Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Ylide-Functionalized Phosphines: Strong Donor Ligands for Homogeneous Catalysis (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39/2018)
- Page: 12587
- First Published: 20 August 2018

Power to phosphines Phosphines are one of the most utilized types of ligands in catalysis and their advancement is indispensable for further developments in this field. In their Communication on page 12859 ff., V. H. Gessner et al. demonstrate that ylide functionalization is a powerful tool to increase the donor strength of phosphines. The YPhos ligands obtained are easy to synthesize, more electron-rich than classical phosphines or even NHCs, and allow for improved catalytic activity in gold catalysis.
Inside Cover: Magnetoluminescence in a Photostable, Brightly Luminescent Organic Radical in a Rigid Environment (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39/2018)
- Page: 12588
- First Published: 10 August 2018

A luminescent radical doped into host molecular crystals exhibits doping concentration-dependent emission properties. In their Communication on page 12711 ff., T. Kusamoto, H. Nishihara, and co-workers report drastic changes in the emission spectra under an applied magnetic field in 10 wt % doped crystals. This is the first observation of magnetoluminescence in organic radicals.
Inside Back Cover: Cascade Reactions in Tunable Lamellar Micro- and Mesopores for C=C Bond Coupling and Hydrocarbon Synthesis (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39/2018)
- Page: 12977
- First Published: 20 August 2018
Brønsted acid sites partially confined at the intercept of micro- and mesopores in two-dimensional MFI zeolite nanosheets are effective for C=C bond-coupling and ring-closure reactions that transform light aldehydes into aromatic compounds. In their Communication on page 12886 ff., Y.-H. Chin et al. establish the roles of these sites and their environment in catalytic aromatization, and of interlamellar mesopores in the efficient transport and removal of products.
Back Cover: Functionalizable Stereocontrolled Cyclopolyethers by Ring-Closing Metathesis as Natural Polymer Mimics (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39/2018)
- Page: 12978
- First Published: 01 August 2018

Topological control in biopolymers relies on control of complex stereoregular cyclic architectures. In their Communication on page 12835 ff., J. Prunet, M. P. Shaver, and M. Alkattan exploit the ring-closing metathesis (RCM) of an olefin-pendant isotactic polymer to prepare a stereocontrolled 1,4-linked cyclopolyether. Post-polymerization dihydroxylation (DH) affords a poly(ethylene glycol) backbone with sugar-like functionalities that mimic the structure of amylose.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Docking Strategy To Construct Thermostable, Single-Crystalline, Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Framework with High Surface Area
- First Published: 19 September 2018
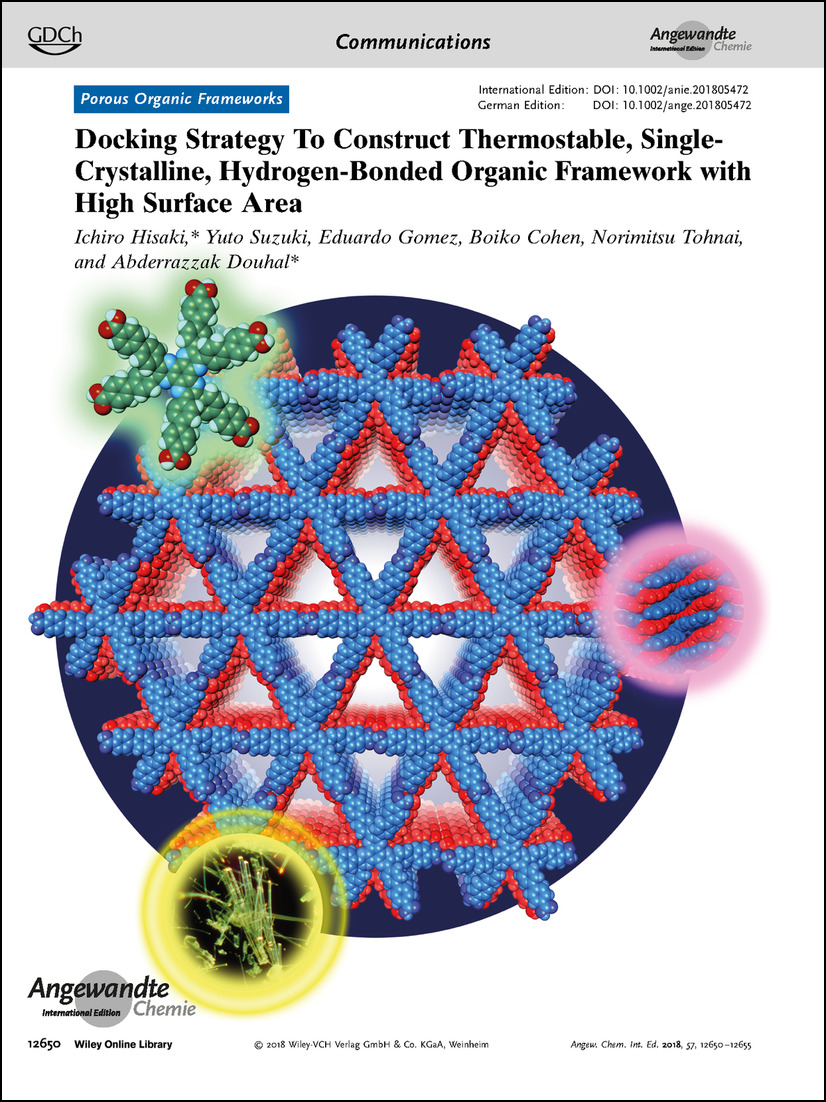
Porous Organic Frameworks. A new thermally and chemical durable hydrogen-bonded porous organic framework based on a hexaazatriphenylene derivative is described by I. Hisaki, A. Douhal, and co-workers in their Communication on page 12650 ff.
Editorial
A New Approach to Sustainability: A Moore's Law for Chemistry
- Pages: 12590-12591
- First Published: 23 May 2018

“… How do we have a major impact on delivering sustainable chemistry? Carbon-neutral laboratories can drive down the environmental costs of chemistry. We propose that sustainable chemistry requires some overarching goal that can be embraced by everyone in the chemical supply chain as well as by the public …” Read more in the Guest Editorial by Martyn Poliakoff, Peter Licence, and Michael W. George.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39/2018
- Pages: 12593-12610
- First Published: 19 September 2018
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39/2018
- Pages: 12614-12618
- First Published: 19 September 2018
Author Profile
News
Reviews
Protein Engineering
Engineering Proteins at Interfaces: From Complementary Characterization to Material Surfaces with Designed Functions
- Pages: 12626-12648
- First Published: 17 April 2018
Communications
Porous Organic Frameworks
Docking Strategy To Construct Thermostable, Single-Crystalline, Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Framework with High Surface Area
- Pages: 12650-12655
- First Published: 09 June 2018
More than one HAT: Hexaazatriphenylene (HAT) derivatives are suitable building blocks for the systematic construction of stable hydrogen-bonded frameworks. The derivative with carboxybiphenyl groups forms a stable single-crystalline porous framework (CBPHAT-1 a) that displays protic solvent durability, heat resistance up to 305 °C, and SA(BET) of 1288 m2 g−1.
N-Doped Graphene | Hot Paper
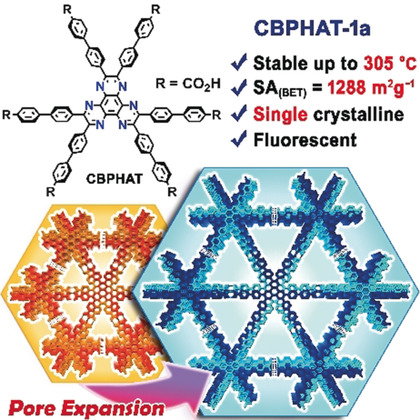
Fast Exfoliation and Functionalisation of Two-Dimensional Crystalline Carbon Nitride by Framework Charging
- Pages: 12656-12660
- First Published: 10 August 2018
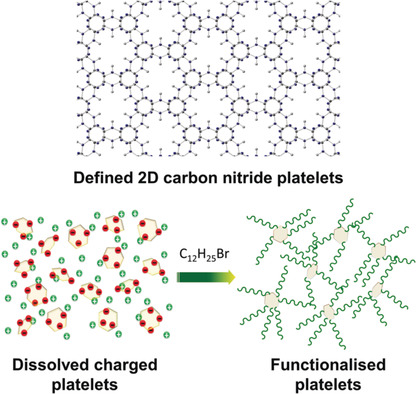
A scalable one-pot reductive method produces stable solutions of single- and few-layer two-dimensional graphitic carbon nitride (gCN) nanosheets in high yield (35 %). Atomic-resolution imaging confirms an undamaged crystalline structure with AB stacking. The anionic charge provides a versatile route for functionalisation, as illustrated by alkylation.
