Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Elucidating the Neurotoxicity of the Star Fruit (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49/2013)
- Page: 12747
- First Published: 07 November 2013

The potent and deadly neurotoxin caramboxin was extracted from star fruits, as N. Garcia-Cairasco, N. P. Lopes, et al. describe in their Communication on page 13067 ff. The main targets of caramboxin intoxication are the kidney and the brain. A worldwide awareness is needed for thousands of people who are exposed to this new phenylalanine-like neurotoxin. (Cover by N. Garcia-Cairasco)
Inside Cover: Thiols and Selenols as Electron-Relay Catalysts for Disulfide-Bond Reduction (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49/2013)
- Page: 12748
- First Published: 11 November 2013

The maintenance of a particular redox state is critical for the proper function of many molecules, including proteins. In their Communication on page 12901 ff., R. T. Raines et al. report that a soluble mixed diselenide can catalyze the efficient relay of electrons from an immobilized dithiol to a protein in an aqueous solution. This system provides a simple means to reduce undesired disulfide bonds as well as to deter oxidative damage. (Graphic by S. B. Johnston and R. T. Raines)
Inside Back Cover: Transparent, Flexible, Superomniphobic Surfaces with Ultra-Low Contact Angle Hysteresis (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49/2013)
- Page: 13105
- First Published: 21 November 2013

Hierarchically textured surfaces that can repel essentially all liquids, including different oils and alcohols, can be fabricated by a method that is described by A. Tuteja et al. in their Communication on page 13007 ff. As these superomniphobic surfaces are also transparent, they might find applications as smartphone screens, eye glasses, windshields, or flat panel displays. The image shows colored droplets of water on top of a transparent superomniphobic surface.
Back Cover: Electron Sharing and Anion–π Recognition in Molecular Triangular Prisms (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49/2013)
- Page: 13106
- First Published: 12 November 2013

Anion-induced π–π stacking with triiodide ions (see picture: purple) binding inside the cavities of homochiral molecular prisms leads to the formation of single-handed supramolecular molecules. In their Communication on page 13100 ff., J. F. Stoddart, M. R. Wasielewski, et al. show that this process happens with chirality transfer and is aided by through-space orbital interactions within the prisms, which lead to electron sharing around a triangular cavity upon reduction.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49/2013
- Pages: 12751-12770
- First Published: 27 November 2013
Corrigendum
Corrigendum: Diastereoselective Synthesis of C3-Quaternary Indolenines Using α,β-Unsaturated N-Aryl Ketonitrones and Activated Alkynes
- Page: 12770
- First Published: 27 November 2013
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49/2013
- Pages: 12772-12774
- First Published: 27 November 2013
Author Profile
News
Helene Lange Prize: M. Schnell / International Young Talent Award in Fluorine Chemistry: S. Riedel / Roy L. Whistler International Award: G.-J. Boons
- Page: 12776
- First Published: 31 October 2013
Book Review
Metallofoldamers. Supramolecular Architectures from Helicates to Biomimetics. Edited by Galia Maayan and Markus Albrecht.
- Page: 12777
- First Published: 15 October 2013
Highlights
Single-Molecule Magnets
Geometry-Mediated Enhancement of Single-Ion Anisotropy: A Route to Single-Molecule Magnets with a High Blocking Temperature†
- Pages: 12780-12782
- First Published: 15 October 2013
Not just any old iron ion: A linear, two-coordinate ionic FeI complex (see scheme) with a S=3/2 ground state has a large energy barrier for magnetization reversal, Ueff=226 cm−1, and undergoes slow magnetic relaxation in the absence of an applied magnetic field. The preparation of complexes with these properties is a step towards the eventual practical application of single-molecule magnets.
GPCR Drug Design
Structures of Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Prospects for Drug Discovery
- Pages: 12783-12785
- First Published: 11 October 2013
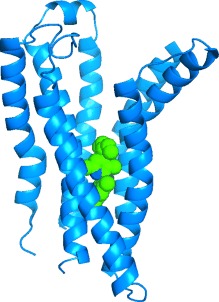
New members in the GPCR photo gallery! Crystal structures of class B G protein-coupled receptors, which bind peptide hormones, have been solved [see picture of the corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 (blue) and a bound allosteric nonpeptide antagonist (green)]. The structures provide a basis for a rational design of better drugs for diabetes, osteoporosis, migraine, or depression.
Minireview
Strained Molecules
Fenestranes in Synthesis: Unique and Highly Inspiring Scaffolds
- Pages: 12786-12798
- First Published: 07 November 2013

Highly strained: Four condensed cycles and a distorted tetracoordinated carbon center with bond angles greater than the regular 109.4° make the scaffold of fenestranes quite unique. A definition and nomenclature of these scaffolds is followed by a detailed overview over recent syntheses of these strained molecules, including their impact on the study of planar tetracoordinate carbon atoms.
Review
Origins of Life
Mechanisms of Autocatalysis
- Pages: 12800-12826
- First Published: 11 October 2013
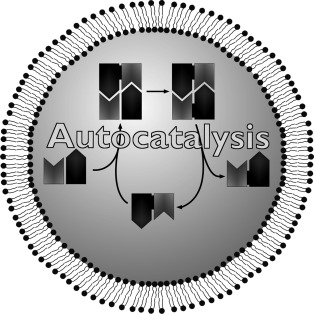
Self-replication is a fundamental concept which lies at the heart of the propagation of life and many other biological processes. Autocatalysis has been implicated in the origin of life itself. Diverse examples of autocatalytic chemical reactions are summarized, including the special case of absolute asymmetric autocatalysis, with special attention paid to their prebiotic relevance.
