Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Evaporite Borate-Containing Mineral Ensembles Make Phosphate Available and Regiospecifically Phosphorylate Ribonucleosides: Borate as a Multifaceted Problem Solver in Prebiotic Chemistry (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2016)
- Page: 15683
- First Published: 12 December 2016

Lightning and UV light convert N2, CO2, and H2O into formamide, urea, formaldehyde, and HCN. In their Communication on page 15816 ff., S. A. Benner et al. show that when these products percolate through igneous peridotite (green) and tourmaline (black with pink boron spheres), borate-stabilized ribose and borophosphate minerals (white with pink and yellow spheres) emerge as borate sequesters phosphate. After nucleoside synthesis, the borophosphates regioselectively phosphorylate the nucleosides, all in a desert environment.
Inside Cover: Chlorophyll-Derived Yellow Phyllobilins of Higher Plants as Medium-Responsive Chiral Photoswitches (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2016)
- Page: 15684
- First Published: 01 December 2016

The beautiful colors of fall leaves appear when chlorophyll is degraded, producing mostly colorless phyllobilins. In their Communication on page 15760 ff., B. Kräutler et al. report that yellow phyllobilins, which naturally occur in fall leaves, have “right-handed” structures, and are extraordinary four-stage photoswitches. Their unique photochemical properties suggest that phyllobilins play roles in leaves that are currently still unknown, possibly in the context of photoregulation.
Inside Back Cover: Initial Carbon–Carbon Bond Formation during the Early Stages of the Methanol-to-Olefin Process Proven by Zeolite-Trapped Acetate and Methyl Acetate (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2016)
- Page: 15929
- First Published: 01 December 2016

The reaction mechanism of the industrially important methanol-to-olefin reaction over zeolite catalysts is investigated. In their Communication on page 15840 ff., M. Baldus, B. M. Weckhuysen et al. show an effective approach, based on solid-state NMR spectroscopy and operando UV/Vis spectroscopy, to provide evidence for a direct mechanism concerning the formation of the first carbon–carbon bond during the initial stages of the reaction.
Back Cover: H2S Sensors: Fumarate-Based fcu-MOF Thin Film Grown on a Capacitive Interdigitated Electrode (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2016)
- Page: 15930
- First Published: 15 November 2016

The detection of H2S at room temperature using a fumarate-based metal–organic framework (fum-fcu-MOF) sensor is demonstrated by K. N. Salama, M. Eddaoudi, et al. in their Communication on page 15879 ff. The MOF-based sensor was prepared by an in situ growth approach with the fum-fcu-MOF thin film as the sensitive layer deposited on a capacitive interdigitated electrode. The sensor shows great sensitivity and stability towards H2S; concentrations down to 100 ppb were detected with a limit of detection around 5 ppb.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Uncovering Key Structural Features of an Enantioselective Peptide-Catalyzed Acylation Utilizing Advanced NMR Techniques
- First Published: 12 December 2016

NMR Spectroscopy In their Communication on page 15754 ff., P. R. Schreiner, C. M. Thiele et al. apply newly developed NMR experiments to confirm the mechanism of a highly enantioselective acylation reaction. Dispersion interactions between catalyst and substrate are key to the reaction.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2016
- Pages: 15687-15698
- First Published: 12 December 2016
Corrigenda
Corrigendum: A Stable Heterocyclic Amino(phosphanylidene-σ4-phosphorane) Germylene
- Page: 15698
- First Published: 12 December 2016
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2016
- Pages: 15700-15703
- First Published: 12 December 2016
Author Profiles
News
Terrae Rarae Award: P. C. Junk and P. W. Roesky / Bau Family Award: H. Xu
- Page: 15705
- First Published: 28 November 2016
Highlights
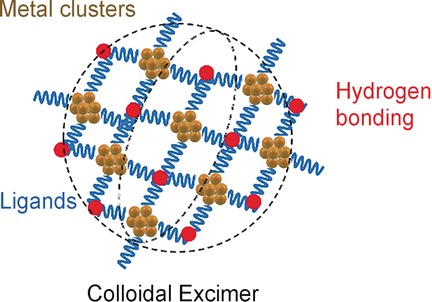
Excimers
Metal-Cluster-Based Colloidal Excimer Superstructures
- Pages: 15708-15710
- First Published: 20 October 2016
Minireviews
Polymers
Conjugated Polymers: Catalysts for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- Pages: 15712-15727
- First Published: 16 August 2016
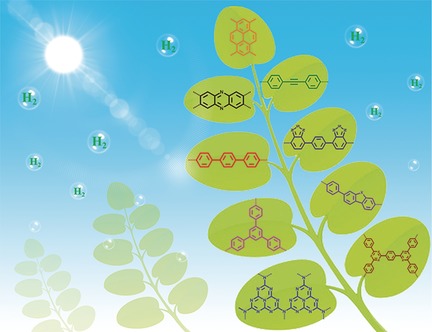
Split up: Organic conjugated photocatalysts provide an emerging platform for sustainable H2 production, through water splitting, by artificial photosynthesis. The catalysts have unique properties, including light weight, low cost, accessibility, and fine-tunability of chemical composition, electronic structure, surface properties, and texture.
