Controlled Retention and Release of Biomolecular Transport Systems Using Shape-Changing Polymer Bilayers
Dr. Georgi Stoychev
College of Engineering, College of Family and Consumer Sciences, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, 30602 USA
Leibniz Institute of Polymer Research e.V. Dresden, Hohe Str. 6, 01069 Dresden, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cordula Reuther
B CUBE—Center for Molecular Bioengineering, Technische Universität Dresden and Max-Planck-Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, 01307 Dresden, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Stefan Diez
B CUBE—Center for Molecular Bioengineering, Technische Universität Dresden and Max-Planck-Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, 01307 Dresden, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Leonid Ionov
College of Engineering, College of Family and Consumer Sciences, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, 30602 USA
Leibniz Institute of Polymer Research e.V. Dresden, Hohe Str. 6, 01069 Dresden, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Georgi Stoychev
College of Engineering, College of Family and Consumer Sciences, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, 30602 USA
Leibniz Institute of Polymer Research e.V. Dresden, Hohe Str. 6, 01069 Dresden, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cordula Reuther
B CUBE—Center for Molecular Bioengineering, Technische Universität Dresden and Max-Planck-Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, 01307 Dresden, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Stefan Diez
B CUBE—Center for Molecular Bioengineering, Technische Universität Dresden and Max-Planck-Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, 01307 Dresden, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Leonid Ionov
College of Engineering, College of Family and Consumer Sciences, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, 30602 USA
Leibniz Institute of Polymer Research e.V. Dresden, Hohe Str. 6, 01069 Dresden, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
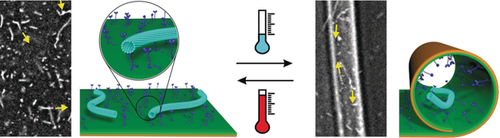
Gliding around: A polymer bilayer is able to undergo reversible transitions between flat and tube-like shapes, which allows the externally controlled retention and release of gliding microtubules. These findings open new possibilities to control biomolecular transport using substrates with switchable shapes.
Abstract
Biomolecular transport systems based on cytoskeletal filaments and motor proteins have become promising tools for a wide range of nanotechnological applications. In this paper, we report control of such transport systems using substrates with switchable shape. We demonstrate this approach on the example of microtubules gliding on surfaces of self-folding polymer bilayers with adsorbed kinesin motors. The polymer bilayers are able to undergo reversible transitions between flat and tube-like shapes that allow the externally controlled retention and release of gliding microtubules. The demonstrated approach, based on surfaces with reconfigurable topography, opens broad perspectives to control biomolecular transport systems for bioanalytical and sensing applications, as well as for the construction of subcellular compartments in the field of synthetic biology.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201608299-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf46.2 KB | Supplementary |
| anie201608299-sup-0001-Movie_S1.avi2.5 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201608299-sup-0001-Movie_S2.avi3.7 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201608299-sup-0001-Movie_S3.avi2 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201608299-sup-0001-Movie_S4.avi2 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201608299-sup-0001-Movie_S5.avi1.4 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201608299-sup-0001-Movie_S6.avi8.8 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1S. Sánchez, L. Soler, J. Katuri, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1414; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 1432.
- 2
- 2aA. Agarwal, H. Hess, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 252;
- 2bA. Agarwal, H. Hess, J. Nanotechnol. Eng. Med. 2009, 1, 011005;
- 2cM. G. L. van den Heuvel, C. Dekker, Science 2007, 317, 333.
- 3
- 3aT. Nitta, H. Hess, Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2013, 6, 109;
- 3bP. Katira, H. Hess, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 567;
- 3cG. D. Bachand, H. Hess, B. Ratna, P. Satir, V. Vogel, Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1661;
- 3dT. Fischer, A. Agarwal, H. Hess, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 162;
- 3eS. Ramachandran, K.-H. Ernst, G. D. Bachand, V. Vogel, H. Hess, Small 2006, 2, 330;
- 3fS. Korten, N. Albet-Torres, F. Paderi, L. ten Siethoff, S. Diez, T. Korten, G. te Kronnie, A. Mansson, Lab Chip 2013, 13, 866.