Dual Catalysis
Microtubing-Reactor-Assisted Aliphatic C−H Functionalization with HCl as a Hydrogen-Atom-Transfer Catalyst Precursor in Conjunction with an Organic Photoredox Catalyst
- Pages: 12661-12665
- First Published: 01 August 2018
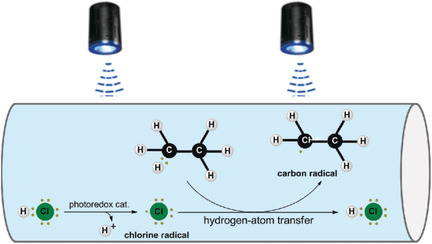
Cl-ever cats: HCl was used as a hydrogen-atom-transfer catalyst precursor and activated to give chlorine radicals by an acridinium photoredox catalyst under visible-light irradiation in a microtubing reactor, which was effective in retaining the volatile HCl catalyst. This photomediated C−H activation strategy enabled the efficient alkylation and allylation of a variety of unactivated, even primary, C(sp3)−H bonds (see scheme).
Protein Immobilization | Hot Paper
Enzyme-Mediated, Site-Specific Protein Coupling Strategies for Surface-Based Binding Assays
- Pages: 12666-12669
- First Published: 06 August 2018
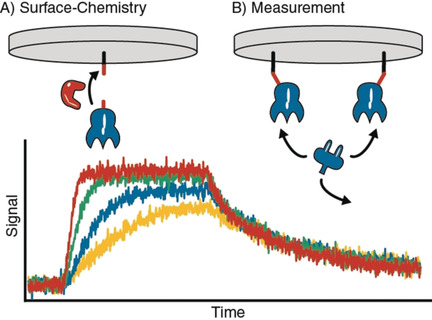
Coupling strategies for surface-based kinetic assays based on the enzymes Sfp, SrtA, and OaAEP were developed to site-specifically and covalently ligate proteins of interest through short recognition sequences. The enzymes function under mild conditions without affecting the receptor fold, thereby enabling study of the binding kinetics of receptor–ligand pairs that are inaccessible to nonspecific surface chemistry.
Polymers
Synthesis of Chiral Sulfur-Containing Polymers: Asymmetric Copolymerization of meso-Epoxides and Carbonyl Sulfide
- Pages: 12670-12674
- First Published: 08 August 2018
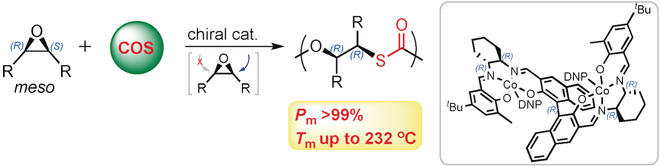
A worthy COS: Chiral sulfur-containing polymers with good thermal and optical properties were synthesized for the first time by stereoselective desymmetrization copolymerization of achiral meso-epoxides and COS. The reaction is catalyzed by an enantiopure binaphthol-linked bimetallic catalyst and provides the polymers with >99 % isotacticity.
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Tuning Gold Nanoparticles with Chelating Ligands for Highly Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- Pages: 12675-12679
- First Published: 10 August 2018
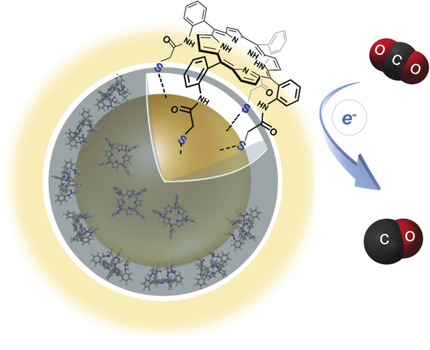
Gold nanoparticles functionalized with a chelating tetradentate porphyrin ligand exhibit significantly improved catalytic activity and stability for electrochemical CO2 reduction. The inherent structural and electronic tunability of these nanoparticles offers an unrivaled degree of control over their reactivity.
Coordination Polymers
A Supramolecular Crosslinker To Give Salt-Resistant Polyion Complex Micelles and Improved MRI Contrast Agents
- Pages: 12680-12684
- First Published: 01 August 2018

Beating brine: Using two different DPA-based oligo-ligands (a bis-ligand, L2 and tris-ligand, L3) and metal ions, a supramolecular polyelectrolyte system was produced with cross-links, the number of which can be varied by varying the L3/L2 ratio. Combining this with a charged-neutral diblock copolymer led to M-L2-L3 micelles with tunable and enhanced salt stability and magnetic relaxivity that perform well as an MRI contrast agent.
Imaging Agents
A Photoactivatable BODIPY Probe for Localization-Based Super-Resolution Cellular Imaging
- Pages: 12685-12689
- First Published: 18 July 2018
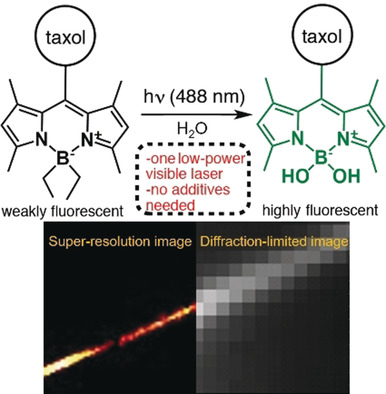
Boron-alkylated BODIPY is used as a probe for single-molecule localization-based super-resolution microscopy. Photoactivation and excitation is achieved with a single visible-light laser and without additives in the imaging medium. Microtubules are imaged with a paclitaxel-attached probe to demonstrate the super-resolution imaging ability of cellular structures.
Fluorine
Exploration of the Synthetic Potential of Electrophilic Trifluoromethylthiolating and Difluoromethylthiolating Reagents
- Pages: 12690-12695
- First Published: 10 July 2018
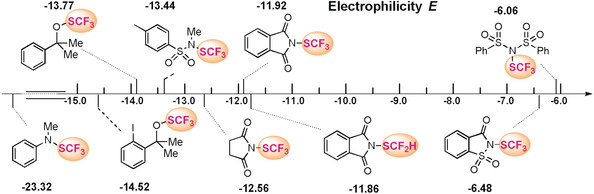
The electrophilicities (E) of trifluoromethylthiolating and difluoromethylthiolating reagents were investigated by following the kinetics of their reactions with a series of enamines and carbanions with known nucleophilicity parameters. The electrophilicity parameters determined for these reagents cover a reactivity range of 17 orders of magnitude.
Photodimerization
Stereoselective Solid-State Synthesis of Substituted Cyclobutanes Assisted by Pseudorotaxane-like MOFs
- Pages: 12696-12701
- First Published: 14 August 2018
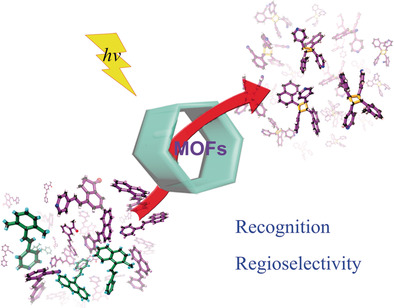
Template synthesis: Pairs of trans-4-styrylpyridine or its derivatives are oriented in a parallel and head-to-tail (HT) manner for the solid-state photodimerization within a pseudorotaxane-like MOF. The high selectivity for the rctt-HT dimers provides a controlled photodimerization within a confined environment. These results are in striking contrast to the mixtures of products and low yields obtained by untemplated photodimerization in organic solvents.
