Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Debugging Eukaryotic Genetic Code Expansion for Site-Specific Click-PAINT Super-Resolution Microscopy (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52/2016)
- Page: 15931
- First Published: 01 December 2016

Cytoplasmic re-targeting of the pyrrolysine-based genetic code expansion machinery by using a nuclear export signal (NES) substantially increases the site-specific incorporation of clickable amino acids (green) into proteins in mammalian cells, as shown by E. A. Lemke and co-workers in their Communication on page 16172 ff. These clickable amino acids can then be modified with annealing sites for small DNA imaging strands (red) to enable high-contrast Click-PAINT super-resolution microscopy.
Inside Cover: A Dynamic and Responsive Host in Action: Light-Controlled Molecular Encapsulation (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52/2016)
- Page: 15932
- First Published: 09 December 2016

Light-driven conformational changes in a macrocyclic host enable the controlled encapsulation and release of guest species. In their Communication on page 16096 ff., J. del Barrio, O. A. Scherman and co-workers describe the rational design and synthesis of a photoresponsive macrocycle that displays remarkable binding affinity towards a set of guest molecules, including N-oxides and carboxylates. The guest molecules are expelled from the macrocyclic cavity when the complex is exposed to UV light.
Inside Back Cover: Nucleophilic Transfer Reactions of the [Si(C2F5)3]− Moiety (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52/2016)
- Page: 16177
- First Published: 01 December 2016
![Inside Back Cover: Nucleophilic Transfer Reactions of the [Si(C2F5)3]− Moiety (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52/2016) Volume 55 Issue 52, 2016](/cms/asset/8380f8ad-ad4d-4594-bb70-462dcc61fbd4/anie201611311-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Whereas tris(trifluoromethyl)silanes tend to decompose violently at room temperature, the corresponding pentafluoroethyl derivatives are thermostable compounds. Preparative synthesis of Li[Si(C2F5)3] enabled efficient nucleophilic transfer of the Si(C2F5)3 unit onto main-group and transition-metal compounds as well as organic scaffolds, as shown by B. Hoge and co-workers in two Communications on page 16156 ff. and on page 16161 ff.
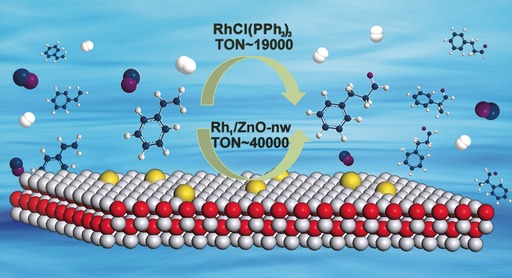
Back Cover: Hydroformylation of Olefins by a Rhodium Single-Atom Catalyst with Activity Comparable to RhCl(PPh3)3 (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52/2016)
- Page: 16178
- First Published: 21 December 2016

Somewhere over the rainbow single-atom catalysts dispersed on a support surface offer a tantalizing bridge between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts. In their Communication on page 16054 ff., B. Qiao, T. Zhang, and co-workers describe rhodium single-atom catalysts supported on ZnO nanowires that show an olefin hydroformylation efficiency comparable to that of homogeneous Wilkinson's catalyst.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Modelling a Linker Mix-and-Match Approach for Controlling the Optical Excitation Gaps and Band Alignment of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks
- First Published: 21 December 2016
Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks: In their Communication on page 16012 ff., R. Grau-Crespo, S. Hamad et al. show that using mixed linkers within zeolitic imidazolate frameworks provides a route for tuning their electronic gaps and band edge positions.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52/2016
- Pages: 15935-15947
- First Published: 21 December 2016
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52/2016
- Pages: 15948-15951
- First Published: 21 December 2016
Author Profiles
News
Alessandro Volta Medal: C. Amatore / Centenary Award: P. Cramer / RUSNANOPRIZE: C. A. Mirkin / Frontiers in Chemical Energy Science Award: W. B. Tolman
- Page: 15954
- First Published: 09 December 2016
Book Reviews
Sustainable Catalysis. Without Metals or Other Endangered Elements, Part 1 and 2 Edited by Michael North.
- Page: 15955
- First Published: 01 December 2016
News
Editorial Board and International Advisory Board of Angewandte Chemie
- Pages: 15957-15959
- First Published: 21 December 2016
Highlights
Drug Design
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Sustained Signaling via Intracellular Megaplexes and Pathway-Specific Drugs
- Pages: 15962-15964
- First Published: 24 October 2016
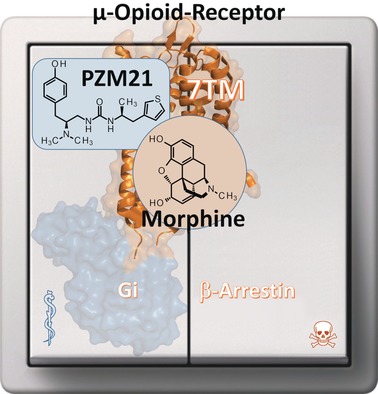
Together forever? Functional selection was applied to finally achieve separation of the analgesic properties of opiods from serious side effects such as potentially lethal respiratory depression. A Gi-biased μ-opioid-receptor agonist (PZM21) was identified that stabilizes previously unexplored receptor conformations. This compound relieves pain in mice without causing hypoventilation or addiction.
