Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Titelbild
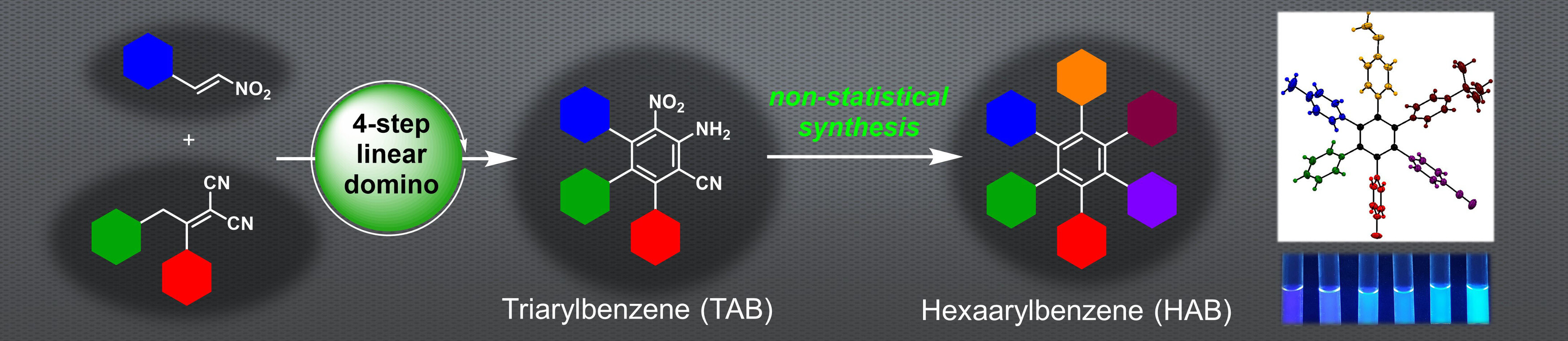
Titelbild: Four-Step Domino Reaction Enables Fully Controlled Non-Statistical Synthesis of Hexaarylbenzene with Six Different Aryl Groups (Angew. Chem. 41/2021)
- Page: 22257
- First Published: 03 September 2021

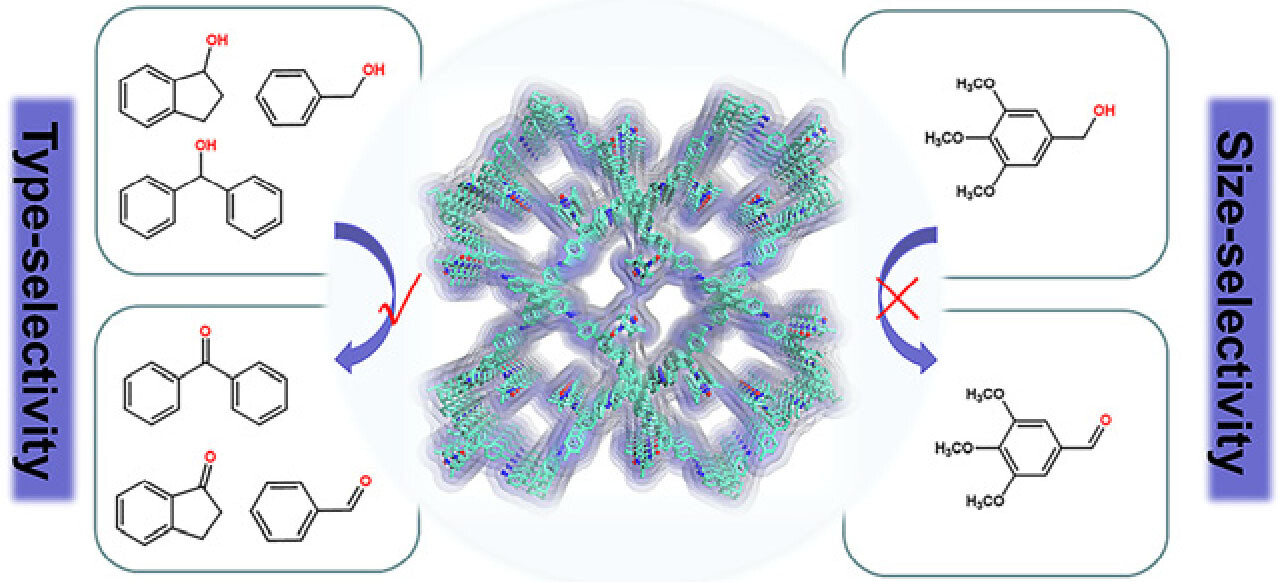
Hexaarylbenzol-Grundgerüste , die sechs verschiedene aromatische Ringe um einen zentralen Benzolkern enthalten, sind eine synthetische Herausforderung. In ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 22481 stellen Svetlana B. Tsogoeva und Mitarbeiter ein Verfahren vor, mit dem sich solche Hexaarylbenzole (HABs) einfach und unkompliziert herstellen lassen. In einer effizienten, vierstufigen Zweikomponenten-Dominoreaktion wird ein funktionalisiertes Triarylbenzol gebildet, das als Schlüsselintermediat verwendet wird, um asymmetrisch substituierte HABs in hoher Gesamtausbeute und ohne Beteiligung statistischer Schritte zu erhalten.
Innentitelbild: Molecular Basis for Two Stereoselective Diels–Alderases that Produce Decalin Skeletons (Angew. Chem. 41/2021)
- Page: 22258
- First Published: 09 August 2021

Bindung einer linksdrehenden oder rechtsdrehenden Faltung mit Flip: Eine lineare Kohlenwasserstoffkette, die ein Dien und ein Dienophil enthält, wird gefaltet und durch intramolekulare [4+2]-Cycloaddition in ein Dekalingrundgerüst umgewandelt. Die Substrate falten entgegengesetzt, binden aber in der gleichen Ausrichtung in die Taschen eines Paares von Diels-Alderasen, um Dekalingerüste mit enantiomeren Konformationen zu liefern, wie Naoki Kato, Shunji Takahashi und Shingo Nagano im Forschungsartikel auf S. 22575 berichten.
Innenrücktitelbild: Particle-by-Particle In Situ Characterization of the Protein Corona via Real-Time 3D Single-Particle-Tracking Spectroscopy (Angew. Chem. 41/2021)
- Page: 22767
- First Published: 21 June 2021

Ein Hochgeschwindigkeits-3D-Mikroskop wurde entwickelt, um die Proteinkorona von Nanopartikeln auf Einzelpartikelebene zu quantifizieren. Wie Xiaochen Tan und Kevin Welsher in ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 22533 berichten, kann das Mikroskop auf frei diffundierende Nanopartikel “einrasten”, um die fest gebundenen “harten” und dynamischen “weichen” Koronaschichten zu quantifizieren.
Rücktitelbild: Control Viscoelasticity of Polymer Networks with Crosslinks of Superposed Fast and Slow Dynamics (Angew. Chem. 41/2021)
- Page: 22768
- First Published: 12 July 2021

Eine supramolekulare Quervernetzung mit überlagerter schneller und langsamer Dynamik wird von Hao Chen, Yi Cao, Yebang Tan et al. im Forschungsartikel auf S. 22506 beschrieben. Diese Quervernetzung weist eine quantitativ maßgeschneiderte Molekulardynamik auf. Die wohldefinierte molekulare Dynamik der Vernetzungen ermöglicht die präzise Kontrolle der Viskoelastizität und des mechanischen Ansprechverhaltens der resultierenden Polymernetzwerke auf molekularer Ebene.
Frontispiz
Frontispiz: Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Decarboxylative Addition of β-Keto Acids to Heteroatom-Substituted Allenes
- First Published: 27 September 2021

Asymmetrische Katalyse Über die Palladium-katalysierte asymmetrische decarbonylierende Addition von β-Ketosäuren an Heteroatom-substituierte Allene berichten Young Ho Rhee et al. in der Zuschrift auf S. 22340.
Frontispiz: Superatom-in-Superatom [RhH@Ag24(SPhMe2)18]2− Nanocluster
- First Published: 27 September 2021
![Frontispiz: Superatom-in-Superatom [RhH@Ag24(SPhMe2)18]2− Nanocluster Volume 133 Issue 41, 2021](/cms/asset/43f3d8c2-cbbf-45b5-acbb-10013ec9c99f/ange202184162-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Nanocluster Im Forschungsartikel auf S. 22467 berichten Eunji Sim, Dongil Lee et al. über den Einbau eines Rhodiumhydrid-Superatoms in ein Cluster-Superatom zur Erzeugung eines stabilen Superatom-in-Superatom-Nanoclusters, [RhH@Ag24(SR)18]2−.
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis: Angew. Chem. 41/2021
- Pages: 22261-22279
- First Published: 27 September 2021
Berichtigungen
Berichtigung: Mechanistic Investigation on Copper–Arylacetylide Polymerization and Sensing Applications
- Page: 22278
- First Published: 27 September 2021
Berichtigung: Beyond the Polysulfide Shuttle and Lithium Dendrite Formation: Addressing the Sluggish Sulfur Redox Kinetics for Practical High-Energy Li-S Batteries
- Page: 22278
- First Published: 27 September 2021
Addendum
Addendum: Imidazotetrazines as Weighable Diazomethane Surrogates for Esterifications and Cyclopropanations
- Page: 22279
- First Published: 27 September 2021
Introducing …
Kurzaufsätze
Drug Transport
Pharma-molecule Transport across Bacterial Membranes: Detection and Quantification Approaches by Electrochemistry and Bioanalytical Methods
- Pages: 22284-22296
- First Published: 12 May 2021
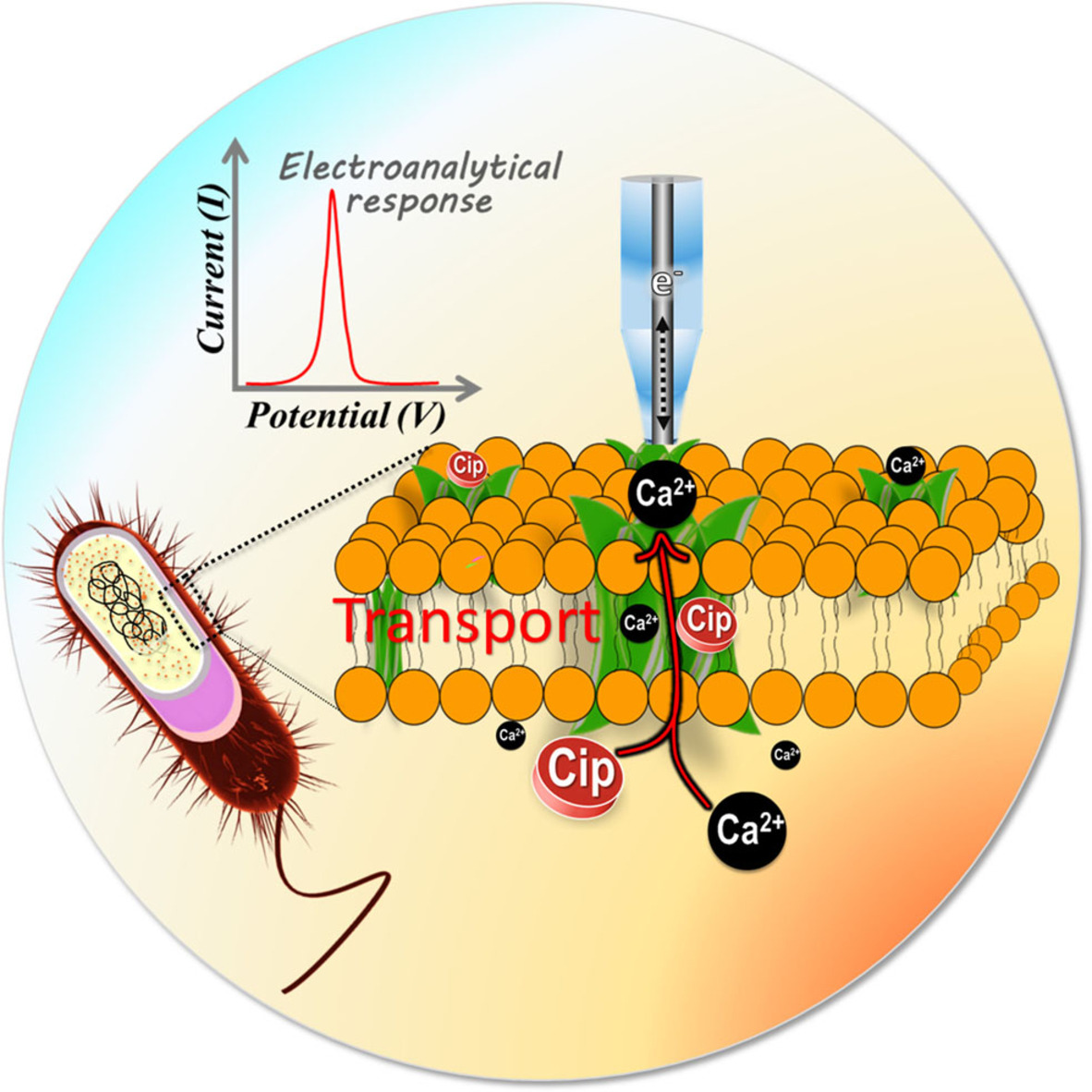
Knowledge about the membrane transport of antibiotics and other pharmacologically relevant molecules in bacteria is crucial towards understanding and overcoming antibiotic resistance. In this review, methods for the detection and quantification of membrane transport of pharma-molecules in bacteria are discussed.
Aufsätze
Medical Imaging
Enabling Clinical Technologies for Hyperpolarized 129Xenon Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy
- Pages: 22298-22319
- First Published: 20 May 2021
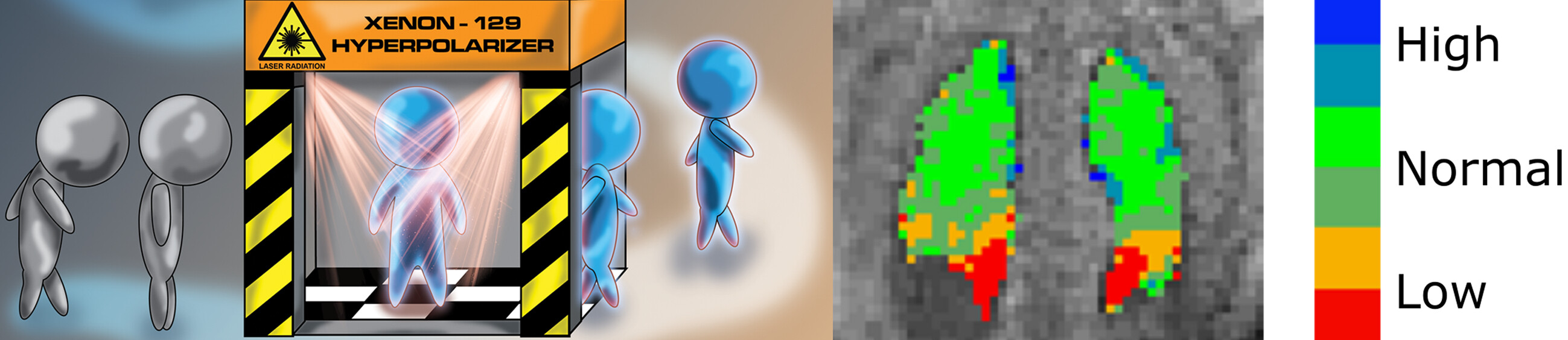

The use of hyperpolarized 129Xe has the potential to revolutionize clinical imaging, offering a non-ionizing contrast of organ function complementary to that of CT imaging and conventional MRI. In this Review, the physics of spin-exchange optical pumping (SEOP) is discussed, production modalities of hyperpolarized 129Xe are explained, and biomedical applications to lung imaging and beyond are described.
Ionische Flüssigkeiten
Ionische Flüssigkeiten und stark eutektische Lösungsmittel in der anorganischen Synthese
- Pages: 22320-22338
- First Published: 25 May 2021
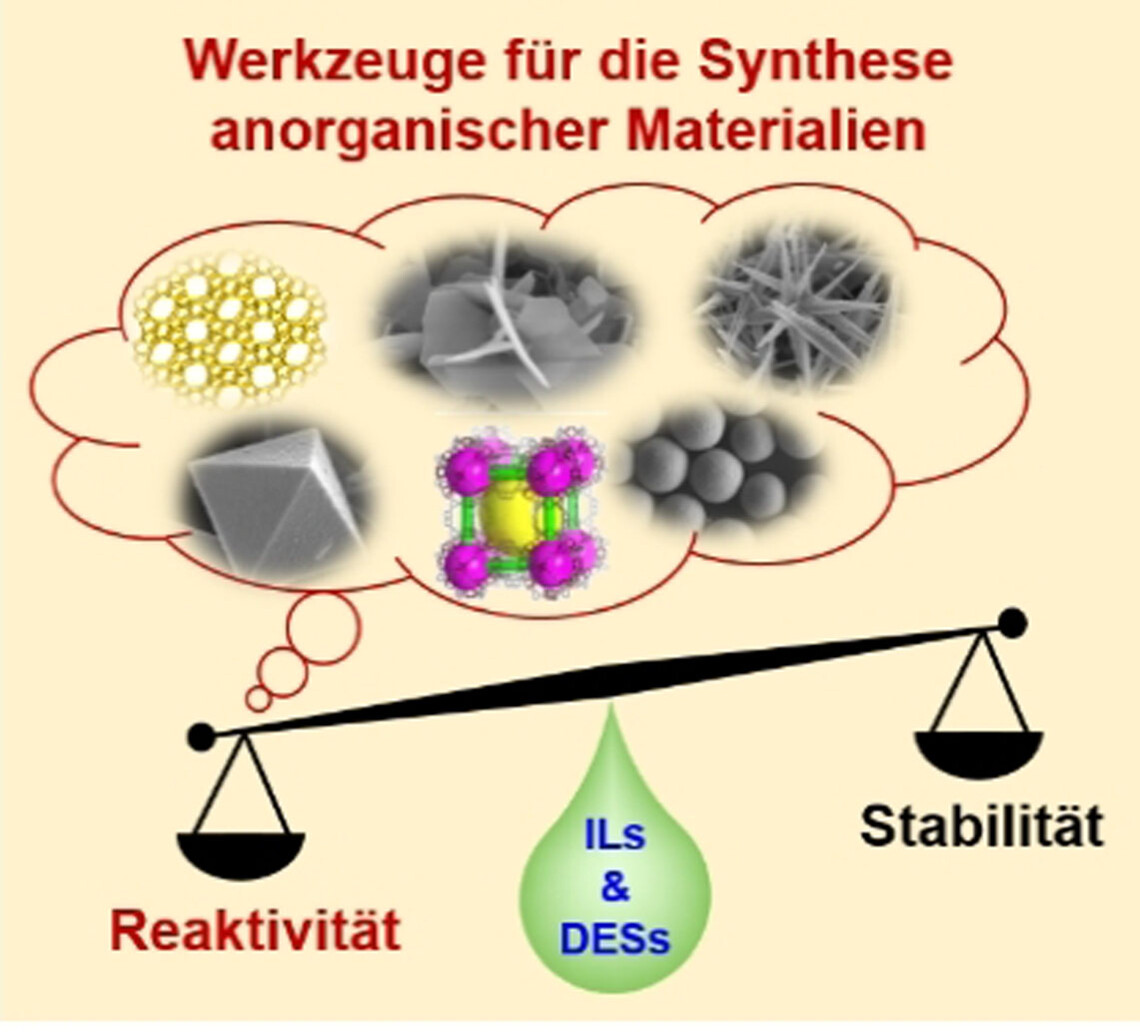
Die chemische Reaktivität ionischer Flüssigkeiten und stark eutektischer Lösungsmittel kann als synthetisches Werkzeug genutzt werden, um anorganische Materialien herzustellen, die über konventionelle Syntheserouten schwierig oder sogar überhaupt nicht zugänglich sind. Dieser Aufsatz fasst neuere Entwicklungen im Gebiet der anorganischen Synthese unter Nutzung von Reaktionen mit ionischen Flüssigkeiten oder stark eutektischen Lösungsmitteln zusammen.
Zuschriften
Palladium Catalysis | Hot Paper
Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Decarboxylative Addition of β-Keto Acids to Heteroatom-Substituted Allenes
- Pages: 22340-22345
- First Published: 15 July 2021
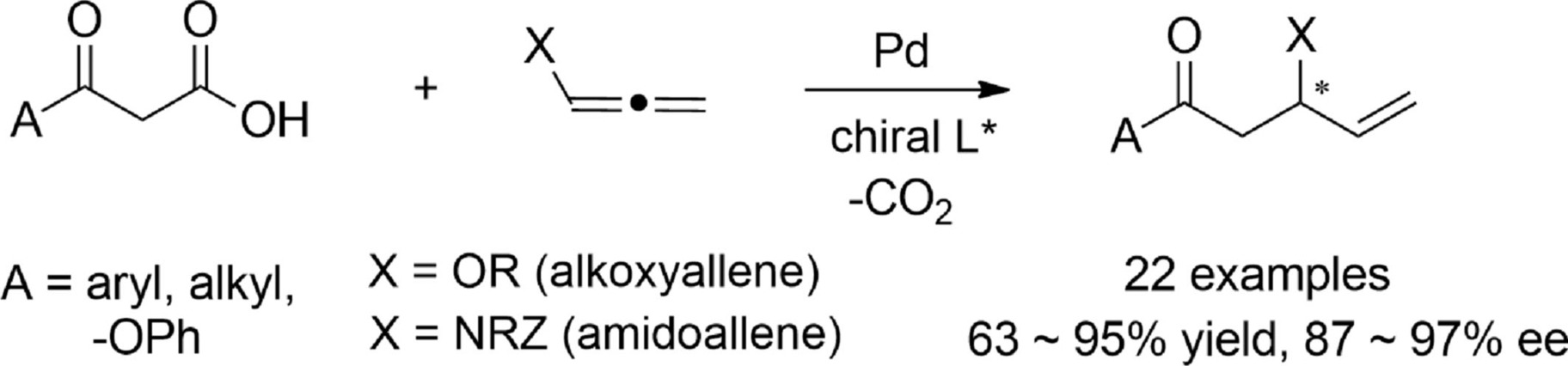
We report here an asymmetric decarboxylative allylation reaction initiated by the hydrocarboxylation reaction of heteroatom-substituted allene. The reaction works particularly well with heteroatom-substituted allenes such as alkoxyallenes and amidoallenes. A number of aryl and alkyl β-keto acids as well as malonic acid mono-phenyl ester participates in the reaction to generate γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl compounds possessing stereogenic heteroatom substituents at the β-position.
Antibiotic Analogues
Metagenome-Guided Analogue Synthesis Yields Improved Gram-Negative-Active Albicidin- and Cystobactamid-Type Antibiotics
- Pages: 22346-22351
- First Published: 05 August 2021

Biosynthetic instructions contained within congener biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) have been used to guide the synthesis of improved antibiotic analogues. ρ-Aminobenzoic acid encoding BGCs cloned from soil metagenomes have guided the synthesis of albicidin and cystobactamid analogues that show increased potency, different spectra of activity, as well as the ability to circumvent resistance conferred by endopeptidase cleavage enzymes.