Reviews
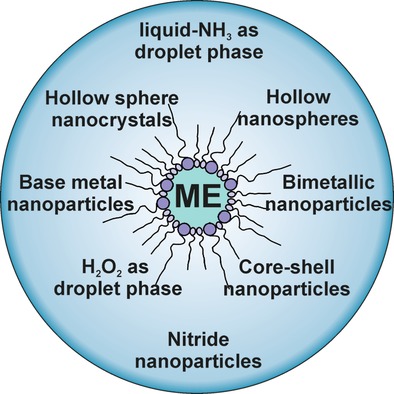
Inorganic Nanoparticles
Microemulsions: Options To Expand the Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles
- Pages: 15728-15752
- First Published: 15 November 2016
Communications
NMR Spectroscopy
Uncovering Key Structural Features of an Enantioselective Peptide-Catalyzed Acylation Utilizing Advanced NMR Techniques
- Pages: 15754-15759
- First Published: 23 November 2016
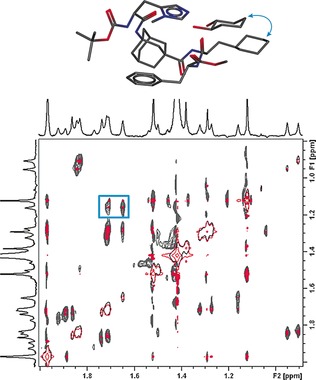
Mission possible: Advanced NMR spectroscopic data support the mechanism proposed for a highly enantioselective acylation reaction. The pocket-like structure of the catalyst is structurally affected upon the addition of the preferentially acetylated diol substrate and key dispersion interactions between catalyst and substrate were uncovered by a newly developed pure shift EASY ROESY experiment.
Phyllobilins
Chlorophyll-Derived Yellow Phyllobilins of Higher Plants as Medium-Responsive Chiral Photoswitches
- Pages: 15760-15765
- First Published: 28 November 2016
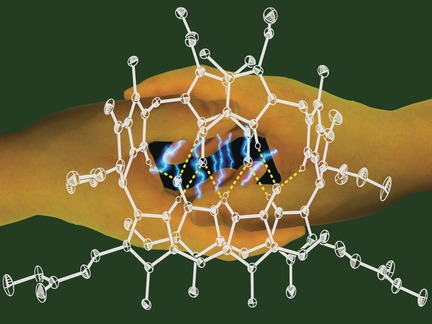
Yellow phyllobilins shake hands: Natural yellow phyllobilins occur in fall leaves and represent medium-responsive “double-duty” photoswitches. In the presence of light, they undergo E/Z isomerization in polar environments and [2+2] cycloaddition reactions in apolar and membrane-mimetic media. The fascinating chemistry of these phyllobilins suggests yet elusive roles in plants.
Noble Metalates
Discrete Silver(I)-Palladium(II)-Oxo Nanoclusters, {Ag4Pd13} and {Ag5Pd15}, and the Role of Metal–Metal Bonding Induced by Cation Confinement
- Pages: 15766-15770
- First Published: 29 November 2016
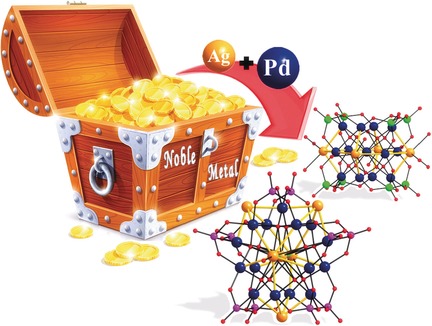
Mixed precious metal clusters: The two discrete silver(I)-palladium(II)-oxo nanoclusters, {Ag4Pd13} and {Ag5Pd15}, are the first examples of noble metal-capped polyoxo-noble-metalates, featuring an unprecedented host–guest bonding mode comprising hetero- and homometallic Ag–Pd and Ag–Ag bonding interactions. Theoretical calculations suggest that the Ag–Pd metallic bonds originate partially from surface confinement that is induced by strong electrostatic forces.
Graphene Derivatives
Highly Intact and Pure Oxo-Functionalized Graphene: Synthesis and Electron-Beam-Induced Reduction
- Pages: 15771-15774
- First Published: 16 November 2016
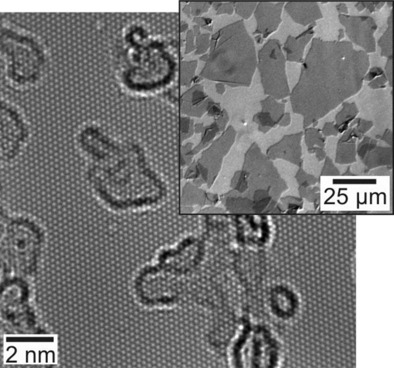
Pure and simple: Highly pure oxo-functionalized graphene is efficiently synthesized by the use of PTFE equipment. The structural integrity of the underlying carbon framework is confirmed by atomic-resolution transmission electron microscopy and the gently electron-beam induced release of surface functional groups is systematically studied as an alternative approach to chemical reduction.