Essays
Origin of Proteins
Functional Proteins from Short Peptides: Dayhoff's Hypothesis Turns 50
- Pages: 15966-15971
- First Published: 16 November 2016

First and foremost: Margaret Dayhoff's 1966 hypothesis on the origin of proteins is now an accepted model for the emergence of large, globular, functional proteins from short, simple peptides. However, the fundamental question of how the first protein(s) emerged still stands. The tools and hypotheses pioneered by Dayhoff, and the over 65 million protein sequences and 12 000 structures known today, enable those who follow in her footsteps to address this question.
Minireviews
Gene Transcription
The Structural Basis of Transcription: 10 Years After the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- Pages: 15972-15981
- First Published: 10 October 2016
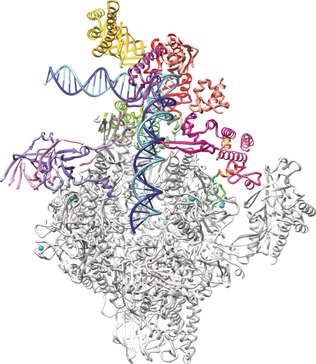
Transcription unlimited: In the 10 years since the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Roger Kornberg for his studies of the molecular basis of transcription, significant advances have been made in our understanding of many aspects of transcription, and progess in cryo-electron microscopy has enabled the study of large molecular assemblies at high resolution. Our current understanding of the structural basis of transcription is discussed in this Minireview.
Medicinal Chemistry
Latest Advances Towards Ras Inhibition: A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective
- Pages: 15982-15988
- First Published: 16 September 2016
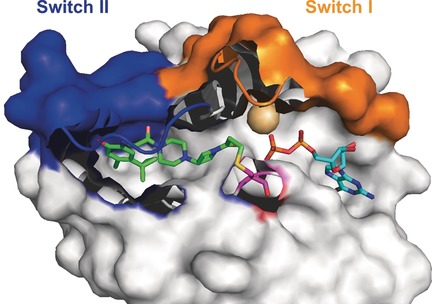
Persistence pays off: After more than 40 years of effort, promising results are finally being reported the field of Ras inhibition. This Minireview presents the latest advances towards Ras inhibitors, as well as a critical assessment from a medicinal chemistry perspective. The picture shows the covalent inhibitor ARS-853 in complex with K-RasG12C.
Reviews
Biomolecular Structure Determination
Deriving Structural Information from Experimentally Measured Data on Biomolecules
- Pages: 15990-16010
- First Published: 08 November 2016
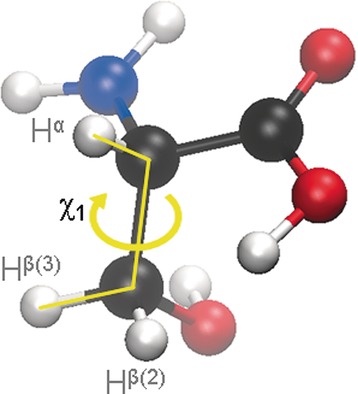
Making the right choice: Deriving structural information from experimentally measured data is a process beset with theoretical and practical problems. The effects of the various assumptions and approximations involved in the process of biomolecular structure determination are discussed and a list of choices to be avoided is provided.
Communications
Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks
Modelling a Linker Mix-and-Match Approach for Controlling the Optical Excitation Gaps and Band Alignment of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks
- Pages: 16012-16016
- First Published: 15 November 2016

The sum of its parts: A computational study shows that using mixed linkers within zeolitic imidazolate frameworks provides a route for tuning their electronic gaps and band edge positions. It is theoretically possible in this way to match the electronic structure requirements for photocatalytic reactions including water splitting and CO2 reduction.
NMR Spectroscopy
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization Provides New Insights into Chromophore Structure in Phytochrome Photoreceptors
- Pages: 16017-16020
- First Published: 23 November 2016
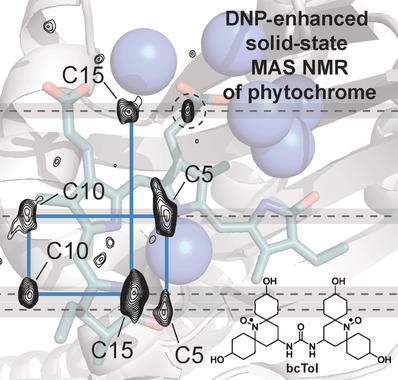
The phytochrome photocycle: The cyanobacterial phytochrome Cph1 regulates cellular processes through light. Dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced solid-state magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy was applied to illuminate the mechanism of phytochrome molecular action. The approach enables the assignment of the phycocyanobilin (PCB) chromophore resonances, which allowed localization of the positive charge in PCB.
Metal–Organic Frameworks
Flexible, Luminescent Metal–Organic Frameworks Showing Synergistic Solid-Solution Effects on Porosity and Sensitivity
- Pages: 16021-16025
- First Published: 28 November 2016
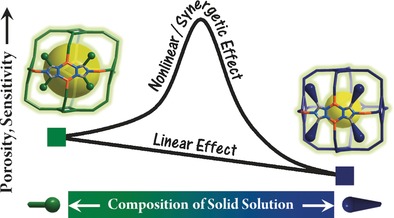
Beyond mixing: The proper combination of non-isostructural metal–organic frameworks in terms of solid solutions can drastically improve the porosity (150 %) and optical O2 sensitivity (410 times) compared with the original phases. An oxygen-sensing MOF (MAF-2) can undergo structure changes and property improvements when its molecular building blocks are mixed and solid solutions are formed.