Protein Modification
Building and Breaking Bonds via a Compact S-Propargyl-Cysteine to Chemically Control Enzymes and Modify Proteins
- Pages: 12702-12706
- First Published: 17 August 2018
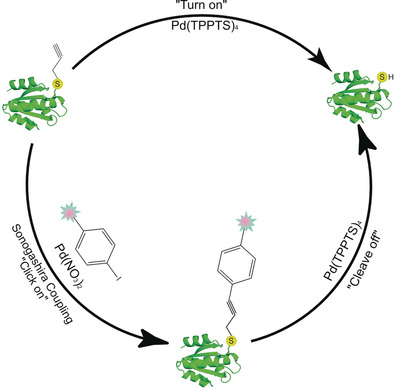
S-propargyl-cysteine (SprC) was genetically encoded into proteins at the interface to cross-link proteins and at the active site to mask an enzyme, which was chemically activated by Pd(TPPTS)4. In addition, molecular modifications were installed onto proteins via Sonogashira cross-coupling on SprC by Pd(NO3)2, and then tracelessly removed with Pd(TPPTS)4.
Antimicrobial Agents | Very Important Paper
Surprising Antibacterial Activity and Selectivity of Hydrophilic Polyphosphoniums Featuring Sugar and Hydroxy Substituents
- Pages: 12707-12710
- First Published: 11 July 2018
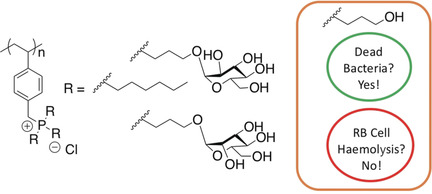
Sweet but deadly: Phosphonium-based polymers appended with hydrophilic groups such as sugars or hydroxy groups can be employed as highly effective antibacterial agents against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria with minimal haemolysis of red blood cells. This challenges the conventional wisdom that hydrophobic appendages are necessary for this class of biocides.
Magnetoluminescence | Very Important Paper
Magnetoluminescence in a Photostable, Brightly Luminescent Organic Radical in a Rigid Environment
- Pages: 12711-12715
- First Published: 10 June 2018
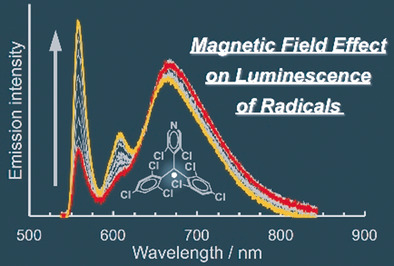
Glowing radical: A photostable luminescent organic radical was doped into host molecular crystals. The 0.05 wt % doped crystals displayed bright luminescence with a room-temperature emission quantum yield of 89 %. The 10 wt % doped crystals show large changes in their emission spectra on applying a magnetic field at 4.2 K. This is the first observation of magnetoluminescence in organic radicals.
Energy Storage
Direct Solar-to-Electrochemical Energy Storage in a Functionalized Covalent Organic Framework
- Pages: 12716-12720
- First Published: 09 August 2018
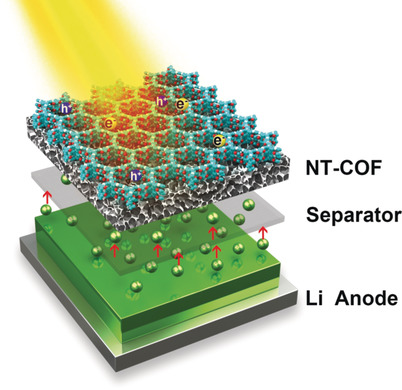
A covalent organic framework functionalized with triphenylamine and naphthalenediimide units was used as a cathode. It could synergize photoinduced charge transfer with reversible electrochemical (de)lithiation processes. This leads to decreased charge voltage (by 0.5 V), increased discharge voltage (by 0.5 V), and an extra 38.7 % battery efficiency under illumination.
Nanocatalysis
Bimetallic Nanoparticles in Supported Ionic Liquid Phases as Multifunctional Catalysts for the Selective Hydrodeoxygenation of Aromatic Substrates
- Pages: 12721-12726
- First Published: 03 September 2018
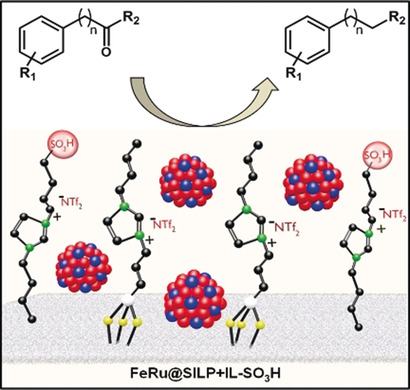
A bimetallic, bifunctional catalyst composed of iron–ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on an acid-functionalized supported ionic liquid phase (FeRu@SILP+IL-SO3H) was developed. This catalyst showed high activity for the hydrodeoxygenation of aromatic ketones and excellent selectivity towards aromatic deoxygenation products.
Mechanoluminescence | Hot Paper
Alkyl Chain Introduction: In Situ Solar-Renewable Colorful Organic Mechanoluminescence Materials
- Pages: 12727-12732
- First Published: 09 August 2018
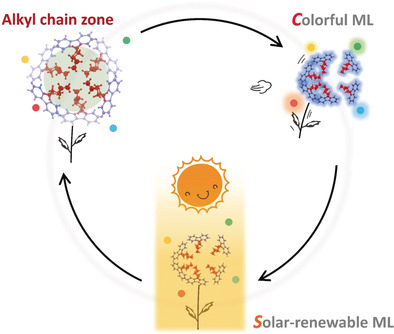
Solar-renewable colorful organic mechanoluminescence (ML) materials are induced by introduction of alkyl chains. Colorful ML from a polycrystalline thin film can be repeated interactively and totally for preliminary sandwich-type ML device applications by simply recrystallizing the fractured crystal in situ after non-contact exposure to sunlight in less than one minute.
18F-Fluorination
Site-Selective, Late-Stage C−H 18F-Fluorination on Unprotected Peptides for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging
- Pages: 12733-12736
- First Published: 07 August 2018
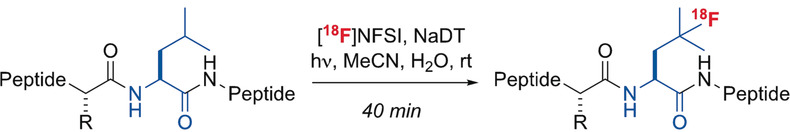
Prosthetic-group-free: The combination of photoactivated sodium decatungstate and [18F]-N-fluorobenzenesulfonimide effects site-selective 18F-fluorination at the branched position in leucine residues in unprotected and unaltered peptides. This streamlined process provides a means to directly convert native peptides into PET imaging agents under mild aqueous conditions.
Synthetic Methods
Reductive C2-Alkylation of Pyridine and Quinoline N-Oxides Using Wittig Reagents
- Pages: 12737-12740
- First Published: 02 August 2018
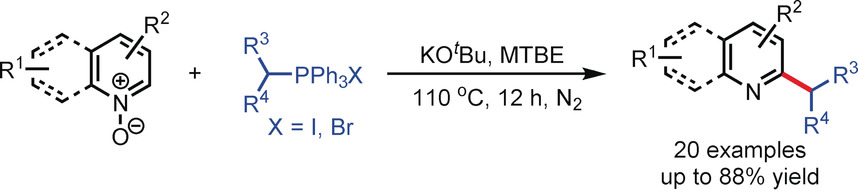
Another trick up their sleeve: Pyridine and quinoline N-oxides underwent efficient reductive alkylation with Wittig reagents under mild conditions to provide a variety of C2-alkylated pyridines and quinolines with excellent site selectivity and functional-group compatibility (see scheme). Straightforward sequential C−H functionalization and postfunctionalization enable the synthesis of diverse bipyridyl ligands by this method.