Synthetic Methods
Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Propargyl Ethers with Grignard Reagents for the Synthesis of Functionalized Allenes and Allenols
- Pages: 22352-22357
- First Published: 28 July 2021
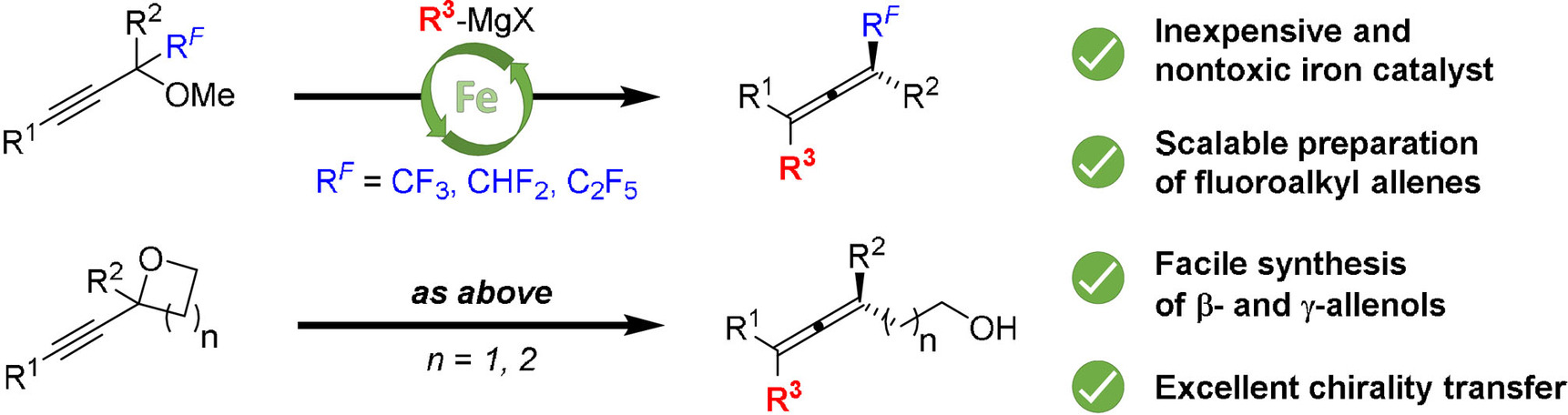
A method for facile synthesis of highly substituted allenols and fluoroalkyl allenes via iron-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of propargyl ethers with Grignard reagents is disclosed. Various tri- and tetrasubstituted fluoroalkyl allenes and β-/γ-allenols were obtained in good to excellent yields. The reaction was demonstrated to be stereospecific occurring with syn-SN2′ displacement of the methoxy group by the Grignard reagent.
Homogeneous Catalysis
Palladium-Catalyzed Dearomative Methoxyallylation of 3-Nitroindoles with Allyl Carbonates
- Pages: 22358-22362
- First Published: 17 July 2021
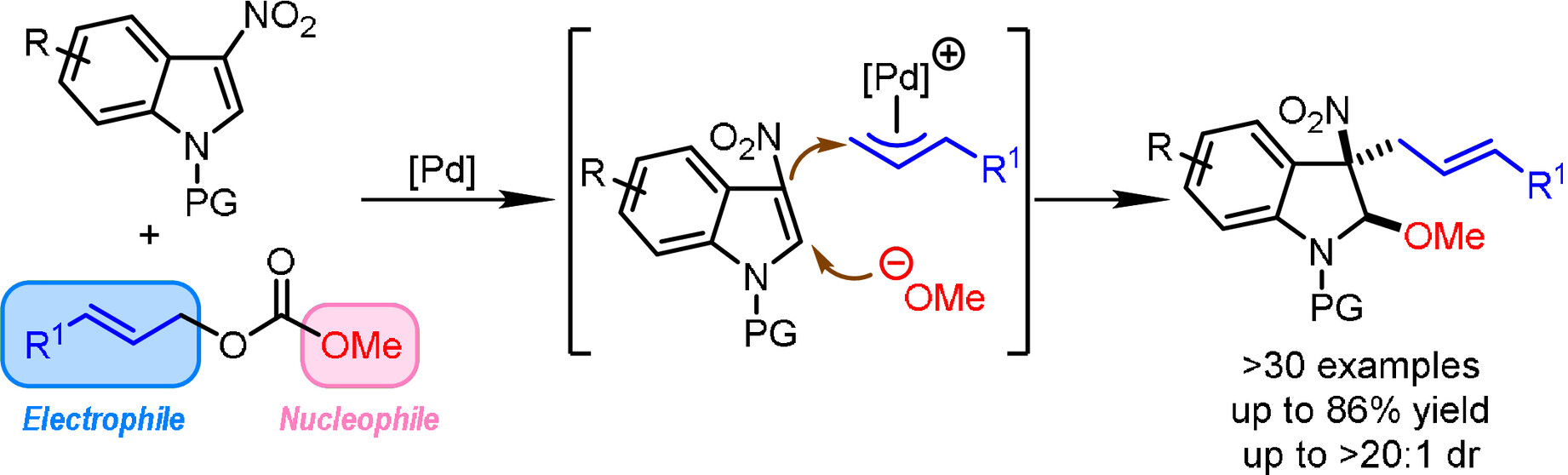
An intermolecular Pd-catalyzed dearomative methoxyallylation of 3-nitroindoles with readily available allyl carbonates was reported. Good yields (up to 86 %) and diastereoselectivity (up to >20:1 dr) are obtained for a wide range of substrates. The compatibility of gram-scale synthesis and the relatively low catalyst loading (down to 1 mol % of [Pd]) enhance the practicality of this method.
Batteries | Hot Paper
Construction of Co–Mn Prussian Blue Analog Hollow Spheres for Efficient Aqueous Zn-ion Batteries
- Pages: 22363-22368
- First Published: 27 July 2021
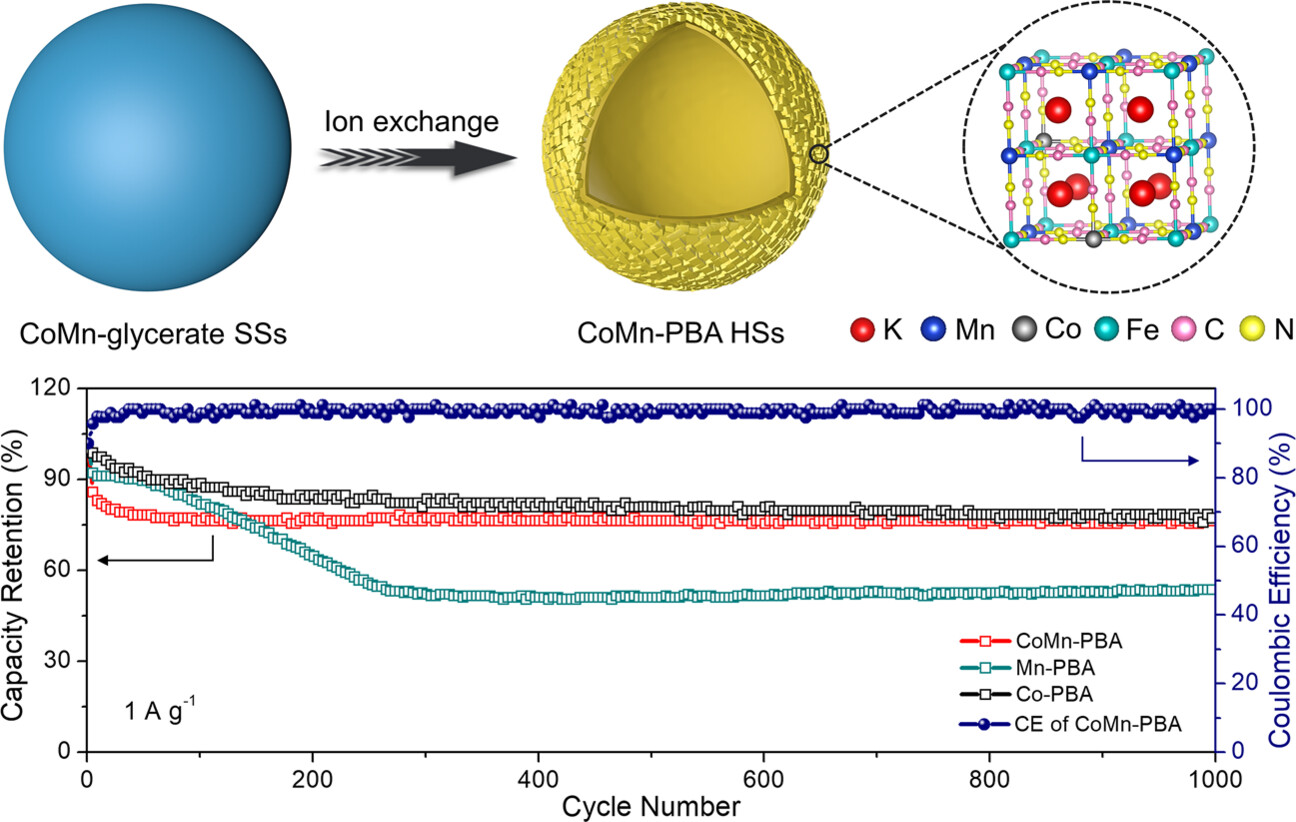
Co-substituted Mn-rich Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) hollow spheres (CoMn-PBA HSs) are rationally designed and synthesized through an efficient self-templating approach. Benefiting from the hollow structure and partial Co substitution, the CoMn-PBA HSs electrode exhibits enhanced zinc ion storage performance with high capacity, favorable rate capability, and impressive cycling stability.
Olefin Polymerization
Photoresponsive Palladium and Nickel Catalysts for Ethylene Polymerization and Copolymerization
- Pages: 22369-22374
- First Published: 26 July 2021
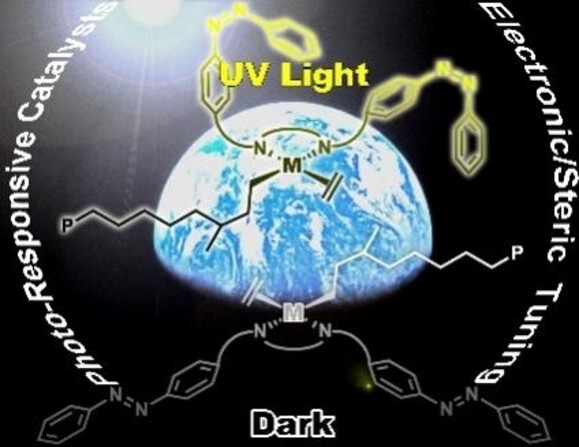
Two photoresponsive olefin polymerization systems were rationally designed. Light can be used to tune their properties in ethylene polymerization and copolymerization with polar comonomers, enabling light-induced control of the polymerization processes, polymer microstructures and polymer properties.
Helical Structures
Rhodium(I) Complexes Bearing an Aryl-Substituted 1,3,5-Hexatriene Chain: Catalysts for Living Polymerization of Phenylacetylene and Potential Helical Chirality of 1,3,5-Hexatrienes
- Pages: 22375-22380
- First Published: 05 August 2021
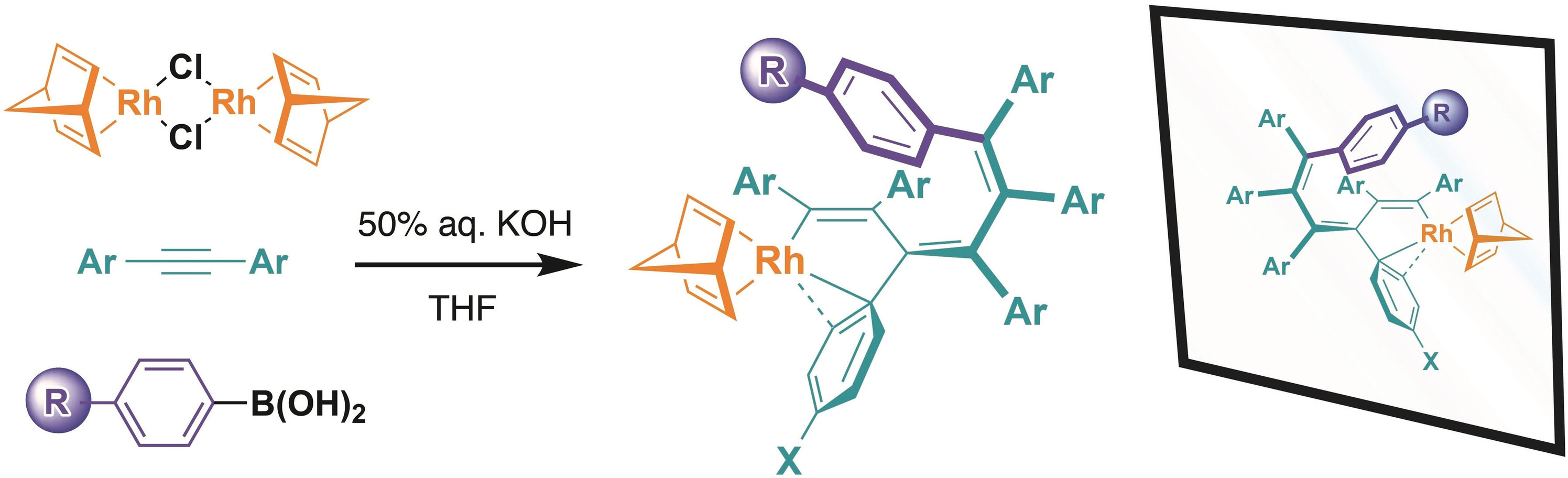
Isolable chiral rhodium(I) complexes bearing a helical aryl-substituted 1,3,5-hexatriene chain were synthesized by one-pot reactions of [Rh(nbd)Cl]2 with aryl boronic acids and diphenylacetylenes in the presence of 50 % aqueous KOH (see scheme). The persistent helical chirality of the complexes enabled their separation into enantiomers by HPLC on a chiral stationary phase. The complexes served as bench-stable catalysts for living polymerization of phenylacetylene.
Cyclic Peptides
Nγ-Hydroxyasparagine: A Multifunctional Unnatural Amino Acid That is a Good P1 Substrate of Asparaginyl Peptide Ligases
- Pages: 22381-22385
- First Published: 15 August 2021
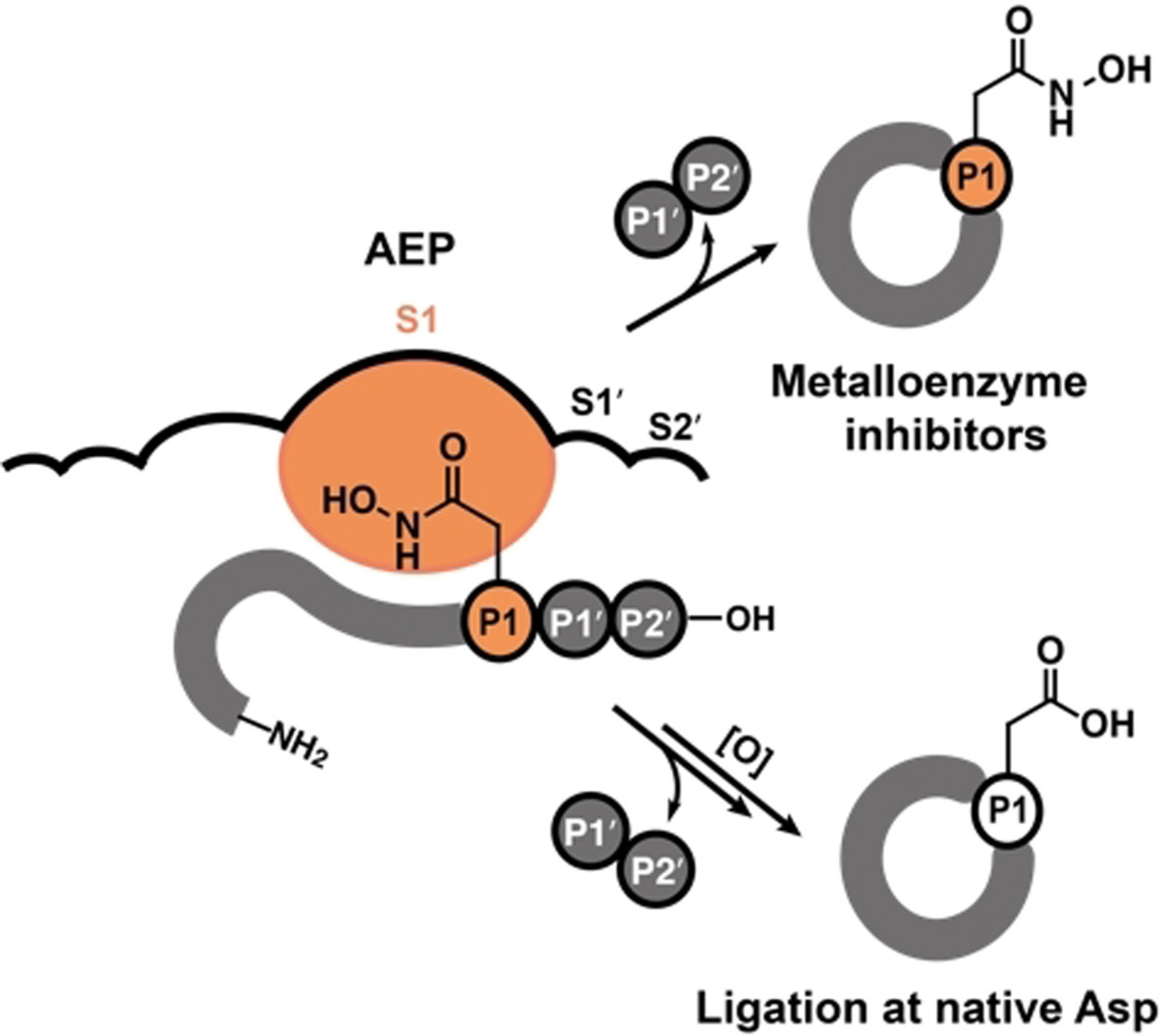
An unnatural amino acid, Asn(OH), mimics P1-Asn in the substrates of asparaginyl ligases, enabling efficient cyclization of P1-Asn(OH) peptides. The hydroxamic acid functionality in Asn(OH) is a metal-ion chelator for metalloenzyme inhibition, and Asn(OH) can be converted into native Asp by periodate oxidation (see scheme).
Polymers
Polymer Topology Reinforced Synergistic Interactions among Nanoscale Molecular Clusters for Impact Resistance with Facile Processability and Recoverability
- Pages: 22386-22392
- First Published: 10 August 2021
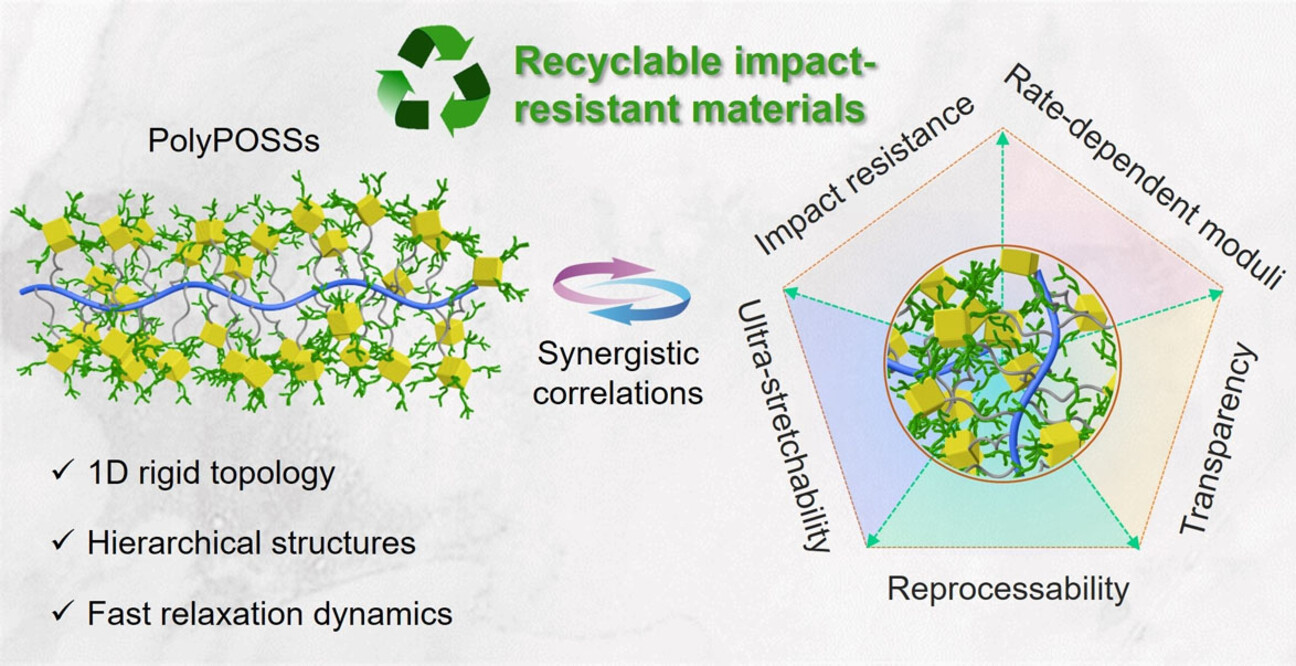
Unique physical interaction facilitated by 1D topologies of molecular cluster-integrated polymers is applied for the design of impact-resistant materials with exceptional energy dissipation capability and strong rate-dependent mechanical strengths, enabling the simultaneous achievement of promising impact resistance and processability/recoverability.
Photoredox Reactions
Truce–Smiles Rearrangements by Strain Release: Harnessing Primary Alkyl Radicals for Metal-Free Arylation
- Pages: 22393-22397
- First Published: 09 August 2021
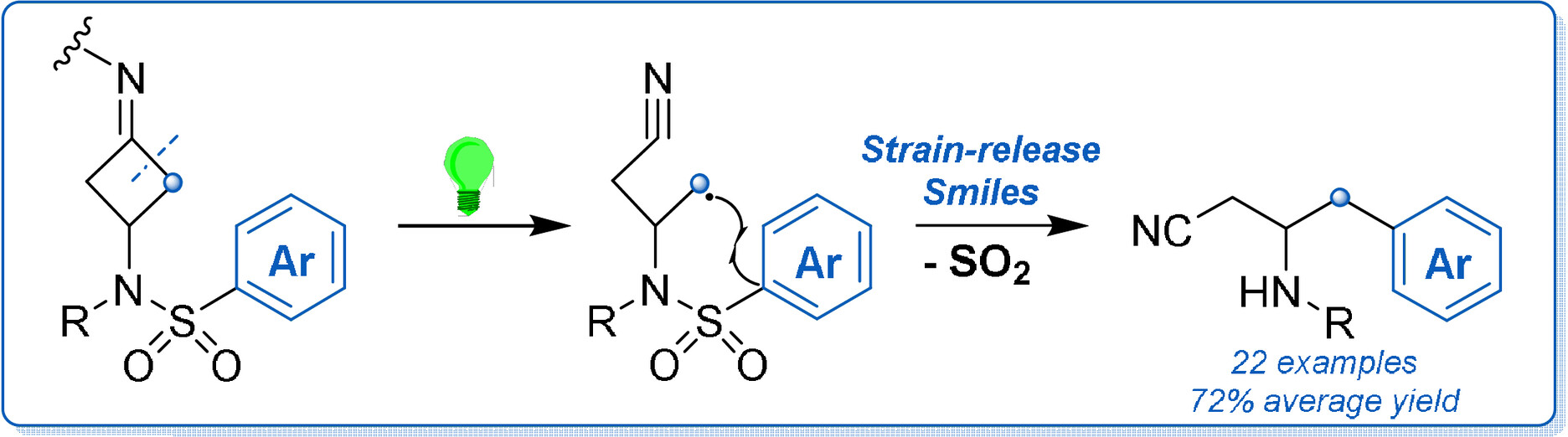
The Truce–Smiles rearrangement has proven to be a powerful tool for the synthesis of new sp3-aryls via ipso substitution. The reaction has been applied to the strain-release ring-opening of 3-aminocyclobutanone oximes, giving cyanide-free access to β-amino nitriles under metal-free, room temperature conditions. The reaction displays a wide scope of migrating arenes.