Organocatalysis
Catalytic Asymmetric Reductive Condensation of N–H Imines: Synthesis of C2-Symmetric Secondary Amines
- Pages: 15775-15778
- First Published: 22 November 2016
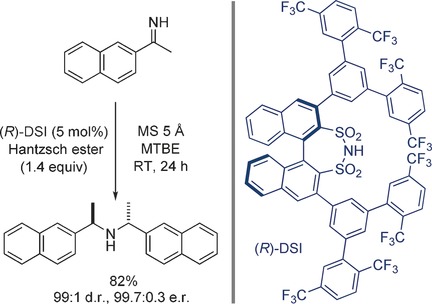
Acids for base building: A highly diastereoselective and enantioselective Brønsted acid catalyzed reductive condensation of N−H imines was developed. This dimerizing reduction is catalyzed by a chiral disulfonimide (DSI), uses Hantzsch esters as a hydrogen source, and delivers useful C2-symmetric secondary amines.
Metal Complexes | Very Important Paper
Binuclear C^C* Cyclometalated Platinum(II) NHC Complexes with Bridging Amidinate Ligands
- Pages: 15779-15782
- First Published: 18 November 2016

Two phosphorescent binuclear C^C* cyclometalated PtII complexes bridged by N,N-diphenylformamidinate ligands were synthesized and characterized by 2D NMR experiments, mass spectrometry, DFT calculations, and solid-state structure analysis. The bridging amidinate ligands bring the two platinum centers into close proximity, which leads to extraordinary photophysical properties.
Carbenes
N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalyzed γ-Dihalomethylenation of Enals by Single-Electron Transfer
- Pages: 15783-15786
- First Published: 22 November 2016
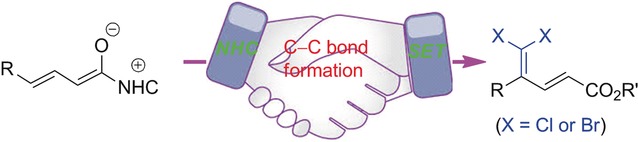
Merger-mania: The title reaction is a rare example of merging N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) catalysis with single-electron chemistry, a challenging topic with limited previous success. Carbon-centered trihalomethyl radicals have been demonstrated, for the first time, to be compatible with an NHC-bound intermediate, thus leading to efficient and regioselective intermolecular C−C bond formation.
Cross-Coupling Reactions
Aryl(triethyl)silanes for Biaryl and Teraryl Synthesis by Copper(II)-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reaction
- Pages: 15787-15791
- First Published: 16 November 2016
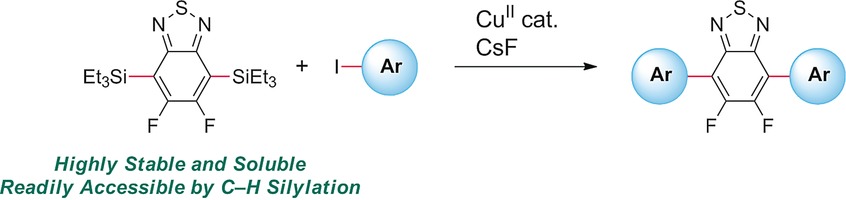
Simple aryl(triethyl)silanes are demonstrated to undergo cross-coupling with iodoarenes to form biaryls and teraryls. The reaction is characterized by a diverse substrate scope, including 4,7-bis(triethylsilyl)-5,6-difluorobenzothiadiazole and thiophene derivatives, and the use of CuBr2 as a crucial catalyst. The employed aryl(triethyl)silanes are accessible by Ir-catalyzed C−H silylation.
Terpene Synthesis
Assembly of Terpenoid Cores by a Simple, Tunable Strategy
- Pages: 15792-15796
- First Published: 17 November 2016

How to Cope with a synthesis problem: Total synthesis of oxygenated, polycyclic terpenes is widely studied, although synthetic strategies that allow for controlled placement of oxygen atoms and other functionality remains a challenge. Here presented is a simple, scalable, and tunable synthetic strategy to assemble terpenoid-like polycycloalkanes from cycloalkanones, malononitrile, and allylic electrophiles.
Cyclization
Metal-Free Enantioselective Oxidative Arylation of Alkenes: Hypervalent-Iodine-Promoted Oxidative C−C Bond Formation
- Pages: 15797-15801
- First Published: 23 November 2016
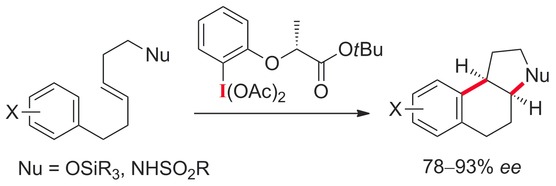
All the hype: Oxyarylation and aminoarylation were achieved in hypervalent iodine(III)-mediated oxidation of (E)-6-aryl-1-silyloxylhex-3-ene and the corresponding sulfonylamide substrate, respectively. A lactate-based chiral hypervalent iodine(III) reagent was used in the presence of boron trifluoride diethyl etherate, and the products were obtained with good to high enantiomeric excess.
