Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Covers
Cover Picture: Hygroscopic Solutes Enable Non-van der Waals Electrolytes for Fire-Tolerant Dual-Air Batteries (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2024)
- First Published: 04 March 2024

Solute-in-air electrolytes are applied in metal-air batteries, introducing dual-air batteries for intrinsic safe energy storage. In their Research Article (e202318369), Xiaodong Chen and co-workers demonstrate that fire-tolerant batteries are achieved, and reveal that the highest tolerance temperature of electrolytes is determined by solute intramolecular bonds instead of solvent intermolecular interactions, inspiring a concept of non-van der Waals electrolytes for their thermal stability.
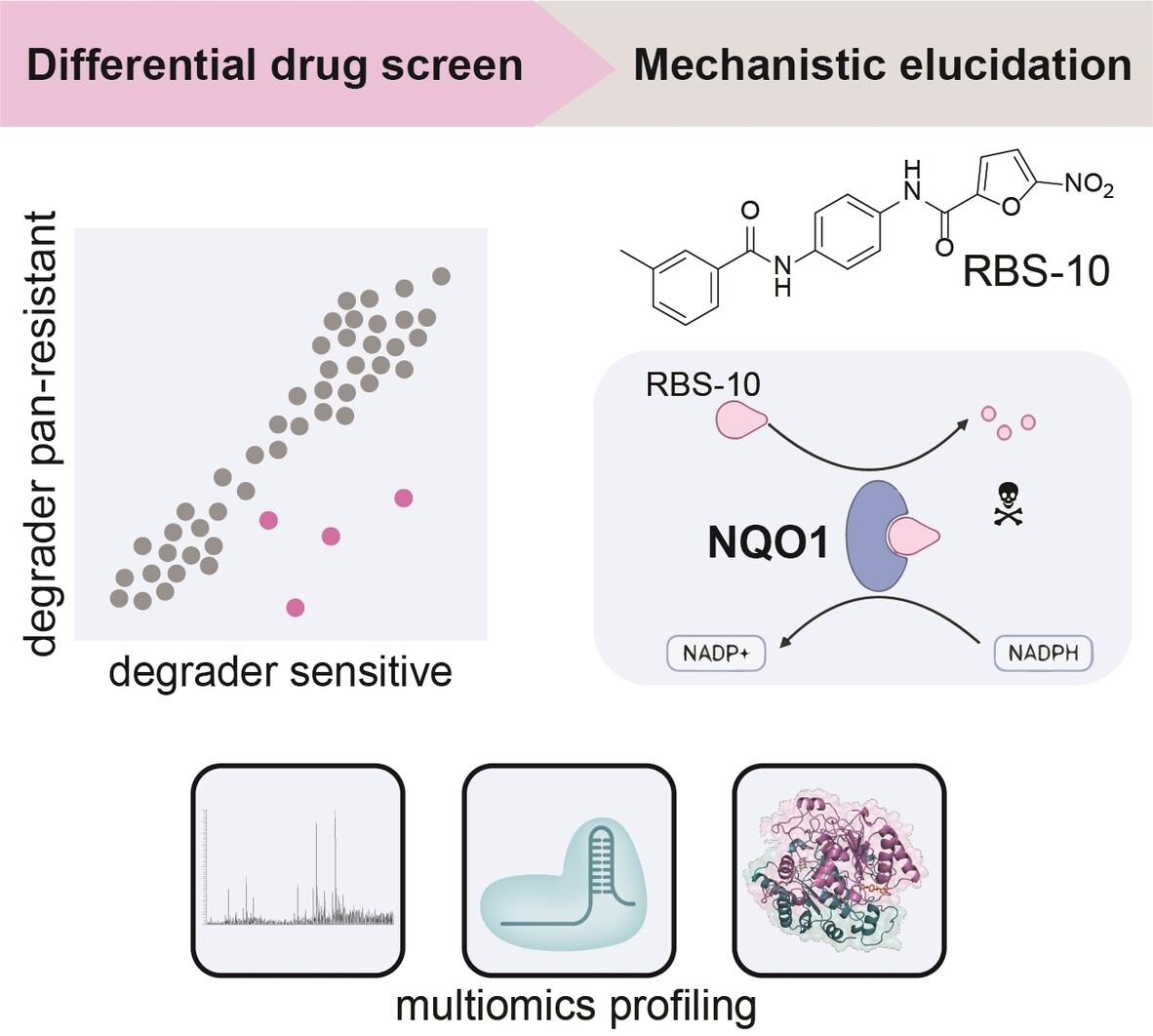
Inside Cover: Discovery and Mechanistic Elucidation of NQO1-Bioactivatable Small Molecules That Overcome Resistance to Degraders (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2024)
- First Published: 04 March 2024

Multiomics-driven elucidation of RBS-10 as a prodrug bioactivated by the enzyme NQO1 is reported by Antoni Riera, Cristina Mayor-Ruiz et al. in their Research Article (e202316730). RBS-10 shows preferential cytotoxicity against cancer cells pan-resistant to degraders.
