Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Covers
Cover Picture: Fundamentals of Unanticipated Efficiency of Gd2O3-based Catalysts in Oxidative Coupling of Methane (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2024)
- First Published: 22 February 2024

The nature of adsorbed oxygen species determines the product selectivity in the oxidative coupling of CH4 as shown on the cover. In their Communication (e202319192), Guiyuan Jiang, Evgenii V. Kondratenko et al. describe how the formation of carbon oxides and ethane correlates with the binding strength of selective mono-atomic oxygen species. The strength affects the probability of their recombination to diatomic oxygen species oxidizing methane to carbon oxides. Cover image credit: Vita A. Kondratenko.
Inside Cover: Selective Intracellular Delivery of Antibodies in Cancer Cells with Nanocarriers Sensing Endo/Lysosomal Enzymatic Activity (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2024)
- First Published: 18 March 2024

Distinguish good from evil by selective endosomal escape. The nuanced endo/lysosomal activity of cathepsin B across cell types can act as a stimulus for cell-specific endosomal escape of proteins before degradation. In their Research Article (e202317817), Kazunori Kataoka, Horacio Cabral, et al. report nanocarriers leveraging on this differentiated cathepsin B activity to achieve cancer cell-specific delivery of antibodies. This innovative approach offers a new means for targeted intracellular delivery.
Inside Back Cover: Site-Selective Photo-Crosslinking of Stilbene Pairs in a DNA Duplex Mediated by Ruthenium Photocatalyst (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2024)
- First Published: 12 March 2024

Site-selective photocrosslinking of DNA duplex was achieved in the Research Article (e202319516) by Hiromu Kashida, Hiroyuki Asanuma et al. A ruthenium complex on a triplex-forming oligonucleotide effectively catalyzed [2+2] photocycloaddition of stilbene moieties in a DNA duplex under visible light. Since the reaction proceeds via triplet–triplet energy transfer, the reaction exhibited excellent site selectivity.
Back Cover: Rapid and Bifunctional Chemoselective Metabolome Analysis of Liver Disease Plasma Using the Reagent 4-Nitrophenyl-2H-azirine (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2024)
- First Published: 29 February 2024

A rapid functional group transformation method that converts metabolic carboxylic acids into a new ketone within 10 minutes using the reagent 4-nitrophenyl-2H-azirine (the bait for the fish) has been developed by Daniel Globisch et al. in their Communication (e202318579). The newly formed ketone was then captured by the chemical probe methodology Quant-SCHEMA (the fishing device) for quantification of all carboxylic acids even at very low quantities (depth of the ocean). This bifunctional methodology represents a new chemical biology tool for biomarker discovery and metabolomics.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Intermediate Color Emission via Nanographenes with Organic Fluorophores
- First Published: 22 March 2024

Nanotechnology. In their Research Article (e202315508), Ryo Sekiya, Takeharu Haino et al. report the utilization of nanographenes as carriers of fluorophores.
Graphical Abstract
Announcement
Introducing …
Sophia Fricke
- First Published: 01 March 2024

“Science is fun because it allows us to occupy a wonderful place at the edge of the known universe, where we can begin to understand our place in the world and then attempt to extend the boundaries of human knowledge … To improve my work-life balance, I maintain a steady supply of nerdy jokes …” Find out more about Sophia Fricke in her Introducing… Profile.
Minireviews
Mechanochemistry
Intermediates in Mechanochemical Reactions
- First Published: 05 January 2024
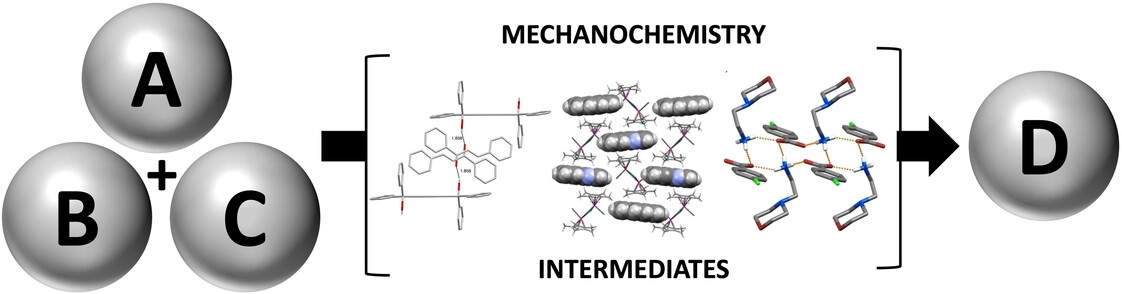
In this Minireview we present and discussed a series of examples from various areas in which reactive intermediates have been detected during mechanochemical reactions. Understanding the factors behind the formation and stabilization of these intermediates could enhance mechanochemical methods and chemical reaction development.
Systems Chemistry
Artificial Homeostasis Systems Based on Feedback Reaction Networks: Design Principles and Future Promises
- First Published: 16 January 2024
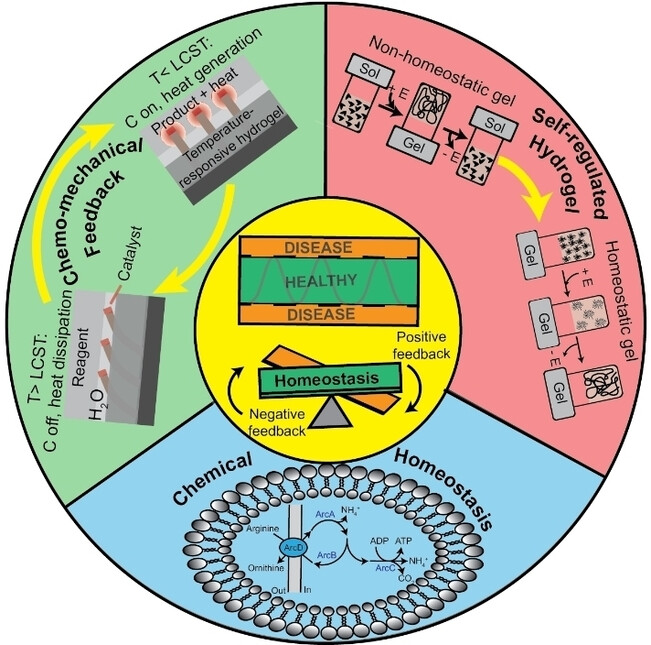
This review shows how to design feedback-controlled reaction networks in different molecular systems that have a range of non-linear functions. These networks are a useful set of tools for creating chemical systems and materials that are interactive and have homeostasis-like animate features. These discoveries pave the way for the development of forthcoming next-generation systems and materials.
Protein Self-Assembly
Designing Multifunctional Biomaterials via Protein Self-Assembly
- First Published: 11 January 2024
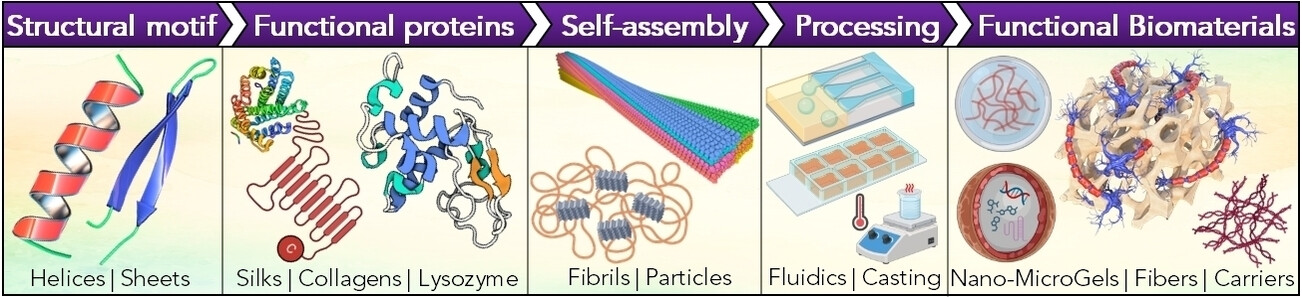
This Minireview sums up cutting-edge concepts regarding the formation of protein-based supramolecular structures, compartmentalization, and self-assembly monitoring; it compares the routes of their modifications and applications in multifunctional biomaterial design. We summarize the current knowledge about machine learning/artificial intelligence applications for protein structure prediction/obtainment and link it to biomaterial performance.
Reviews
Radiochemistry
Light-Driven Radiochemistry with Fluorine-18, Carbon-11 and Zirconium-89
- First Published: 22 December 2023

This review explores recent developments in light-driven radiochemistry, focusing on key isotopes (fluorine-18, carbon-11, zirconium-89) in positron emission tomography (PET). These technologies have been used to radiolabel small molecules, peptides and larger biomolecules such as monoclonal antibodies.
Photocatalysis
Light-Driven Synthesis and Functionalization of Bicycloalkanes, Cubanes and Related Bioisosteres
- First Published: 05 January 2024
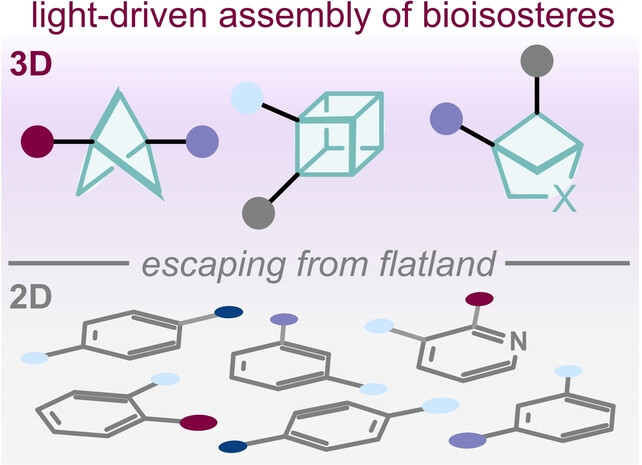
This Review aims to provide an overview on the recent photochemical strategies for the construction and/or functionalization of bicycloalkanes, cubanes, and some of their heterocyclic structural analogues. The synthetic methods have been organized according to the molecular target, and with a particular emphasis on the type of photochemical mechanisms involved. Future perspectives and open synthetic challenges within the field are presented.
Research Articles
Nanographene
Intermediate Color Emission via Nanographenes with Organic Fluorophores
- First Published: 08 January 2024

Nanographenes (NGs) produced by top-down methods carry multiple functional groups. We utilized this aspect for the reproduction of purple light by adding red- and blue-light emitting fluorophores. Based on our results, NGs can be utilized as carriers of fluorophores capable of generating intermediate colors of light.
Bioconjugation
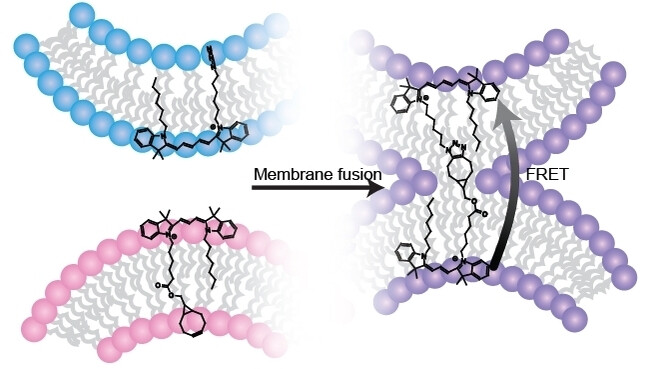
Strain-Promoted Cycloadditions in Lipid Bilayers Triggered by Liposome Fusion
- First Published: 04 March 2024
Gene Delivery
Supramolecular Genome Editing: Targeted Delivery and Endogenous Activation of CRISPR/Cas9 by Dynamic Host-Guest Recognition
- First Published: 05 February 2024
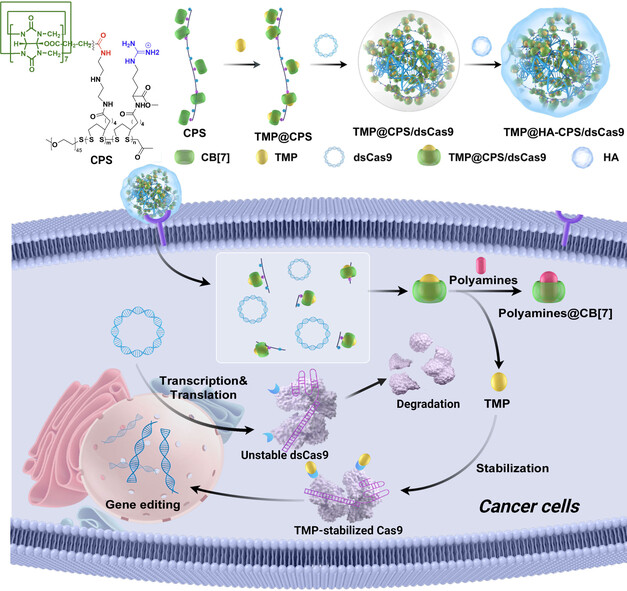
We synthesized a kind of supramolecular cationic polymer bearing cucurbit[7]uril (CB[7]) for the delivery of the plasmid encoding destabilized Cas9 (dsCas9) and single-guide RNA. The dynamic host-guest complexation between CB[7] moieties and trimethoprim, a stabilizer for dsCas9, can be competitively decomplexed by elevated polyamines in the tumor cells to activate Cas9-based genome editing in vivo, thereby ensuring the highly specific therapeutic genome editing for cancer gene therapy.
Drug Design | Very Important Paper
Development of a Small Molecule Downmodulator for the Transcription Factor Brachyury
- First Published: 13 February 2024
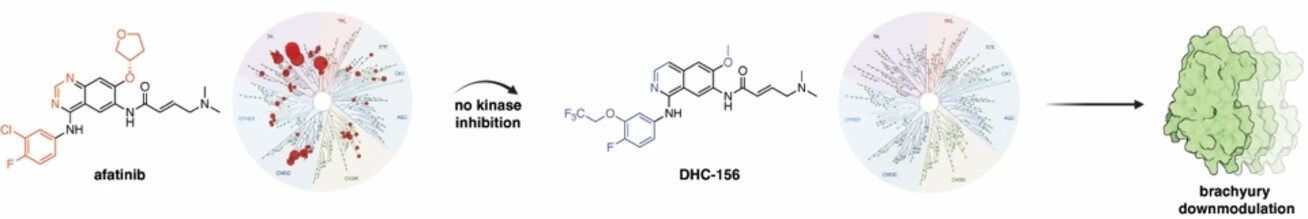
The small-molecule brachyury downmodulator DHC-156 was developed through the optimization of afatinib, an FDA-approved inhibitor. A series of structure–activity relationships, guided by biochemical assays and crystallography, lead to the discovery of DHC-156, which was shown to spare all wild-type kinases and downmodulates brachyury in a post-translational manner.