Communications
Molecular Domino Mechanism
Controlling Mechano- and Seeding-Triggered Single-Crystal-to-Single-Crystal Phase Transition: Molecular Domino with a Disconnection of Aurophilic Bonds†
- Pages: 12828-12832
- First Published: 07 November 2013
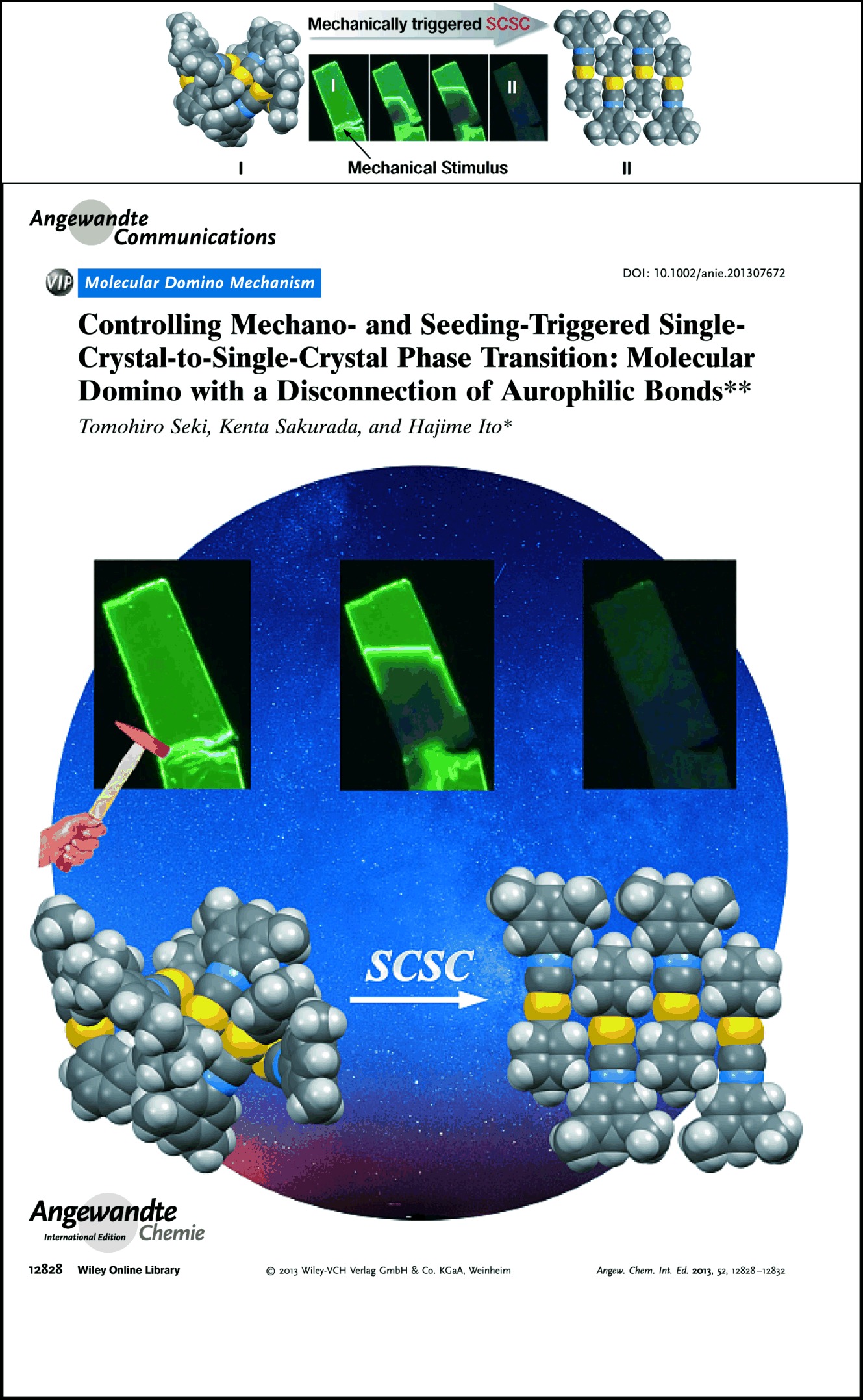
Green and blue polymorphs: A single-crystal-to-single-crystal (SCSC) phase transition of phenyl(3,5-dimethylphenyl isocyanide)gold(I) was triggered by mechanical picking or solid seeding and propagated spontaneously with a domino-like mechanism (see picture). As a result, one phase with intense green emission was transformed to another phase with weaker blue emission.
High-Valent Iron
Observing the Formation and the Reactivity of an Octahedral Iron(V) Nitrido Complex in Real Time†
- Pages: 12833-12837
- First Published: 14 October 2013
One-Electron Oxidants
XeF2/Fluoride Acceptors as Versatile One-Electron Oxidants†
- Pages: 12838-12842
- First Published: 11 October 2013
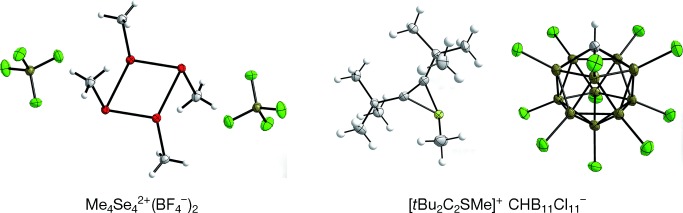
No phlogiston but xenon is released when XeF2/F− acceptors act as new one-electron oxidants. F− acceptors are Lewis acids BF3, B(C6F5)3, and Al{OC(CF3)3}3, and silyl derivatives TfOSiMe3, Tf2NSiMe3, Me3Si+ B(C6F5)4−, and Me3Si+ CHB11Cl11−. The anions BF4−, TfO−, Tf2N−, FB(C6F5)3−, FAl{OC(CF3)3}3−, B(C6F5)4−, or CHB11Cl11− can be introduced into oxidation products of R2E2 (E=S, Se, Te), [FeCp2], [(FeCpS)4], tetrathiafulvalene, thianthrene, and (2,4-Br2C6H3)3N.
G-Quadruplex DNA
Reversible Stabilization of Transition-Metal-Binding DNA G-Quadruplexes†
- Pages: 12843-12847
- First Published: 07 November 2013
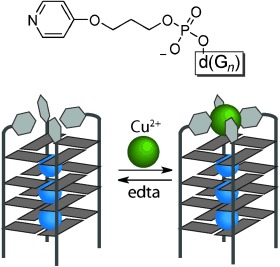
You can't top the CopperTop: Tetramolecular G-quadruplexes modified with terminal pyridine ligands exhibit metal-triggered stabilization as monitored by thermal denaturation studies, circular dichroism, and nondenaturing gel electrophoresis. Formation of the square-planar CuII(pyridine)4 complex was confirmed by EPR measurements. The metal complexation is fully reversible by removal of the transition metal with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (edta).
Cholesterol
Cholesterol’s Aliphatic Side Chain Modulates Membrane Properties†
- Pages: 12848-12851
- First Published: 25 November 2013
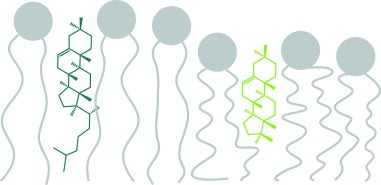
The influence of cholesterol's alkyl side chain on membrane properties was studied using a series of synthetic cholesterol derivatives without a side chain or with a branched side chain consisting of 5 to 14 carbon atoms. Cholesterol's side chain is crucial for all membrane properties investigated and therefore essential for the membrane properties of eukaryotic cells.
Bipolarons
Multiple Reduction of 2,5-Bis(borolyl)thiophene: Isolation of a Negative Bipolaron by Comproportionation†
- Pages: 12852-12855
- First Published: 09 October 2013
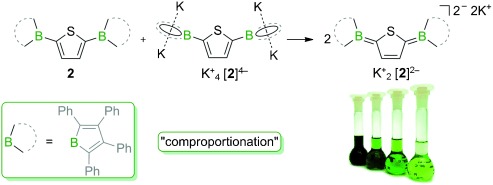
The 2,5-bis(borolyl)thiophene 2, a conjugated acceptor–π–acceptor system, can be reduced to the monoradical anion [2].−, the dianion [2]2−, and the tetraanion [2]4−. The dianion [2]2− was also prepared by a comproportionation reaction (see scheme) and features an absorption maximum in the near-IR region (λmax=800 nm), which is characteristic of a bipolaron with a quinoidal structure.
