Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover
Titelbild: Highly Dispersed Pd@ZIF-8 for Photo-Assisted Cross-Couplings and CO2 to Methanol: Activity and Selectivity Insights (Angew. Chem. 48/2024)
- First Published: 08 October 2024

The Janus bifunctionality of Pd nanoparticles or atoms encapsulated in a Zn-based metal-organic framework is reported by Magnus Rueping, Pedro Castaño et al. in their Research Article (e202409490). As illustrated in the cover picture, on one side the catalyst is active and selective in photo-assisted cross-couplings, and on the other side selective and stable in the carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methanol.
Innentitelbild: Living Hybrid Exciton Materials: Enhanced Fluorescence and Chiroptical Properties in Living Supramolecular Polymers with Strong Frenkel/Charge-Transfer Exciton Coupling (Angew. Chem. 48/2024)
- First Published: 24 October 2024

Chiral supramolecular living polymers with strongly coupled, delocalized Frenkel excitations (FE) and charge-transfer excitations (CTE) were developed by Jianlei Han, Shigenori Fujikawa, and Nobuo Kimizuka in their Research Article (e202410431). Suitably designed, chiral perylene diimides (PDIs) show spontaneous transformation from kinetically formed nanoparticles into thermodynamically stable, luminescent helical and tubular nanostructures with enhanced chiroptical properties, fluorescence quantum yields, and living polymerization characteristics.
Innenrücktitelbild: Rationalizing Acidic Oxygen Evolution Reaction over IrO2: Essential Role of Hydronium Cation (Angew. Chem. 48/2024)
- First Published: 24 October 2024

Acid environment was found to play a critical role in regulating the catalytic behavior of IrO2 during the oxygen evolution reaction (OER). As demonstrated by Jingguang G. Chen, Ping Liu et al. in their Research Article (e202409526), the presence of hydronium cation (H3O+) introduces an internal electric field at the interface. It allows selective bond-tuning of the reaction intermediates and formation of partial surface hydroxylation under the operational conditions, which actively catalyzed the OER.
Rücktitelbild: Eine makrozyklische Hybrid-PET/MRT-Sonde für die quantitative Perfusionsbildgebung in vivo (Angew. Chem. 48/2024)
- First Published: 24 October 2024

A novel hybrid PET/MRI probe integrating stable gadolinium chelate with radioactive fluorine-18 was designed for precision imaging of perfusion and excretion dynamics. In their Research Article (e202409520), André F. Martins, Miloslav Polasek et al. demonstrate how merging quantitative PET signal with MRI contrast within a single molecule improves diagnostic capabilities. Employing sophisticated image analysis, this innovative probe can reveal hidden health issues, such as early stages of kidney dysfunction.
Frontispiz
Frontispiz: Simultaneously Strengthening and Toughening All-Natural Structural Materials via 3D Nanofiber Network Interfacial Design
- First Published: 17 November 2024

Organic Materials. An all-natural structural material is simultaneously strengthened and toughened through its interfacial interlocking structure and intermolecular interactions, as reported by Shu-Hong Yu et al. in their Research Article (e202408458).
Frontispiz: Catalytic Asymmetric Construction of C- and Si-Stereogenic Silacyclopentanes via Hydrosilylation of Arylmethylenecyclopropanes
- First Published: 17 November 2024

Asymmetric Hydrosilylation. In their Communication (e202413753), Chuan He et al. report an efficient Cu-catalyzed asymmetric cascade hydrosilylation protocol, which allows the rapid assembly of carbon- and silicon-stereogenic silacyclopentanes with good to excellent enantioselectivities and diastereoselectivities.
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis: Angew. Chem. 48/2024
- First Published: 17 November 2024
Introducing …
Marco Deiana
- First Published: 25 October 2024

“My long-term goal is to popularize biocatalysis in India so that more and more people work in this area and invent new-to-nature chemistry… If I could have dinner with a well-known historic figure, I would invite Nikola Tesla and I would ask him how I can get rid of all the wires on my table…” Find out more about Syed Masood Husain in his Introducing… Profile.
Highlight
Supramolecular Chemistry
Mechanistic Insights into Curvature Formation in Synthetic Vesicles
- First Published: 29 July 2024
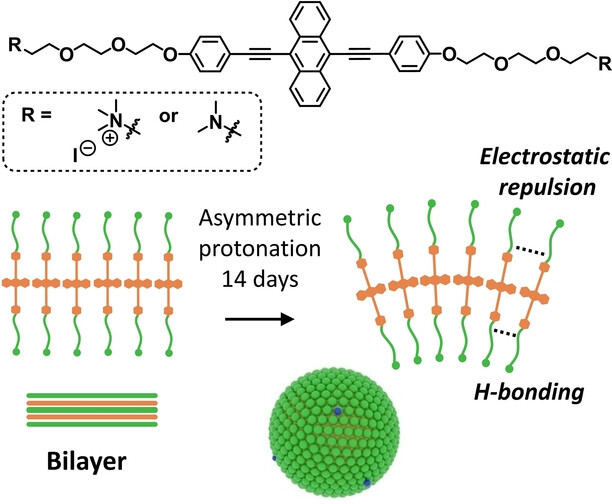
A new bilayer-forming supramolecular amphiphile, reported by Elizebath et al., helps elucidate mechanisms of curvature induction in synthetic membranes. Assembly in water led initially to aggregates but, over time, membrane budding and vesicle formation were observed due to asymmetric protonation of the water-exposed terminal tertiary amines. Insights could lead to the development of new hierarchical life-like materials and artificial cells.
Korrespondenz
Photoswitches
Correspondence on “Visible-Light-Switchable Chalcone-Flavylium Photochromic Systems in Aqueous Media”
- First Published: 23 September 2024
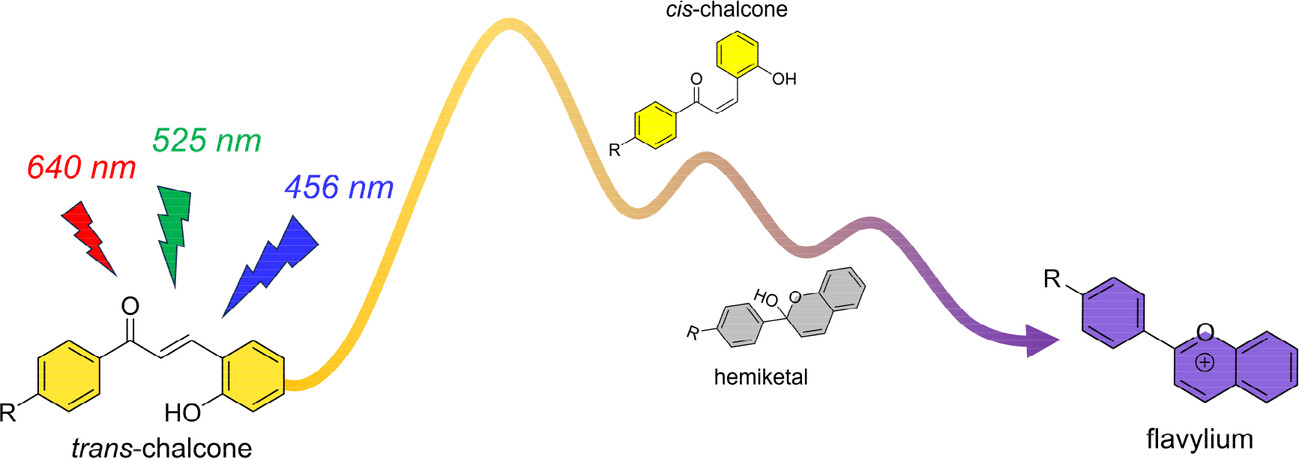
Recently, Bandyopadhyay and co-workers reported new chalcone photoswitches claimed to display advantageous optical and photochemical properties for potential biological applications, i.e., switching with blue, green and red light in aqueous solution. In this Correspondence, we argue that further experimental evidence is required to support the proposed design, data interpretation, and main conclusions.
Reply to the Correspondence on “Visible Light-Switchable Chalcone-Flavylium Photochromic Systems in Aqueous Media”
- First Published: 17 October 2024
Scientific Perspective
Machine Learning
Contrasting Historical and Physical Perspectives in Asymmetric Catalysis: ΔΔG≠ versus Enantiomeric Excess
- First Published: 15 October 2024
We explore the difference between enantiomeric excess (ee) and relative Gibbs free activation energies (ΔΔG≠) as modeling targets in asymmetric catalysis. Through data analysis and application of modern machine learning methods, we unveil the strengths and limitations of each approach. Our results offer critical insights into which target more accurately predicts enantioselectivity, providing a guide for future research in machine learning for catalysis.
Aufsatz
Carbon Nanomaterials
Carbon Dot Synthesis and Purification: Trends, Challenges and Recommendations
- First Published: 20 August 2024
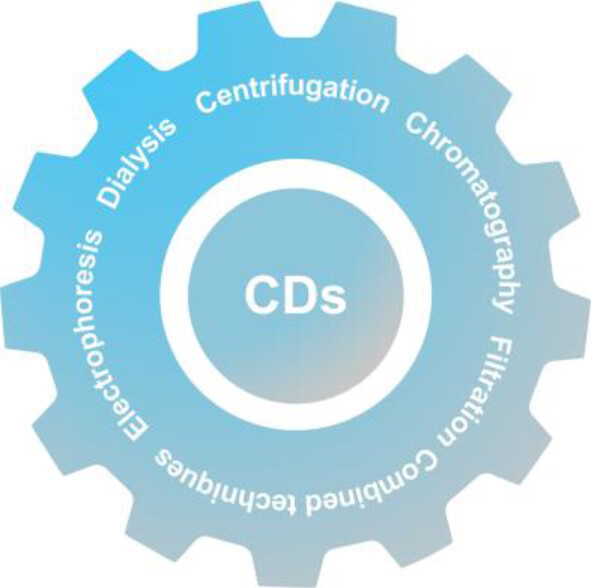
This Review analyzes the current trends and challenges in the synthesis and purification of carbon dots prepared through various methods and using a wide variety of precursors. Diverse purification techniques, including centrifugation, filtration, dialysis, column chromatography, and electrophoresis, are systematically and thoroughly described, along with pointing out the gaps in the synthesis, purification, and assessment of CD purity.
Forschungsartikel
Nanofibers | Very Important Paper
Simultaneously Strengthening and Toughening All-Natural Structural Materials via 3D Nanofiber Network Interfacial Design
- First Published: 13 June 2024
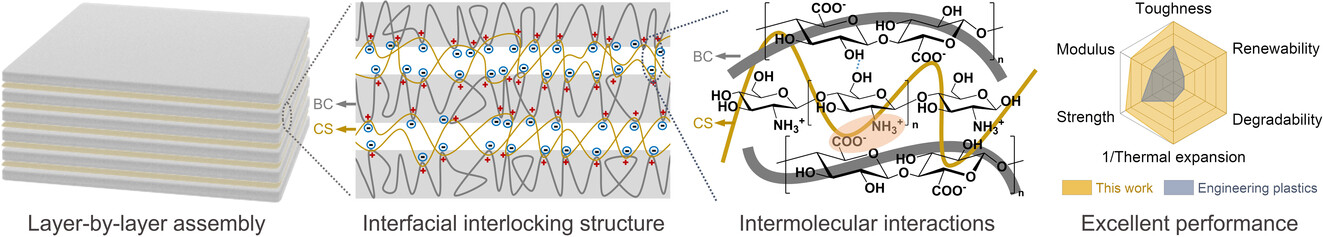
An interfacial interlocking structure is designed by introducing protonated chitosan (CS) at the interface between the surface oxidized 3D nanonetwork of bacterial cellulose (BC). This interfacial structure provides enough physical contact sites for hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions. The obtained structural material shows better environmental friendliness and mechanical and thermal properties than engineering plastics.
CO2 Hydrogenation
Highly Dispersed Pd@ZIF-8 for Photo-Assisted Cross-Couplings and CO2 to Methanol: Activity and Selectivity Insights
- First Published: 09 August 2024
Supramolecular Chemistry | Hot Paper
Living Hybrid Exciton Materials: Enhanced Fluorescence and Chiroptical Properties in Living Supramolecular Polymers with Strong Frenkel/Charge-Transfer Exciton Coupling
- First Published: 10 July 2024
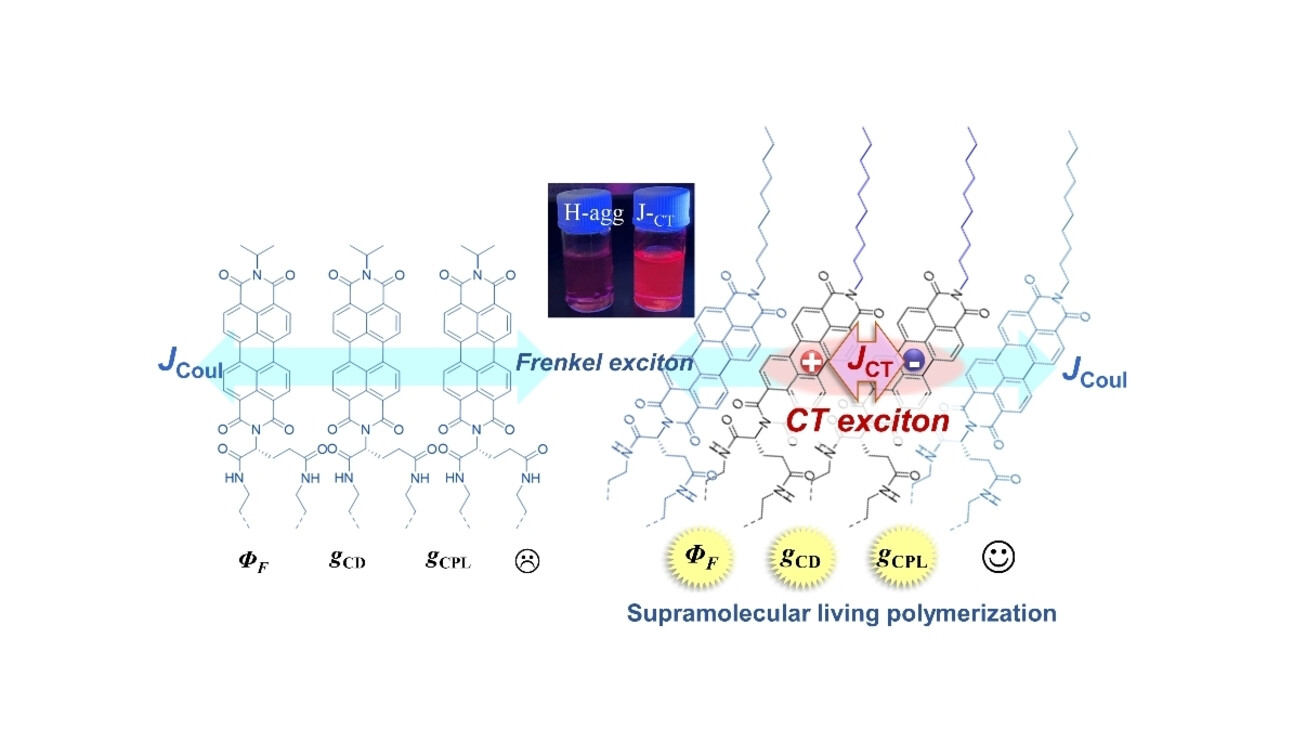
Asymmetrically L/D-glutamate-derived PDIs having linear alkyl chains exhibit living supramolecular polymerization in thermodynamically stable chiral molecular orientation, which shows the coupling of Frenkel and charge transfer exciton states, resulting in significantly enhanced fluorescence quantum yield, CD and CPL properties. Meanwhile, PDIs with branched chains only show common H-aggregates. Thus, molecular control on living hybrid exciton nanomaterials is achieved.
Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Rationalizing Acidic Oxygen Evolution Reaction over IrO2: Essential Role of Hydronium Cation
- First Published: 20 July 2024
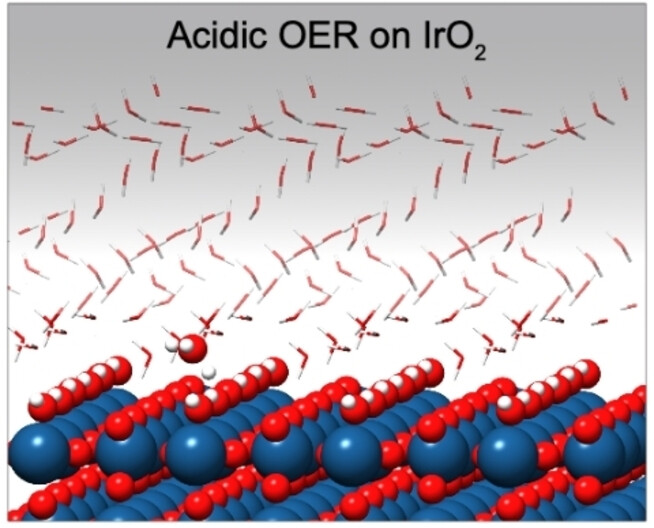
Hydronium cation (H3O+) was found to be critical to regulating the observed behaviors of IrO2 during acidic oxygen evolution reaction. The H3O+ cation induced an internal electric field at the interface, enabling selective bond-tuning to the reaction intermediates. As a result, 0.5 monolayer of *OH species was stabilized under OER operational condition, and the overall conversion was revealed to be hindered by *OH→*O.
