Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Regulating Crystal Packing by Terminal tert-Butylation for Enhanced Solid-State Emission and Efficacious Charge Transport in an Anthracene-Based Molecular Crystal (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45/2022)
- First Published: 25 October 2022

An anthracene-based molecular crystal with a unique "slipped herringbone" packing motif was developed by crystal engineering through terminal tert-butylation. Appropriate exciton–exciton coupling/electron–phonon coupling originating from the unique crystal packing induces a remarkably strong solid-state emission and efficient charge transport, as reported by Wenping Hu et al. in their Research Article (e202206825).
Inside Cover: A Proton Conductive Porous Framework of an 18-Crown-6-Ether Derivative Networked by Rigid Hydrogen Bonding Modules (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45/2022)
- First Published: 25 October 2022

A proton conductive hydrogen-bonded organic framework (HOF) was constructed from a C3-symmetric hexatopic carboxylic acid derivative with an 18-crown-6-ether component. Despite the flexibility of the macrocycle, H-bonding modules allow the derivative to yield a hexagonally networked framework with permanent porosity. As reported by Takayoshi Nakamura, Ichiro Hisaki, and co-workers in their Communication (e202211686), the HOF possesses 1D channels with a bottleneck composed of the macrocycles and shows proton conductivity (1.12×10−7 S cm−1) through the Grotthuss mechanism (Ea=0.27 eV) under 98 %RH.
Inside Back Cover: A Library of Rare Earth Oxide Ultrathin Nanowires with Polymer-Like Behaviors (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45/2022)
- First Published: 27 October 2022

The formation of ultrathin nanowires has thermodynamic advantages at low temperature. However, at low temperatures the monomers for nanocrystal growth are difficult to generate through precursor decomposition. In their Research Article (e202212251), Di Qiu, Yaping Du, and co-workers report an efficient growth process based on adding polyoxometalate clusters to the monomers. Fifteen types of rare earth oxide ultrathin nanowires were synthesized, all exhibiting polymer-like behavior due to the extremely high aspect ratio.
Back Cover: On-Site Non-enzymatic Orthogonal Activation of a Catalytic DNA Circuit for Self-Reinforced In Vivo MicroRNA Imaging (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45/2022)
- First Published: 25 October 2022

A non-enzymatic circuitry activation strategy can realize an orthogonally controlled catalytic DNA (CCD) circuit through multiple molecular recognition events and progressively accelerated signal amplification, as reported by Fuan Wang and co-workers in their Research Article (e202206529). The on-site activated CCD circuitry system has considerable potential for high-precision in vivo imaging of low-abundance microRNA.
Graphical Abstract
Corrigenda
Corrigendum: Synergy of Weakly-Solvated Electrolyte and Optimized Interphase Enables Graphite Anode Charge at Low Temperature
- First Published: 31 October 2022
Introducing …
Joanna Olesiak-Bańska
- First Published: 13 October 2022

“My favorite example of science in everyday life is a soap bubble—simple to create and beautiful, but simultaneously rich in interesting concepts from physics and chemistry … When I want to treat myself to something, I listen to my favorite songs …” Find out more about Joanna Olesiak-Bańska in her Introducing … Profile.
Highlights
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis of the Plant-Produced Toxin Strychnine Elucidated
- First Published: 20 September 2022
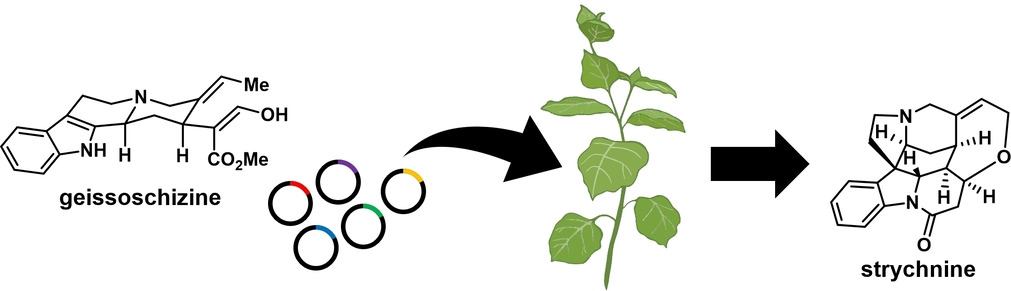
Strychnine is a notorious neurotoxic plant alkaloid that has been studied for centuries. A recent report from the O'Connor group has successfully elucidated the biosynthesis of strychnine for the first time using modern transcriptomics and protein expression methods, laying a foundation for future studies to engineer production or modifications of this important natural product.
Minireviews
Dual Catalysis
Bimetallic Catalysis in Stereodivergent Synthesis
- First Published: 02 August 2022
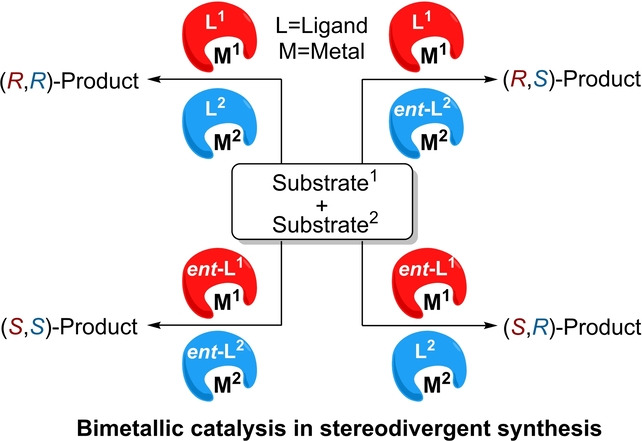
Bimetallic catalysis has emerged as an important strategy for developing new reactions in stereodivergent synthesis. This strategy is also a simple and powerful approach for synthesizing all the possible stereoisomers of products bearing two stereocenters from the same set of starting materials. This Minireview summarizes recent progress and briefly gives perspectives for the future advancement of this field.
Reviews
Heterogeneous Catalysis
The Control of the Coordination Chemistry for the Genesis of Heterogeneous Catalytically Active Sites in Oxidation Reactions
- First Published: 10 August 2022
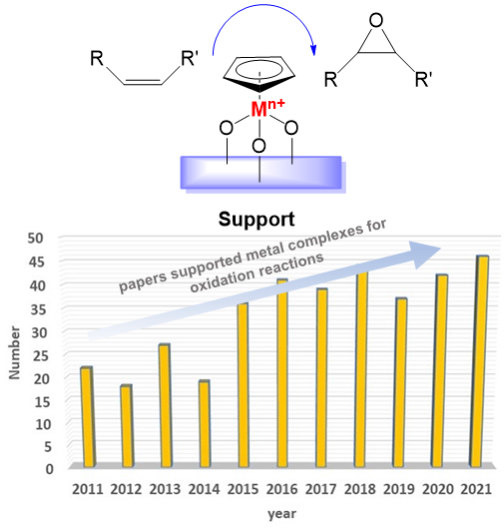
The role of coordination metal complexes as precursors for the generation of heterogeneous catalysts for the oxidation of fine chemicals is reviewed. Specific attention is paid to describing the phenomena leading to the genesis of the active sites, the clear characterization of the surface species, and their catalytic performance.
Imaging Agents
Antibiotic-Derived Radiotracers for Positron Emission Tomography: Nuclear or “Unclear” Infection Imaging?
- First Published: 14 July 2022
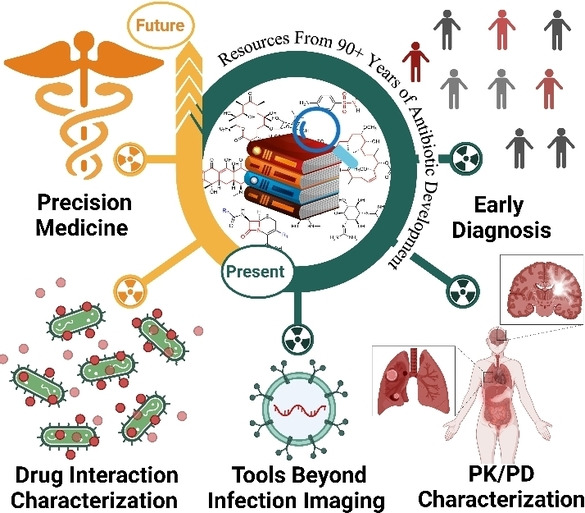
This Review provides summary and critical evaluation, including the challenges and pitfalls, of antibiotic-derived positron emission tomographic radiopharmaceutical development efforts aimed at infection imaging either considered for radiotracer development for infection imaging or radio-antibiotic PET imaging supplementing other tools for pharmacologic drug characterization.
Water Splitting
Rationally Designing Efficient Electrocatalysts for Direct Seawater Splitting: Challenges, Achievements, and Promises
- First Published: 23 August 2022
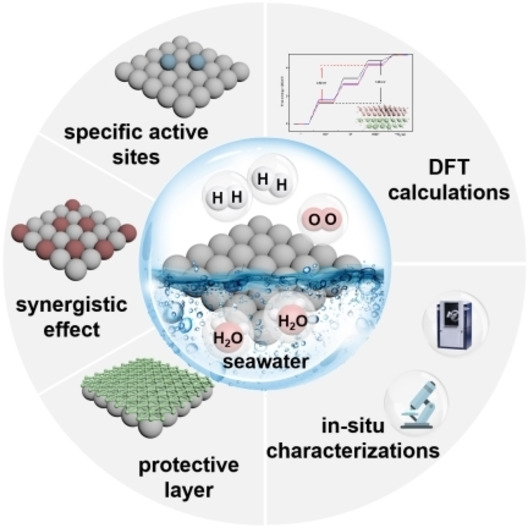
This Review provides an overview of electrocatalysts designed for the direct splitting of seawater. The mechanism of seawater splitting is introduced before the primary principles for designing catalysts (noble metal, noble metal free, and metal-free) for seawater splitting are analyzed in terms of both the hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. The future development of electrocatalysts for clean hydrogen generation is also discussed.
Communications
Crystal Engineering | Hot Paper
A Proton Conductive Porous Framework of an 18-Crown-6-Ether Derivative Networked by Rigid Hydrogen Bonding Modules
- First Published: 14 September 2022
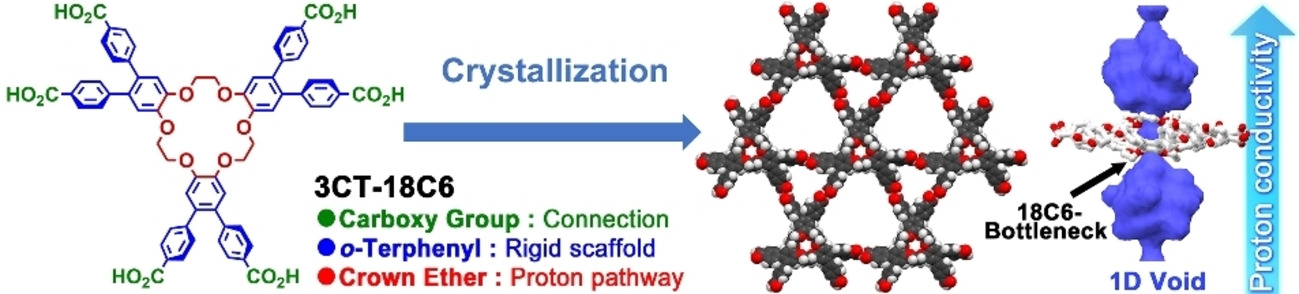
A porous hydrogen-bonded framework (HOF) was constructed from a 18-crown-6-ether (18C6) derivative. Although a 18C6 macrocycle is flexible and has many possible conformations, directional intermolecular hydrogen bonds of 4,4′-dicarboxy-o-terphenyl modules in the periphery of the 18C6 allowed to form a rigid HOF with 1D channels with a bottleneck composed of 18C6 rings. The wet HOF shows proton conductivity (1.12×10−7 S cm−1) through a Grotthuss mechanism (Ea=0.27 eV) under 98 %RH.