- 4
- 4aC. Reuther, R. Tucker, L. Ionov, S. Diez, Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4050;
- 4bO. Idan, A. Lam, J. Kamcev, J. Gonzales, A. Agarwal, H. Hess, Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 240;
- 4cL. Ionov, V. Bocharova, S. Diez, Soft Matter 2009, 5, 67.
- 5
- 5aB. Nitzsche, F. Ruhnow, S. Diez, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 552;
- 5bC. Schmidt, V. Vogel, Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2195.
- 6
- 6aT. Korten, W. Birnbaum, D. Kuckling, S. Diez, Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 348;
- 6bH. Hess, J. Clemmens, D. Qin, J. Howard, V. Vogel, Nano Lett. 2001, 1, 235.
- 7
- 7aL. Ionov, M. Stamm, S. Diez, Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1982;
- 7bM. G. L. van den Heuvel, C. T. Butcher, S. G. Lemay, S. Diez, C. Dekker, Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 235.
- 8M. G. L. van den Heuvel, M. P. de Graaff, C. Dekker, Science 2006, 312, 910.
- 9G. D. Bachand, S. B. Rivera, A. Carroll-Portillo, H. Hess, M. Bachand, Small 2006, 2, 381.
- 10
- 10aT. Sunagawa, A. Tanahashi, M. E. Downs, H. Hess, T. Nitta, Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2827;
- 10bT. Nitta, A. Tanahashi, Y. Obara, M. Hirano, M. Razumova, M. Regnier, H. Hess, Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2305.
- 11
- 11aH. Hess, C. M. Matzke, R. K. Doot, J. Clemmens, G. D. Bachand, B. C. Bunker, V. Vogel, Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1651;
- 11bJ. Clemmens, H. Hess, R. Lipscomb, Y. Hanein, K. F. Böhringer, C. M. Matzke, G. D. Bachand, B. C. Bunker, V. Vogel, Langmuir 2003, 19, 10967;
- 11cJ. Clemmens, H. Hess, J. Howard, V. Vogel, Langmuir 2003, 19, 1738;
- 11dV. Schroeder, T. Korten, H. Linke, S. Diez, I. Maximov, Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3434;
- 11eC. Reuther, L. Hajdo, R. Tucker, A. A. Kasprzak, S. Diez, Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2177;
- 11fM. G. L. van den Heuvel, C. T. Butcher, R. M. M. Smeets, S. Diez, C. Dekker, Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1117.
- 12M. Lard, L. ten Siethoff, J. Generosi, A. Månsson, H. Linke, Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3041.
- 13S. Zakharchenko, N. Puretskiy, G. Stoychev, M. Stamm, L. Ionov, Soft Matter 2010, 6, 2633.
- 14G. Stoychev, S. Zakharchenko, S. Turcaud, J. W. C. Dunlop, L. Ionov, ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3925.
- 15
- 15aJ. Howard, Nature 1997, 389, 561;
- 15bJ. Howard, Mechanics of Motor Proteins and the Cytoskeleton, Sinauer Press, Sunderland, Massachusetts, 2001.
- 16R. D. Vale, Cell 2003, 112, 467.
- 17J. Li, Y. Jia, W. Dong, X. Feng, J. Fei, J. Li, Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6160.
- 18C. Gell, C. T. Friel, B. Borgonovo, D. N. Drechsel, A. A. Hyman, J. Howard in Microtubule Dynamics: Methods and Protocols (Ed.: ), Humana Press, Totowa, 2011, pp. 15–28.
10.1007/978-1-61779-252-6_2 Google Scholar
- 19T. Korten, S. Chaudhuri, E. Tavkin, M. Braun, S. Diez, IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2016, 15, 62.
- 20A. Papra, N. Gadegaard, N. B. Larsen, Langmuir 2001, 17, 1457.
- 21B. Nitzsche, V. Bormuth, C. Bräuer, J. Howard, L. Ionov, J. Kerssemakers, T. Korten, C. Leduc, F. Ruhnow, S. Diez in Methods in Cell Biology, Vol. 95 (Eds.: ), Academic Press, New York, 2010, pp. 247–271.