Li–S Batteries
P-doped RuSe2 on Porous N-Doped Carbon Matrix as Catalysts for Accelerated Sulfur Redox Reactions
- First Published: 28 August 2024
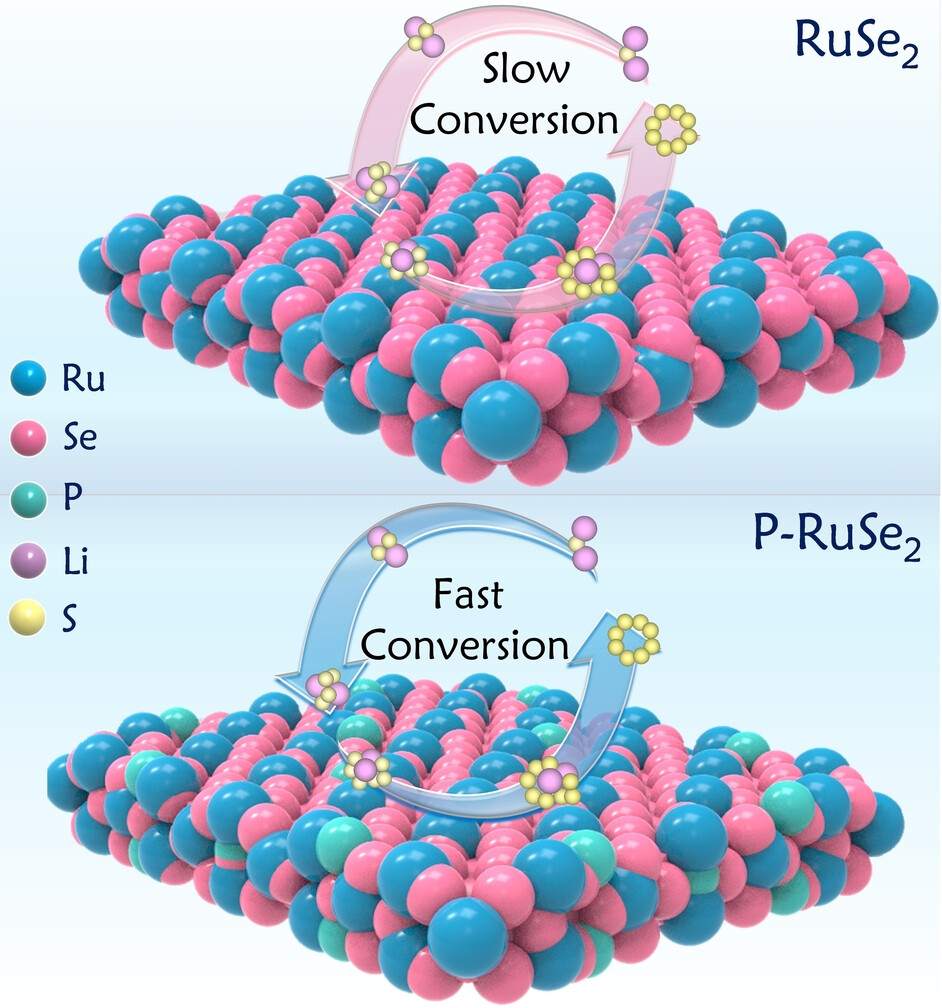
A new catalyst of phosphorus doped RuSe2 (P-RuSe2) with the enhanced conductivity and the modulation of the d-band center is engineered via a rational screening strategy, which augments its effectiveness in interacting with LiPSs and hence exhibits enhanced electrochemical performance in terms of high capacity, superior rate capability and stable cycle life.
Dissipative Self-Assembly | Hot Paper
Non-Equilibrium Dissipative Assembly with Switchable Biological Functions
- First Published: 22 August 2024
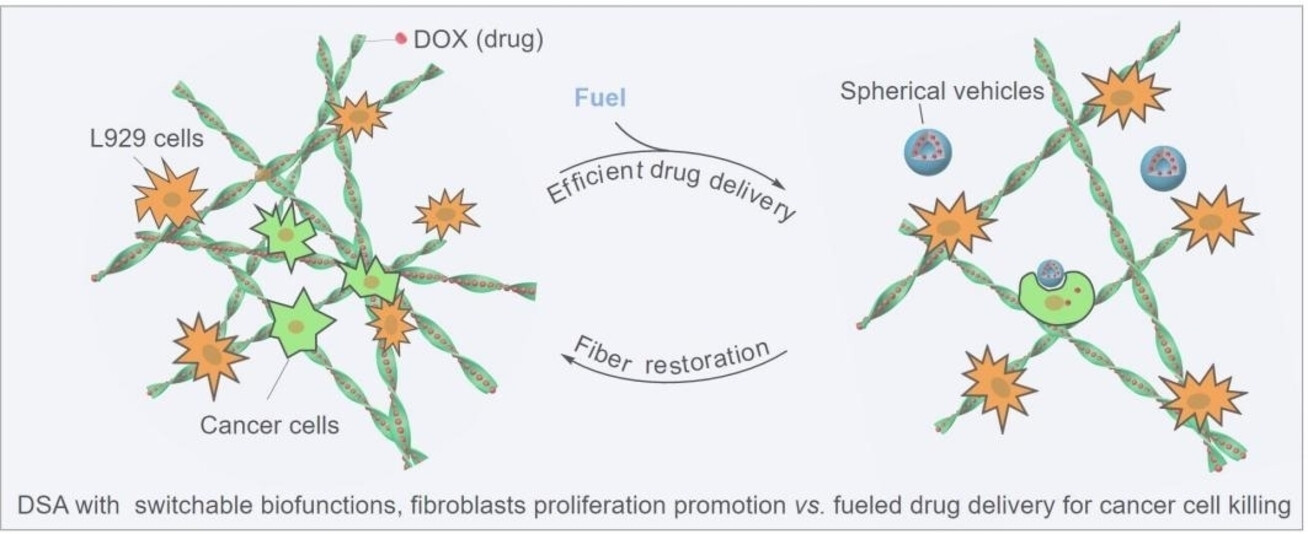
A switchable non-equilibrium dissipative assembly promoting fibroblast adhesion/proliferation and efficient drug delivery was developed using chemical fuel. Nanofibers acted as chiral hydrogel scaffolds for cell adhesion and drug reservoirs. This system transitions between nanofiber and nanospherical forms, enabling targeted drug delivery and recovery, highlighting its scientific significance.
H2O2 Production | Very Important Paper
Azobenzene-Bridged Covalent Organic Frameworks Boosting Photocatalytic Hydrogen Peroxide Production from Alkaline Water: One Atom Makes a Significant Improvement
- First Published: 13 August 2024
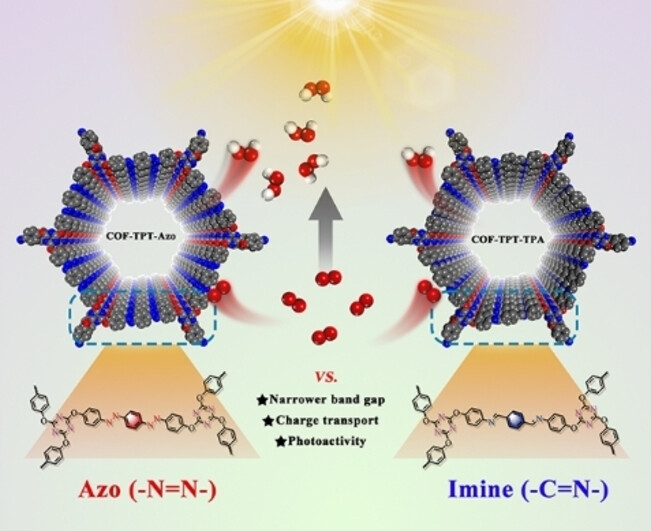
A novel photoactive azobenzene-bridged 2D COF (COF-TPT-Azo) shows an excellent photocatalytic H2O2 production rate up to 1498 μmol g−1 h−1 at pH = 11, which is 7.9 times higher than its corresponding imine-linked 2D COF (COF-TPT-TPA), although only one atom is different in the two 2D COFs (−N=N− vs. −C=N−). COF-TPT-Azo exhibits much narrower band gap, enhanced charge transport, and prompted photoactivity, which is benefited from its azo linkages.
Porphyrinoids
Fused Hexabenzocoronene-Porphyrin Conjugates with Tailorable Excited-State Lifetimes
- First Published: 06 August 2024
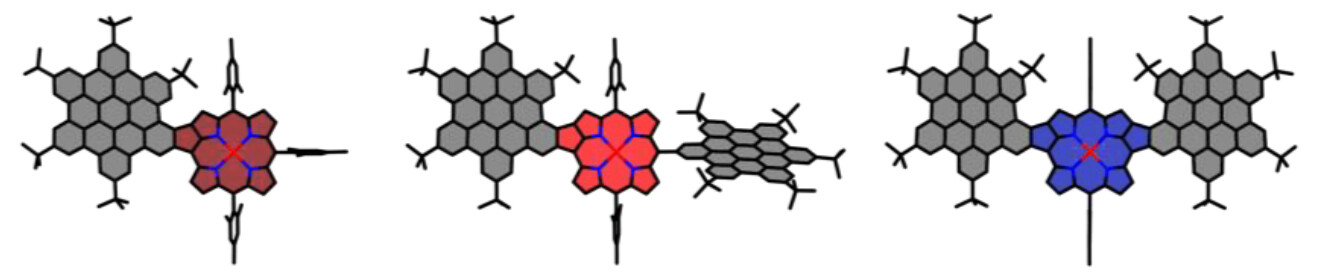
The synthesis of three novel C−C bond-fused porphyrin-hexabenzocoronene (HBC) conjugates is presented. By connecting the aromatic systems of the macrocycles via 5-membered rings under standard Scholl conditions, the formation of highly soluble and stable π-extended porphyrins is achieved. The described planarization led to significant alterations regarding the photophysical and optoelectronic characteristics of the molecules.
Synthetic Methods
Skeletal Editing of Aromatic N-Heterocycles via Hydroborative Cleavage of C−N Bonds—Scope, Mechanism, and Property
- First Published: 21 August 2024
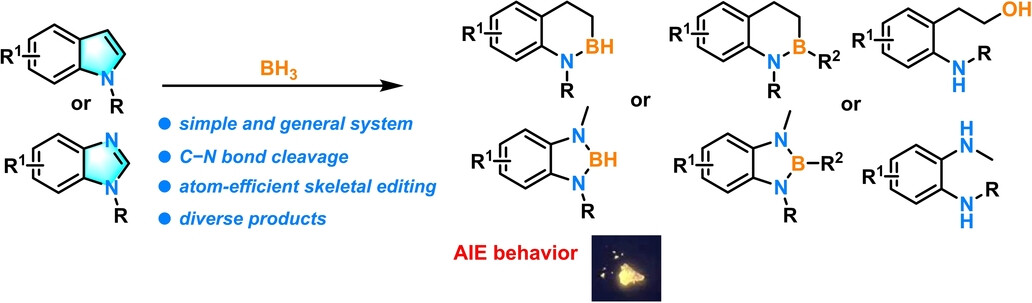
A straightforward and facile BH3-mediated skeletal editing of aromatic heterocycles via hydroborative cleavage of C−N bonds is reported. Structurally diverse products, including tetrahydrobenzo azaborinines, diazaboroles, O-anilinophenylethyl alcohols, benzene-1,2-diamines, and more were readily obtained. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations and natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis revealed an interesting and counterintuitive indole hydroboration phenomenon, including −BH2 shift from C3-position to C2-position. Moreover, the photophysical properties of the synthesized diazaboroles was studied, and an interestingly and pronounced aggregation-induced emission (AIE) behavior was disclosed.
Hydrogen Production | Hot Paper
High-Entropy Sulfide Catalyst Boosts Energy-Saving Electrochemical Sulfion Upgrading to Thiosulfate Coupled with Hydrogen Production
- First Published: 31 July 2024
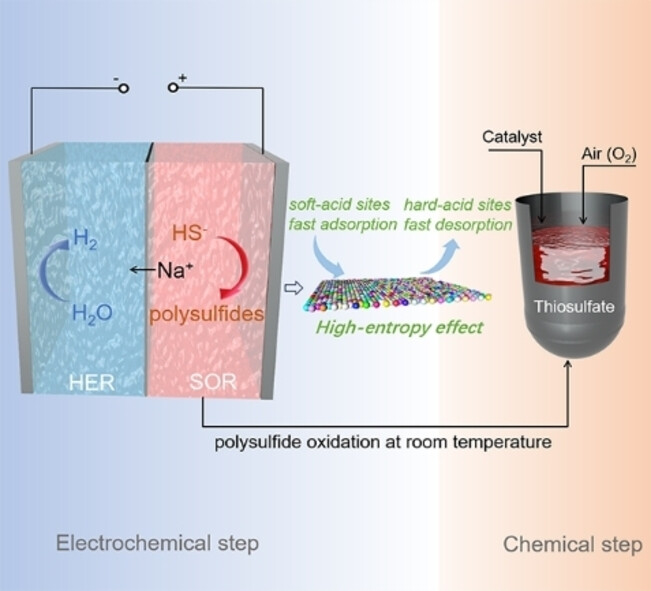
Amorphous high-entropy sulfide catalyst of CuCoNiMnCrSx/NF, with the manipulated chemical environments and electron states surrounding “soft-acid” sites and the sulfophobic properties of “hard-acid” metal sites, shows excellent sulfion-oxidation reaction performance coupled with hydrogen evolution at the industrial-level current density for long-time stability. This demonstration of the electrochemical-chemical tandem reaction process gives a new avenue for sulfions upgrading from wastewater and simultaneous efficient hydrogen production
Solar Cells | Very Important Paper
Molecular Design of Hole Transport Materials to Immobilize Ion Motion for Photostable Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 16 August 2024
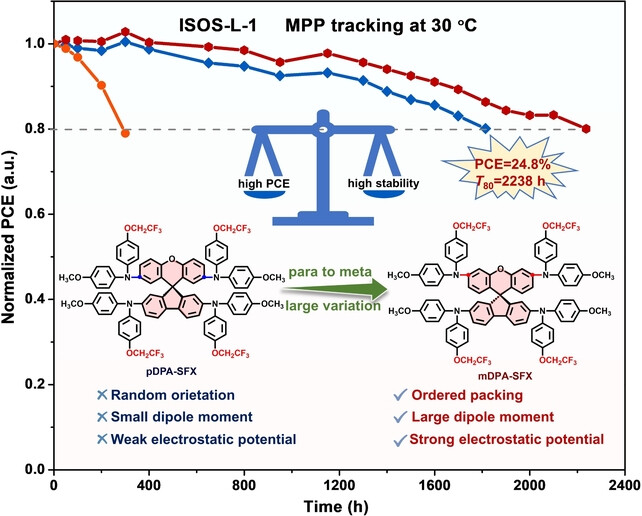
This work demonstrates that the capability of hole molecules to strengthen the interface bonding and interactions between molecules and interfaces is crucial to maximally passivate defects, affording robust interface, inhibition of ion migration, and photostable perovskite solar cells. Consequently, the newly developed mDPA-SFX enables cells with a PCE of 24.8 %, and an excellent T80 lifetime of 2,238 h at maximum power point tracking.
CO2 Electroreduction
Promoting CO2 Electroreduction to Hydrocarbon Products via Sulfur-Enhanced Proton Feeding in Atomically Precise Thiolate-Protected Cu Clusters
- First Published: 21 August 2024
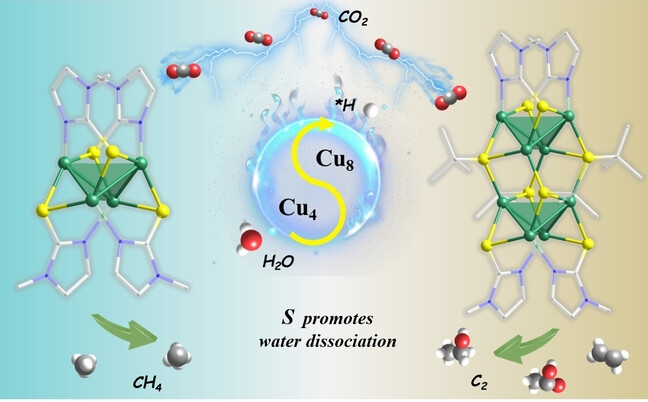
Two model Cu4(MMI)4 and Cu8(MMI)4(tBuS)4 clusters with well-defined structures and stable low-coordinated Cu+ species are prepared to explore the synergistic effect of Cu+ and adjacent S site on CO2RR. Cu4(MMI)4 reduce CO2 to deep-reduced products with a FE of 91.0 % (including 53.7 % for CH4) while maintaining remarkable stability. Cu8(MMI)4(tBuS)4 shows a notable preference for C2+ products with a maximum FE of 58.5 % and a JC2+ of 152.1 mA⋅cm−2.