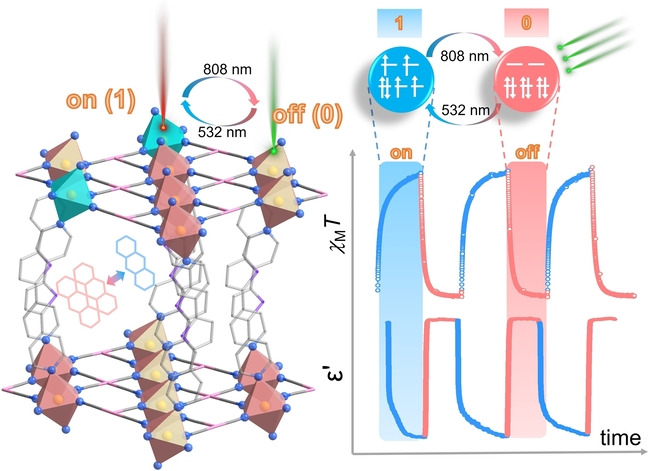
Molecular Magnets | Very Important Paper
Modelling Conformational Flexibility in a Spectrally Addressable Molecular Multi-Qubit Model System
- First Published: 12 October 2022
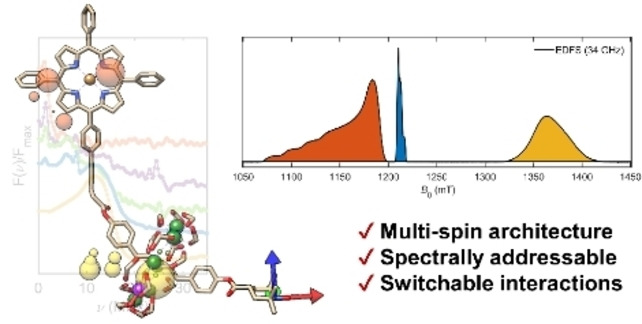
Systems with weak dipolar interactions have the potential to be used for molecular quantum computing. Orientation selective pulsed EPR was used to model the conformational flexibility of a molecular multi-qubit model system. Spectrally addressable centres allowed for the individual manipulation of each spin qubit, while differing relaxation dynamics resulted in a proposed handle for the implementation of quantum algorithms.
Luminescence
Chiral-at-Cage Carboranes for Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Aggregation-Induced Electrochemiluminescence
- First Published: 14 September 2022
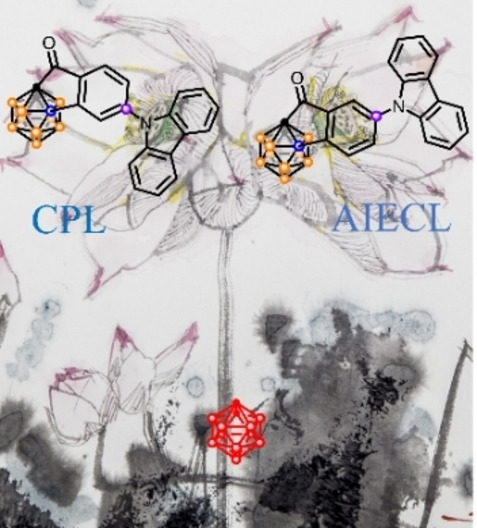
Two chiral-at-cage carbazole-modified carboranes emit circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) and aggregation-induced electrochemiluminescence (AIECL). The |gPL| factors of (R/S)-Cb1 and (R/S)-Cb2 enantiomers in films reached 7.38×10−3. Significant solvation effect was observed in the fluorescence and CPL of Cb1, while Cb2 showed remarkable AIECL effect with excellent ECL stability and dopamine detection ability.
Methanol Oxidation | Very Important Paper
Engineering Support and Distribution of Palladium and Tin on MXene with Modulation of the d-Band Center for CO-resilient Methanol Oxidation
- First Published: 16 September 2022
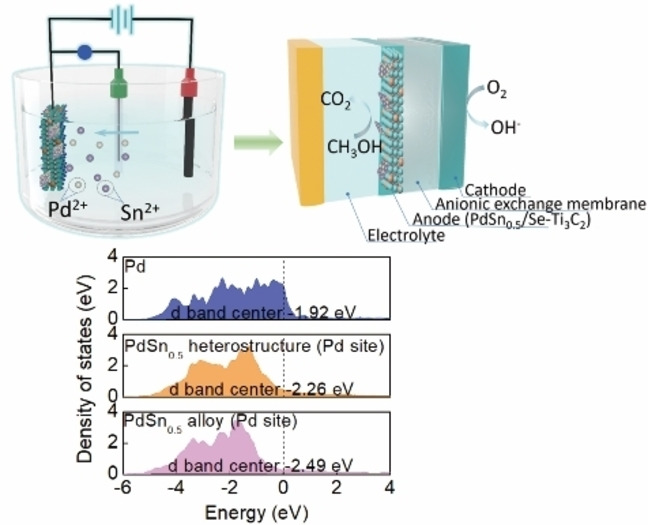
Boosted electron interaction of metal nano-alloy with Se-doped MXene and optimized distribution of Pd−Sn sites on PdSn0.5/Se−Ti3C2 can modulate the d band center, decrease adsorption energies of CO* at Pd site and enhance OH* generation at Sn site, thus removing CO poisonous intermediates, and thereby significantly enhancing methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) efficiency and durability of the anodic catalyst for a direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC).
Gas Separation | Very Important Paper
New Insights into Physical Aging-Induced Structure Evolution in Carbon Molecular Sieve Membranes
- First Published: 12 September 2022
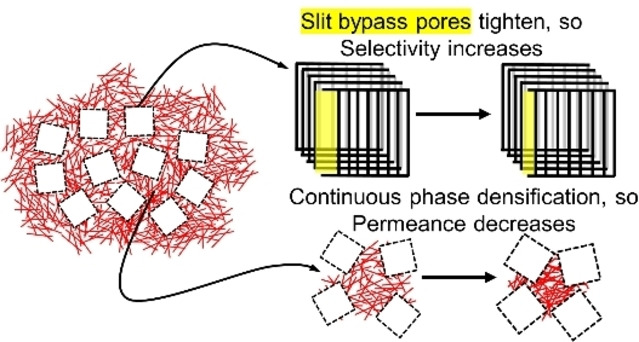
CMS membranes derived from polyimide precursors show dual model morphologies comprising a disordered continuous phase and distributed molecular sieving Langmuir domains. Our study showed that during physical aging, pore structure changes in the two different “C” phase and “L” domains both occur, which affects the gas separation performance of CMS membranes.
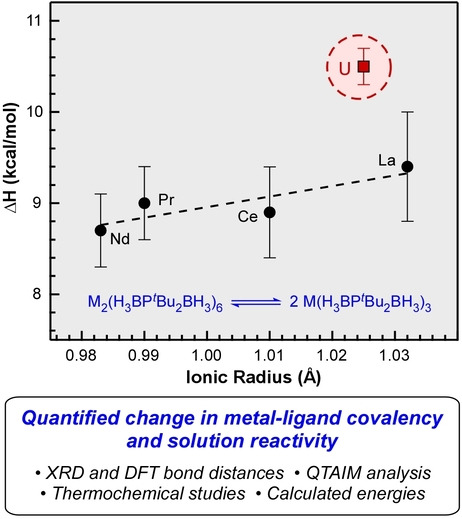
Uranium Complexes
Quantifying the Influence of Covalent Metal-Ligand Bonding on Differing Reactivity of Trivalent Uranium and Lanthanide Complexes
- First Published: 12 September 2022
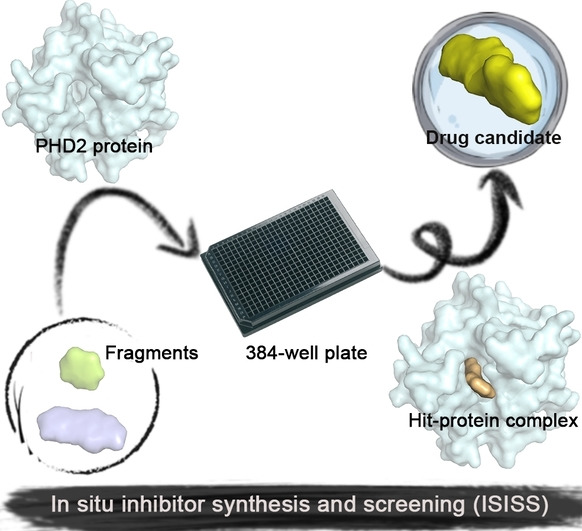
Drug Discovery
In Situ Inhibitor Synthesis and Screening by Fluorescence Polarization: An Efficient Approach for Accelerating Drug Discovery
- First Published: 16 September 2022
Xe(IV) Complexes | Hot Paper
Synthesis, Structure, and Bonding of a XeIV Transition-Metal Coordination Complex, F3XeFb- - -WOF4
- First Published: 06 September 2022
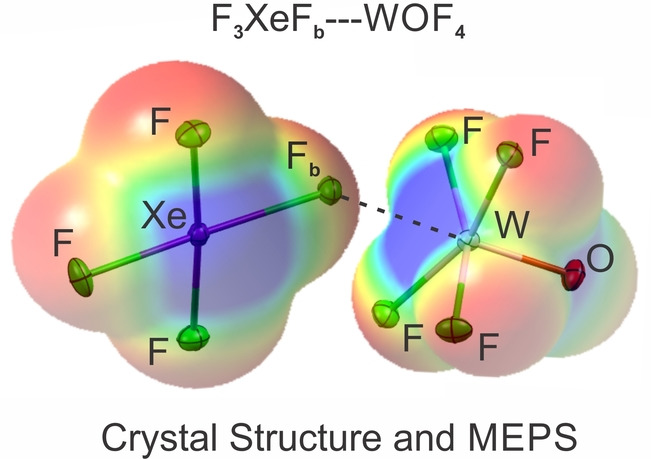
Xenon tetrafluoride and WOF4 react in CFCl3 solvent to form the first transition-metal coordination complex of XeIV, F3XeFb- - -WOF4. The complex was structurally characterized by Raman spectroscopy and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Quantum-chemical analyses, such as MEPS, show the W- - -Fb bond is primarily an electrostatic, σ-hole bond with a smaller degree of covalent character.
Pseudorotaxanes
Conformational Effects on the Threading Kinetics of Dumbbell-Shaped Guests into the Cavity of Oxatub[4]arene
- First Published: 15 September 2022
![Conformational Effects on the Threading Kinetics of Dumbbell-Shaped Guests into the Cavity of Oxatub[4]arene](/cms/asset/5ee9d9c5-a90b-4717-860f-aaf0a6a21298/anie202212305-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Complex kinetic behavior was observed in a two-component system containing a viologen-based guest and oxatub[4]arene through the involvement of the three conformers of the host. In addition, an unprecedented threading mechanism involving the tilted conformation of the guests was revealed to be responsible for the very fast kinetics and for the threading of guests with very large stoppers.
