Uncertainty Quantification of Michaelis–Menten Kinetic Rates and Its Application to the Analysis of CRISPR-Based Diagnostics
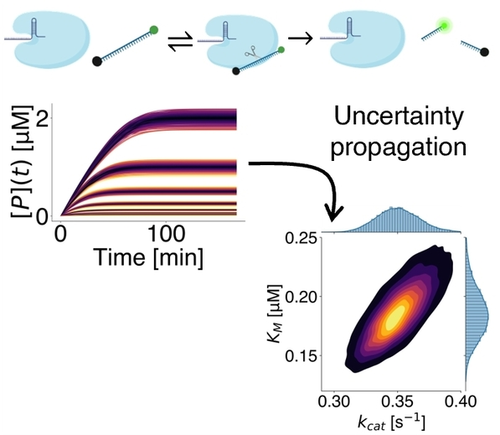
Graphical Abstract
The estimation of Michaelis–Menten kinetic parameters is highly sensitive to small experimental errors, even though the quantification of such parameters is critical. Monte Carlo simulations show that the kinetic efficiency, which governs limit of detection of assays that require low background, is the most precise kinetic parameter.
Abstract
Michaelis–Menten kinetics is an essential model to rationalize enzyme reactions. The quantification of Michaelis–Menten parameters can be very challenging as it is sensitive to even small experimental errors. We here present a quantification of the uncertainty inherent to the experimental determination of kinetic rate parameters for enzymatic reactions. We study the influence of several sources of uncertainty and bias, including the inner filter effect, pipetting errors, number of points in the Michaelis–Menten curve, and flat-field correction. Using Monte Carlo simulations and analyses of experimental data, we compute typical uncertainties of  ,
,  , and catalytic efficiency
, and catalytic efficiency 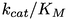 . As a salient example, we analyze the extraction of such parameters for CRISPR-Cas systems. CRISPR diagnostics have recently attracted much interest and yet reports of these enzymatic kinetic rates have been highly unreliable and inconsistent.
. As a salient example, we analyze the extraction of such parameters for CRISPR-Cas systems. CRISPR diagnostics have recently attracted much interest and yet reports of these enzymatic kinetic rates have been highly unreliable and inconsistent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.