Enantioselective Catalysis
Enantioselective Lactonization by π-Acid-Catalyzed Allylic Substitution: A Complement to π-Allylmetal Chemistry
- Pages: 22398-22403
- First Published: 22 August 2021
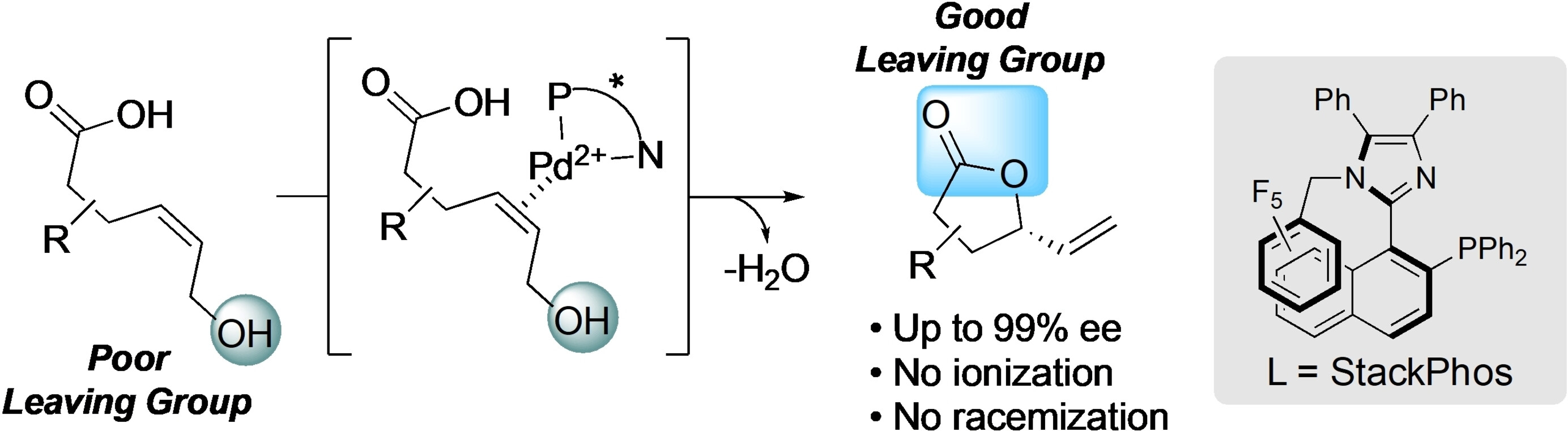
A highly enantioselective lactonization of unactivated allylic alcohols is reported under mild conditions. The transformation is catalyzed by a PdII⋅StackPhos complex and facilitates the substitution of a poor leaving group with what would ostensibly be a better leaving group in the product without selectivity issues arising from racemization.
Covalent Organic Frameworks
Three-Dimensional Radical Covalent Organic Frameworks as Highly Efficient and Stable Catalysts for Selective Oxidation of Alcohols
- Pages: 22404-22409
- First Published: 13 August 2021
Asymmetric Synthesis
Catalytic Asymmetric Darzens-Type Epoxidation of Diazoesters: Highly Enantioselective Synthesis of Trisubstituted Epoxides
- Pages: 22410-22414
- First Published: 04 August 2021
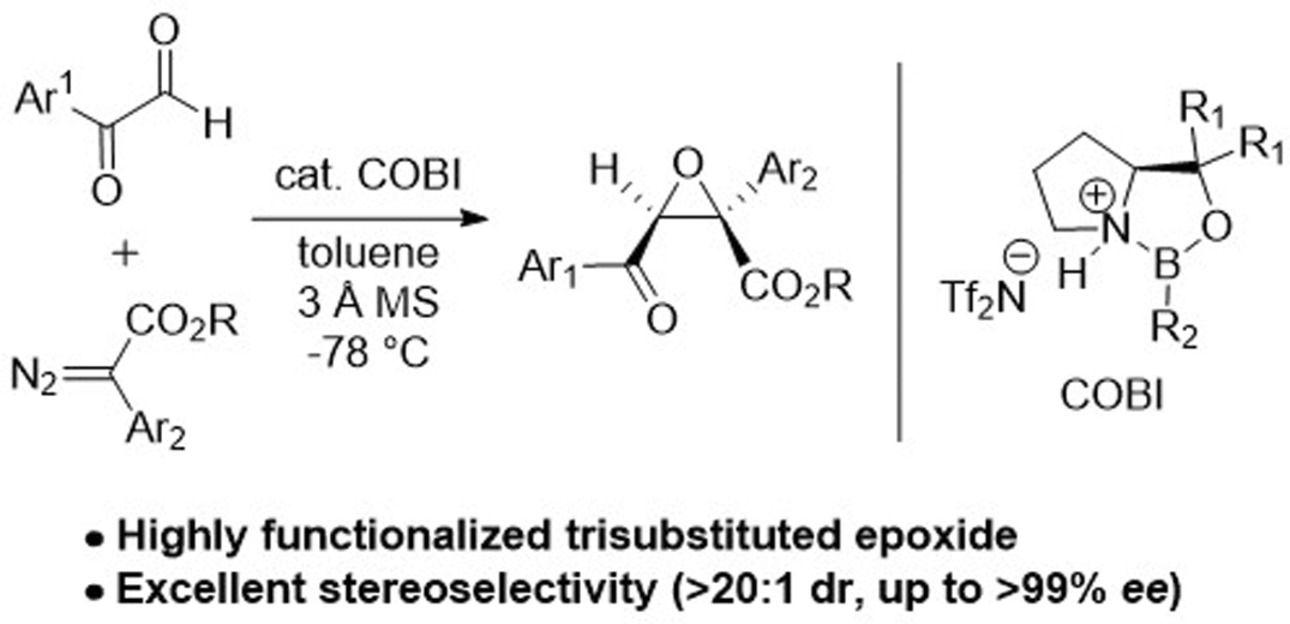
Chiral trisubstituted epoxides were synthesized by boron–Lewis acid-catalyzed Darzens-type epoxidation of diazoesters in high yields with excellent enantio- and diastereoselectivity. The developed reaction provides an efficient synthetic route to various chiral compounds such as epoxy γ-butyrolactone, tertiary β-hydroxy ketone, and epoxy diester.
Electroluminescence
High-Performance Ultraviolet Organic Light-Emitting Diode Enabled by High-Lying Reverse Intersystem Crossing
- Pages: 22415-22421
- First Published: 13 August 2021
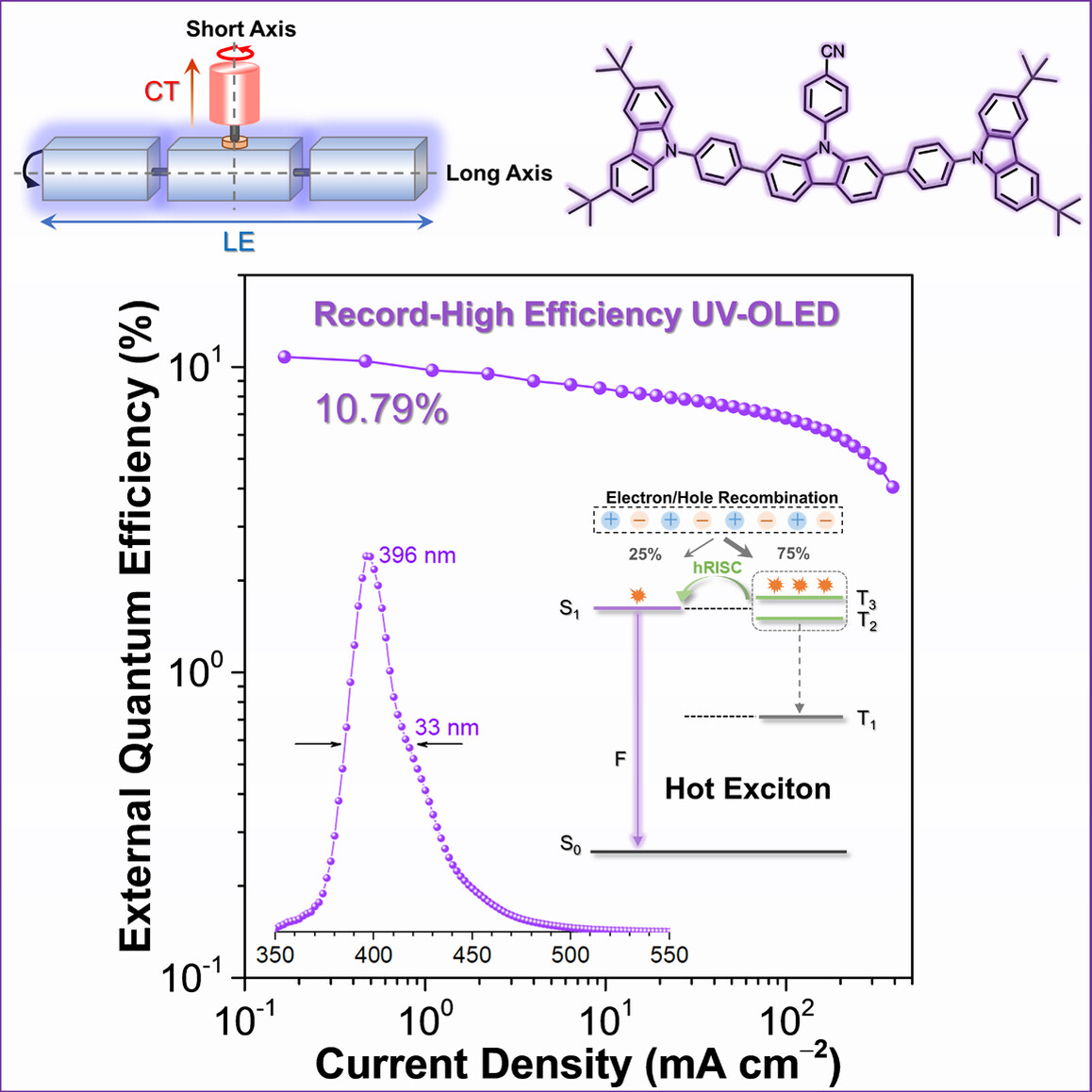
Through the proposed long-short axis molecular design, an HLCT-type ultraviolet emitter is reported. Benefiting from the features of the low-lying LE emissive state and high-lying reverse intersystem crossing process, the ultraviolet OLED furnishes a record-high EQE of 10.79 %, accompanied by a satisfactory color purity and a small efficiency roll-off.
Perovskites
Double Double to Double Perovskite Transformations in Quaternary Manganese Oxides
- Pages: 22422-22426
- First Published: 09 August 2021
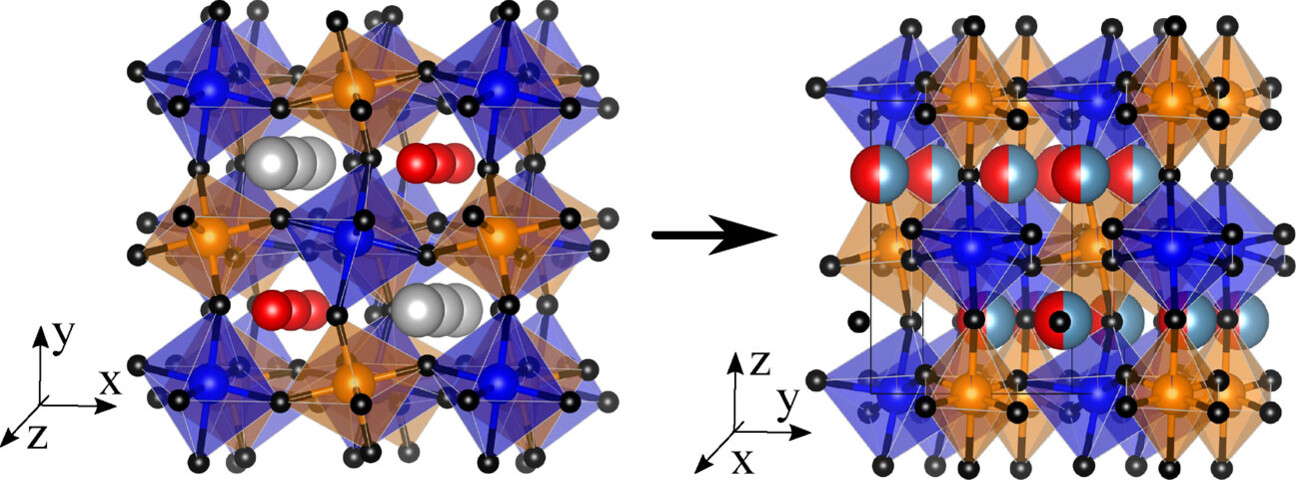
Thermal transformations under pressure of AA′BB′O6 double double perovskites, where both A and B sites have 1:1 cation order, to (A0.5A′0.5)2BB′O6 double perovskites with disordered A/A′ cations are demonstrated for CaMnMnWO6 and SmMnMnTaO6, leading to a dramatic switch in magnetic properties from ferrimagnetic order to spin glass behaviour in the former.
Afterglow Materials
Near-Infrared-Excited Multicolor Afterglow in Carbon Dots-Based Room-Temperature Afterglow Materials
- Pages: 22427-22433
- First Published: 13 August 2021
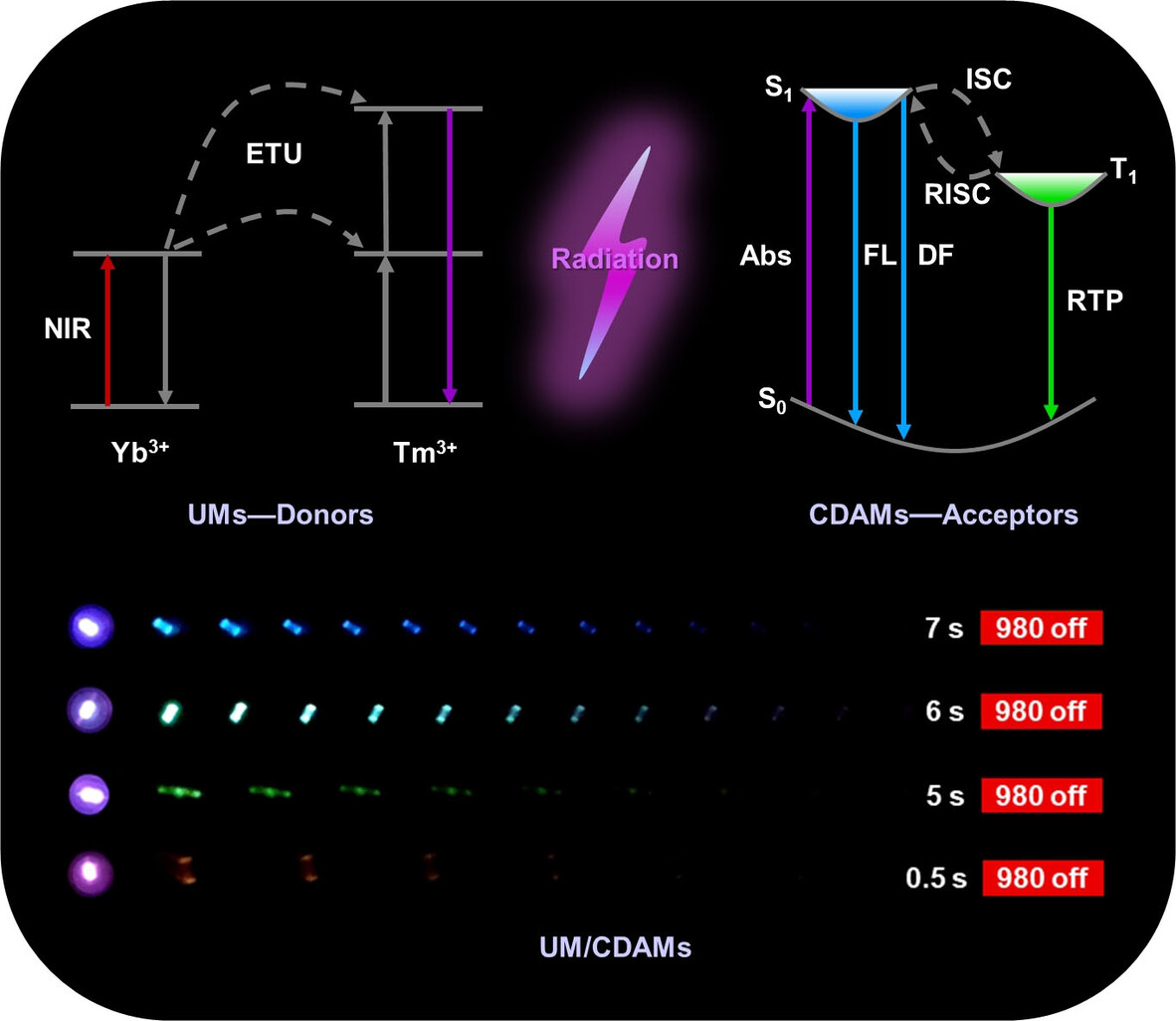
A universal method is developed to activate near-infrared-excited multicolor afterglow of carbon dots-based RTA materials (CDAMs) through radiative energy transfer from NaYF4:Yb,Tm upconversion materials (UMs). The resulting UM/CDAMs demonstrate bright and persistent afterglow from blue to orange under NIR CW laser excitation at 980 nm.
High-Pressure Chemistry
Preparation of Bulk-Phase Nitride Perovskite LaReN3 and Topotactic Reduction to LaNiO2-Type LaReN2
- Pages: 22434-22438
- First Published: 06 August 2021
Membrane Separation
A Lamellar MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/PSS Composite Membrane for Fast and Selective Lithium-Ion Separation
- Pages: 22439-22443
- First Published: 11 August 2021
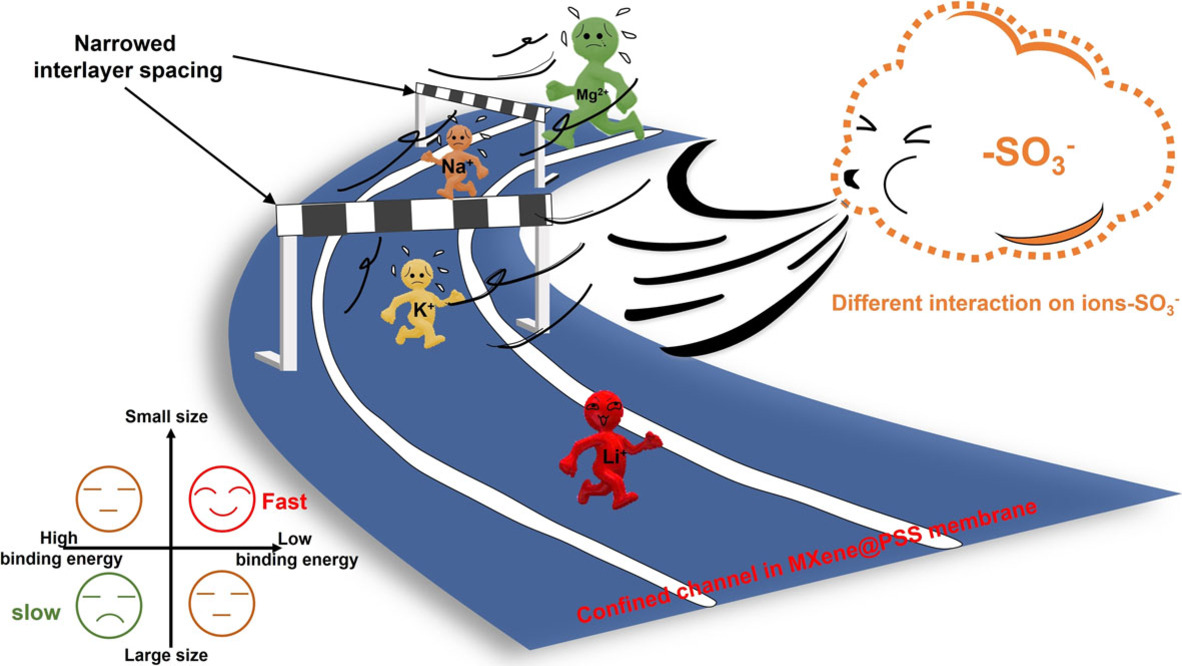
Lamellar MXene (Ti3C2Tx)@PSS membranes with specific size exclusion and Li+ identification property show excellent mono/multi-valent ions separation performance. Compared with the traditional 2D membranes, the selectivity of Li+/Na+, Li+/K+, and Li+/Mg2+ through such membranes is five to ten times improved.
Natural Products
Forrestiacids A and B, Pentaterpene Inhibitors of ACL and Lipogenesis: Extending the Limits of Computational NMR Methods in the Structure Assignment of Complex Natural Products
- Pages: 22444-22449
- First Published: 10 August 2021
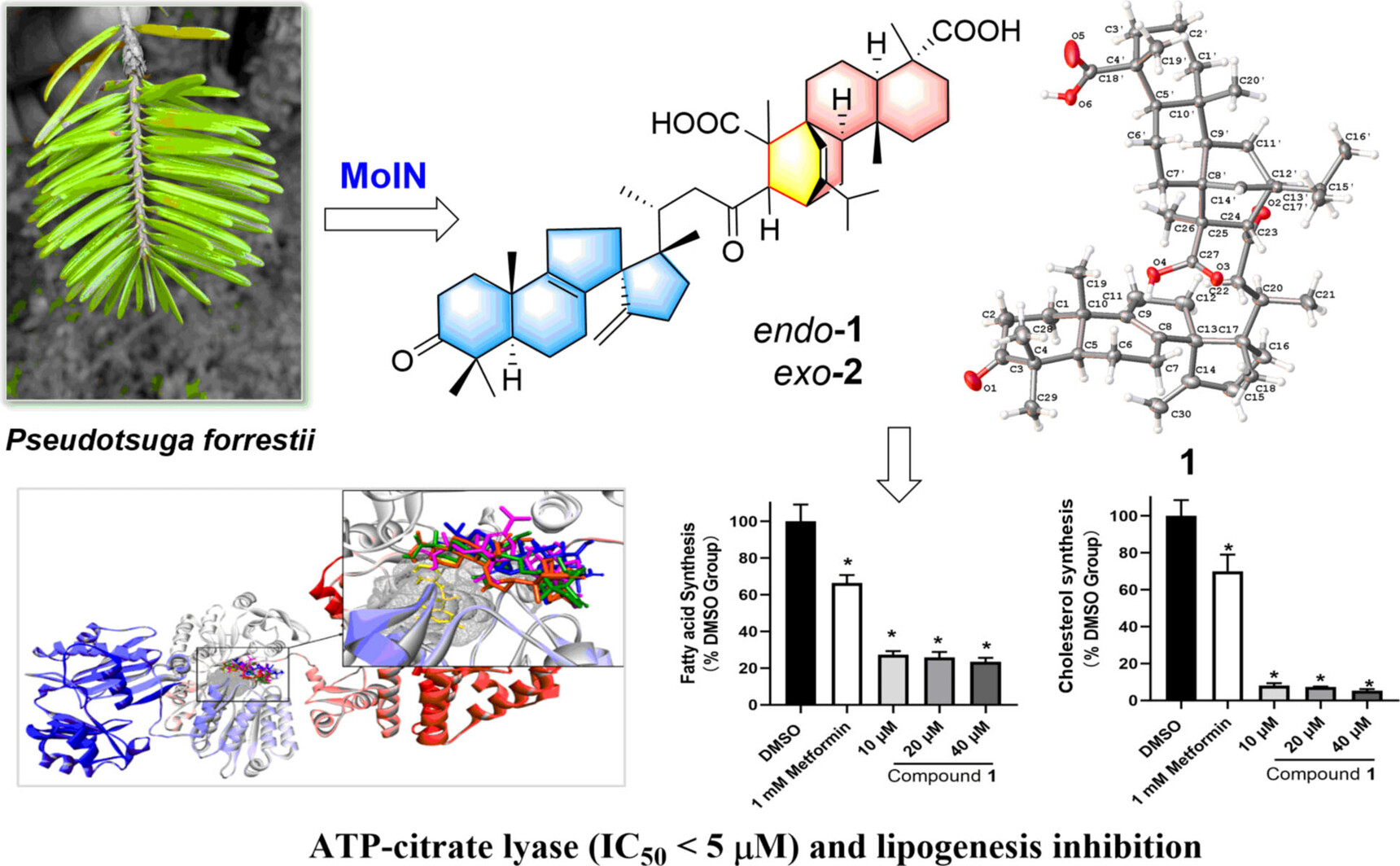
Forrestiacids A (1) and B (2), comprising a rearranged spiro-lanostane unit fused with an abietene by a Diels–Alder cycloaddition, represent a novel class of pentaterpenoids obtained from Pseudotsuga forrestii. Chemical computations demonstrate to be an effective strategy in the structure elucidation of complex molecules. Both 1 and 2 showed potent ACL inhibitory effects, and 1 even significantly attenuated the de novo lipogenesis in HepG2 cells.
