Harnessing Catalytic RNA Circuits for Construction of Artificial Signaling Pathways in Mammalian Cells
Chao-Qun Wu
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorRuo-Yue Wu
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qiu-Long Zhang
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
School of Pharmacy and Medical Technology, Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Laboratory Medicine of Fujian Province, Putian University, Putian, 351100 China
Search for more papers by this authorLiang-Liang Wang
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorYang Wang
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorChu Dai
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorChen-Xi Zhang
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Liang Xu
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorChao-Qun Wu
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorRuo-Yue Wu
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qiu-Long Zhang
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
School of Pharmacy and Medical Technology, Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Laboratory Medicine of Fujian Province, Putian University, Putian, 351100 China
Search for more papers by this authorLiang-Liang Wang
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorYang Wang
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorChu Dai
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorChen-Xi Zhang
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Liang Xu
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
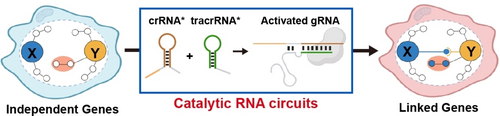
This study describes an amplifiable RNA circuit based on the system of catalytic hairpin assembly with combination of controllable CRISPR-Cas9 function, which can directly build regulatory connections between originally independent endogenous genes in mammalian cells. With this design, artificial signaling pathways can be introduced into mammalian cells to control cellular responses and phenotypes through differentiated RNA expression.
Abstract
Engineering of genetic networks with artificial signaling pathways (ASPs) can reprogram cellular responses and phenotypes under different circumstances for a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. However, construction of ASPs between originally independent endogenous genes in mammalian cells is highly challenging. Here we report an amplifiable RNA circuit that can theoretically build regulatory connections between any endogenous genes in mammalian cells. We harness the system of catalytic hairpin assembly with combination of controllable CRISPR-Cas9 function to transduce the signals from distinct messenger RNA expression of trigger genes into manipulation of target genes. Through introduction of these RNA-based genetic circuits, mammalian cells are endowed with autonomous capabilities to sense the changes of RNA expression either induced by ligand stimuli or from various cell types and control the cellular responses and fates via apoptosis-related ASPs. Our design provides a generalized platform for construction of ASPs inside the genetic networks of mammalian cells based on differentiated RNA expression.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202319309-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.2 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1N. Nandagopal, M. B. Elowitz, Science 2011, 333, 1244–1248.
- 2J. B. Black, P. Perez-Pinera, C. A. Gersbach, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 249–277.
- 3A. Cubillos-Ruiz, T. Guo, A. Sokolovska, P. F. Miller, J. J. Collins, T. K. Lu, J. M. Lora, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2021, 20, 941–960.
- 4F. Sedlmayer, D. Aubel, M. Fussenegger, Nat Biomed Eng 2018, 2, 399–415.
- 5M. Xie, M. Fussenegger, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 507–525.
- 6H. Nakanishi, H. Saito, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 52, 16–22.
- 7E. Ferro, C. Enrico Bena, S. Grigolon, C. Bosia, Cells 2019, 8.
- 8Z. Chen, M. B. Elowitz, Cell 2021, 184, 2284–2301.
- 9D. Chakraborty, R. Rengaswamy, K. Raman, ACS Synth Biol 2022, 11, 1377–1388.
- 10J. A. Brophy, C. A. Voigt, Nat Methods 2014, 11, 508–520.
- 11Y. Krishnan, F. C. Simmel, Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2011, 50, 3124–3156.
- 12T. Wang, H. Hellmer, F. C. Simmel, Curr Opin Biotechnol 2023, 79, 102867.
- 13E. A. Davidson, A. D. Ellington, Nat Chem Biol 2007, 3, 23–28.
- 14K. Rinaudo, L. Bleris, R. Maddamsetti, S. Subramanian, R. Weiss, Y. Benenson, Nat Biotechnol 2007, 25, 795–801.
- 15Z. Xie, L. Wroblewska, L. Prochazka, R. Weiss, Y. Benenson, Science 2011, 333, 1307–1311.