Osmotic Energy Conversion
Horizontal Transport in Ti3C2Tx MXene for Highly Efficient Osmotic Energy Conversion from Saline-Alkali Environments
- First Published: 15 August 2024
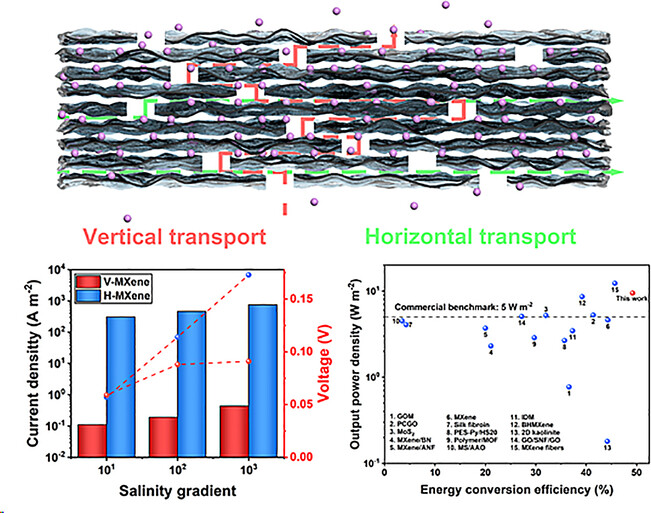
MXene with horizontal ionic transport channels (H-MXene) to withstand extreme saline-alkali conditions, significantly outperforms that with vertical ionic transport channels (V-MXene) in ion selectivity and permeability, achieving a current density over three orders of magnitude higher without significant polarization, an osmotic power density of 9.47 W m−2, and an exceptional energy conversion efficiency of 45.7 %.
Photocatalysis
Photocatalytic Synthesis of Glycine from Methanol and Nitrate
- First Published: 13 August 2024
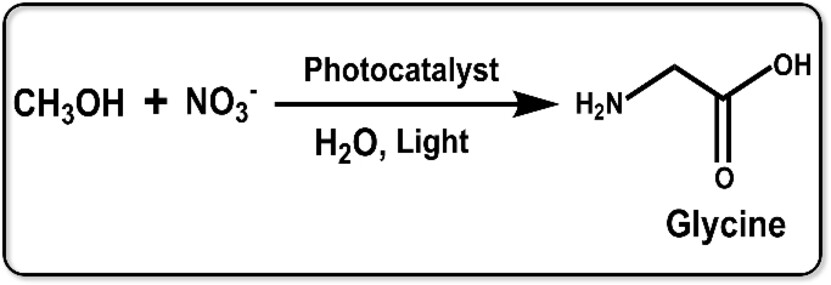
Herein we report a novel photocatalytic system for the synthesis of glycine directly from methanol and nitrate. Ba2+−TiO2 nanoparticles show a high glycine photosynthesis rate under mild conditions. The success of this work provides a sustainable pathway for the valorization of green “liquid sunlight” and nitrate waste.
Diradicals
Azaacene Diradicals Based on Non-Kekulé Meta-Quinodimethane with Large Two-Photon Cross-Sections in the Infrared Spectral Region
- First Published: 27 August 2024
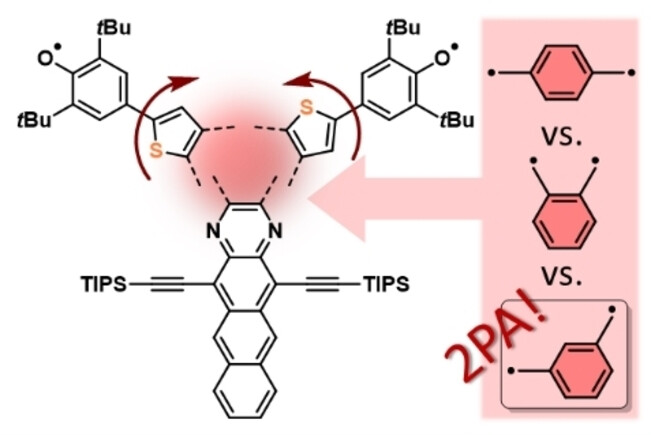
Exchanging a sulfur atom against a methine group in a series of azaacene based diradicals furnishes non-Kekulé, meta-quinodimethane based diradicals with singlet ground states and small singlet-triplet gaps. Zwitterionic contributions are ruled out experimentally and quantum-chemically, and the diradicals display huge two-photon cross sections in the infrared spectral region.
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
Intracellular Gold Nanocluster/Organic Semiconductor Heterostructure for Enhancing Photosynthesis
- First Published: 13 August 2024
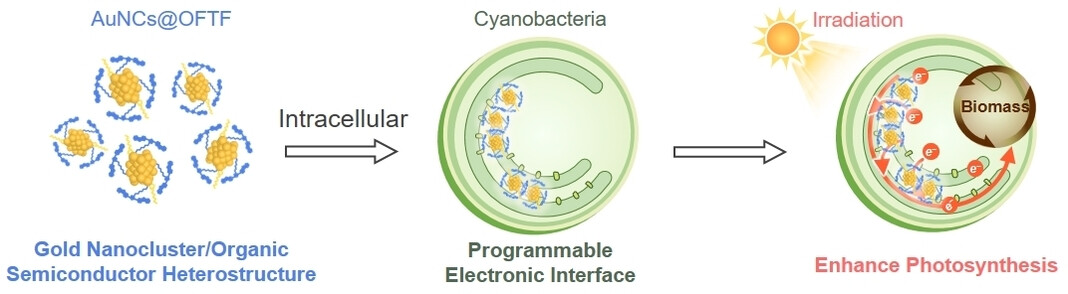
Ultra-small heterostructures (AuNCs@OFTF) with amphiphilicity were developed. They can be rapidly internalized in cyanobacteria and provide a programmable electronic interface, where the strong energetic coupling accelerates electron transfer in living cyanobacteria. Exogenous photogenerated electrons from AuNCs@OFTF enable a five-fold increase in photocurrent and enhance biomass production of cyanobacteria.
Asymmetric Synthesis
Zinc-Catalyzed Enantioselective Formal (3+2) Cycloadditions of Bicyclobutanes with Imines: Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Azabicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes
- First Published: 01 September 2024
Immunotherapy
Peptide Degrader-Based Targeting of METTL3/14 Improves Immunotherapy Response in Cutaneous Melanoma
- First Published: 13 August 2024
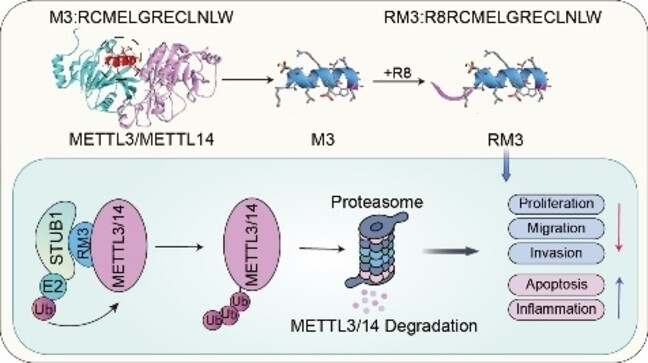
Our study unveils METTL3’s oncogenic role in melanoma. RM3, a designed peptide inhibitor disrupting METTL3/14 complex, induces proteasomal degradation via STUB1. RM3 reduces melanoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induces apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Combined with anti-PD-1 antibody, RM3 elicits significantly enhanced tumor response in vivo, with a favorable safety profile.
Kinetic Resolution
Isothiourea-Catalysed Acylative Kinetic Resolution of Tertiary Pyrazolone Alcohols
- First Published: 23 August 2024
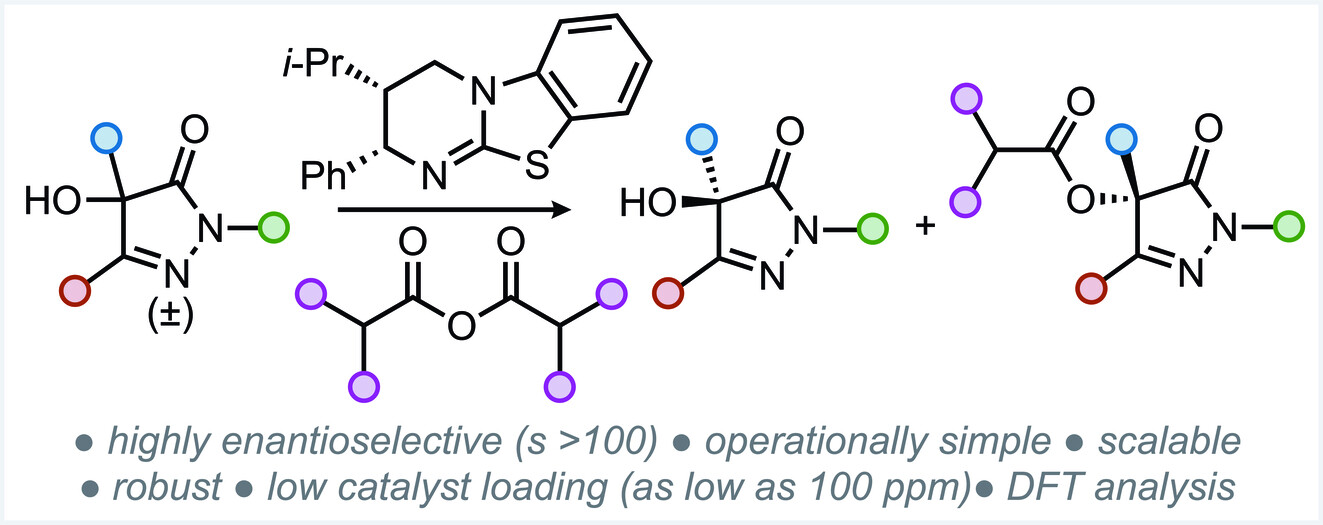
The highly selective acylative kinetic resolution of racemic pyrazolone tertiary alcohols catalysed by chiral isothioureas is described (s=>100 in >25 examples). This method was applied to highly functionalised pharmaceutically derived compounds, demonstrated at a decagram scale, and at ppm catalyst loading with DFT analysis indicating an NC=O⋅⋅⋅isothiouronium interaction key to enantiorecognition.
Solar Cells
Configurational Isomerization-Induced Orientation Switching: Non-Fused Ring Dipodal Phosphonic Acids as Hole-Extraction Layers for Efficient Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 30 August 2024
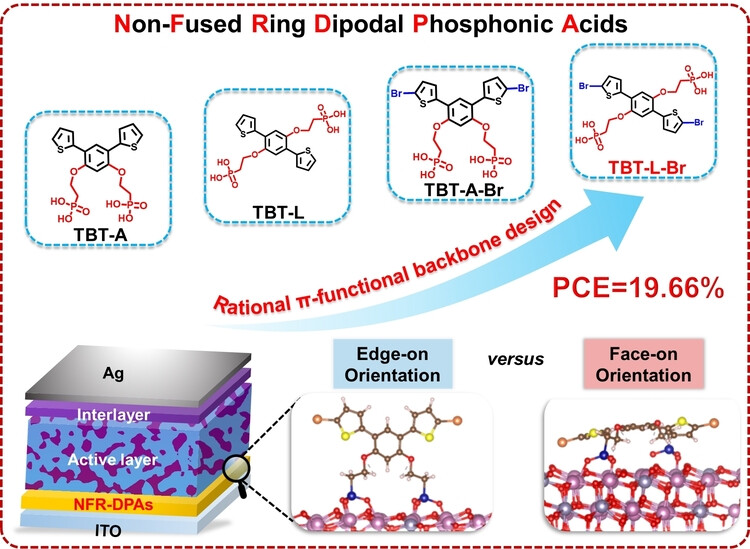
Non-fused ring dipodal phosphonic acids, characterized by non-fused ring backbones and dipodal phosphonic acid anchors, are developed and used as hole-extraction layers in organic solar cells. Such simple and tailorable backbones offer a novel platform to study structural effect on their self-assembly behaviors on ITO, which leads to an impressive performance of 19.66 % owing to optimized interfacial contact and active layer morphology.
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Discovery, Characterization and Synthetic Application of a Promiscuous Nonheme Iron Biocatalyst with Dual Hydroxylase/Desaturase Activity
- First Published: 29 August 2024
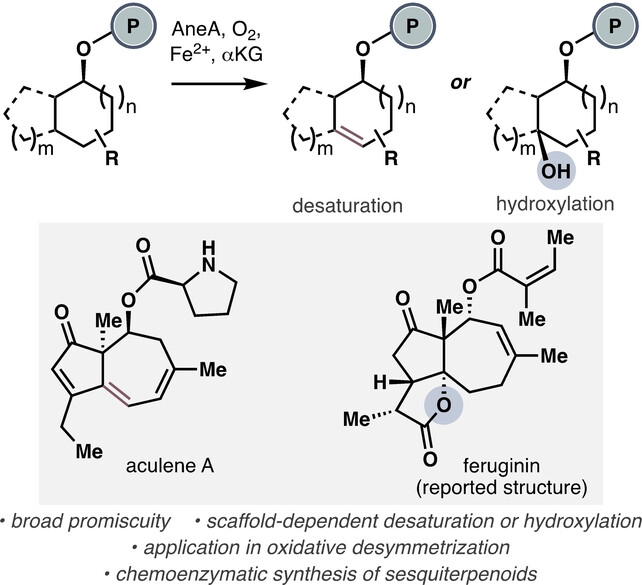
A putative α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase from aculene biosynthesis, AneA, was functionally characterized and explored as biocatalyst for C−H oxidation. AneA exhibits broad substrate promiscuity and is capable of both hydroxylation and desaturation depending on its substrate structure. The utility of the biocatalytic reaction was demonstrated in several oxidative desymmetrizations and in the chemoenzymatic synthesis of complex sesquiterpenoids.
Gas Tunnel Engineering of Prolyl Hydroxylase Reprograms Hypoxia Signaling in Cells
- First Published: 21 August 2024
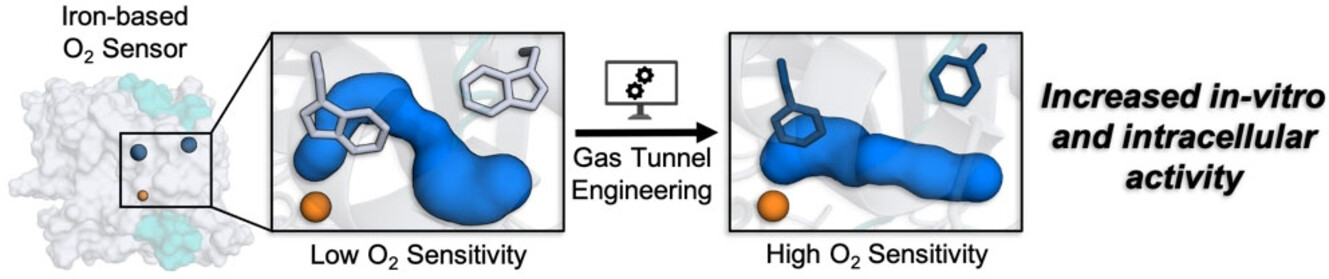
The gas tunnel of PHD2, an iron-based O2 sensing enzyme, is engineered using a computation-guided rational design approach. The engineered mutants exhibit an increased rate of gas transport to the active site, along with increased catalytic activity in vitro. These mutants also display enhanced intracellular activity demonstrating the ability to reprogram hypoxia signaling by activating PHD2.
Biomass Valorization
Polyphenol Oxidase Activity on Guaiacyl and Syringyl Lignin Units
- First Published: 17 September 2024
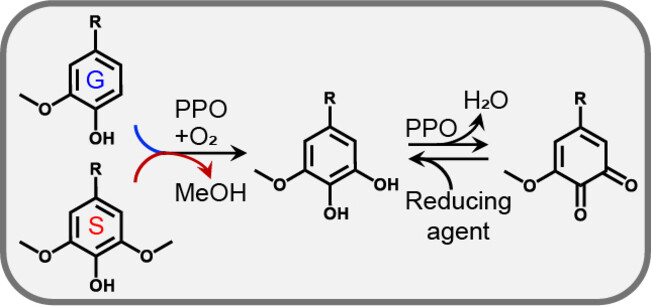
The conversion of lignin-derived guaiacyl (G) and syringyl (S) compounds into methoxy-ortho-diphenols through oxidative ortho-hydroxylation and ortho-demethoxylation reactions catalyzed by novel fungal polyphenol oxidases (PPOs) is presented. The formation of o-diphenols rather than reactive quinones can be steered by the addition of a reductant. These PPOs offer new methods to reduce the heterogeneity of G and S lignin-derived product mixtures.