Solar Cells
Multifunctional Trifluoroborate Additive for Simultaneous Carrier Dynamics Governance and Defects Passivation to Boost Efficiency and Stability of Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 10 February 2024
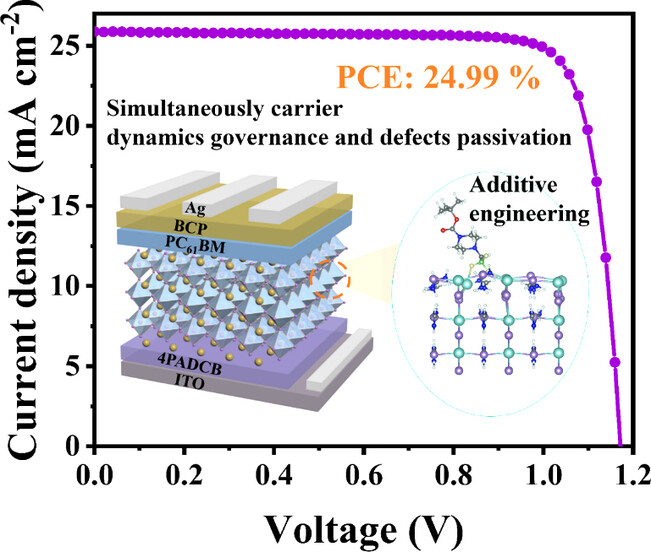
PTFBK has been employed as a multifunctional additive to target and modulate bulk perovskite defects and carrier dynamics of PSCs, endowing the decrease of Young′s modulus and residual stress in the perovskite layer. Moreover, benefit to the dominant crystal orientation and the suppression of non-radiative recombination, excellent stable inverted device with PCE of 24.99% was achieved.
Mechanocatalysis | Hot Paper
Mechanocatalytic Synthesis of Ammonia: State of the Catalyst During Reaction and Deactivation Pathway
- First Published: 19 February 2024
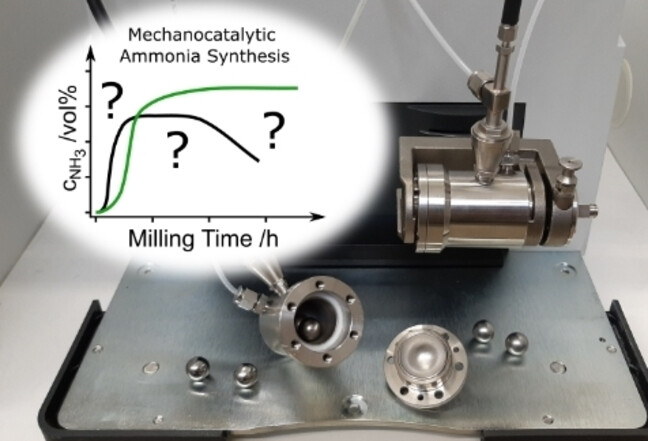
The synthesis of ammonia over a Cs-promoted Fe catalyst via the novel approach of mechanocatalysis is carefully studied by ex situ characterizations of the catalyst. Physicochemical changes are related to the different stages of ammonia formation. Optimizations based on these results resulted in the intrinsically complicated low-temperature ammonia synthesis being one of the longest stable mechanocatalytic gas-phase reactions to date.
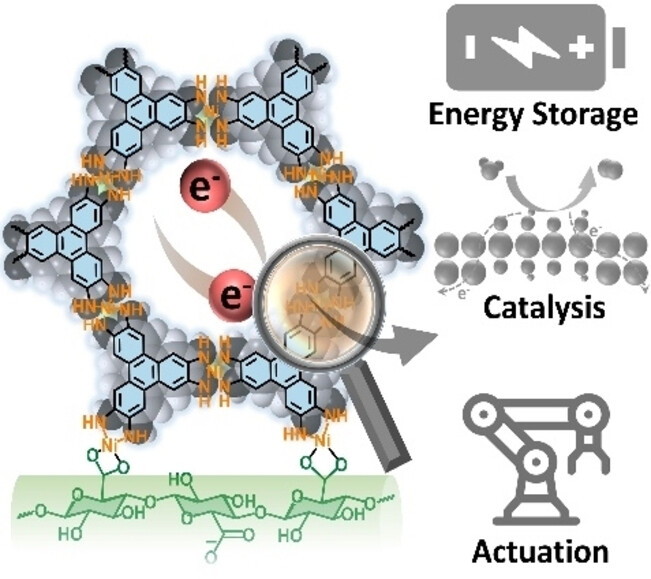
Lithium-organic Batteries
Porphyrin-Thiophene Based Conjugated Polymer Cathode with High Capacity for Lithium-Organic Batteries
- First Published: 09 February 2024
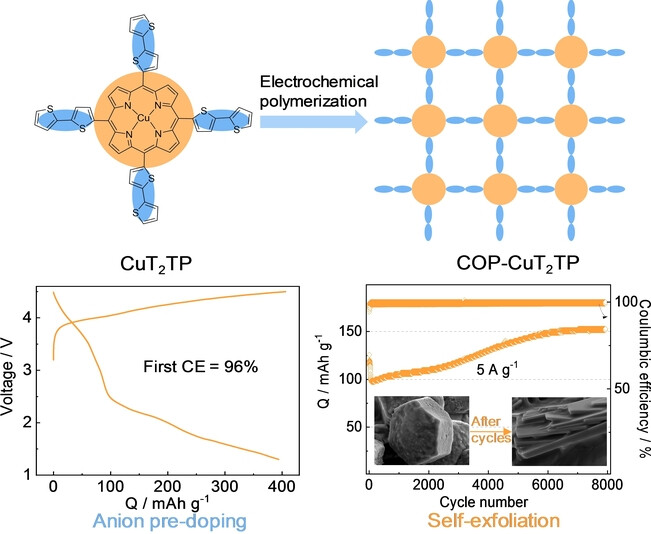
A new porphyrin conjugated polymer cathode, COP500-CuT2TP is achieved under electrochemical polymerization. Self-exfoliation of polymer cathode promotes charge storage, leading to a specific capacity of 420 mAh g−1 and 900 Wh Kg−1. Excellent cycling stability up to 8000 cycles at 5 A g−1 is achieved. Mechanistic insights by combining experimental and computational investigations supports the charge storage performance.
Electrocatalysis | Very Important Paper
Descriptor-Based Volcano Relations Predict Single Atoms for Hydroxylamine Electrosynthesis
- First Published: 07 February 2024
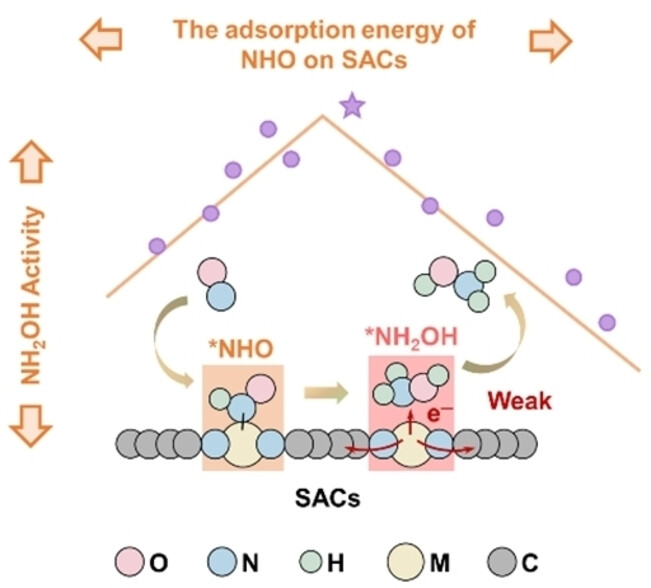
A weak *NH2OH binding affinity and a favorable reaction pathway (*NHO pathway) jointly enable single-atom catalysts (SACs) with superior hydroxylamine (NH2OH) selectivity. Then, an activity volcano plot of Gad(*NHO) is established to predict Mn SACs as optimal electrocatalysts that exhibit pH-dependent activity. Furthermore, Mn−Co geminal-atom catalysts are predicted to optimize Gad(*NHO) and are experimentally proven to enhance NH2OH formation.
Synthetic Methods
SN2 Reaction at the Amide Nitrogen Center Enables Hydrazide Synthesis
- First Published: 17 February 2024
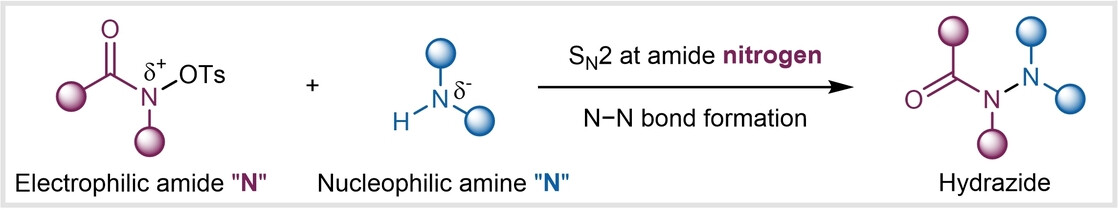
A new N−N coupling approach to the practical synthesis of hydrazides is disclosed by employing an SN2 strategy at electrophilic amides with nucleophilic amines. The reaction exhibits mild conditions, broad substrate scope, excellent functional group tolerance, easy scalability, and is applicable to the late-stage modification of various approved drug molecules, thus enabling complex hydrazide scaffold synthesis.
Oxidative Folding | Hot Paper
Ultrafast Biomimetic Oxidative Folding of Cysteine-rich Peptides and Microproteins in Organic Solvents
- First Published: 11 February 2024
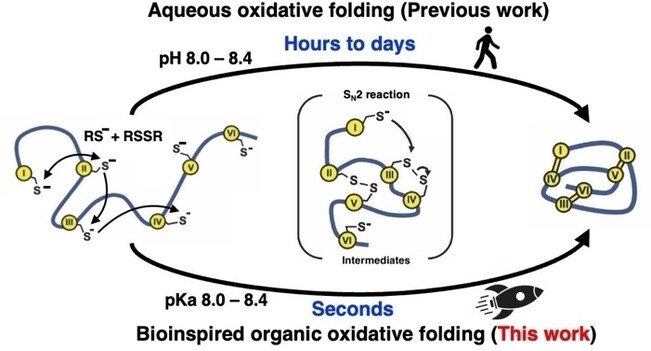
In this report, we established a method that replicates a hydrophobic environment akin to that of the endoplasmic reticulum, leading to effective suppression in dead-end products and acceleration of reaction rates through high thiolate concentrations for the oxidative folding of cysteine-rich peptides and microproteins.
Drug Delivery
Selective Intracellular Delivery of Antibodies in Cancer Cells with Nanocarriers Sensing Endo/Lysosomal Enzymatic Activity
- First Published: 11 February 2024
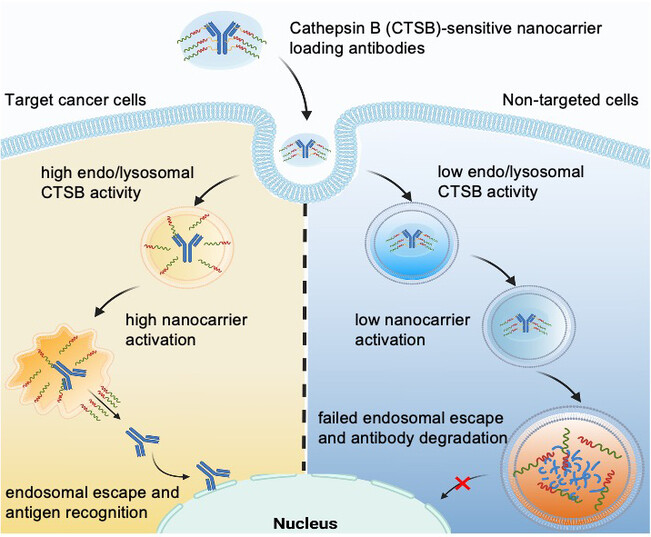
Endo/lysosomal cathepsin B activity differentiates among cell types and serves as a stimulus to trigger cell-specific endosomal escape. By designing nanocarriers armed with cathepsin B-activatable endosomal escape function, endosomal escape can be controlled to only occur in targeted cancer cells with upregulated endo/lysosomal cathepsin B activity. This innovative approach offers a new means to achieve targeted intracellular protein delivery.
Fuel Cells | Hot Paper
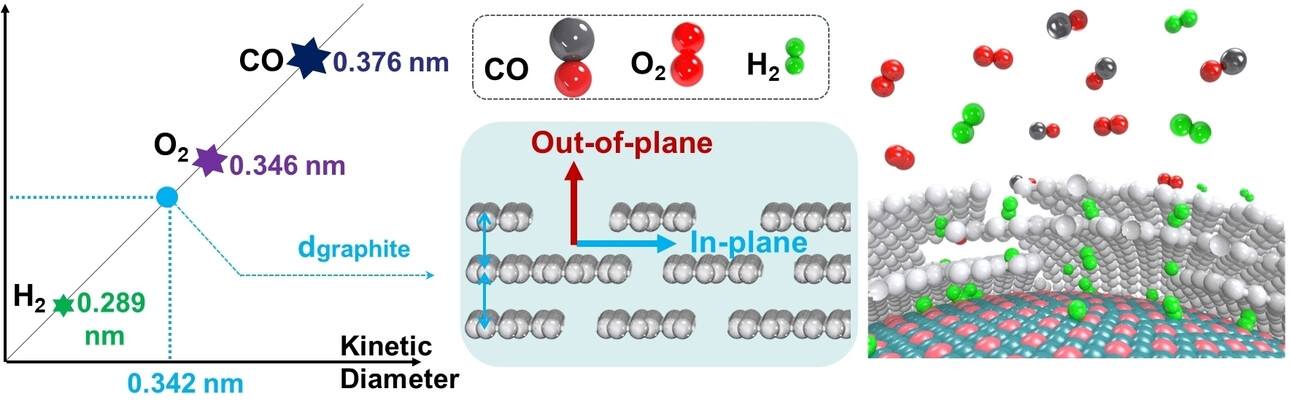
Graphitic Armor: A Natural Molecular Sieve for Robust Hydrogen Electroxidation
- First Published: 16 February 2024
Electrochromic Batteries
Flexible Zn-ion Electrochromic Batteries with Multiple-color Variations
- First Published: 08 February 2024
Nanoparticle | Hot Paper
Creating 3D Nanoparticle Structural Space via Data Augmentation to Bidirectionally Predict Nanoparticle Mixture's Purity, Size, and Shape from Extinction Spectra
- First Published: 15 February 2024
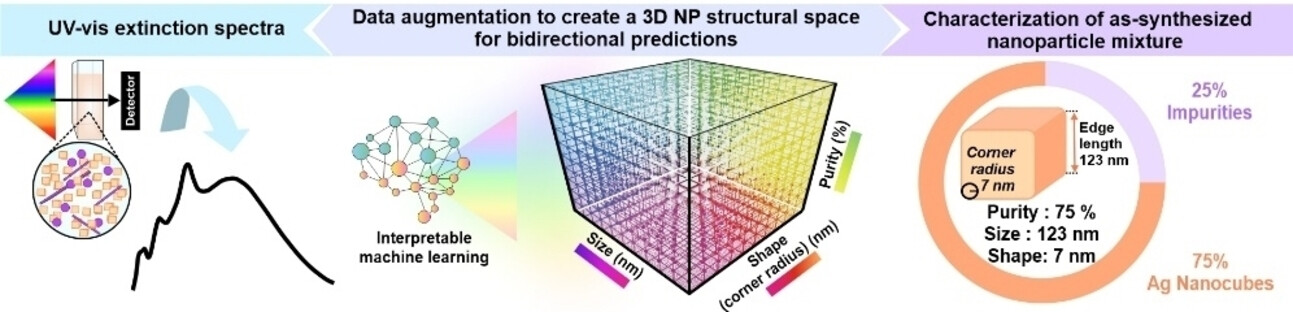
Leveraging plasmonically-driven feature enrichment and machine learning-directed data augmentation to create a 3-dimensional (3D) nanoparticle structural space for bidirectional predictions of silver nanocube's purity, size, and shape (corner radius) in as-synthesized nanoparticle mixtures using extinction spectra and vice versa.