Single-Atom Catalysis
High-Areal Density Single-Atoms/Metal Oxide Nanosheets: A Micro-Gas Blasting Synthesis and Superior Catalytic Properties
- First Published: 14 September 2022
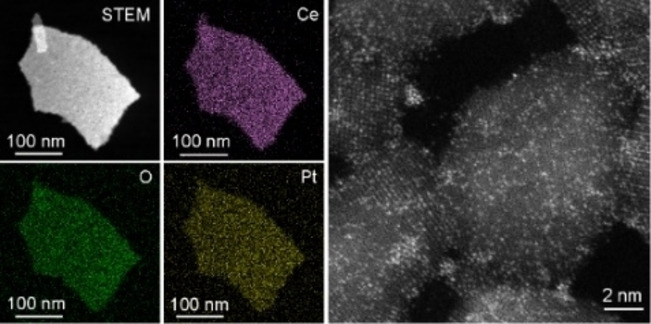
An efficient and general micro-gas blasting (MGB) synthesis is developed to access versatile high-areal density noble metal single-atoms/metal oxide nanosheets, including Pt1/CeO2, Ir1/CoOx, Pd1/CeO2, etc. The as-prepared Pt1/CeO2−S catalysts are revealed to possess superior reactivity and tolerance than routinely structured alternatives by using water-gas shift (WGS) as a model reaction.
Oxygen Evolution | Very Important Paper
Surface-Exposed Single-Ni Atoms with Potential-Driven Dynamic Behaviors for Highly Efficient Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution
- First Published: 12 September 2022
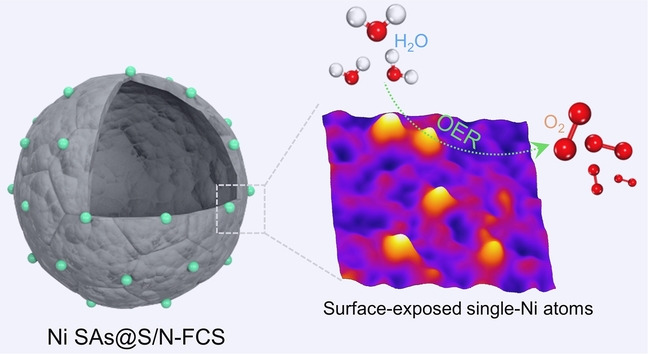
An advanced electrocatalyst has been developed by decorating single-Ni atoms on hollow S/N-doped football-like carbon spheres (Ni SAs@S/N-FCS) for the oxygen evolution reaction. Thanks to the abundantly surface-exposed single-Ni atoms, hollow S/N-codoped carbon matrix, as well as their strong synergistic interactions, the resultant Ni SAs@S/N-FCS electrocatalyst exhibits outstanding activity and stability for alkaline oxygen evolution reaction.
Prebiotic Chemistry
Isoxazole Nucleosides as Building Blocks for a Plausible Proto-RNA
- First Published: 05 September 2022
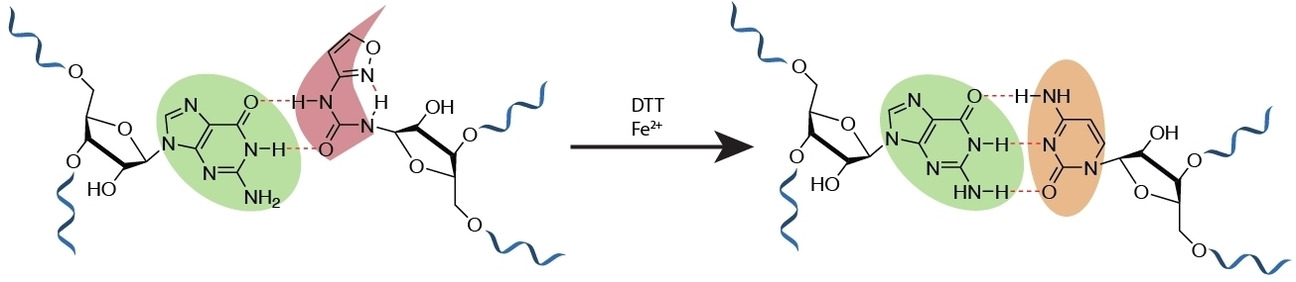
Prebiotically plausible isoxazole nucleosides are shown to be excellent candidates for proto-nucleosides and proto-RNAs. The proto-nucleoside forms 2 instructive H-bonds with guanosine and can directly rearrange in RNA to give cytidine. The stereochemical outcome of the reaction is controlled by already present canonical seed-nucleosides.
Research Articles
DNA Nanotechnology | Very Important Paper
On-Site Non-enzymatic Orthogonal Activation of a Catalytic DNA Circuit for Self-Reinforced In Vivo MicroRNA Imaging
- First Published: 01 July 2022
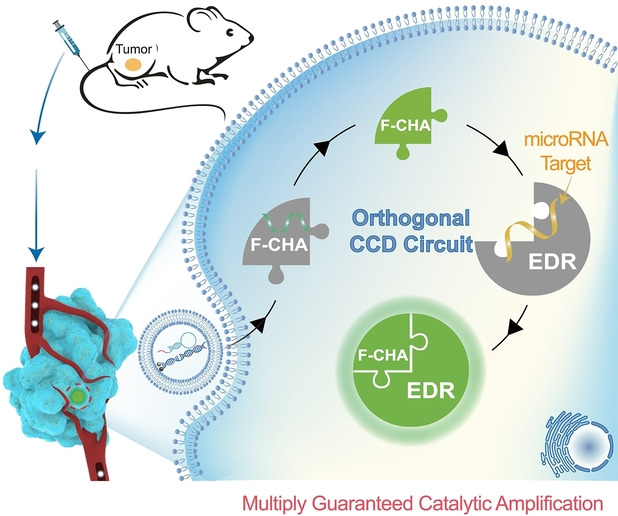
A non-enzymatically and orthogonally controlled catalytic DNA (CCD) circuit was prepared for on-site and efficient in vivo microRNA (miRNA) imaging without off-site signal leakage. The CCD circuit integrates the cell-specific endogenous stimulation of the auxiliary catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) with the orthogonal activation of the main entropy-driven DNA reaction (EDR) for sensitive target detection.
Crystal Engineering | Hot Paper
Regulating Crystal Packing by Terminal tert-Butylation for Enhanced Solid-State Emission and Efficacious Charge Transport in an Anthracene-Based Molecular Crystal
- First Published: 21 August 2022
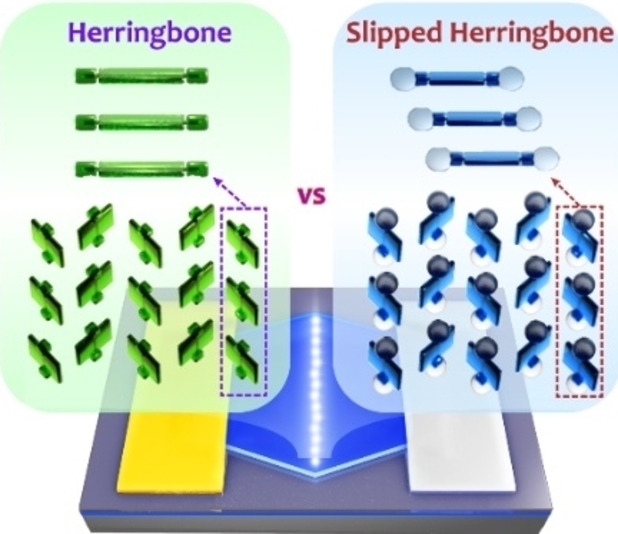
An anthracene-based molecular crystal with a unique “slipped herringbone” packing motif has been developed by delicate crystal engineering through terminal tert-butylation. Appropriate exciton-exciton coupling/electron-phonon coupling originating from the unique crystal packing induces a remarkably strong solid-state emission (photoluminescence quantum efficiency, ΦF=74.9 %) and efficacious charge transport (carrier mobility, μ=5.0 cm2 V−1 s−1).
Bioorthogonal Tags
Affinity Bioorthogonal Chemistry (ABC) Tags for Site-Selective Conjugation, On-Resin Protein-Protein Coupling, and Purification of Protein Conjugates
- First Published: 04 September 2022
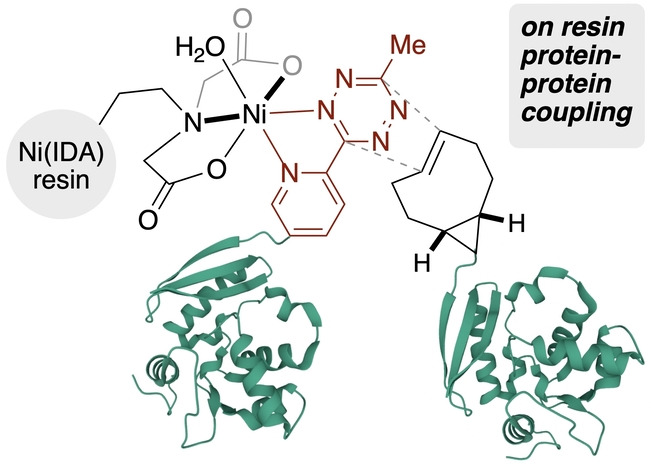
Affinity Bioorthogonal Chemistry tags (ABC-tags) based on 2-pyridyltetrazines serve a dual role by enabling protein purification through metal chelation and still maintaining their rapid kinetics in bioorthogonal reactions. ABC-tagging is successful for proteins tagged at the C- or N-terminus or at internal positions, is successful in complex mixtures including cell lysate, and can be carried out on-resin to generate multidomain proteins.
Coordination Polymers | Hot Paper
Linker Redox Mediated Control of Morphology and Properties in Semiconducting Iron-Semiquinoid Coordination Polymers
- First Published: 07 September 2022
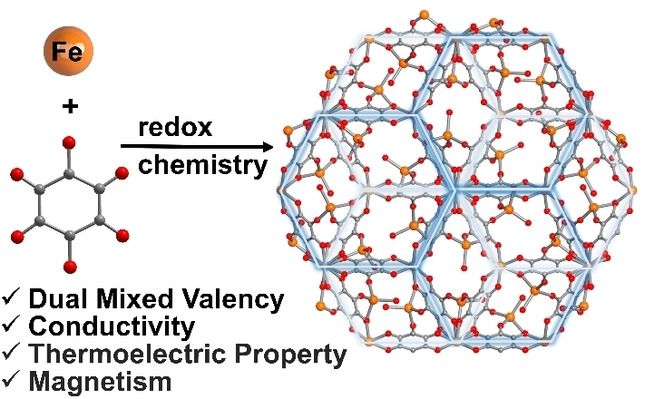
A novel 3D semiconducting coordination polymer Fe5(C6O6)3 is reported with high conductivity, broad electronic transitions and interesting thermoelectric/magnetic properties. The unique structure and properties of this material illustrate that controlling the oxidation states of redox-active components in conducting metal-organic materials can be a “pre-synthetic” strategy to carefully tune material topologies, properties, and functionalities.