Aerobic Oxidation
Simple Copper Catalysts for the Aerobic Oxidation of Amines: Selectivity Control by the Counterion
- Pages: 15802-15806
- First Published: 22 November 2016
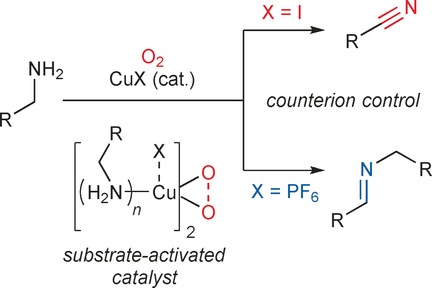
Not satisfied with an observer role, the counteranion determined the outcome of the copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of amines to nitriles or imines (see scheme). Selectivity was controlled by ion pairing to the counterion in these reactions, which proceeded at ambient temperature and pressure without expensive ligands or additives.
Synthetic Methods
PhSO2SCF2H: A Shelf-Stable, Easily Scalable Reagent for Radical Difluoromethylthiolation
- Pages: 15807-15811
- First Published: 17 November 2016
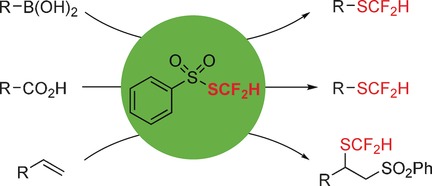
S-(difluoromethyl)benzene sulfonothioate (PhSO2SCF2H) is a powerful reagent for radical difluoromethylthiolation of aryl and alkyl boronic acids, decarboxylative difluoromethylthiolation of aliphatic acids, and a phenylsulfonyl-difluoromethylthio difunctionalization of alkenes under mild reaction conditions.
C−N Coupling
Metal-free Synthesis of Aryl Amines: Beyond Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
- Pages: 15812-15815
- First Published: 16 November 2016
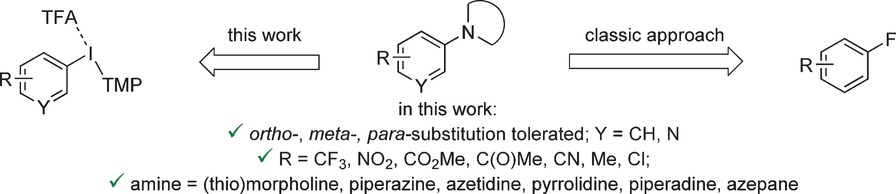
A new challenger: Aryl amines are synthesized in a metal-free reaction between unsymmetrical aryl(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)iodonium salt electrophiles and alicyclic amine nucleophiles. Yields and scope exceed those of the classical SNAr approach. The reaction conditions are mild and lead to highly regiospecific substitution of the iodonium moiety in the iodonium reagents.
Prebiotic Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Evaporite Borate-Containing Mineral Ensembles Make Phosphate Available and Regiospecifically Phosphorylate Ribonucleosides: Borate as a Multifaceted Problem Solver in Prebiotic Chemistry
- Pages: 15816-15820
- First Published: 09 November 2016
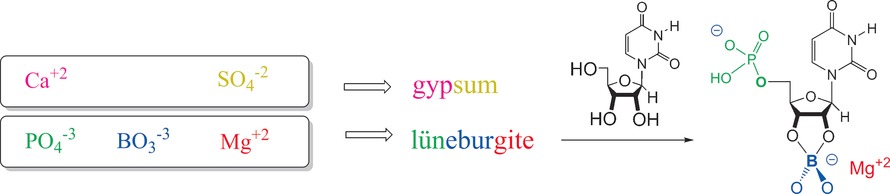
It's RNAs’ world: Geological strata show that Ca2+ does not take phosphate to form prebiotically unreactive apatite if borate, SO42−, and Mg2+ are present. Rather, phosphate is sequestered in the mineral lüneburgite. Upon evaporation, lüneburgite converts ribonucleosides regiospecifically to their phosphates. Thus, borate solves many problems in the synthesis of prebiotic RNA.
Metal–Hydride Clusters
Co6H8(PiPr3)6: A Cobalt Octahedron with Face-Capping Hydrides
- Pages: 15821-15825
- First Published: 16 November 2016
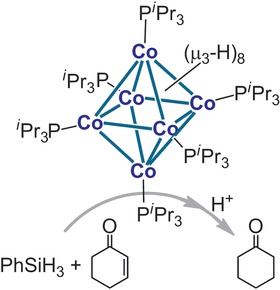
Reactive cobalt clusters: The octahedral Co6–hydride cluster Co6H8(PiPr3)6 and the square-planar Co4 cluster Co4{N(SiMe3)2}4 were synthesized from the reactions of a CoII amide complex with pinacolborane in the presence and absence of PiPr3, respectively. The Co6–hydride cluster catalyzes the conjugate hydrosilylation of 2-cyclohexen-1-one.
Zeolite Active Sites
Synergic Effect of Active Sites in Zinc-Modified ZSM-5 Zeolites as Revealed by High-Field Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 15826-15830
- First Published: 17 November 2016
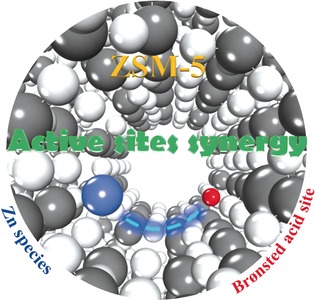
Together forever: High-field 67Zn solid-state NMR spectroscopy reveals the synergy between active sites in Zn-modified ZSM-5 zeolites. The internuclear spatial proximity/interaction between Zn2+ ions and Brønsted acid sites of the zeolites leads to a synergic effect in the C−H bond activation of methane.