Macrocyclization
Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Macrocyclization towards Crown Ethers Using Hydroamination of Bis(allenes)
- First Published: 07 February 2024
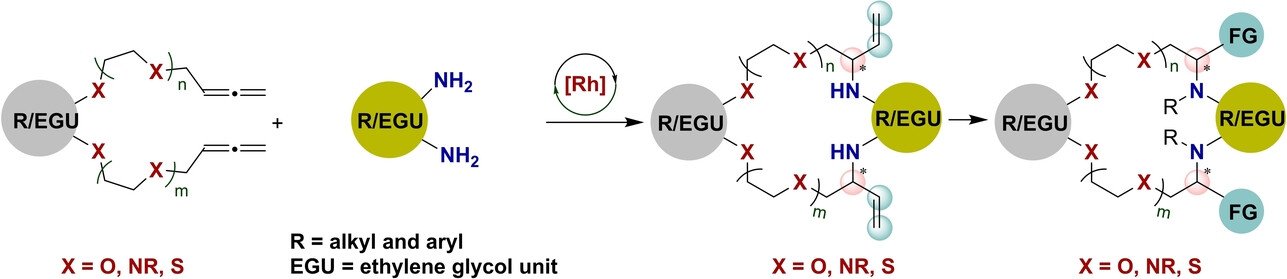
The Rh-catalyzed hydroamination of bis(allenes) with diamines was found to be an efficient strategy to access chiral crown ethers starting from achiral substrates. This new strategy is characterized by high chemo-, enantio-and diastereoselectivity with a wide range of substrates and with good functional group tolerance to access a wide range of chiral macrocycles in high yields under mild conditions.
Prebiotic Chemistry | Hot Paper
Binding of Precursors to Replicator Assemblies Can Improve Replication Fidelity and Mediate Error Correction
- First Published: 21 February 2024
C-H Activation
Post-synthetic Rhodium (III) Complexes in Covalent Organic Frameworks for Photothermal Heterogeneous C−H Activation
- First Published: 19 January 2024
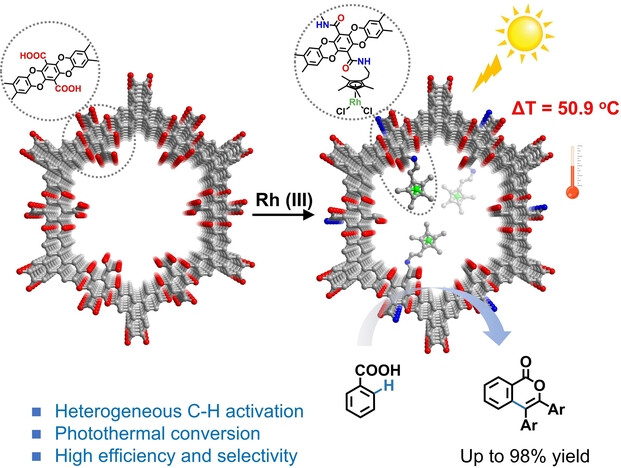
In this work, a general post-synthetic strategy for constructing bifunctional catalysts, Rh-COF, which connect photosensitive covalent organic frameworks and transition-metal catalytic groups through covalent bonding, was developed. Fascinatingly, such complexes enable efficient photothermal conversion properties, which can improve the photothermal catalytic performances in C−H activation to obtain excellent yield, substrate suitability and recyclability.
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
Oxygen-Activated Boron Nitride for Selective Photocatalytic Coupling of Methanol to Ethylene Glycol
- First Published: 07 February 2024

Oxygen-activated boron nitride fibers (BNH) have been successfully synthesized and applied for the selective photocatalytic coupling of methanol to ethylene glycol (EG) reaction. The OB3 unit in the BNH plays an important role in the selective dehydrogenation and C−C coupling of methanol molecules, leading to excellent activity and selectivity of BNH for EG production.
Metal-Organic Frameworks | Very Important Paper
Electrochemical Doping and Structural Modulation of Conductive Metal-Organic Frameworks
- First Published: 13 February 2024
Theranostics | Hot Paper
Thiophene π-Bridge Manipulation of NIR-II AIEgens for Multimodal Tumor Phototheranostics
- First Published: 12 February 2024
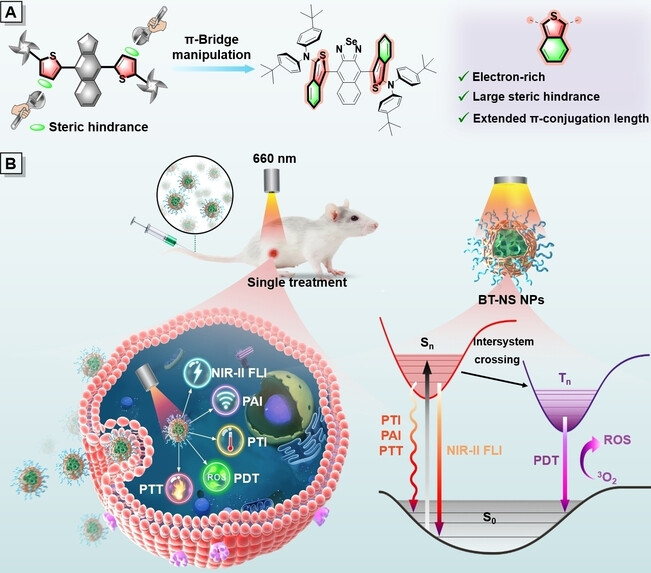
By elaborate thiophene π-bridge manipulation, BT-NS in which benzo[c]thiophene serves as π-bridge is constructed. An integration of experimental and theoretical studies disclosed BT-NS is advantageous for NIR-II FLI/PAI/PTI trimodal imaging-guided PDT/PTT treatment of tumors, displaying outstanding therapeutic efficacy and excellent biocompatibility.
Electrocatalysis
Unveiling pH-Dependent Adsorption Strength of *CO2− Intermediate over High-Density Sn Single Atom Catalyst for Acidic CO2-to-HCOOH Electroreduction
- First Published: 15 February 2024
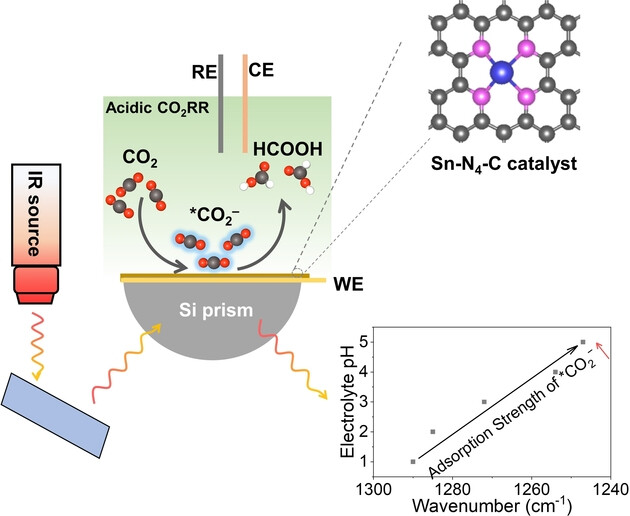
A high-density Sn single atom catalyst is presented and ATR-FTIR is used to reveal the pH-dependent adsorption strength of *CO2−, a key intermediate in acidic electrolyte on its surface. It is shown that the increase of electrolyte pH results in a redshift of the peak position of the *CO2− intermediate, i.e., the adsorption strength of the *CO2− intermediate increases, which in turn affects the performance of CO2RR to direct HCOOH in acidic electrolyte.
Enzyme Mechanisms
Flavin-N5OOH Functions as both a Powerful Nucleophile and a Base in the Superfamily of Flavoenzymes
- First Published: 01 February 2024
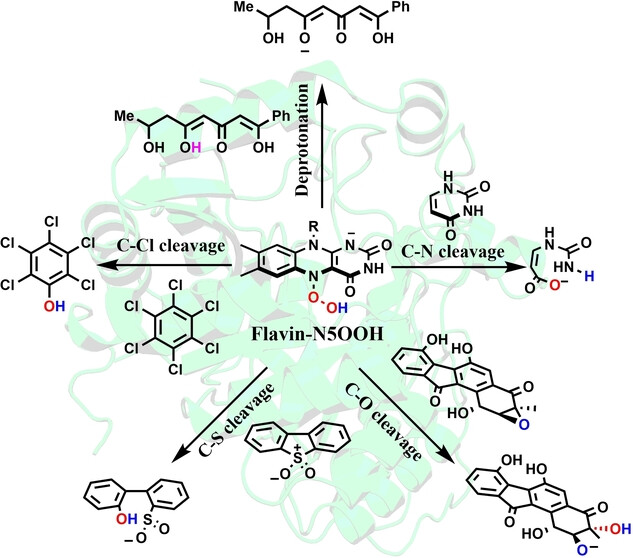
A computational study demonstrates that Flavin-N5OOH species can function as both powerful nucleophiles and bases in the superfamily of flavoenzymes, which can mediate many kinds of challenging non-redox reactions, such as the cleavage of C−X (X=N, O, S, Cl) bonds. The findings revive oxygen activation chemistry by flavoenzymes and are expected to spur the discovery of many other Flavin-N5OOH-dependent enzymes.
Chemical Protein Synthesis
An Enzyme-Cleavable Solubilizing-Tag Facilitates the Chemical Synthesis of Mirror-Image Proteins
- First Published: 07 February 2024
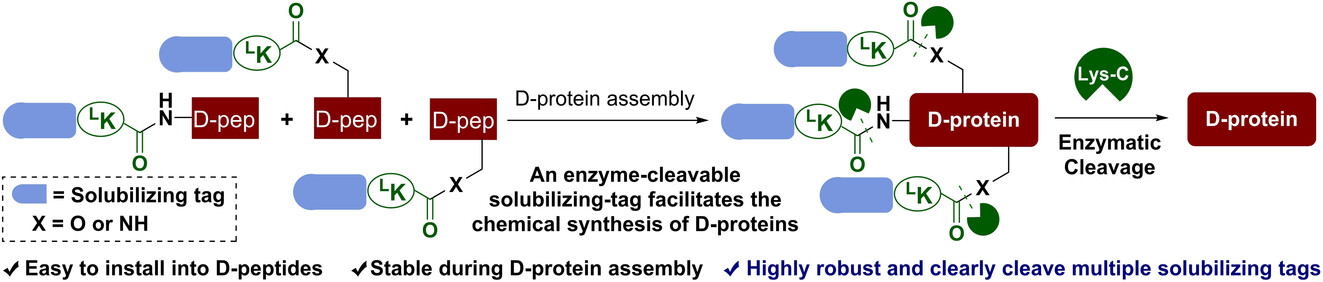
An enzyme-cleavable solubilizing tag was described for the chemical synthesis of mirror-image proteins. Solubilizing tags were easily installed on the side chain groups of DLys/DSer/DThr and the N-terminal α-amino group of D-peptides via an L-Lys linker. Solubilizing tags were impervious to various commonly used reagents in D-protein synthesis. After protein assembly, multiple solubilizing tags can be removed under denaturing conditions.
Gold Chemistry
Valence Tautomerism Induced Proton Coupled Electron Transfer:X−H Bond Oxidation with a Dinuclear Au(II) Hydroxide Complex
- First Published: 07 February 2024
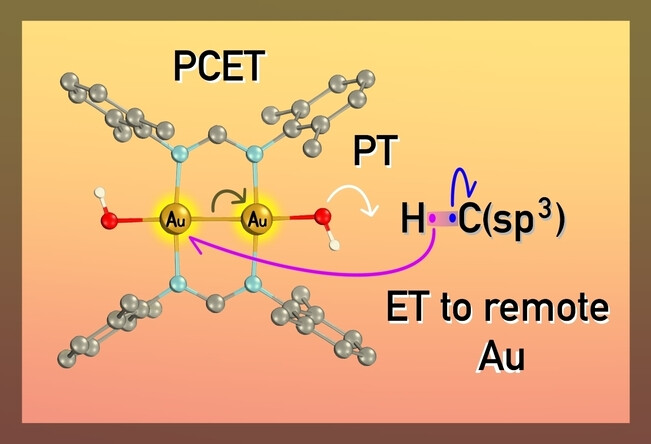
Proton-Coupled electron transfer (PCET)-type reactivity of the dinuclear AuII hydroxide complex AuII2(L)2(OH)2 (L=N,N′-bis (2,6-dimethyl) phenylformamidinate) towards weak X−H bonds is reported. For C(sp3)−H oxidation Au−Au σ-bond polarization leads to an adjustment of oxidation levels for both Au centers prior to the PCET event. The oxidation event for C(sp3)−H bonds is therefore described as a valence tautomerism induced PCET, where a basic reduced Au−OH unit serves as proton acceptor and the second more oxidized Au center as an electron acceptor.
Structured Liquids
Highly Interfacial Active Gemini Surfactants as Simple and Versatile Emulsifiers for Stabilizing, Lubricating and Structuring Liquids
- First Published: 21 February 2024
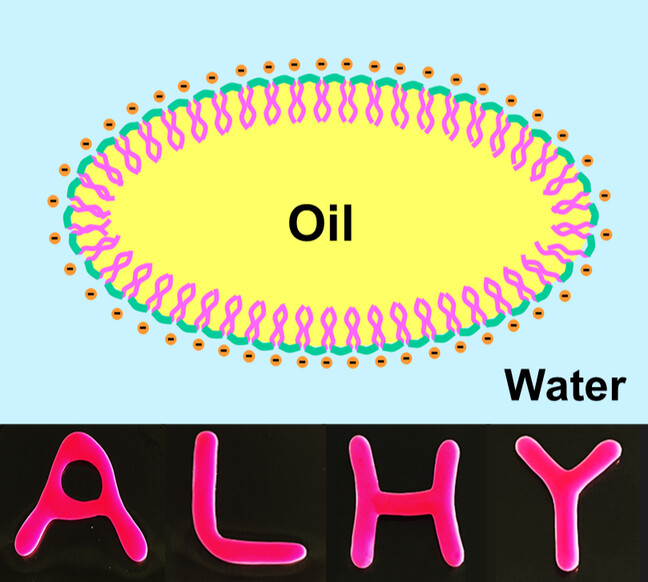
Liquid structuring usually relies on the interfacial jamming of nanoparticle surfactants. Here we show that not only droplets in non-equilibrium shapes but also printed liquid patterns with useful geometries can be created from a highly interfacial active molecular Gemini surfactant that generates elastic, “solid-like” monolayers at the oil/water interface. The surfactant can also be used to produce ultra-stable emulsions with potent lubricity.
