Development of Azo-Based Fluorescent Probes to Detect Different Levels of Hypoxia†
Wen Piao
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorSatoru Tsuda
Department of Ophthalmology, Tohoku University, Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8574 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yuji Tanaka
Department of Ophthalmology, Tohoku University, Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8574 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Satoshi Maeda
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University, Kita 10 Nishi 8, Kita-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido 060-0808 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Fengyi Liu
Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University, 34-4 Takano Nishihiraki-cho, Sakyo, Kyoto 606-8103 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorShodai Takahashi
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorYu Kushida
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Toru Komatsu
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Tasuku Ueno
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Takuya Terai
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Toru Nakazawa
Department of Ophthalmology, Tohoku University, Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8574 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Masanobu Uchiyama
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Advanced Elements Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Keiji Morokuma
Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University, 34-4 Takano Nishihiraki-cho, Sakyo, Kyoto 606-8103 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tetsuo Nagano
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Kenjiro Hanaoka
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)===Search for more papers by this authorWen Piao
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorSatoru Tsuda
Department of Ophthalmology, Tohoku University, Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8574 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yuji Tanaka
Department of Ophthalmology, Tohoku University, Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8574 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Satoshi Maeda
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University, Kita 10 Nishi 8, Kita-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido 060-0808 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Fengyi Liu
Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University, 34-4 Takano Nishihiraki-cho, Sakyo, Kyoto 606-8103 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorShodai Takahashi
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorYu Kushida
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Toru Komatsu
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Tasuku Ueno
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Takuya Terai
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Toru Nakazawa
Department of Ophthalmology, Tohoku University, Graduate School of Medicine, 1-1 Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8574 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Masanobu Uchiyama
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Advanced Elements Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Keiji Morokuma
Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University, 34-4 Takano Nishihiraki-cho, Sakyo, Kyoto 606-8103 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tetsuo Nagano
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Kenjiro Hanaoka
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 (Japan)===Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported in part by MEXT (Specially Promoted Research Grant 22000006 to T.N., 24689003 and 24659042 to K.H., and 24655147 to T.K.) and SENTAN and JST( K.H.). K.H. was also supported by The Asahi Glass Foundation, The Uehara Memorial Foundation, the Tokyo Biochemical Research Foundation, the Inoue Foundation for Science, the Takeda Science Foundation, and The Cosmetology Research Foundation. The authors thank Mr. Yu Harabuchi of Hokkaido University for helpful discussions on photoreactions of azobenzene. Some of the theoretical calculations were carried out using the computational resources of the Institute for Molecular Science, Okazaki (Japan). W.P. was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows.
Graphical Abstract
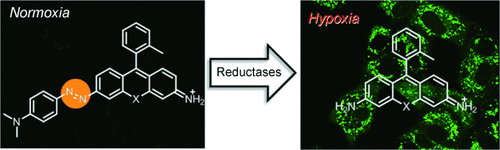
Let it shine: New hypoxia-sensitive fluorescent probes were developed; they consist of a rhodamine moiety with an azo group directly conjugated to the fluorophore. Because of an ultrafast conformational change around the NN bond, the compounds are nonfluorescent under normoxia. However, under hypoxia, the azo group is reduced, and a strongly fluorescent rhodamine derivative is released.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201305784_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf2.8 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1G. L. Semenza, N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 537–547.
- 2P. Vaupel, K. Schlenger, C. Knoop, M. Höckel, Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 3316–3322.
- 3U. Lendahl, K. L. Lee, H. Yang, L. Poellinger, Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 821–832.
- 4N. Rohwer, T. Cramer, Drug Resist. Updates 2011, 14, 191–201.
- 5J. A. Raleigh, C. J. Koch, Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 40, 2457–2464.
- 6J. Chan, S. C. Dodani, C. J. Chang, Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 973–984.
- 7
- 7aY. Liu, Y. Xu, X. Qian, J. Liu, L. Shen, J. Li, Y. Zhang, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 2935–2941;
- 7bL. Cui, Y. Zhong, W. Zhu, Y. Xu, Q. Du, X. Wang, X. Qian, Y. Xiao, Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 928–931;
- 7cK. Xu, F. Wang, X. Pan, R. Liu, J. Ma, F. Kong, B. Tang, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2554–2556;
- 7dH. Komatsu, H. Harada, K. Tanabe, M. Hiraoka, S. Nishimoto, MedChemComm 2010, 1, 50–53;
- 7eS. Zhang, M. Hosaka, T. Yoshihara, K. Negishi, Y. Iida, S. Tobita, T. Takeuchi, Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4490–4498;
- 7fE. Nakata, Y. Yukimachi, H. Kariyazono, S. Im, C. Abe, Y. Uto, H. Maezawa, T. Hashimoto, Y. Okamoto, H. Hori, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6952–6958;
- 7gZ. Li, X. Li, X. Gao, Y. Zhang, W. Shi, H. Ma, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3926–3932.