Li Metal Batteries | Very Important Paper
Scalable Production of Thin and Durable Practical Li Metal Anode for High-Energy-Density Batteries
- First Published: 29 August 2024
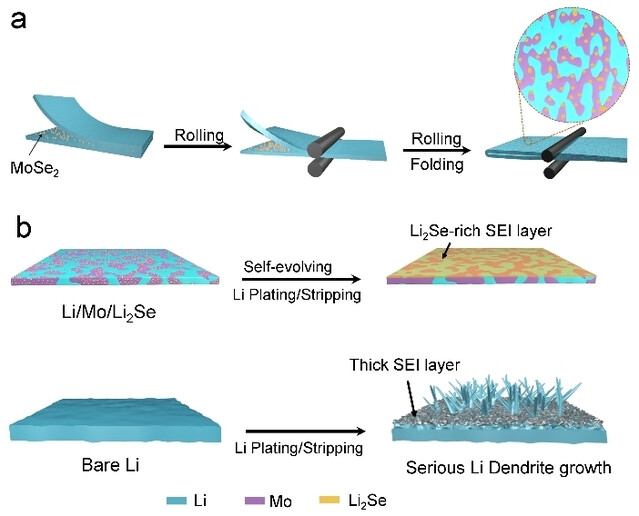
A practical thin (10–40 μm) Li/Mo/Li2Se anode with concurrently modulated interphase and mechanical properties was achieved via a scalable mechanical rolling process. The Li/Mo/Li2Se demonstrates ultrahigh-rate performance and ultralong-lifespan cycling sustainability. The Li|LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 pouch cells deliver enhanced cycling stability with a superior energy density of 329.2 Wh kg−1 even under the harsh cycling conditions.
Perovskite Solar Cells
Multifunctional Modification of the Buried Interface in Mixed Tin-Lead Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 05 August 2024
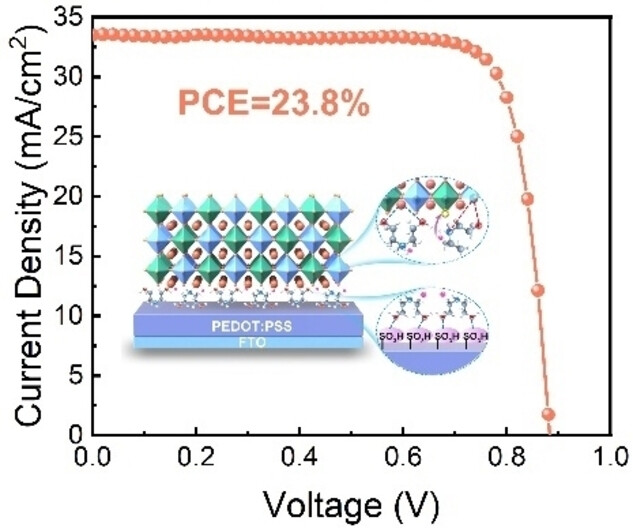
Regulating the buried interface is crucial for perovskite crystallization and charge transport. An innovative approach, using hydroxylamine salts for interface modification precisely anchors perovskite ions, promoting controlled crystal growth. This approach significantly enhances the efficiency and long-term stability of Sn−Pb perovskite solar cells, critical for future development of all-perovskite tandems.
Dual-Ion Batteries
Extending the π-Conjugation of a Donor-Acceptor Covalent Organic Framework for High-Rate and High-Capacity Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 13 August 2024
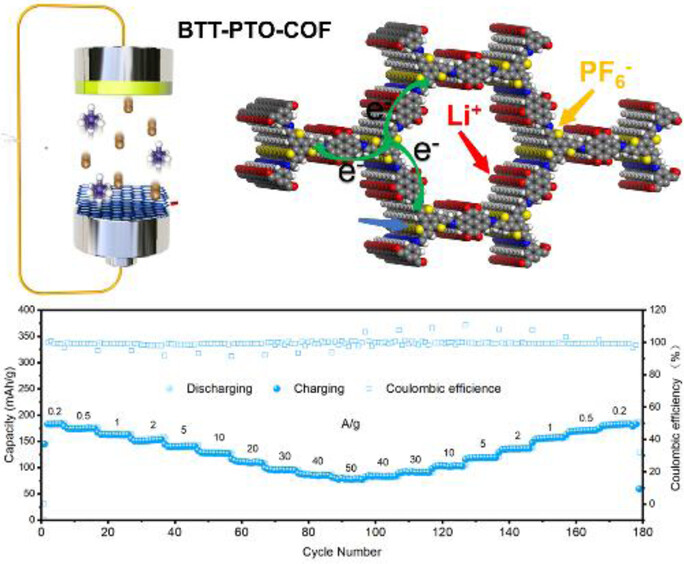
A conjugated donor-acceptor covalent organic frameworks BTT-PTO-COF containing BTT (p-type) and PTO (n-type) as dual-active centers enable high-rate and high-capacity for LIBs. BTT-PTO-COF with mesoscale porosity and dual redox-active centers promotes fast charge transfer and multi-electron processes, leading to high specific capacity, outstanding rate capability and impressive stability for long-term cycling.
Hydrogen Evolution
S−S Bond Strategy at Sulfide Heterointerface: Reversing Charge Transfer and Constructing Hydrogen Spillover for Boosted Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 28 August 2024
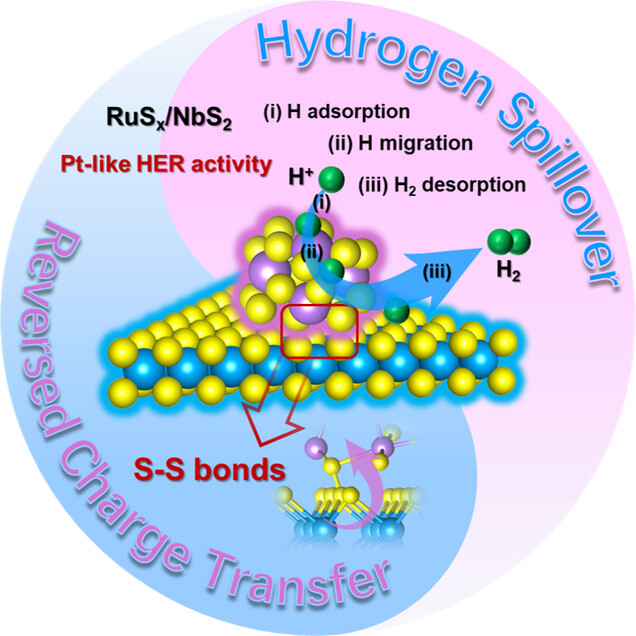
RuSx/NbS2 heterostructure was synthesized by the introducing of amorphous RuSx onto crystalline NbS2 surface. It shows a Pt-like HER activity with a low overpotential as 38 mV at 10 mA ⋅ cm−2, which is mainly benefit from hydrogen spillover caused by reversing charge transfer that induced by S−S bonds at RuSx/NbS2 heterointerface.
Nitrogen Reduction Reaction
Plasmon-Promoted Interatomic Hot Carriers Regulation Enhanced Electrocatalytic Nitrogen Reduction Reaction
- First Published: 01 September 2024
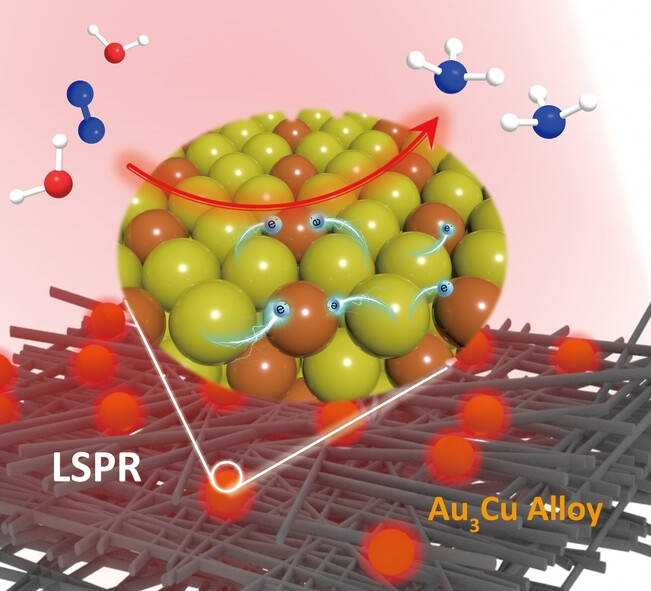
The LSPR effect can efficiently promote interatomic transfer of plasmon hot carriers and the extra hot electrons transferred on Cu atoms from Au atoms effectively enhance the desorption of ammonia molecules, thereby accelerating the ENRR. This study provides an important reference for understanding the distribution and mechanism of plasmon hot carriers on the surface of alloy heterogeneous nanostructure.
Surface Chemistry
The Fate of the Formic Acid Proton on the Anatase TiO2(101) Surface
- First Published: 30 July 2024
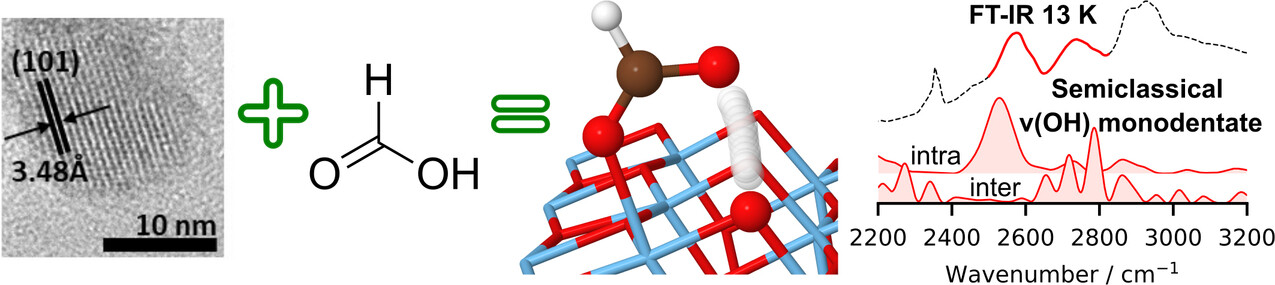
High vacuum FTIR experiments at temperatures as low as 13 K, together with divide-and-conquer semiclassical and path integral molecular dynamics simulations, indicate that a short and strong hydrogen bond is formed during the adsorption of HCOOH on the anatase (101) TiO2 surface. Such unusual H-bond has previously escaped direct spectral detection because of a huge red shift of its vibrational frequency.
Asymmetric Synthesis | Hot Paper
Enantioconvergent and Site-Selective Etherification of Carbohydrate Polyols through Chiral Copper Radical Catalysis
- First Published: 16 August 2024
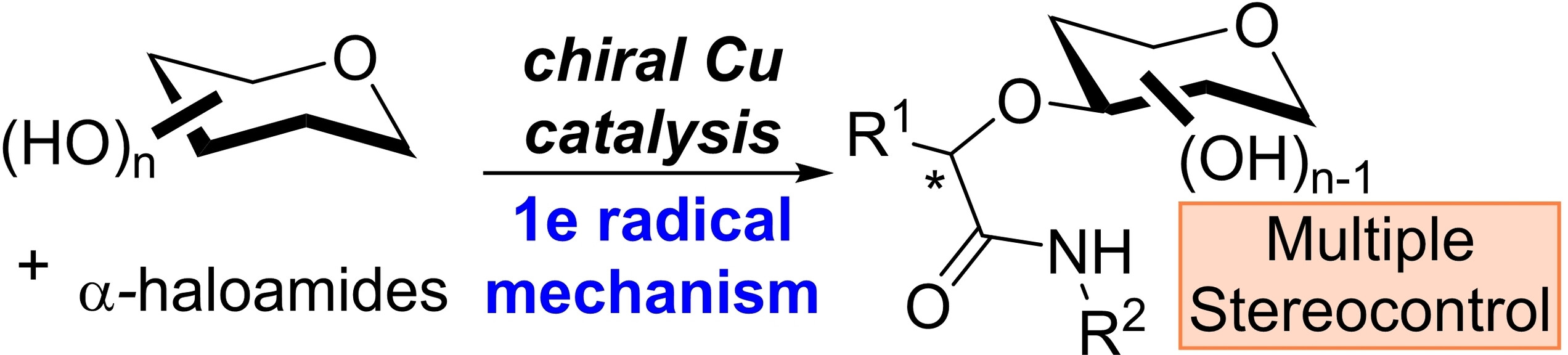
By harnessing a chiral radical copper catalytic system, the challenging enantioconvergent and site-selective etherification of carbohydrate polyols is achieved. Besides being broadly applicable over a considerable range of sugars, multiple dimensions of stereocontrol can be tackled simultaneously. Remarkably, when anomeric unprotected reducing sugars were employed, dynamic kinetic resolution is further activated to achieve β-O-glycosylation.
Zinc-Ion Batteries | Very Important Paper
Transforming Zinc-Ion Batteries with DTPA-Na: A Synergistic SEI and CEI Engineering Approach for Exceptional Cycling Stability and Self-Discharge Inhibition
- First Published: 22 July 2024
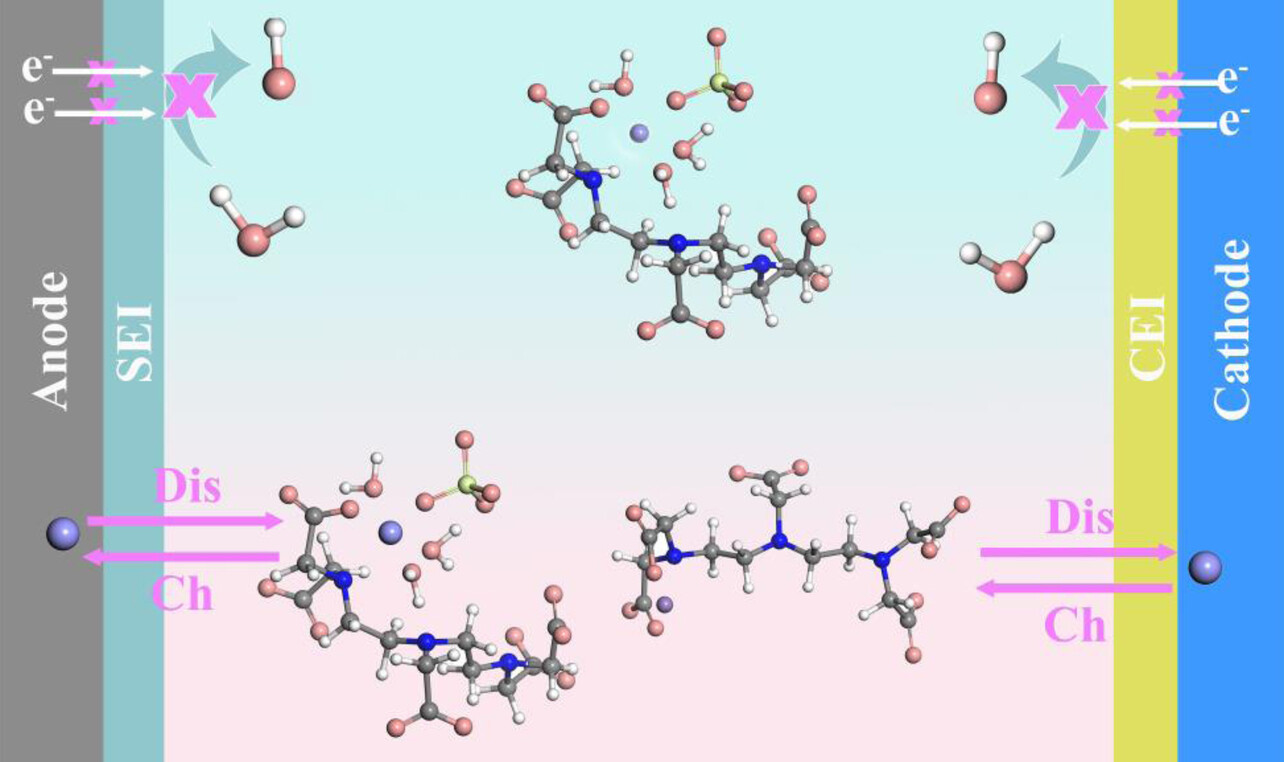
A novel strategy is developed to enhance the stability of aqueous zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs). Incorporation of DTPA-Na additive enables a synergistic formation of robust solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI). This strategy effectively regulates the solvation structure and interfacial chemistry, promoting uniform zinc deposition, inhibiting detrimental side reactions, and preventing manganese dissolution, ultimately achieving high-performance ZIBs.