Aqueous Zn Batteries
Multifunctional Cellulose Nanocrystals Electrolyte Additive Enable Ultrahigh-Rate and Dendrite-Free Zn Anodes for Rechargeable Aqueous Zinc Batteries
- First Published: 02 February 2024
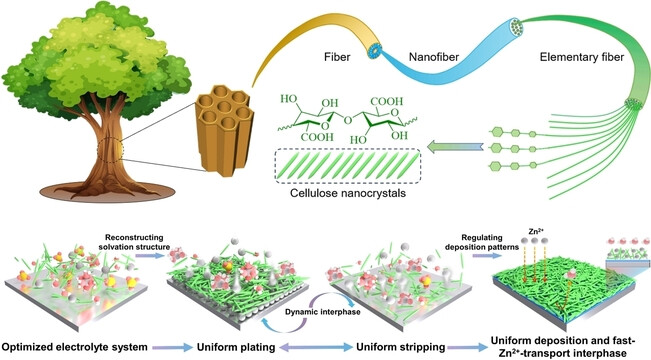
A highly reversible aqueous Zn battery was built by taking advantages of the biomass-derived cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) electrolyte additive with unique physical and chemical characteristics simultaneously. The CNCs additive not only serves as fast ion carriers for enhancing Zn2+ transport kinetics but regulates the coordination environment and interface chemistry to form dynamic and self-repairing protective interphase, resulting in building ultra-stable Zn anodes under extreme conditions.
DNA Nanotechnology
A Smart DNA Hydrogel Enables Synergistic Immunotherapy and Photodynamic Therapy of Melanoma
- First Published: 14 February 2024
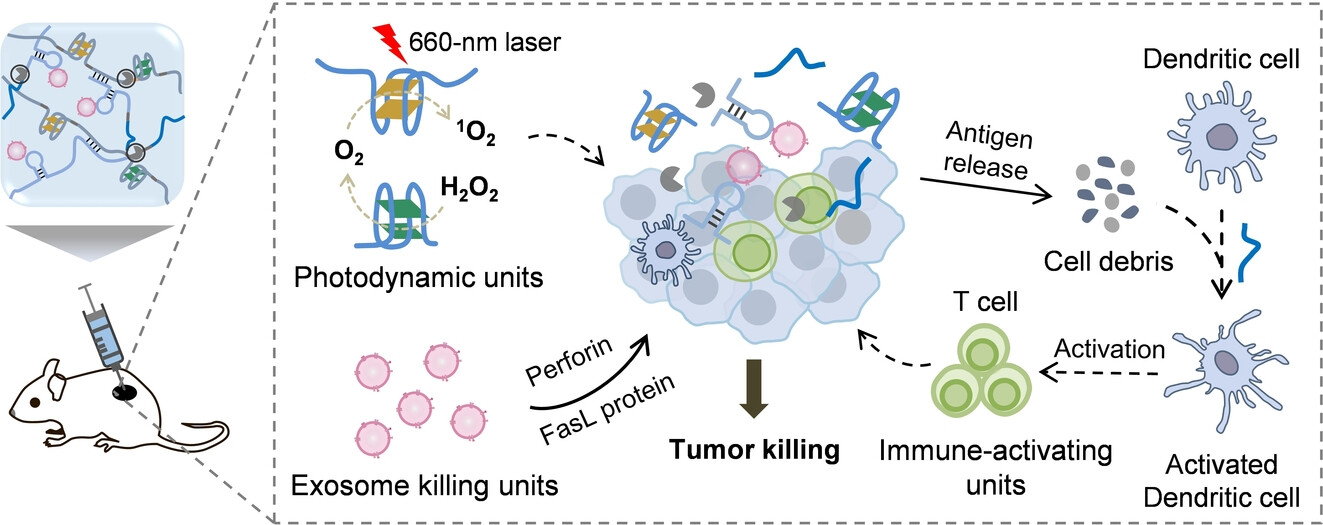
A smart DNA hydrogel that responds to the inflammatory environment by releasing multivalent functional units including photodynamic units, immune-activating units, and exosome killing units is constructed. The functional units have excellent tumor cell killing and immune activation efficacy, and the functional units can also synergistically modulate the immune microenvironment for efficient combination therapy.
Zn-Ion Batteries
Interfacial Engineering of Zn Metal via a Localized Conjugated Layer for Highly Reversible Aqueous Zinc Ion Battery
- First Published: 02 February 2024
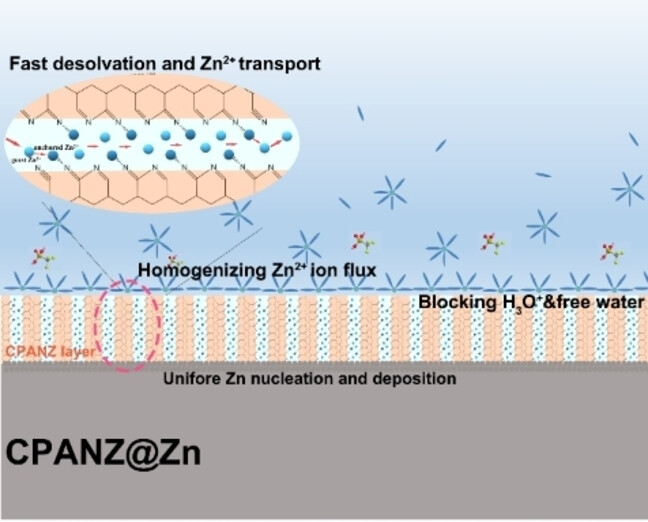
A polyacrylonitrile-based zinc ion conductor (CPANZ) with a localized conjugated structure is induced and achieved at low temperature by Lewis acidic Zn(OTf)2. The CPANZ layer effectively accelerates the Zn2+ migration but restricts the H+ migration. Encouragingly, the chemical corrosion, hydrogen evolution reaction and other side reactions are significantly mitigated at the CPANZ@Zn anode and homogeneous Zn deposition/dissolution is guaranteed.
Solar Cells
Amine-releasable Mediator In situ Repair Perovskites for Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 09 February 2024
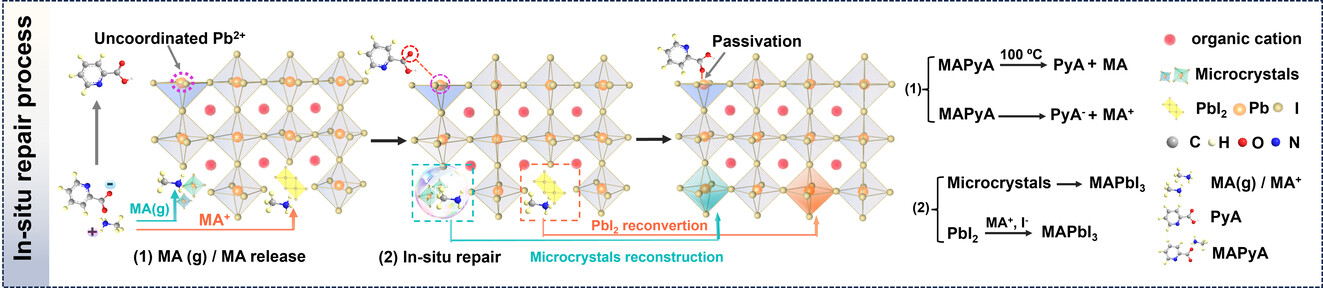
Amine-releasable mediator methylammonium pyridine-2-carboxylic (MAPyA) is demonstrated to in situ repair the imperfections in perovskite film. The specific mechanism is that MAPyA-released methylamine gifts a crystal reconstruction environment by inducing liquid intermediate phase, thus reconvert the microcrystals and residual PbI2 to perfect perovskites in situ. The optimized device exhibits efficiency of 24.06 % and excellent photostability.
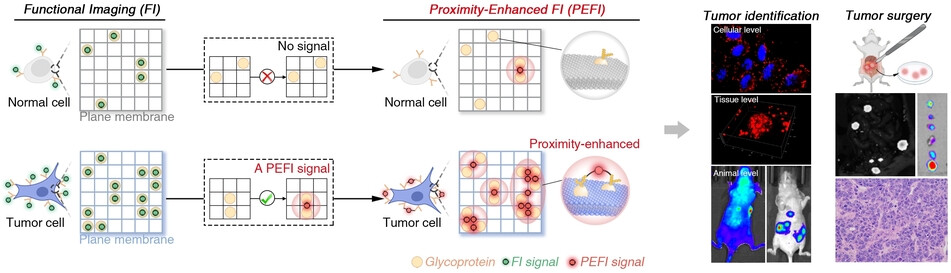
Bioimaging | Hot Paper
Proximity-Enhanced Functional Imaging Analysis of Engineered Tumors
- First Published: 02 February 2024
Fluorination | Very Important Paper
Where do the Fluorine Atoms Go in Inorganic-Oxide Fluorinations? A Fluorooxoborate Illustration under Terahertz Light
- First Published: 12 February 2024
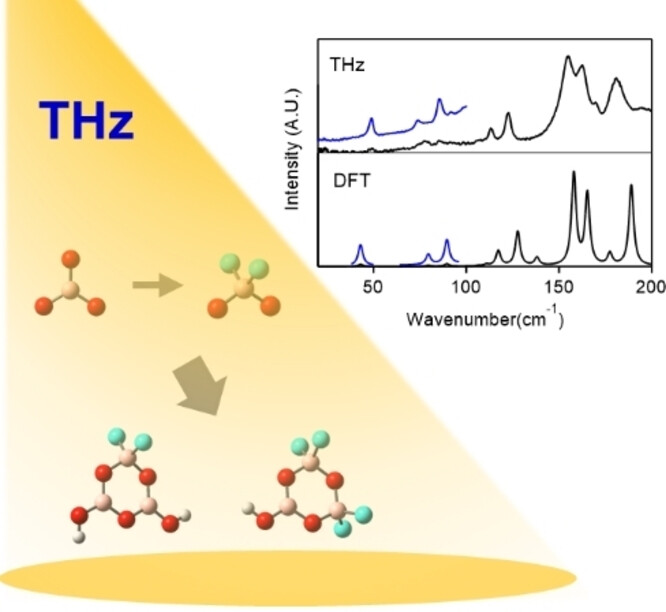
THz spectroscopy is used to show that fluorine atoms have a discernible preference for bonding with sp3-boron over sp2-boron in the fluorination reactions of boric acid. This result helps resolve the F/OH substitution structural ambiguity. A reaction pathway for fluorination via the hydrothermal and room-temperature evaporation reactions is presented which gives insights into previously obscured aspects of the borate-fluorination process.
Biomass Upgrading
Synergistic Lewis and Brønsted Acid Sites Promote OH* Formation and Enhance Formate Selectivity: Towards High-efficiency Glycerol Valorization
- First Published: 14 February 2024
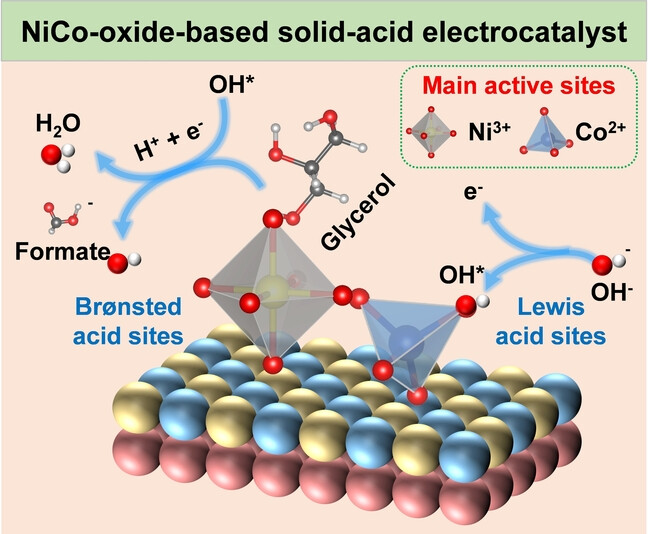
Synergistic Lewis and Brønsted acid sites in solid-acid electrocatalysts could achieve low potential and high formate selectivity toward glycerol valorization, because the Lewis centers promote OH* formation and the Brønsted centers enhance selective oxidation of glycerol to formate. This study demonstrates the vital roles of solid-acid sites in improving the activity and product selectivity for electrocatalytic biomass upcycling.