Fluorescent Probes | Hot Paper
Bioorthogonal Probes for the Study of MDM2-p53 Inhibitors in Cells and Development of High-Content Screening Assays for Drug Discovery
- Pages: 16026-16030
- First Published: 22 November 2016
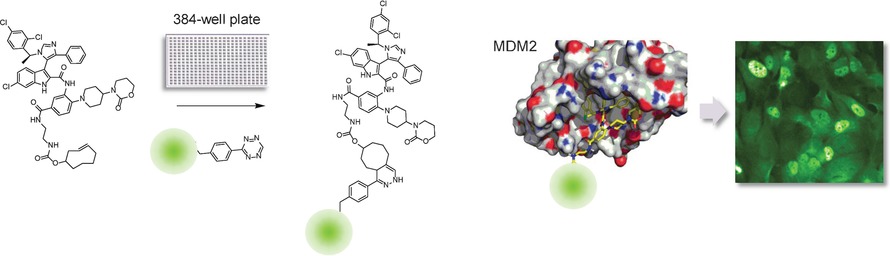
Bioorthogonal probes were developed to study MDM2-p53 inhibitors in an osteosarcoma cell model. Target engagement of the probe, target upregulation upon MDM2-p53 inhibition, and target occupancy of non-tagged MDM2-p53 inhibitors could be monitored by using high-content screening assays and automated single-cell imaging analysis.
Zinc–Hydride Complexes
Trajectory of Approach of a Zinc–Hydrogen Bond to Transition Metals
- Pages: 16031-16034
- First Published: 23 November 2016
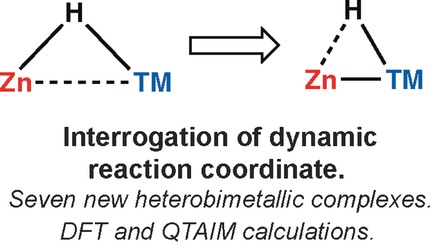
Seven new zinc–transition-metal hydrides have been prepared and crystallographically characterized. Through variation of the transition-metal fragment, a series of snapshots of the reaction coordinate of the approach of the Zn−H bond toward the transition-metal is obtained. The reaction trajectory is characterized by the transfer of electron density from the largely ionic Zn−H bond to increasingly covalent TM−H and TM−Zn bonds.
Supramolecular Chemistry
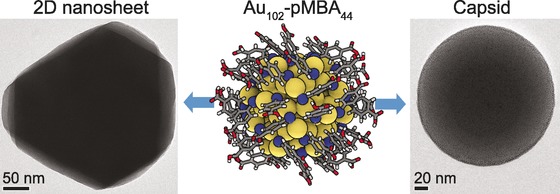
Template-Free Supracolloidal Self-Assembly of Atomically Precise Gold Nanoclusters: From 2D Colloidal Crystals to Spherical Capsids
- Pages: 16035-16038
- First Published: 23 November 2016
Nanoparticles | Very Important Paper
Tailoring Renal Clearance and Tumor Targeting of Ultrasmall Metal Nanoparticles with Particle Density
- Pages: 16039-16043
- First Published: 24 November 2016
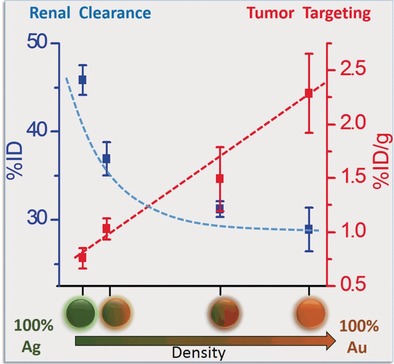
Density matters: Four different metal nanoparticles with the same size and surface chemistry but different densities were synthesized. It was then shown that the renal clearance of ultrasmall metal nanoparticles decreases exponentially with an increase in particle density while tumor targeting linearly increases.
Zeolites
Template–Framework Interactions in Tetraethylammonium-Directed Zeolite Synthesis
- Pages: 16044-16048
- First Published: 22 November 2016
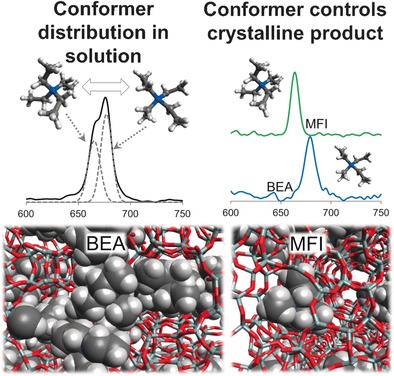
Insight into host-guest interactions: Using a combination of experimental and computational techniques, template–framework interactions have been probed in a variety of zeolites. The findings demonstrate that the phase that crystallizes is determined by a complex interplay of framework inorganic elements, template conformation, template–heteroatom interactions and framework stabilization by the space-filling template molecules.