Spin Crossover
Simultaneous Photo-Induced Magnetic and Dielectric Switching in an Iron(II)-Based Spin-Crossover Hofmann-Type Metal-Organic Framework
- First Published: 14 September 2022
Analytical Methods | Hot Paper
Dual-Gradient Unified Chromatography: A New Paradigm for Versatility in Simultaneous Multicomponent Analysis
- First Published: 16 September 2022
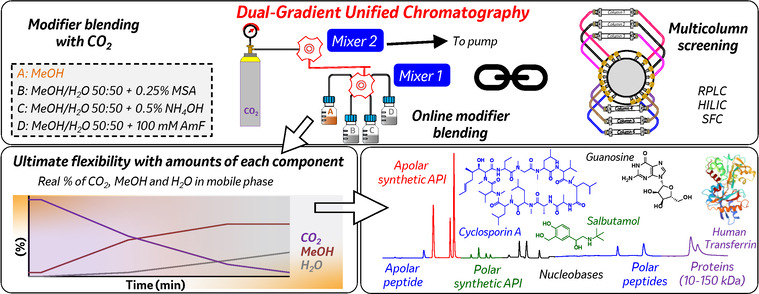
A hybrid separation technique, referred to as Dual-Gradient Unified Chromatography (DGUC), enabling simultaneous multicomponent analysis of both small and large molecules across a wide polarity range is introduced. DGUC lays the foundation for the next generation of hybrid chromatographic techniques with the deployment of universal elution profiles obtained via multi-eluent blending beyond traditional separation modes.
Protocells
Mechanistic Insights into the Phase Separation Behavior and Pathway-Directed Information Exchange in all-DNA Droplets
- First Published: 16 September 2022
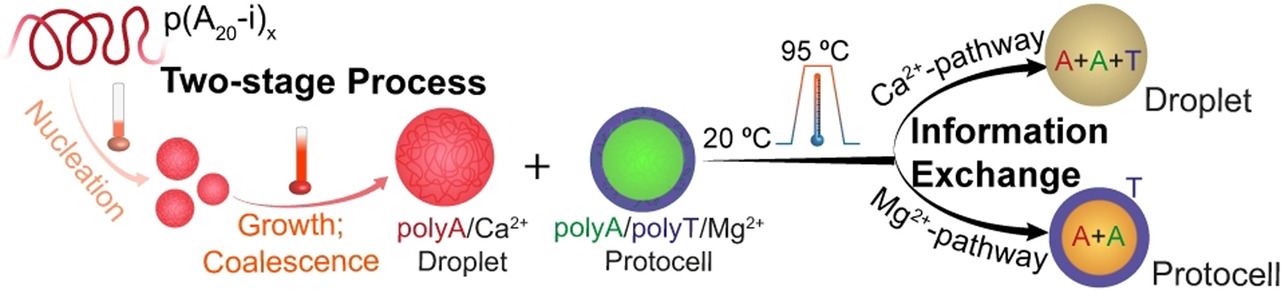
A two-stage mechanism is discovered in the metal-dependent phase separation pathways of ssDNA to form all-DNA coacervates. Distinct ion-specific pathways allow the generation of new coacervate structures by mixing multiple coacervate systems, leading to pathway-controlled coacervate-protocell communication and information exchange.
Analytical Methods
Uncertainty Quantification of Michaelis–Menten Kinetic Rates and Its Application to the Analysis of CRISPR-Based Diagnostics
- First Published: 19 September 2022
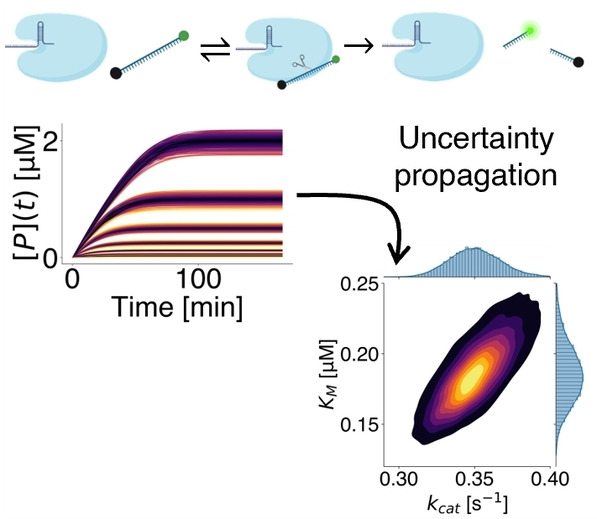
The estimation of Michaelis–Menten kinetic parameters is highly sensitive to small experimental errors, even though the quantification of such parameters is critical. Monte Carlo simulations show that the kinetic efficiency, which governs limit of detection of assays that require low background, is the most precise kinetic parameter.
Metal-Free Reactions
Metal-Free Allylic C−H Amination of Vinylsilanes and Vinylboronates using Silicon or Boron as a Regioselectivity Switch
- First Published: 14 September 2022
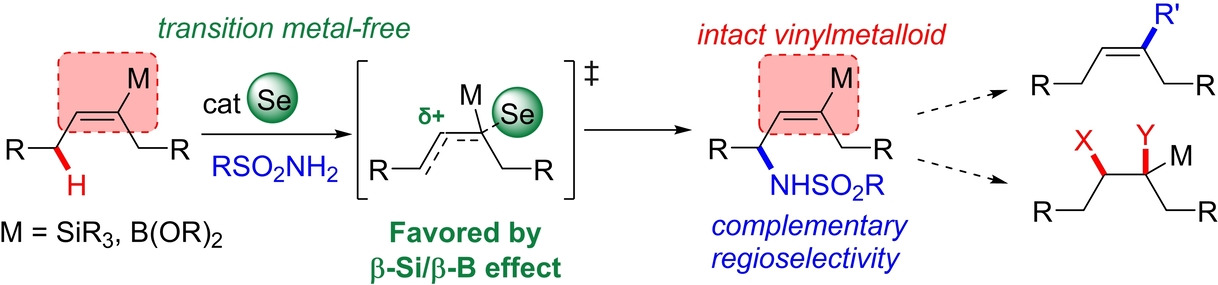
A metal-free allylic C−H amination protocol allows simple vinylsilanes and vinylboronates to be selectively functionalized without competitive consumption of the reactive vinylmetalloid core structure, preserving its reactivity for future transformations such as cross-coupling or addition reactions. The silicon/boron group directs the regioselectivity of amination to the distal side of the C=C bond, allowing access to a complementary substitution pattern.
Biosensors | Hot Paper
Target-Triggered Formation of Artificial Enzymes on Filamentous Phage for Ultrasensitive Direct Detection of Circulating miRNA Biomarkers in Clinical Samples
- First Published: 15 September 2022
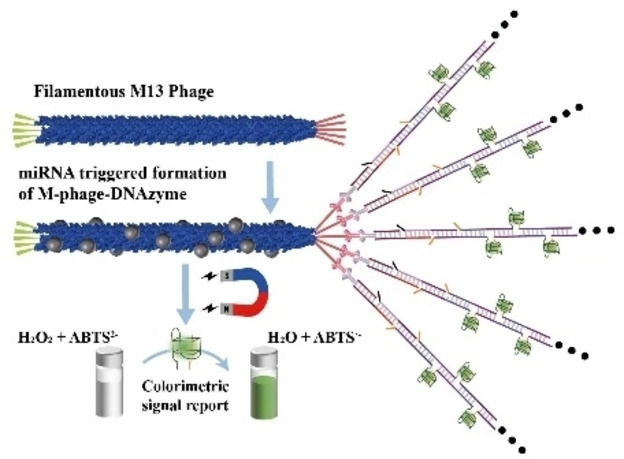
As triggered by the target, an artificial enzyme was site-specifically formed at the tip of filamentous M13 phage, generating a novel catalytic nanomaterial for miRNA analysis. miRNAs in human plasma samples, tumor cells, and tissues were detected with high sensitivity comparable to qRT-PCR, showing a great possibility of clinical applications.
Alcohol Electrooxidation | Hot Paper
Salting-Out Aldehyde from the Electrooxidation of Alcohols with 100 % Selectivity
- First Published: 08 September 2022
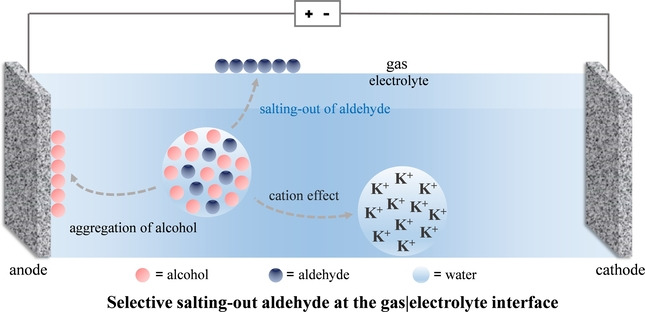
Selective electrocatalytic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes has significant challenges, for example, it cannot realize the preparation of aldehydes selectively in alkaline aqueous solutions. By tuning the local microenvironment over the electrocatalyst, and thus selectively salting-out the aldehyde at the gas|electrolyte interface, the electrocatalytic synthesis of aldehydes was achieved in an efficient and green way.
Polymerization
Cascade Cyclopolymerization of 5-Ethynyl-1,8-Nonadiyne Derivatives to Synthesize Low Band Gap Conjugated Polyacetylenes Containing a Fused Bicyclic Structure
- First Published: 06 September 2022
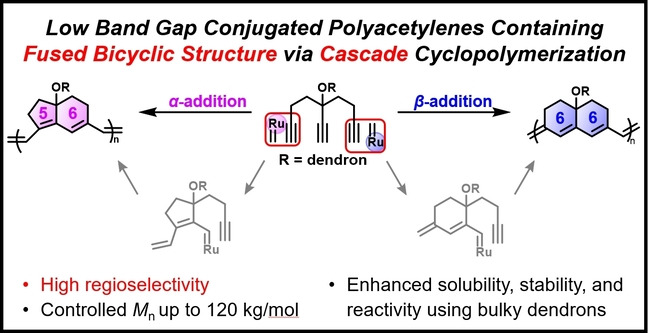
A novel cascade cyclopolymerization is developed to synthesize polyacetylenes containing fused bicyclic rings via sequential cascade ring-closing metathesis. The regioselectivity is controlled by altering the structure of the catalyst, affording polymers containing fused bicyclo[4,3,0] or [4,4,0] rings. The resulting polymers show narrow band gaps due to the planarization of the conjugated segment resulting from the fused bicyclic structure.
Phosphorus Chemistry
Decarboxylative Selective Phosphorylation of Aliphatic Acids: A Transition-Metal- and Photocatalyst-Free Avenue to Dialkyl and Trialkyl Phosphine Oxides from White Phosphorus
- First Published: 16 September 2022
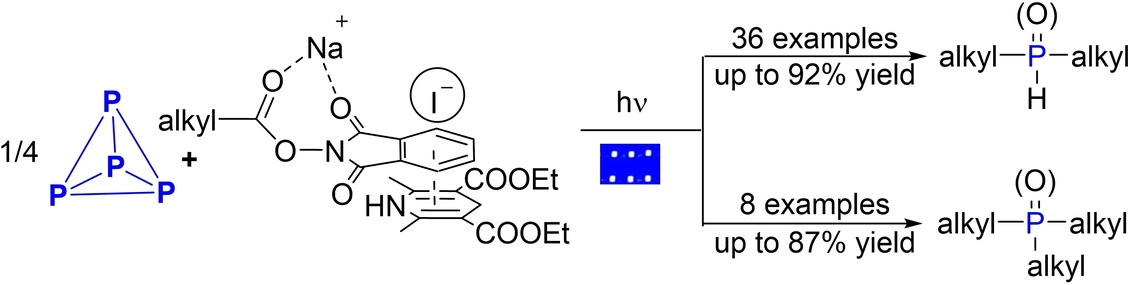
Functionalization of white phosphorus (P4) with N-hydroxyphthalimide esters to synthesize dialkylphosphines and trialkylphosphines under transition-metal- and photocatalyst-free conditions is presented. The oxidation products can be isolated in high yield via the air oxidation of alkylated phosphines.