Supramolecular Chemistry
A Multi-Component Sensor System for Detection of Amphiphilic Compounds
- Pages: 12741-12744
- First Published: 05 August 2018
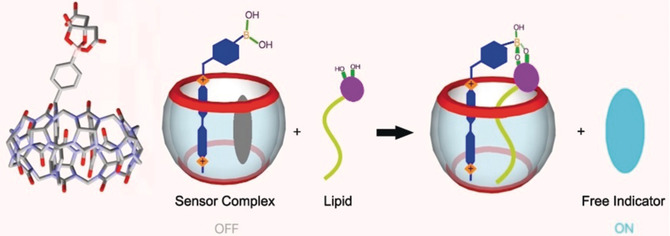
A CB[8]-receptor-indicator complex for detection of amphiphilic compounds has been prepared. It has a hydrophilic receptor to bind a sugar head group, a hydrophobic macrocycle to bind the lipid portion of the analyte, and an indicator. Upon addition of a glycolipid, a clear increase of fluorescence was detected.
Solar Cells
All-Inorganic CsPb1−xGexI2Br Perovskite with Enhanced Phase Stability and Photovoltaic Performance
- Pages: 12745-12749
- First Published: 01 August 2018
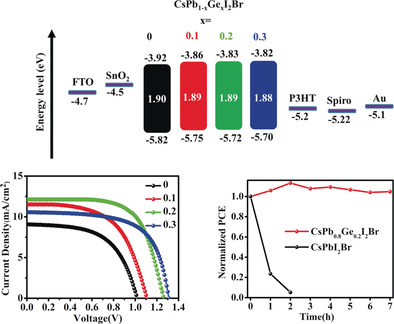
Germanium is for the first time reported to incorporate in all-inorganic CsPbI2Br perovskite and lead to enhanced phase stability and photovoltaic performance. A large VOC of up to 1.34 V and a high PCE of 10.8 % were achieved by planar perovskite solar cells (PSCs) that were prepared in an uncontrolled humid air atmosphere without a glovebox, which are remarkable records for the CsPbI2Br PSCs.
Electrochemistry
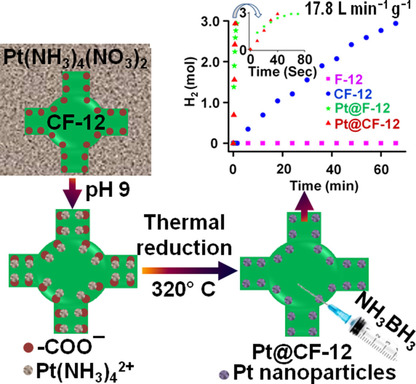
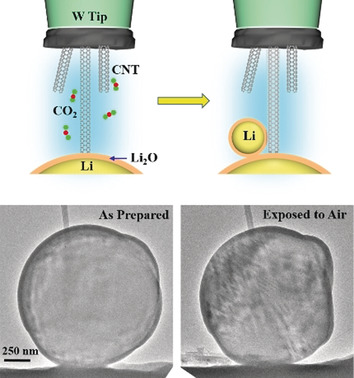
Air-Stable Lithium Spheres Produced by Electrochemical Plating
- Pages: 12750-12753
- First Published: 31 July 2018
Metalloenzymes
Two-Color Valence-to-Core X-ray Emission Spectroscopy Tracks Cofactor Protonation State in a Class I Ribonucleotide Reductase
- Pages: 12754-12758
- First Published: 03 August 2018
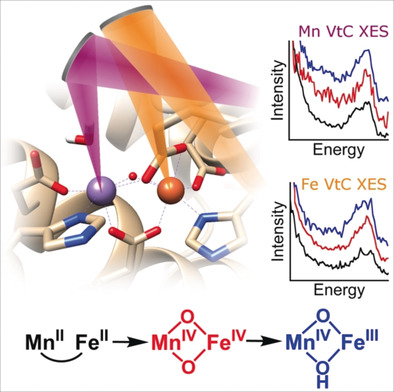
Probing protonation: Two-color valence-to-core X-ray emission spectroscopy is used to probe the protonation patterns of several metallocofactor oxidation states involved in the activation of a class I-c ribonucleotide reductase from Chlamydia trachomatis. These spectra—augmented by insight from DFT computations—allow assignment of MnIV(O)2FeIV and MnIV(O)(OH)FeIII states during enzyme activation.
Copolymerization
Ring-Opening Copolymerization of Maleic Anhydride with Functional Epoxides: Poly(propylene fumarate) Analogues Capable of Post-Polymerization Modification
- Pages: 12759-12764
- First Published: 06 August 2018
Perovskites | Hot Paper
Small-Band-Gap Halide Double Perovskites
- Pages: 12765-12770
- First Published: 07 August 2018
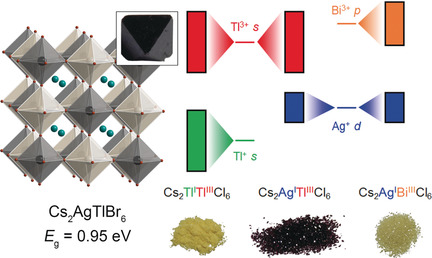
Unlike in ABX3 perovskites (X=halide), the band-gap transition in A2BB′X6 double perovskites has substantial metal-to-metal (B to B′) charge-transfer character, which allows access to small band gaps by aligning the energies of the B-site metal frontier orbitals, as exemplified in the new double perovskites Cs2AgTlX6; X=Cl and Br.
Drug Delivery
Modular Redesign of a Cationic Lytic Peptide To Promote the Endosomal Escape of Biomacromolecules
- Pages: 12771-12774
- First Published: 12 August 2018
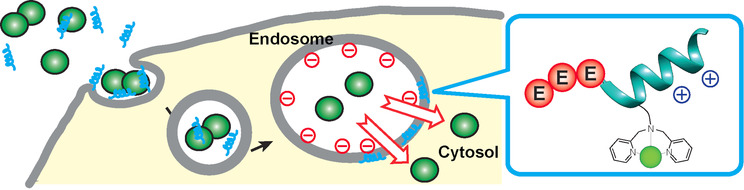
Break the trap: Inefficient endosomal escape into the cytosol has been a bottleneck in intracellular delivery of biomacromolecules. With appropriate chemical modifications, a cationic amphiphilic peptide, Mastoparan X, became a useful delivery tool that selectively disrupts the endosomal membranes and releases entrapped materials.
Silver Clusters
Smart Transformation of a Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Shell Controlled by Thiolate Silver(I) Nanocluster Core in Cluster@Clusters Dendrimers
- Pages: 12775-12779
- First Published: 14 August 2018
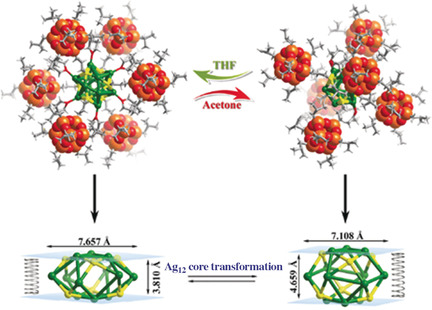
An atom-precise Ag12@POSS6 dendritic complex (POSS=polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) has been synthesized. The central silver(I) cluster core underwent a reversible structural transformation with solvent stimuli, leading to the rearrangement of the shell POSS clusters from pseudo-octahedral to quasi-octahedral.
Cytotoxic Copper Complexes
Leveraging γ-Glutamyl Transferase To Direct Cytotoxicity of Copper Dithiocarbamates against Prostate Cancer Cells
- Pages: 12780-12784
- First Published: 19 July 2018
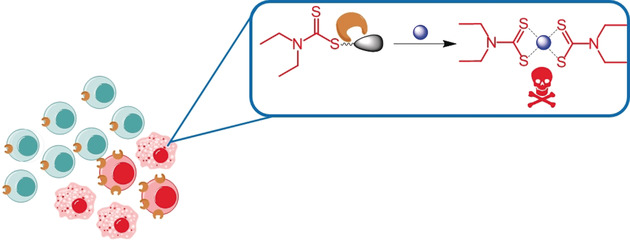
Chelator in disguise: Dithiocarbamate, a metal ion chelator, is masked for its ability to bind to CuII with a γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) enzyme trigger. Activated by GGT overexpressed in cancer cells, the chelator is unveiled to form cytotoxic Cu complexes in situ selectively in GGT-expressing cancer cells.