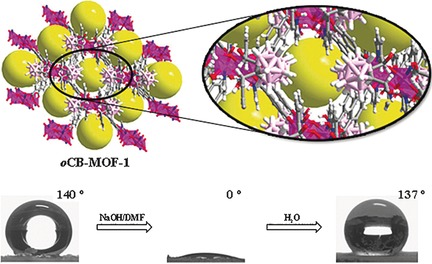
Metal–Organic Frameworks
Switchable Surface Hydrophobicity–Hydrophilicity of a Metal–Organic Framework
- Pages: 16049-16053
- First Published: 28 November 2016
Single-Atom Catalysts | Hot Paper
Hydroformylation of Olefins by a Rhodium Single-Atom Catalyst with Activity Comparable to RhCl(PPh3)3
- Pages: 16054-16058
- First Published: 09 November 2016
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium Germanate (Li2GeO3): A High-Performance Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Pages: 16059-16063
- First Published: 23 November 2016
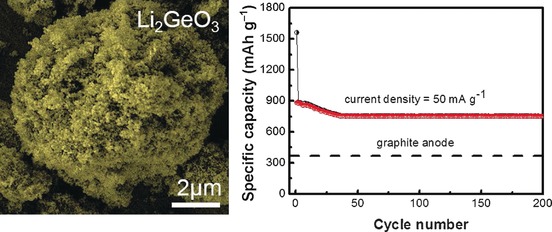
A synthetic route to a high-performance Li2GeO3 anode as a carbon-coating-free electrode for lithium-ion batteries has been developed. The Li2GeO3 material consists of micrometer-sized porous clusters, which is beneficial for both faster ion diffusion and electron transfer. The Li2GeO3 electrode exhibits long-term cycling stability and high charge capacity.
Protein Design
Conversion of the Native 24-mer Ferritin Nanocage into Its Non-Native 16-mer Analogue by Insertion of Extra Amino Acid Residues
- Pages: 16064-16070
- First Published: 25 November 2016
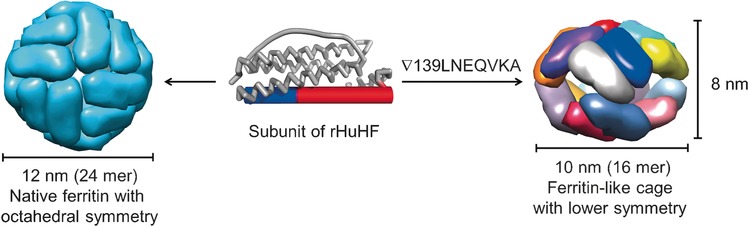
Shaping proteins: The ferritin cage exhibits high selectivity and has been utilized as a delivery vehicle for anticancer drugs or imaging agents. However, its assembly has been limited to a single size and shape. By tuning the interfacial interaction of recombinant human H-chain ferritin (rHuHF) subunits through amino acid residues insertion, a novel, lower symmetrical ferritin-like nanocage was produced and crystallographically investigated.
Single-Molecule Magnets
On Approaching the Limit of Molecular Magnetic Anisotropy: A Near-Perfect Pentagonal Bipyramidal Dysprosium(III) Single-Molecule Magnet
- Pages: 16071-16074
- First Published: 22 November 2016
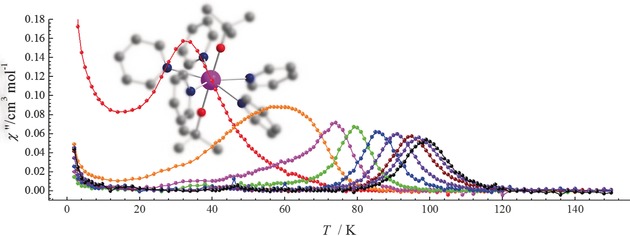
Record-breaking: A monometallic dysprosium complex, [Dy(OtBu)2(py)5][BPh4], displaying near-perfect pentagonal bipyramid geometry defined by two strong axial tert-butoxide ligands and five weak equatorial pyridine donors is reported. This complex displays massive magnetic anisotropy, approaching the limit of a two-coordinate complex, with an energy barrier to magnetic relaxation of Ueff=1815(1) K and a blocking temperature of TB=14 K.
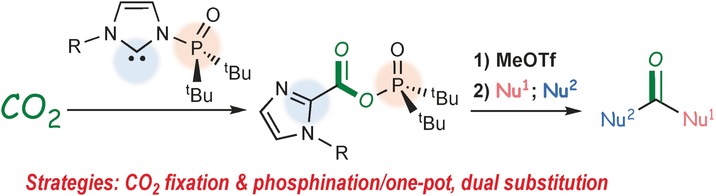
Carbon Dioxide Fixation
Strategic Utilization of Multifunctional Carbene for Direct Synthesis of Carboxylic–Phosphinic Mixed Anhydride from CO2
- Pages: 16075-16079
- First Published: 28 November 2016
Photobiology | Hot Paper
Phototriggered Secretion of Membrane Compartmentalized Bioactive Agents
- Pages: 16080-16083
- First Published: 22 November 2016
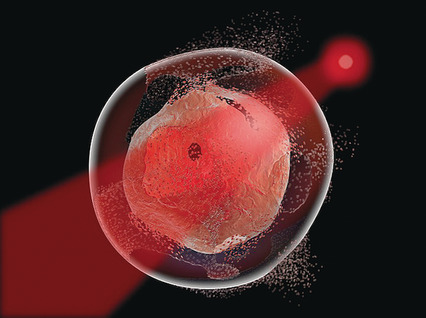
Drug delivery: Membrane-impermeable, photoresponsive conjugates have been developed that can be inserted into and retained by membrane-enclosed compartments. Illumination generates a membrane-permeable biologically active agent, which is rapidly secreted. The wavelength of photorelease can be unambiguously pre-assigned, enabling the specific discharge of different bioagents from a common carrier.