Inside Back Cover: Photoswitchable PROTACs for Reversible and Spatiotemporal Regulation of NAMPT and NAD+ (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2024)
- First Published: 06 March 2024

Reversible and spatiotemporal regulation of protein degradation is important for chemical biology and drug discovery. In their Research Article (e202315997), Guoqiang Dong, Chunquan Sheng et al. developed activator-based photoswitchable proteolysis-targeting chimera (PS-PROTAC) for the optical control of NAMPT and NAD+ both in vitro and in vivo.
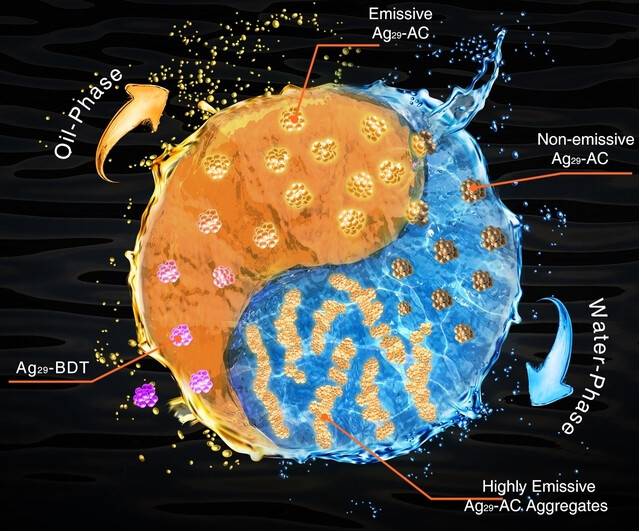
Back Cover: Photoluminescence Quenching of Hydrophobic Ag29 Nanoclusters Caused by Molecular Decoupling during Aqueous Phase Transfer and EmissionRecovery through Supramolecular Recoupling (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2024)
- First Published: 04 March 2024

In the sunlight (oil phase), the Morning Stars (the Ag29 nanoclusters) shine brightly, but when night falls (aqueous phase transfer), the stars may lose their luster (photoluminescence quenching). Yet, there are always some special stars. When they come together (supramolecular recoupling), they become the shining Big Dipper (emission recovery) for guiding the direction (downstream hydrophilic applications). Details of the research are reported by Xi Kang, Wenxiong Shi, Manzhou Zhu et al. (e202317995).
Frontispiece
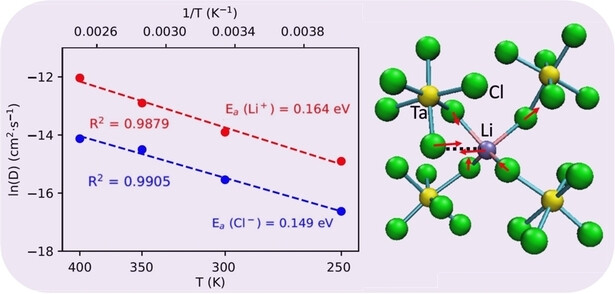
Frontispiece: Dynamic Monkey Bar Mechanism of Superionic Li-ion Transport in LiTaCl6
- First Published: 11 March 2024
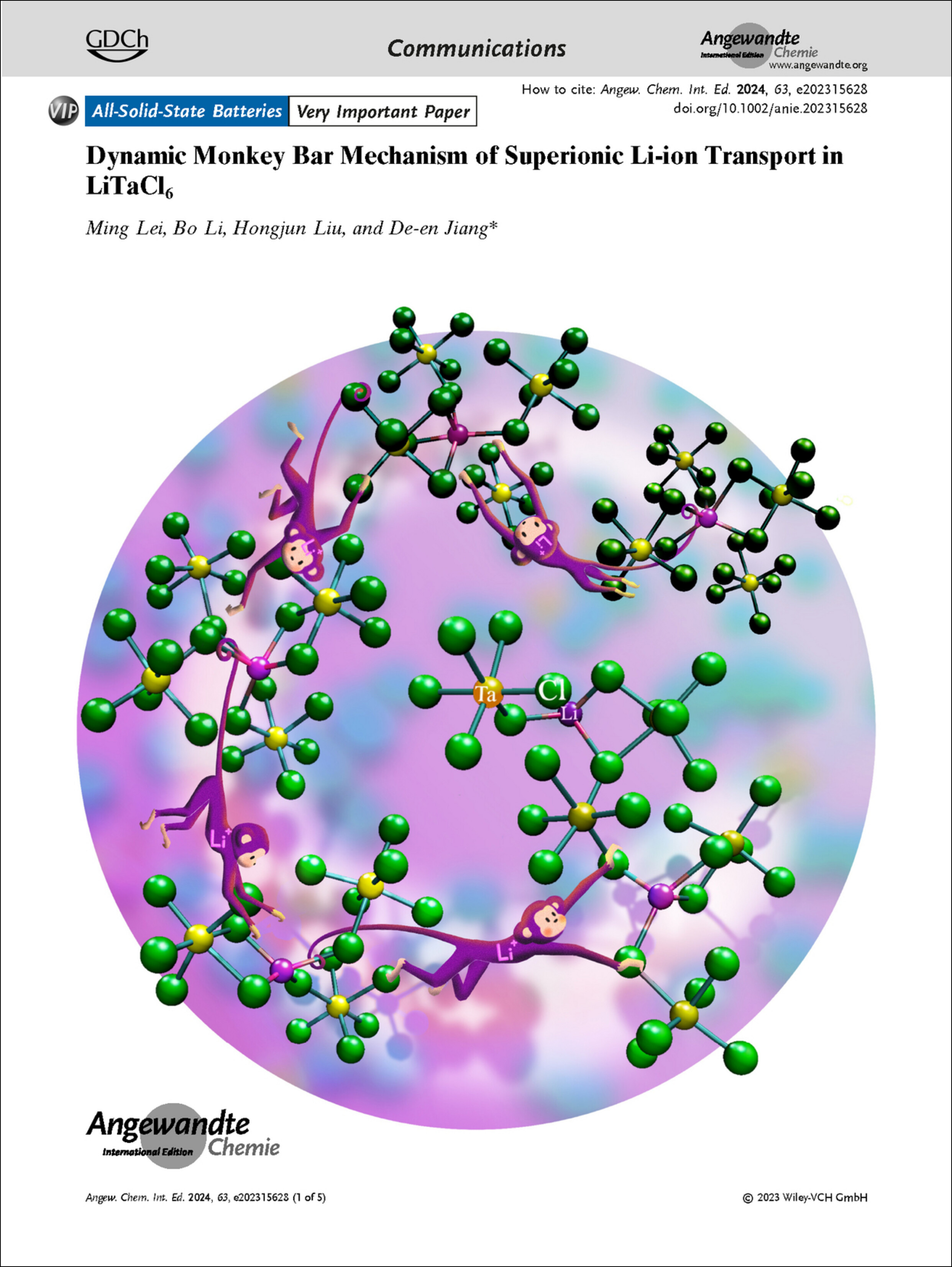
Lithium-Ion Batteries. In their Communication (e202315628), De-en Jiang et al. reveal through machine-learning force field molecular dynamics simulations the superionic Li+ transport in glassy LiTaCl6 via a dynamic “monkey bar” mechanism.