Trifluoromethylsulfenylation
N-Trifluoromethylthiophthalimide: A Stable Electrophilic SCF3-Reagent and its Application in the Catalytic Asymmetric Trifluoromethylsulfenylation†
- Pages: 12856-12859
- First Published: 07 October 2013
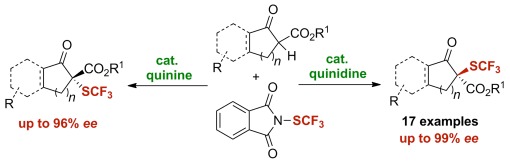
Cinchona alkaloid catalysts in combination with air- and moisture-stable N-trifluoromethylthiophthalimide as electrophilic SCF3 source enabled the catalytic enantioselective trifluoromethylsulfenylation. Thus, a series of α-SCF3 esters that bear a quaternary carbon stereogenic center were obtained with excellent yield and enantioselectivity. Moreover, the products can be readily converted into valuable α-SCF3 β-hydroxyesters.
Trifluoromethylthiolation
Enantioselective Electrophilic Trifluoromethylthiolation of β-Ketoesters: A Case of Reactivity and Selectivity Bias for Organocatalysis†
- Pages: 12860-12864
- First Published: 02 September 2013
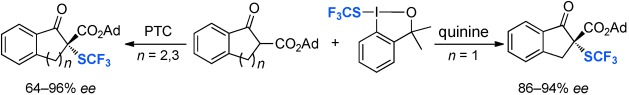
A chiral Lewis base or a phase-transfer catalyst (PTC) can mediate the highly enantioselective trifluoromethylthiolation of β-ketoesters with the previously developed SCF3 reagent (see scheme). Reactions of indanone-derived β-ketoesters occurred with high yield and excellent enantioselectivity with quinine as catalyst. Reactions of tetralone- or 1-benzosuberone-derived β-ketoesters occurred with moderate to good enantioselectivity with a quinine-derived PTC.
Anodic Cyclizations
Oxidative Cyclization Reactions: Controlling the Course of a Radical Cation-Derived Reaction with the Use of a Second Nucleophile†
- Pages: 12865-12868
- First Published: 19 November 2013
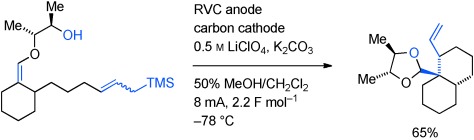
Construction of new ring systems: Oxidative cyclizations (see picture; RVC=reticulated vitreous carbon) have been conducted that use two separate intramolecular nucleophiles to trap an enol ether-derived radical cation intermediate. The reactions provide a means for rapidly trapping the radical cation intermediate in a manner that avoids competitive decomposition reactions.
Disilyne Complexes
Palladium and Platinum η2-Disilyne Complexes Bearing an Isolable Dialkyldisilyne as a Ligand†
- Pages: 12869-12873
- First Published: 08 November 2013
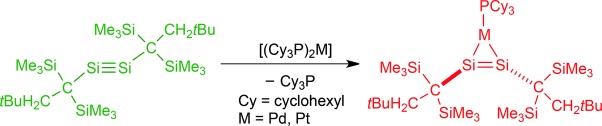
Not so alkyne like: A dialkyldisilyne (left, green) that can be isolated is synthesized and fully characterized. It coordinates to palladium and platinum in a η2-fashion giving complexes (red) with a trans-bent geometry, in contrast to η2-alkyne complexes. The complexes showed significant metallacycle character.
Conjugated Polyelectrolytes
Facile Doping of Anionic Narrow-Band-Gap Conjugated Polyelectrolytes During Dialysis†
- Pages: 12874-12878
- First Published: 07 November 2013
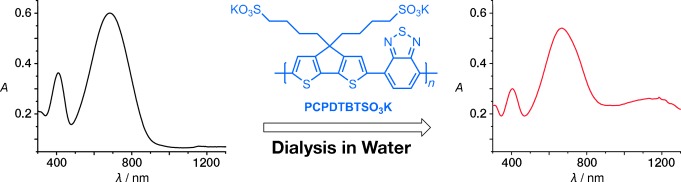
PCPDTBTSO3K, an anionic, narrow-band-gap conjugated polyelectrolyte, was found to be doped after dialysis. The proposed doping mechanism involves protonation of the polymer backbone, followed by electron transfer from a neutral chain, to generate radical cations, which are stabilized by the pendant sulfonate anions. Formation of polarons is supported by spectroscopy and electrical-conductivity measurements.
DNA Damage
Detection and Characterization of 1,2-Dibromoethane-Derived DNA Crosslinks Formed with O6-Alkylguanine-DNA Alkyltransferase†
- Pages: 12879-12882
- First Published: 15 October 2013
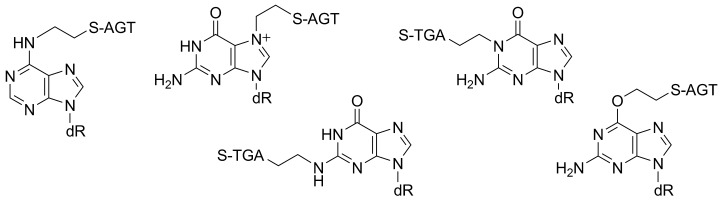
A combination of chemical modifications and LC-tandem MS was used for the structure elucidation of various ethylene crosslinks of DNA with O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AGT, see picture). The elucidation of the chemical structures of such DNA–protein crosslinks is necessary to understand mechanisms of mutagenesis.
Dual Catalysis
An Iron/Amine-Catalyzed Cascade Process for the Enantioselective Functionalization of Allylic Alcohols†
- Pages: 12883-12887
- First Published: 15 October 2013
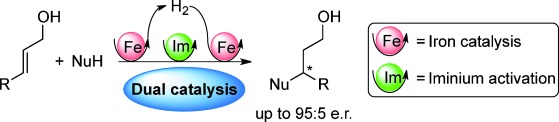
Three is a lucky number: An enantioselective transformation of allylic alcohols into β-chiral saturated alcohols has been developed by combining two distinct metal- and organocatalyzed catalytic cycles. This waste-free triple cascade process merges an iron-catalyzed borrowing-hydrogen step with an aminocatalyzed nucleophilic addition reaction.
Synthetic Methods
Generation of Stereochemically Defined Tetrasubstituted Enolborinates by 1,4-Hydroboration of α,β-Unsaturated Morpholine Carboxamides with (Diisopinocampheyl)borane†
- Pages: 12888-12891
- First Published: 15 October 2013
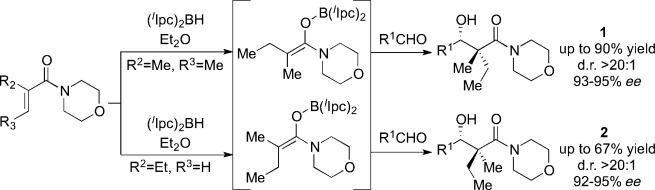
On all fours: The title reaction with (Ipc)2BH provides tetrasubstituted enolborinates which undergo aldol reactions with aldehydes to form products with all-carbon quaternary centers with exceptional diastereo- and enantioselectivity. A change to the substitution pattern of the starting amide leads to either diastereomer of the α-methyl-α-ethyl-β-hydroxy carboxamide (1 or 2).