Kinetic Analysis | Hot Paper
Variable Time Normalization Analysis: General Graphical Elucidation of Reaction Orders from Concentration Profiles
- Pages: 16084-16087
- First Published: 25 November 2016

Overlaid concentration profiles: The order in any component of a reaction is determined by visual comparison of variably normalized concentration profiles. Variable time normalization analysis (VTNA) is easy and quick to perform, is run under synthetically relevant conditions, and provides information on the entire reaction course.
Separation Technology | Hot Paper
Solid Separation from a Mixed Suspension through Electric-Field-Enhanced Crystallization
- Pages: 16088-16091
- First Published: 18 November 2016
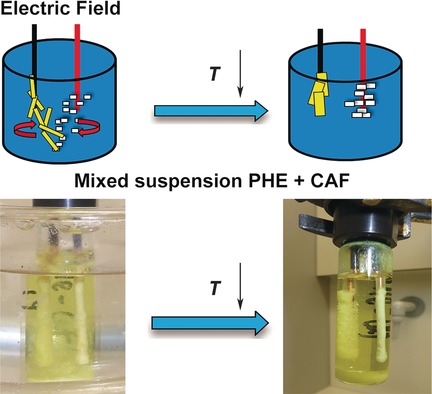
Crystallization from a multicomponent mixture requires additional steps for product purification. The application of an inhomogeneous electric field on a mixed suspension enables simultaneous particle separation and crystal growth. Crystals of the two solutes (CAF=caffeine, PHE=phenazine) are then separately collected from the two electrodes.
Enantioselective Synthesis
Iridium-Catalyzed Stereoselective Allylic Alkylation Reactions with Crotyl Chloride
- Pages: 16092-16095
- First Published: 28 November 2016
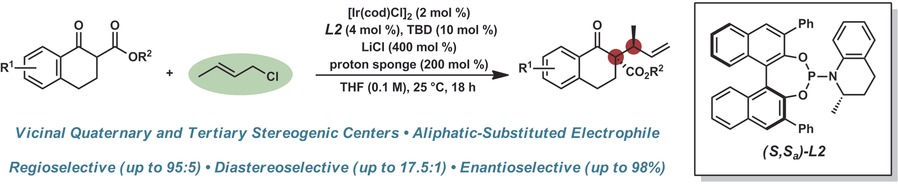
Sponge worthy: The unique combination of crotyl chloride, LiCl, and proton sponge has delivered the first enantio-, diastereo-, and regioselective iridium-catalyzed allylic alkylation reaction to form an all-carbon quaternary stereocenter with an aliphatic-substituted electrophile. The reaction proceeds with good to excellent selectivity for a range of substituted tetralones, providing products bearing a newly formed vicinal tertiary and all-carbon quaternary stereodyad.
Supramolecular Chemistry | Hot Paper
A Dynamic and Responsive Host in Action: Light-Controlled Molecular Encapsulation
- Pages: 16096-16100
- First Published: 28 October 2016
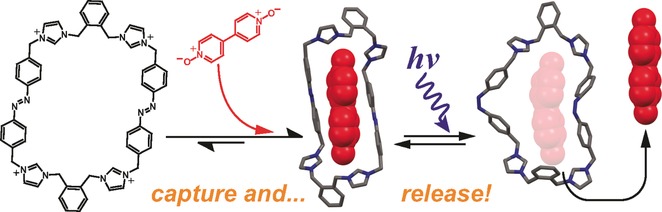
One ring to rule them all … and in the darkness bind them: A photoresponsive tetracationic macrocycle features a facile three-step synthesis and makes possible the noncovalent binding of a set of guest molecules, including N-oxide and carboxylate derivatives. The guest molecules can be actively released by UV light irradiation in a remote fashion.
Halogenation
Highly ortho-Selective Chlorination of Anilines Using a Secondary Ammonium Salt Organocatalyst
- Pages: 16101-16105
- First Published: 30 November 2016
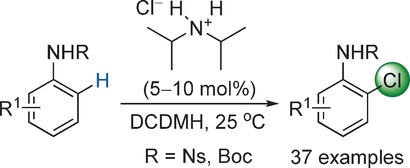
Worth its salt: An efficient regioselective ortho-chlorination of anilines is described. A secondary ammonium chloride salt is employed as the organocatalyst and the reaction can be conducted at room temperature without protection from air and moisture. This catalytic protocol has broad substrate scope, is scalable, and was applied to the efficient synthesis of a potent c-Met kinase inhibitor. DCDMH=1,3-dichloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin.