Nitrogen Doping | Hot Paper
Hollow Nanotubes of N-Doped Carbon on CoS
- Pages: 15831-15834
- First Published: 16 November 2016
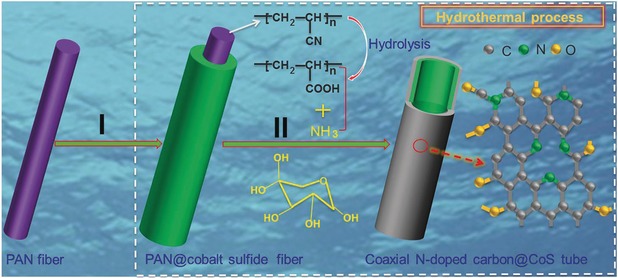
A PANacea: A low-cost, single-step synthesis has been developed to induce the hydrolysis of electrospun polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers to take advantage of their capability for bringing about in situ N-doping. The resulting N-doped carbon@CoS coaxial nanotubes show excellent lithium and sodium storage.
Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
Insight into the Interfacial Process and Mechanism in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries: An In Situ AFM Study
- Pages: 15835-15839
- First Published: 17 November 2016
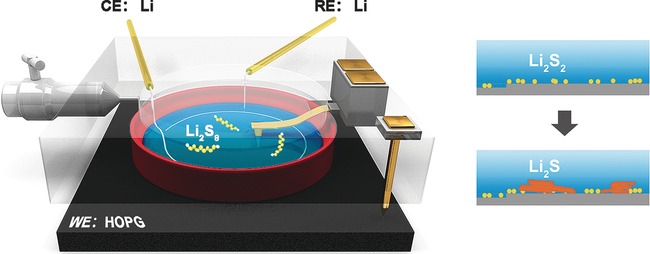
Why do batteries fail? To study the performance fading of Li–S batteries, the nanoscale processes at a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) cathode/polysulfide-electrolyte interface were directly observed by using in situ AFM and spectroscopic methods. The morphology and growth processes of insoluble products Li2S2 and Li2S were monitored and provided evidence for a mechanism for capacity fading.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Initial Carbon–Carbon Bond Formation during the Early Stages of the Methanol-to-Olefin Process Proven by Zeolite-Trapped Acetate and Methyl Acetate
- Pages: 15840-15845
- First Published: 02 November 2016
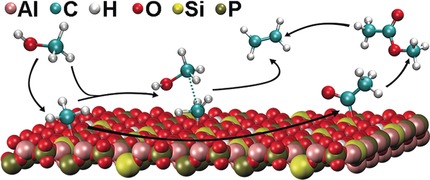
Direct formation of a C–C bond: By using a combination of UV/Vis spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and advanced NMR spectroscopy, evidence was found for the formation of methyl acetate, dimethoxymethane and surface acetate species during the methanol-to-olefin (MTO) reaction over the zeolite catalyst H-SAPO-34. New insights in the formation of the first carbon–carbon bond during the MTO process are provided.
CO Prodrugs
Click and Release: A Chemical Strategy toward Developing Gasotransmitter Prodrugs by Using an Intramolecular Diels–Alder Reaction
- Pages: 15846-15851
- First Published: 23 November 2016
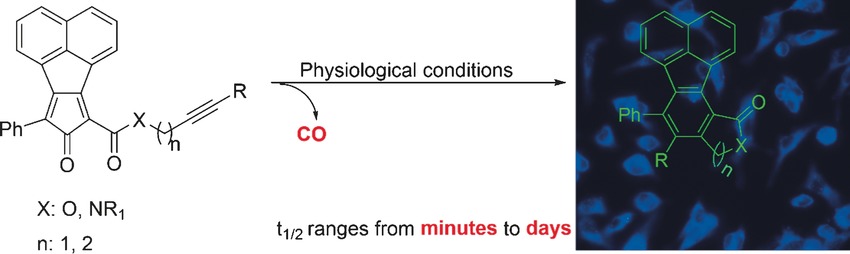
Metal-free CO prodrugs: An intramolecular inverse electron-demand Diels–Alder reaction was employed for developing organic CO prodrugs with tunable release rate and fluorescence formation upon CO release. These prodrugs showed anti-inflammatory effect in Raw 264.7 cells and an induced colitis mouse model.
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Characterization and Crystal Structure of a Robust Cyclohexanone Monooxygenase
- Pages: 15852-15855
- First Published: 22 November 2016
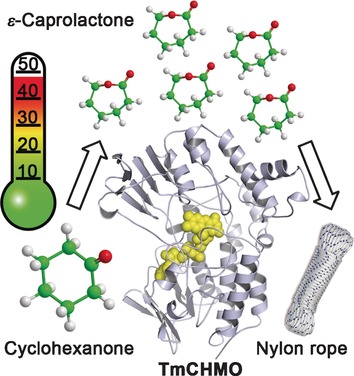
Looking like a true survivor: The discovery of a robust cyclohexanone monooxygenase (CHMO) that shows great promise as an oxidative biocatalyst is reported. This enzyme (TmCHMO) efficiently converts a variety of aliphatic, aromatic, and cyclic ketones, as well as prochiral sulfides, and was found to be much more thermostable and solvent tolerant than known CHMOs.