- 16A. A. Green, P. A. Silver, J. J. Collins, P. Yin, Cell 2014, 159, 925–939.
- 17A. A. Green, J. Kim, D. Ma, P. A. Silver, J. J. Collins, P. Yin, Nature 2017, 548, 117–121.
- 18L. Nissim, M. R. Wu, E. Pery, A. Binder-Nissim, H. I. Suzuki, D. Stupp, C. Wehrspaun, Y. Tabach, P. A. Sharp, T. K. Lu, Cell 2017, 171, 1138–1150 e1115.
- 19B. Groves, Y. J. Chen, C. Zurla, S. Pochekailov, J. L. Kirschman, P. J. Santangelo, G. Seelig, Nat Nanotechnol 2016, 11, 287–294.
- 20J. Kim, Y. Zhou, P. D. Carlson, M. Teichmann, S. Chaudhary, F. C. Simmel, P. A. Silver, J. J. Collins, J. B. Lucks, P. Yin, A. A. Green, Nature Chemical Biology 2019, 15, 1173–1182.
- 21E. M. Zhao, A. S. Mao, H. de Puig, K. H. Zhang, N. D. Tippens, X. Tan, F. A. Ran, I. Han, P. Q. Nguyen, E. J. Chory, T. Y. Hua, P. Ramesh, D. B. Thompson, C. Y. Oh, E. S. Zigon, M. A. English, J. J. Collins, Nature Biotechnology 2022, 40, 539–545.
- 22Y. Qian, J. Li, S. Zhao, E. A. Matthews, M. Adoff, W. Zhong, X. An, M. Yeo, C. Park, X. Yang, B. S. Wang, D. G. Southwell, Z. J. Huang, Nature 2022, 610, 713–721.
- 23K. E. Kaseniit, N. Katz, N. S. Kolber, C. C. Call, D. L. Wengier, W. B. Cody, E. S. Sattely, X. J. Gao, Nat Biotechnol 2023, 41, 482–487.
- 24K. Jiang, J. Koob, X. D. Chen, R. N. Krajeski, Y. Zhang, V. Volf, W. Zhou, S. R. Sgrizzi, L. Villiger, J. S. Gootenberg, F. Chen, O. O. Abudayyeh, Nature Biotechnology 2023, 41, 698–707.
- 25K.-H. Siu, W. Chen, Nature Chemical Biology 2019, 15, 217–220.
- 26V. M. Hunt, W. Chen, Chem Commun 2022, 58, 6215–6218.
- 27V. M. Hunt, W. Chen, Acs Synthetic Biology 2022, 11, 397–405.
- 28L. Oesinghaus, F. C. Simmel, Nat Commun 2019, 10, 2092.
- 29Z. M. Ying, F. Wang, X. Chu, R. Q. Yu, J. H. Jiang, Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2020, 59, 18599–18604.
- 30M. H. Hanewich-Hollatz, Z. Chen, L. M. Hochrein, J. Huang, N. A. Pierce, ACS Cent Sci 2019, 5, 1241–1249.
- 31L. Oesinghaus, F. C. Simmel, Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2021, 60, 23894–23902.
- 32L. M. Hochrein, H. Y. Li, N. A. Pierce, Acs Synthetic Biology 2021, 10, 964–971.
- 33S. P. Collins, W. Rostain, C. Y. Liao, C. L. Beisel, Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, 2985–2999.
- 34X. W. Wang, L. F. Hu, J. Hao, L. Q. Liao, Y. Z. Chiu, M. Shi, Y. M. Wang, Nat Cell Biol 2019, 21, 522–530.
- 35J. Lin, Y. Liu, P. D. Lai, H. X. Ye, L. Xu, Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 11773–11784.
- 36J. Lin, W. J. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, L. Xu, J Am Chem Soc 2021, 143, 19834–19843.
- 37W.-J. Wang, J. Lin, C.-Q. Wu, A.-L. Luo, X. Xing, L. Xu, Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, 7691–7703.