Graphical Abstract
Announcement
Classifieds: Jobs and Awards, Products and Services
- First Published: 11 March 2024
Are you looking for a (new) job? Do you know someone who deserves an award? Are you trying to find a product or service to make your work more efficient? Our partners can help.
Introducing …
Cristina Mayor-Ruiz
- First Published: 19 February 2024

“I advise my students to embrace the interdisciplinary nature of chemical biology and seek inspiration from different angles… My favorite example of chemistry/science in everyday life is the complex process of signal transduction within cells.” Find out more about Cristina Mayor-Ruiz in her Introducing … Profile.
Obituary
Günter Wulff (1935 –2023): Father of Molecular Imprinting
- First Published: 19 February 2024

Günter Wulff, internationally well known for his invention of Molecular Imprinting, passed away on December 11, 2023 in Erkrath-Hochdahl, Germany, not far from the University of Düsseldorf, where he made his greatest discoveries. A passionate researcher and deep conceptual thinker, he greatly advanced our understanding of polymer chemistry.
Minireviews
Metal-Organic Frameworks
Bridging Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis: Phosphine-Functionalized Metal-Organic Frameworks
- First Published: 22 December 2023
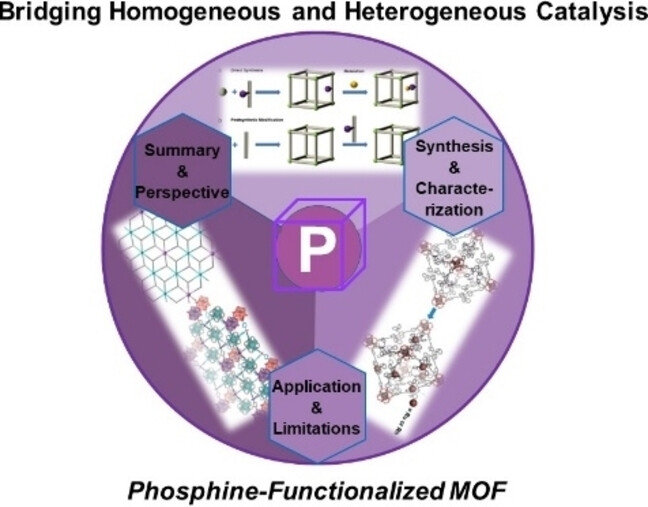
Phosphine-functionalized MOFs (P-MOFs) offer novel opportunities in heterogeneous catalysis. In this Minireview, we summarize the synthetic strategies, characterization and catalytic reactions based on the reported P-MOFs. In particular, we remark the current obstacles and possible solutions, including new reaction types and techniques as the perspectives for the development of P-MOF catalysts, highlighting the opportunities behind challenges.