Chiral Fluorescent Nanoparticles
Enantiomeric NIR-II Emitting Rare-Earth-Doped Ag2Se Nanoparticles with Differentiated In Vivo Imaging Efficiencies
- First Published: 19 September 2022
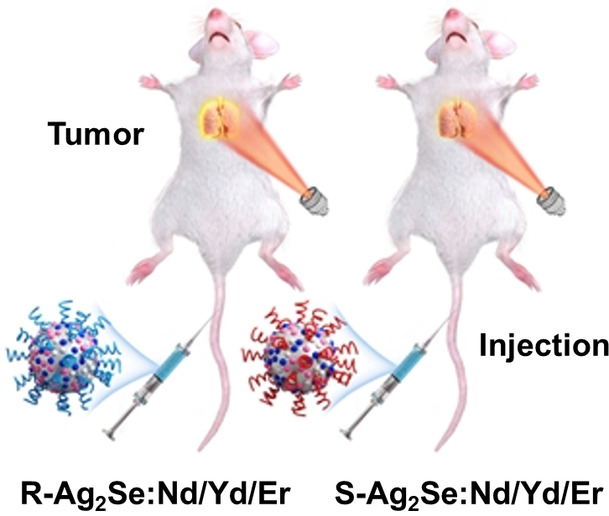
Chiral Ag2Se:Nd/Yd/Er NPs by introducing RuCl[(p-cymene(BINAP)]Cl as ligands were synthesized. Nd3+, Yb3+ and Er3+ as sensitizers case a fluorescence red-shift to 1550 nm with an intensity increased by 145.7-fold compared with Ag2Se:Nd/Yd/Er NPs. The fluorescence imaging efficiency of R-Ag2Se:Nd/Yd/Er NPs was 2-fold higher than that of S-Ag2Se:Nd/Yd/Er NPs.
Cancer Immunotherapy
An Ion-Enhanced Oncolytic Virus-Like Nanoparticle for Tumor Immunotherapy
- First Published: 18 September 2022
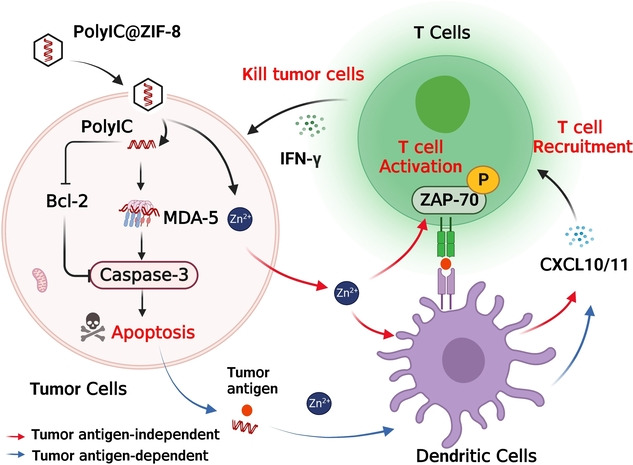
An oncolytic virus-mimicking strategy is proposed to enhance T cell-mediated tumor immunotherapy by synthesizing an ion-enhanced nanoplatform PolyIC@ZIF-8. This nanoplatform not only mimics an oncolytic virus-like function by inducing cell apoptosis to recruit T cells in a tumor antigen-dependent manner but also releases Zn2+ to enhance T cell recruitment and activation in a tumor antigen-independent manner.
Fluorescence
Aggregation-Dependent Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence from Chiral Carbene-CuI-Amide Enantiomers
- First Published: 15 September 2022
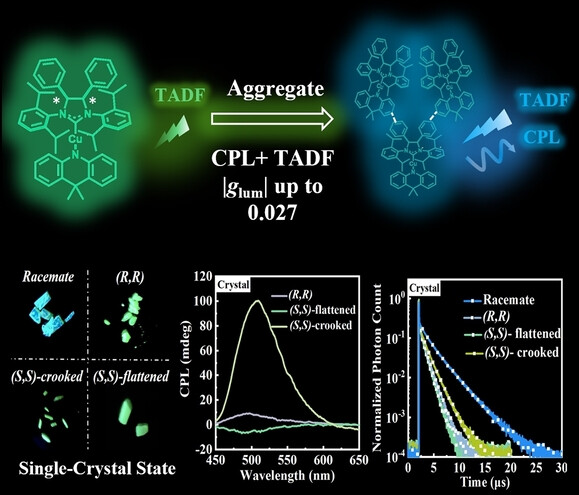
A pair of chiral CuI-based CMA enantiomers, (R,R)-PSIPr*-Cu-DMAC and (S,S)-PSIPr*-Cu-DMAC, have been constructed to exhibit aggregation-dependent circularly polarized luminescence with large luminescence dissymmetry factor of up to +0.027. Inspiring aggregation-dependent TADF properties strongly associated with ligand-ligand rotation of enantiomer molecules were also demonstrated.
C-H Activation | Very Important Paper
Regio- and Diastereoselective Formal [2+2] Cycloaddition of Allenes with Amino-Functionalized Alkenes by Rare-Earth-Catalyzed C(sp2)−H Activation
- First Published: 19 September 2022
![Regio- and Diastereoselective Formal [2+2] Cycloaddition of Allenes with Amino-Functionalized Alkenes by Rare-Earth-Catalyzed C(sp2)−H Activation](/cms/asset/8b4d1e70-f28d-4591-ba82-4dbd5a46f77d/anie202210624-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Half-sandwich rare-earth catalysts serve as a unique platform for the regio- and diastereoselective formal [2+2] cycloaddition of a wide range of allenes with amino-functionalized alkenes via allene C(sp2)−H activation, affording a new family of cyclobutane and cyclobutene derivatives which were difficult to access previously.
Hydrogen Sulfide Donors
Intramolecular Thiol- and Selenol-Assisted Delivery of Hydrogen Sulfide
- First Published: 14 September 2022
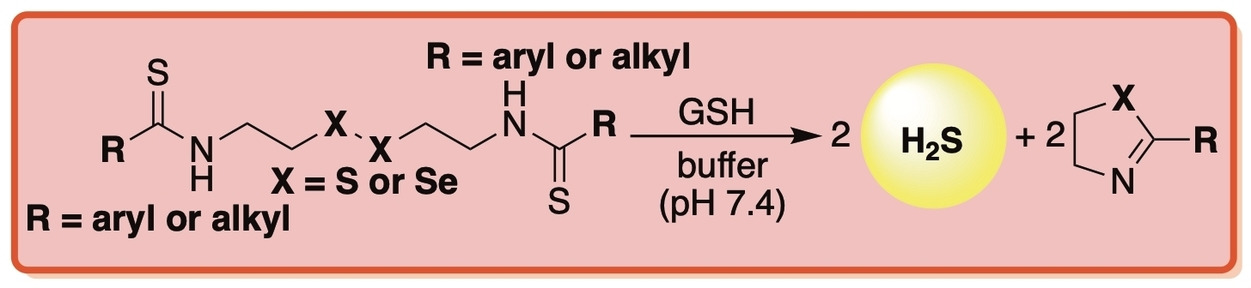
Although aryl thioamides are often used to assess the pharmacological effects of H2S, their reactivity is extremely sluggish and their release of H2S is highly inefficient. Herein, we report that H2S liberation from this donor class can be augmented with intramolecular nucleophilic assistance. We envision this new chemistry serving as a general design strategy for accessing efficient donors that selectively respond to various biological stimuli.
Organic Electronics | Hot Paper
Vibration-Assisted Charge Transport through Positively Charged Dimer Junctions
- First Published: 13 September 2022
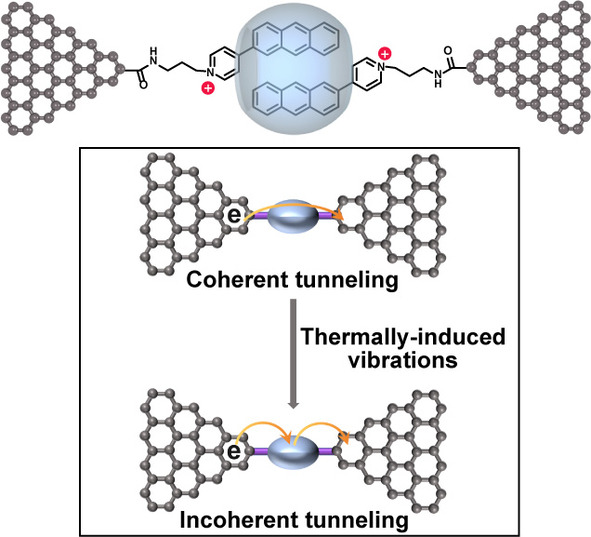
A dimer single-molecule junction with positively charged units is constructed through host–guest interaction using graphene-based static molecular junctions. A transition mechanism from temperature-independent coherent tunneling to temperature-dependent incoherent transport is observed, which is caused by thermally-induced specific molecular vibration modes. The introduction of positive charge can improve the incoherent transport process.
Photochemistry
Photoredox-Catalyzed Deoxygenation of Hexafluoroacetone Hydrate Enables Hydroxypolyfluoroalkylation of Alkenes
- First Published: 16 September 2022
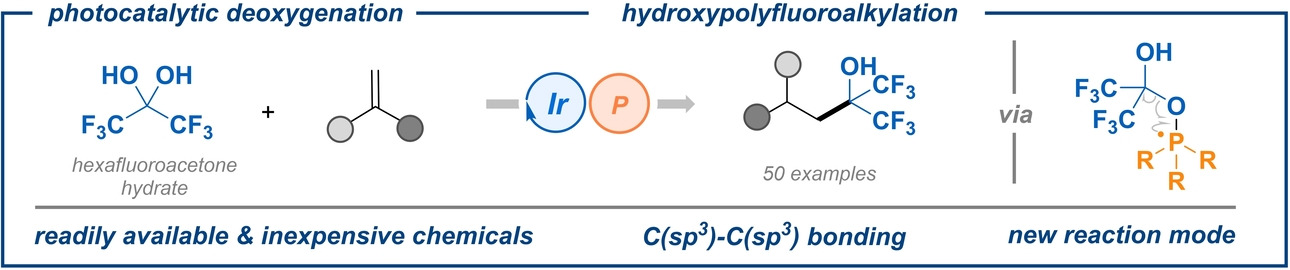
The hydroxypolyfluoroalkylation of alkenes is reported, wherein the intrinsic aldehyde/ketone-gem-diol equilibrium and photocatalytic phosphine-mediated deoxygenation play key roles. A range of electron-deficient alkenes are compatible in this transformation, thus leading to structurally varied bis(trifluoromethyl)carbinols in moderate to excellent yields.