- 38C. Jung, A. D. Ellington, Acc Chem Res 2014, 47, 1825–1835.
- 39Y. J. Chen, B. Groves, R. A. Muscat, G. Seelig, Nat Nanotechnol 2015, 10, 748–760.
- 40D. Scalise, R. Schulman, Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2019, 21, 469–493.
- 41F. C. Simmel, B. Yurke, H. R. Singh, Chem Rev 2019, 119, 6326–6369.
- 42S. J. Green, D. Lubrich, A. J. Turberfield, Biophys J 2006, 91, 2966–2975.
- 43P. Yin, H. M. T. Choi, C. R. Calvert, N. A. Pierce, Nature 2008, 451, 318-U314.
- 44Z. Y. Tian, C. Zhou, C. Y. Zhang, M. F. Wu, Y. X. Duan, Y. X. Li, J Mater Chem B 2022, 10, 5303–5322.
- 45J. S. Bois, S. Venkataraman, H. M. Choi, A. J. Spakowitz, Z. G. Wang, N. A. Pierce, Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 4090–4095.
- 46R. P. Goguen, O. Del Corpo, C. M. G. Malard, A. Daher, S. P. Alpuche-Lazcano, M. J. Chen, R. J. Scarborough, A. Gatignol, Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 1020–1034.
- 47T. Frei, F. Cella, F. Tedeschi, J. Gutiérrez, G.-B. Stan, M. Khammash, V. Siciliano, Nature Communications 2020, 11, 4641.
- 48M. O. Duff, S. Olson, X. Wei, S. C. Garrett, A. Osman, M. Bolisetty, A. Plocik, S. E. Celniker, B. R. Graveley, Nature 2015, 521, 376–379.
- 49L. Fagerberg, B. M. Hallstrom, P. Oksvold, C. Kampf, D. Djureinovic, J. Odeberg, M. Habuka, S. Tahmasebpoor, A. Danielsson, K. Edlund, A. Asplund, E. Sjostedt, E. Lundberg, C. A. Szigyarto, M. Skogs, J. O. Takanen, H. Berling, H. Tegel, J. Mulder, P. Nilsson, J. M. Schwenk, C. Lindskog, F. Danielsson, A. Mardinoglu, A. Sivertsson, K. von Feilitzen, M. Forsberg, M. Zwahlen, I. Olsson, S. Navani, M. Huss, J. Nielsen, F. Ponten, M. Uhlen, Mol Cell Proteomics 2014, 13, 397–406.
- 50H. W. Yang, M. Chung, T. Kudo, T. Meyer, Nature 2017, 549, 404–408.
- 51C. Liu, M. Rokavec, Z. Huang, H. Hermeking, Cell Death Differentiation 2023, 30, 1771–1785.
- 52D. Hockenbery, G. Nunez, C. Milliman, R. D. Schreiber, S. J. Korsmeyer, Nature 1990, 348, 334–336.
- 53K. Okazaki, H. Anzawa, Z. Liu, N. Ota, H. Kitamura, Y. Onodera, M. M. Alam, D. Matsumaru, T. Suzuki, F. Katsuoka, S. Tadaka, I. Motoike, M. Watanabe, K. Hayasaka, A. Sakurada, Y. Okada, M. Yamamoto, T. Suzuki, K. Kinoshita, H. Sekine, H. Motohashi, Nature Communications 2020, 11, 5911.
- 54J. Li, Z. Chen, Y. Xiang, L. Zhou, T. Wang, Z. Zhang, K. Sun, D. Yin, Y. Li, G. Xie, Biosens Bioelectron 2016, 86, 75–82.
- 55A. C. Komor, A. H. Badran, D. R. Liu, Cell 2017, 169, 559.
- 56N. S. McCarty, A. E. Graham, L. Studena, R. Ledesma-Amaro, Nat Commun 2020, 11, 1281.
- 57G. T. Hess, J. Tycko, D. Yao, M. C. Bassik, Mol Cell 2017, 68, 26–43.