Asymmetric Catalysis
Catalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of Functionalized Tropanes Reveals Novel Inhibitors of Hedgehog Signaling†
- Pages: 12892-12896
- First Published: 21 October 2013
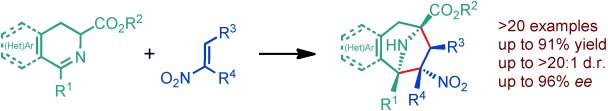
Dipolar cycloaddition: A highly efficient copper(I)-catalyzed enantioselective [3+2] cycloaddition reaction of 1,3-fused cyclic azomethine ylides and nitroalkenes has been developed. This method provides access to functionalized tropane scaffolds with several quaternary and tertiary stereocenters in a single step under mild reaction conditions.
Electrochemistry
Covalent Attachment of Porphyrins and Ferrocenes to Electrode Surfaces through Direct Anodic Oxidation of Terminal Ethynyl Groups†
- Pages: 12897-12900
- First Published: 11 October 2013
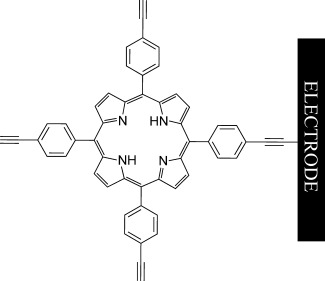
One with the surface: A method is presented for electrode modification with terminal alkynes and alkenes. Direct oxidation of these moieties leads to efficient grafting onto glassy carbon, gold, platinum, and indium tin oxide surfaces. Various ferrocenes and 5,10,15,20-(4-ethynylphenyl)porphyrin were attached in this way.
Thiol–Disulfide Interchange
Thiols and Selenols as Electron-Relay Catalysts for Disulfide-Bond Reduction†
- Pages: 12901-12904
- First Published: 10 October 2013
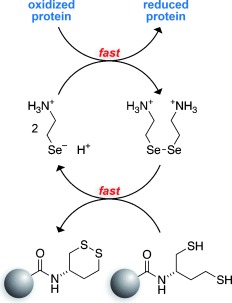
Pass them on! Dithiobutylamine immobilized on a resin is a useful reagent for the reduction of disulfide bonds. Its ability to reduce a disulfide bond in a protein is enhanced greatly if used along with a soluble strained cyclic disulfide or mixed diselenide that relays electrons from the resin to the protein. This electron-relay catalysis system provides distinct advantages over the use of excess soluble reducing agent alone.
Biomass Conversion
Expanding the Scope of Biomass-Derived Chemicals through Tandem Reactions Based on Oxorhenium-Catalyzed Deoxydehydration†
- Pages: 12905-12909
- First Published: 12 November 2013
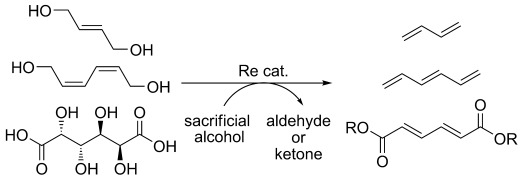
New modes of DODH: Oxorhenium compounds act as deoxydehydration(DODH)/acid dual-purpose catalysts to transform biomass-derived diol substrates into a variety of commodity chemical precursors. The power of this approach is highlighted by a tandem [1,3]-OH shift/DODH of 2-ene-1,4-diols and 2,4-diene-1,6-diols, and by a DODH/esterification sequence of sugar acids to unsaturated esters for the production of polymers and plasticizers.
Synthetic Methods
A Tandem Isomerization/Prins Strategy: Iridium(III)/Brønsted Acid Cooperative Catalysis†
- Pages: 12910-12914
- First Published: 11 November 2013
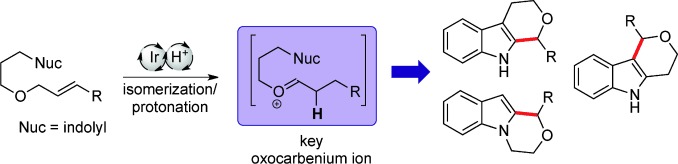
Working together: A mild and efficient isomerization/protonation sequence generates pyran-fused indoles by cooperative catalysis between cationic iridium(III) and Bi(OTf)3. Three distinct cyclization manifolds lead to the corresponding bioactive scaffolds in good yields. In addition, N-substituted indoles can be synthesized enantioselectively in the presence of a chiral phosphate.
CH Functionalization
A Traceless Directing Group for CH Borylation†
- Pages: 12915-12919
- First Published: 12 November 2013
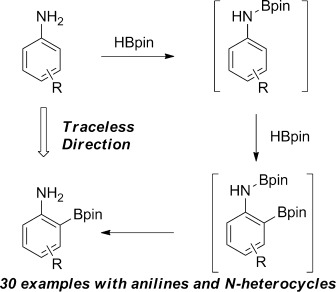
Not a trace: Borylation of the nitrogen in nitrogen heterocycles or anilines provides a traceless directing group for subsequent catalytic CH borylation. Selectivities that previously required Boc protection can be achieved; furthermore, the NBpin directing group can be installed and removed in situ, and product yields are substantially higher. Boc=tert-butoxycarbonyl, pin=pinacolato.
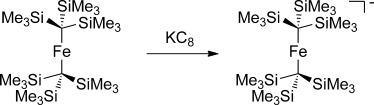
Copper Hydrides
Bonding and Reactivity of a μ-Hydrido Dicopper Cation†
- Pages: 12920-12923
- First Published: 16 October 2013
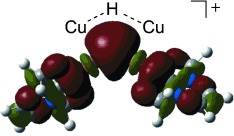
A bent dicopper–hydride cation that has an N-heterocyclic carbene supporting ligand has a Cu-H-Cu angle of 122° in the solid state. Density functional theory suggests an open three-centered metal–hydrogen interaction. The hydride reacts readily with methanol and with carbon dioxide; insertion of phenylacetylene affords a gem-dicopper vinyl complex.
Total Synthesis
Highly Enantioselective Bromocyclization of Tryptamines and Its Application in the Synthesis of (−)-Chimonanthine†
- Pages: 12924-12927
- First Published: 10 October 2013
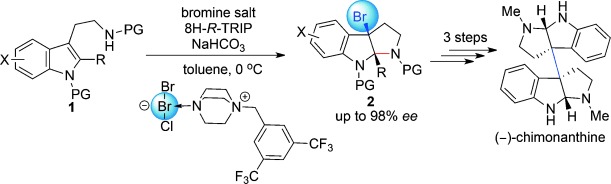
A shorter path: A highly enantioselective bromocyclization of tryptamine has been developed using an anionic chiral phase-transfer catalyst. This method provides a direct approach for preparing chiral 3-bromopyrroloindoline from tryptamine, which enables a four-step enantioselective synthesis of (−)-chimonanthine. PG=protecting group.
Fullerene Isomers
Unexpected Isomerism in cis-2 Bis(pyrrolidino)[60]Fullerene Diastereomers†
- Pages: 12928-12931
- First Published: 16 October 2013
![Unexpected Isomerism in cis-2 Bis(pyrrolidino)[60]Fullerene Diastereomers](/cms/asset/4e10bdac-6e39-402e-b19e-4314d240c831/mcontent.jpg)
Similar yet different: A one-step regio- and diastereoselective synthesis of three new bis(pyrrolidine)[60]fullerenes, one cis-1 and two unprecedented cis-2 diastereoisomers, is reported (see scheme). The compounds are easily purified using simple chromatographic techniques, and were fully characterized by spectroscopic techniques and X-ray crystallography. A mechanism for the isomeric conversion observed is proposed.