- 8Y. Urano, D. Asanuma, Y. Hama, Y. Koyama, T. Barrett, M. Kamiya, T. Nagano, T. Watanabe, A. Hasegawa, P. L. Choyke, Nat. Med. 2008, 15, 104–109.
- 9H. Sunahara, Y. Urano, H. Kojima, T. Nagano, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5597–5604.
- 10K. Kiyose, K. Hanaoka, D. Oushiki, T. Nakamura, M. Kajimura, M. Suematsu, H. Nishimatsu, T. Yamane, T. Terai, Y. Hirata, T. Nagano, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15846–15848.
- 11S. Zbaida, Drug Metab. Rev. 1995, 27, 497–516.
- 12A. Chevalier, C. Massif, P. Renard, A. Romieu, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 1686–1699.
- 13
- 13aI. K. Lednev, T.-Q. Ye, P. Matousek, M. Towrie, P. Foggi, F. V. R. Neuwahl, S. Umapathy, R. E. Hester, J. N. Moore, Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 290, 68–74;
- 13bM. Poprawa-Smoluch, J. Baggerman, H. Zhang, H. P. A. Maas, L. De Cola, A. M. Brouwer, J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 11926–11937;
- 13cJ. Yoshino, N. Kano, T. Kawashima, Chem. Commun. 2007, 559–561;
- 13dH. M. D. Bandara, S. C. Burdette, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1809–1825.
- 14
- 14aY.-H. Ahn, J.-S. Lee, Y.-T. Chang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4510–4511;
- 14bL. D. Lavis, T.-Y. Chao, R. T. Raines, ACS Chem. Biol. 2006, 1, 252–260;
- 14cJ. Li, S. Q. Yao, Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 405–408;
- 14dM. Sakabe, D. Asanuma, M. Kamiya, R. J. Iwatate, K. Hanaoka, T. Terai, T. Nagano, Y. Urano, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 409–414;
- 14eS. Kenmoku, Y. Urano, H. Kojima, T. Nagano, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7313–7318.
- 15Y. Kushida, K. Hanaoka, T. Komatsu, T. Terai, T. Ueno, K. Yoshida, M. Uchiyama, T. Nagano, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3908–3911.
- 16I. Conti, M. Garavelli, G. Orlandi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5216–5230.
- 17E. Merino, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3835–3853.
- 18
- 18aG. L. Baker, R. J. Corry, A. P. Autor, Ann. Surg. 1985, 202, 628–641;
- 18bB. C. Dickinson, C. J. Chang, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 504–511.
- 19S. Yamaguchi, K. Tamao, J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1998, 3693–3702.
- 20Y. Koide, Y. Urano, K. Hanaoka, T. Terai, T. Nagano, ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 600–608.
- 21
- 21aS. Chakraborty, V. Massey, J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41507–41516;
- 21bV. B. O’Donnell, G. C. Smith, O. T. Jones, Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 778–785;
- 21cD. G. Tew, Biochemistry 1993, 32, 10209–10215.
- 22W. R. Wilson, M. P. Hay, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410.
- 23J. A. Raleigh, S. C. Chou, G. E. Arteel, M. R. Horsman, Radiat. Res. 1999, 151, 580–589.
- 24E. Takahashi, M. Sato, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 299, C 1318–1323.
- 25
- 25aS. Kuroiwa, N. Katai, H. Shibuki, T. Kurokawa, J. Umihira, T. Nikaido, K. Kametani, N. Yoshimura, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 1998, 39, 610–617;
- 25bL. Daugeliene, M. Niwa, A. Hara, H. Matsuno, T. Yamamoto, Y. Kitazawa, T. Uematsu, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2000, 41, 2743–2747.
- 26
- 26aF. Moroni, G. Lombardi, S. Pellegrini-Faussone, F. Moroni, Vision Res. 1993, 33, 1887–1891;
- 26bY. Zhang, C.-H. Cho, L. Atchaneeyasakul, T. McFarland, B. Appukuttan, J. T. Stout, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2005, 46, 2133–2139.
- 27Y. Tamaki, M. Araie, E. Kawamoto, S. Eguchi, H. Fujii, Exp. Eye Res. 1995, 60, 373–383.