Drug Discovery
Discovery of the First-in-Class Inhibitors of Hypoxia Up-Regulated Protein 1 (HYOU1) Suppressing Pathogenic Fibroblast Activation
- First Published: 10 February 2024
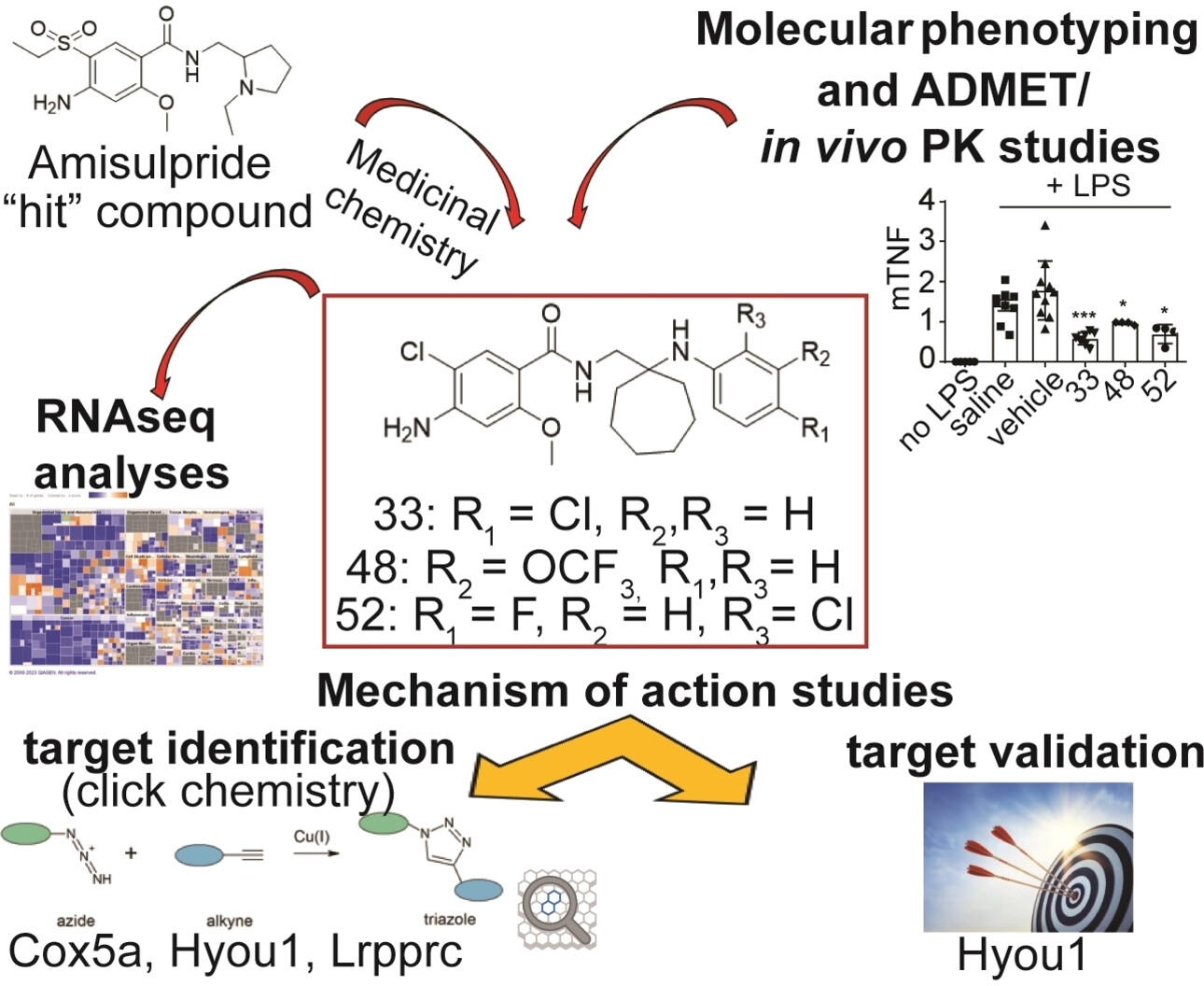
A multidisciplinary pipeline consisting of medicinal chemistry, molecular phenotyping, chemoproteomics, RNA-sequencing, short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs)-mediated gene silencing and in vivo studies led to a novel series of compounds suppressing pathogenic fibroblast activation via Hypoxia up-regulated protein 1 (HYOU1) inhibition. The first reported HYOU1 inhibitors are presented as a promising therapeutic approach in fibroblast-related diseases.
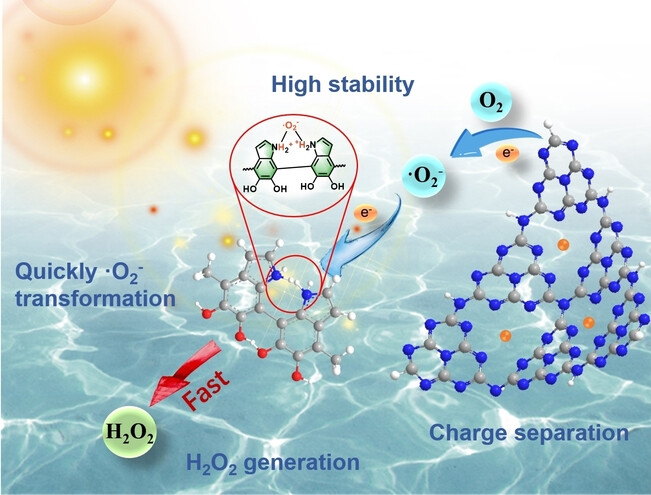
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
Reduction of Superoxide Radical Intermediate by Polydopamine for Efficient Hydrogen Peroxide Photosynthesis
- First Published: 09 February 2024
MXenes
Role of Surface Terminations for Charge Storage of Ti3C2Tx MXene Electrodes in Aqueous Acidic Electrolyte
- First Published: 07 February 2024
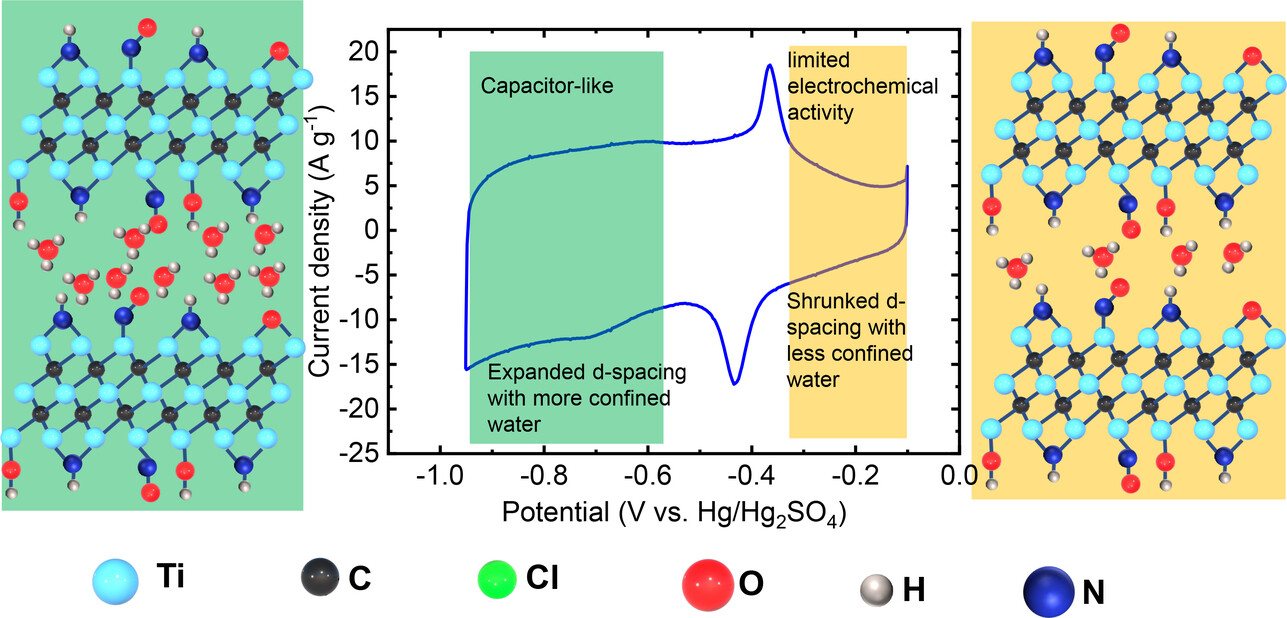
A transition from electrochemically inactive Cl-terminated Ti3C2 to fast, pseudocapacitive behavior is reported for N,O-terminated Ti3C2 MXene, attributed to the presence of confined water between the MXene layers. This study evidences the crucial role surface terminations and confined water in charge storage and reaction kinetics in MXene materials.
Electrocatalytic H2O Splitting
Cobalt-based Co3Mo3N/Co4N/Co Metallic Heterostructure as a Highly Active Electrocatalyst for Alkaline Overall Water Splitting
- First Published: 05 February 2024
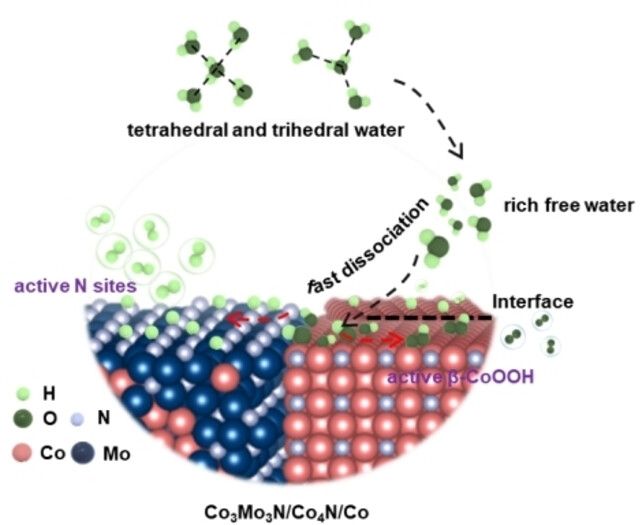
In this work, the novel metallic heterostructure Co3Mo3N/Co4N/Co was prepared and exhibited excellent water splitting performance. This metallic heterostructure enhances the electron transport efficiency and accelerates the reaction rate of water molecules on its surface by optimizing the electronic structure of the heterointerface.
Gas-Phase Studies
Terminal Copper Nitrenoid Formation and Reactivity Induced by Absorption to an Antenna Ligand
- First Published: 05 February 2024
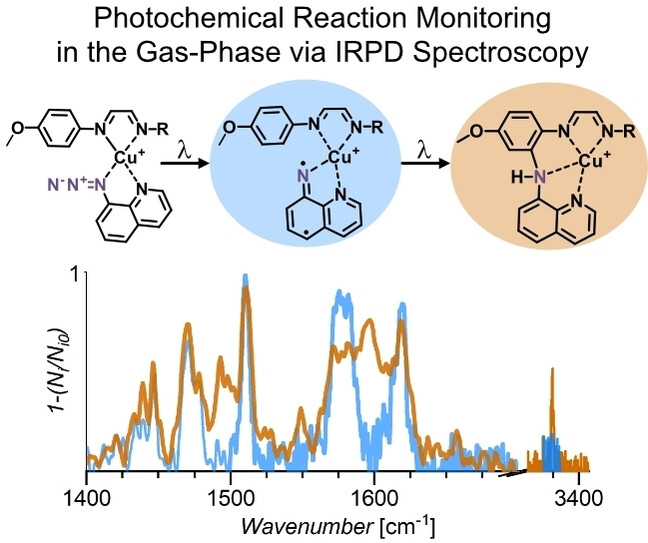
Copper nitrenoids are key intermediates in copper-catalyzed direct C−H amination reactions but are difficult to study due to their high reactivity. This research shows that absorption to an antenna ligand can promote the denitrogenation of copper azide complexes in the gas phase and also channel the internal energy to promote the C−H amination reaction, which opens a new way to study the reactivity of highly reactive species under well-defined conditions.
Solar Cells
Kinetics Controlled Perovskite Crystallization for High Performance Solar Cells
- First Published: 25 January 2024
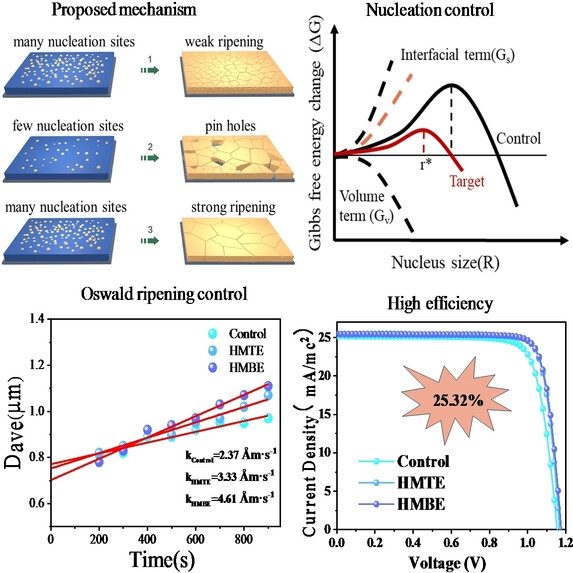
Crystallization control of perovskite thin films is the key in commerciallization of perovskite solar cells. However, the fast crystallization of the thin film including nucleation, growth and Oswald ripening, is still a mystery though some efforts made. According to the theories of nucleation and Oswald ripening, we modified the perovskite surface energy and improved the grain solubility, and quantified the nucleation and ripening rate in experiments.
Non-Fully Conjugated Dimerized Giant Acceptors with Different Alkyl-Linked Sites for Stable and 19.13 % Efficiency Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 09 February 2024
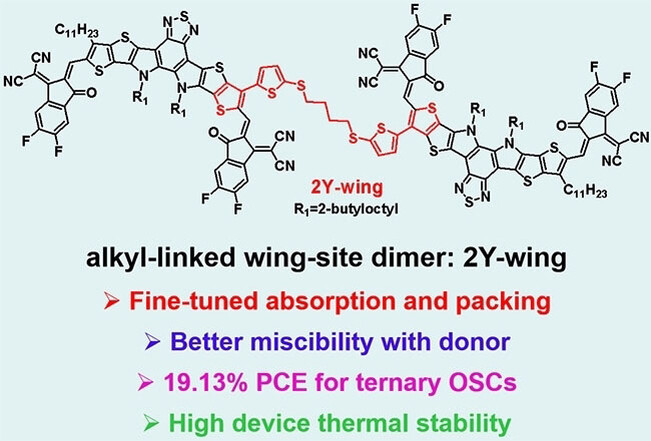
Three new non-fully conjugated dimerized giant acceptors with different alkyl-linked sites are developed. Among them, wing-sited 2Y-wing has fine-tuned packing and better miscibility with donor, allowing to 19.13 % efficiency (which is the highest value among the devices with giant acceptors) and highly stable organic solar cells.
RNA Circuits
Harnessing Catalytic RNA Circuits for Construction of Artificial Signaling Pathways in Mammalian Cells
- First Published: 31 January 2024
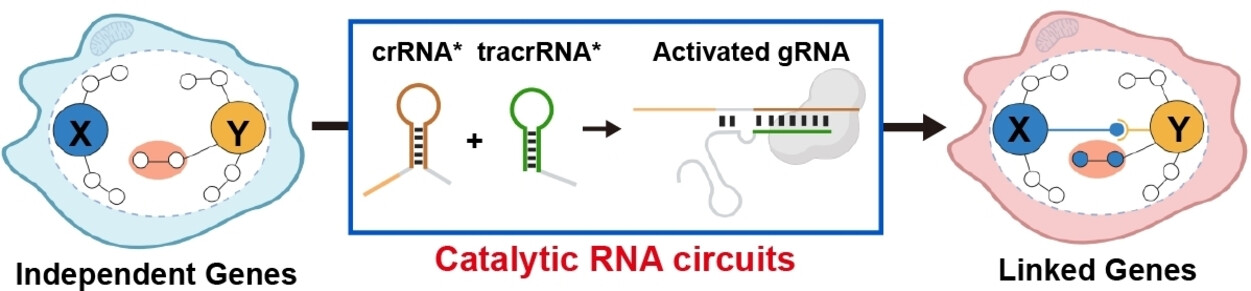
This study describes an amplifiable RNA circuit based on the system of catalytic hairpin assembly with combination of controllable CRISPR-Cas9 function, which can directly build regulatory connections between originally independent endogenous genes in mammalian cells. With this design, artificial signaling pathways can be introduced into mammalian cells to control cellular responses and phenotypes through differentiated RNA expression.
