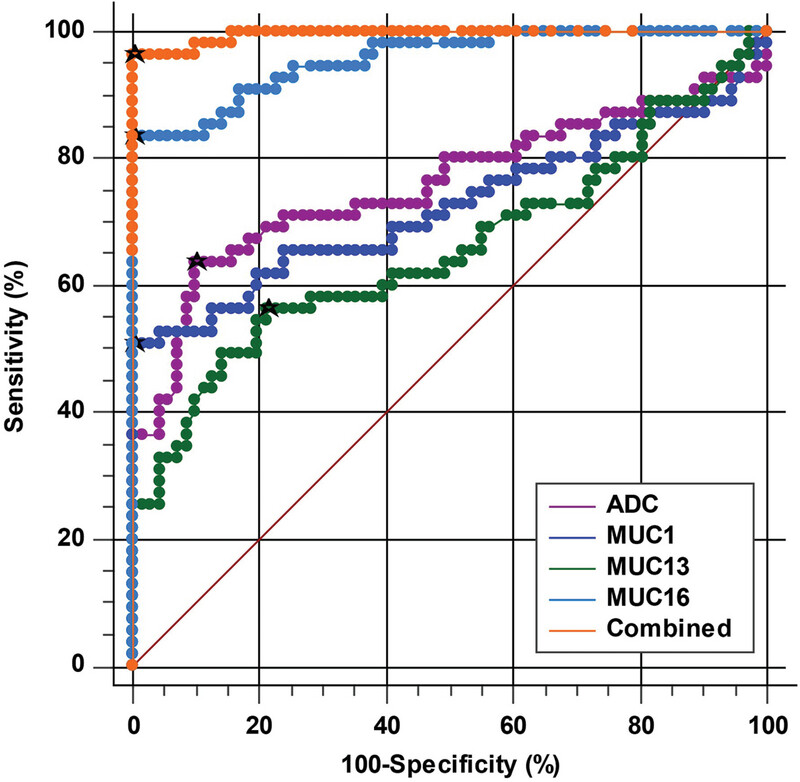
Diagnostic efficacy of combining diffusion‐weighted magnetic resonance imaging with serum Mucin 1, Mucin 13, and Mucin 16 in distinguishing borderline from malignant epithelial ovarian tumors
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 115-122
- 14 January 2024
Association of optimism and social support with health‐related quality of life among Australian women cancer survivors – A cohort study
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 221-231
- 21 May 2024
Graphical Abstract
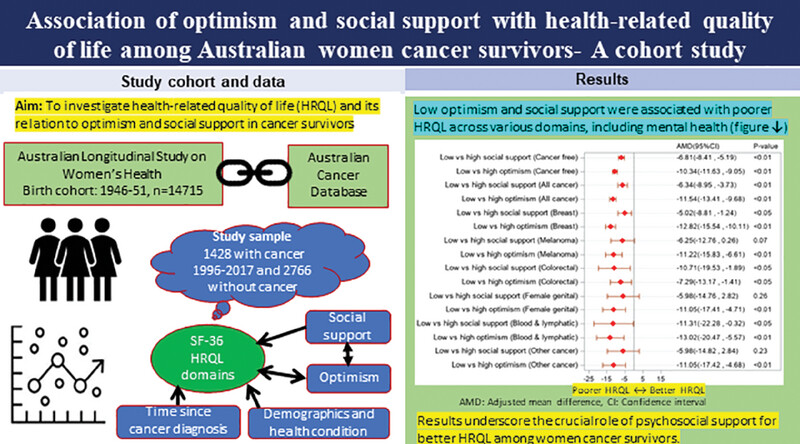
The study found that lower optimism was associated with poorer health-related quality of life (HRQL) across all domains. Social support and its interaction with optimism were significant in women with any cancer or breast cancer across various domains, highlighting the crucial role of psychosocial support for better HRQL.
Breast conservation versus mastectomy for metaplastic breast cancer: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 150-155
- 29 May 2024
Graphical Abstract

Metaplastic breast cancer is an aggressive subtype of breast cancer without clear surgical treatment guidelines. This systematic review and meta-analysis showed no difference in overall survival between breast conservation and mastectomy, suggesting that both may be reasonable treatment approaches for this condition.
Multi‐omic analysis of dysregulated pathways in triple negative breast cancer
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 450-462
- 20 June 2024
Graphical Abstract
Association of chemotherapy dose intensity and age with outcomes in patients with Ewing's family sarcoma
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 87-94
- 11 August 2023
Graphical Abstract
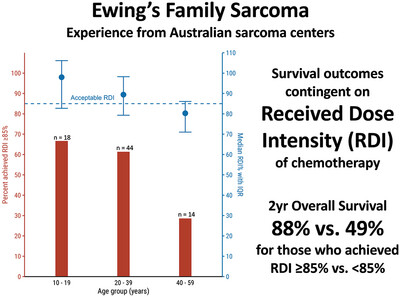
A multicenter study of clinicopathological characteristics and treatment outcomes of patients aged ≥10 years diagnosed with Ewing's family sarcoma was performed using retrospective data from the ANZSA ACCORD sarcoma database and medical records. Older patients had poorer survival outcomes, which may be driven by lower received dose intensity of chemotherapy .