Organocatalysis
Chiral Phosphoric Acid Directed Regioselective Acetalization of Carbohydrate-Derived 1,2-Diols†
- Pages: 12932-12936
- First Published: 09 October 2013
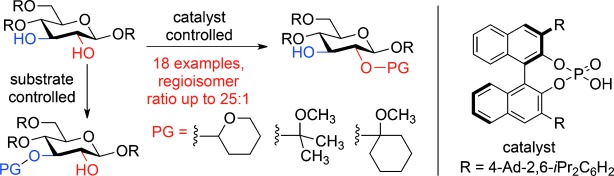
In control: A chiral phosphoric acid catalyst (see scheme) significantly enhances or completely overrides the inherent regioselective acetalization profiles exhibited by monosaccharide-derived 1,2-diol substrates. This study represents the first example of chiral-catalyst-directed regio- and enantioselective intermolecular acetalizations, which are complementary to existing methods for substrate-controlled functionalization of polyols.
Bio-nanotechnology
Efficient Electron Transfer in i-Motif DNA with a Tetraplex Structure†
- Pages: 12937-12941
- First Published: 04 November 2013
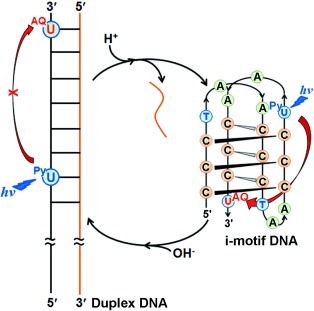
Electron transfer through DNA: The electron-transfer dynamics of i-motif DNA conjugated with pyrene (Py) and anthraquinone (AQ) has been investigated by fluorescence up-conversion and transient absorption spectroscopic methods. Electron transfer (see red arrows) in i-motif DNA is more efficient than in duplex DNA, suggesting that i-motif DNA can be used as electron carrier in nanoelectronic devices.
Oxidative Cross-Coupling
Iron-Catalyzed Oxidative CH/CH Cross-Coupling: An Efficient Route to α-Quaternary α-Amino Acid Derivatives†
- Pages: 12942-12945
- First Published: 25 September 2013
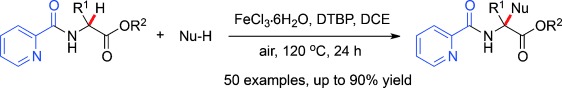
Fully loaded: A coordinating activation strategy has been developed to furnish α-quaternary α-amino acids through the iron(III)-catalyzed oxidative functionalization of α-C(sp3)H bonds of α-tertiary α-amino acid esters. The reaction exhibits a broad substrate scope for both α-amino acids and nucleophiles (Nu) as well as good functional-group tolerance (see scheme, DTBP=di-tert-butyl peroxide, DCE=1,2-dichloroethane).
Photochemistry
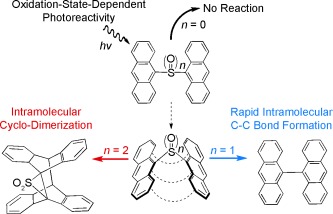
Oxidation-State-Dependent Photochemistry of Sulfur-Bridged Anthracenes†
- Pages: 12946-12950
- First Published: 04 November 2013
Amino Acid Synthesis
Stereospecific Biosynthesis of β-Methyltryptophan from L-Tryptophan Features a Stereochemical Switch†
- Pages: 12951-12955
- First Published: 25 October 2013
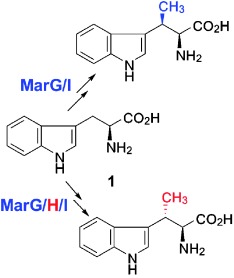
Make the switch: The three-enzyme cassette MarG/H/I is responsible for stereospecific biosynthesis of β-methyltryptophan from L-tryptophan (1). MarG/I convert 1 into (2S,3R)-β-methyltryptophan, while MarG/I combined with MarH convert 1 into (2S,3S)-β-methyltryptophan. MarH serves as a stereochemical switch by catalyzing the stereoinversion of the β-stereocenter.
Carbanions
Enantiodivergent Deprotonation/Acylation of α-Amino Nitriles†
- Pages: 12956-12960
- First Published: 09 October 2013
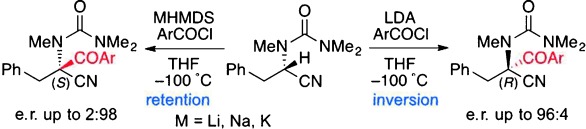
Back to ‘base'ics: The title reaction of enantioenriched α-ureidonitriles was found to proceed in a highly enantiodivergent manner despite the intermediacy of stereolabile α-nitrile metallocarbanions. Enantiodivergence is dependent upon the base used. For the less basic hexamethyldisilazides (HMDS), deprotonation in which a metal (M) cation is precomplexed with an electrophile is proposed. LDA=lithium diisopropylamide.
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Catalysis by Coke Deposits: Synthesis of Isoprene over Solid Catalysts
- Pages: 12961-12964
- First Published: 15 October 2013
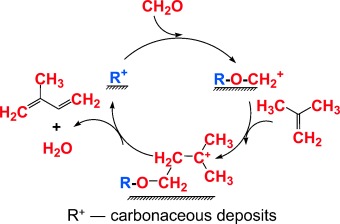
A help rather than a hindrance: Carbonaceous deposits have been found to play a key role in the selective synthesis of isoprene from formaldehyde and isobutene over solid catalysts. They accumulate on the catalyst surface during the induction period and promote the interaction of the substrates at the steady state. The proposed mechanism (see scheme) shows the way forward for the design of efficient solid catalysts for the synthesis of isoprene.
Nitrogen–Carbon Bond Formation
Activation of Dinitrogen-Derived Hafnium Nitrides for Nucleophilic NC Bond Formation with a Terminal Isocyanate†
- Pages: 12965-12969
- First Published: 09 October 2013
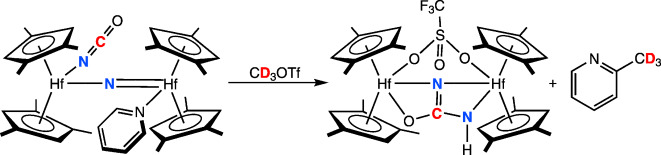
Better by Hf: Anion coordination to a bridging hafnocene nitride complex, prepared from CO-induced N2 cleavage, increases the nucleophilicity of the nitrogen atom, thus promoting additional NC bond formation with a typically inert terminal isocyanate ligand. This cascade sequence allows synthesis of otherwise challenging mono-substituted ureas using N2, CO, and an appropriate electrophile.
CH Activation
N-Oxide as a Traceless Oxidizing Directing Group: Mild Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed CH Olefination for the Synthesis of ortho-Alkenylated Tertiary Anilines†
- Pages: 12970-12974
- First Published: 12 November 2013
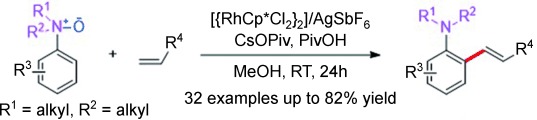
Double role: A traceless directing group also acts as an internal oxidant in a novel RhIII-catalyzed protocol developed for the synthesis of ortho-alkenylated tertiary anilines (see scheme). A five-membered cyclometalated RhIII complex is proposed as a plausible intermediate and confirmed by X-ray crystallographic analysis.