Motor Proteins
Controlled Retention and Release of Biomolecular Transport Systems Using Shape-Changing Polymer Bilayers
- Pages: 16106-16109
- First Published: 24 November 2016
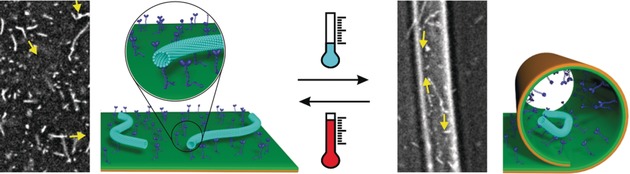
Gliding around: A polymer bilayer is able to undergo reversible transitions between flat and tube-like shapes, which allows the externally controlled retention and release of gliding microtubules. These findings open new possibilities to control biomolecular transport using substrates with switchable shapes.
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Gram-Scale Synthesis of Chiral Cyclopropane-Containing Drugs and Drug Precursors with Engineered Myoglobin Catalysts Featuring Complementary Stereoselectivity
- Pages: 16110-16114
- First Published: 25 November 2016
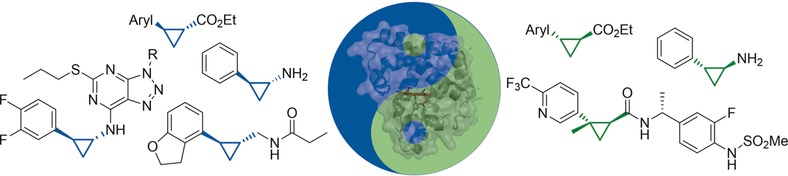
Chiral cyclopropanes à la carte: Myoglobin-based cyclopropanation catalysts featuring complementary stereoselectivity were developed for the synthesis of 1-carboxy-2-aryl-cyclopropanes. The engineered hemoproteins were applied in whole-cell reactions to afford cyclopropane-containing drugs and precursors thereof at the gram scale, in high yield, and with excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivity.
Prodrugs
Targeting Cancer with PCPA-Drug Conjugates: LSD1 Inhibition-Triggered Release of 4-Hydroxytamoxifen
- Pages: 16115-16118
- First Published: 24 November 2016
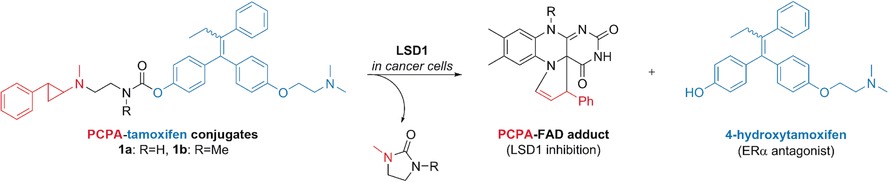
I want a new drug: PCPA-drug conjugates (PDCs) were designed as the basis of a new prodrug strategy. The prototype PCPA-tamoxifen conjugates 1 a and 1 b released 4-hydroxytamoxifen upon inhibition of LSD1. While 1 a and 1 b exhibited antiproliferative activity in breast cancer cells through the simultaneous inhibition of LSD1 and ERα, no cytotoxicity was observed in normal cells.
Cross-Coupling
Regioselective Hydrohydroxyalkylation of Styrene with Primary Alcohols or Aldehydes via Ruthenium-Catalyzed C−C Bond Forming Transfer Hydrogenation
- Pages: 16119-16122
- First Published: 02 December 2016

Feedstocks to building blocks: Transfer hydrogenative coupling of styrene with primary alcohols using the precatalyst HClRu(CO)(PCy3)2 modified by AgOTf or HBF4 delivers branched or linear adducts from benzylic or aliphatic alcohols, respectively. Related 2-propanol mediated reductive couplings also are described.
Proton-Conducting Materials
Cost-Effective, High-Performance Porous-Organic-Polymer Conductors Functionalized with Sulfonic Acid Groups by Direct Postsynthetic Substitution
- Pages: 16123-16126
- First Published: 25 November 2016
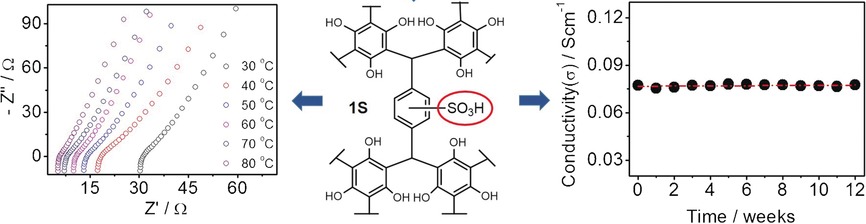
Save the best for last: The postsynthetic substitution of a porous organic polymer 1 produced the sulfonated solid polymer 1S (see scheme), which exhibited a remarkable conductivity of 7.72×10−2 S cm−1 at 80 °C and 90 % relative humidity. The sulfonated material also revealed long-term performance over more than 3 months without conductivity decay, and its cost-effective synthesis is scalable for mass production.