Metal–Organic Frameworks | Hot Paper
Electronic Modulation Caused by Interfacial Ni-O-M (M=Ru, Ir, Pd) Bonding for Accelerating Hydrogen Evolution Kinetics
- Pages: 22450-22456
- First Published: 23 August 2021
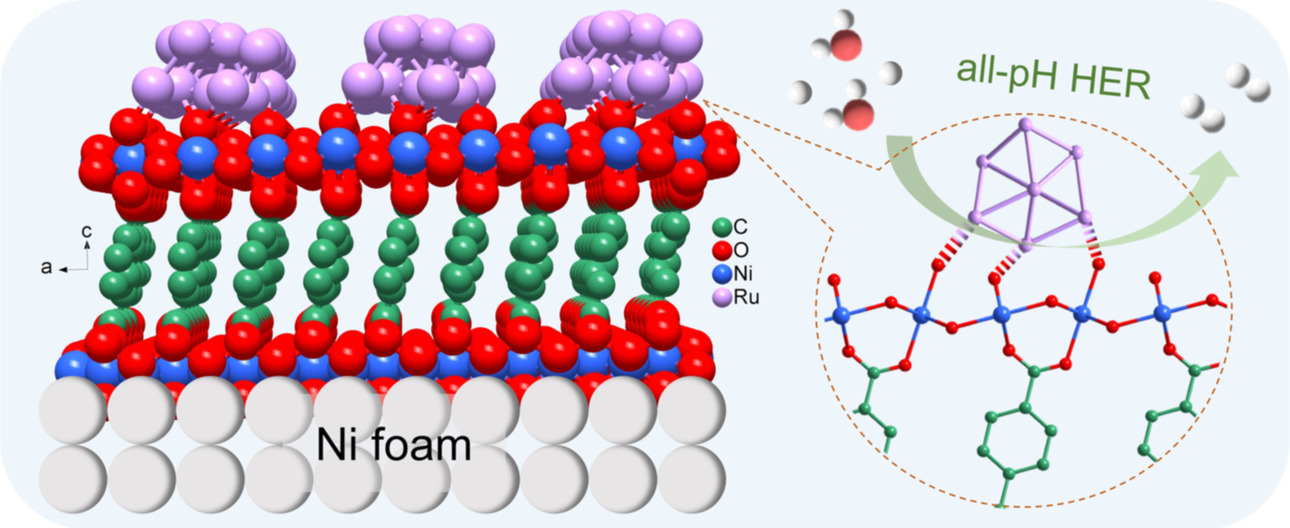
A facile and spontaneous strategy is presented for synthesizing Ru-nanoparticle-anchored metal–organic framework nanohybrids on Ni foam. The nanohybrids exhibit excellent HER performance at all pH values owing to the optimized adsorption free energies of intermediates by the interfacial-bond-induced electron redistribution.
Fabrication of Integrated Copper-Based Nanoparticles/Amorphous Metal–Organic Framework by a Facile Spray-Drying Method: Highly Enhanced CO2 Hydrogenation Activity for Methanol Synthesis
- Pages: 22457-22462
- First Published: 11 August 2021
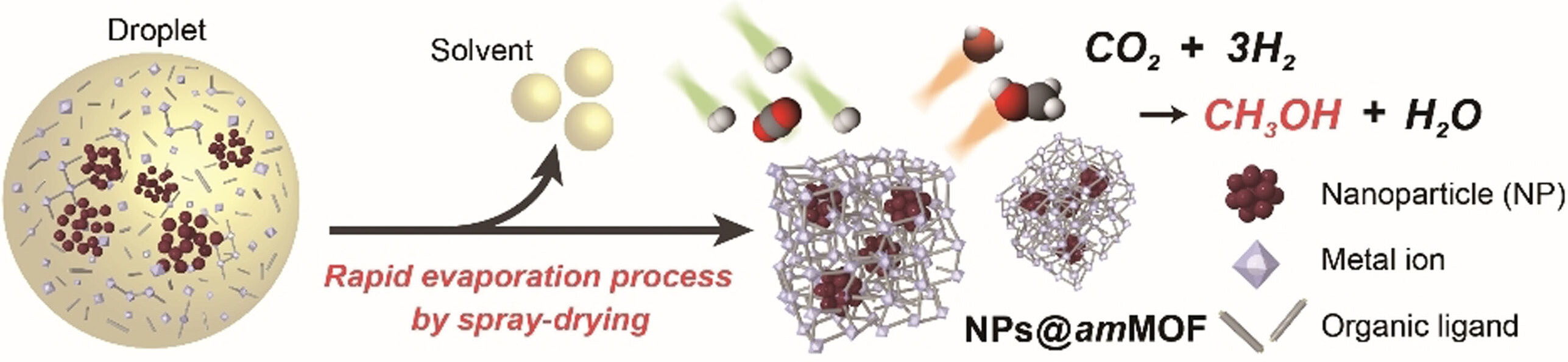
We report on a first demonstration for a catalyst comprising metal NPs and amorphous MOF in a gas-phase reaction. Cu/amorphous UiO-66 exhibited 3-fold catalytic activity for CO2 hydrogenation into methanol over Cu/crystalline UiO-66. Amorphous UiO-66 coating on Cu-ZnO nanocomposites showed 1.5-fold catalytic activity enhancement over that of Cu/amorphous UiO-66.
Dihydrogen Activation
Dihydrogen Activation by Lithium- and Sodium-Aluminyls
- Pages: 22463-22466
- First Published: 16 August 2021
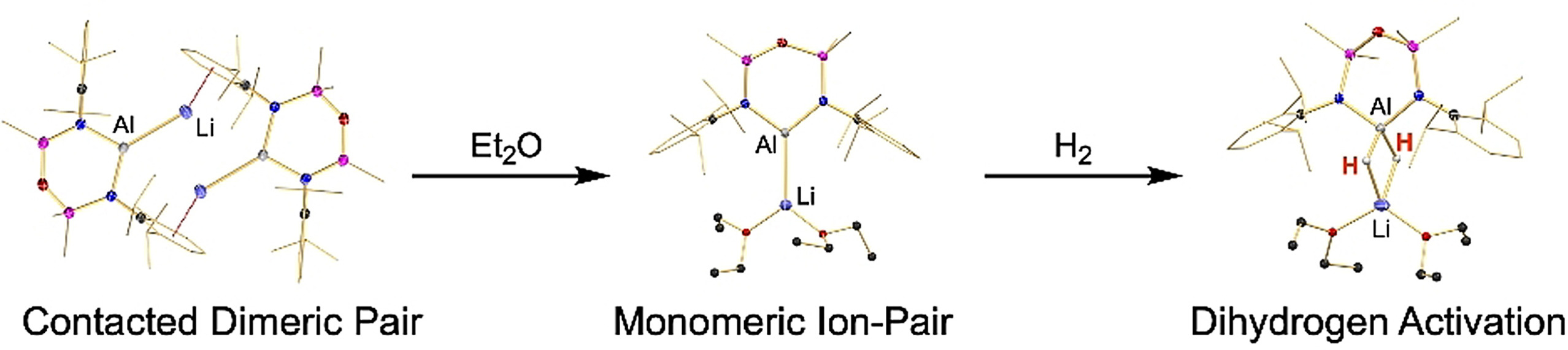
It turns out there is nothing special about potassium after all: Sodium and lithium metal reduce AlIII iodide precursors to the M2[Al(NONDipp)]2 aluminyls (M=Li, Na). Addition of Et2O afforded the monomeric ion pairs (NONDipp)Al-M(Et2O)2 containing unsupported Al−Li and Al−Na bonds. All species activate dihydrogen, albeit at significantly different rates of reaction.
Forschungsartikel
Superatoms | Hot Paper
Superatom-in-Superatom [RhH@Ag24(SPhMe2)18]2− Nanocluster
- Pages: 22467-22474
- First Published: 05 July 2021
![Superatom-in-Superatom [RhH@Ag24(SPhMe2)18]2− Nanocluster](/cms/asset/27de8855-7d48-4b1a-9349-774035412d42/ange202106311-toc-0001-m.jpg)
The superatom-in-superatom concept was demonstrated for the first time. A rhodium hydride (RhH) superatom could be incorporated into a cluster superatom to generate a stable superatom-in-superatom [RhH@Ag24(SR)18]2− nanocluster. The Rh atom with open d-shells ([Kr]4d85s1) could be incorporated into the Ag24(SR)18 framework by forming the RhH superatom resembling the closed d-shell Pd atom ([Kr]4d10).
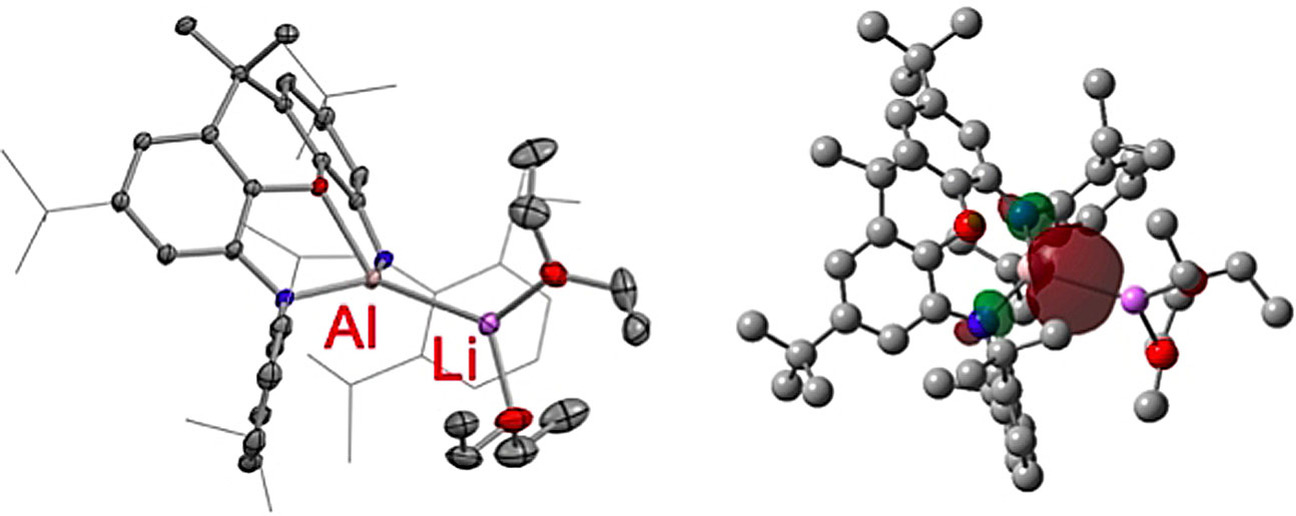
Low-Valent Compounds | Hot Paper
Probing the Extremes of Covalency in M−Al bonds: Lithium and Zinc Aluminyl Compounds
- Pages: 22475-22480
- First Published: 15 August 2021
Organic Chemistry | Hot Paper
Four-Step Domino Reaction Enables Fully Controlled Non-Statistical Synthesis of Hexaarylbenzene with Six Different Aryl Groups
- Pages: 22481-22488
- First Published: 01 June 2021
Biocatalysis
In-Situ Encapsulation of Protein into Nanoscale Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Frameworks for Intracellular Biocatalysis
- Pages: 22489-22495
- First Published: 12 August 2021
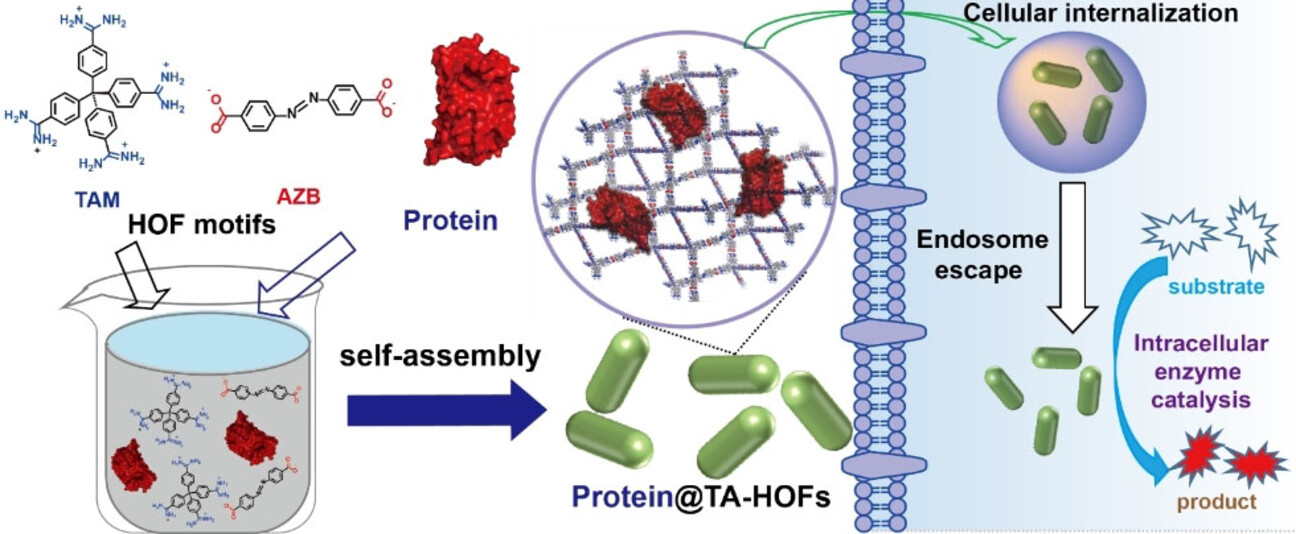
The in situ encapsulation of protein by self-assembly of hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks (HOFs) enables the formation of nanoscale protein@TA-HOFs under mild conditions. Moreover, this strategy is generally applicable to proteins with different surface charge and molecular weight, facilitating the cellular internalization of proteins for efficient enzyme catalysis inside living cells.
Molecular Sieves
Key Features of Polyimide-Derived Carbon Molecular Sieves
- Pages: 22496-22505
- First Published: 04 August 2021
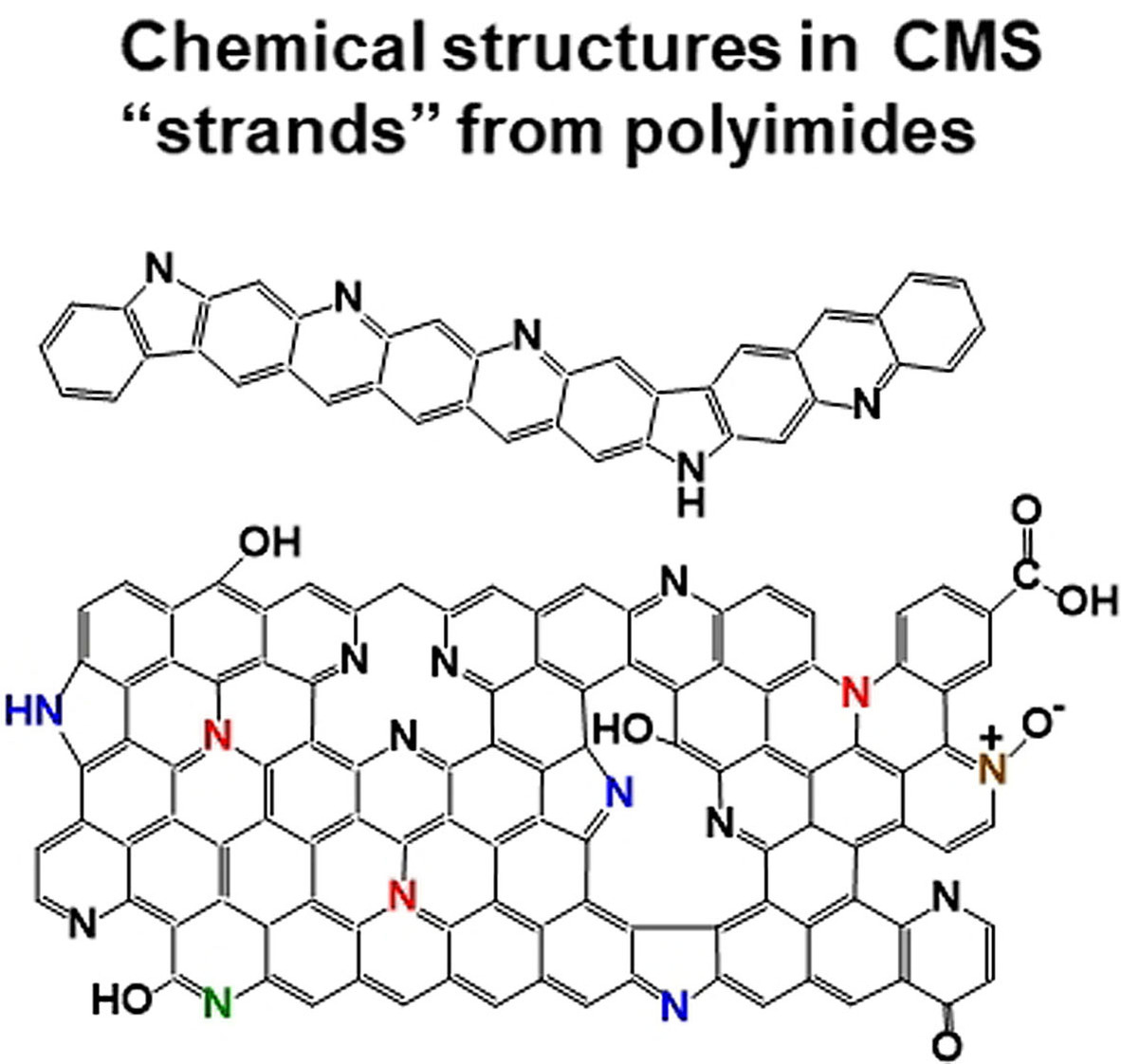
The chemical structures of fragments that are composed of CMS strands from varied polyimide precursors are similar, however, the texture or morphology structure is greatly affected by precursors, determining CMS membrane separation performance. The CMS properties can be tuned via controlling the strand′s structure, thereafter the plate and cellular structures, by designing precursor polymer chemical structure and pyrolysis conditions.
Supramolecular Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Control Viscoelasticity of Polymer Networks with Crosslinks of Superposed Fast and Slow Dynamics
- Pages: 22506-22512
- First Published: 19 May 2021
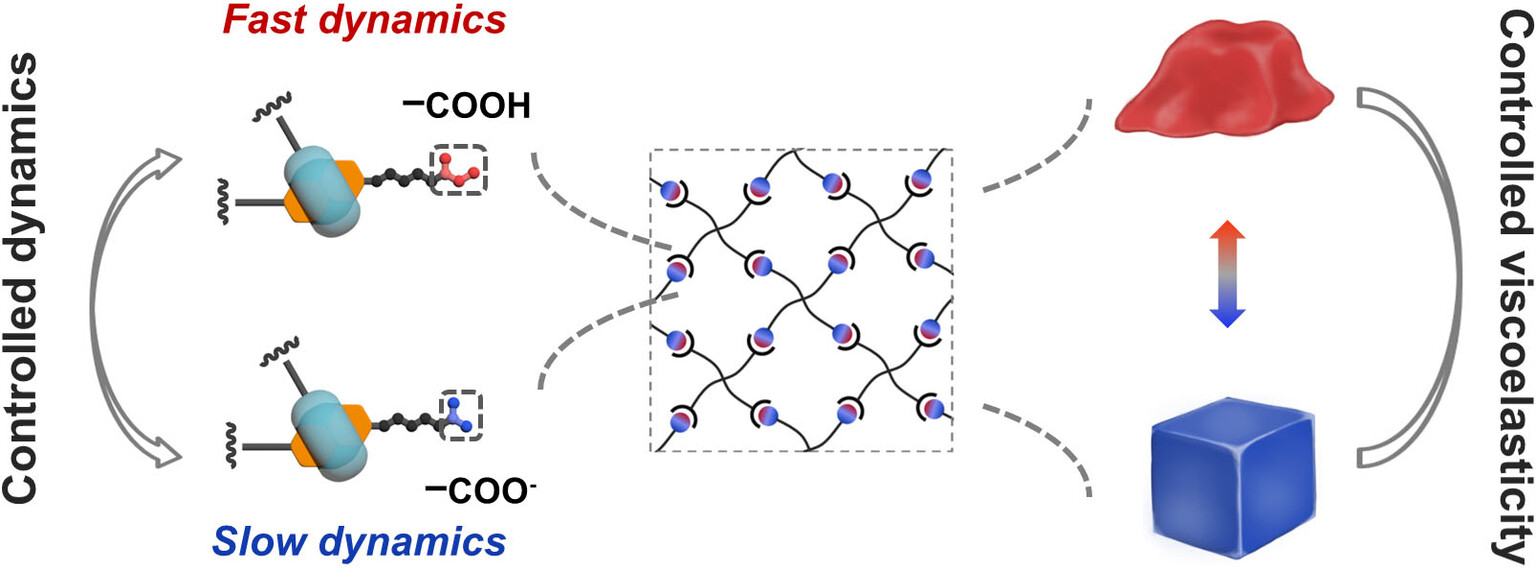
By means of designing a crosslink of superposed fast and slow dynamics, we show the quantitative control of the association/dissociation rate constants of this crosslink over 5 orders of magnitude. With this crosslink, we achieved precise control over viscoelasticity and mechanical response of polymer networks.
Metal–Support Interactions | Very Important Paper
Facet-Dependent Oxidative Strong Metal-Support Interactions of Palladium–TiO2 Determined by In Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy
- Pages: 22513-22518
- First Published: 05 August 2021
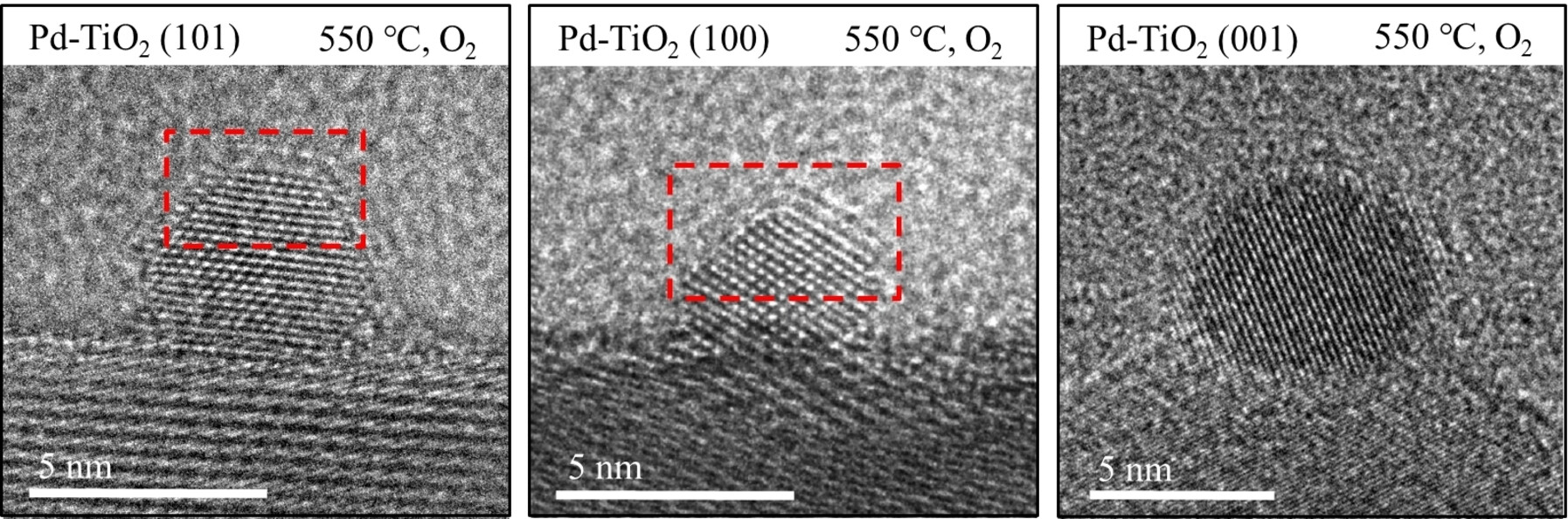
The strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) of well-defined Pd-TiO2 catalysts under high temperature oxidation was studied via in situ atmospheric pressure TEM. On the different facets of TiO2 supports there were significant differences in the encapsulation behaviors with a facet-dependent SMSI. Obvious cover layers were observed on Pd NPs supported on TiO2 (101) and (100) facets, while no such phenomenon appeared on TiO2 (001) facets.