Direct Annulation
An Approach to Benzophosphole Oxides through Silver- or Manganese-Mediated Dehydrogenative Annulation Involving CC and CP Bond Formation†
- Pages: 12975-12979
- First Published: 11 October 2013
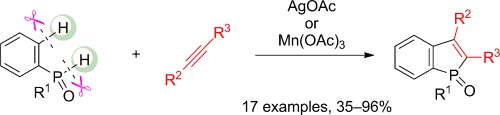
Benzophosphole construction was achieved through the AgI-mediated dehydrogenative annulation of phenylphosphine oxides with internal alkynes in a process involving CC and CP bond formation. A wide range of asymmetrical phenylacetylenes could be employed and the reactions proceeded with perfect regioselectivity. Moreover, the annulation could be conducted even at room temperature when a MnIII promoter was used in place of AgI.
Electrochemistry
Electrochemical Sizing of Organic Nanoparticles†
- Pages: 12980-12982
- First Published: 16 October 2013
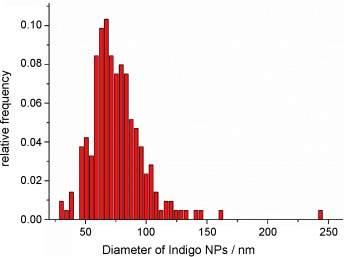
The size of organic nanoparticles (NPs) can be electrochemically determined by Faradaic charge transfer when nanoparticles strike an electrode. Indigo NPs were used as a model (see distribution of the NP diameter). This strategy could be used for monitoring the size of a wide range of organic nanoparticles.
Photocatalysis
Visible-Light Photocatalytic Conversion of Carbon Monoxide to Methane by Nickel(II) Oxide†
- Pages: 12983-12987
- First Published: 24 October 2013
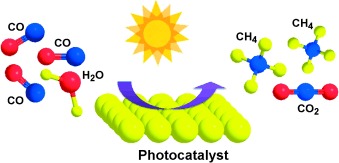
Solar Fuels: Different n- and p-type semiconductors have been investigated for sustainable solar fuel production. p-Type semiconductors, such as NiO, Fe3O4, Co3O4, and CuO, are able to reduce carbon monoxide by water or hydrogen to methane (see picture). The highest CH4 yield achieved was 17.26 mmol of CH4 per gram of catalyst using NiO in an excess of H2.
Natural Product Synthesis
Total Synthesis of the Indole Alkaloid (±)- and (+)-Methyl N-Decarbomethoxychanofruticosinate†
- Pages: 12988-12991
- First Published: 20 November 2013
Homogeneous Catalysis
Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Cyclizative Cross-Coupling of ortho-Alkynylanilines with ortho-Alkynylbenzamides under Aerobic Conditions†
- Pages: 12992-12996
- First Published: 04 November 2013

Born to couple: The Pd(OAc)2-catalyzed reaction of o-alkynylanilines (1) with o-alkynylbenzamides (2) affords the cyclizative cross-coupling products 3 in good to excellent yields. Three bonds are created in the formation of two heterocycles tethered by a tetrasubstituted double bond. Mechanistic studies indicate that the reaction is initiated by aminopalladation with subsequent oxypalladation, N-demethylation, and reductive elimination.
Porphyrinoids
Modulation of Dual Electronic Circuits of [26]Hexaphyrins Using Internal Aromatic Straps†
- Pages: 12997-13001
- First Published: 11 November 2013
![Modulation of Dual Electronic Circuits of [26]Hexaphyrins Using Internal Aromatic Straps](/cms/asset/7e2d9e1a-3da8-4f8c-a0a0-aed0426837c9/mcontent.jpg)
Internal bridges: [26]Hexaphyrins with an aromatic strap in 5,20 position have two potentially cyclic conjugated networks, that is, [18]porphyrin and [26]hexaphyrin (see picture), and show a formal analogy with [18]annuleno[18]annulens. 1,3-Phenylene-, 2,5-thienylene-, and 2,5-pyrrylene-bridged [26]hexaphyrins have been synthesized and characterized.
Near-Infrared Imaging
Biological Imaging Using Nanoparticles of Small Organic Molecules with Fluorescence Emission at Wavelengths Longer than 1000 nm†
- Pages: 13002-13006
- First Published: 31 October 2013
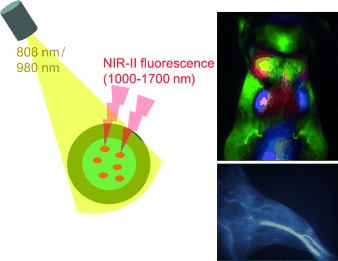
Embedded in a polymer: A hydrophobic organic molecule that fluoresces in the near-infrared II (NIR-II) region was made water-soluble and biocompatible by its embedment in a polymer nanoparticle, which was then coated with hydrophilic poly(ethylene glycol) chains. The resulting nanoparticles exhibit bright fluorescence in the NIR-II window and high photostability in aqueous media and were used for in vivo imaging in mice.
Surface Chemistry
Transparent, Flexible, Superomniphobic Surfaces with Ultra-Low Contact Angle Hysteresis†
- Pages: 13007-13011
- First Published: 13 November 2013
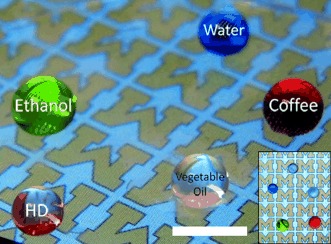
See-through surfaces: High transparency is required to use superomniphobic surfaces, which can be self-cleaning, stain-proof, anti-bio-fouling, drag-reducing, or anti-fogging, for smartphone screens (see picture), eye glasses, windshields, or flat panel displays. A spray-based method has now been developed that can fabricate transparent, flexible, and highly superomniphobic surfaces. HD=hexadecane.
Bio-orthogonal Chemistry
Selective Exo-Enzymatic Labeling of N-Glycans on the Surface of Living Cells by Recombinant ST6Gal I†
- Pages: 13012-13015
- First Published: 15 October 2013
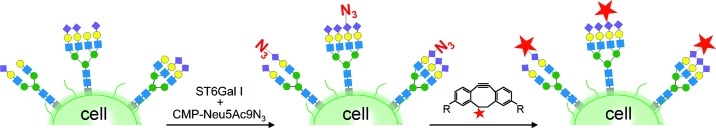
A game of tag: N-Glycans on the surface of living cells were selectively tagged by exogenously administering recombinant ST6Gal I sialyltransferase and azide-modified CMP-Neu5Ac. This modification was followed by a strain-promoted cycloaddition using a biotin-modified dibenzylcyclooctynol (red star=biotin). The methodology will make it possible to dissect the mechanisms that underlie altered glycoconjugate recycling and storage in disease.