Nitrate Reduction
Enhanced Charge-Carrier Dynamics and Efficient Photoelectrochemical Nitrate-to-Ammonia Conversion on Antimony Sulfide-Based Photocathodes
- First Published: 12 July 2024
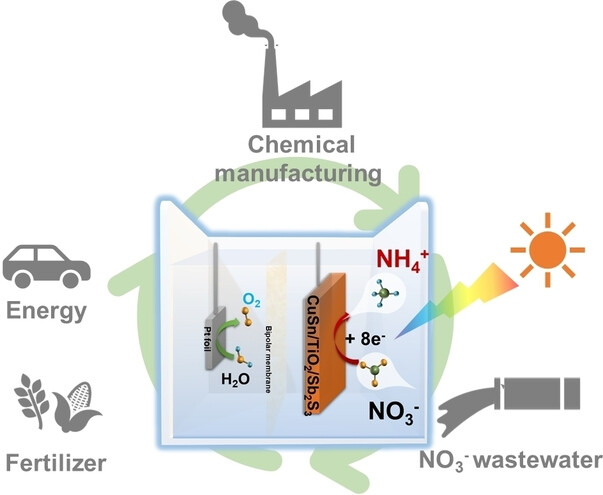
This work integrates a CuSn alloy-modified CuSn/TiO2/Sb2S3 photocathode for efficient nitrate-to-ammonia conversion. The photocathode possesses an excellent onset potential of 0.62 VRHE, achieves the highest ammonia Faraday efficiency of 97.82 % with a yields up to 16.96 μmol h−1 cm−2 at 0 VRHE. The excellent charge carrier kinetics and moderate NO2− adsorption provide an effective strategy for achieving stable and efficient photoelectrochemical ammonia synthesis.
Mechanochemistry
Navigating Ball Mill Specifications for Theory-to-Practice Reproducibility in Mechanochemistry
- First Published: 15 August 2024
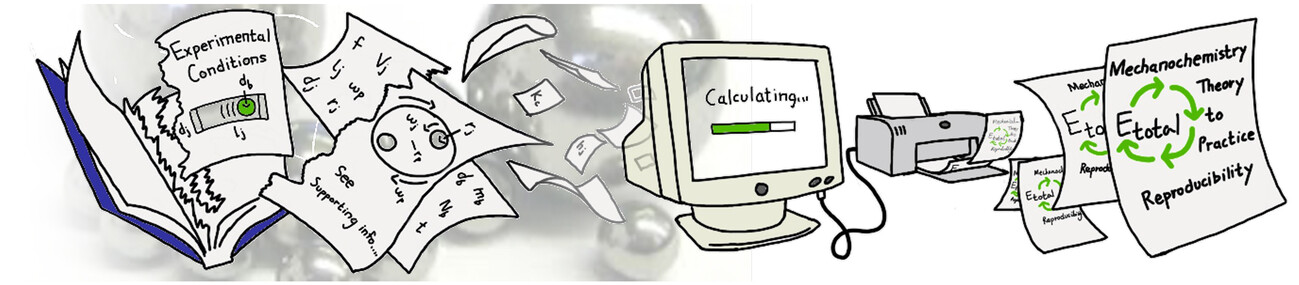
Commonly reported parameters such as time, rpm, and ball mass are often insufficient to replicate mechanochemical syntheses accurately. By demonstrating that reaction outcomes are tied to the cumulative total energy, we can enhance the reproducibility of mechanochemical reactions across various laboratory mills, including planetary and mixer mills. To aid in this, we offer a free online calculator to compute and report all necessary parameters.
Layered Oxide Cathodes
Mitigating the Kinetic Hysteresis of Co-Free Ni-Rich Cathodes via Gradient Penetration of Nonmagnetic Silicon
- First Published: 02 September 2024
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Engineering the Substrate Specificity of UDP-Glycosyltransferases for Synthesizing Triterpenoid Glycosides with a Linear Trisaccharide as Aided by Ancestral Sequence Reconstruction
- First Published: 22 August 2024
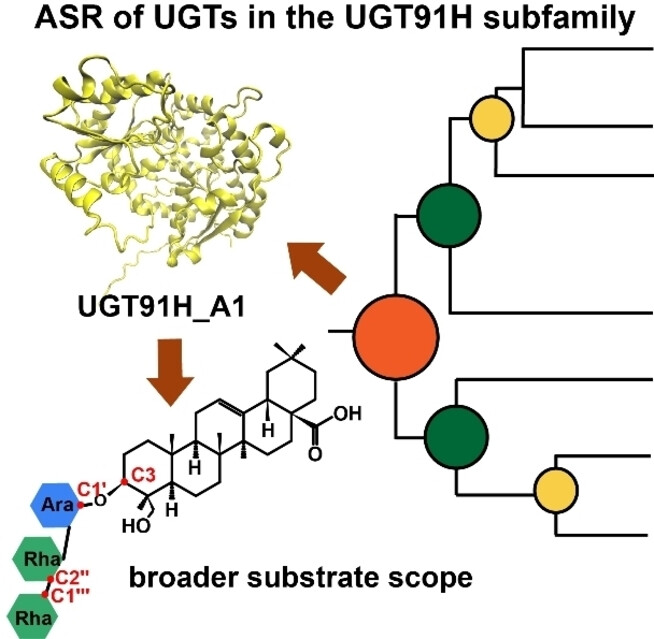
UDP-glycosyltransferase UGT91H enzymes for the regioselective 2“-O-glycosylation of triterpenoids to generate triterpenoid glycosides with a linear trisaccharide are described. Ancestral sequence reconstruction was successfully applied to expand the substrate scope of UGT91H enzymes, and an RTAS loop was identified to affect the substrate specificity of UGT91H enzymes.
CO2 Reduction | Hot Paper
Vinylene-Linked Donor-π-Acceptor Metal-Covalent Organic Framework for Enhanced Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- First Published: 03 September 2024
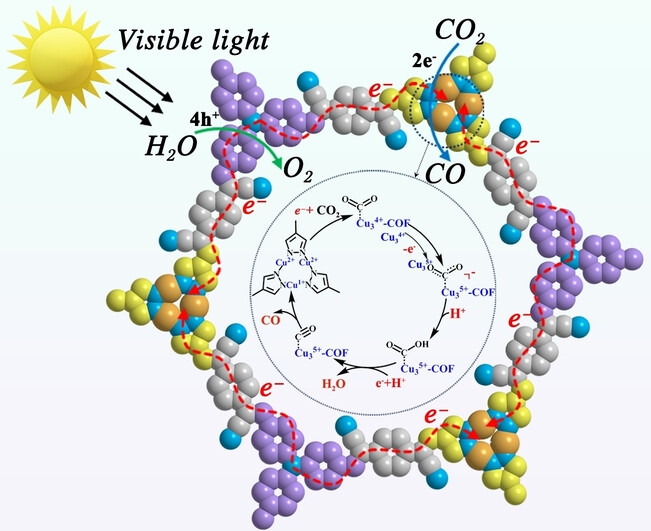
A three-component vinylene-linked D-π-A copper-cyclic trinuclear units (Cu-CTUs)-based metal-covalent organic framework (MCOF) with reinforced intramolecular charge separation driving force was designed and prepared, achieving highly-efficient charge spatial separation efficiency and photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance. The Cu-CTUs active sites can effectively adsorb and activate CO2 to further enhance photocatalytic performance.
Memristors
High Performance Memristors Based on Imine-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks Obtained Using a Protonation Modification Strategy
- First Published: 18 August 2024
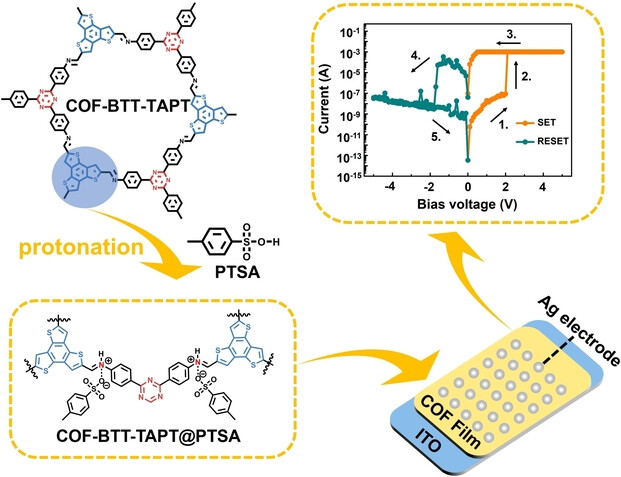
A protonation-modification strategy has been employed to modify imine-linked donor-acceptor (D-A) type covalent organic frameworks (COFs), significantly improving the electron delocalization capabilities of the imine bonds and constructing advanced memory devices. The obtained novel COF-BTT-TAPT@PTSA thin film-based rewritable memristors exhibit high ON/OFF current ratio (ca. 105) and unprecedented endurance (more than 1300 number of cycles).
Metalloradicals | Hot Paper
Redox Activity and Potentials of Bidentate N-Ligands Commonly Applied in Nickel-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions
- First Published: 12 September 2024
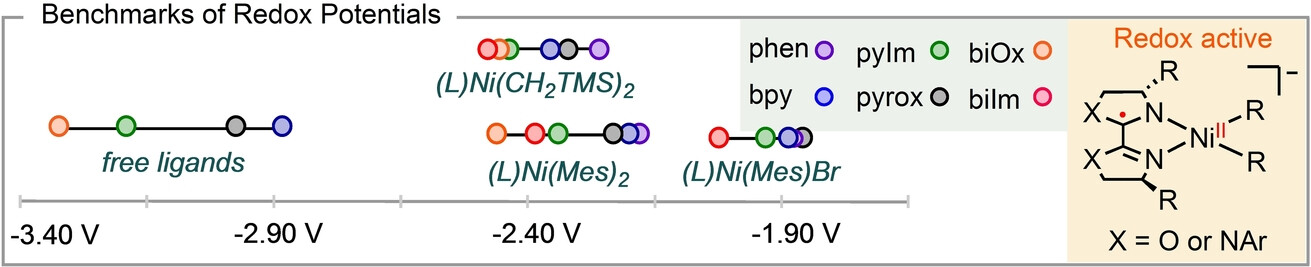
This report establishes the redox activity of biOx (bi-oxazoline), biIm (bi-imidazoline), and pyIm (pyridine-imidazoline) ligands in stabilizing nickel radical complexes. Direct comparison of the redox potentials of bidentate N-ligands provides crucial benchmarks for controlling catalytic activity and enhancing catalyst stability.
Batteries | Very Important Paper
A Supramolecular Deep Eutectic Electrolyte Enhancing Interfacial Stability and Solution Phase Discharge in Li−O2 Batteries
- First Published: 02 September 2024
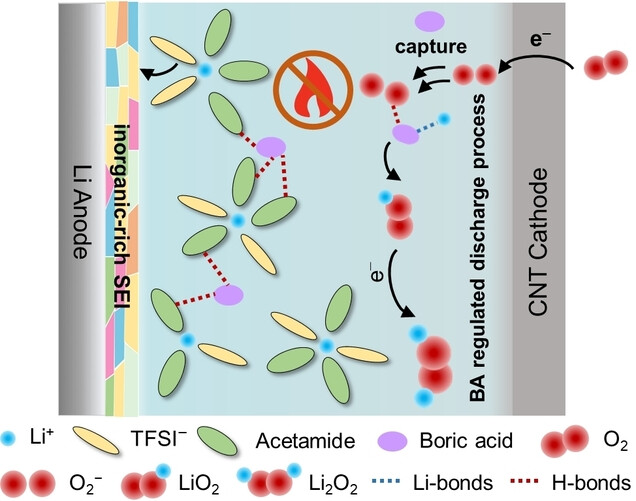
The proposed supramolecular deep eutectic electrolyte (DEE) based on LiTFSI, acetamide and boric acid, improving the oxidation voltage up to 4.5 V, and enhancing the solution phase discharge mechanism by forming Li-bonds and H-bonds with Li+ and O2−. The introduction of boric acid also promotes the formation of inorganic-rich SEI, which induces Li+ uniform deposition. The Li−O2 battery with this DEE delivers ultrahigh discharge capacity, improved cycling performance and intrinsic safety.
Lithium Metal Anodes
The Impact of Supersaturated Electrode on Heterogeneous Lithium Nucleation and Growth Dynamics
- First Published: 11 August 2024
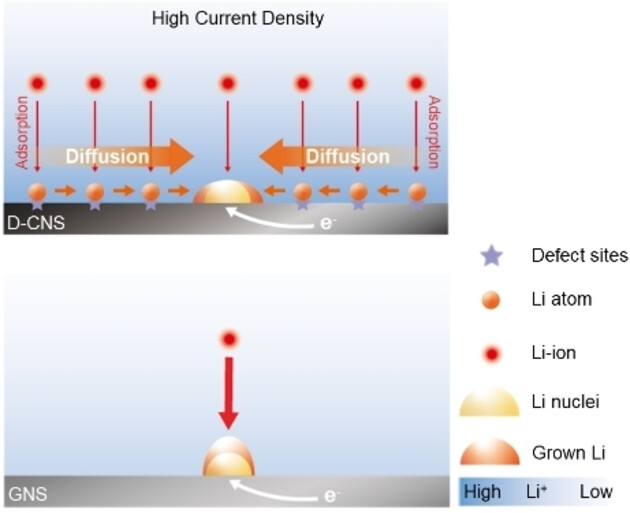
This study introduces new insights into the heterogeneous lithium nucleation and growth dynamics that directly influence the performance of lithium metal anodes (LMAs). It reveals that high-performance electrodes for LMAs, characterized by a high active lithium adsorption capacity and fast surface diffusion kinetics, can be defined as ′supersaturated electrodes.
CO2 Reduction
Quantifying Interface-Performance Relationships in Electrochemical CO2 Reduction through Mixed-Dimensional Assembly of Nanocrystal-on-Nanowire Superstructures
- First Published: 28 August 2024
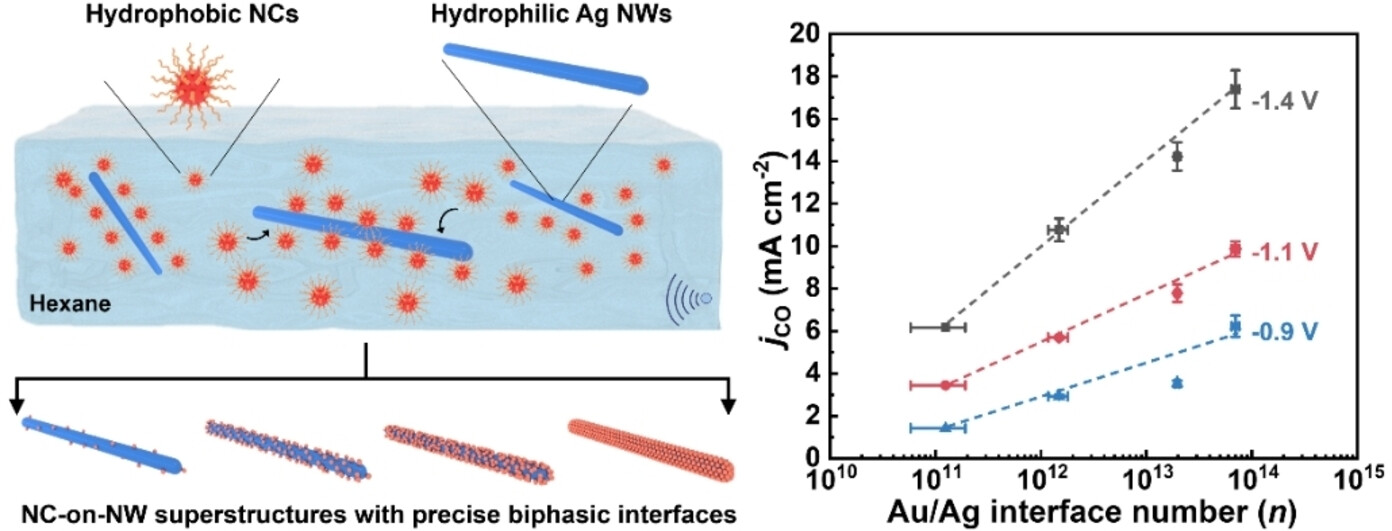
A versatile mixed-dimensional assembly approach is proposed to construct nanocrystal-on-nanowire superstructures with accurately tailored biphasic interfaces. Using Au-on-Ag superstructures as a model catalyst for electrochemical CO2-to-CO conversion, this work establishes a logarithmic linear relationship between catalytic activity and the number of Au/Ag interfaces per unit mass of the catalyst.