DNA Modification
2-Substituted dATP Derivatives as Building Blocks for Polymerase-Catalyzed Synthesis of DNA Modified in the Minor Groove
- Pages: 15856-15859
- First Published: 23 November 2016
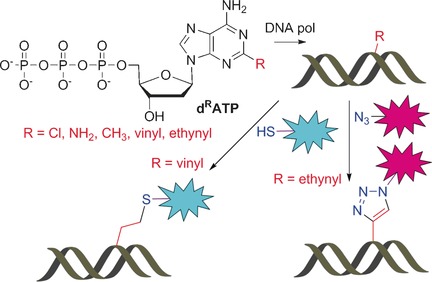
Get into the (minor) groove: Enzymatic synthesis of minor-groove-modified DNA was achieved through the polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of 2-substituted 2′-deoxyadenosine nucleotides. Postsynthetic minor-groove labelling was subsequently carried out through thiol–ene or CuAAC reaction of the vinyl-modified or ethynyl-modified DNA, respectively.
Polymerization
Thiol-Ene Step-Growth as a Versatile Route to Functional Polymers
- Pages: 15860-15863
- First Published: 22 November 2016
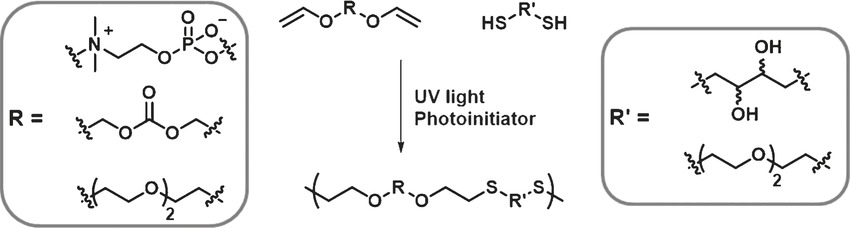
Click together: Through the click reaction of tailored dithiols and divinyl ethers, functional polymers containing both main-chain (carbonate, zwitterion) and pendant (diol) functional groups were synthesized. The thioethers in these polymers were quantitatively oxidized to yield either sulfoxides (with aqueous H2O2) or sulfones (with m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid), thus further adding to the overall polymer functionality.
Sensors
Self-Powered Multimodal Temperature and Force Sensor Based-On a Liquid Droplet
- Pages: 15864-15868
- First Published: 16 November 2016
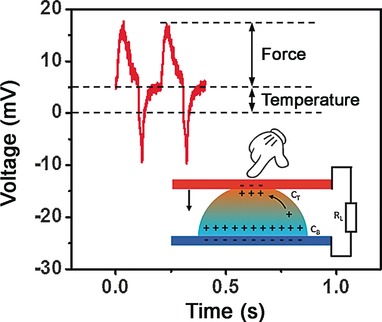
A temperature drop: A self-powered temperature and force sensor is based on the reverse electrowetting effect and the thermogalvanic effect of a liquid droplet. The drop is sandwiched between two plates. The degree of force and temperature applied to the top plate can be converted into a response. It has promising applications in a wide range of artificial intelligence systems.
Structural Biology
Capturing Excited States in the Fast-Intermediate Exchange Limit in Biological Systems Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 15869-15872
- First Published: 17 November 2016
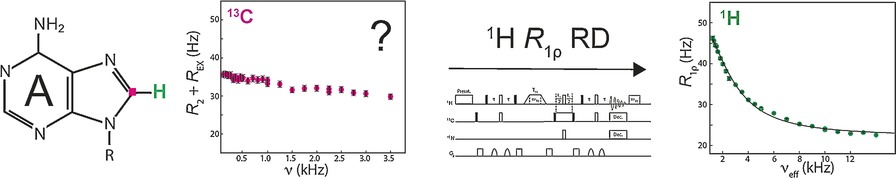
Let's move fast: A universally applicable single-proton relaxation dispersion method was developed to advance the measurement of dynamics in biological molecules. No selective labeling is required and dynamics on timescales down to 20 μs are accessible, thereby enabling the characterization of excited states in RNA, DNA, and proteins by NMR.
Supramolecular Polymers
Supramolecular Diblock Copolymers Featuring Well-defined Telechelic Building Blocks
- Pages: 15873-15878
- First Published: 17 November 2016
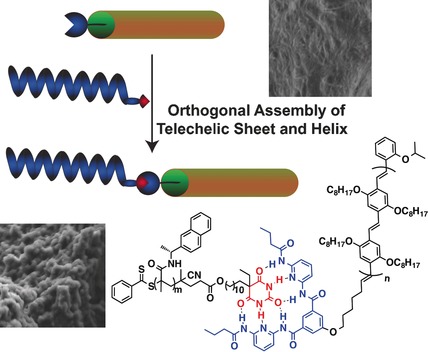
A plug-and-play approach to fabricate hybrid π-sheet/helix, π-sheet/coil, and helix/coil architectures by directional self-assembly is reported. On a basic level, these dynamic diblock architectures featuring hybrid topologies of coils, helices, and/or π-stacked sheets mimic protein structural motifs in fully synthetic systems.