Polymer Chemistry
Degradable Block Copolymer Nanoparticles Synthesized by Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly
- First Published: 28 December 2023
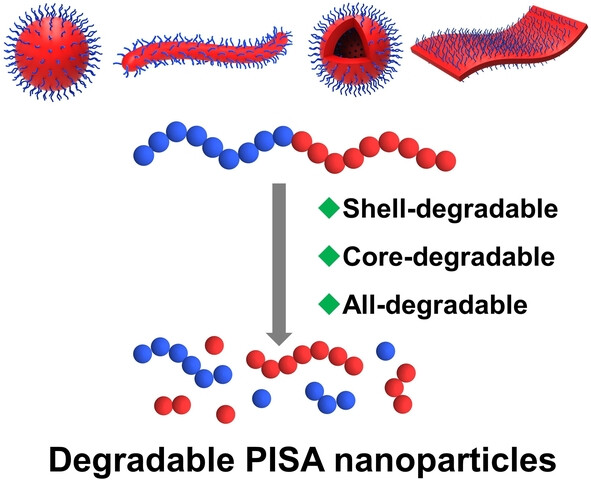
This Minireview summarizes developments in degradable block copolymer nanoparticles, including shell-degradable, core-degradable and all-degradable nanoparticles, synthesized by polymerization-induced self-assembly (PISA). The high production efficiency of PISA coupled with degradability provides the next generation of particulate materials that can better serve the need for sustainability.
Electrocatalysis
Designing and Engineering Atomically Dispersed Metal Catalysts for CO2 to CO Conversion: From Single to Dual Metal Sites
- First Published: 27 December 2023
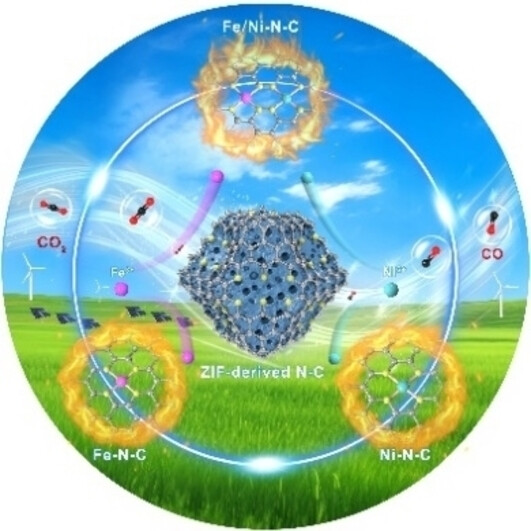
Progress, challenges, and opportunities for designing and engineering atomic metal catalysts are discussed from single to dual metal sites for CO2 to CO conversion. In particular, designing optimal dual metal site catalysts could offer additional sites to break the scaling relationship limitation and activity-stability trade-off. Challenges and solutions of CO2RR electrolysis in flow reactors are highlighted for improved CO2 utilization, reaction kinetics, and mass transport.
Reviews
London Dispersion
Advances and Prospects in Understanding London Dispersion Interactions in Molecular Chemistry
- First Published: 05 December 2023
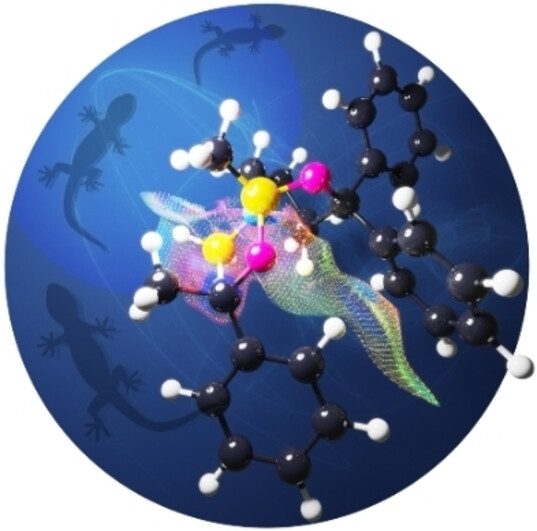
It has by now been realized that London dispersion (LD) interactions, the main contributor to the attractive part of the van der Waals potential, are ubiquitously present and need to be taken into consideration in structures and dynamics of chemical reactions. This review highlights recent experimental and theoretical advances in utilizing LD interactions as a design element.
Bioconjugations
Empowering Site-Specific Bioconjugations In Vitro and In Vivo: Advances in Sortase Engineering and Sortase-Mediated Ligation
- First Published: 11 December 2023

Sortase-mediated ligation (SML) is extensively employed in site-specific bioconjugations. This review presents an overview of recent advancements in sortase engineering and the resulting innovative in vitro and in vivo SML applications. Moreover, we explore the potential future impact of integrating SML with cutting-edge techniques, such as click chemistry, unnatural amino acid incorporation, and CRISPR-Cas9, for interdisciplinary research.