Halogen Bonding
Dramatically Enhanced Solubility of Halide-Containing Organometallic Species in Diiodomethane: The Role of Solvent⋅⋅⋅Complex Halogen Bonding
- Pages: 12785-12789
- First Published: 03 August 2018
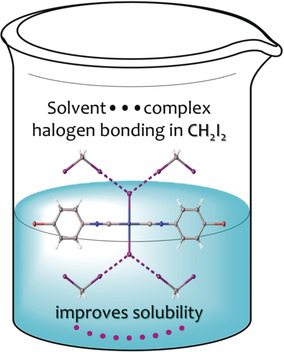
The unique solvation properties of diiodomethane towards halide-containing organometallic species are associated with its enhanced σ-hole-donating ability, which leads to stronger solvent–(metal complex) halogen bonding. The introduction of additional halogen atoms in the organometallic species attenuates the strength of the halogen bonding.
Electrocatalysis
Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots Enhance the Activity of Bi2O3 Nanosheets for Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 in a Wide Negative Potential Region
- Pages: 12790-12794
- First Published: 03 August 2018
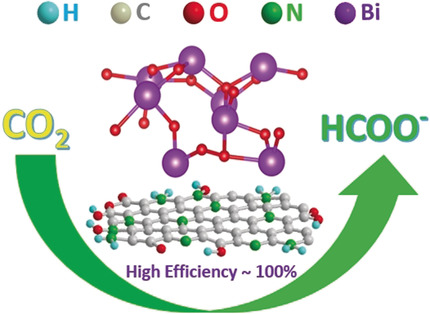
Waiting for a mate: A bismuth oxide nanosheet/nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot composite catalyst (NGQDs) for the highly efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate was prepared. NGQDs significantly enhance the activity of Bi2O3 nanosheets, achieving almost 100 % formate Faraday efficiency at a moderate overpotential of 0.7 V and an average formate Faraday efficiency of 95.6 % over a wide negative potential range from −0.9 V to −1.2 V vs. RHE.
Proteins
A Carboxylate to Amide Substitution That Switches Protein Folds
- Pages: 12795-12798
- First Published: 10 August 2018
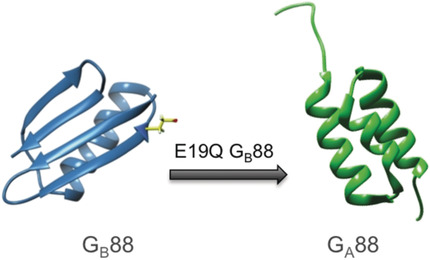
Metamorphic proteins are prone to adopting alternative conformations. By performing a comparative study on the denatured states of two proteins sharing nearly identical amino acid sequences (88 %) but different topologies, a site-directed mutant, resulting in a switch in the folding, was designed. This finding represents a direct demonstration of the role of the denatured state in dictating the selection of pathways to the native state.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Enantioselective Construction of Tertiary Boronic Esters by Conjunctive Cross-Coupling
- Pages: 12799-12803
- First Published: 09 August 2018
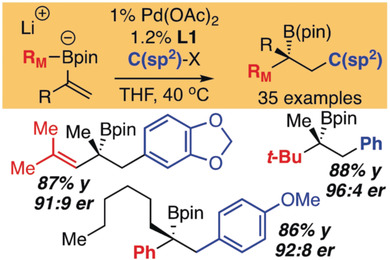
Catalytic conjunctive cross-coupling has been developed to construct enantiomerically enriched tertiary alkylboronic esters. These reactions occur with good yield and enantioselectivity for a range of substrates. Mechanistic experiments reveal aspects of the catalytic cycle that allow hindered substrates to react without significant complicating side reactions.
Fullerenes
Construction of a Metal-Free Electron Spin System by Encapsulation of an NO Molecule Inside an Open-Cage Fullerene C60 Derivative
- Pages: 12804-12808
- First Published: 30 July 2018
Intermetallic Compounds | Hot Paper
Lithium–Oxygen Batteries
An Extremely Simple Method for Protecting Lithium Anodes in Li-O2 Batteries
- Pages: 12814-12818
- First Published: 06 August 2018
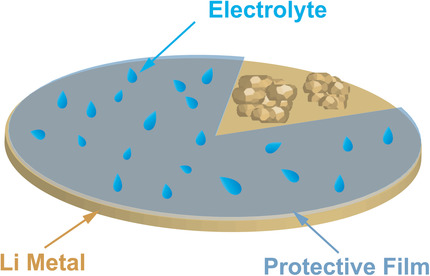
Protective coating: The stability of lithium anodes plays a vital role in improving the cycle life of Li-O2 batteries. A convenient method is presented to produce a film on a lithium surface by chemical reactions between lithium metal and 1,4-dioxacyclohexane. The protective film could reduce the morphology changes and suppress the parasitic reactions of lithium anodes and endow Li-O2 batteries with enhanced cycling stability.
Photochemistry
Photo-Organocatalytic Enantioselective Radical Cascade Reactions of Unactivated Olefins
- Pages: 12819-12823
- First Published: 10 August 2018
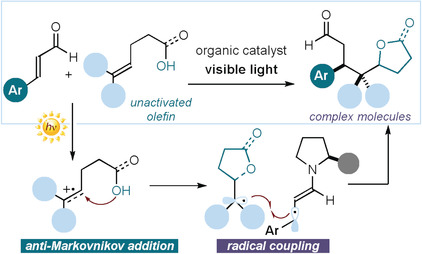
A radical approach: A photochemical asymmetric radical cascade process that converts unactivated olefins and α,β-unsaturated aldehydes into chiral adducts in a single step is reported. This enantioselective strategy, which is triggered by the excited-state reactivity of chiral iminium ion intermediates, combines two sequential radical-based bond-forming events.
Upconversion Nanoparticles | Very Important Paper
High-Capacity Upconversion Wavelength and Lifetime Binary Encoding for Multiplexed Biodetection
- Pages: 12824-12829
- First Published: 12 August 2018
Analytical Methods
Rationally Designed Fluorescence .OH Probe with High Sensitivity and Selectivity for Monitoring the Generation of .OH in Iron Autoxidation without Addition of H2O2
- Pages: 12830-12834
- First Published: 14 August 2018
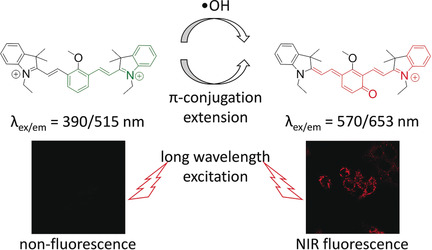
A sensitive fluorescent probe capable of detecting trace .OH from iron autoxidation is developed by utilizing both the unique aromatic hydroxylation and the electrophilicity of .OH. The capability of the probe is demonstrated by imaging .OH generated in living cells under iron autoxidation and various stimuli, revealing that the basal .OH level in RAW 264.7 cells is lower than that in HeLa cells.
Polymer Synthesis | Very Important Paper
Functionalizable Stereocontrolled Cyclopolyethers by Ring-Closing Metathesis as Natural Polymer Mimics
- Pages: 12835-12839
- First Published: 06 June 2018
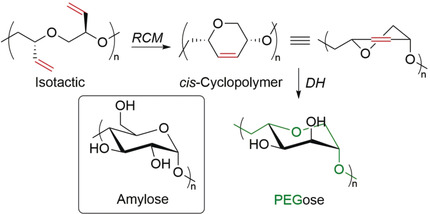
Off the PEG: Ruthenium-catalyzed ring-closing metathesis (RCM) under careful control of the catalyst, concentration, and temperature allows the stereocontrolled synthesis of 1,4-linked six-membered cyclopolyethers. Post-polymerization modification by dihydroxylation (DH) affords polymers with a poly(ethylene glycol) backbone and sugar-like functionalities (“PEGose”).