Analytical Chemistry | Hot Paper
Long-Term and Continuous Plasmonic Oligonucleotide Monitoring Enabled by Regeneration Approach
- First Published: 15 August 2024
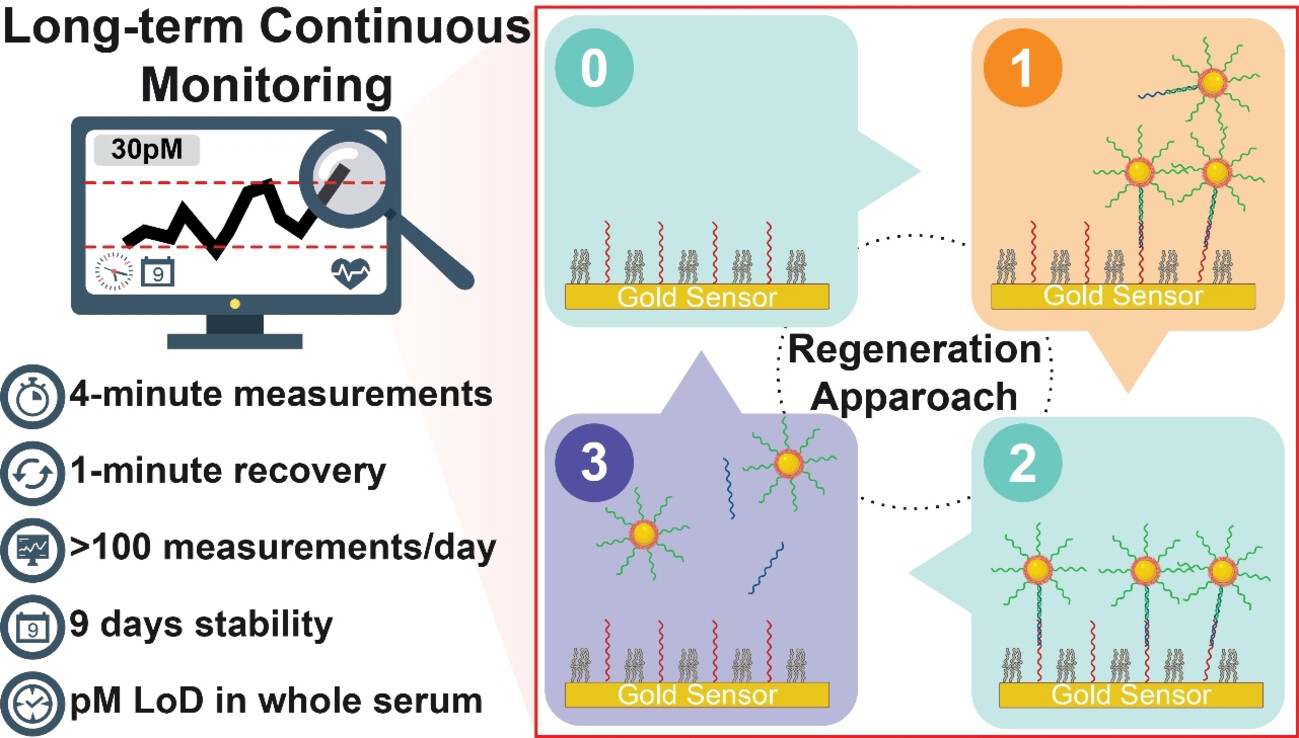
This study presents a method for long-term, continuous plasmonic biosensing of oligonucleotides with 5-minute temporal resolution by using regeneration-based reversibility approach. A picomolar limit of detection (LoD) in both buffered and serum complexes is achieved, and reliable performance for over 100 measurements per day and stability over 9 days were demonstrated.
Urea Electrosynthesis
A Strongly Coupled Metal/Hydroxide Heterostructure Cascades Carbon Dioxide and Nitrate Reduction Reactions toward Efficient Urea Electrosynthesis
- First Published: 07 September 2024
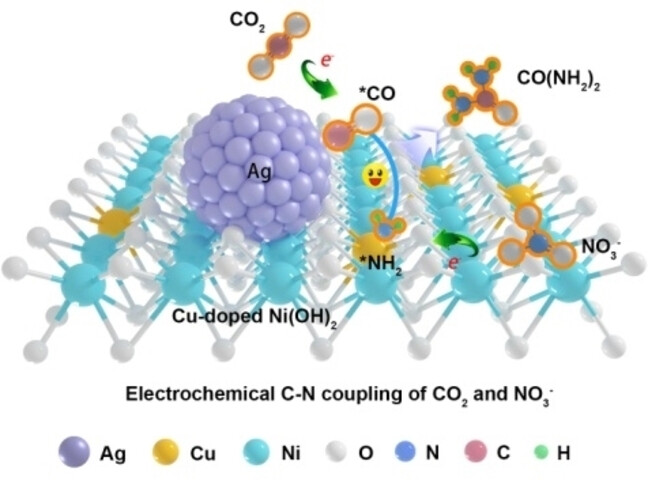
A strongly coupled metal/hydroxide heterostructure was constructed. The heterostructure provides dual-sites for carbon dioxide reduction and nitrate reduction reactions, and thus facilitate efficient C−N coupling toward urea formation. The obtained Ag−CuNi(OH)2 composite delivers greatly enhanced urea yield rate and Faradaic efficiency compared with individual Ag and CuNi(OH)2.
Chemical Biology
Suspension Bead Loading (SBL): An Economical Protein Delivery Platform to Study URM1’s Behavior in Live Cells
- First Published: 09 September 2024
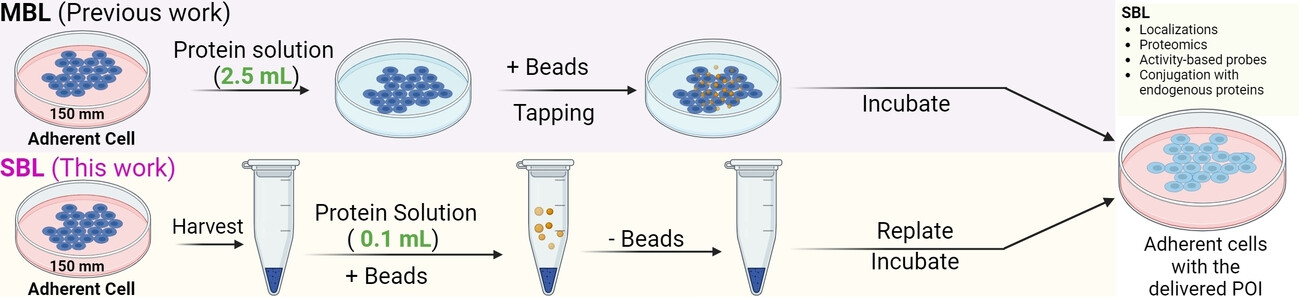
We have developed a “Suspension bead loading” (SBL) approach that serves as a general and economical delivery method to address fundamental biological questions. We applied SBL to investigate the cellular behavior of synthetic Ubiquitin related modifier 1 (URM1) under normal and oxidative stress conditions. Created with BioRender.com.
Isotope Labeling
Deuteration and Tritiation of Pharmaceuticals by Non-Directed Palladium-Catalyzed C−H Activation in Heavy and Super-Heavy Water
- First Published: 07 August 2024
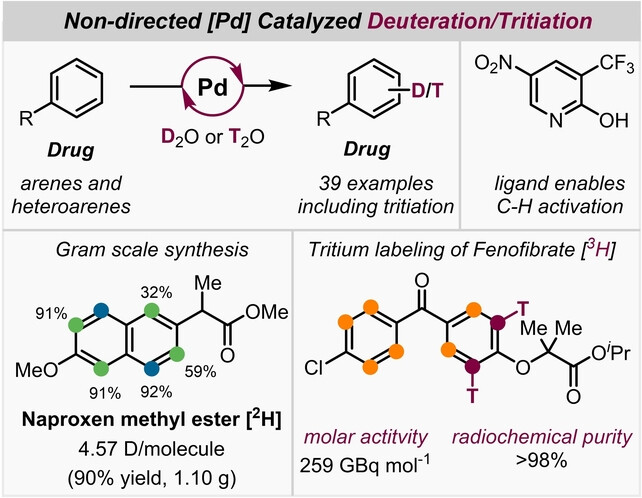
We present a hydrogen isotope exchange reaction using non-directed homogeneous Pd-catalysis. The catalytic system relies on a commercially available pyridine ligand that enables aromatic C−H activation. Labelling of 39 pharmaceuticals was achieved by utilizing D2O as the deuterium source and solvent, without requiring fluorinated cosolvents. Expansion to T/H exchange on three different pharmaceuticals by using T2O as isotopic source was demonstrated.
Biomass Valorization | Hot Paper
Unlocking the Anion Effect on Steerable Production of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural
- First Published: 04 September 2024
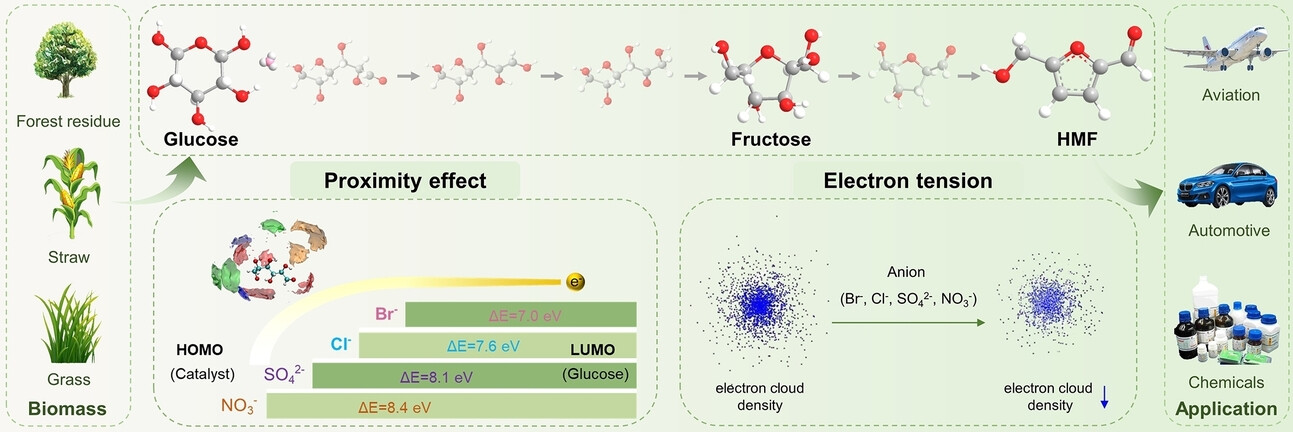
We first proposed the anion effect on steerable production of HMF using metal salts with different anions as catalyst in a biphasic system of THF/NaCl aq, which is attributed to the proximity effect and electron tension. The anion promotes electron transfer through proximity effects and also induces a decrease in the electron cloud density of glucose carbon atoms, generating electron tension, thereby increasing the HMF yield.
Sodium-Ion Batteries | Hot Paper
High-Energy Sodium Ion Batteries Enabled by Switching Sodiophobic Graphite into Sodiophilic and High-Capacity Anodes
- First Published: 31 August 2024
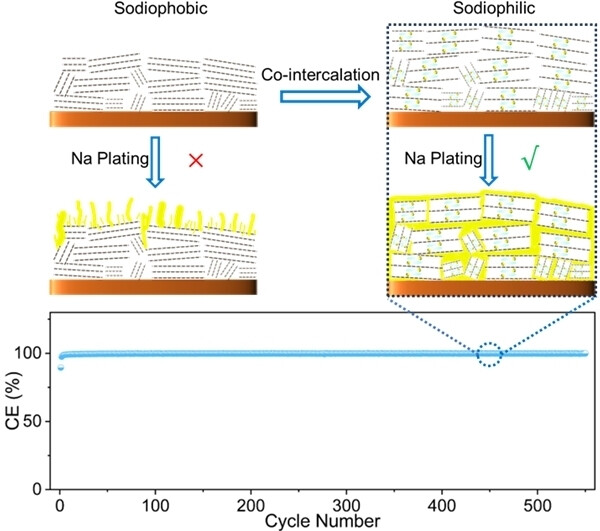
Sodiophobic graphite can be converted to sodiophilic graphite intercalation compounds through solvated-sodium-ion co-intercalation mechanisms, thus facilitating dendrite-free sodium metal plating/stripping with enhanced Coulombic efficiencies. This finding propels the achievement of cost-effective and high capacity anodes for advanced sodium ion batteries with energy densities of above 250 Wh kg−1.
Antibiotics
Calcium-Dependent Lipopeptide Antibiotics against Drug-Resistant Pathogens Discovered via Host-Dependent Heterologous Expression of a Cloned Biosynthetic Gene Cluster
- First Published: 22 August 2024
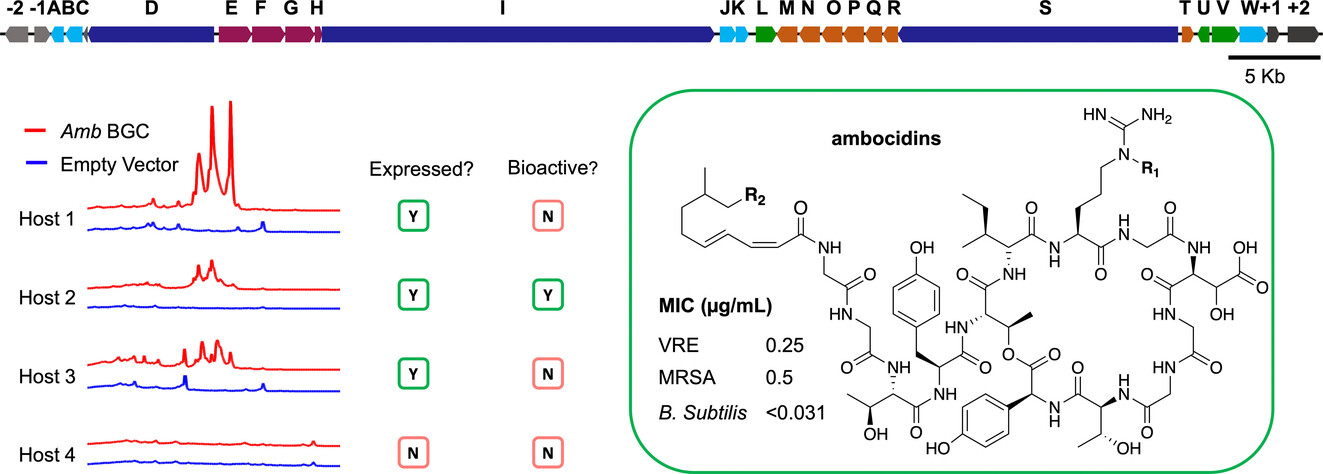
The ambocidins are calcium-dependent lipopeptide antibiotics with a unique peptide core that are active against drug-resistant Gram-positive pathogens. Heterologous expression of their biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) in multiple hosts resulted in production of new metabolites. However, only one heterologous host was capable of supporting production of the ambocidins. The ambocidins bind lipid II at a site distinct from the target of vancomycin.
Batteries
A High Capacity p-Type Organic Cathode Material for Aqueous Zinc Batteries
- First Published: 02 September 2024
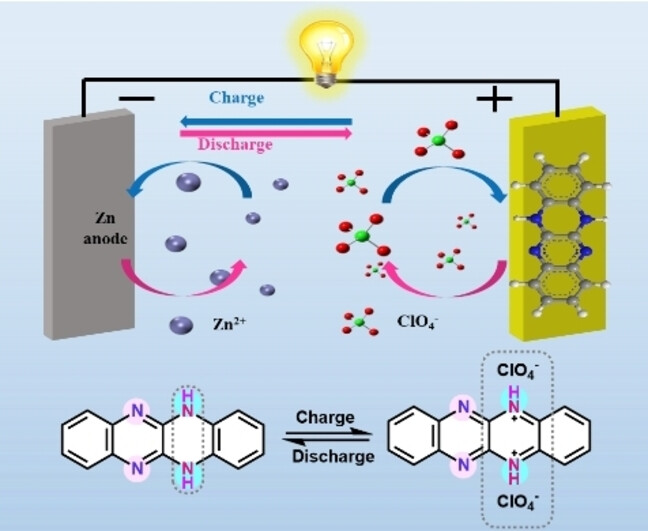
This work reports a high-voltage p-type organic cathode material of DHTAT for application in aqueous zinc batteries, exhibiting a high capacity of 224 mAh g−1 at a current density of 50 mA g−1. After 5000 cycles at 5 A g−1, the DHTAT electrode retains 73 % of its initial capacity, indicating promising cycling stability. Additionally, DHTAT also exhibits good low-temperature performance and can stably cycle at −40 °C for 4000 cycles at 1 A g−1, making it a competitive candidates cathode material for low-temperature batteries.
Biocatalysis
One-Pot Biocatalytic Conversion of Chemically Inert Hydrocarbons into Chiral Amino Acids through Internal Cofactor and H2O2 Recycling
- First Published: 26 August 2024
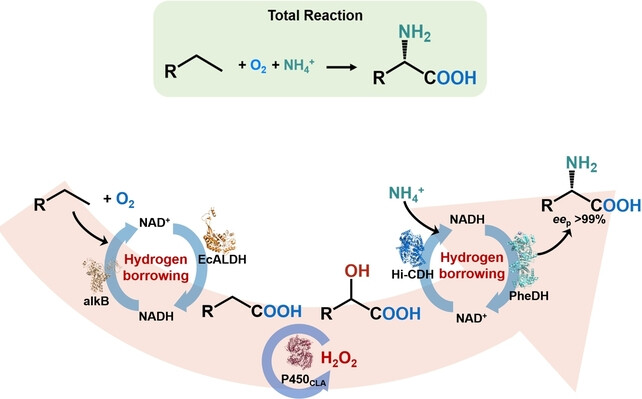
A multi-enzyme cascade conversion system was developed using O2 as the oxidant and ammonium as the amination reagent. This system is based on internal cofactor and H2O2 recycling. It is designed to facilitate the one-pot enzymatic conversion from chemically inert hydrocarbons to chiral amino acids under environmentally friendly conditions, which is a highly challenging transformation in traditional organic synthesis.