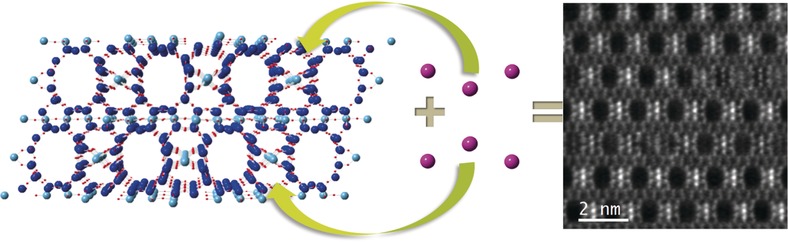
Electron Microscopy
Imaging the Atomic Position of Light Cations in a Porous Network and the Europium(III) Ion Exchange Capability by Aberration-Corrected Electron Microscopy
- Pages: 16127-16131
- First Published: 24 November 2016
Nitrogen Heterocycles
Synthesis and Investigation of Advanced Energetic Materials Based on Bispyrazolylmethanes
- Pages: 16132-16135
- First Published: 25 November 2016
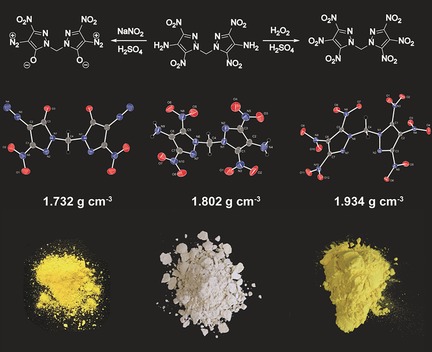
Safer, greener, stronger: Trinitropyrazoles are a powerful class of energetic materials. The connection of two nitropyrazole rings by a methylene bridge afforded three energetic compounds (see picture) with high potential as explosives for different applications. Besides the low sensitivity and high thermal stability of the compounds, their high performance was demonstrated by combined theoretical and experimental studies.
NHC Catalysis
Enantioselective (4+2) Annulation of Donor–Acceptor Cyclobutanes by N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis
- Pages: 16136-16140
- First Published: 28 November 2016
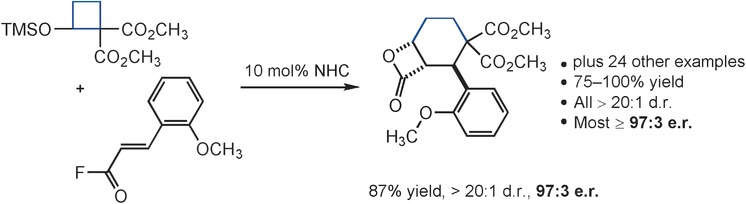
Feeling a little strained? The enantioselective (4+2) annulation of donor–acceptor cyclobutanes with unsaturated acyl fluorides using N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) catalysis has been discovered. The reaction provides a 3-step entry to cyclohexyl β-lactones (25 examples) in excellent chemical yield (most ≥90 %) and stereochemical integrity (all >20:1 d.r., most ≥97:3 e.r.).
Main-Group Chemistry
Cyclic Amino(Ylide) Silylene: A Stable Heterocyclic Silylene with Strongly Electron-Donating Character
- Pages: 16141-16144
- First Published: 25 November 2016
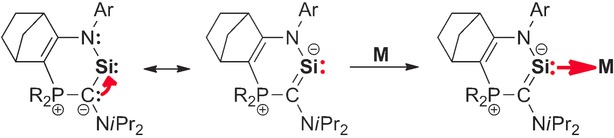
An isolable cyclic silylene stabilized by two different strongly π-donating groups, an amino group and a phosphonium ylide, was synthesized. The combination of these two π-donating substituents confers high thermal stability and strong nucleophilic character on the silylene. Its electron-donating character is comparable to that of NHC ligands, despite the fact that stable silylenes have been thought to be more weakly donating than phosphines.
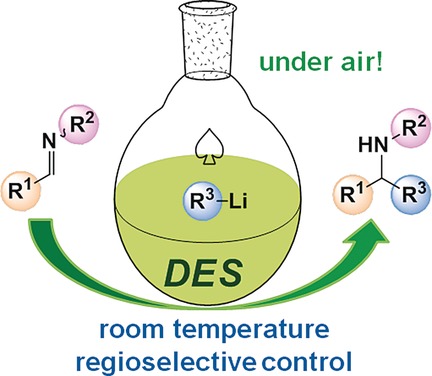
Organolithium Chemistry
Exploiting Deep Eutectic Solvents and Organolithium Reagent Partnerships: Chemoselective Ultrafast Addition to Imines and Quinolines Under Aerobic Ambient Temperature Conditions
- Pages: 16145-16148
- First Published: 28 November 2016
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Hydrogen-Permeable Tubular Membrane Reactor: Promoting Conversion and Product Selectivity for Non-Oxidative Activation of Methane over an Fe©SiO2 Catalyst
- Pages: 16149-16152
- First Published: 24 November 2016
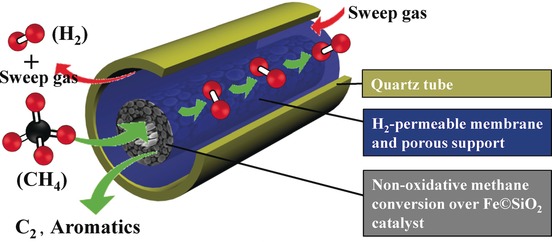
Adding value to natural gas: A hydrogen-permeable tubular ceramic membrane reactor was developed, enabling Fe©SiO2-catalyzed CH4 upgrading to higher hydrocarbons. The Fe©SiO2 catalyst demonstrated a stable 30 % C2+ single-pass yield, with up to 30 % CH4 conversion and 99 % selectivity to C2 and aromatic products.