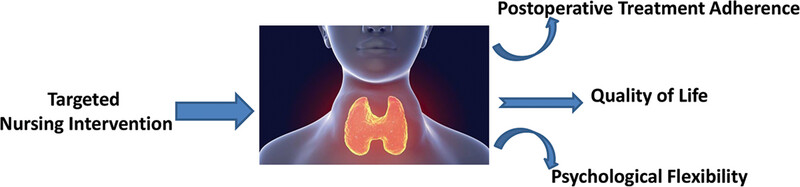
The impact of targeted nursing intervention on postoperative medication adherence, quality of life, and psychological flexibility of thyroid cancer patients
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 102-107
- 7 December 2023
Risk classification system using the detailed positive surgical margin status for predicting biochemical recurrence after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 156-162
- 21 March 2024
Graphical Abstract
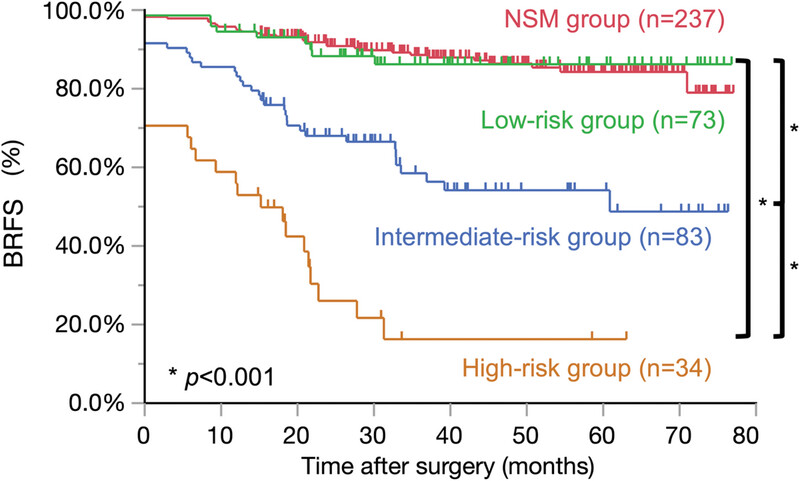
We found that maximum positive surgical margin (PSM) length > 5.0 mm and the International Society of Urological Pathology grade group at the PSM ≥3 were particularly strong predictive factors for biochemical recurrence (BCR) after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP). We could stratify patients according to the detailed PSM status. This risk classification might be useful to predict early BCR and help guide urologists in decision-making in relation to additional treatment after RARP .
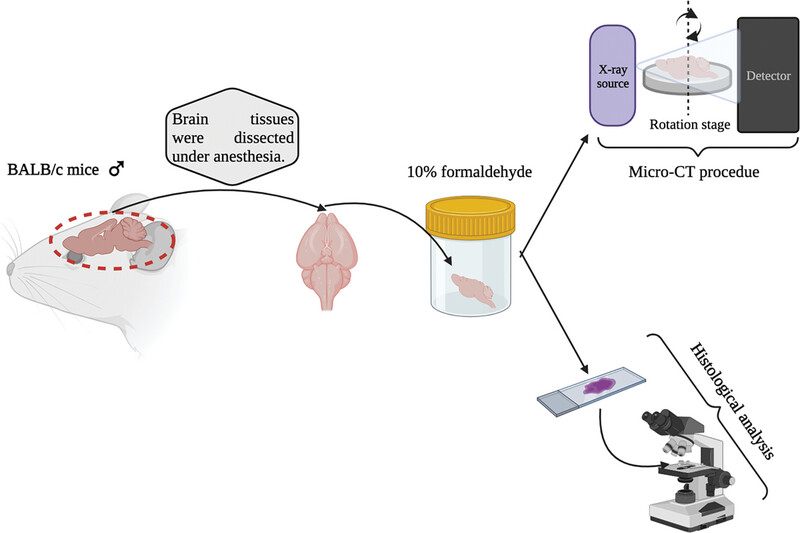
Evaluation of the anticarcinogenic effects of Rutin on brain tissue in mice with Ehrlich ascites carcinoma by micro‐computed tomography and histological methods
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 174-179
- 25 March 2024
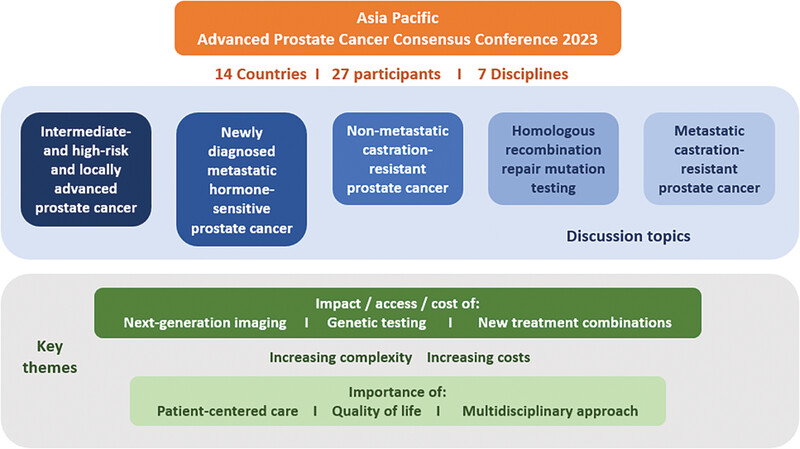
Management of advanced prostate cancer in the Asia‐Pacific region: Summary of the Asia‐Pacific Advanced Prostate Cancer Consensus Conference 2023
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology
- 481-490
- 16 April 2024