Multiple Bonding
A Cerium(IV)–Carbon Multiple Bond†
- Pages: 13016-13019
- First Published: 15 October 2013
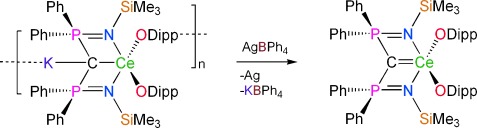
Straightforward access to a cerium(IV)–carbene complex was provided by one-electron oxidation of an anionic “ate” cerium(III)–carbene precursor, thereby avoiding decomposition reactions that plague oxidations of neutral cerium(III) compounds. The cerium(IV)–carbene complex is the first lanthanide(IV)–element multiple bond and involves a twofold bonding interaction of two electron pairs between cerium and carbon.
Biosensors
Multiplex Detection of DNA Mutations by the Fluorescence Fingerprint Spectrum Technique†
- Pages: 13020-13023
- First Published: 11 October 2013
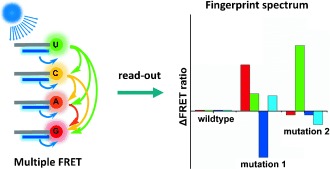
A fingerprint spectrum technique that utilizes cationic conjugated-polymer-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) is used for multiplex detection of DNA mutations. This method detects as low as 5 % mutation of the total DNA. Ten PIK3CA mutations originating from 30 clinical breast cancer samples could be detected.
CO2 Sequestration
Solvation of Carbon Dioxide in [C4mim][BF4] and [C4mim][PF6] Ionic Liquids Revealed by High-Pressure NMR Spectroscopy†
- Pages: 13024-13027
- First Published: 09 October 2013
![Solvation of Carbon Dioxide in [C4mim][BF4] and [C4mim][PF6] Ionic Liquids Revealed by High-Pressure NMR Spectroscopy](/cms/asset/74aa400e-98d0-43e5-bf3f-727bc357c48e/mcontent.jpg)
Where is CO2? The intermolecular interactions of [C4mim]BF4 and [C4mim]PF6 ionic liquids and CO2 have been determined by high-pressure NMR spectroscopy in combination with molecular dynamic simulations. The anion and the cation are both engaged in interactions with CO2. A detailed picture of CO2 solvation in these ILs is provided. CO2 solubility is essentially determined by the microscopic structure of the IL.
Fluorescent Probes
Development of Azo-Based Fluorescent Probes to Detect Different Levels of Hypoxia†
- Pages: 13028-13032
- First Published: 14 October 2013
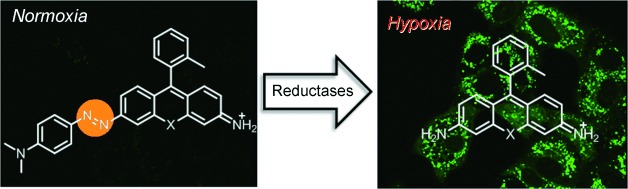
Let it shine: New hypoxia-sensitive fluorescent probes were developed; they consist of a rhodamine moiety with an azo group directly conjugated to the fluorophore. Because of an ultrafast conformational change around the NN bond, the compounds are nonfluorescent under normoxia. However, under hypoxia, the azo group is reduced, and a strongly fluorescent rhodamine derivative is released.
Medium-Ring Compounds
Diastereoselective Synthesis of Eight-Membered-Ring Allenes from Propargylic Epoxides and Aldehydes by Silylene Insertion into Carbon–Oxygen Bonds†
- Pages: 13033-13036
- First Published: 09 October 2013
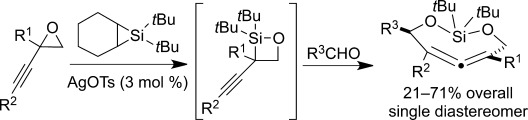
Bent out of shape: Silver-catalyzed insertions of silylenes into propargylic CO bonds of epoxides regioselectively form 1,2-silaoxetanes, which add to aldehydes to give the title allenes as single diastereomers (see scheme; Ts=4-toluenesulfonyl). An X-ray crystal structure confirmed the stereochemistry of the allene, which is bent significantly from linearity (164°).
Click Chemistry
Copper(I)-Catalyzed Cycloaddition of Bismuth(III) Acetylides with Organic Azides: Synthesis of Stable Triazole Anion Equivalents†
- Pages: 13037-13041
- First Published: 15 October 2013
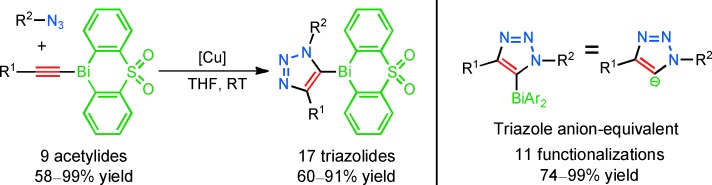
Fully loaded: Readily accessible and shelf-stable 1-bismuth(III) acetylides react rapidly and regiospecifically with organic azides in the presence of a copper(I) catalyst (see scheme). The reaction tolerates many functional groups and gives excellent yields of the previously unreported 5-bismuth triazolides. This uniquely reactive intermediate is functionalized under mild reaction conditions to give fully substituted 1,2,3-triazoles.
Chemical Imaging
Label-Free Quantitative Imaging of Cholesterol in Intact Tissues by Hyperspectral Stimulated Raman Scattering Microscopy†
- Pages: 13042-13046
- First Published: 14 October 2013
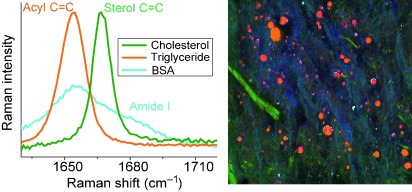
A finger on the pulse: Current molecular analysis of cells and tissues routinely relies on separation, enrichment, and subsequent measurements by various assays. Now, a platform of hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering microscopy has been developed for the fast, quantitative, and label-free imaging of biomolecules in intact tissues using spectroscopic fingerprints as the contrast mechanism.
Cancer
Magnetically Triggered Dual Functional Nanoparticles for Resistance-Free Apoptotic Hyperthermia†
- Pages: 13047-13051
- First Published: 04 November 2013
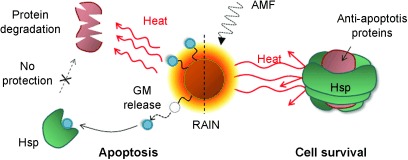
Overcoming resistance: Heat-treated cancer cells possess a protective mechanism for resistance and survival. Resistance-free apoptosis-inducing magnetic nanoparticles (RAINs) successfully promote hyperthermic apoptosis, obstructing cell survival by triggering two functional units of heat generation and the release of geldanamycin (GM) for heat shock protein (Hsp) inhibition under an alternating magnetic field (AMF).
Mesoporous Materials
Enhancement of Chemical Stability and Crystallinity in Porphyrin-Containing Covalent Organic Frameworks by Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds†
- Pages: 13052-13056
- First Published: 14 October 2013
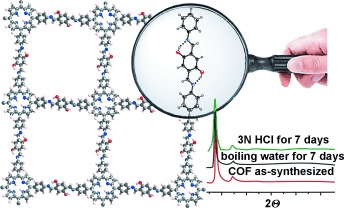
A strong bond: A strategy based on intramolecular hydrogen-binding interactions in 2D covalent organic frameworks (COFs) is shown to improve the crystallinity, porosity, and chemical stability of the material (see picture). The concept is validated by removing the hydrogen-bonding interaction in the methoxy analog which showed a lower stability and crystallinity.
