Mechanistic Studies on the Organocatalytic α-Chlorination of Aldehydes: The Role and Nature of Off-Cycle Intermediates
Graphical Abstract
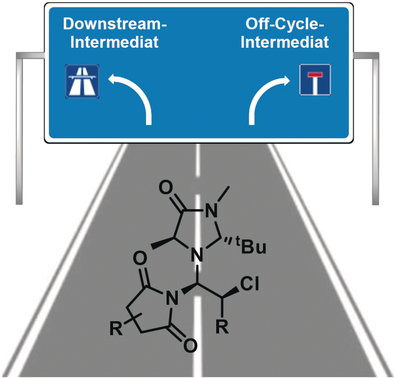
My way or the highway: The organocatalytic α-chlorination of aldehydes has been investigated. It was possible to isolate and characterize the off-cycle intermediates for the first time, elucidate their role in the catalytic cycle and to suppress their accumulation. Remarkably, the catalyst loading was reduced from 20–30 mol % to 5 mol %. The new catalytic system was applied to many different substrates.
Abstract
Herein we report the isolation and characterization of aminal intermediates in the organocatalytic α-chlorination of aldehydes. These species are stable covalent ternary adducts of the substrate, the catalyst and the chlorinating reagent. NMR-assisted kinetic studies and isotopic labeling experiments with the isolated intermediate did not support its involvement in downstream stereoselective processes as proposed by Blackmond. By tuning the reactivity of the chlorinating reagent, we were able to suppress the accumulation of rate-limiting off-cycle intermediates. As a result, an efficient and highly enantioselective catalytic system with a broad functional group tolerance was developed.