Synthetic Methods
Iron-Catalyzed Reductive Cyclization by Hydromagnesiation: A Modular Strategy Towards N-Heterocycles
- Pages: 22519-22525
- First Published: 18 August 2021
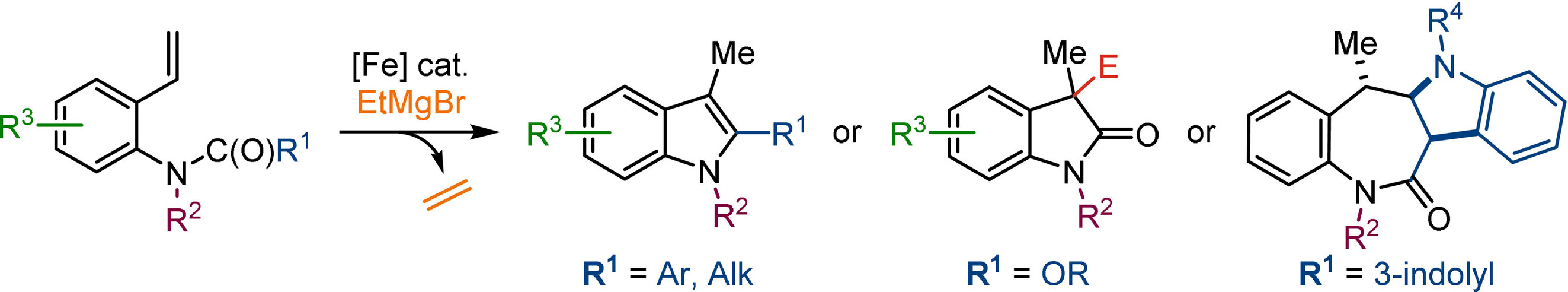
An iron-catalyzed reductive cyclization of 2-vinylanilides to prepare a variety of N-heterocycles is reported. The reaction, which usually occurs at room temperature over a short reaction time, employs an inexpensive and bench-stable iron catalyst and EtMgBr as a hydride source. The breadth of this strategy was demonstrated by the synthesis of densely substituted indoles, oxindoles and novel tetrahydrobenzoazepinoindolones, as well as the application towards the formal syntheses of bioactive compounds.
Photochemistry | Hot Paper
Photodriven Elimination of Chlorine From Germanium and Platinum in a Dinuclear PtII→GeIV Complex
- Pages: 22526-22532
- First Published: 16 August 2021
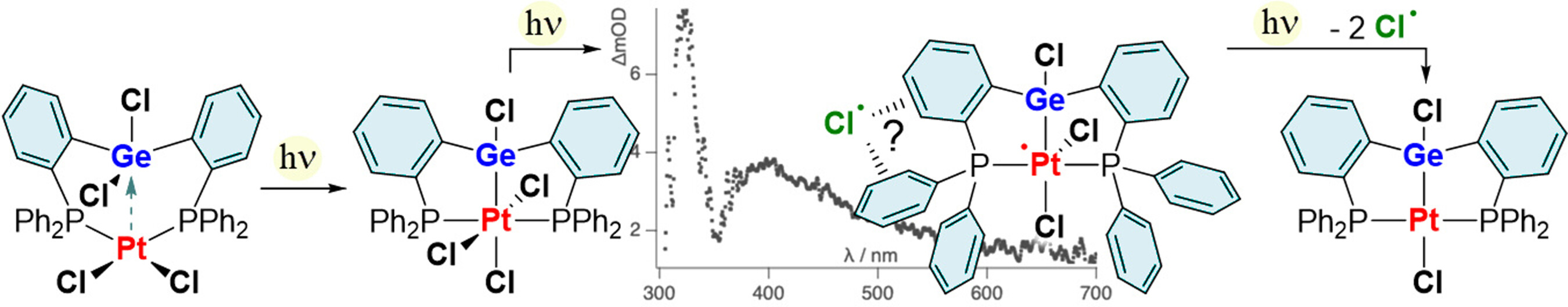
A novel platinum dichloride complex supported by an ambiphilic bisphosphinodichlorogermane ligand photo-isomerizes into a tetravalent platinum trichloride germyl complex. Further irradiation of this new complex triggers the elimination of chlorine and the formation of a covalent Pt–Ge bond. Transient absorption spectroscopy points to the intermediacy of a charge-transfer complex involving the nascent chlorine atom and the aromatic ligand.
Analytical Methods | Hot Paper
Particle-by-Particle In Situ Characterization of the Protein Corona via Real-Time 3D Single-Particle-Tracking Spectroscopy
- Pages: 22533-22541
- First Published: 20 May 2021
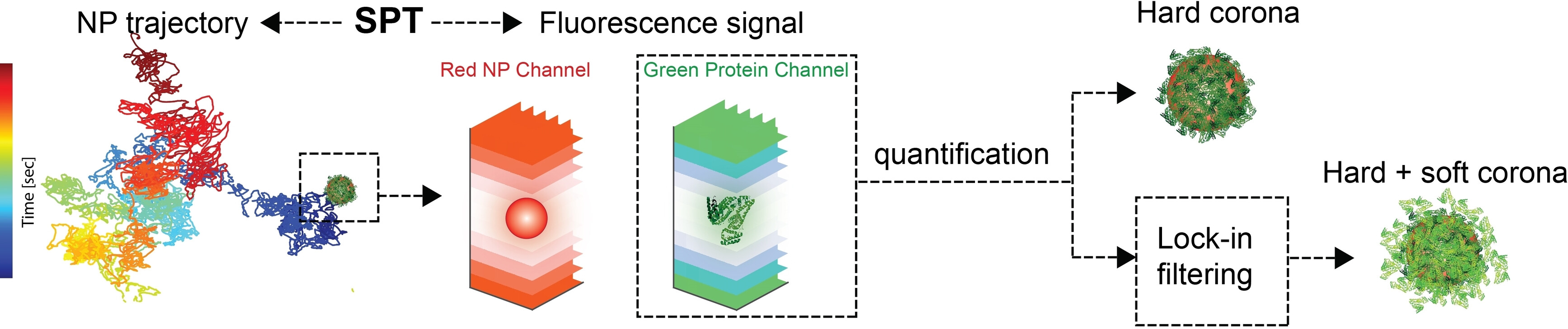
3D single-particle-tracking microscopy combined with a lock-in filtering algorithm for the quantitative observation of individual protein–nanoparticle (NP) interactions without surface immobilization is presented. This highly sensitive method, which can be applied in various protein–NP systems, gives insight into in situ protein corona on a per-particle basis and provides the possibility to study transient protein–NP interactions.
Photoluminescence
Discrete Heteropolynuclear Yb/Er Assemblies: Switching on Molecular Upconversion Under Mild Conditions
- Pages: 22542-22549
- First Published: 12 August 2021
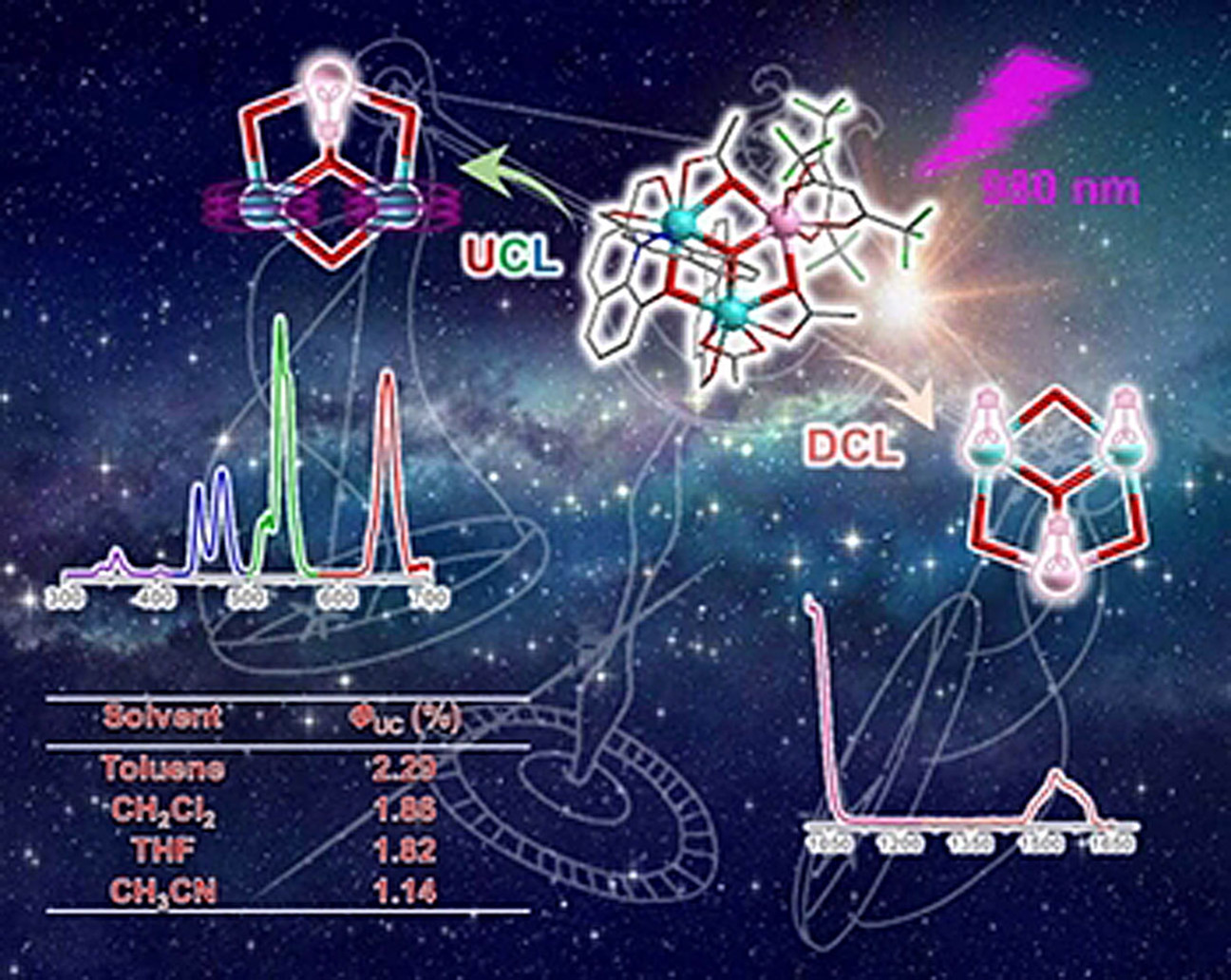
The performance of discrete heteropolynuclear Yb/Er salts is switched from a Yb/Er doublet to competitive upconversion luminescence exploiting fluoride association. A more than 20-fold enhancement of the relative quantum yield ϕUC under low power densities in non-deuterated solvents at room temperature was recorded.
Photothermal Therapy | Hot Paper
A Borondifluoride-Complex-Based Photothermal Agent with an 80 % Photothermal Conversion Efficiency for Photothermal Therapy in the NIR-II Window
- Pages: 22550-22558
- First Published: 20 July 2021
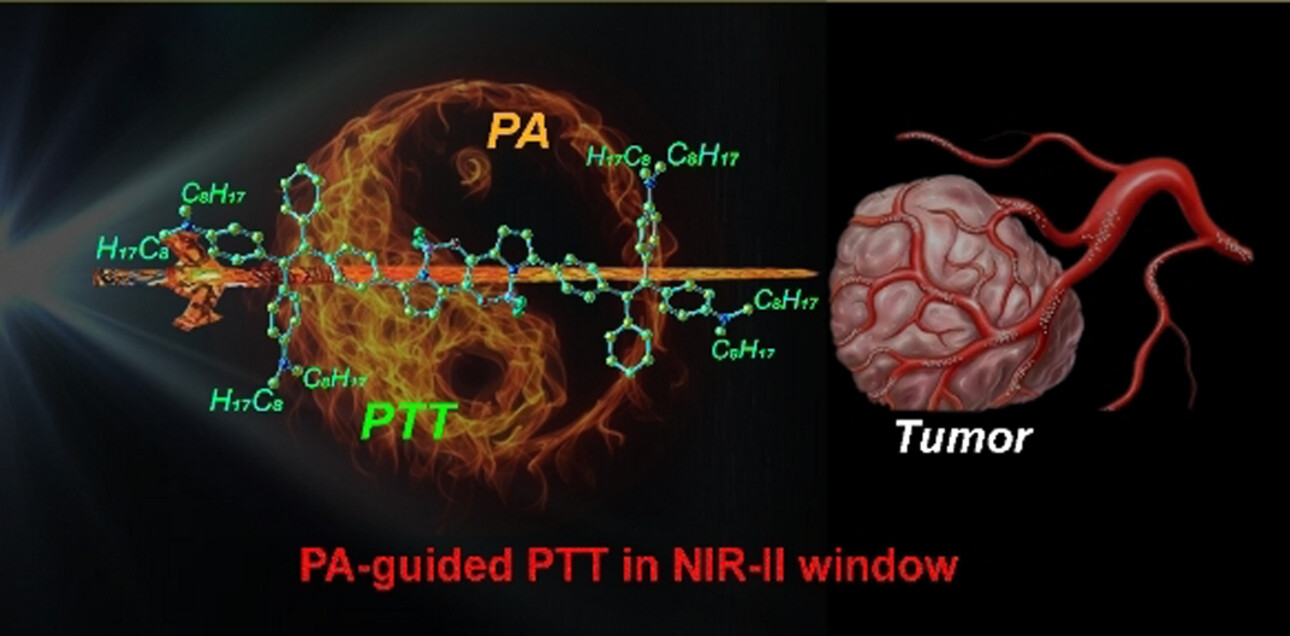
A NIR-II absorbing BF2 complex with high photothermal performance was designed. The complex achieves a high photothermal conversion efficiency value of 80 % under 1064 nm laser irradiation. In vivo studies reveal the great potential of the complex in photoacoustic imaging-guided photothermal therapy in the NIR-II window.
Heterocycles
A Tale of Two Isomers: Enhanced Antiaromaticity/Diradical Character versus Deleterious Ring-Opening of Benzofuran-fused s-Indacenes and Dicyclopenta[b,g]naphthalenes
- Pages: 22559-22566
- First Published: 12 August 2021
![A Tale of Two Isomers: Enhanced Antiaromaticity/Diradical Character versus Deleterious Ring-Opening of Benzofuran-fused s-Indacenes and Dicyclopenta[b,g]naphthalenes](/cms/asset/fa6b3252-2194-4349-9c99-08c2e391e24a/ange202107855-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Fusion of benzofuran to either s-indacene or dicyclopenta[b,g]naphthalene results in two dramatically different outcomes depending upon heterocycle orientation. Whereas the „anti“ isomers are unstable and hydrolyze readily to ring-opened products, the „syn“ isomers are quite stable and afford molecules that either possess a high degree of antiaromaticity or exhibit pronounced diradical character.
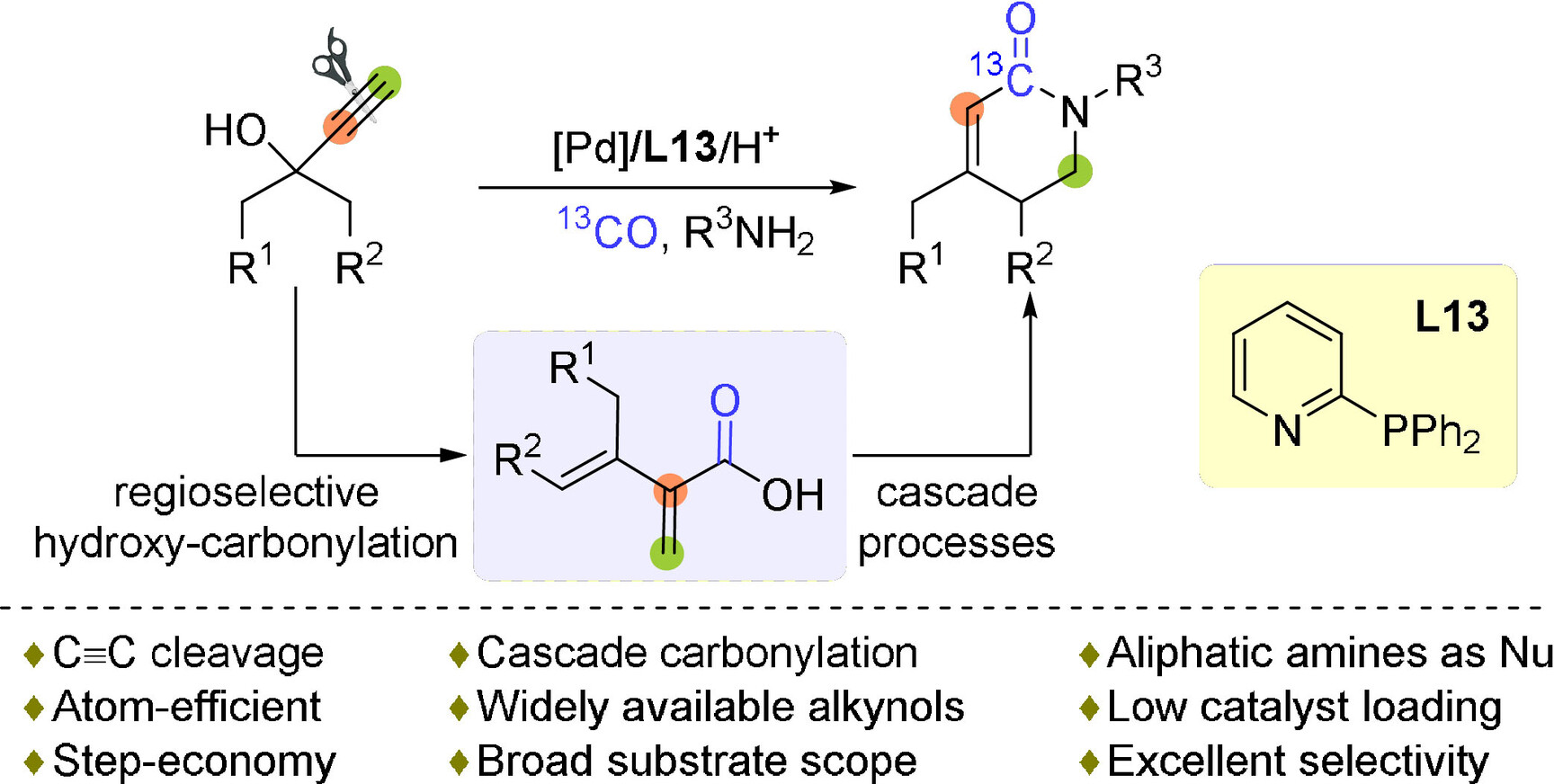
Homogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
Palladium-Catalyzed Cascade Carbonylation to α,β-Unsaturated Piperidones via Selective Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon Triple Bonds
- Pages: 22567-22574
- First Published: 12 August 2021
Biosynthesis | Hot Paper
Molecular Basis for Two Stereoselective Diels–Alderases that Produce Decalin Skeletons
- Pages: 22575-22584
- First Published: 13 June 2021
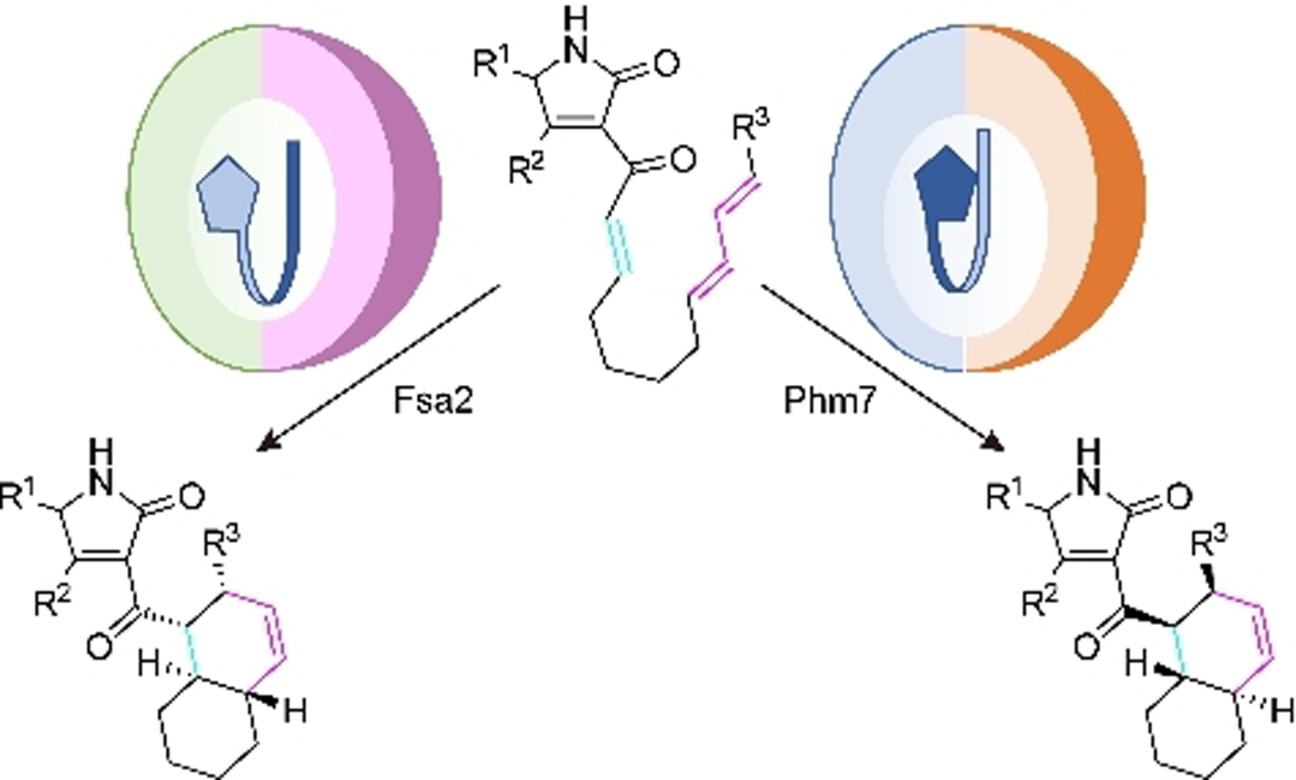
Powerful combination of experimental methods and calculations highlights the distinct molecular mechanisms underlying stereoselective [4+2] cycloadditions catalyzed by a pair of decalin synthases, Fsa2 and Phm7, that catalyze intramolecular cycloadditions to form enantiomeric decalin scaffolds. Our proposed mechanism would open a new window on the enzymatic [4+2] cycloadditions.