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Operando X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Shows Iron Oxidation Is Concurrent with Oxygen Evolution in Cobalt–Iron (Oxy)hydroxide Electrocatalysts
- Pages: 12840-12844
- First Published: 15 August 2018
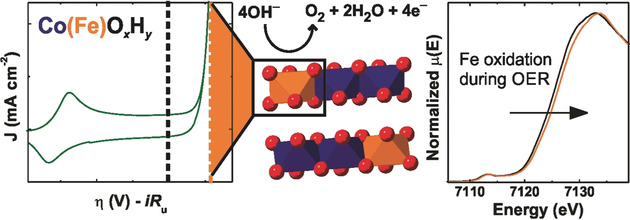
Fe-containing Co and Ni (oxy)hydroxides are the fastest-known catalysts for water oxidation in alkaline conditions. Fe is essential to the high activity, but its role in the mechanism is under active investigation. Now it is shown that oxygen evolution is concurrent with the oxidation of Fe cations and shortening of Fe−O bonds. The results are consistent with density functional theory calculations and may indicate Fe-based active sites.
Hydrocarbon Separation
Separation of Aromatics/Cyclic Aliphatics by Nonporous Adaptive Pillararene Crystals
- Pages: 12845-12849
- First Published: 08 August 2018
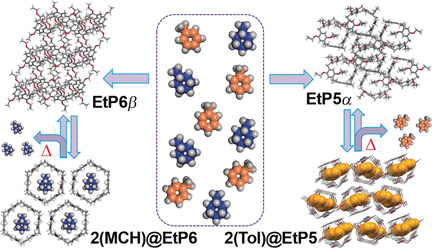
Energy-efficient separation of aromatics and cyclic aliphatics is a major industrial sustainability challenge. A flexible molecular material, namely nonporous adaptive crystals of pillararenes, can be used to separate them. Pillar[5]arene is shown to separate vapors of toluene from methylcyclohexane, while pillar[6]arene separates methylcyclohexane from toluene with over 98 % specificity in the solid state.
Functional Nucleic Acids
Selection of Anti-gluten DNA Aptamers in a Deep Eutectic Solvent
- Pages: 12850-12854
- First Published: 02 August 2018
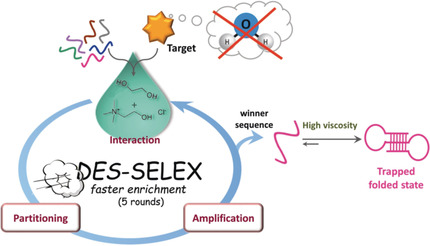
DES-SELEX: Aptamers can be selected in deep eutectic solvents composed of choline chloride and 1,2-ethanediol faster than in aqueous media. These highly solubilizing media, mimicking the intracellular environment, allow targeting non-soluble or poorly water-soluble species, which include targets of great interest in biomedical, pharmaceutical, and food analysis.
Electrochemistry | Hot Paper
Adsorbed Intermediates in Oxygen Reduction on Platinum Nanoparticles Observed by In Situ IR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 12855-12858
- First Published: 12 July 2018
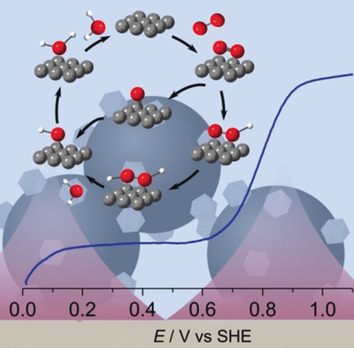
In situ IR spectroscopy provides insight into the mechanism of the oxygen reduction reaction on supported platinum. Observation of adsorbed superoxide and hydroperoxide provides evidence for an associative contribution to the mechanism. Further correlation with the catalytic current suggests that an additional pathway is also important at high potential.
Homogeneous Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Ylide-Functionalized Phosphines: Strong Donor Ligands for Homogeneous Catalysis
- Pages: 12859-12864
- First Published: 03 June 2018
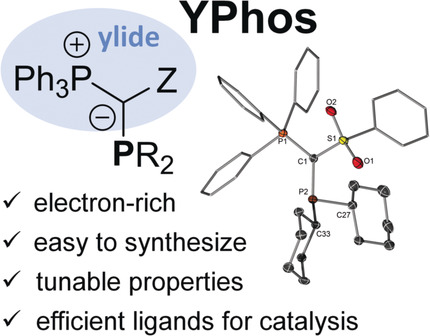
YPhos: The ylide-functionalized phosphines (YPhos), a novel class of strong donor ligands, are readily accessible from commercially available starting materials and exhibit easily tunable electronic and steric properties. The huge potential of these ligands in catalysis is demonstrated by their use in gold catalysis, with excellent performance observed at low catalyst loadings under mild reaction conditions.
Nitride Functionalization
Room-Temperature Functionalization of N2 to Borylamine at a Molybdenum Complex
- Pages: 12865-12868
- First Published: 24 July 2018
Halogenation
Applications of Selenonium Cations as Lewis Acids in Organocatalytic Reactions
- Pages: 12869-12873
- First Published: 07 August 2018
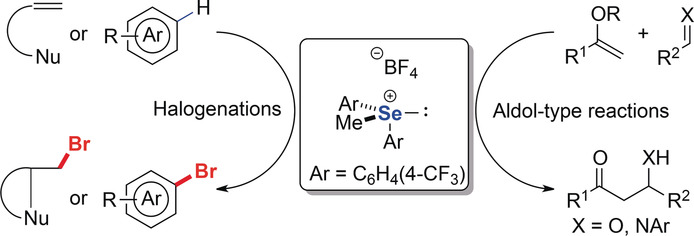
Se salt: The use of trisubstituted selenonium salts as organic Lewis acids in electrophilic halogenation and aldol-type reactions has been developed. The substrate scope is broad. The reaction conditions are mild and compatible with various functionalities. This study opens a new avenue for the development of non-metallic Lewis acid catalysis.
Ruthenium Complexes
Syntheses and Structures of Ruthenium Complexes Containing a Ru-H-Tl Three-Center–Two-Electron Bond
- Pages: 12874-12879
- First Published: 07 August 2018
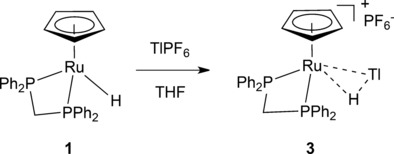
Although η2-H−EXn σ-complexes are well-known when E is a Group 13 or 14 element (E=B, Al, Ga, C, Si, Ge, Sn), η2-H−EXn σ-complexes where E is a period 6 main-group element were previously unknown. Now the synthesis and structural characterization is presented of ruthenium σ-complexes [CpRu(PP)(η2-(H-Tl))]+ (PP=dppm, dppe), which contain TlH, a hydride of a period-6 main group element.
Oligosaccharide Synthesis
Synthesis of Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate Nonasaccharide as a Novel Anticoagulant Targeting Intrinsic Factor Xase Complex
- Pages: 12880-12885
- First Published: 01 August 2018
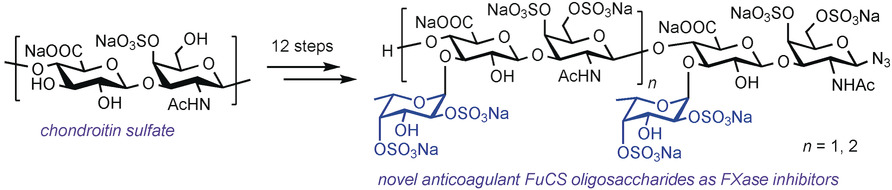
To the nines: Structurally defined fucosylated chondroitin sulfate hexa- and nonasaccharides were synthesized in 12 linear steps from chondroitin sulfate through the enzymatic degradation of chondroitin (see scheme). The nonasaccharide displayed selective intrinsic factor Xase complex inhibitory activity by binding to factor IXa with high affinity, thus showing promise for the development of anticoagulant agents targeting the intrinsic coagulation pathway.