Plastic Recycling | Hot Paper
Microbial Fermentation of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Plastic Waste for the Production of Chemicals or Electricity
- First Published: 14 September 2022
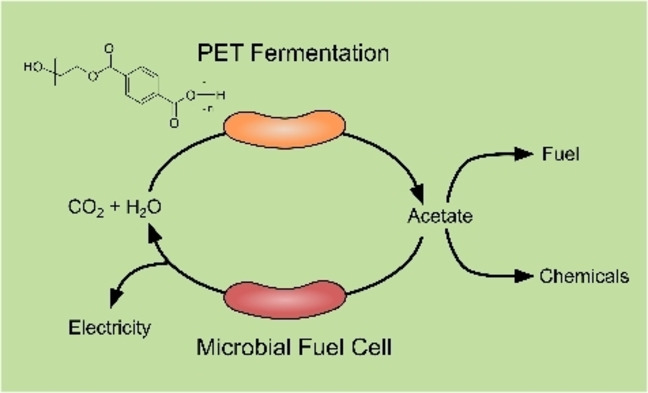
Microbial degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) with Ideonella sakaiensis releases the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide. Here, a fermentative metabolic pathway in Ideonella sakaiensis was uncovered facilitating PET degradation while producing valuable feedstock chemicals or electricity in a microbial fuel cell with Geobacter sulfurreducens. This ‘plastic fermentation’ process provides opportunities for future bioenergy technologies while combating plastic pollution.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Asymmetric Construction of an Aryl-Alkene Axis by Palladium-Catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura Coupling Reaction
- First Published: 16 September 2022

The construction of axially chiral acyclic aryl-alkene skeletons via classic Suzuki–Miyaura reaction has been challenging compared to the biaryls. Rational optimization established an enabling 3,3′-triphenylsilyl-substituted phosphite ligand for asymmetric coupling of hindered aryl halides and vinyl boronates under mild conditions, affording the acyclic aryl-alkenes in good yield, atroposelectivity and E/Z selectivity.
Sensors | Hot Paper
Human Cyclophilin B Nuclease Activity Revealed via Nucleic Acid-Based Electrochemical Sensors
- First Published: 23 August 2022
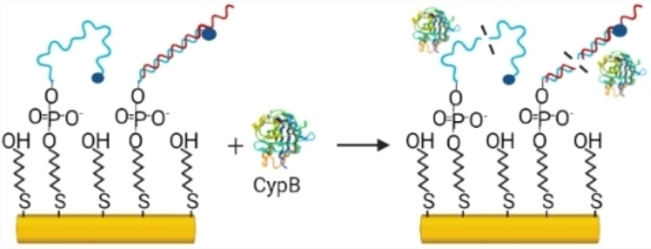
This study employs electrochemical DNA-based sensors to investigate the hydrolytic activity of a previously unknown nuclease, cyclophilin B. The protein is secreted by pancreatic cancer cells and could be a biomarker for early-stage cancer diagnoses. However, the demonstrated nuclease activity will limit bioassay development based on natural nucleic acid aptamers. Instead, we propose DNA stereoisomers (l-DNA) to overcome this challenge.
Nitrate Reduction | Hot Paper
Diatomic Pd−Cu Metal-Phosphorus Sites for Complete N≡N Bond Formation in Photoelectrochemical Nitrate Reduction
- First Published: 31 August 2022
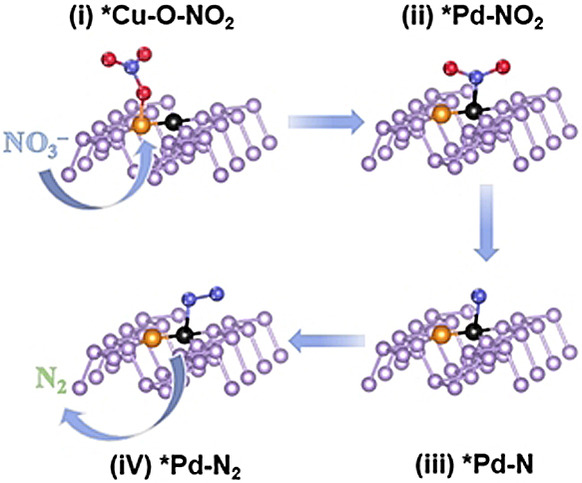
An in situ photoreduction strategy is taken to synthesize diatomic Pd−Cu catalysts on 2D phosphorene. Owing to the strength of the unique synergistic effect of PdCuP4 coordination, the adsorption of NO3−, the transfer of intermediates, and the formation of N≡N bond are all enhanced, leading to a high NO3− removal rate and N2 selectivity.
Enzyme Catalysis | Hot Paper
Discovery of a Unique Structural Motif in Lanthipeptide Synthetases for Substrate Binding and Interdomain Interactions
- First Published: 14 September 2022
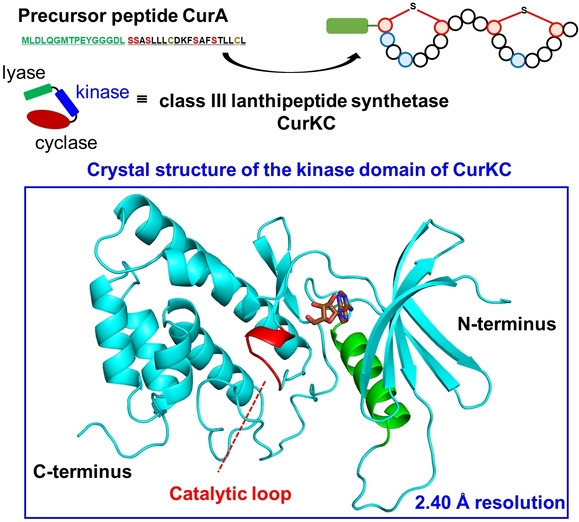
A unique structural motif for leader binding and interdomain interactions was identified in the crystal structure of the kinase domain of class III lanthipeptide synthetase CurKC responsible for the biosynthesis of curvopeptin. This motif consists of two N-terminal antiparallel β-sheets, a central α-helix, and three C-terminal antiparallel β-sheets.
Antibiotics
Redesign of Rifamycin Antibiotics to Overcome ADP-Ribosylation-Mediated Resistance
- First Published: 12 October 2022
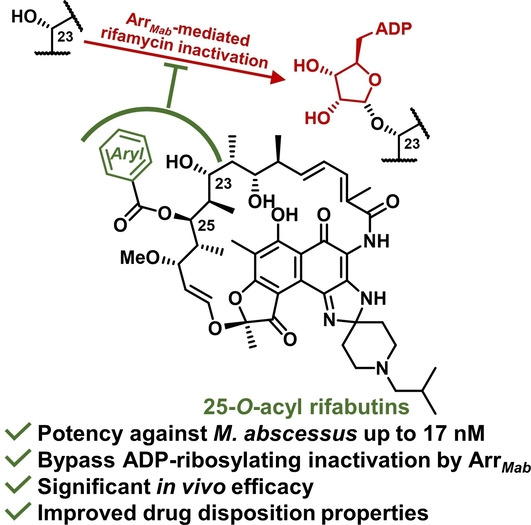
The first antibiotics with low nanomolar activity against the multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus are achieved by rational redesign of rifamycins. Structure-based modification on the rifamycin ansa-chain, together with microbiological, biochemical, biophysical and in vivo characterizations, provides novel candidates that are 300-fold more active than rifampicin, completely bypass the resistance, and possess promising pharmacokinetic profiles.
Fluorescent Ag Clusters
Ag22 Nanoclusters with Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Protected by Ag/Cyanurate/Phosphine Metallamacrocyclic Monolayers through In-Situ Ligand Transesterification
- First Published: 14 September 2022
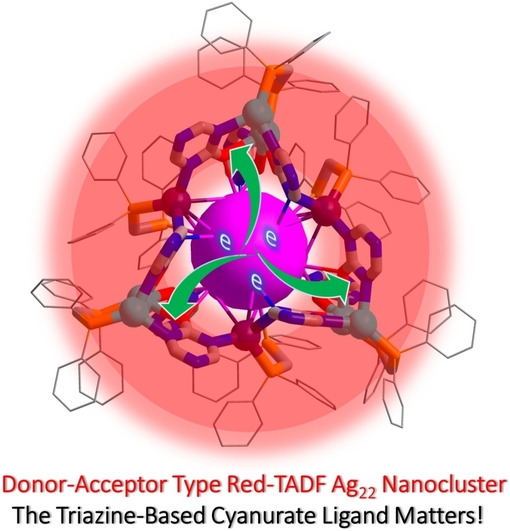
Four isostructural Ag22 nanoclusters protected by a metallamacrocyclic monolayer were synthesized in high yields by in-situ ligand formation strategy. The high-electron-affinity triazine-based cyanurate ligands endow the clusters with unique core-shell interfacial bonding structure and donor-acceptor type electronic structure, resulting in the first mixed valence Ag0/I nanocluster with thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) characteristic.
Density Functional Calculations | Very Important Paper
Mechanistic Origin of Favorable Substituent Effects in Excellent Cu Cyclam Based HNO Sensors
- First Published: 01 September 2022
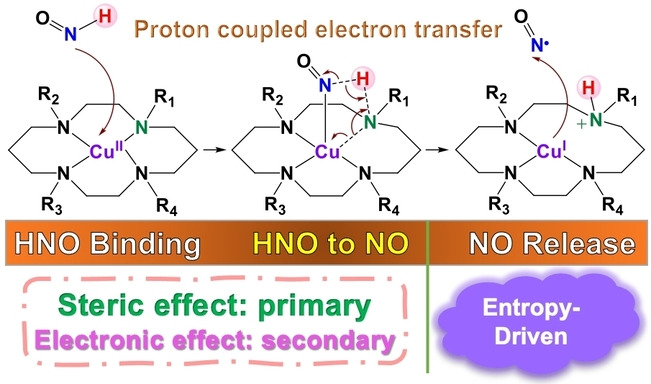
HNO has broad chemical and biomedical properties and Cu cyclam is a useful platform to make excellent HNO sensors including imaging agents. A computational study reproduced their various experimental reactivities and revealed subtle and sometimes unexpected interwoven effects of steric and electronic factors, which offer the first mechanistic understanding of substituent effects for excellent HNO sensors to facilitate future development.
Fluorescent Probes
Integrating a Far-Red Fluorescent Probe with a Microfluidic Platform for Super-Resolution Imaging of Live Erythrocyte Membrane Dynamics
- First Published: 19 September 2022
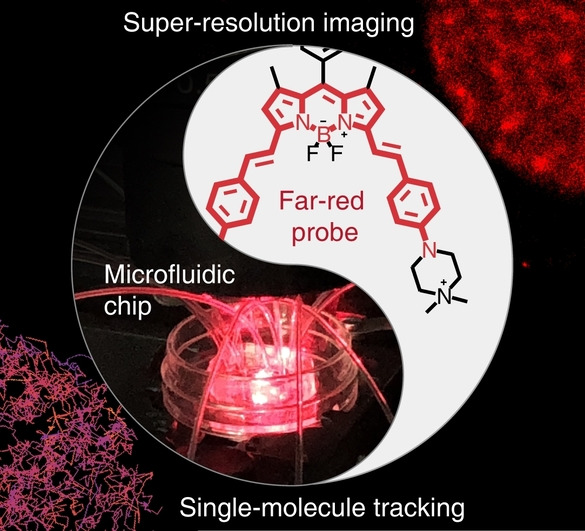
A far-red fluorescent probe with blinking and lasting emission is developed to meet the contradictory requirements of super-resolution imaging and single-molecule tracking. A microfluidic device is fabricated to trap red blood cells (RBCs) and to enable the manipulation of the microenvironment. The integration of the probe and device has uncovered nanoscale dynamics of living RBC membranes, providing a means to advance diagnostics to the molecular level.