Supramolecular Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Light-Triggered Disassembly of Molecular Motor-based Supramolecular Polymers Revealed by High-Speed AFM
- First Published: 19 February 2024
Porous Polymer Networks | Very Important Paper
Simple Functionalization of a Donor Monomer to Enhance Charge Transfer in Porous Polymer Networks for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 14 February 2024
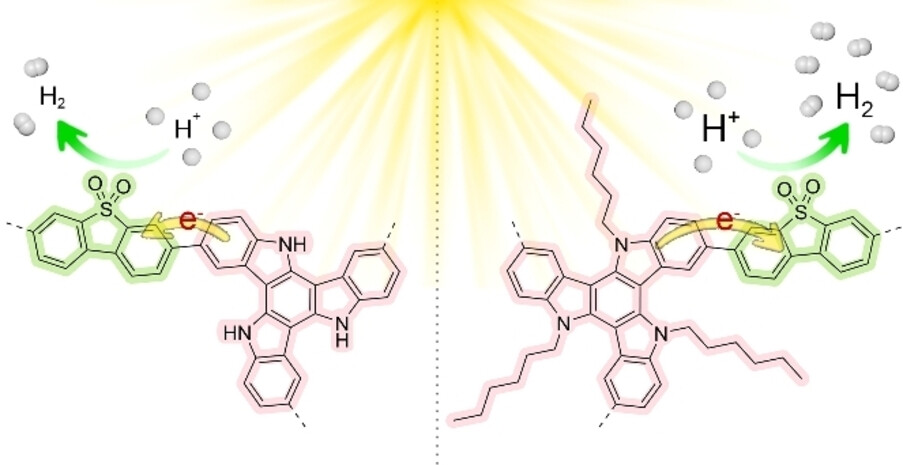
Triazatruxene (TAT)-based PPNs were synthesized to investigate how the existence of a hexyl functional group would affect charge transfer. The hexyl group on the TAT unit ensured the transfer of photoexcited electrons from a donor unit to an acceptor unit, resulting in improved photocatalytic activity and hydrogen production.
Solid-State Batteries
Making Plasticized Polymer Electrolytes Stable Against Sodium Metal for High-Energy Solid-State Sodium Batteries
- First Published: 14 February 2024
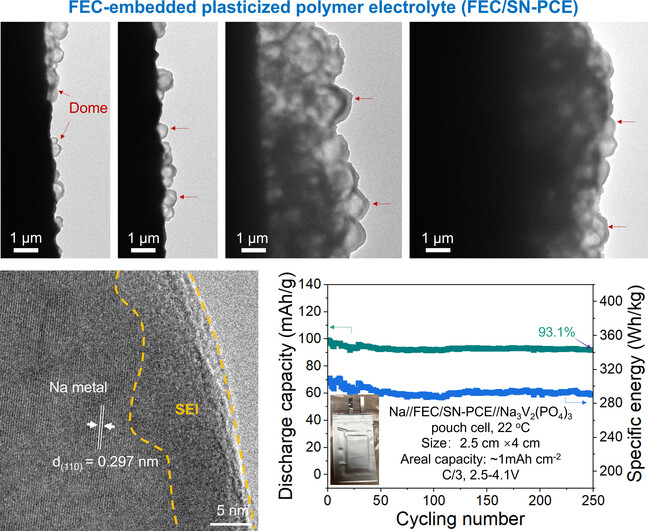
A new plasticized polymer electrolyte integrated with fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) additive was reported to address the interface instability issue existing in sodium metal batteries. Impressively, dome-like Na0 nucleation/growth with thin, amorphous, and fluoride-rich SEIs was identified, enabling excellent long-term cycling stability in Na//Na3V2(PO4)3 pouch cells (93.1 % capacity retention after 250 cycles at C/3) at room temperature.
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Boosting CO2 Electroreduction over a Covalent Organic Framework in the Presence of Oxygen
- First Published: 06 February 2024
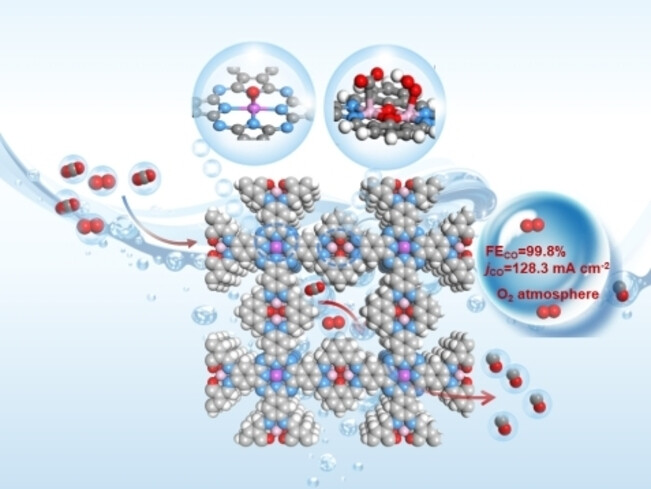
An oxygen-containing-species coordination strategy to boost CO2 electroreduction in the presence of O2 was proposed. In the presence of O2, one of the Co sites in the NiPc-Salen(Co)2-COF that coordinated with the intermediate of *OOH from the oxygen reduction reaction could decrease the energy barrier for the activation of CO2 molecules and stabilize the key intermediate *COOH of the CO2RR over the adjacent Co center and thus boost the CO2RR performance.
Host-Guest Systems
Guest-Regulated Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species from Porphyrin-Based Multicomponent Metallacages for Selective Photocatalysis
- First Published: 02 February 2024
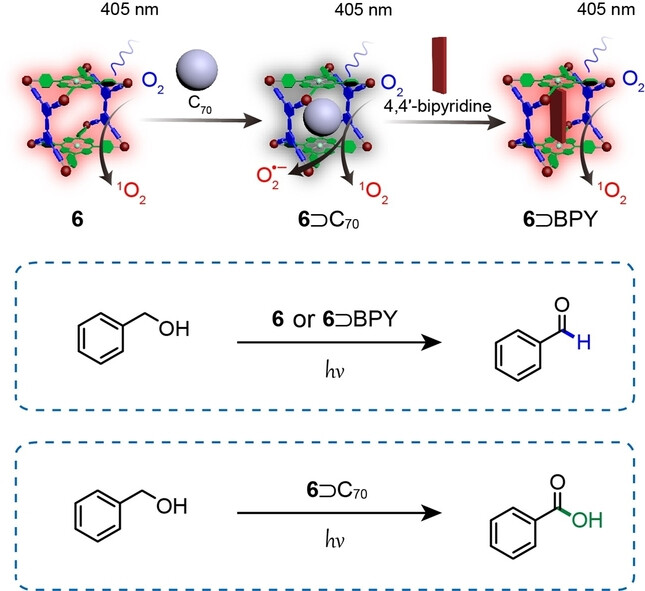
A Zn-porphyrin-based metallacage exhibited strong host-guest interactions with fullerene derivatives. The complexes could be dissembled by the further addition of 4,4′-bipyridine to form a more stable coordinated complex. This tunable host-guest complexation was further employed to generate different types of reactive oxygen species, enabling the highly efficient and selective photocatalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohols.
Photochemistry | Hot Paper
Site-Selective Photo-Crosslinking of Stilbene Pairs in a DNA Duplex Mediated by Ruthenium Photocatalyst
- First Published: 28 January 2024
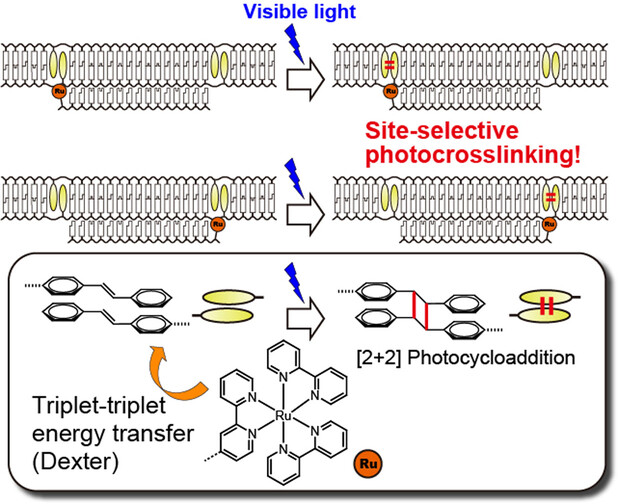
A novel method to site-specifically crosslink DNA duplex upon visible light irradiation. Ru complex on the third strand catalyzed [2+2] photocycloaddition of stilbene moieties via triplet-triplet energy transfer. Site specificity is realized owing to steep distance dependence of the energy transfer. This method will be useful in construction of complex photoresponsive DNA circuits, nanodevices and biological tools.
Ferroelectrics | Very Important Paper
Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Ferroelectric and Antiferroelectric with Afterglow Emission
- First Published: 26 January 2024
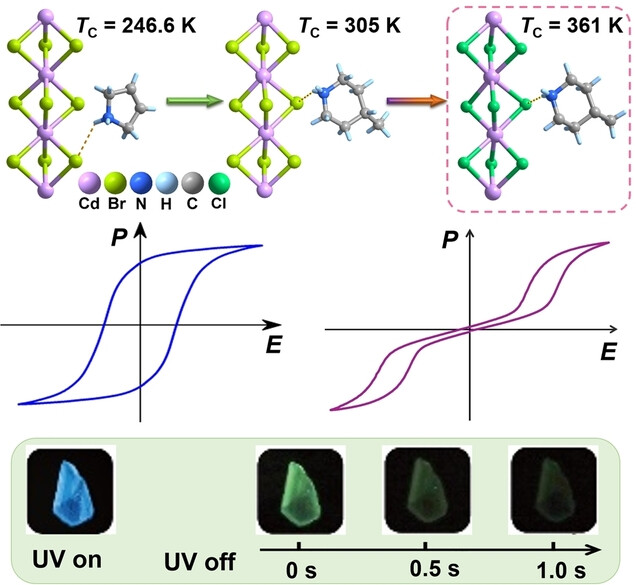
Implementing cationic customization and halogen engineering not only enable a dramatic enhancement of Curie temperature (ΔTC=114.4 K), but also realize the first integration of notable ferroelectricity and long afterglow emission in (4-methylpiperidium)CdCl3 with one-dimensional hybrid perovskite architecture.
Asymmetric Hydrogenation
Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation and Transfer Hydrogenation of 1,3-Dipolar Nitrones
- First Published: 17 February 2024
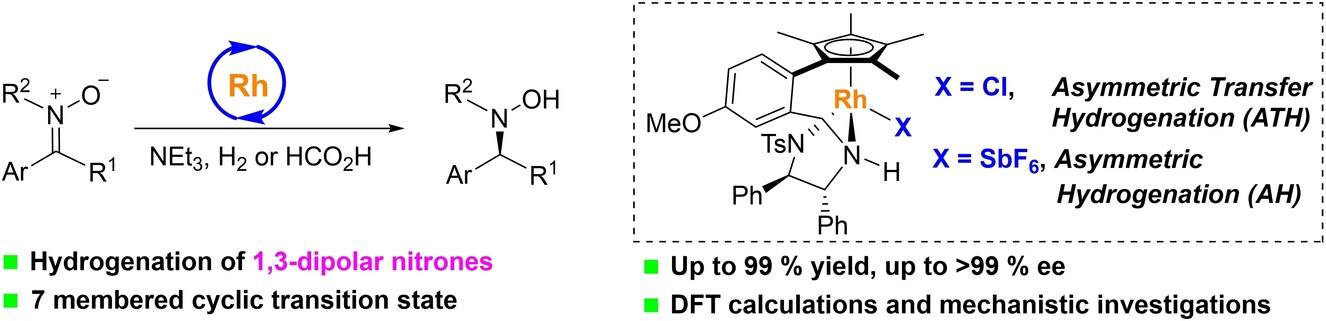
The enantioselective reduction of 1,3-dipolar nitrones to hydroxylamines was achieved by Rh(III)-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenation. A wide range of chiral N,N-disubstituted hydroxylamines were synthesized with up to 99 % yield and >99 % ee. Mechanistic investigations and DFT calculations were conducted to elucidate the origin of reactivity and enantioselectivity.
Antibacterial Therapy | Hot Paper
Breaking Iron Homeostasis: Iron Capturing Nanocomposites for Combating Bacterial Biofilm
- First Published: 06 February 2024
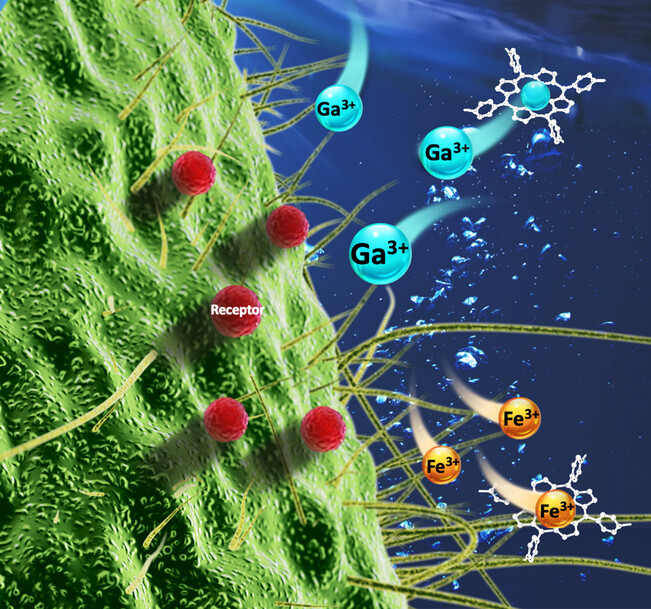
Bacteria spend years in a dormant, inactive state, yet revive in some nutrient environments. Iron nutritional immunity strategy was proposed to target iron nutrients. We developed a nanoplatform that can deceive bacteria to uptake “fake iron” and concurrently extract iron ions from the surrounding bacteria milieu, starving pathogens to death.
Communications
Bioanalytical Chemistry
Rapid and Bifunctional Chemoselective Metabolome Analysis of Liver Disease Plasma Using the Reagent 4-Nitrophenyl-2H-azirine
- First Published: 18 January 2024
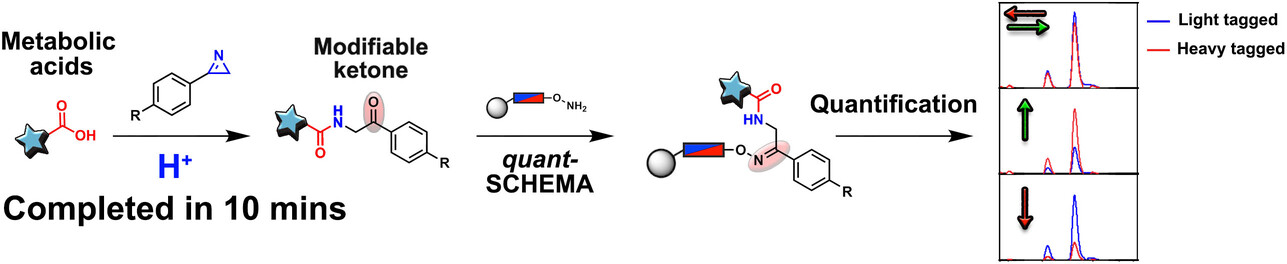
Rapid functional group transformation of carboxylic acids into a new ketone under mild conditions using the reagent 4-nitrophenyl-2H-azirine. The newly formed ketone was captured by our chemical probe methodology for quantification with enhanced mass spectrometric sensitivity. This bifunctional methodology is a new chemical biology tool for biomarker discovery and metabolomics.