Research Articles
Biosensors
Nucleic Acid-based Electrochemical Sensors Facilitate the Study of DNA Binding by Platinum (II)-based Antineoplastics
- First Published: 16 January 2024
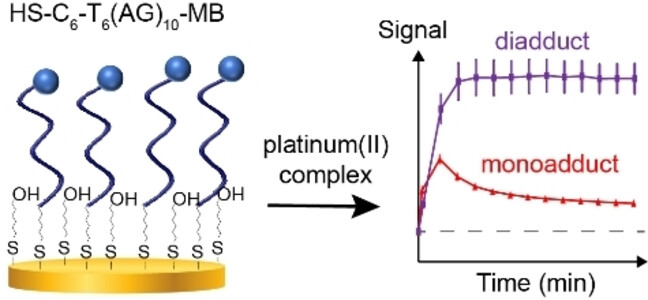
Nucleic acid-based sensors unveil the DNA binding mechanisms of platinum(II) complexes. Based on signals generated at dual frequencies of square wave voltammetry upon introduction of platinum(II) antineoplastics, the sensors can resolve formation of monovalent adducts and bivalent adducts on the purine-rich DNA sequences.
Synthetic Methods
Dual Nickel/Photoredox-Catalyzed Asymmetric Carbamoylation of Benzylic C(sp3)−H Bonds
- First Published: 12 January 2024
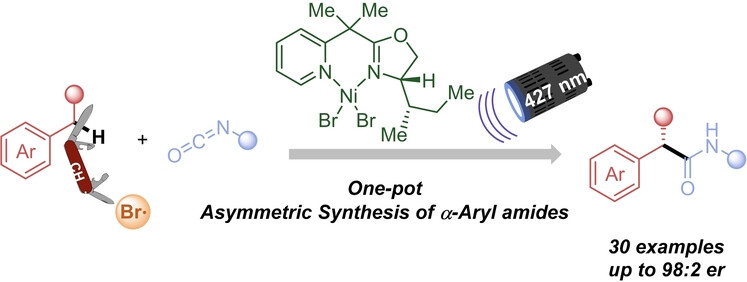
An asymmetric nickel/metallaphotoredox catalyzed C(sp3)−H benzylic carbamoylation employing alkylarenes and isocyanates is described. A broad array of 2-arylamides can be prepared in one pot under mild reaction conditions. Mechanistic studies, including control experiments and DFT calculations, shed light on the rate and stereodetermining step of this transformation.
DNA Nanotechnology
Design and Thermodynamics Principles to Program the Cooperativity of Molecular Assemblies
- First Published: 17 November 2023
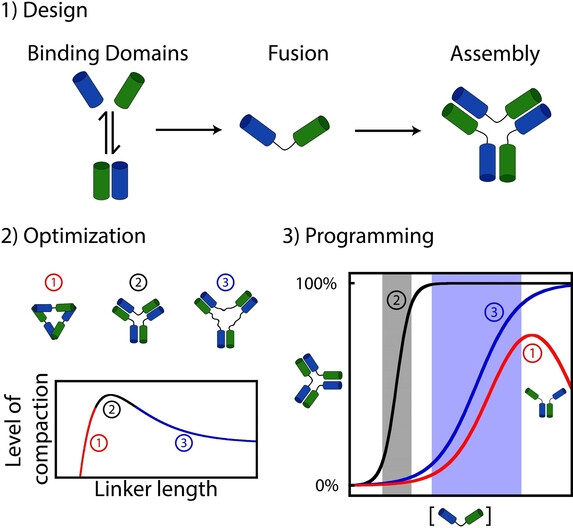
Molecular assembly can be designed by fusing binding domains. A precise optimization of the level of compaction of the assembly using linker of different lengths or compositions can provide a simple strategy to program their assembly properties (e.g., midpoint, dynamic range, and inhibition). The thermodynamic and mechanistic principles demonstrated herein also shine light behind the evolution of biological molecular assembly.
Cancer Immunotherapy | Hot Paper
Metal-Phenolic Nanocloaks on Cancer Cells Potentiate STING Pathway Activation for Synergistic Cancer Immunotherapy
- First Published: 01 February 2024
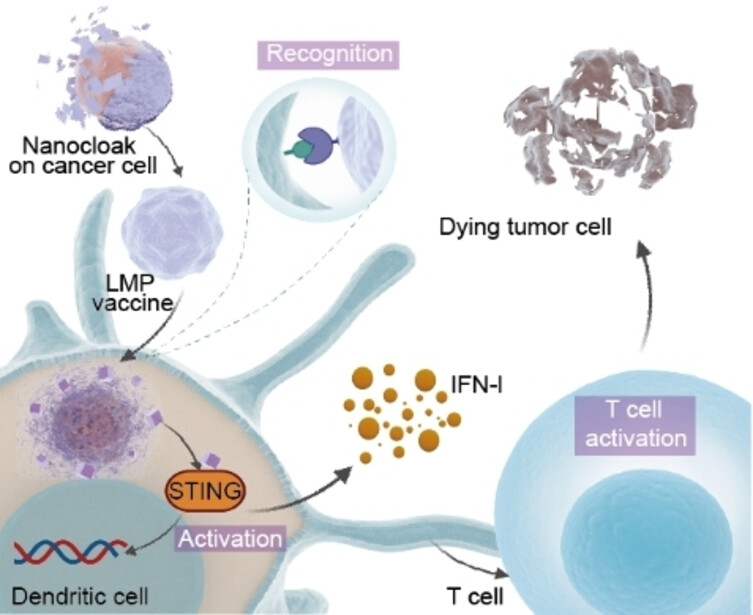
A biohybrid system (LMP vaccine) that is based on living cancer cells and a manganese-phenolic nanocloak is developed for synergistic immunotherapy. The nanocloak affords an immunoactive exoskeleton by integrating the toll-like receptor ligand to enhance dendritic cell engulfment and Mn2+ ions to sensitize the stimulator of the interferon genes (STING) pathway, leading to superior therapeutic efficacy against melanoma.
