A Calixarene-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Highly Selective NO2 Detection
Marcel Schulz
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and ZFM—Center for Solid State Chemistry and New Materials, Leibniz University Hannover, Callinstraße 9, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAdrian Gehl
Institute of Electrical Engineering and Measurement Technology, Leibniz University Hannover, Appelstraße 9A, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorJakob Schlenkrich
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and ZFM—Center for Solid State Chemistry and New Materials, Leibniz University Hannover, Callinstraße 9, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorHendrik A. Schulze
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and ZFM—Center for Solid State Chemistry and New Materials, Leibniz University Hannover, Callinstraße 9, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Stefan Zimmermann
Institute of Electrical Engineering and Measurement Technology, Leibniz University Hannover, Appelstraße 9A, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Andreas Schaate
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and ZFM—Center for Solid State Chemistry and New Materials, Leibniz University Hannover, Callinstraße 9, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorMarcel Schulz
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and ZFM—Center for Solid State Chemistry and New Materials, Leibniz University Hannover, Callinstraße 9, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAdrian Gehl
Institute of Electrical Engineering and Measurement Technology, Leibniz University Hannover, Appelstraße 9A, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorJakob Schlenkrich
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and ZFM—Center for Solid State Chemistry and New Materials, Leibniz University Hannover, Callinstraße 9, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorHendrik A. Schulze
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and ZFM—Center for Solid State Chemistry and New Materials, Leibniz University Hannover, Callinstraße 9, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Stefan Zimmermann
Institute of Electrical Engineering and Measurement Technology, Leibniz University Hannover, Appelstraße 9A, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Andreas Schaate
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and ZFM—Center for Solid State Chemistry and New Materials, Leibniz University Hannover, Callinstraße 9, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Laboratory for Nano and Quantum Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Schneiderberg 39, 30167 Hannover, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
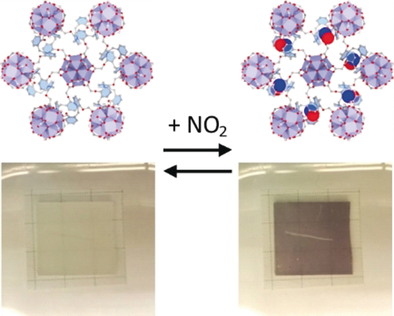
A zirconium-based MOF with calixarene linkers was synthesized and characterized. It exhibits a complex three-dimensional pore system that exposes the calixarenes for the selective detection of NO2. The impressive and reversible color change from white to blue makes the material a visual sensor for NO2 at room temperature.
Abstract
A calixarene-based metal–organic framework (Zr-cal, [Zr6O4(OH)4(FA)6]2(cal)3], FA=formate, cal=1,3-alt-25,26,27,28-tetrakis[(carboxy)methoxy]calixarene) was synthesized and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The three-dimensional framework is a 4,6-connected network of gar topology and exhibits two equal but nonintersecting three-dimensional pore systems. It has a specific BET surface area of 670 m2 g−1, and the calixarene cavities are accessible through the pore systems. The exposed calixarenes can be used for the visual detection and encapsulation of NO2 through the formation of deeply colored charge–transfer complexes inside the MOF. The highly selective complexation was analyzed by UV/Vis and IR spectroscopy, and the stability of the material was confirmed by powder X-ray diffraction and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Finally, the MOF was used as a sensor material in a home-made sensor cell and showed high sensitivity for NO2.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201805355-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1,001.8 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1C. T. Driscoll et al., BioScience 2003, 53, 357.
- 2
- 2aM. Kampa, E. Castanas, Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362;
- 2bM. Kraft, T. Eikmann, A. Kappos, N. Künzli, R. Rapp, K. Schneider, H. Seitz, J.-U. Voss, H. E. Wichmann, Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2005, 208, 305;
- 2cU. Latza, S. Gerdes, X. Baur, Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2009, 212, 271.
- 3
- 3aR. Kumar, O. Al-Dossary, G. Kumar, A. Umar, Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 97;
- 3bL. Valentini, I. Armentano, J. M. Kenny, C. Cantalini, L. Lozzi, S. Santucci, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 961.
- 4S. R. Nalage, A. T. Mane, R. C. Pawar, C. S. Lee, V. B. Patil, Ionics 2014, 20, 1607.
- 5
- 5aJ. Kong, N. R. Franklin, C. Zhou, M. G. Chapline, S. Peng, K. Cho, H. Dai, Science 2000, 287, 622;
- 5bS. Cui, H. Pu, S. A. Wells, Z. Wen, S. Mao, J. Chang, M. C. Hersam, J. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8632;
- 5cH. Xia, Y. Wang, F. Kong, S. Wang, B. Zhu, X. Guo, J. Zhang, S. Wu, Sens. Actuators B 2008, 134, 133.
- 6S.-I. Ohira, E. Wanigasekara, D. M. Rudkevich, P. K. Dasgupta, Talanta 2009, 77, 1814.
- 7
- 7aD. M. Rudkevich, Y. Kang, A. V. Leontiev, V. G. Organo, G. V. Zyryanov, Supramol. Chem. 2005, 17, 93;
- 7bR. Rathore, S. H. Abdelwahed, I. A. Guzei, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13582.