Cluster Compounds | Hot Paper
Tertiary Chiral Nanostructures from C−H⋅⋅⋅F Directed Assembly of Chiroptical Superatoms
- Pages: 22585-22590
- First Published: 04 August 2021
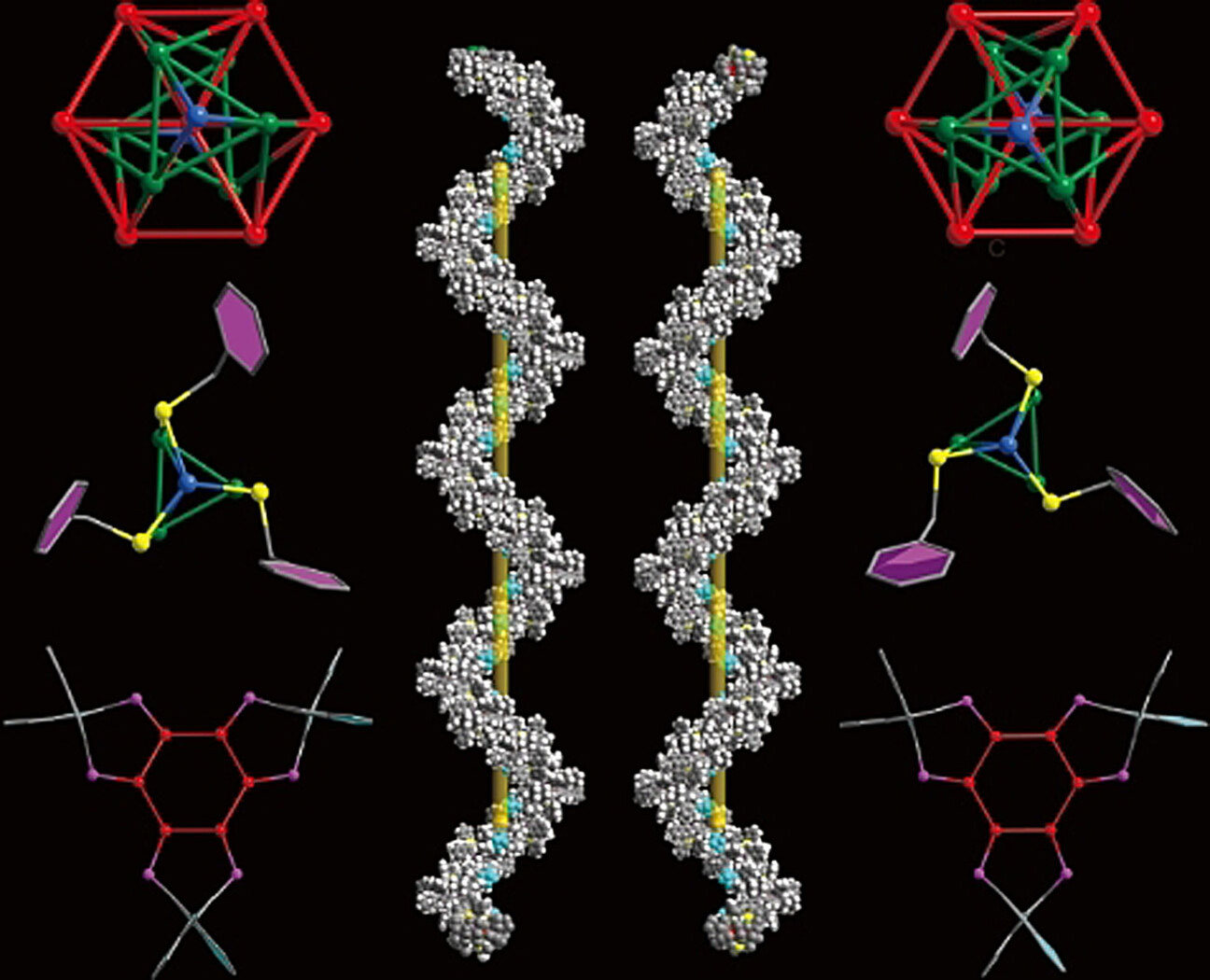
Tertiary chiral nanostructures have been created by assembling chiroptical superatoms of [Au7Ag6Cu2(S- or R-BINAP)3(SCH2Ph)6]+ (BINAP=2,2′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl). Both metal framework (primary structure) and surface ligands (secondary) of the nanocluster display perfect mirror symmetry. C−H⋅⋅⋅F hydrogen bonding between the clusters and SbF6− counterions direct formation of left- or right-handed helices.
Metal–Organic Frameworks | Hot Paper
Restriction of Intramolecular Vibration in Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens: Applications in Multifunctional Luminescent Metal–Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 22591-22597
- First Published: 03 August 2021
Crystal Engineering
Bending for Better: Flexible Organic Single Crystals with Controllable Curvature and Curvature-Related Conductivity for Customized Electronic Devices
- Pages: 22598-22605
- First Published: 10 August 2021
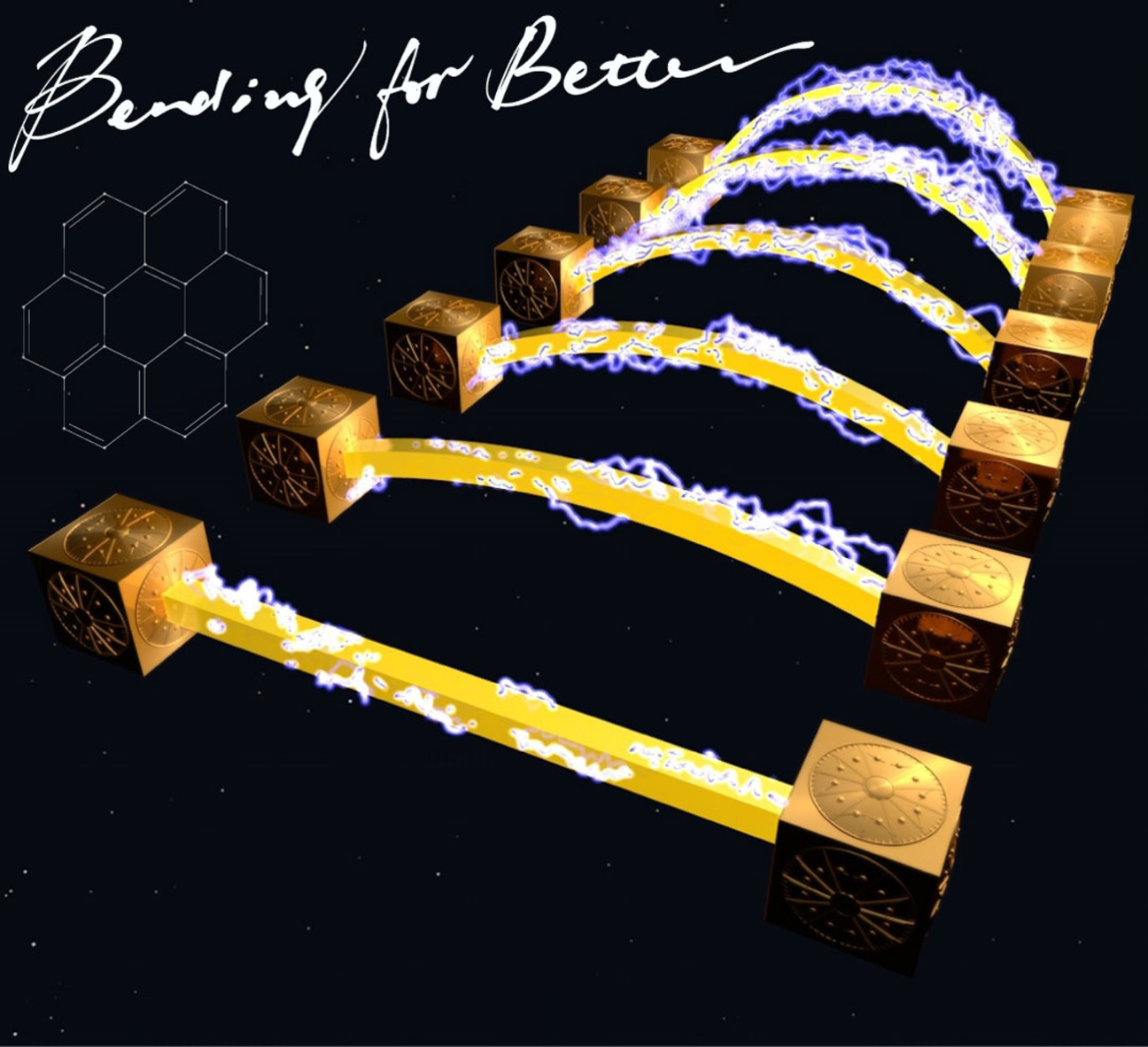

Self-bending organic single crystals of coronene with controlled width, length, and curvature are constructed for customized electronic micro-devices. The bending crystal device presents a huge improvement beyond seven orders of magnitude in the conductivity over the straight one, which benefited from both π electron level changing and carrier mobility enhancement caused by the structural deformation in the bent regions.
Iodine Capture | Very Important Paper
Ionic Functionalization of Multivariate Covalent Organic Frameworks to Achieve an Exceptionally High Iodine-Capture Capacity
- Pages: 22606-22614
- First Published: 24 August 2021
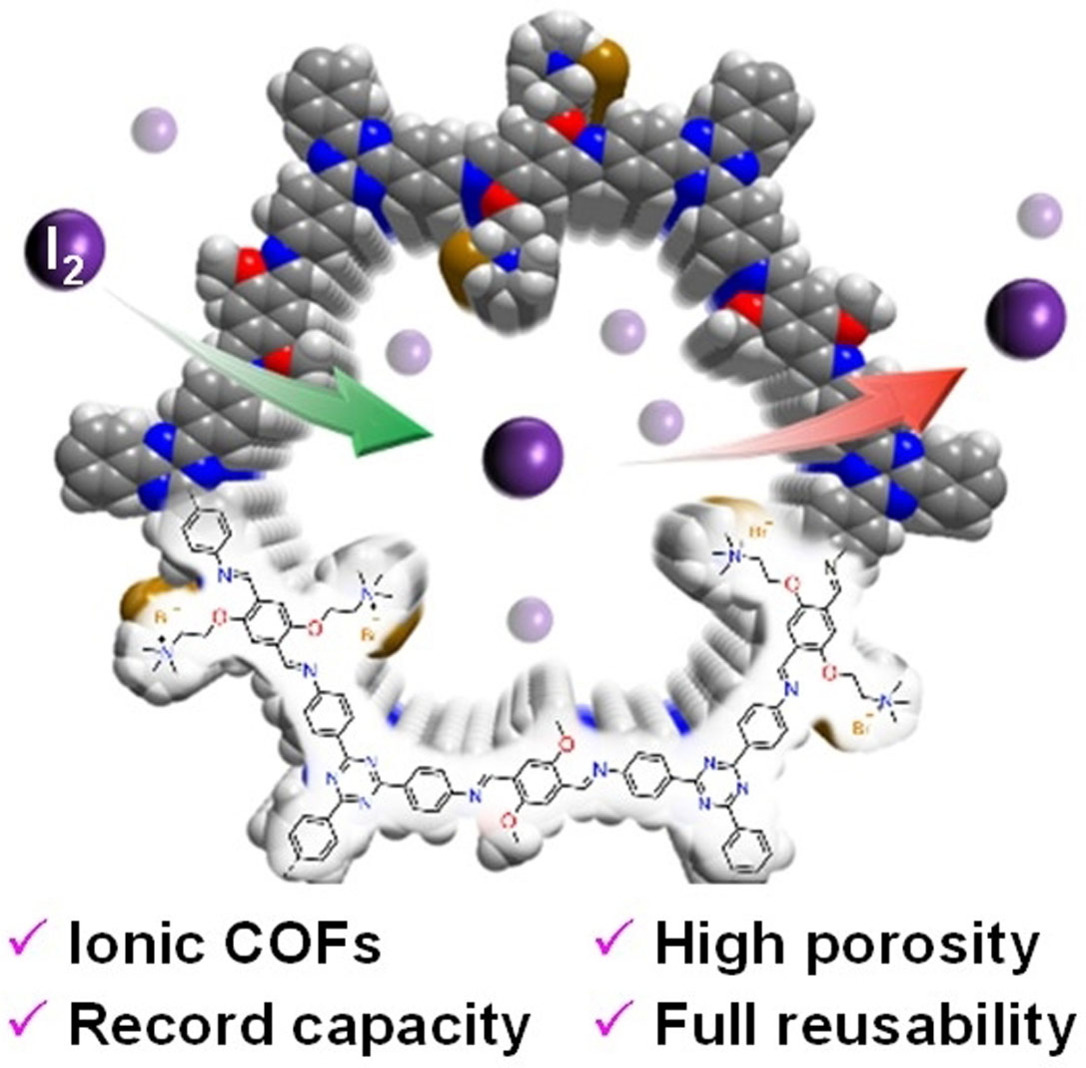
Multivariate covalent organic frameworks provide an ideal platform for ionic functionalization, enabling the integration of large surface areas, high pore volumes, and abundant binding sites, thereby leading to unprecedented levels of I2-capture performance under both static and dynamic adsorption conditions.
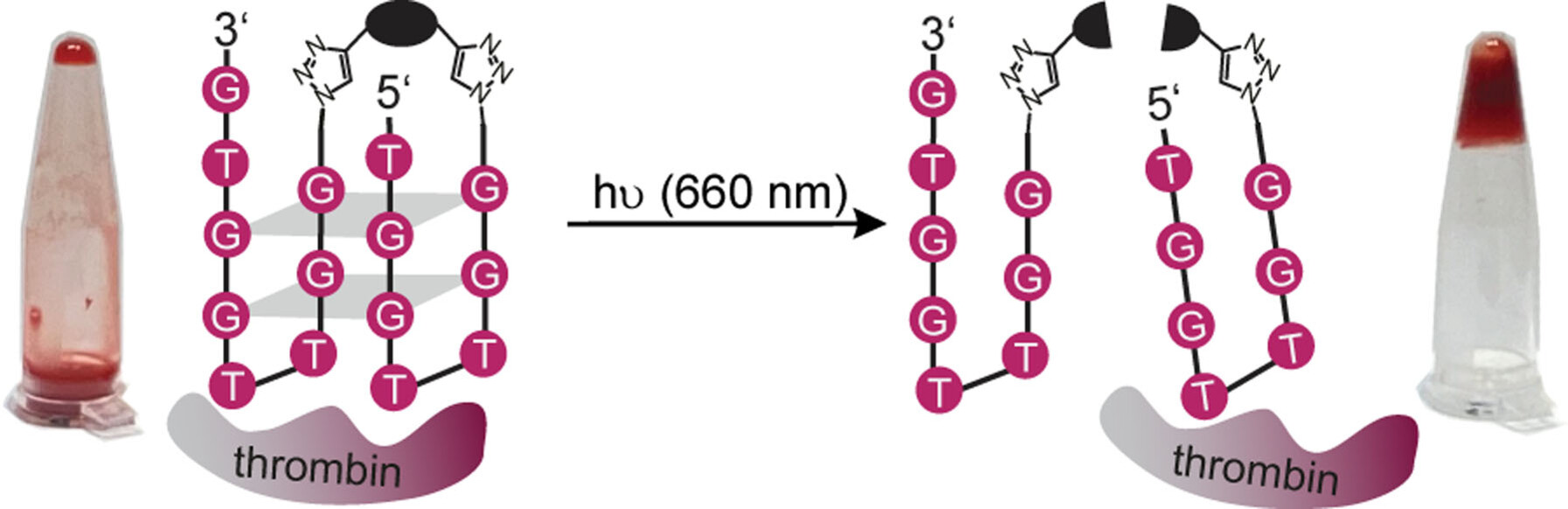
Phototherapy
Controlling Coagulation in Blood with Red Light
- Pages: 22615-22620
- First Published: 22 July 2021
Nonlinear Optics | Hot Paper
A Congruent-Melting Mid-Infrared Nonlinear Optical Vanadate Exhibiting Strong Second-Harmonic Generation
- Pages: 22621-22627
- First Published: 04 August 2021
Access to the elusive mid-infrared by direct second-harmonic generation (SHG) enabled by a vanadate crystal is reported. Cs4V8O22 exhibits a wide transparent range, a strong SHG response, a large laser damage threshold and congruent-melting behavior. Quantum mechanical calculations demonstrate the key role played by its quasi-rigid layered structure in the improvement in linear and second-order nonlinear optical performance.
Homogeneous Catalysis
Regio-controllable Cobalt-Catalyzed Sequential Hydrosilylation/Hydroboration of Arylacetylenes
- Pages: 22628-22634
- First Published: 04 August 2021
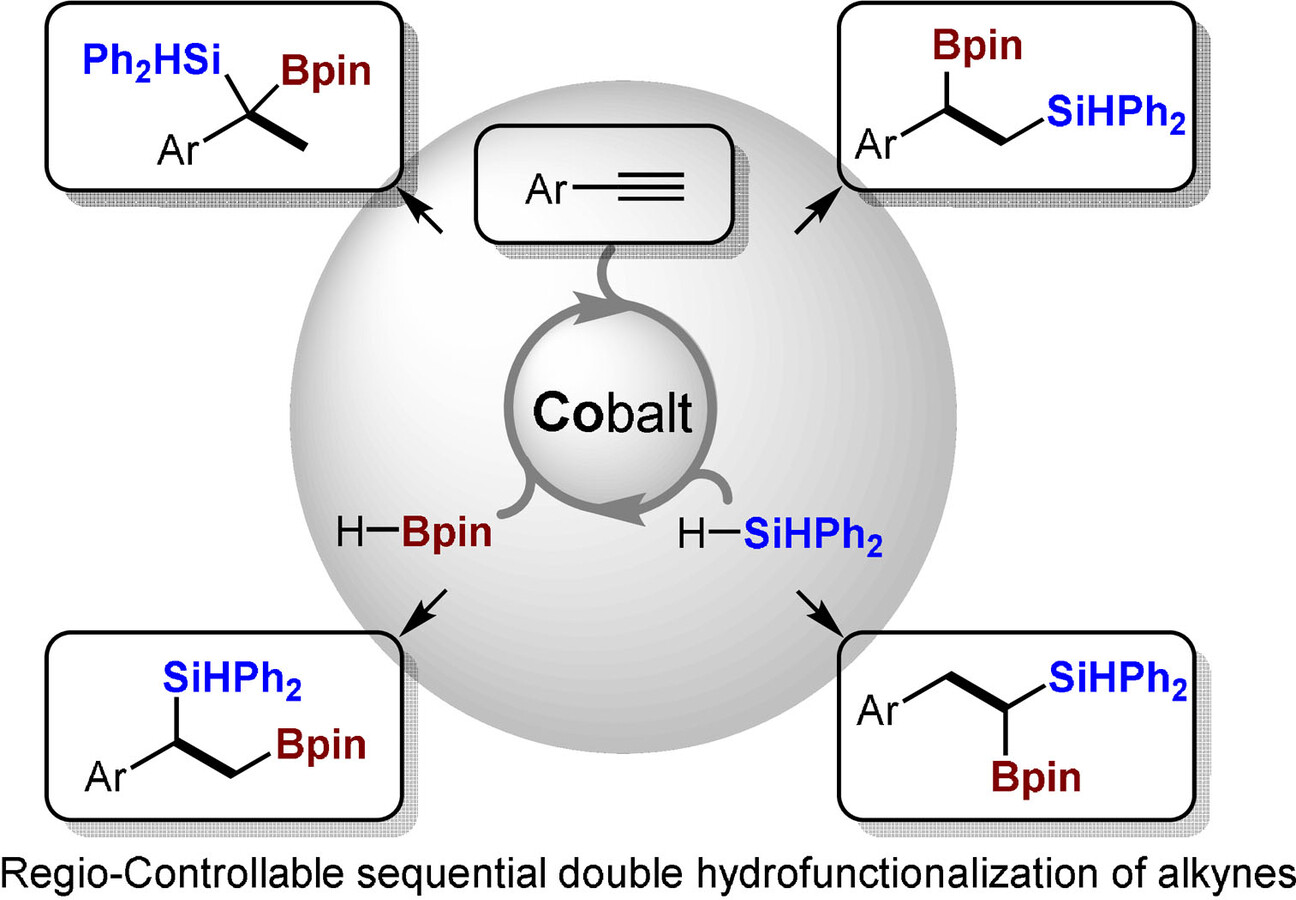
A cobalt-catalyzed regio-controllable sequential hydrosilylation/hydroboration of alkynes has been developed with complete control of all the possible regioselectivities for the double addition processes (up to >20/1 rr for all the cases). Various silylboronate regioisomers can be efficiently obtained from the same materials, with good functional group tolerance, regioselectivities as well as atom and pot economy.
Cross-Coupling | Hot Paper
Base-Activated Latent Heteroaromatic Sulfinates as Nucleophilic Coupling Partners in Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions
- Pages: 22635-22642
- First Published: 02 August 2021
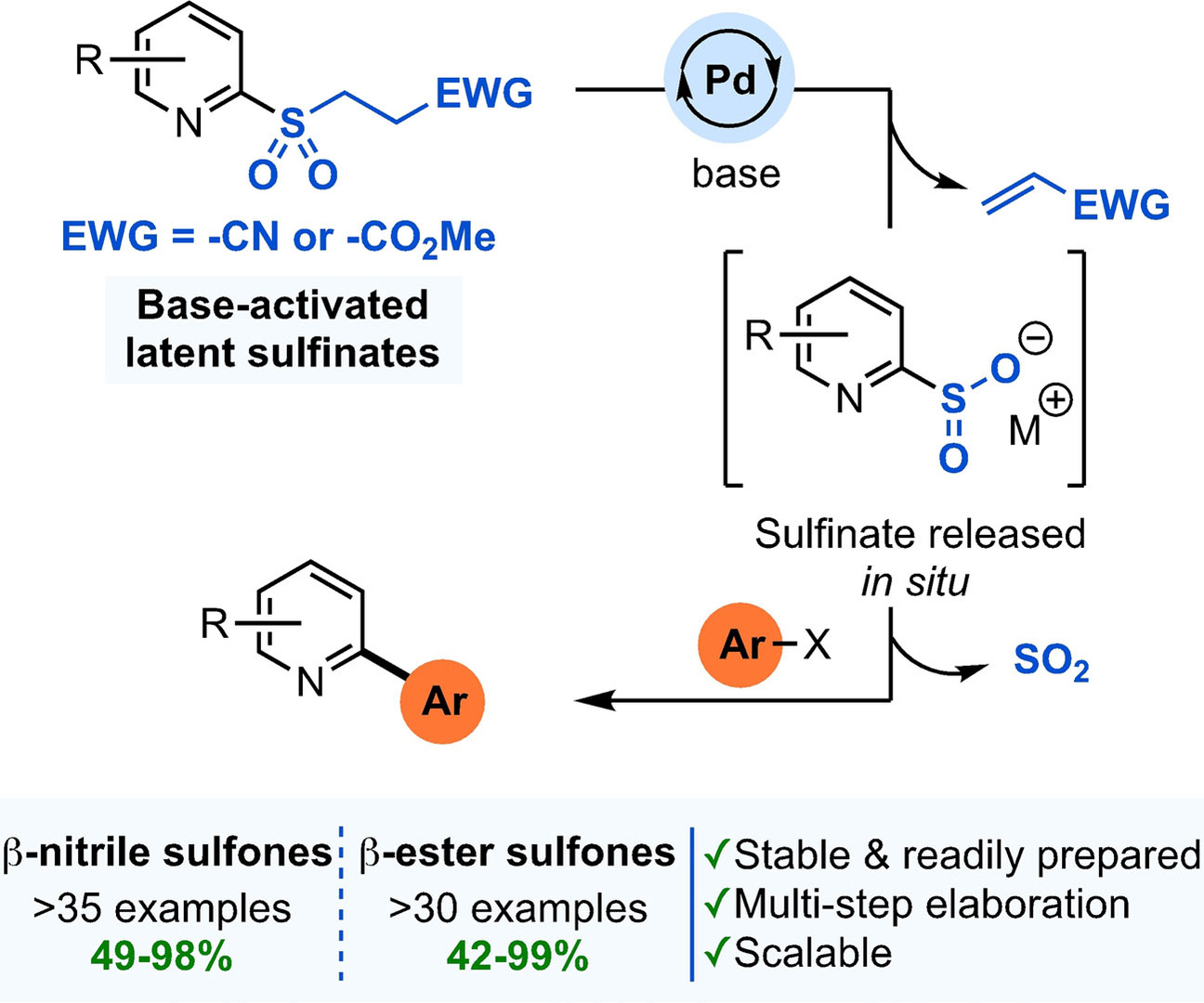
Next-generation, base-activated latent sulfinate reagents have been successfully developed for use in the construction of heteroaromatic frameworks, such as 2-arylpyridines. Under Pd-catalyzed conditions, these species unmask to give the sulfinate in situ, which then undergoes efficient desulfinative cross-coupling with an array of (hetero)aryl halides.