MOFs as Sensors
H2S Sensors: Fumarate-Based fcu-MOF Thin Film Grown on a Capacitive Interdigitated Electrode
- Pages: 15879-15883
- First Published: 31 October 2016
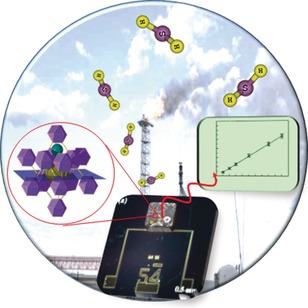
Sense and sense ability: The detection of hydrogen sulfide at room temperature using the metal–organic framework (fum-fcu-MOF) as a sensitive layer deposited on capacitive interdigitated electrodes is demonstrated. H2S concentrations down to 100 ppb were detected with a limit of detection around 5 ppb.
Nanotechnology
Protein-Sized Bright Fluorogenic Nanoparticles Based on Cross-Linked Calixarene Micelles with Cyanine Corona
- Pages: 15884-15888
- First Published: 16 November 2016
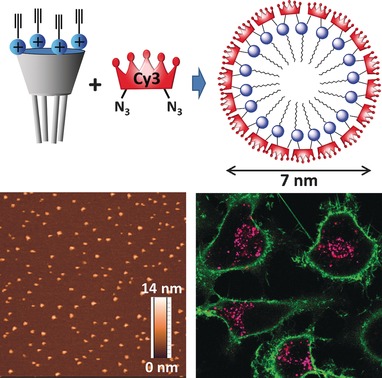
Protein-sized fluorescent nanoparticles were developed, in which PEGylated cyanine bis-azides form a covalently attached corona on micelles of amphiphilic calixarene bearing alkyne groups. The obtained 7-nm nanoparticles are circa twofold brighter than quantum dots 585. FRET studies suggest that they are highly stable in aqueous and organic media as well as in living cells, in which they show excellent imaging contrast.
Computational Chemistry
Stacking and Electrostatic Interactions Drive the Stereoselectivity of Silylium-Ion Asymmetric Counteranion-Directed Catalysis
- Pages: 15889-15893
- First Published: 17 November 2016
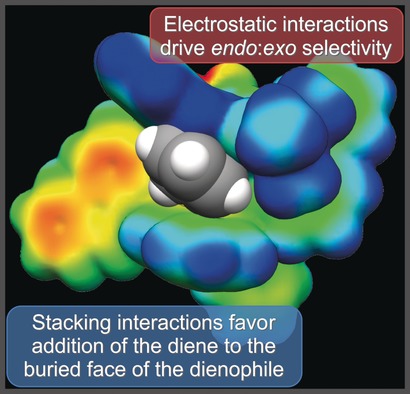
Catalysis conundrum cracked computationally: The enantioselectivity of asymmetric Lewis acid organocatalysis of the Diels–Alder cycloaddition of cyclopentadiene to cinnamates arises from stacking interactions that favor the addition of the diene to the more hindered face of the dienophile, while electrostatic interactions control the diastereoselectivity by selectively stabilizing the endo transition state.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
Magnetically Induced Continuous CO2 Hydrogenation Using Composite Iron Carbide Nanoparticles of Exceptionally High Heating Power
- Pages: 15894-15898
- First Published: 22 November 2016
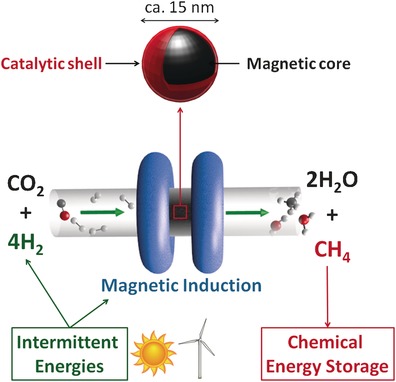
Magnetic heating: Iron carbide nanoparticles displaying unprecedented heating power were synthesized. Associated to a catalytic metal, these nanoparticles are able to efficiently achieve the magnetically induced hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to methan in a dedicated continuous-flow reactor. Magnetic induction can be successfully applied in heterogeneous catalysis, and in particular to the chemical storage of intermittent energies.
Main-Group Chemistry
A Germylene Stabilized by Homoconjugation
- Pages: 15899-15904
- First Published: 17 November 2016
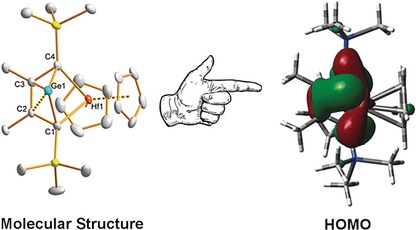
A germane approach to stabilization: A germylene stabilized by homoconjugation is described. The structural parameters and a theoretical analysis of the bonding situation revealed a homoconjugative interaction between the C=C bond and the empty Ge 4p orbital. Reactivity studies confirmed its nucleophilic character, and bimetallic hafnium/iron and hafnium/tungsten complexes were synthesized.