- 8R. Rathore, S. V. Lindeman, K. S. S. P. Rao, D. Sun, J. K. Kochi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2123;
10.1002/1521-3773(20000616)39:12<2123::AID-ANIE2123>3.0.CO;2-4 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2000, 112, 2207.
- 9G. V. Zyryanov, Y. Kang, D. M. Rudkevich, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2997.
- 10
- 10aE. Wanigasekara, A. V. Leontiev, V. G. Organo, D. M. Rudkevich, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 2254;
- 10bP. K. Thallapally, B. P. McGrail, J. L. Atwood, Chem. Commun. 2007, 1521.
- 11G. V. Zyryanov, Y. Kang, S. P. Stampp, D. M. Rudkevich, Chem. Commun. 2002, 2792.
- 12C. M. Kane, A. Banisafar, T. P. Dougherty, L. J. Barbour, K. T. Holman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4377.
- 13Y. Kang, D. M. Rudkevich, Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11219.
- 14D. M. Rudkevich, G. V. Zyryanov, Comments Inorg. Chem. 2015, 35, 128.
- 15V. Sgarlata, V. G. Organo, D. M. Rudkevich, Chem. Commun. 2005, 5630.
- 16J. L. C. Rowsell, O. M. Yaghi, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 73, 3.
- 17C. Janiak, J. K. Vieth, New J. Chem. 2010, 34, 2366.
- 18
- 18aH. Bux, A. Feldhoff, J. Cravillon, M. Wiebcke, Y.-S. Li, J. Caro, Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 2262;
- 18bK. Adil, Y. Belmabkhout, R. S. Pillai, A. Cadiau, P. M. Bhatt, A. H. Assen, G. Maurin, M. Eddaoudi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3402.
- 19F. Vermoortele et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11465.
- 20
- 20aD. Farrusseng, S. Aguado, C. Pinel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7502; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 7638;
- 20bS. M. J. Rogge et al., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3134.
- 21D. Cunha, C. Gaudin, I. Colinet, P. Horcajada, G. Maurin, C. Serre, J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1101.
- 22N. J. Hinks, A. C. McKinlay, B. Xiao, P. S. Wheatley, R. E. Morris, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 129, 330.
- 23
- 23aM. G. Campbell, S. F. Liu, T. M. Swager, M. Dincă, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13780;
- 23bV. Stavila, A. A. Talin, M. D. Allendorf, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5994.
- 24
- 24aO. Dalstein, E. Gkaniatsou, C. Sicard, O. Sel, H. Perrot, C. Serre, C. Boissière, M. Faustini, Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 14199;
10.1002/ange.201706745 Google Scholar
- 24bL. E. Kreno, K. Leong, O. K. Farha, M. Allendorf, R. P. van Duyne, J. T. Hupp, Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1105;
- 24cW. P. Lustig, S. Mukherjee, N. D. Rudd, A. V. Desai, J. Li, S. K. Ghosh, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3242.
- 25O. Shekhah, J. Liu, R. A. Fischer, C. Wöll, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1081.
- 26J. Park, J. H. Lee, J. Jaworski, S. Shinkai, J. H. Jung, Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 7181.
- 27
- 27aK.-M. Park, E. Lee, C. S. Park, S. S. Lee, Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 12085;
- 27bE. Lee, H. Ju, Y. Kang, S. S. Lee, K.-M. Park, Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 6052;
- 27cE. Lee, Y. Kim, J. Heo, K.-M. Park, Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 3556.
- 28
- 28aG. Zahn, P. Zerner, J. Lippke, F. L. Kempf, S. Lilienthal, C. A. Schröder, A. M. Schneider, P. Behrens, CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 9198;
- 28bA. Schaate, P. Roy, A. Godt, J. Lippke, F. Waltz, M. Wiebcke, P. Behrens, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 6643.
- 29C. G. Almeida, I. F. Souza, N. A. Liberto, M. J. Da Silva, S. A. Fernandes, M. Le Hyaric, Monatsh. Chem. 2015, 146, 1927.
- 30
- 30aK. S. Park, Z. Ni, A. P. Côté, J. Y. Choi, R. Huang, F. J. Uribe-Romo, H. K. Chae, M. O'Keeffe, O. M. Yaghi, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186;
- 30bM. Dincǎ, A. Dailly, J. R. Long, Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 10280;
- 30cX.-C. Shan, F.-l. Jiang, D.-Q. Yuan, H.-B. Zhang, M.-Y. Wu, L. Chen, J. Wei, S.-Q. Zhang, J. Pan, M.-C. Hong, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 1484.
- 31V. Alfredsson, M. W. Anderson, Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1141.
- 32
- 32aC. Caratelli, J. Hajek, F. G. Cirujano, M. Waroquier, F. X. Llabrés i Xamena, V. van Speybroeck, J. Catal. 2017, 352, 401;
- 32bY. Jiao, Y. Liu, G. Zhu, J. T. Hungerford, S. Bhattacharyya, R. P. Lively, D. S. Sholl, K. S. Walton, J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 23471.
- 33Z. Hu, D. Zhao, CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 4066.
- 34S. V. Rosokha, S. V. Lindeman, R. Rathore, J. K. Kochi, J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 3947.
- 35S. V. Rosokha, J. K. Kochi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8985.
- 36J. P. Manfred Reichenbächer, Strukturanalytik organischer und anorganischer Verbindungen, Teubner, Wiesbaden, 2007.