Polymer Chemistry
Water-Degradable Oxygen-Rich Polymers with AB/ABB Units from Fast and Selective Copolymerization
- First Published: 27 January 2024
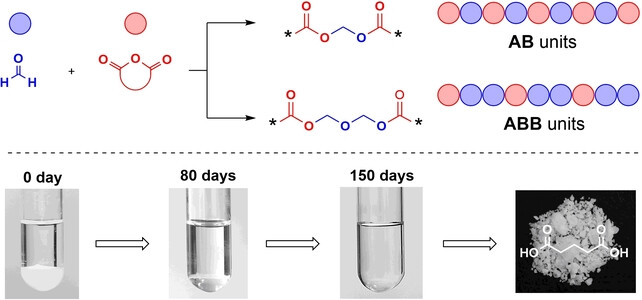
We for the first time report the copolymerization of formaldehyde and cyclic anhydride, which is fast and chemo-selective under mild conditions using common acids as catalysts. The versatile method yields a series of sustainable polymers with tunable AB/ABB units, which can be completely degraded into valuable diacids in water or seawater at ambient temperature.
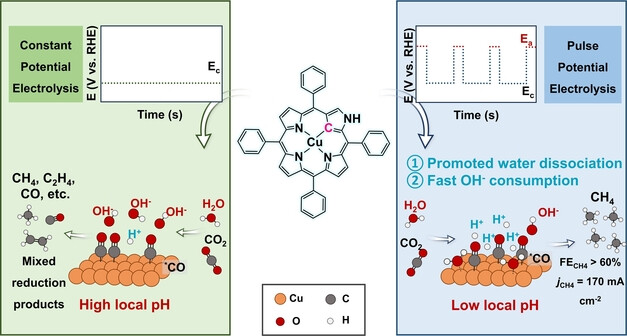
Electrocatalysis
Pulse Electrolysis Turns on CO2 Methanation through N-Confused Cupric Porphyrin
- First Published: 29 January 2024
Polymer Prodrug
Coarse-Grained Model-Assisted Design of Polymer Prodrug Nanoparticles with Enhanced Cytotoxicity: A Combined Theoretical and Experimental Study
- First Published: 12 February 2024
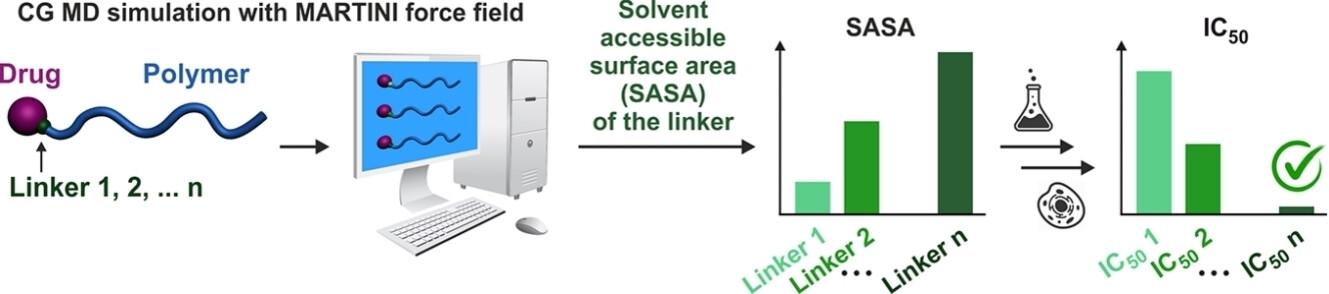
By choosing the solvent accessible surface area as the critical parameter for predicting relative drug release and hence cytotoxicity of polymer prodrug nanoparticles, an optimized polymer-drug linker with enhanced hydrophilicity and solvation has been developed. This hypothesis was experimentally validated by the synthesis of the corresponding polymer prodrugs based on two different drugs, which demonstrated greater drug release and cytotoxicity on two cancer cell lines.