Biosynthesis | Hot Paper
Bacterial Avenalumic Acid Biosynthesis Includes Substitution of an Aromatic Amino Group for Hydride by Nitrous Acid Dependent Diazotization
- First Published: 17 September 2022
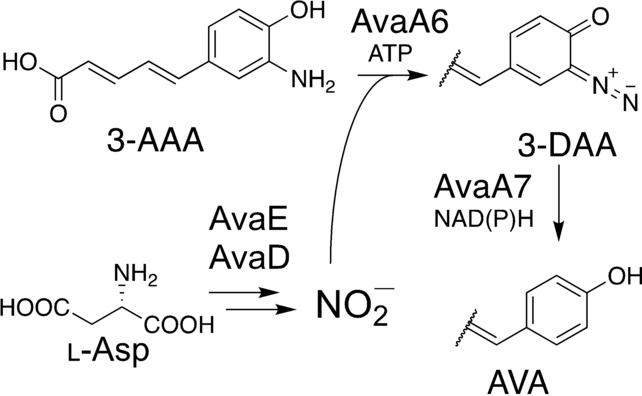
The diazo group is highly reactive and provides biological activity to natural products. By genome mining of the diazo group-biosynthesizing enzymes, an avenalumic acid (AVA) biosynthetic gene cluster was identified in Streptomyces sp. RI-77. This pathway includes two enzymes, AvaA6 and AvaA7, catalyzing the diazotization of 3-aminoavenalumic acid using nitrous acid and substitution of the diazo group for hydride to synthesize AVA, respectively.
Enzyme Immobilization
Co-compartmentalization of Enzymes and Cofactors within Pickering Emulsion Droplets for Continuous-Flow Catalysis
- First Published: 16 September 2022
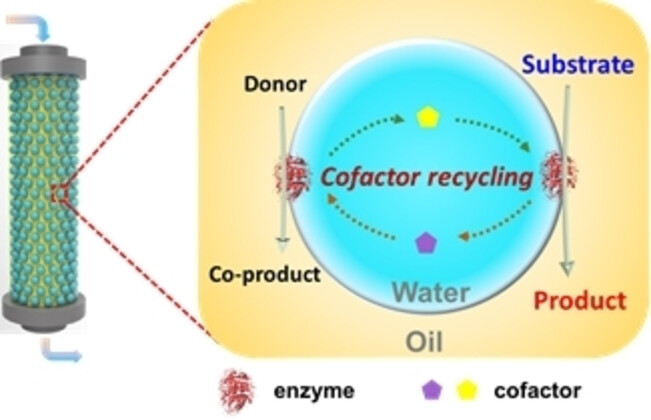
A continuous-flow biocatalytic system based on the co-compartmentalization of enzymes and cofactors within Pickering emulsion droplets has been developed. As exemplified by enzyme-catalyzed ketone enantioselective reduction and enantioselective transamination, this system features long-term operational stability, excellent catalytic efficiency and no need for exogenous cofactors.
Polymerization | Hot Paper
Stereomodulation of Poly(4-methyl-1-pentene): Adoption of a Neglected and Misunderstood Commercial Polyolefin
- First Published: 13 September 2022
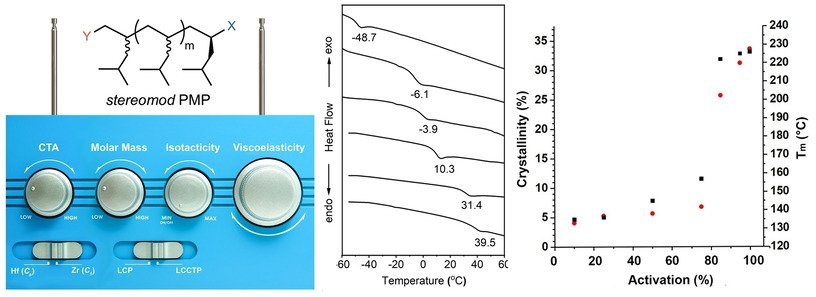
A toolbox of living polymerization methods has been applied for the stereomodulation of poly(4-methyl-1-pentene) (PMP) to provide new fundamental forms in which thermal phase transitions, Tg and Tm, can be adjusted over a wide range. Also reported for the first time are the synthesis and properties of authenticated 1,2-regioregular atactic PMP, which serves to correct past errors and misinformation.
Upconversion Luminescence | Hot Paper
Modulating the Rise and Decay Dynamics of Upconversion Luminescence through Controlling Excitations
- First Published: 14 September 2022
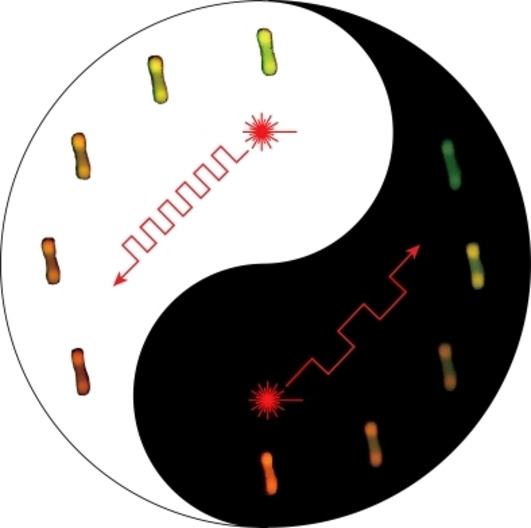
In contrast to the extensively investigated steady-state upconversion luminescence (UCL), systematic studies on temporal UCL are carried out, which have enabled wide modulation of the rise and decay dynamics of the UCL, and consequently a record adjustment of 20-fold lifetime, ≈70-fold red-to-green intensity ratio, as well as reversibly definable Er3+ emission color by simply tuning the pulse width of the excitation laser.
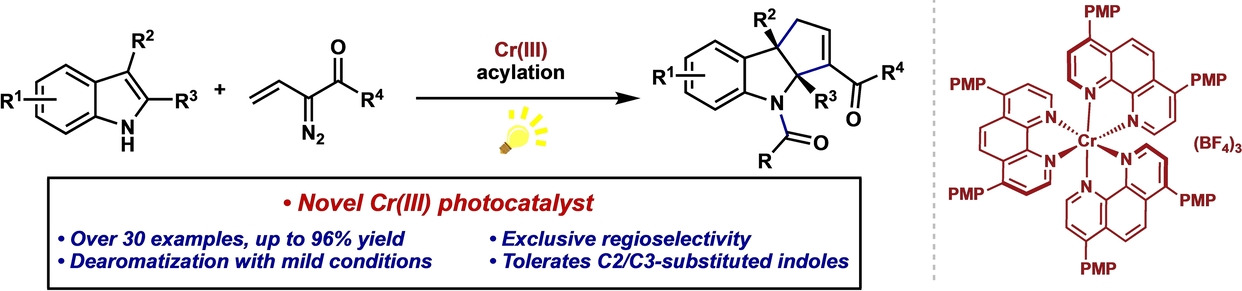
Photocatalysis
Dearomative (3+2) Cycloadditions between Indoles and Vinyldiazo Species Enabled by a Red-Shifted Chromium Photocatalyst
- First Published: 05 September 2022
Photocatalytic H2O Splitting
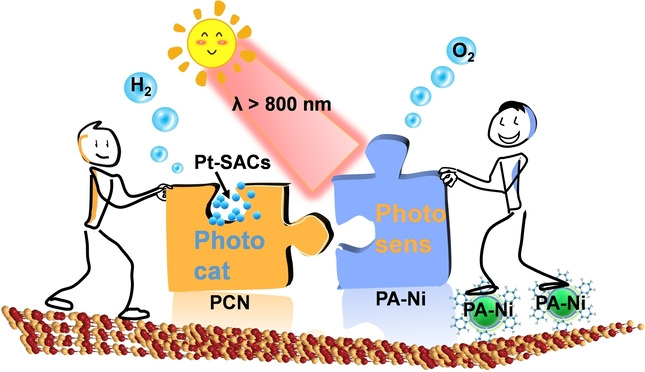
Pt Atoms/Clusters on Ni-phytate-sensitized Carbon Nitride for Enhanced NIR-light-driven Overall Water Splitting beyond 800 nm
- First Published: 09 September 2022
Self-assembled Photocatalysts | Hot Paper
Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen and Oxygen Evolution by Side-Group Engineered Benzodiimidazole Oligomers with Strong Built-in Electric Fields and Short-Range Crystallinity
- First Published: 20 September 2022
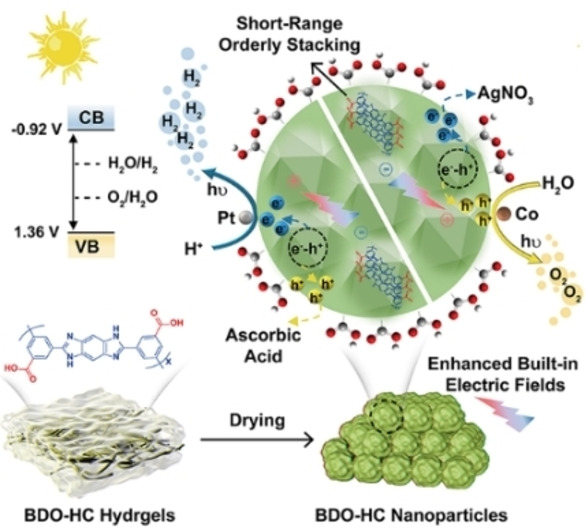
Carboxyl-rich benzodiimidazole oligomers (BDO-HC) are obtained through a side-group assisted self-assembly. The carboxyl-based strong built-in electric field promotes charge separation, and the nano-range crystals provide short channels for charge transfer. The photocatalyst is capable of efficient hydrogen and oxygen evolution.
Nanowires | Hot Paper
A Library of Rare Earth Oxide Ultrathin Nanowires with Polymer-Like Behaviors
- First Published: 15 September 2022
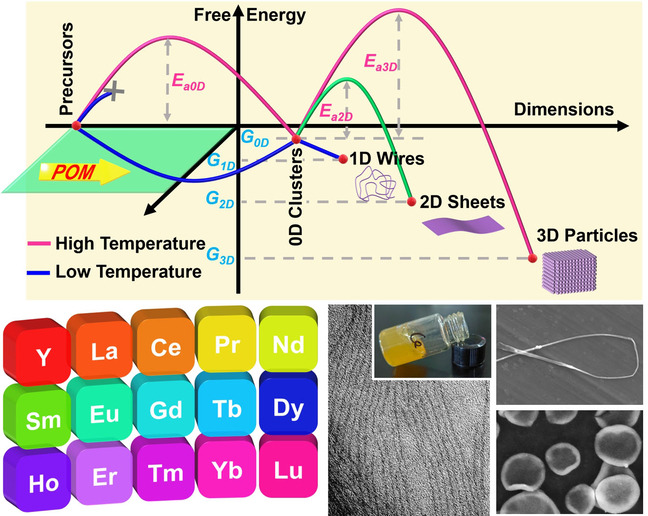
A general and facile colloidal method to synthesize ultrathin nanowires at atmospheric pressure and low temperature (50 °C) is developed. The mechanism of nanocrystal growth along different dimensions is discussed. Fifteen kinds of RE-Mo-O (RE=Y, La-Nd, and Sm-Lu) ultrathin nanowires could be synthesized using this method. All of them exhibited polymer-like behavior.