Kontrastmittel
Eine makrozyklische Hybrid-PET/MRT-Sonde für die quantitative Perfusionsbildgebung in vivo
- First Published: 26 July 2024

Diese Arbeit zeigt, dass die Integration von PET und MRT in der molekularen Bildgebung das Potenzial hat, die diagnostische Genauigkeit und die Patientenversorgung zu verbessern. Wir haben eine hybride PET/MR-Sonde, [18F][Gd(FL1)], entwickelt, die außergewöhnlich stabil ist, schnell synthetisiert und effizient radioaktiv markiert werden kann und eine gleichzeitige PET/MR-Bildgebung ermöglicht. Das Potenzial für die In vivo-Anwendung wird durch die quantitative Charakterisierung von Gewebe und Nierenfunktion bei Mäusen demonstriert.
Elektrochemie | Hot Paper
Elektrochemische Homo- und Kreuzcyclisierung von Alkinen und Nitrilen für die regio- und chemoselektive Synthese von 3,6-Diarylpyridinen
- First Published: 26 August 2024
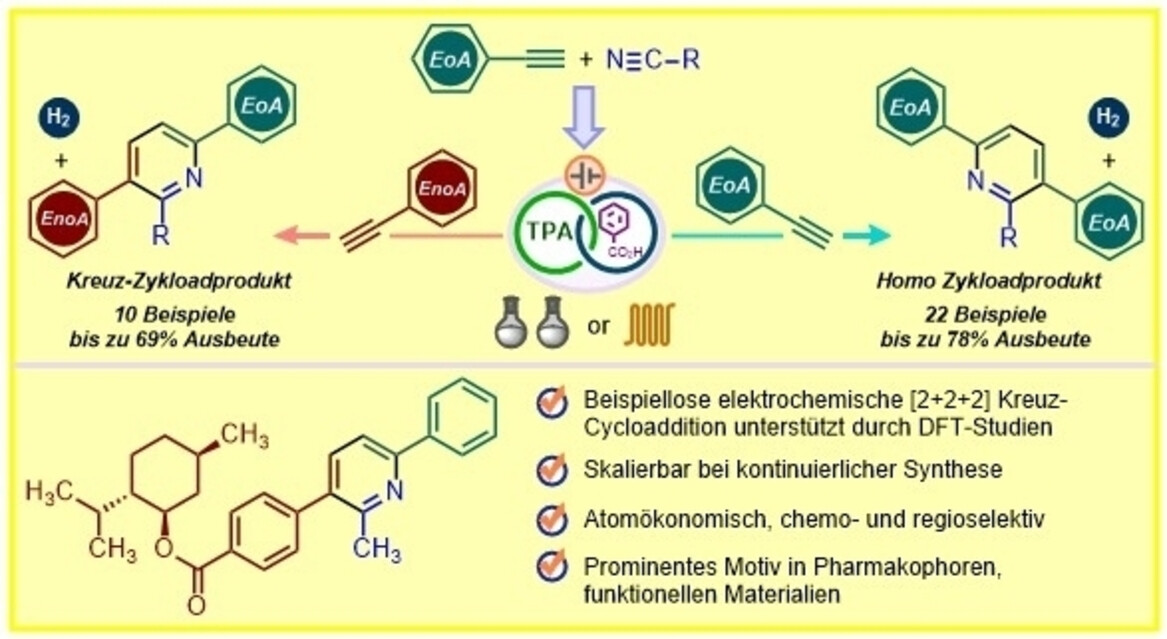
Intermolekulare Homo-Kopplungen, aber vor allem Kreuz-Kopplungen sind eine Herausforderung! Wir berichteten über eine elektrochemische [2+2+2]-Annulation von Alkinen mit Nitrilen unter Verwendung von Triarylamin als Redox-Mediator zur Bildung substituierter Pyridine. Unser Verfahren zeigt eine beispiellose Kontrolle der Chemoselektivität und ermöglicht sowohl Homo- als auch Heterokupplungen von Alkinen und Nitrilen. Es wird ein mechanistisches Grundprinzip vorgeschlagen, das durch CV, EPR, NMR und Berechnungsstudien unterstützt wird.
Borchemie
Experimentelle Beobachtung eines terminalen Borylen-Distickstoff-Addukts durch Spaltung eines 1,2,3,4,5-Diboratriazolins
- First Published: 26 August 2024
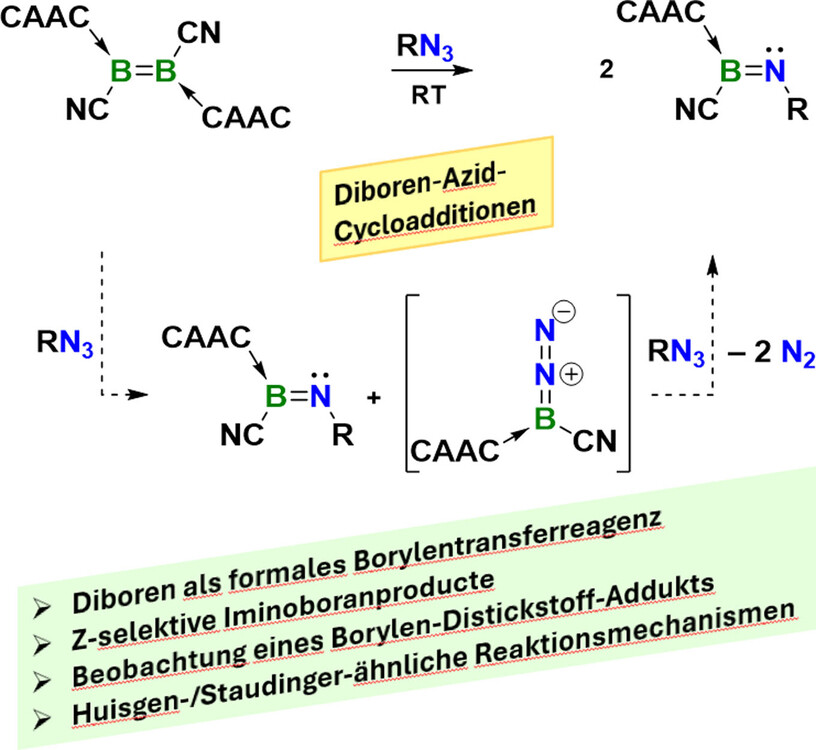
Die Reaktion eines zweifach durch cyclische Alkyl(amino)carbene (CAAC) stabilisierten Dicyanodiborens mit organischen Aziden führt zu stabilen CAAC-Iminoboran-Addukten. Experimentelle und rechnerische Daten bestätigen die entscheidende Beteiligung eines relativ langlebigen terminalen Borylen-Distickstoff-Addukts (d. h. Diazoboran), [(CAAC)B(CN)(η1-N2)].
Krebstherapie
Ferroptose-induzierender Co(III) Polypyridin Sulfasalazin Komplex für die verbesserte Krebstherapie
- First Published: 13 August 2024
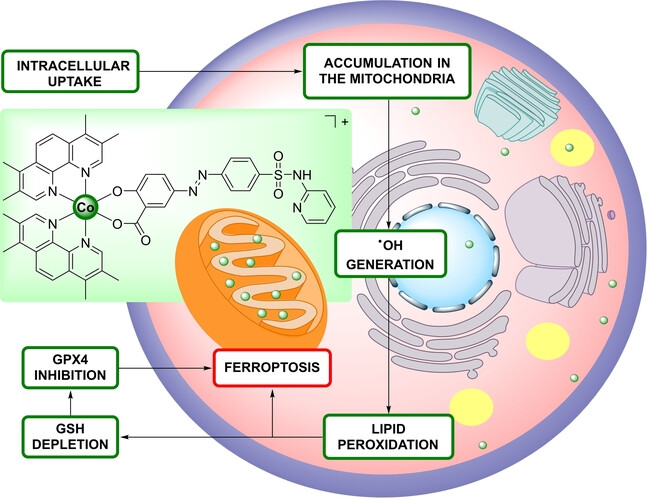
Der gezielte Einsatz der Ferroptose ist ein neuer Weg, um die Grenzen der apoptotischen Krebsbekämpfung zu überwinden. Der hier beschriebene Co(III)-Polypyridin-Sulfasalazin-Komplex wirkt als starker Ferroptose-Induktor für die Krebstherapie. Dieser Komplex reichert sich selektiv in Mitochondrien an, wobei er reaktive Sauerstoffspezies erzeugt, die Lipidperoxidation auslöst, Glutathion abbaut, die Glutathionperoxidase 4 hemmt und schließlich die Ferroptose auslöst.
Kunststoffabbau
Anodisches Recycling von gängigen Polymeren: Die Kombination von Eisen-Elektrokatalyse und skalierbarer Wasserstoffentwicklungsreaktion
- First Published: 10 September 2024
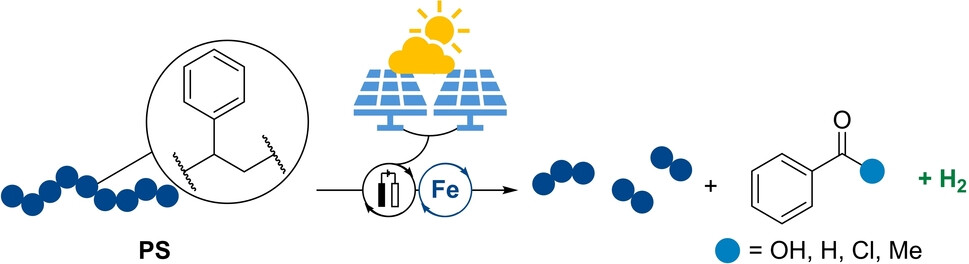
Ein des auf dem in der Erde häufig vorkommenden Elements Eisen beruhender Katalysator ermöglichte das effiziente elektrochemische Recycling von Polystyrol mit Wasserstoff als einzigem Nebenprodukt, was das Potenzial für eine kreislauforientierte Kohlenstoffwirtschaft mit einer skalierbaren grünen Wasserstoffentwicklung hervorhebt.
Photoschalter
Oberflächenspannungsmanipulation mit sichtbarem Licht durch sensibilisierte Disäquilibrierung von photoschaltbaren Amphiphilen
- First Published: 15 August 2024
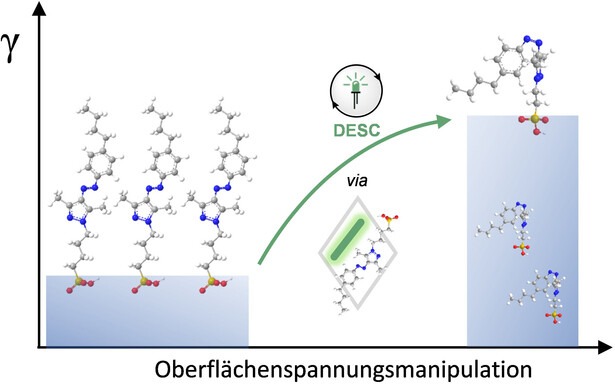
Disäquilibrierung durch Sensibilisierung unter Einschluss wird erstmals verwendet, um die Oberflächenspannung von Wasser mit Hilfe von photoschaltbaren Tensiden zu modulieren. Die Tenside POS oder NEG werden zusammen mit einem Photosensibilisator in einem makrozyklischen Käfig eingekapselt, sodass Bestrahlung mit sichtbarem Licht (grün oder rot) eine Isomerisierung induziert und somit die Oberflächenspannung auf Grundlage der veränderten Oberflächenaktivität der Amphiphile steuert.
Zuschrift
Asymmetric Catalysis
Catalytic Asymmetric Construction of C- and Si-Stereogenic Silacyclopentanes via Hydrosilylation of Arylmethylenecyclopropanes
- First Published: 13 August 2024
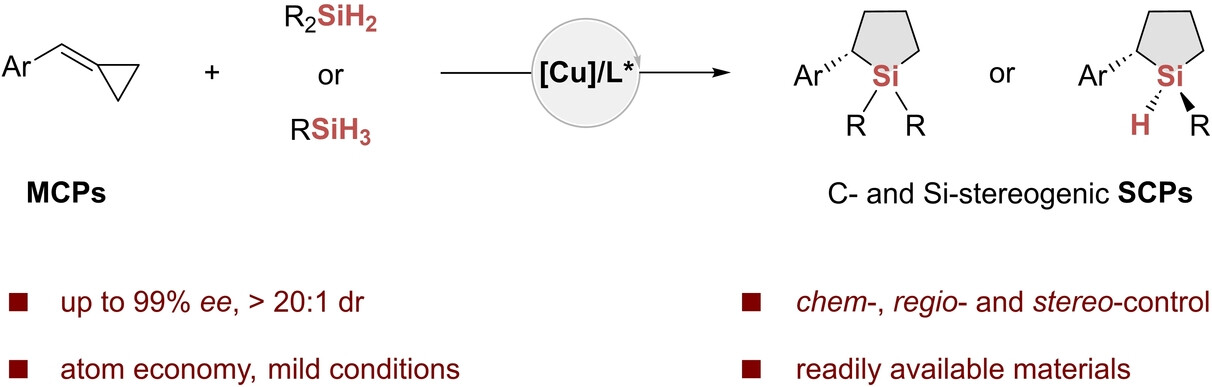
We report an efficient Cu-catalyzed asymmetric cascade hydrosilylation of arylmethylenecyclopropanes with dihydrosilanes or primary silanes, which gives access to a variety of C-stereogenic and Si-stereogenic silacyclopentanes in decent yields with good to excellent enantioselectivities and diastereoselectivities under mild conditions.
CO2 Reduction
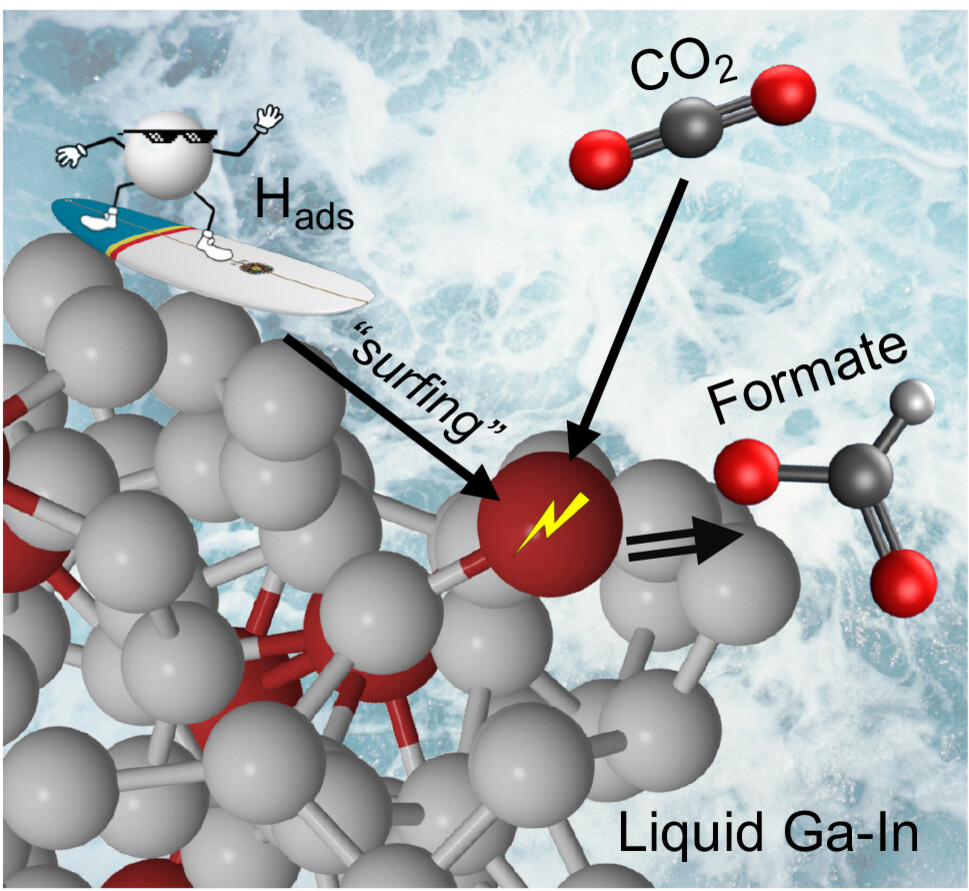
An Atomic-Scale Explanation for The High Selectivity Towards Carbon Dioxide Reduction Observed On Liquid Metal Catalysts
- First Published: 09 September 2024
Cluster Compounds
Atomically Precise Ternary Cluster: Polyoxometalate Cluster Sandwiched by Gold Clusters Protected by N-Heterocyclic Carbenes
- First Published: 29 August 2024
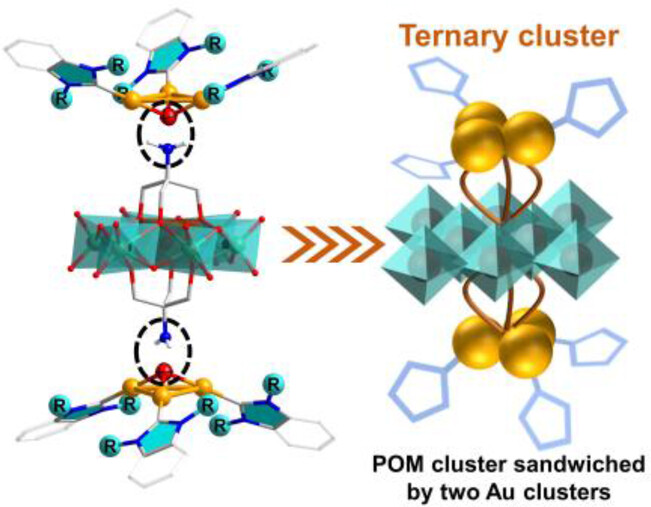
For the first time, a ternary cluster consisting of a polyoxometalate cluster sandwiched by two gold clusters protected by N-heterocyclic carbenes was synthesized through ligand exchange, whose atomically precise structures were characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. These composite clusters demonstrate excellent catalytic capabilities for reducing H2O2 via the intercluster synergistic effects.