Polymers
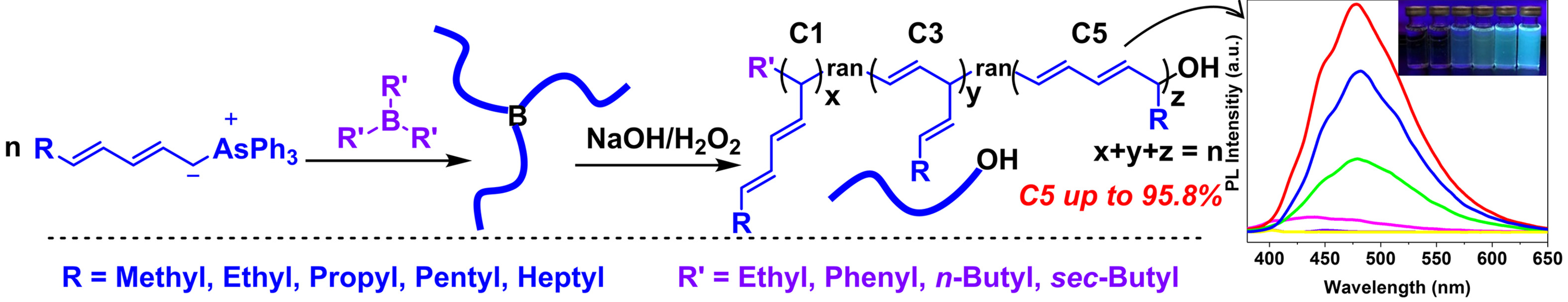
Steric Hindrance Drives the Boron-Initiated Polymerization of Dienyltriphenylarsonium Ylides to Photoluminescent C5-Polymers
- Pages: 22643-22651
- First Published: 13 August 2021
Carbon Materials
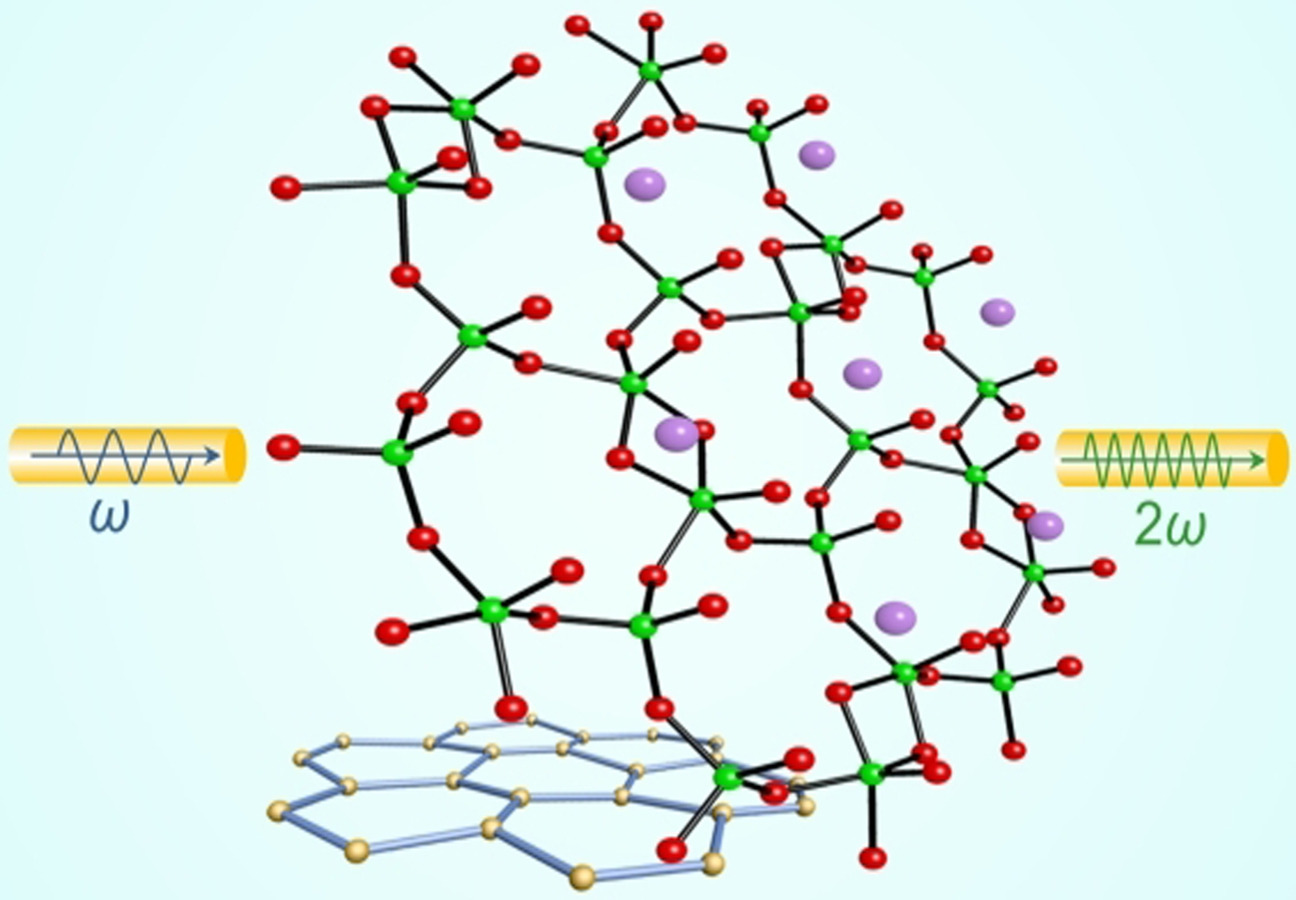
Rapid Access to Ordered Mesoporous Carbons for Chemical Hydrogen Storage
- Pages: 22652-22660
- First Published: 12 August 2021
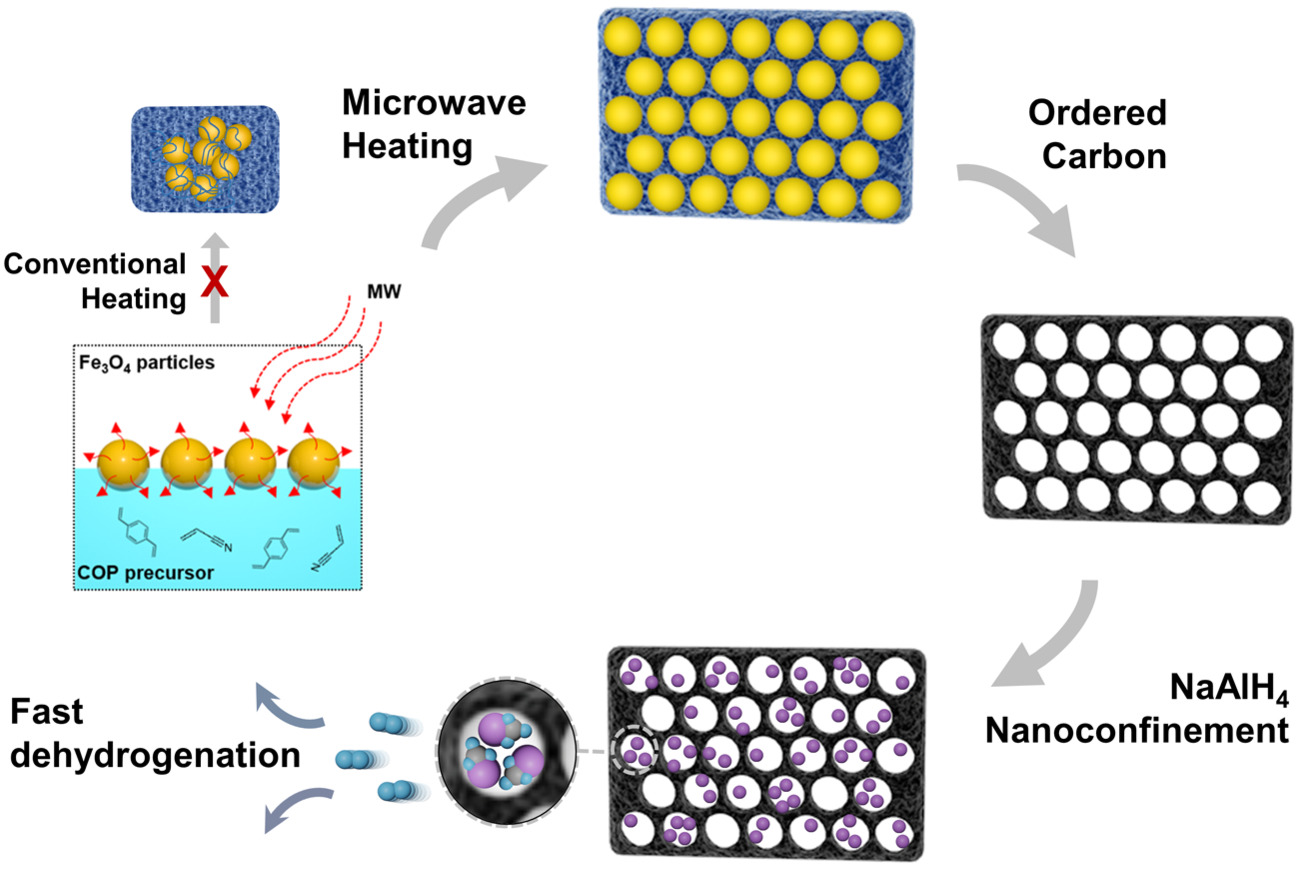
Nitrogen-doped ordered porous carbon was synthesized by microwave heating using Fe3O4 nanoparticles as hard templates. The microwave-assisted method reduces the reaction time and provides highly ordered structure with large surface area and nitrogen doping. NaAlH4 was confined into the pores of the carbon scaffold and the hydrogen sorption kinetics is improved by the synergistic effects of nanoconfinement and nitrogen doping.
Organofluorine Compounds
Radical Trifluoroacetylation of Alkenes Triggered by a Visible-Light-Promoted C–O Bond Fragmentation of Trifluoroacetic Anhydride
- Pages: 22661-22669
- First Published: 27 July 2021
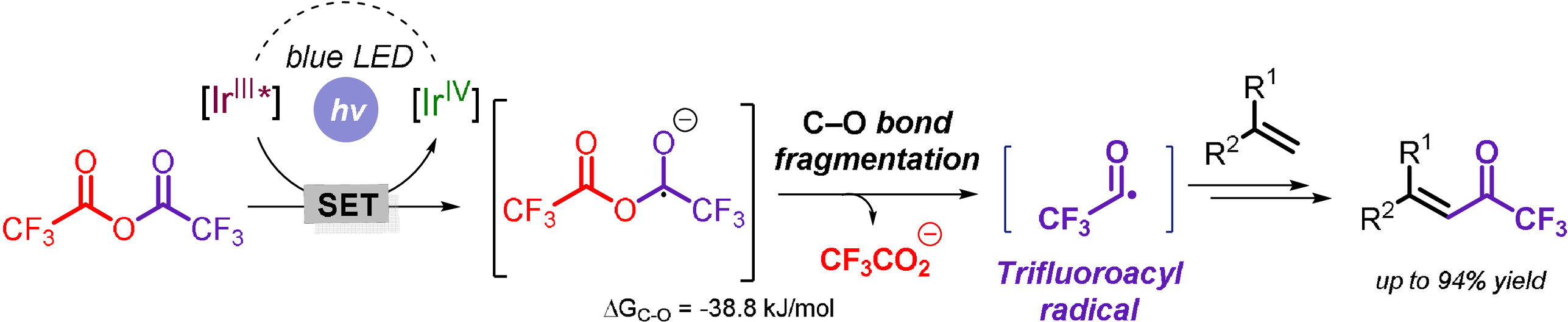
The trifluoroacyl radical is generated by C−O bond fragmentation of trifluoroacetic anhydride under photoredox conditions and undergoes olefinic C−H bond trifluoroacetylation in a mechanistically unique fashion. The protocol is operationally simple, scalable, and enables the late-stage diversification of complex biorelevant molecules delivering the corresponding α,β-unsaturated trifluoromethyl ketones in one step.
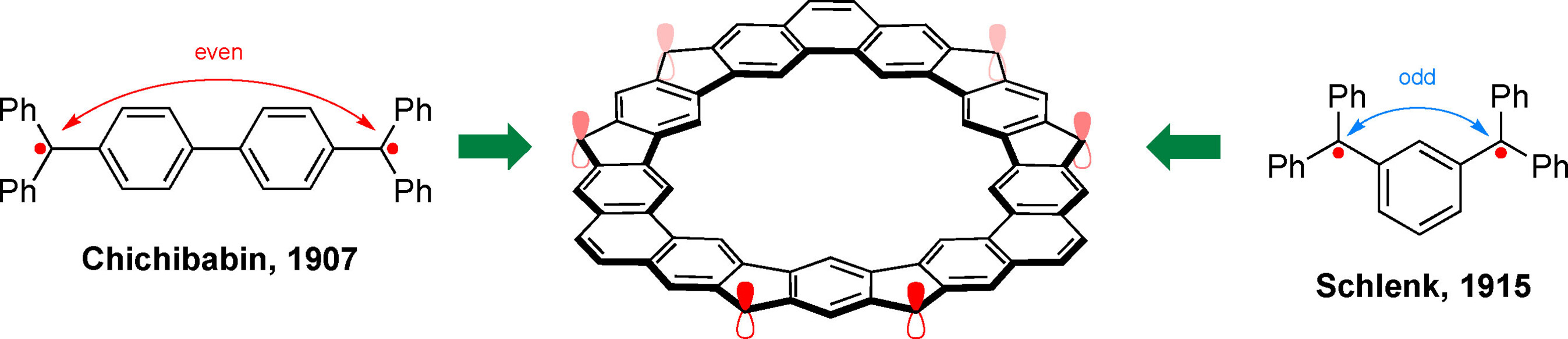
Aromaticity
An Open-Shell Coronoid with Hybrid Chichibabin–Schlenk Conjugation
- Pages: 22670-22678
- First Published: 12 August 2021
Antibacterial Agents
Dynamic Constitutional Frameworks as Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Agents
- Pages: 22679-22686
- First Published: 04 August 2021
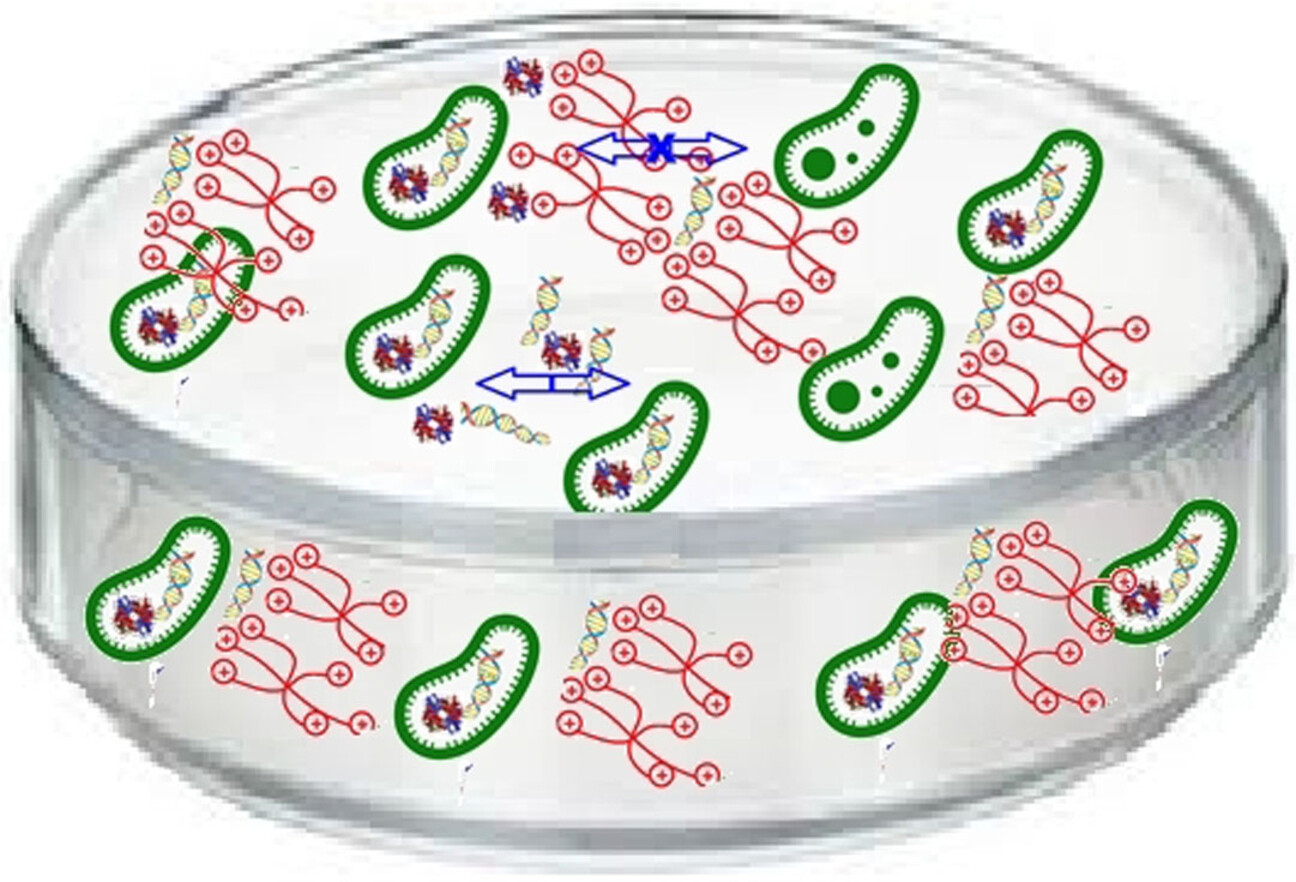
Dynamic constitutional frameworks are expressed in the presence of bacteria templating from dynamic covalent libraries made of aromatic cores, PEGylated connectors, and ionic heads. This templated DCFs further translate into the multivalent presentation of cationic heads, subsequently promoting antibacterial and antibiofilm activities.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Activity Trends and Mechanisms in Peroxymonosulfate-Assisted Catalytic Production of Singlet Oxygen over Atomic Metal-N-C Catalysts
- Pages: 22687-22695
- First Published: 13 August 2021
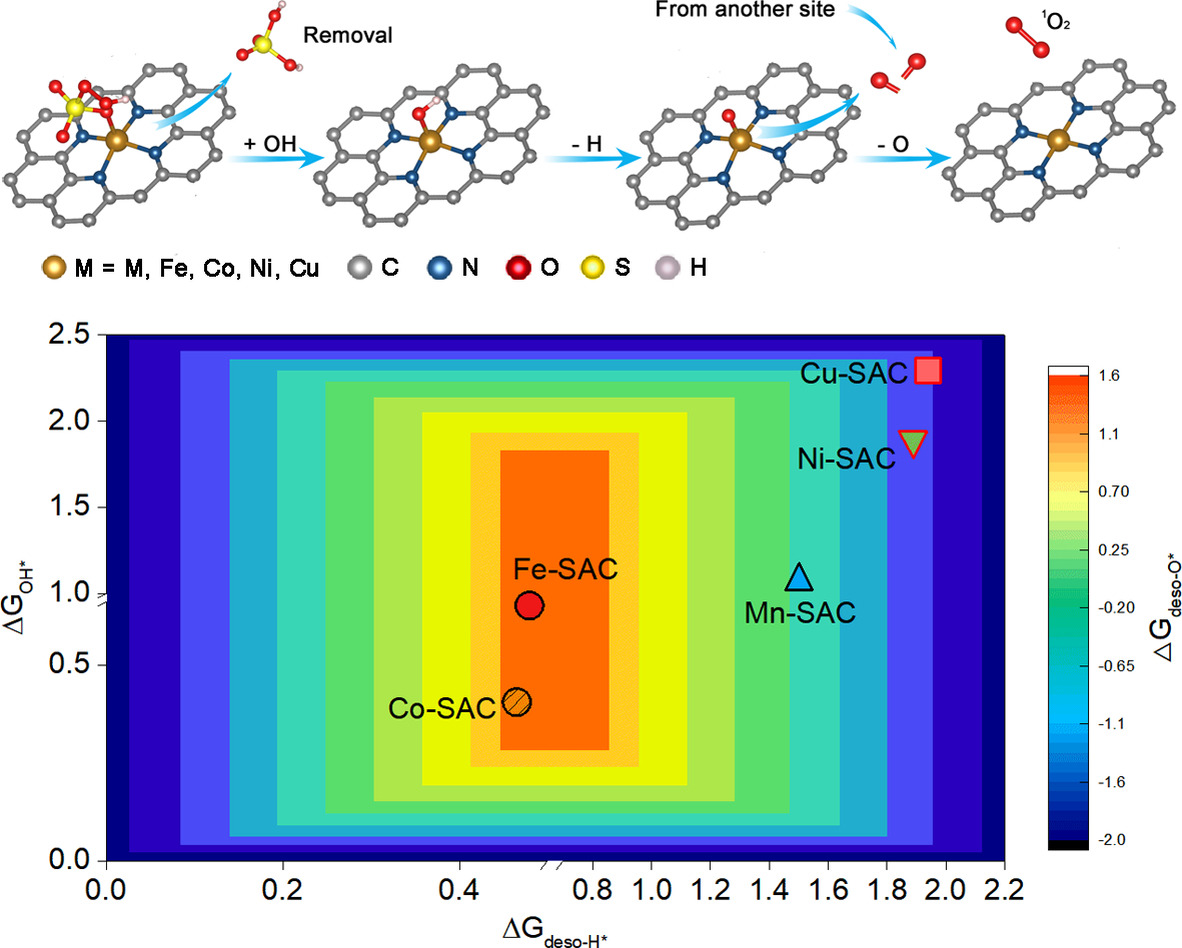
A series of carbon-supported atomic metal-N-C catalysts with similar structural and physicochemical properties were synthesized to uncover the activity trends and mechanisms in peroxymonosulfate-assisted reactive oxygen species production. Fe-SAC displays the best single-site kinetic value (1.65×105 min−1 mol−1), and the PMS→OH*→O*→1O2 is the most reasonable 1O2 reaction pathway.