Hydrocarbon Synthesis | Hot Paper
Cascade Reactions in Tunable Lamellar Micro- and Mesopores for C=C Bond Coupling and Hydrocarbon Synthesis
- Pages: 12886-12890
- First Published: 05 July 2018
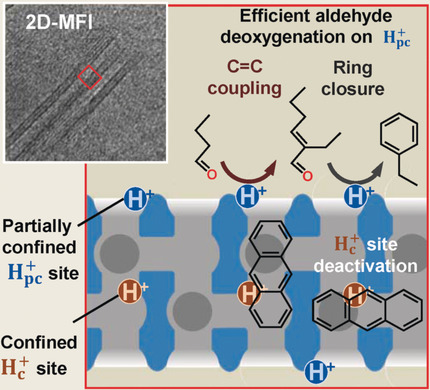
Lamellar MFI zeolite nanosheets (2D-MFI) contain a large fraction of partially confined H+ sites ( ) residing at the micro- and mesopore intercepts, which are effective for C=C bond coupling and ring closure of aldehydes to produce aromatic compounds. These sheets resemble a nanometer-sized plug flow reactor; they promote formation and effective removal of aromatic products in cascade reactions, thus mitigating coke deposition.
) residing at the micro- and mesopore intercepts, which are effective for C=C bond coupling and ring closure of aldehydes to produce aromatic compounds. These sheets resemble a nanometer-sized plug flow reactor; they promote formation and effective removal of aromatic products in cascade reactions, thus mitigating coke deposition.
C−H Functionalization
Metal- and Oxidant-Free Alkenyl C−H/Aromatic C−H Cross-Coupling Using Electrochemically Generated Iodosulfonium Ions
- Pages: 12891-12895
- First Published: 29 August 2018
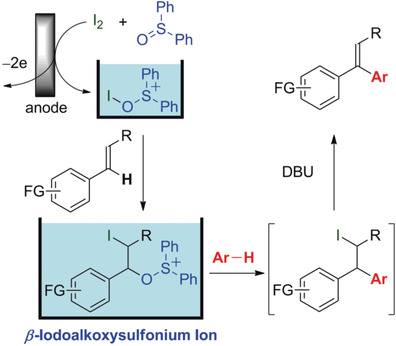
A three-step transformation consisting of 1) addition of electrochemically generated iodosulfonium ions to vinylarenes, 2) nucleophilic substitution by subsequently added aromatic compounds, and 3) elimination of HI with a base enables metal- and oxidant-free alkenyl C−H/aromatic C−H cross-coupling. This one-pot transformation provides an easy access to various 1,1-diarylethylenes.
Biosensors
Fluorescence Probes for ALKBH2 Allow the Measurement of DNA Alkylation Repair and Drug Resistance Responses
- Pages: 12896-12900
- First Published: 11 August 2018
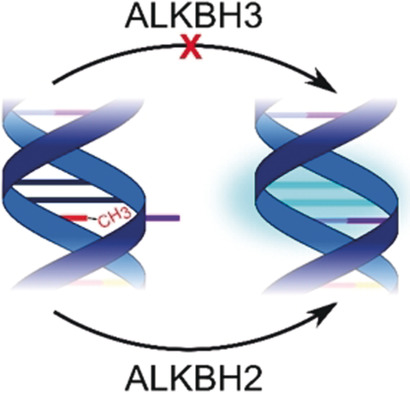
Fluoresce de Résistance: The demethylase ALKBH2 is critical for repairing DNA; however, it can be hijacked in tumors to develop chemotherapy resistance. The first fluorescent sensors for ALKBH2 are reported that specifically detect its activity in real-time both in vitro and in cell lysates. Assays are developed for direct quantification of cellular ALKBH2 activity in response to chemotherapeutics as well as high-throughput screening.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Access to P- and Axially Chiral Biaryl Phosphine Oxides by Enantioselective CpxIrIII-Catalyzed C−H Arylations
- Pages: 12901-12905
- First Published: 25 July 2018
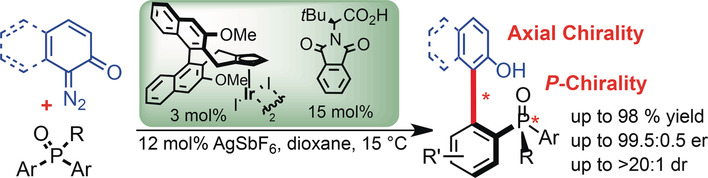
An enantioselective C−H arylation of phosphine oxides with o-quinone diazides is catalyzed by a CpxIrIII complex and chiral carboxylic acid co-catalyst. It provides a unifying access to P-chiral phosphine oxides, atropo-enantioselective construction of sterically demanding biaryl backbones, and a selective assembly of axial and P-chiral compounds in excellent yields and diastereo- and enantioselectivities.
Manganese Catalysis
Selective Hydroarylation of 1,3-Diynes Using a Dimeric Manganese Catalyst: Modular Synthesis of Z-Enynes
- Pages: 12906-12910
- First Published: 13 August 2018
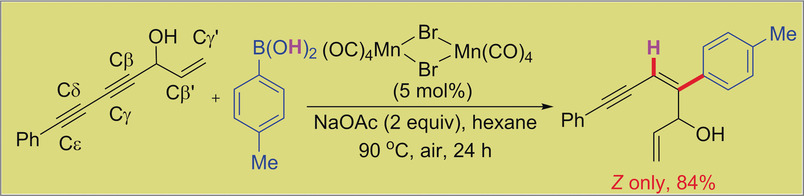
Doubling up on M n' Mn: Hydroarylation of unsymmetrical 1,3-diyne alcohols with arylboronic acids, catalyzed by a dimeric MnI catalyst, has been achieved with predictive regio-, stereo-, and chemoselectivity. It offers a general, convenient, and practical strategy for the modular synthesis of multisubstituted Z-configurated conjugated enynes.
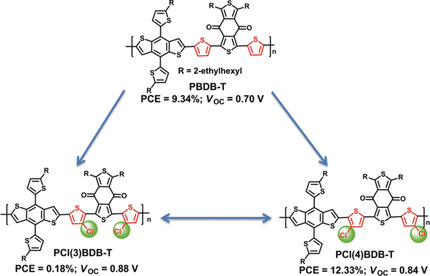
Polymer Solar Cells | Hot Paper
The Crucial Role of Chlorinated Thiophene Orientation in Conjugated Polymers for Photovoltaic Devices
- Pages: 12911-12915
- First Published: 02 August 2018
Chiral Allenes
Enantio- and Diastereoselective Synthesis of Chiral Allenes by Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric [3+2] Cycloaddition Reactions
- Pages: 12916-12920
- First Published: 02 August 2018
![Enantio- and Diastereoselective Synthesis of Chiral Allenes by Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric [3+2] Cycloaddition Reactions](/cms/asset/fcf078ad-d00f-46c5-a073-84b7ae837081/anie201808345-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A palladium-catalyzed [3+2] cycloaddition of racemic allenes to form densely functionalized chiral allenes has been developed. This catalytic asymmetric procedure was utilized to obtain various cyclopentanes, pyrrolidines, and spirocycles with very good control over the regio-, enantio-, and diastereoselectivity.
Cyclizations
Synthesis of Spirocyclic Ethers by Enantioselective Copper-Catalyzed Carboetherification of Alkenols
- Pages: 12921-12924
- First Published: 17 August 2018
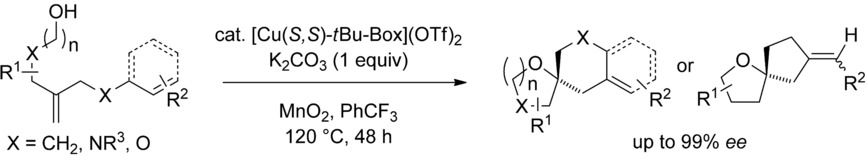
Two rings: A copper-catalyzed enantioselective alkene carboetherification that provides 5,5-, 5,6-, and 6,6-spirocyclic products containing fully substituted chiral carbon centers, with up to 99 % enantiomeric excess, is disclosed. This reaction features the formation of two rings from acyclic 1,1-disubstituted alkenols functionalized with arenes, alkenes, or alkynes, and is a powerful approach to the synthesis of chiral spirocyclic ethers.