Asymmetric Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Chiral Bismuth-Rhodium Paddlewheel Complexes Empowered by London Dispersion: The C−H Functionalization Nexus
- First Published: 14 September 2022
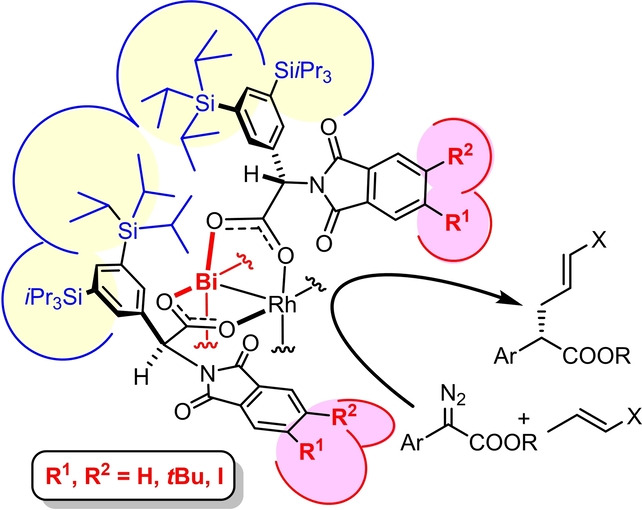
The encounter of a donor/acceptor diazo derivative with a hydrocarbon inside the chiral binding pocket crafted by London dispersion about a heterobimetallic [BiRh] paddlewheel complex entails highly effective asymmetric C−H insertion; the resulting products formally correspond to the outcome of classical ester alkylation, allylation, benzylation, or aldol reactions.
Anticancer Metallodrug
Organogold(III) Complexes Display Conditional Photoactivities: Evolving From Photodynamic into Photoactivated Chemotherapy in Response to O2 Consumption for Robust Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 15 September 2022
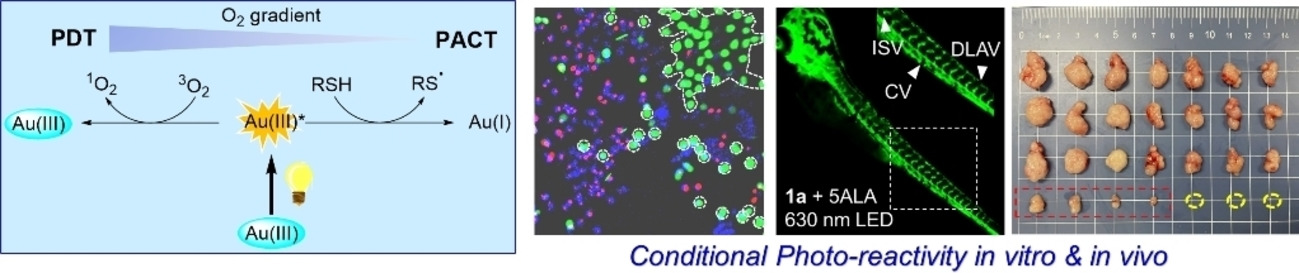
Oxygen-dependent photo-reactivity for robust tumor therapy: A PDT-to-PACT evolving photo-reactivity with response to oxygen-consumption was found in cyclometalated gold(III)-alkyne complexes, leading to potent cytotoxicity towards cancer cells, strong anti-angiogenesis in zebrafish, and efficient suppression of mouse tumor xenografts.
Coordination Cages
Exploring the Gas-Phase Formation and Chemical Reactivity of Highly Reduced M8L6 Coordination Cages
- First Published: 14 September 2022
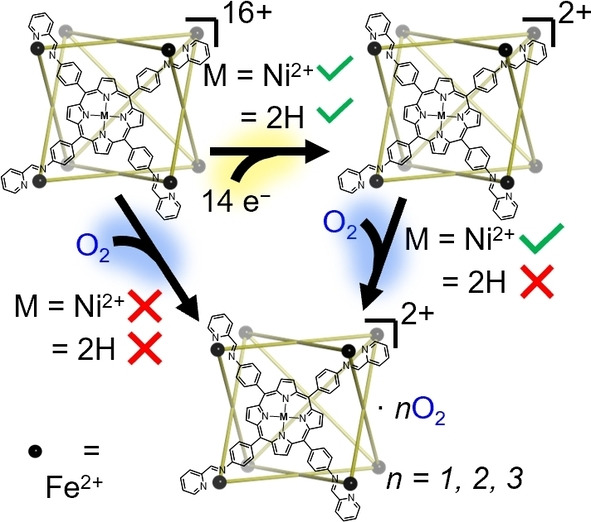
Coordination cages containing porphyrin subunits are reduced up to fourteen times in the gas phase. While the presence or absence of Nickel(II) coordinated in the porphyrin binding site does not affect the rate of reduction, the reactivity of the reduced species toward molecular O2 is significantly enhanced in the former case. Additionally, the presence of a C60 fullerene guest within the nickelated cage reduces its reactivity.
OLEDs
Exceeding 30 % External Quantum Efficiency in Non-doped OLEDs Utilizing Solution Processable TADF Emitters with High Horizontal Dipole Orientation via Anchoring Strategy
- First Published: 21 September 2022
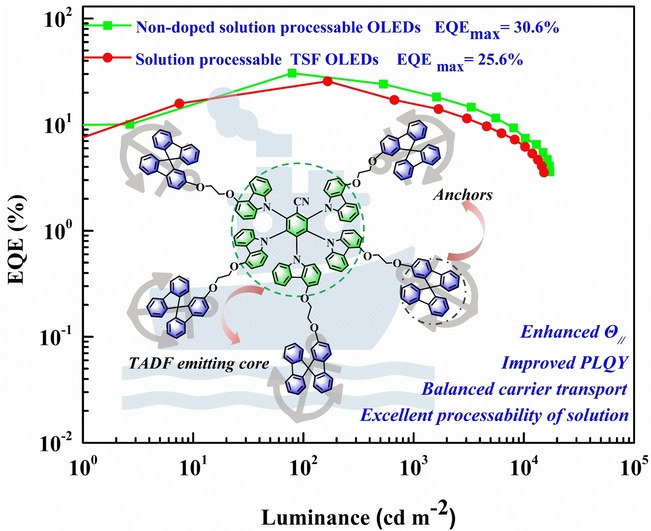
An anchoring strategy was firstly proposed to generate solution processable TADF emitters from isotropic orientation to horizontal one by attaching bipolar 9,9′-spirobi[fluorene] subunits as anchoring groups onto TADF emitting core via flexible chains. With outstanding characteristics in pristine films, unprecedented EQEmaxs of 30.6 % and 25.6 % were achieved for solution processable non-doped OLEDs and TSF OLEDs, respectively.
Thermoelectrics | Hot Paper
Realizing zT>2 in Environment-Friendly Monoclinic Cu2S—Tetragonal Cu1.96S Nano-Phase Junctions for Thermoelectrics
- First Published: 19 September 2022
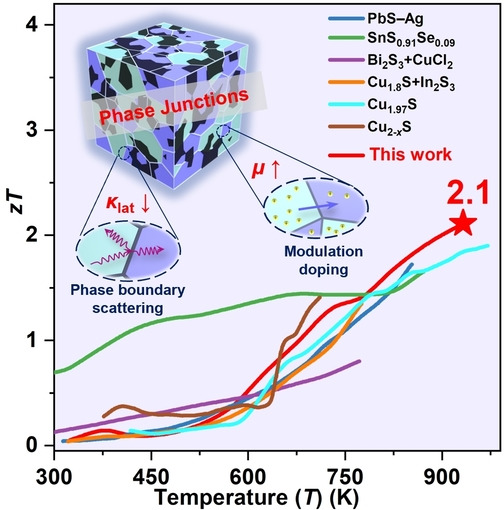
Well-controlled phase junction nanocomposites are prepared by a novel surface ligand (decanethiol)-directed strategy. The conductivity is increased by modulation doping, and the phase boundary enhances phonon scattering, which helps to reduce lattice thermal conductivity. The combined effects yield a record-high zT=2.1 in metal sulfide thermoelectric materials.
Enzymes
Sactipeptide Engineering by Probing the Substrate Tolerance of a Thioether-Bond-Forming Sactisynthase
- First Published: 01 September 2022
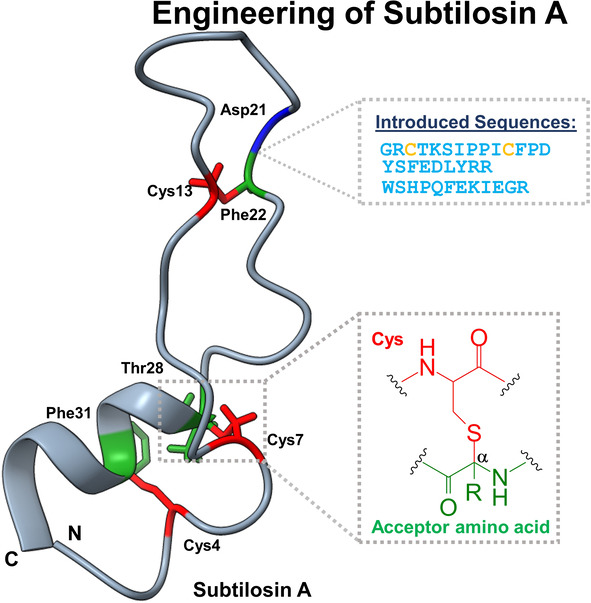
Sactipeptides are a class of microbial peptides possessing thioether crosslinks. We demonstrate sactipeptide engineering without compromising their post-translational modification introduced by sactisynthases. A variety of natural and hybrid sactipeptide constructs were generated and analyzed for the presence of thioether crosslinks, demonstrating the possibility to design variants with novel functionalities.
Molecular Electronics
Quantum Interference in Mixed-Valence Complexes: Tuning Electronic Coupling Through Substituent Effects
- First Published: 28 August 2022
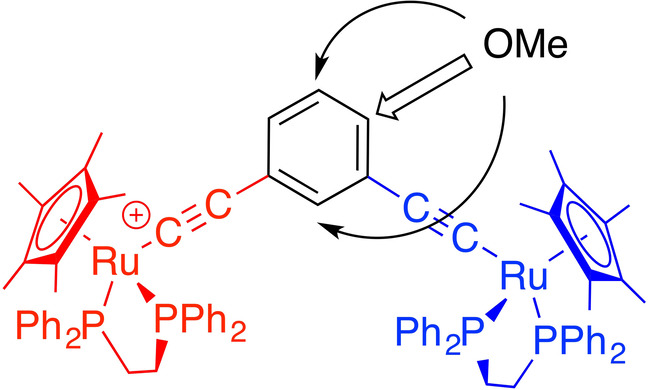
The degree of ground state electronic interaction in the mixed-valence complex [{Cp*(dppe)RuC≡C}2(μ-1,3-C6H4)]+ can be tuned through the introduction of an OMe substituent to the bridging ligand. These effects are sensitive to the position of the substituent, and follow the same patterns as those predicted by quantum circuit rules for weakly coupled molecules in molecular junctions.