Heterocycles
Combining Organocatalysis and Lanthanide Catalysis: A Sequential One-Pot Quadruple Reaction Sequence/Hetero-Diels–Alder Asymmetric Synthesis of Functionalized Tricycles
- Pages: 16153-16155
- First Published: 23 November 2016
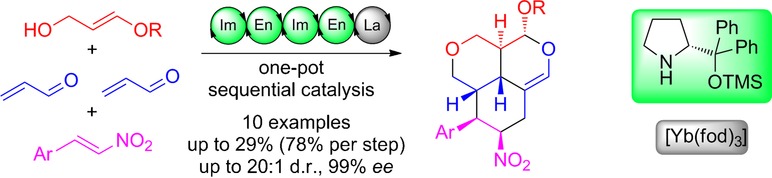
Targeting complexity: A unique combination of organocatalysis with lanthanide catalysis directly leads to complex tricyclic structures from readily available and simple compounds. Six new bonds and six stereocenters are formed with virtually complete stereoselectivity in this multicomponent one-pot procedure. fod=2,2-dimethyl-6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptafluorooctane-3,5-dionato.
Silanides | Very Important Paper
The Tris(pentafluoroethyl)silanide Anion
- Pages: 16156-16160
- First Published: 30 November 2016
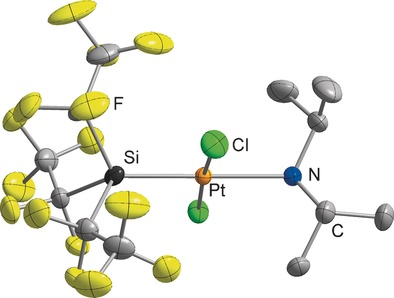
Tris(pentafluoroethyl)silane was used for hydrosilylation reactions. It can be deprotonated by sterically demanding bases at low temperatures, which leads to the formation of the corresponding silanide ion. Addition of crown ethers or cryptands allows the isolation and characterization of the salt-like tris(pentafluoroethyl)silanide at room temperature. Interception of the silanide with PtIICl2 resulted in the formation of a silyl-substituted platinum complex.
Silanides
Nucleophilic Transfer Reactions of the [Si(C2F5)3]− Moiety
- Pages: 16161-16164
- First Published: 30 November 2016
![Nucleophilic Transfer Reactions of the [Si(C2F5)3]− Moiety](/cms/asset/c5e29e72-c50e-406d-a81a-be9a9c4d0c3e/anie201609575-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Easily transferred: The tris(pentafluoroethyl)silanide anion is accessible by the deprotonation of Si(C2F5)3H at low temperatures. Subsequent quenching with suitable electrophiles leads to a plethora of tris(pentafluoroethyl)silane derivatives and underlines the versatility of Li[Si(C2F5)3] as a powerful nucleophilic transfer reagent of the [Si(C2F5)3]− unit.
Structural Inorganic Chemistry
Polysulfates [SnO3n+1]2−: With the [S6O19]2− Anion, has the End been Reached?
- Pages: 16165-16167
- First Published: 22 November 2016
![Polysulfates [SnO3n+1]2−: With the [S6O19]2− Anion, has the End been Reached?](/cms/asset/d923962c-bc91-4244-833e-01d7f17f8482/anie201607629-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Where is the n-d? The connection of sulfate tetrahedra leads to polysulfate chains according to [SnO3n+1]2− and brings up the question how long the chains might be? The structural details of the new hexasulfate anion [S6O19]2− anion and theoretical investigations on such polysulfate anions seems to answer the question: The end is probably reached.
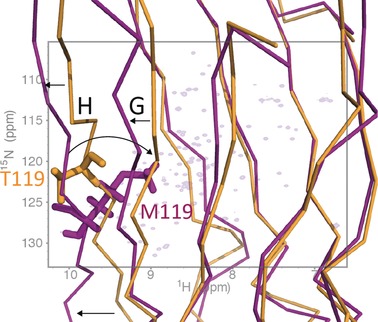
Protein NMR Spectroscopy
Structure of Monomeric Transthyretin Carrying the Clinically Important T119M Mutation
- Pages: 16168-16171
- First Published: 25 November 2016
In-Cell Protein Labeling | Hot Paper
Debugging Eukaryotic Genetic Code Expansion for Site-Specific Click-PAINT Super-Resolution Microscopy
- Pages: 16172-16176
- First Published: 02 November 2016
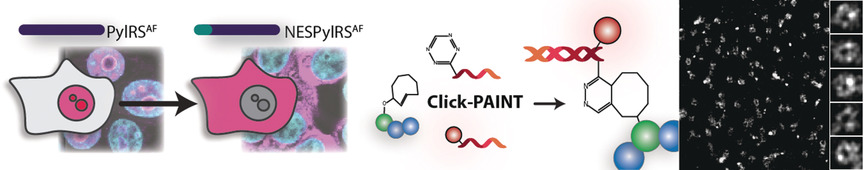
On target: Cytoplasmic re-targeting of the most widely used eukaryotic genetic code expansion machinery substantially increases the residue-specific incorporation of noncanonical amino acids into proteins in mammalian cells. This approach can be combined with ultrafast Diels–Alder click reactions for DNA-PAINT-based super-resolution microscopy. The “Click-PAINT” system enables high-contrast, residue-specific imaging of even low-abundance proteins.