Li Superionic Conductors
Cubic Iodide LixYI3+x Superionic Conductors through Defect Manipulation for All-Solid-State Li Batteries
- First Published: 20 January 2024
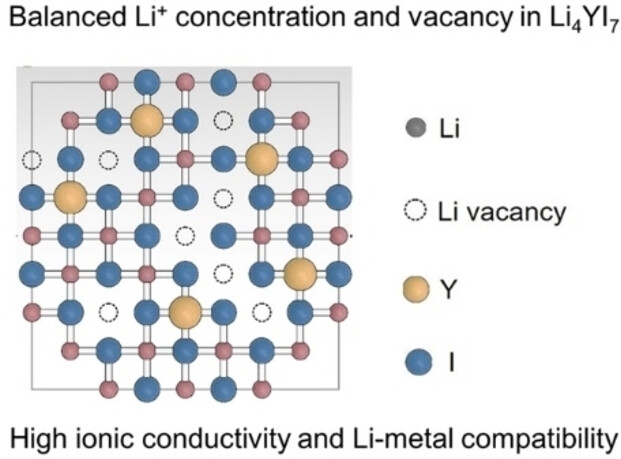
Manipulating defects within a highly symmetric iodide crystal has successfully yielded a remarkable ionic conductivity exceeding 1 mS cm−1 at room temperature in a novel Li4YI7 solid-state electrolyte. This achievement not only demonstrates its promising compatibility with lithium metal but also enables the realization of high-performance iodide-based all-solid-state lithium batteries.
Protein Degraders
Discovery and Mechanistic Elucidation of NQO1-Bioactivatable Small Molecules That Overcome Resistance to Degraders
- First Published: 28 December 2023
Chemical Biology
Global Reactivity Profiling of the Catalytic Lysine in Human Kinome for Covalent Inhibitor Development
- First Published: 22 January 2024
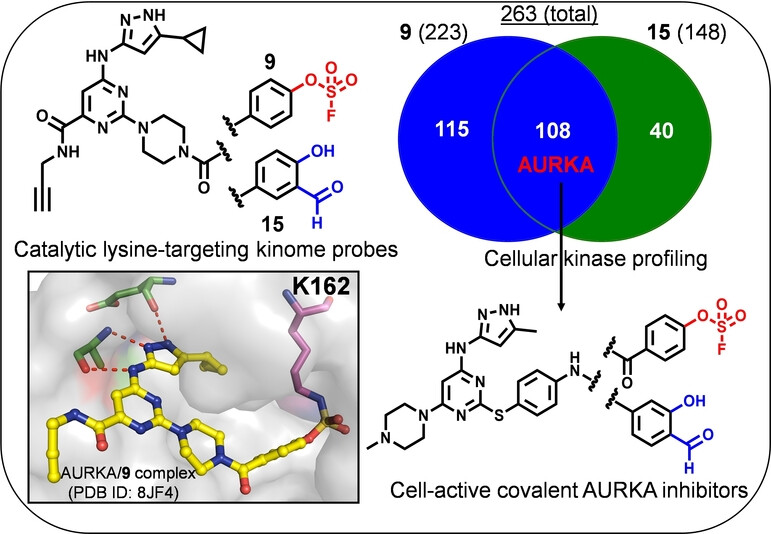
Lysine-reactive activity-based probes based on aryl fluorosulfates (ArOSO2F) are reported, enabling successful profiling of >300 endogenous kinases and providing a global landscape of ligandable catalytic lysines of the human kinome. Introduction of these aminophiles into a noncovalent Aurora A kinase inhibitor led to novel lysine-reactive inhibitors that exhibited excellent in vitro potency and cellular activities with prolonged residence time.
Al-Ion Batteries
Entropy-Regulated Cathode with Low Strain and Constraint Phase-Change Toward Ultralong-Life Aqueous Al-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 29 January 2024
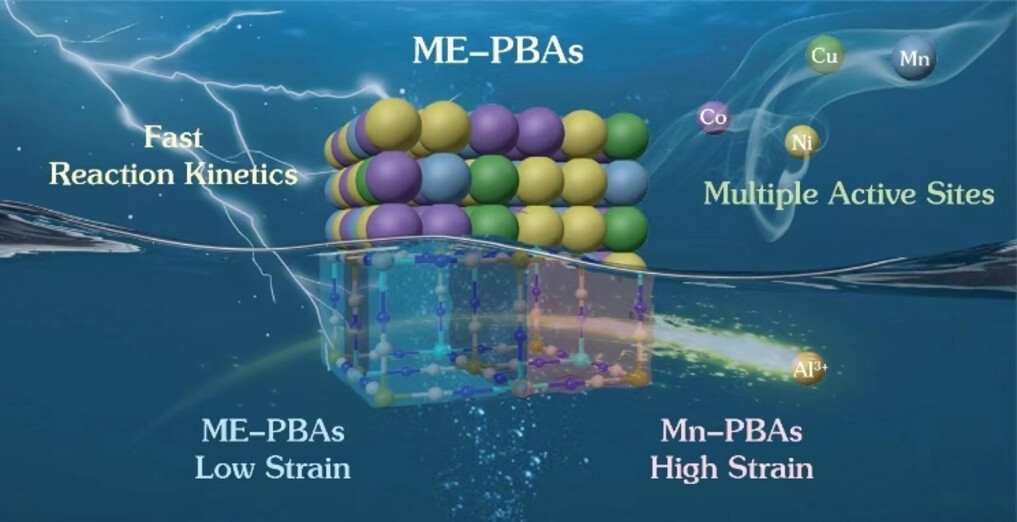
The successful implementation of an entropy-regulation approach is proposed by using PBAs as cathode for aqueous AIBs, resulting in excellent electrochemical performance. As-designed medium-entropy cathode could deliver a high capacity for reversible Al3+ storage, which is attributed to the activation of numerous redox centres and low strain, further enabling ultra-high rates of ion storage and an exceptionally long lifespan.