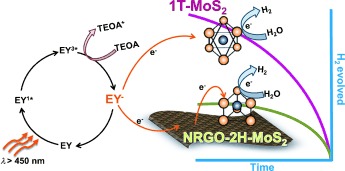
Hydrogen Generation with MoS2
Highly Effective Visible-Light-Induced H2 Generation by Single-Layer 1T-MoS2 and a Nanocomposite of Few-Layer 2H-MoS2 with Heavily Nitrogenated Graphene
- Pages: 13057-13061
- First Published: 11 November 2013
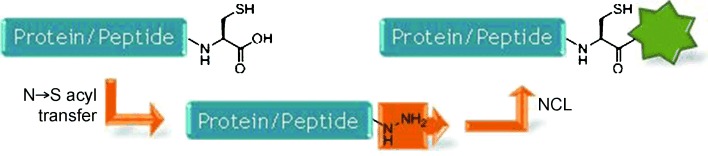
N→S Acyl Transfer
Cysteine Promoted C-Terminal Hydrazinolysis of Native Peptides and Proteins†
- Pages: 13062-13066
- First Published: 09 October 2013
Natural Products
Elucidating the Neurotoxicity of the Star Fruit†
- Pages: 13067-13070
- First Published: 07 November 2013
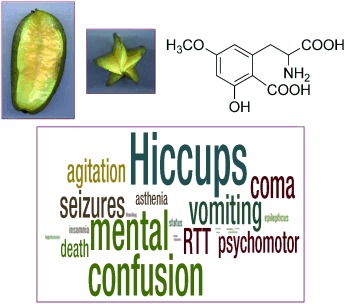
Caramboxin: Patients suffering from chronic kidney disease are frequently intoxicated after ingesting star fruit. The main symptoms of this intoxication are named in the picture. Bioguided chemical procedures resulted in the discovery of caramboxin, which is a phenylalanine-like molecule that is responsible for intoxication. Functional experiments in vivo and in vitro point towards the glutamatergic ionotropic molecular actions of caramboxin, which explains its convulsant and neurodegenerative properties.
Heterocycles
Formal Ring-Opening/Cross-Coupling Reactions of 2-Pyrones: Iron-Catalyzed Entry into Stereodefined Dienyl Carboxylates†
- Pages: 13071-13075
- First Published: 10 October 2013
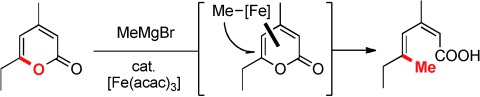
Open access: Despite the exceptional level of sophistication in cross-coupling chemistry, reactions of substrates that incorporate the leaving group as an integral part into a heterocyclic scaffold are scarce. The title reaction outlines the utility of this reaction format (see scheme; acac=acetylacetonate), provides a convenient entry into stereodefined diene carboxylates, and adds a new chapter to the field of iron catalysis.
Synthetic Methods
Organoytterbium Ate Complexes Extend the Value of Cyclobutenediones as Isoprene Equivalents†
- Pages: 13076-13079
- First Published: 23 October 2013
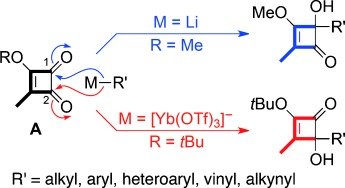
Changing course: While organolithium and Grignard reagents favor addition to C1 of A (R=Me), the corresponding organoytterbium reagents add to C2 (R=tBu). Computational studies provide insights into the nature of organoytterbium species and their reactivity, and a total synthesis of (−)-mansonone B illustrates the utility of the method in terpenoid synthesis. Tf=trifluoromethanesulfonyl.
Organized Nanotubes
Ionic Self-Assembly Provides Dense Arrays of Individualized, Aligned Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes†
- Pages: 13080-13085
- First Published: 15 October 2013
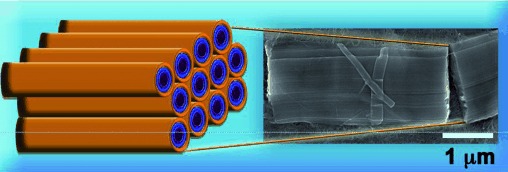
Wrap and stack: Polyanionic [arylene]ethynylene polymers that helically wrap single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) enable the production of functionalized SWNTs that are soluble in organic solvents. These SWNTs can assemble into structures featuring aligned nanotubes that maintain the optoelectronic properties of individual SWNTs.
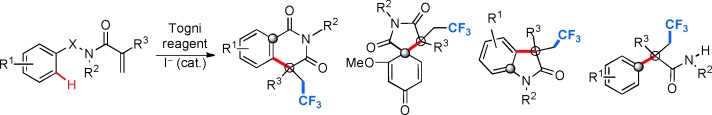
Aryltrifluoromethylation
Metal-Free Aryltrifluoromethylation of Activated Alkenes†
- Pages: 13086-13090
- First Published: 31 October 2013
Structure Elucidation
Water Mediation Is Essential to Nucleation of β-Turn Formation in Peptide Folding Motifs†
- Pages: 13091-13095
- First Published: 15 October 2013
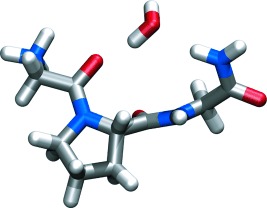
Water-mediated bond formation: The structure of the peptide GPG-NH2 (see picture) has been investigated in aqueous solution to understand the role of water in the formation of a β-turn. Using a combination of neutron diffraction enhanced by isotopic substitution, NMR spectroscopy, and computer simulations, it was found that water is an essential component to initiate folding in solution.
Polyketide Biosynthesis
A Common Origin for Guanidinobutanoate Starter Units in Antifungal Natural Products†
- Pages: 13096-13099
- First Published: 11 November 2013
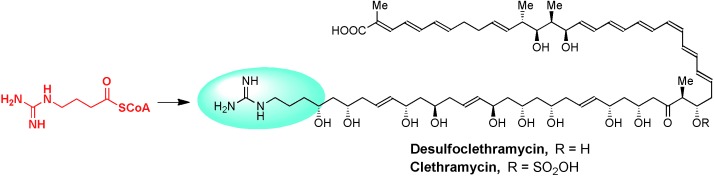
Keeping it basic: Arginine provides the exotic 4-guanidinobutanoate starter unit for two different types of zwitterionic polyketide (an example for one type is shown in the picture) produced by the same Streptomyces bacterium. The three-step precursor pathway is initiated by a remarkable decarboxylating monooxygenase with high specificity for arginine.
Anion–π Interactions
Electron Sharing and Anion–π Recognition in Molecular Triangular Prisms†
- Pages: 13100-13104
- First Published: 13 November 2013

Stacking on a full belly: Triangular molecular prisms display electron sharing among their triangularly arranged naphthalenediimide (NDI) redox centers. Their electron-deficient cavities encapsulate linear triiodide anions, leading to the formation of supramolecular helices in the solid state. Chirality transfer is observed from the six chiral centers of the filled prisms to the single-handed helices.