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Fundamentals of Unanticipated Efficiency of Gd2O3-based Catalysts in Oxidative Coupling of Methane
- First Published: 25 January 2024
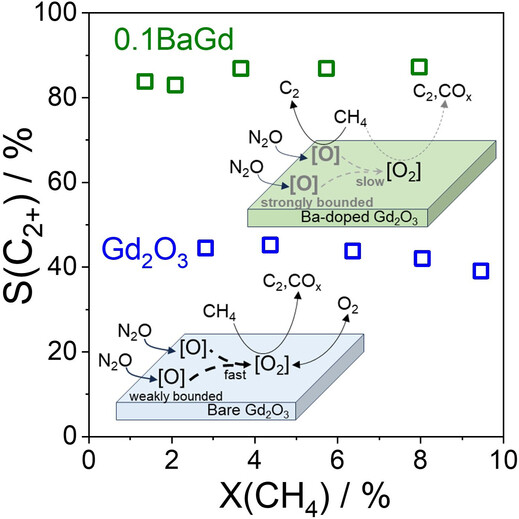
Kinetic tests combined with temporal analysis of products revealed the fundamentals relevant for regulating the efficiency of the oxidative coupling of CH4 to C2H6 over Gd-based catalysts. When Gd2O3 is modified with Na, Sr or Ba, the use of N2O instead of O2 significantly improves the selectivity even at 650 °C. The promoters affect the binding strength of monoatomic oxygen species derived from N2O and thus control the methane oxidation to carbon oxides.
Photochemistry
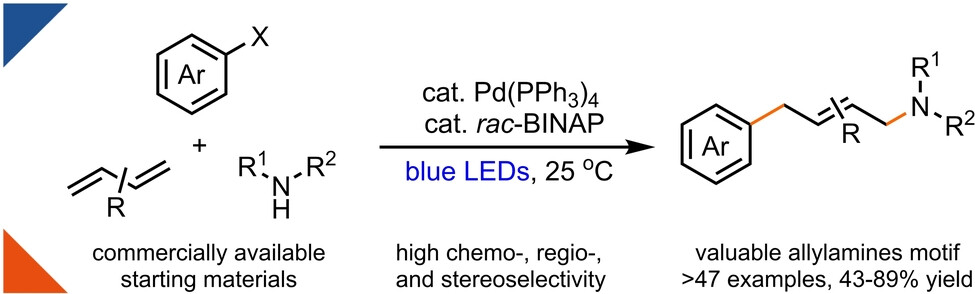
1,4-Aminoarylation of Butadienes via Photoinduced Palladium Catalysis
- First Published: 09 February 2024
Foldamers
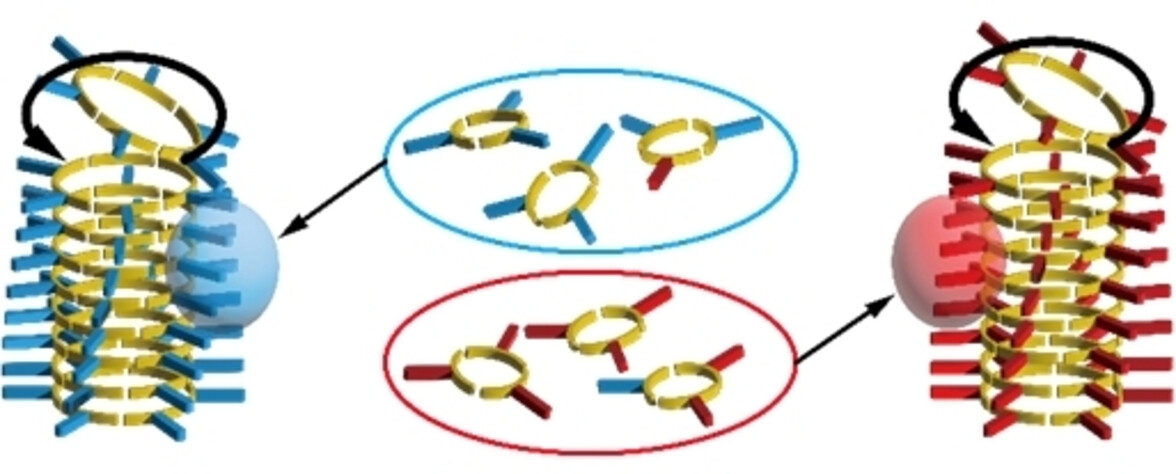
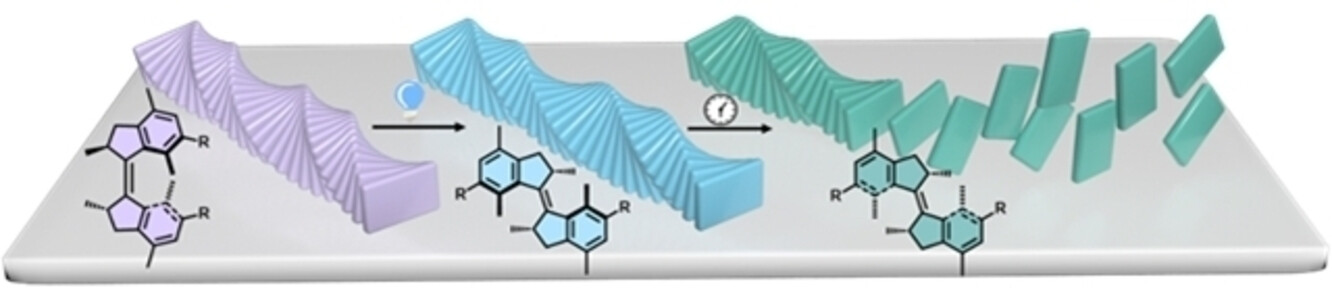
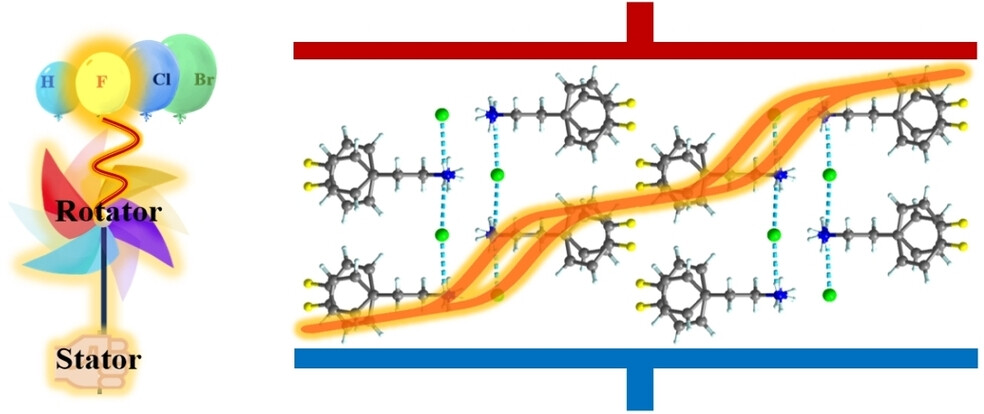
Foldaxane-Based Switchable [c2]Daisy Chains
- First Published: 12 February 2024
![Foldaxane-Based Switchable [c2]Daisy Chains](/cms/asset/993cfaf9-d7e6-48b8-9afd-1b8aac032205/anie202315668-toc-0001-m.jpg)
An aromatic helical foldamer linked to a peptide rod, which is incapable of self-complexation or polymerization, has been shown to preferentially assemble through inter-strand hydrogen-bonding interactions into a [c2]daisy chain that undergoes fast contraction/stretching muscle-like motion without dissociation. The introduction of multiple recognition sites confers the system with contraction and stretching motion actuated by chemical stimuli.
Protein Engineering
Sortase-Catalyzed Protein Domain Inversion
- First Published: 17 February 2024

A strategy to mimic the conventional N-terminal sortase substrate at protein C-termini is reported, enabling C- to C-terminal ligation. Installing this mimetic at the C-terminus of a protein with an internal sortase recognition motif enables sortase-catalyzed inversion of the C-terminal portion of the protein.
Nucleic Acids
A New Architecture for DNA-Templated Synthesis in Which Abasic Sites Protect Reactants from Degradation
- First Published: 12 February 2024
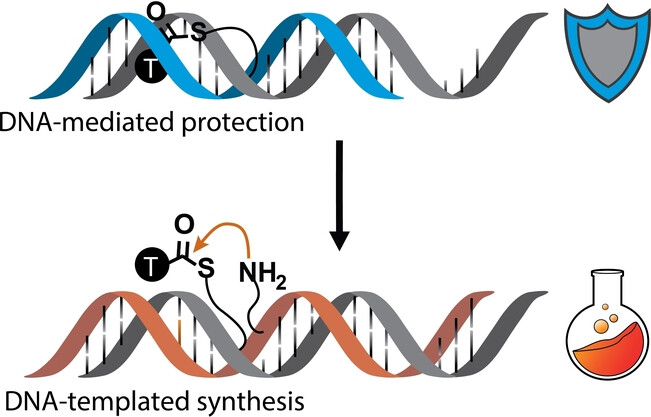
An abasic site within a DNA duplex reduces hydrolysis of a colocalised DNA-thioester. This forms the basis for an architecture for DNA-templated synthesis which protects DNA-tagged building blocks until a DNA strand exchange reaction removes the protective site and colocalizes a second reactive group.
C-H Activation | Hot Paper
Tertiary Amides as Directing Groups for Enantioselective C−H Amination using Ion-Paired Rhodium Complexes
- First Published: 13 February 2024
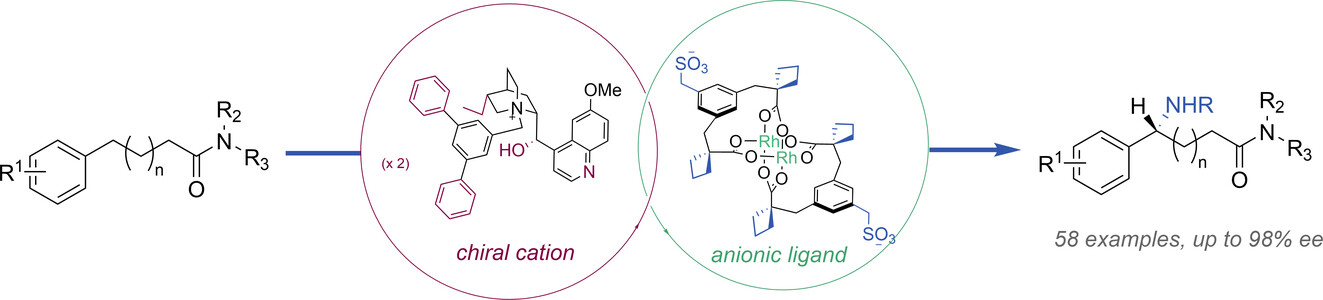
Direct amination of benzylic C−H bonds generates important stereocenters. Our approach, in which the chirality of a bimetallic rhodium complex is located on its associated cations, achieves this on tertiary amide-containing substrates to give amination of arylbutyric and arylvaleric acid-derived amides. We believe that the amide most likely interacts directly with the chiral cation to provide a highly organised transition state for C−H amination.
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
π-Radical Cascade to a Chiral Saddle-Shaped Peropyrene
- First Published: 26 January 2024
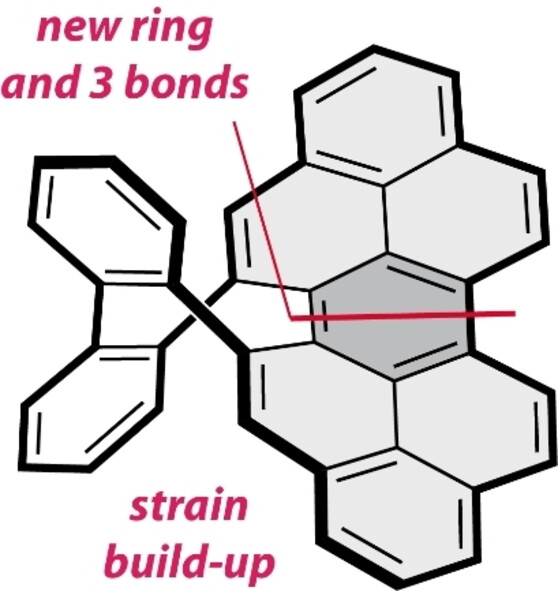
Undesired reaction pathways of open-shell graphene fragments can be synthetically useful! To demonstrate their transformative potential, we employed oxidative dimerization of phenalenyl to peropyrene—the well-known π-radical “decomposition” process—to build up strain and access negatively curved and configurationally stable chiral polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon.
Organometallic Chemistry | Hot Paper
Synthesis and Reactivity of Ruthenium(BINAP)(PPh3)
- First Published: 09 February 2024
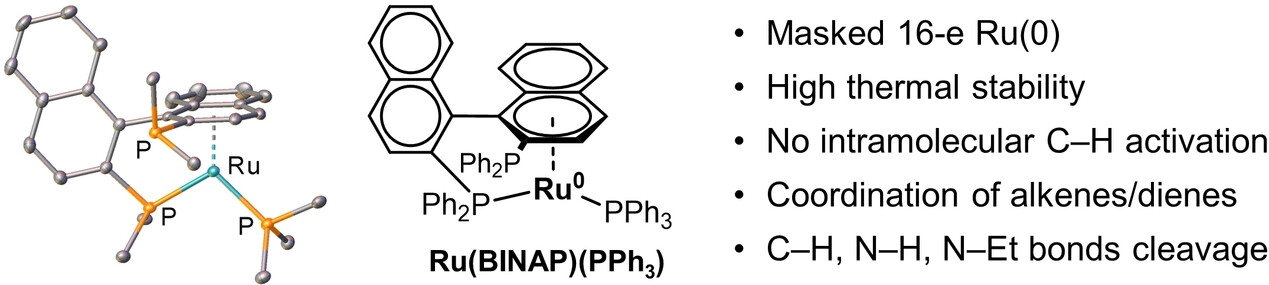
The synthesis of a Ru(0)(BINAP)(PPh3) complex (BINAP:2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl) is reported. It behaves as a “masked” 16-electron Ru(0) complex: while being quite stable, it is capable to substitute PPh3 with alkenes/dienes, and activate C−H, N−H or inert N−Et bonds. This compound gives novel insight into Ru(0) stabilization approaches while maintaining a high specific reactivity potentially useful for catalytic applications.
