Site-Selective Photo-Crosslinking of Stilbene Pairs in a DNA Duplex Mediated by Ruthenium Photocatalyst
Graphical Abstract
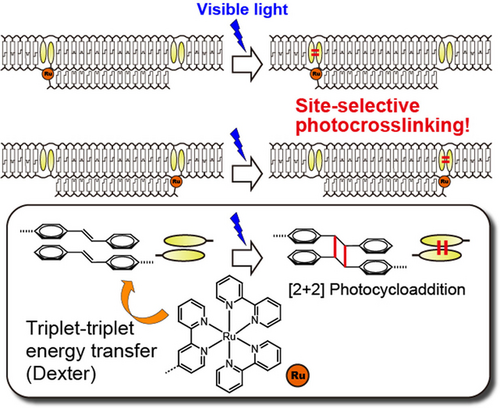
A novel method to site-specifically crosslink DNA duplex upon visible light irradiation. Ru complex on the third strand catalyzed [2+2] photocycloaddition of stilbene moieties via triplet-triplet energy transfer. Site specificity is realized owing to steep distance dependence of the energy transfer. This method will be useful in construction of complex photoresponsive DNA circuits, nanodevices and biological tools.
Abstract
We herein report a method for site-selective photo-crosslinking of a DNA duplex. A stilbene pair was introduced into a DNA duplex and a ruthenium complex was conjugated with a triplex-forming oligonucleotide. We demonstrated that [2+2] photocycloaddition of the stilbene pair occurred upon irradiation with visible light when the ruthenium complex was in close proximity due to triplex formation. No reaction occurred when the ruthenium complex was not in proximity to the stilbene pair. The wavelength of visible light used was of lower energy than the wavelength of UV light necessary for direct excitation of stilbene. Quantum chemical calculation indicated that ruthenium complex catalyzed the photocycloaddition via triplet-triplet energy transfer. Site selectivity of this photo-crosslinking system was evaluated using a DNA duplex bearing two stilbene pairs as a substrate; we showed that the site of crosslinking was precisely regulated by the sequence of the oligonucleotide linked to the ruthenium complex. Since this method does not require orthogonal photoresponsive molecules, it will be useful in construction of complex photoresponsive DNA circuits, nanodevices and biological tools.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.