Structural Biology
Long Distance Measurements up to 160 Å in the GroEL Tetradecamer Using Q-Band DEER EPR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 15905-15909
- First Published: 17 November 2016
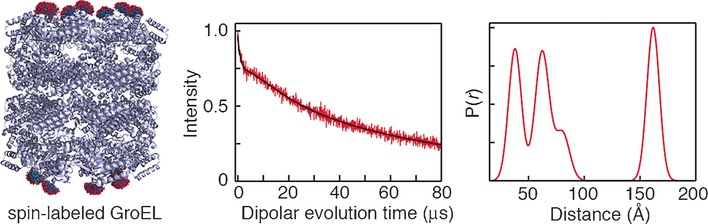
Sparse nitroxide spin-labeling of symmetric, fully deuterated multimeric proteins extends DEER distance measurements up to 170 Å. This is achieved by increasing the length and amplitude of the slow component of phase memory relaxation, thereby permitting DEER data to be collected out to longer evolution times. The approach is demonstrated on the GroEL chaperone comprising 14 identical subunits arranged in two heptameric rings.
Photochemistry
Arenophile-Mediated Dearomative Reduction
- Pages: 15910-15914
- First Published: 23 November 2016
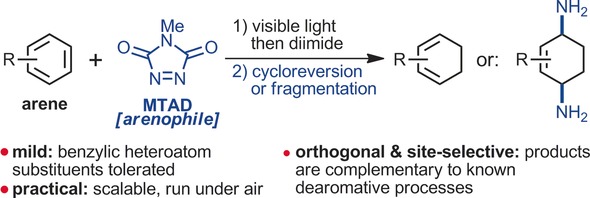
Light it up: A dearomative strategy based on the visible-light-promoted para-cycloaddition of arenophile with arenes and in situ diimide reduction was developed that provides access to 1,3-cyclohexadienes or unsaturated 1,4-diamines. These products are complementary to known dearomative processes and are amenable to further diversification.
Host–Guest Systems
Highly Enhanced Fluorescence of Supramolecular Polymers Based on a Cyanostilbene Derivative and Cucurbit[8]uril in Aqueous Solution
- Pages: 15915-15919
- First Published: 18 November 2016
![Highly Enhanced Fluorescence of Supramolecular Polymers Based on a Cyanostilbene Derivative and Cucurbit[8]uril in Aqueous Solution](/cms/asset/c1a541d4-0700-4fd0-863c-c6185e7e5e6d/anie201609699-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A supramolecular polymer system based on a cucurbit[8]uril (CB[8]) host and cyanostilbene guest was designed and showed photoluminescence quantum yield of 91% upon complexation in water, without the use of organic solvents or harsh conditions. This robust response opens up new applications in fluorescence bioimaging and sensors.
Asymmetric Synthesis
Short Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Tatanan A and 3-epi-Tatanan A Using Assembly-Line Synthesis
- Pages: 15920-15924
- First Published: 16 November 2016
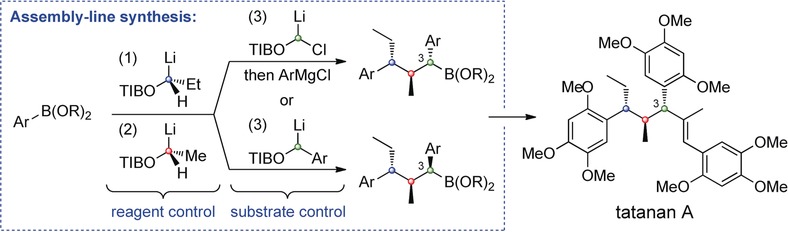
An assembly-line synthesis involving iterative lithiation-borylations enabled a short, highly enantio- and diastereoselective synthesis of tatanan A, and its C3 epimer. High substrate-controlled diastereoselectivity with a lithiated primary benzyl benzoate furnished the C3 epimer. A complete switch in selectivity was achieved using a novel substrate-controlled diastereoselective Matteson homologation to provide access to the natural product in only eight steps.
Sodium-Ion Batteries | Hot Paper
Double-Helix Structure in Carrageenan–Metal Hydrogels: A General Approach to Porous Metal Sulfides/Carbon Aerogels with Excellent Sodium-Ion Storage
- Pages: 15925-15928
- First Published: 23 November 2016
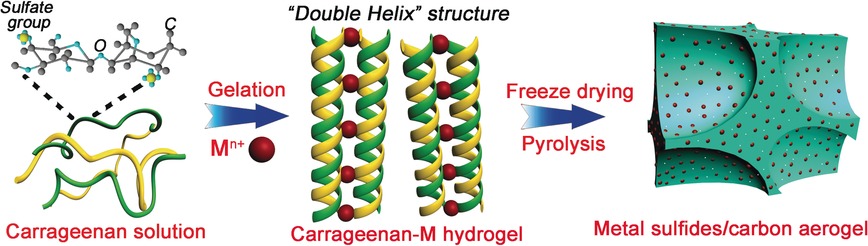
Gels and batteries: The “double-helix” structure in carrageenan–metal hydrogel was used as a new precursor for making the multiple metal sulfides/carbon aerogels with ultra-small nanoparticles and hierarchical porous structure. These aerogels exhibit high reversible capacity, excellent rate ability, and cycling stability for sodium-ion batteries.