Single-Atom Catalysis | Hot Paper
Polyoxometalate-Based Metal–Organic Framework as Molecular Sieve for Highly Selective Semi-Hydrogenation of Acetylene on Isolated Single Pd Atom Sites
- Pages: 22696-22702
- First Published: 09 August 2021
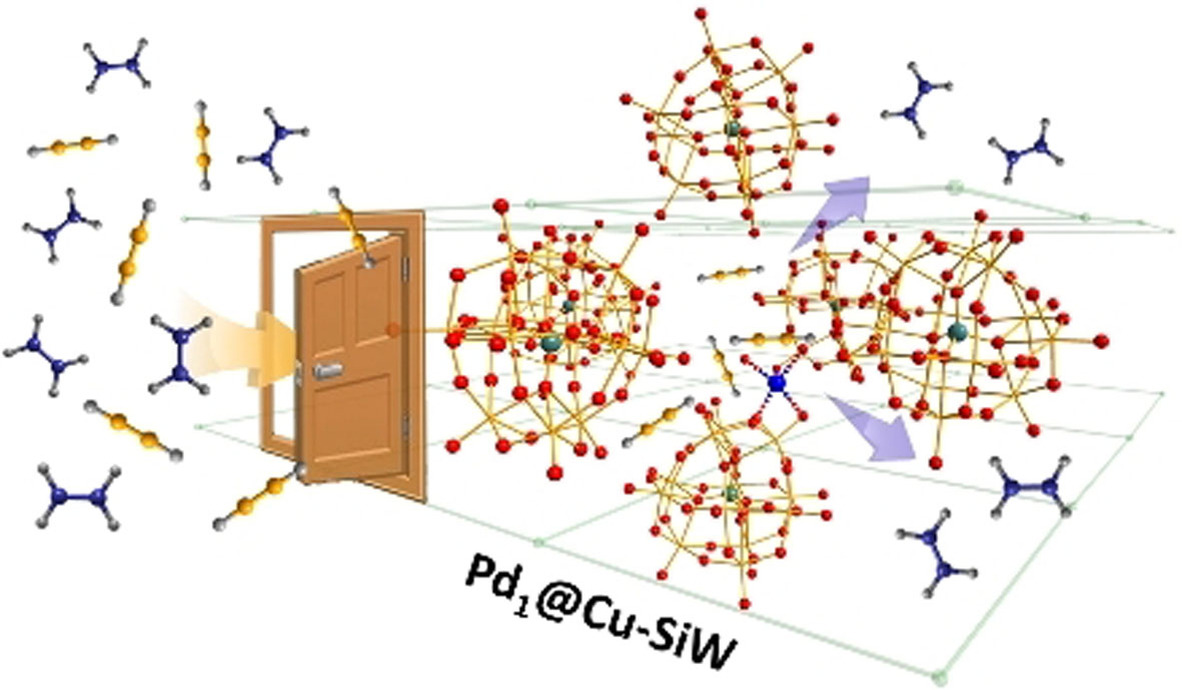
Highly selective acetylene semi-hydrogenation is realized using a polyoxometalate-based metal–organic framework supported single Pd atom catalyst by creating dynamic confinement regions which preferentially adsorb acetylene from acetylene/ethylene gas mixtures and release the produced ethylene. This catalyst combines the advantages of MOFs for gas separation and single atomic sites for catalysis.
Vesicles
Ordered Conformation-Regulated Vesicular Membrane Permeability
- Pages: 22703-22710
- First Published: 14 August 2021
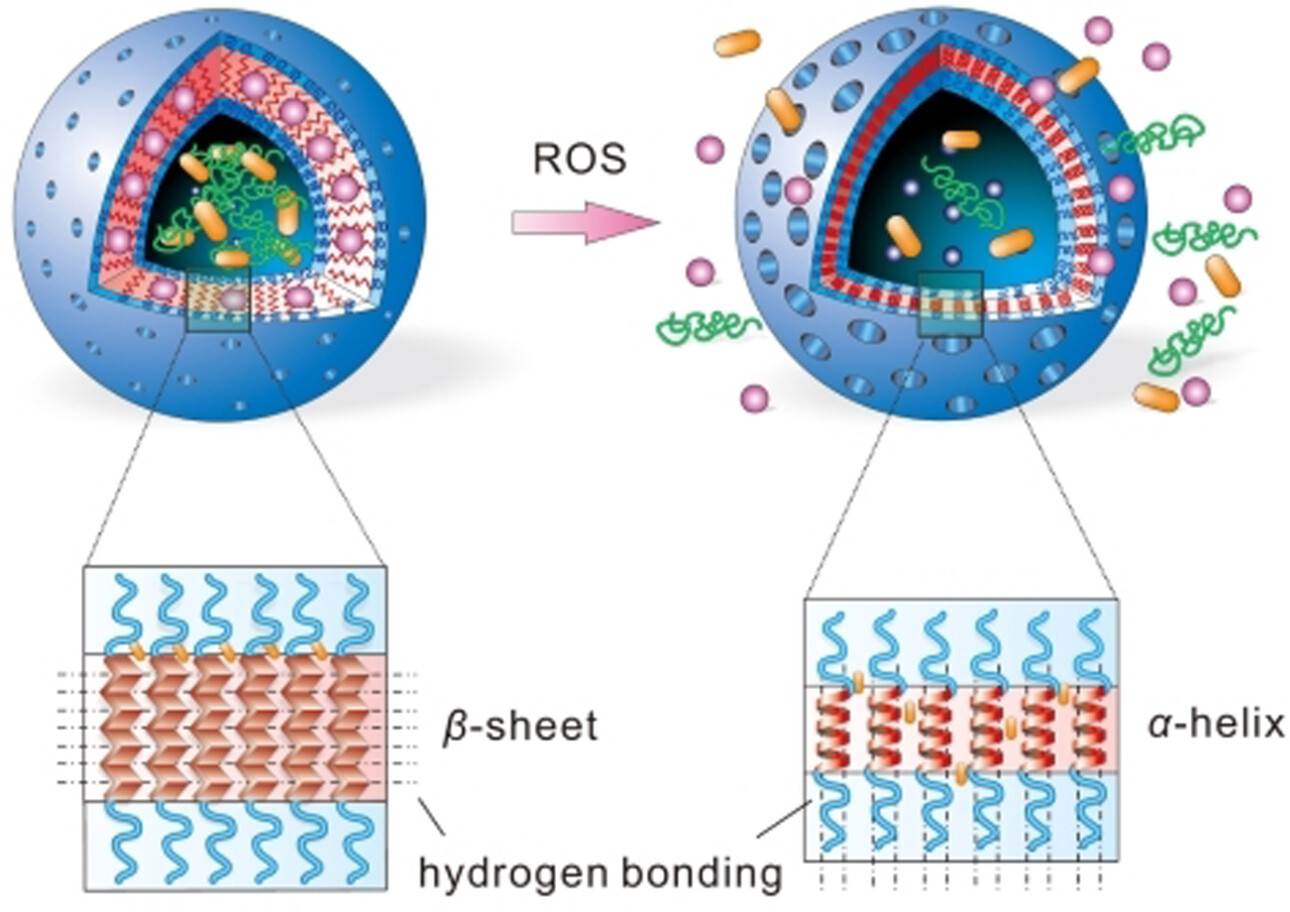
Synthetic polypeptide vesicles can regulate their membrane permeability via ordered transition of secondary conformations. Particularly, a transformation from extended β-strands to compact α-helices in response to reactive oxygen species reduces the vesicular wall thickness and remodels the membrane structure, thereby enhancing the membrane permeability for efficient nanoreaction, glucose-triggered insulin secretion and effective therapy of diabetes mellitus.
Systems Chemistry
Feedback and Communication in Active Hydrogel Spheres with pH Fronts: Facile Approaches to Grow Soft Hydrogel Structures
- Pages: 22711-22720
- First Published: 04 August 2021
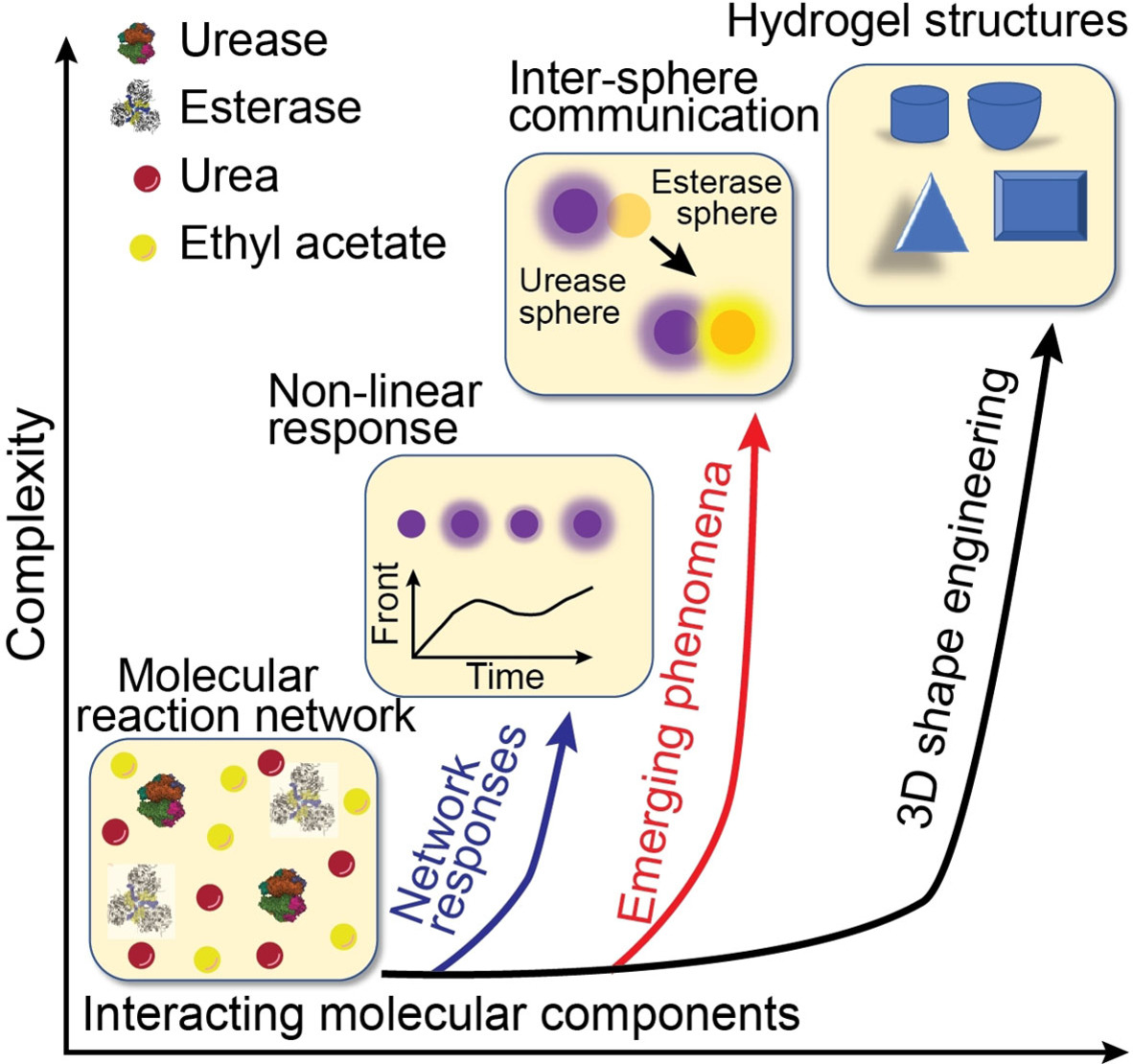
pH fronts are generated from feedback-controlled reaction networks encapsulated in hydrogel spheres. The pH front/reaction diffusion chemistry is utilized to understand the systems such as membrane activity and inter-sphere communication. Further, its potential to develop smart self-growing materials as 2D and 3D hydrogel structures is showcased as an alternative to 3D printing tool.
Polymerization | Hot Paper
O-to-S Substitution Enables Dovetailing Conflicting Cyclizability, Polymerizability, and Recyclability: Dithiolactone vs. Dilactone
- Pages: 22721-22727
- First Published: 23 August 2021
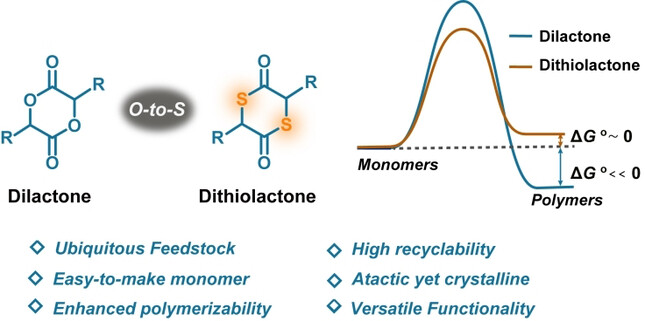
Dithiolactone monomers derived from abundant feedstocks show appealing chemical properties, including accelerated ring closure and polymerizability, high depolymerizability and selectivity. The derived polymers constitute a unique class of polythioester materials exhibiting controlled molecular weight, atactic yet high crystallinity, structural diversity, and chemical recyclability.
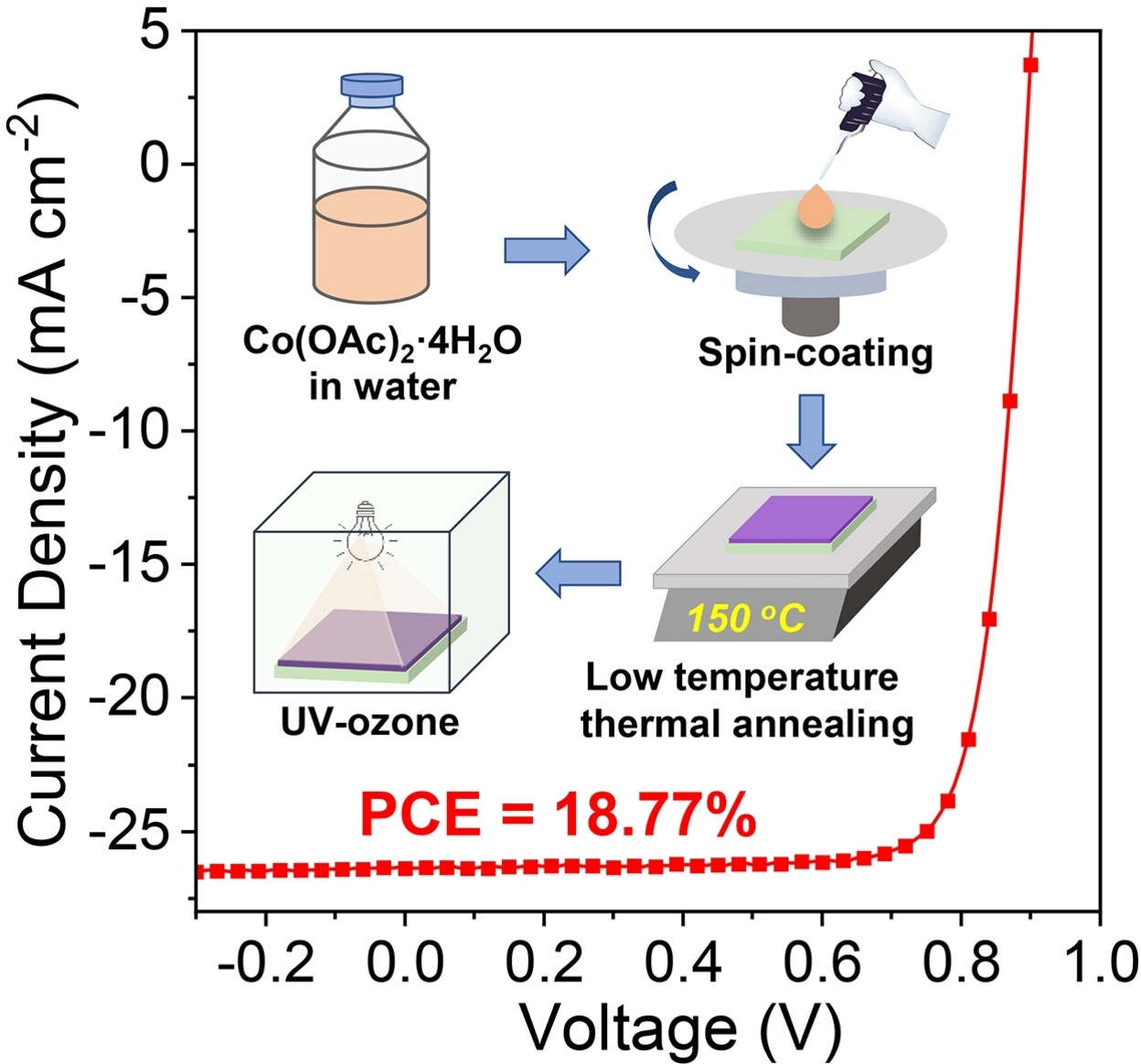
Organic Solar Cells | Very Important Paper
18.77 % Efficiency Organic Solar Cells Promoted by Aqueous Solution Processed Cobalt(II) Acetate Hole Transporting Layer
- Pages: 22728-22735
- First Published: 21 August 2021
Spin-Crossover | Hot Paper
Eine Familie von Heterobimetallischen Würfeln zeigt Spin-Crossover-Verhalten nahe Raumtemperatur
- Pages: 22736-22743
- First Published: 12 August 2021
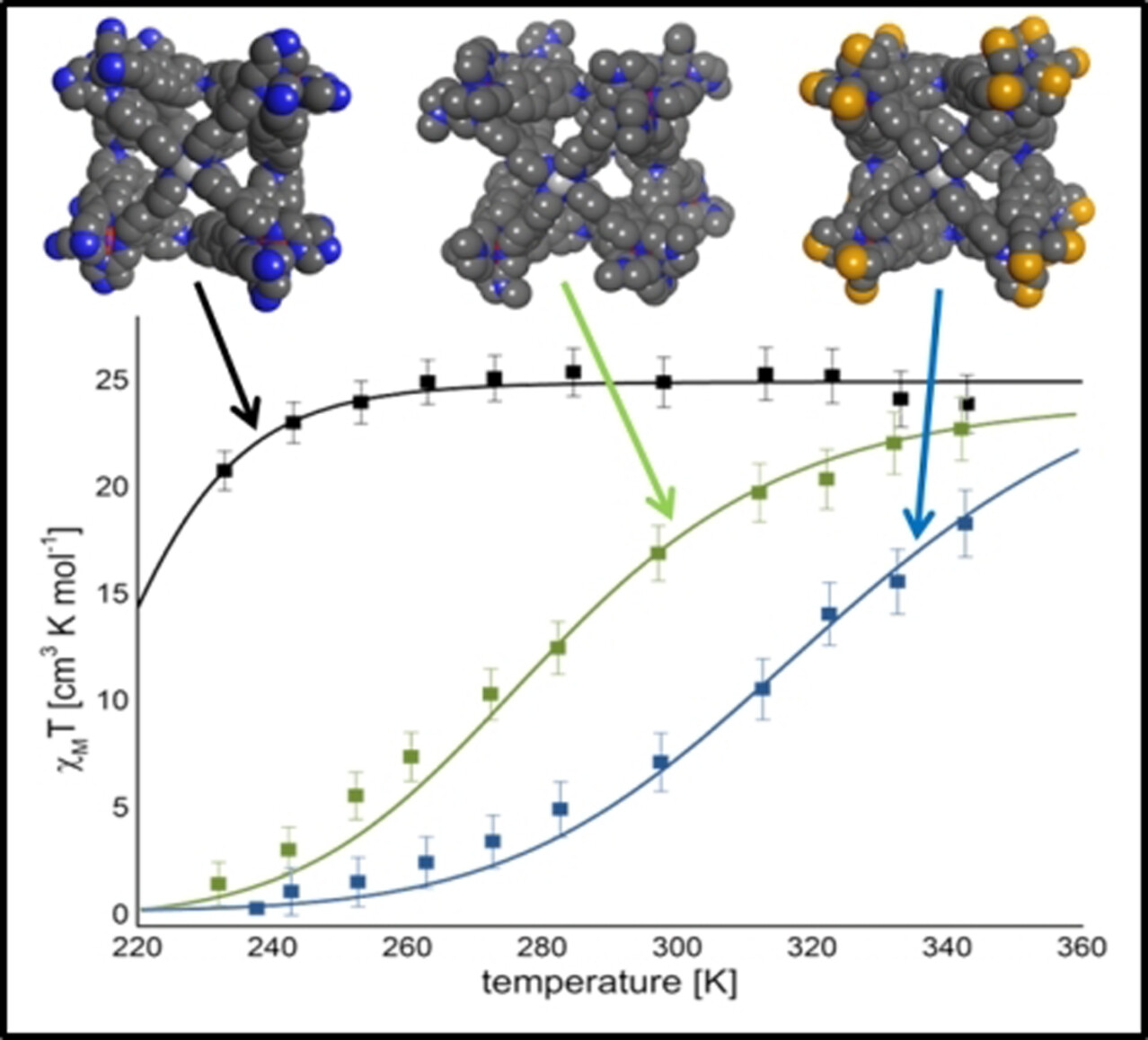
Ausgehend von einfachen Bausteinen wurden sechs heterobimetallische Würfel durch einfache Subkomponenten Selbstorganisation hergestellt. Drei der Käfige auf Basis von Eisen(II)ionen zeigten Spin-Crossover-Verhalten in Lösung. Dabei hing die Übergangstemperatur stark von der verwendeten Aldehydkomponenten ab, wodurch eine effiziente Strategie zur Beeinflussung des magnetischen Verhaltens der Komplexe etabliert werden konnte.
Chalkogenide | Very Important Paper
Chalkogenide durch Reduktion ihrer Dioxide in ultra-alkalischen Medien
- Pages: 22744-22752
- First Published: 10 August 2021
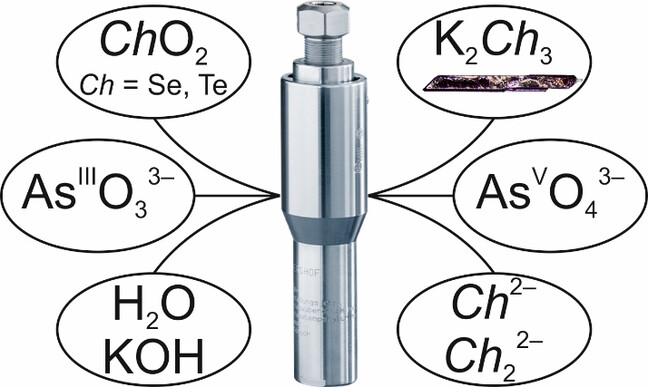
Die unerwartete Reduktion von Selen(IV)- und Tellur(IV)-Oxiden zu Chalkogeniden wurde unter ultraalkalischen Bedingungen durch die Verwendung von As2O3 als Reduktionsmittel ermöglicht. Durch Optimierung der Reaktionsbedingungen konnten innerhalb von zwei Tagen große Kristalle von K2Se3, K2Te3 und K2Se2Te gezüchtet werden. In der letztgenannten Verbindung wurde das neue gemischte Chalkogenid-Anion (SeTe)2− entdeckt.
Pigmente des Lebens
Tetrapyrrolische Pigmente aus dem Häm- und Chlorophyllabbau interagieren mit Aktin
- Pages: 22753-22760
- First Published: 26 July 2021
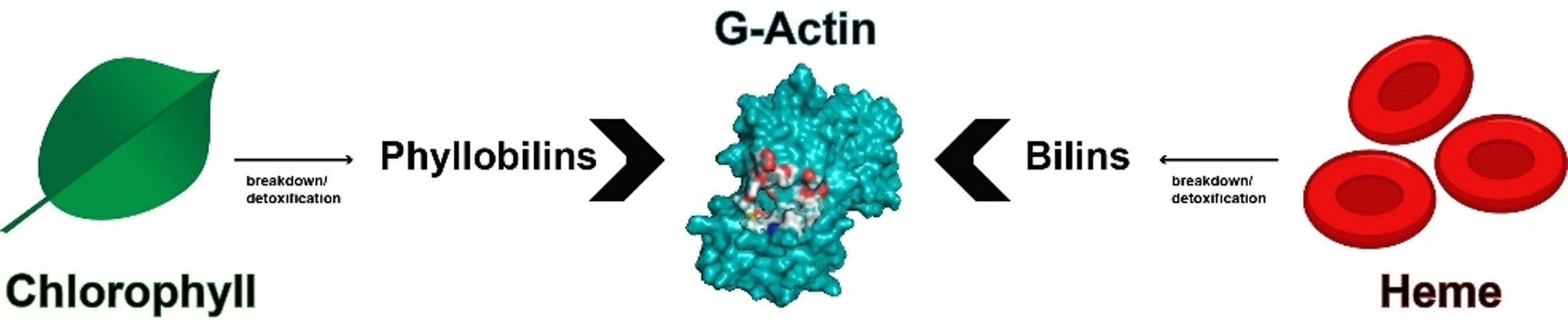
Die physiologische Rolle der Abbauprodukte von Chlorophyll und Häm, der exogenen Phyllobiline bzw. endogenen Biline, blieb jahrzehntelang ein ungelöstes Rätsel. Wir beschreiben den Einfluss dieser Tetrapyrrole auf das Aktin-Zytoskelett und stellen G-Aktin als erstes menschliches Zielprotein für Phyllobiline und als neue Zielstruktur für Biline vor. Diese Studie eröffnet eine völlig neue Perspektive auf die Bedeutung dieser ubiquitären Naturstoffe.