Hypervalent Compounds | Very Important Paper
Phosphorane-Promoted C−C Coupling during Aryne Annulations
- First Published: 07 February 2024
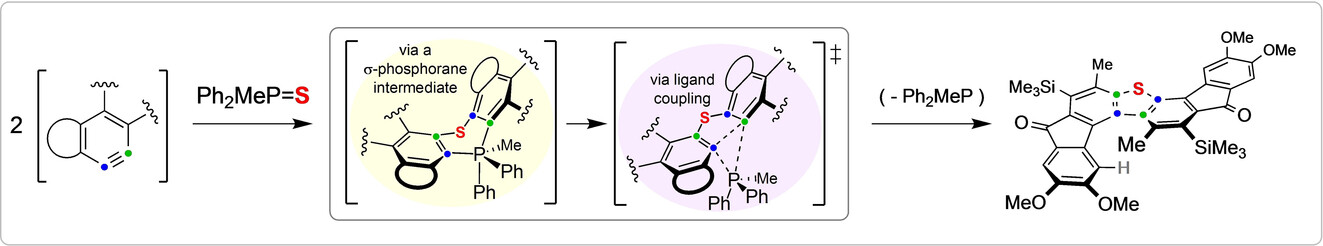
The high potential energy of aryne intermediates can induce reactions that proceed through unorthodox mechanisms. Herein we report the aryne-promoted formation of various helical dibenzochalcophenes from phosphine chalcogenides. Based on DFT computations we propose a mechanism to account for the final C−C bond formation that involves a rare, concerted ligand-coupling event within a hypervalent σ-phosphorane.
Perovskites
Data-Driven Controlled Synthesis of Oriented Quasi-Spherical CsPbBr3 Perovskite Materials
- First Published: 05 February 2024
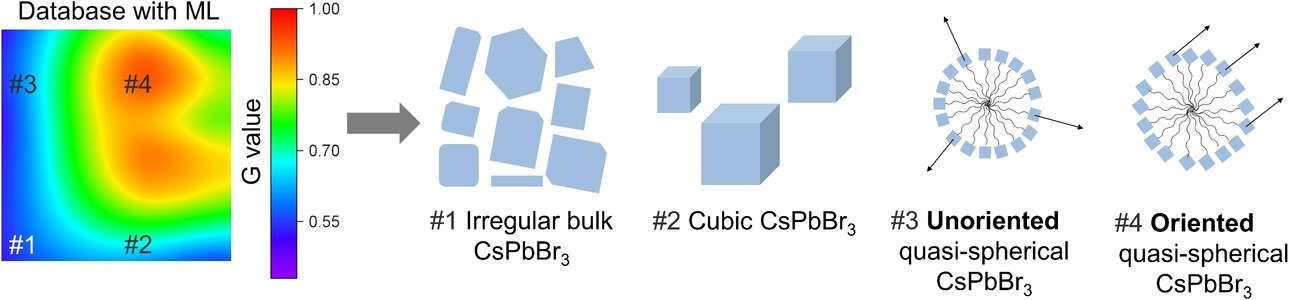
A data-driven approach is employed to achieve the controlled synthesis of four types of CsPbBr3 crystals and successfully control the orientation of quasi-spherical CsPbBr3 structures. Synthesis parameters are optimized using high-throughput characterization combined with machine learning. Furthermore, the synthetic mechanism is determined. Oriented quasi-spherical CsPbBr3, screened by using the data-driven approach, exhibit significantly improved optical properties.
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
Deoxygenative Coupling of CO with a Tetrametallic Magnesium Hydride Complex
- First Published: 13 February 2024
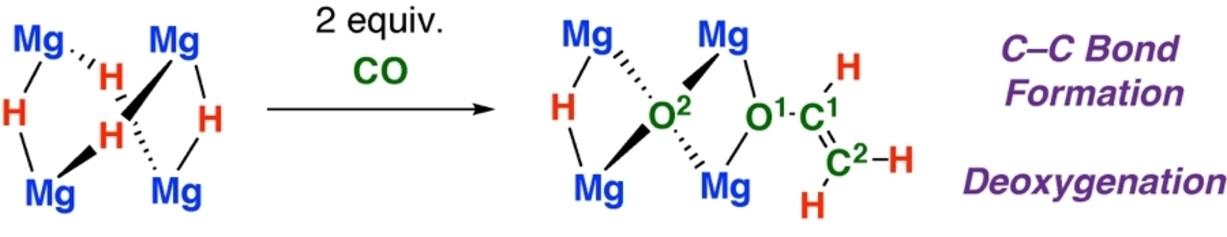
Addition of CO to a tetrametallic magnesium hydride cluster results in both carbon-carbon bond formation and deoxygenation to generate an acetaldehyde enolate [C2OH3]− which remains coordinated to the cluster. DFT studies suggest that key steps in the mechanism involve nucleophilic attack of an oxymethylene on a formyl ligand to generate an unstable [C2O2H3]3− fragment, which undergoes subsequent deoxygenation.
Crystal Engineering | Hot Paper
Achieving High-Temperature Phosphorescence by Organic Cocrystal Engineering
- First Published: 05 February 2024
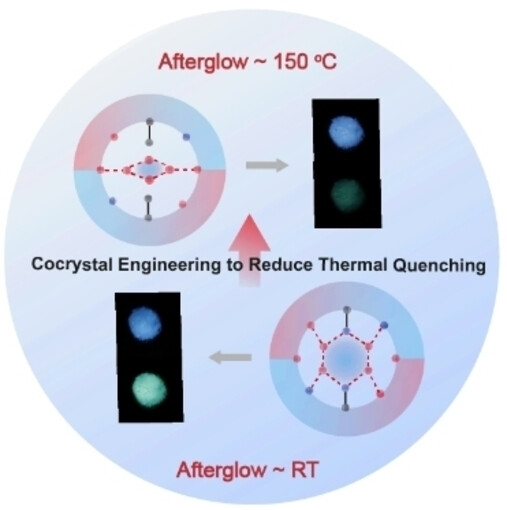
In this study, we propose a new design strategy to stabilize triplet excitons for high-temperature phosphorescence by organic cocrystal engineering. The reported cocrystal has an ultralong emission lifetime of up to 2.16 s, which is the best performance in the case of organic cocrystals under ambient conditions so far.
Porphyrin Nanorings | Very Important Paper
Template-Directed Synthesis of Strained meso-meso-Linked Porphyrin Nanorings
- First Published: 17 January 2024
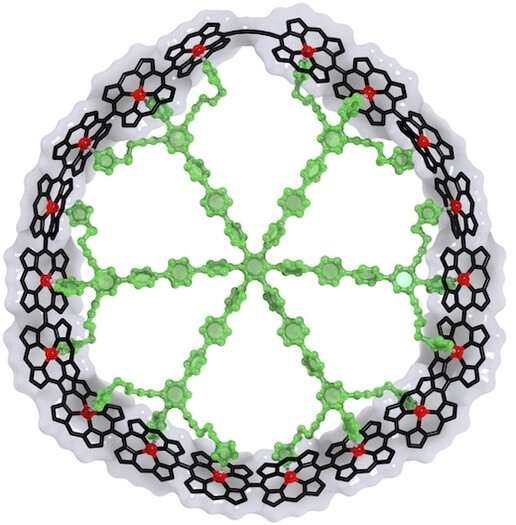
Binding to a template bends a photonic wire consisting of 18 meso-meso linked porphyrins into a ring, allowing covalent cyclization by Glaser coupling, to yield a strained nanoring. The 18-legged template was synthesized efficiently via six-fold iridium-catalyzed C−H borylation. The nanoring was characterized by scanning tunneling microscopy (STM).
Proton Conduction | Hot Paper
A Three-Dimensionally Extended Metal–Organic Ladder Compound Exhibiting Proton Conduction
- First Published: 09 February 2024
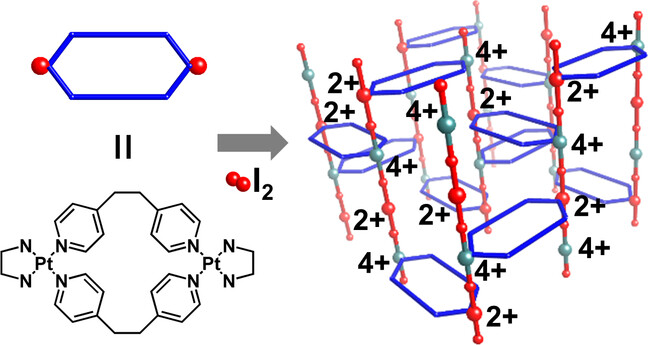
The synthesis of a three-dimensionally (3D) extended two-legged ladder compound was reported for the first time. The unique 3D extended lattice consists of one-dimensional (1D) mixed-valence halogen-bridged metal chains (⋅⋅⋅Pt−I−Pt−I⋅⋅⋅) and helically arranged macrocyclic units as the constituent legs and rungs. The out-of-phase mixed-valence Pt2+/Pt4+ arrangement arises from the weak interchain correlation among adjacent legs.
Fluorine Chemistry
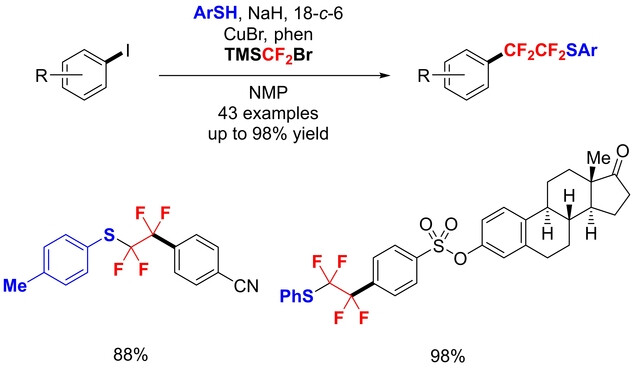
Controllable Double Difluoromethylene Insertions into S−Cu Bonds: (Arylthio)tetrafluoroethylation of Aryl Iodides with TMSCF2Br
- First Published: 15 February 2024
Photoredox Catalysis
Sequential C−F Bond Transformation of the Difluoromethylene Unit in Perfluoroalkyl Groups: A Combination of Fine-Tuned Phenothiazine Photoredox Catalyst and Lewis Acid
- First Published: 21 February 2024
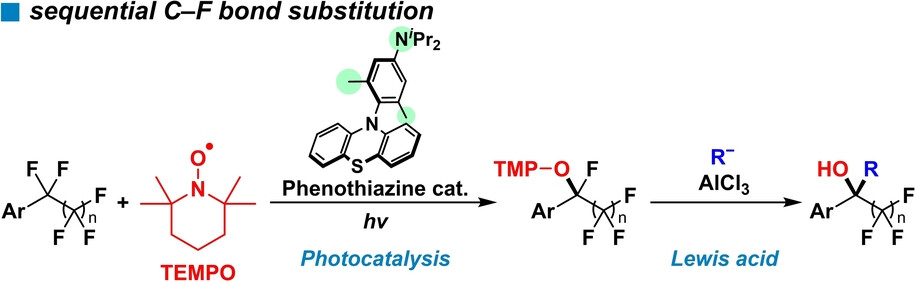
The sequential defluorinative transformation of a difluoromethylene (CF2) unit in perfluoroalkyl compounds has been achieved by a combination of photoredox catalysis and Lewis acid activation. A newly developed phenothiazine-based catalyst served as an efficient catalyst for defluoroaminoxylation. Spectroscopic measurements revealed the reaction mechanism. AlCl3 facilitated further defluorinative transformation of the aminoxylated compounds.
Antiferroelectrics | Hot Paper
Renewing Halogen Substitution Strategy for the Rational Design of High-Curie Temperature Metal-Free Molecular Antiferroelectrics
- First Published: 11 February 2024
Helicates | Hot Paper
Incorporation of an Anion-Coordinated Triple Helicate into a Thin Film for Choline Recognition in an Aqueous System
- First Published: 14 February 2024
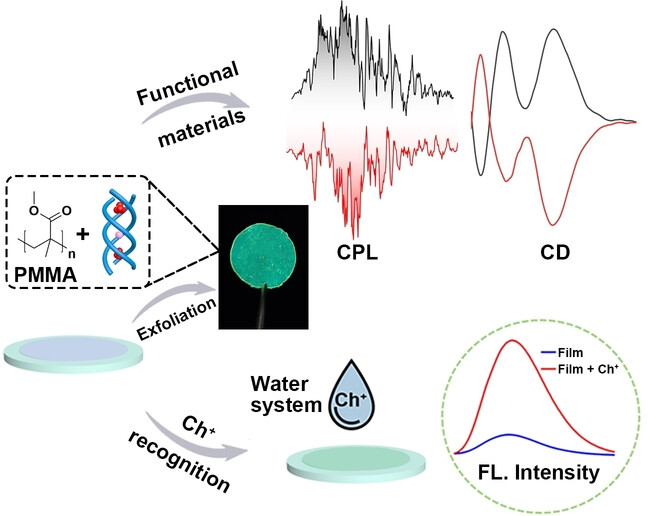
A series of ‘aniono’ helicates have been formed by the coordination of tetraphenylethene-decorated anion-binding ligand with phosphate ions. The triple helicates can be solution-processed with a polymethyl methacrylate matrix to generate functional thin films with multiple optical properties and used to recognize choline and its derivatives in water.
Main-Group Chemistry
Cr5.7Si2.3P8N24—A Chromium(+IV) Nitridosilicate Phosphate with Amphibole-Type Structure
- First Published: 15 February 2024
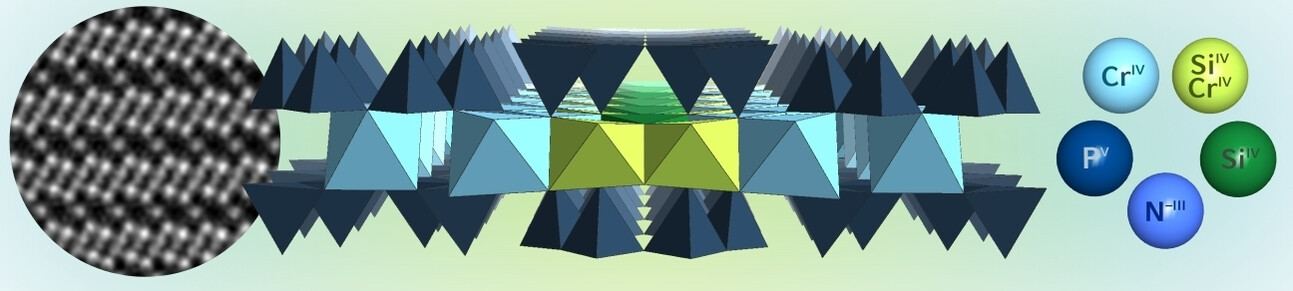
Cr5.7Si2.3P8N24, the first nitridic analog to amphibole minerals, was obtained at high-pressure high-temperature conditions. The structure was elucidated by microfocused synchrotron diffraction, atomic-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and magnetic measurements, which were able to prove the partial disorder of Si and Cr and the oxidation state +IV of chromium.