Analytical Methods
Native Proteomics by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry
- First Published: 28 August 2024
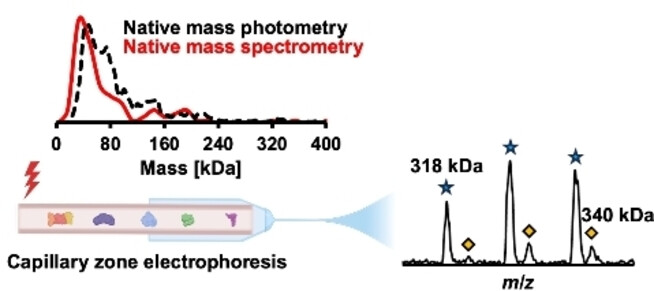
Native proteomics enabled the measurement of protein complexes up to 400 kDa from a complex proteome, via online coupling of native capillary zone electrophoresis to an ultra-high mass range Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Mass spectrometry-based native proteomics agreed well with native mass photometry regarding the mass distribution of detected proteins.
Oxabicyclo[4.1.1]octanes
Lewis Acid-Catalyzed Unusual (4+3) Annulation of para-Quinone Methides with Bicyclobutanes: Access to Oxabicyclo[4.1.1]Octanes
- First Published: 22 August 2024
![Lewis Acid-Catalyzed Unusual (4+3) Annulation of para-Quinone Methides with Bicyclobutanes: Access to Oxabicyclo[4.1.1]Octanes](/cms/asset/b562bb35-34d3-4aa8-a12d-87a7e9461c0d/ange202408610-toc-0001-m.jpg)
The synthesis of oxabicyclo[4.1.1.]octanes is demonstrated via the Lewis acid catalyzed (4+3) annulation of para-quinone methides with bicyclo[1.1.0]butanes. The reaction proceeds with the simultaneous activation of p-QMs and BCBs by Lewis acid. Mechanistically, the reaction entails the activation of the ester enolate of BCB by the Lewis acid. This method is notably straightforward in operation, proceeds efficiently under mild conditions, and exhibits excellent compatibility with various functional groups, demonstrating a broad scope.
Photocatalysis
Solar-Driven Methanogenesis through Microbial Ecosystem Engineering on Carbon Nitride
- First Published: 02 August 2024
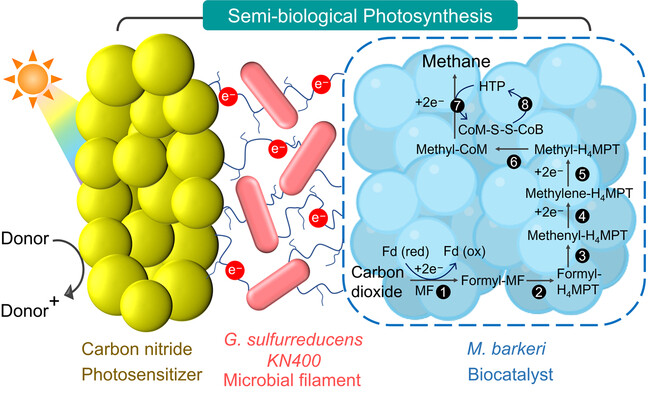
Microbial ecosystem engineering enables efficient solar-driven methanogenesis over a biohybrid photocatalyst. The syntrophic coculture of Methanosarcina barkeri (M. barkeri) with the electron transport specialist Geobacter sulfurreducens KN400 (KN400) over carbon nitride produced a semi-biological photocatalyst for the sunlight-driven methane synthesis from carbon dioxide.
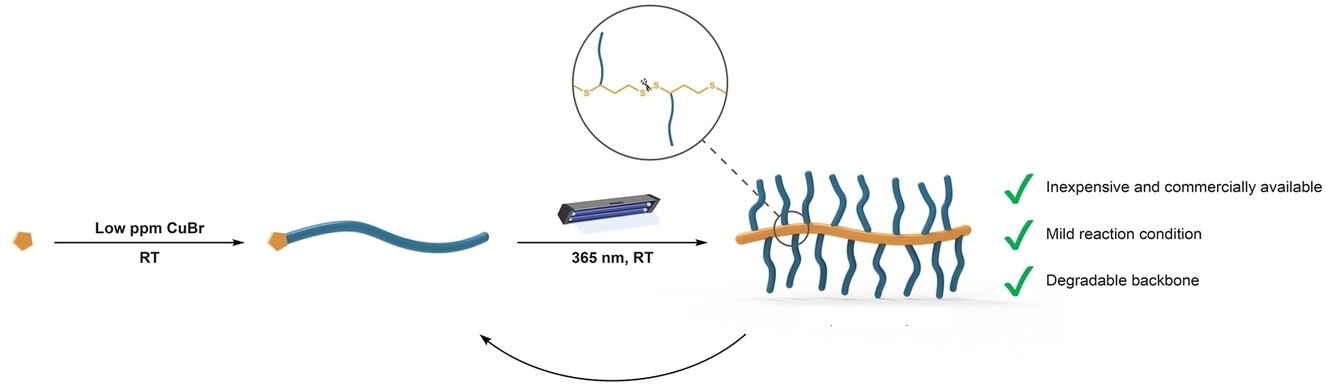
Polymer Chemistry | Hot Paper
Versatile Light-Mediated Synthesis of Degradable Bottlebrush Polymers Using α-Lipoic Acid
- First Published: 16 August 2024
Vibrational Strong Coupling | Hot Paper
Polaritonic Chemistry Enabled by Non-Local Metasurfaces
- First Published: 19 August 2024
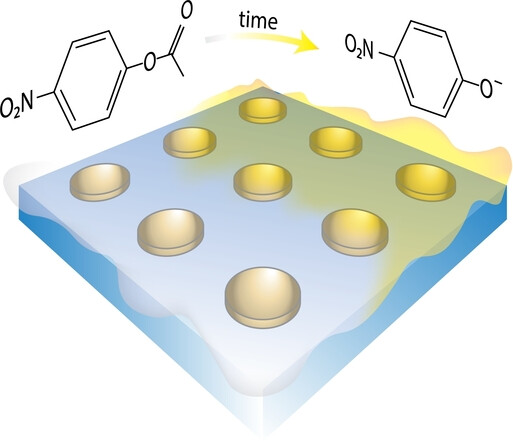
We have designed a non-local metasurface to achieve vibrational strong coupling (VSC) between surface lattice resonance and the C=O stretching modes of both ethyl acetate and p-nitrophenyl acetate (PNPA). Within this VSC system, we observed a 2.7-fold increase in the solvolysis reaction of PNPA compared to the bare reaction. This finding highlights the robustness of metasurfaces in catalyzing chemical reactions via VSC.
Asymmetrische Katalyse
Enantio- und regiokonvergente, nickelkatalysierte Veretherung von Phenolen durch Allylierung zur Darstellung chiraler C(sp3)−O-Allylarylether
- First Published: 19 August 2024
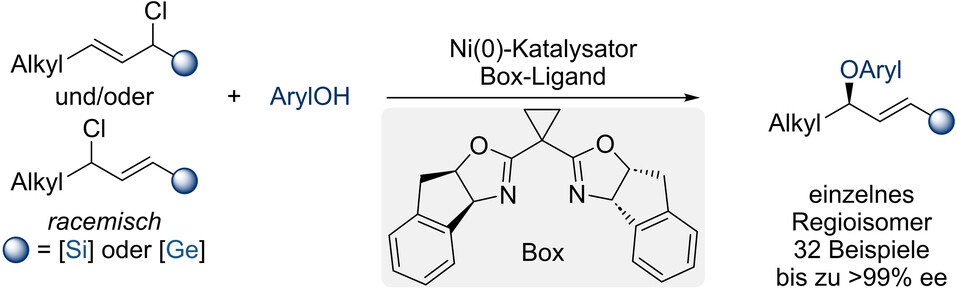
Eine nickelkatalysierte Veretherung von Phenolen mit regioisomeren Gemischen aus racemischen silylierten und germylierten Allylchloriden ermöglicht die enantio- und regiokonvergente Bildung von unsymmetrischen 1,3-disubstituierten chiralen Allylarylethern als einzelnes Regioisomer (siehe Schema). Der Schlüssel zum Erfolg ist die dirigierende Metalloidgruppe, die die Regioselektivität kontrolliert, und die gebildeten hochfunktionalisierten Allylether können anschließend in chemoselektiven Folgereaktionen umgesetzt werden.
Arzneimittelforschung
Screening fluoreszenter RNA-Methyltransferase-Sonden im Nanomolmaßstab ermöglicht die Entdeckung von METTL1-Inhibitoren
- First Published: 15 August 2024
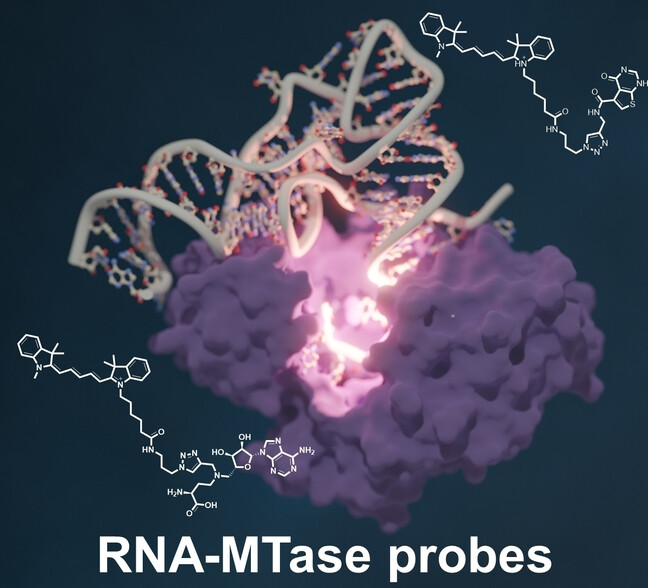
Ein modularer Syntheseansatz im Nanomolmaßstab ermöglicht die schnelle Entwicklung fluoreszenter RNA-MTase-Sonden und ermöglicht damit Hochdurchsatz-Screenings für Wirkstoffentwicklungen. Dieser innovative Ansatz erlaubt signifikante Fortschritte in der medizinischen Chemie von RNA-MTasen, wie die Entdeckung der ersten METTL1-Inhibitoren ihrer Klasse eindrucksvoll zeigt.
Flüchtige organische Verbindungen | Hot Paper
Supramolekulare Chemie
Quartärstrukturen abiotischer Foldamere
- First Published: 04 September 2024
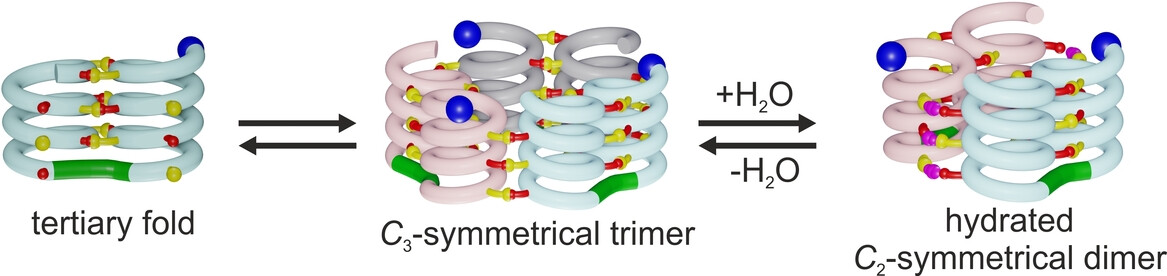
Die Einführung von Wasserstoffbrückenbindungsdonoren an bestimmten Stellen der Peripherie einer stabilen Helix-Turn-Helix-Tertiärfaltung eines aromatischen Foldamers führte zu seiner Aggregation in Chloroform und dabei zur Bildung von echten, abgrenzbaren abiotischen Quartärstrukturen, in denen die Tertiärfaltungen konserviert sind. Die Quartärstrukturen wurden einem C3-symmetrischen Trimer entsprechend dem ursprünglichen Entwurf und einem unerwarteten hydratisierten C2-symmetrischen Dimer zugeordnet.
DNA-Polymerase | Hot Paper
Eine DNA-Polymerase-Variante erkennt den epigenetischen Marker 5-Methylcytosin durch erhöhten Fehleinbau
- First Published: 24 October 2024
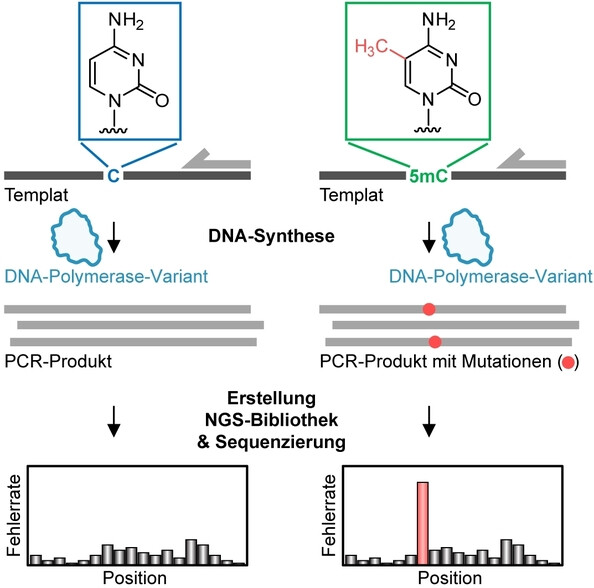
Entwicklung einer DNA-Polymerase aus Thermus aquaticus, die methylierte von unmethylierter DNA durch einen erhöhten Fehleinbau gegenüber 5-Methylcytosin (5 mC) während der DNA-Synthese unterscheidet. Durch die Erzeugung von 5 mC-abhängigen Mutationssignaturen im PCR-Produkt ist das Enzym in der Lage, methylierte Stellen zu erkennen und ermöglicht den direkten Nachweis durch Auslesen erhöhter Fehlerraten an 5 mC-Positionen nach der Sequenzierung ohne vorherige Umwandlung der Templat-DNA.
Silylierung | Hot Paper
Tricyanmethan oder Dicyanketenimin – Silylierung macht den Unterschied
- First Published: 22 August 2024
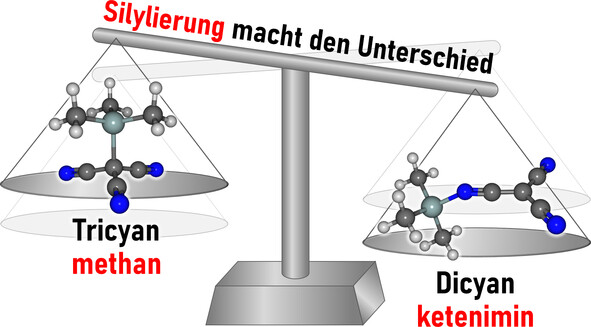
Die erste Synthese eines vollständig charakterisierten Dicyanketenimins, Me3Si−NC−C(CN)2, wurde durch Einführung einer sperrigen Me3Si-Gruppe erreicht, während die protonierte Spezies zum Tricyanmethan-Isomer HC(CN)3 führt. Eine weitere Silylierung mit [Me3Si−H−SiMe3][B(C6F5)4] führte zur Bildung eines ungewöhnlichen, persilylierten Dikations [C(CN−SiMe3)3]2+, das durch ein schwach koordinierendes Anion stabilisiert wird.






![Zinc-Catalyzed Enantioselective Formal (3+2) Cycloadditions of Bicyclobutanes with Imines: Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Azabicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes](/cms/asset/9e26e571-496c-40c9-bd96-416a08a24dbb/ange202406548-toc-0001-m.jpg)