Amides
Nickel-Catalyzed Amide Bond Formation from Methyl Esters
- Pages: 12925-12929
- First Published: 16 August 2018
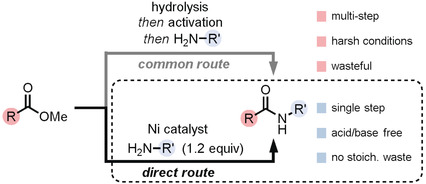
The cross-coupling between diverse esters and amines to form amides is enabled by the use of Ni catalysis. Unlike traditional approaches to amide bond formation, the reaction works in the absence of acidic or basic additives, and both aliphatic amines and aniline derivatives can be effectively utilized.
Organometallics
Generation and Application of (Diborylmethyl)zinc(II) Species: Access to Enantioenriched gem-Diborylalkanes by an Asymmetric Allylic Substitution
- Pages: 12930-12934
- First Published: 02 July 2018
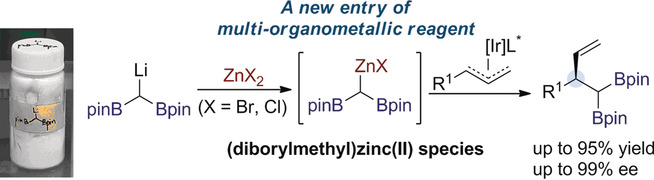
Asymmetric catalysis: (Diborylmethyl)zinc(II) species have been generated by transmetalation between isolable (diborylmethyl)lithium and zinc(II) halides. The zinc(II) species have been applied to the synthesis of enantioenriched gem-diborylalkanes through iridium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic alkylation reaction.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Cobalt-Catalyzed Enantioselective Synthesis of Chiral gem-Bis(boryl)alkanes
- Pages: 12935-12939
- First Published: 16 August 2018
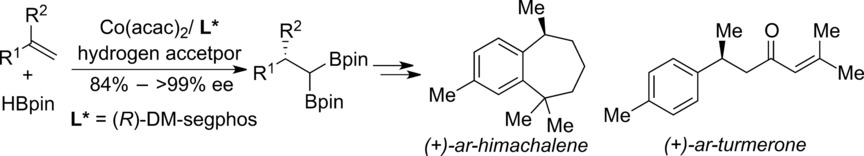
The cobalt-catalyzed asymmetric diborylation of gem-disubstituted alkenes enables the highly enantioselective synthesis of chiral gem-bis(boryl)alkanes. The synthetic utility of these products was exemplified through several stereospecific derivatizations and the synthesis of sesquiterpene and sesquiterpenoid natural products.
Radicals
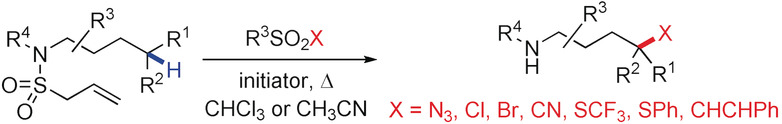
Site-Selective Remote Radical C−H Functionalization of Unactivated C−H Bonds in Amides Using Sulfone Reagents
- Pages: 12940-12944
- First Published: 06 August 2018
Photochemistry
Photoinduced Remote Functionalization of Amides and Amines Using Electrophilic Nitrogen Radicals
- Pages: 12945-12949
- First Published: 03 August 2018
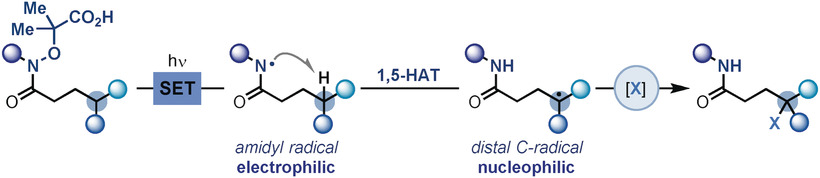
With HAT in hand: Reported here is a photoinduced radical cascade strategy for the divergent functionalization of amides and protected amines. It is based on the oxidative generation of electrophilic amidyl radicals and their subsequent transposition by 1,5-H-atom transfer, which results in remote fluorination, chlorination, thioetherification, cyanation, and alkynylation. This strategy was used for the late-stage functionalization of amino acids and a dipeptide.
Cluster Compounds
Charged Si9 Clusters in Neat Solids and the Detection of [H2Si9]2− in Solution: A Combined NMR, Raman, Mass Spectrometric, and Quantum Chemical Investigation
- Pages: 12950-12955
- First Published: 16 July 2018
![Charged Si9 Clusters in Neat Solids and the Detection of [H2Si9]2− in Solution: A Combined NMR, Raman, Mass Spectrometric, and Quantum Chemical Investigation](/cms/asset/af1d9d1a-0ee0-4c29-abd3-a41b38b2556f/anie201804756-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Polyanionic silicon clusters are provided by the Zintl phases K4Si4, comprising [Si4]4− units, and K12Si17, consisting of [Si4]4− and [Si9]4− clusters. Charged Si9 clusters were detected for the first time by 29Si NMR spectroscopy in the solid state and in solution. 29Si and 1H NMR spectra reveal the [H2Si9]2− cluster anion in solution and J(29Si—1H) coupling shows these is proton scrambling.
Silicides
The Structure of [HSi9]3− in the Solid State and Its Unexpected Highly Dynamic Behavior in Solution
- Pages: 12956-12960
- First Published: 13 July 2018
![The Structure of [HSi9]3− in the Solid State and Its Unexpected Highly Dynamic Behavior in Solution](/cms/asset/2282afab-dcf7-4c53-8c43-d06de45547c1/anie201807080-toc-0001-m.jpg)
It's flexible! The characteristic multiplicity patterns of 29Si and 1H NMR resonances and CEST studies reveal the highly dynamic behavior of [HSi9]3− in solution. Theoretical considerations corroborate a highly dynamic Si8 entity and a Si−H moiety with slow proton hopping. A monocapped square-antiprismatic structure with the H atom localized at one vertex of the basal plane was identified in single-crystal studies.
Molecular Recognition
A Calixarene-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Highly Selective NO2 Detection
- Pages: 12961-12965
- First Published: 20 July 2018
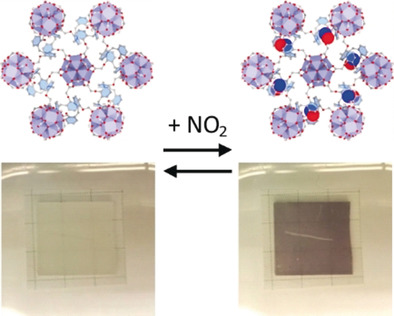
A zirconium-based MOF with calixarene linkers was synthesized and characterized. It exhibits a complex three-dimensional pore system that exposes the calixarenes for the selective detection of NO2. The impressive and reversible color change from white to blue makes the material a visual sensor for NO2 at room temperature.
Gold Catalysis
Gold-Catalyzed Dimerization of Diarylalkynes: Direct Access to Azulenes
- Pages: 12966-12970
- First Published: 06 August 2018
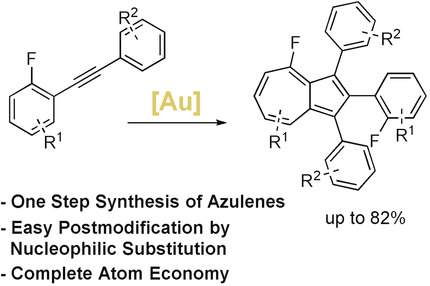
A fully atom-economic gold-catalyzed reaction enables the direct synthesis of substituted azulenes from easily accessible starting materials. A fluorine substituent as a strong +M donor initiates this reaction. The obtained scaffolds can be easily functionalized at the seven-membered ring in a selective manner.
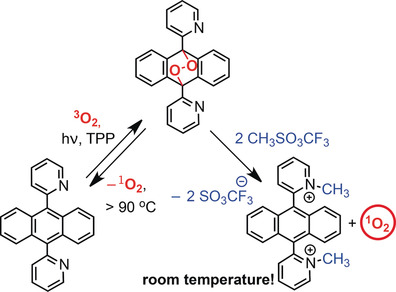
Singlet Oxygen
Release of Singlet Oxygen from Aromatic Endoperoxides by Chemical Triggers
- Pages: 12971-12975
- First Published: 02 August 2018