Al-MXene batteries
The Reverse of Electrostatic Interaction Force for Ultrahigh-Energy Al-Ion batteries
- First Published: 29 January 2024

The electrostatic repulsion effect between the surface negative charges and the active anions (AlCl4−) hinders the intercalation of AlCl4−. Here, we propose a charge regulation strategy for MXene cathodes to overcome this challenge, which is a breakthrough for achieving ultrahigh-energy-density aluminum-ion batteries and other rechargeable batteries by tuning surface charge of electrode materials.
Cancer Therapy
Biodegradable Monometallic Aluminum as a Biotuner for Tumor Pyroptosis
- First Published: 01 February 2024
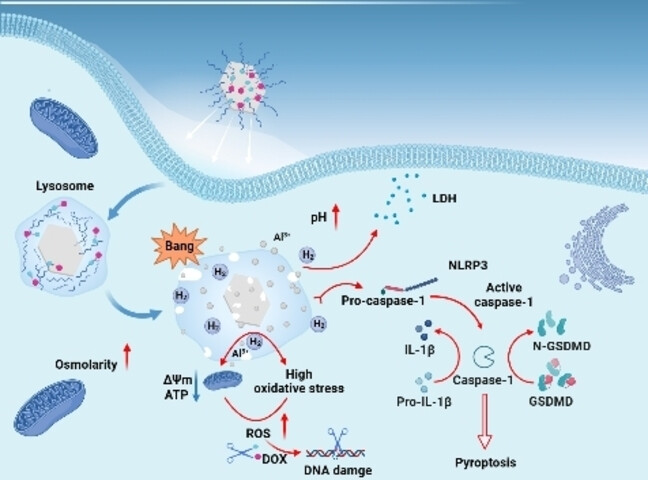
Biodegradable monometallic Al is used for the first time as a pyroptosis biotuner for tumor therapy. Al reacts with H+ to form H2 and Al3+, which not only remodels the TME but also enables its degradation. H2 and Al3+ disrupt redox balance and ionic homeostasis, inducing the generation of abundant ROS, which activates ROS-responsive prodrugs, ultimately achieving efficient tumor therapy.
Nanocage | Hot Paper
High-nuclearity Luminescent Lanthanide Nanocages for Tumor Drug Delivery
- First Published: 29 January 2024
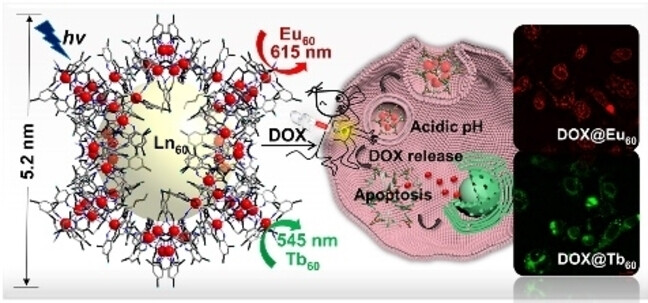
Two 60-metal lanthanide nanocages (Ln60, Ln=Eu and Tb) constructed from Schiff base ligands were used as molecular drug delivery agents (DOX@Ln60, DOX=doxorubicin). They provided for effective tumor therapy in a murine model with negligible side effects. Moreover, DOX@Ln60 proved luminescent and efficiently internalized by breast cancer cells, allowing these cells to be readily visualized.
Enzyme Mechanisms
The Structural Role of N170 in Substrate-Assisted Deacylation in KPC-2 β-Lactamase
- First Published: 16 January 2024
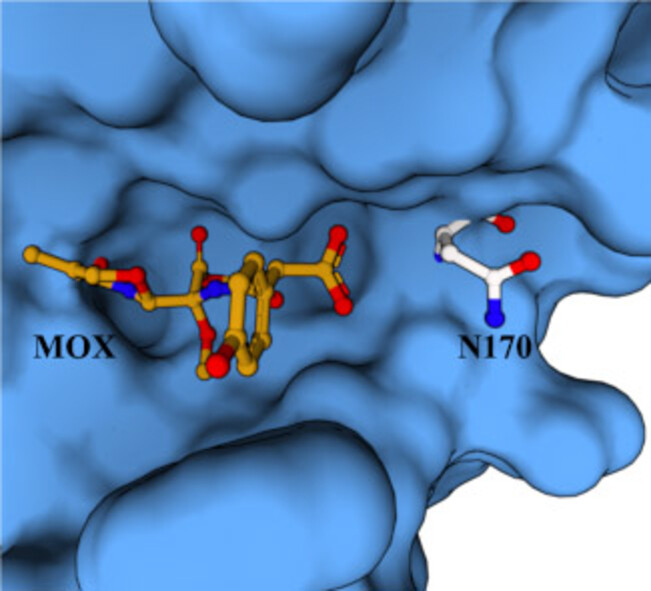
Specific substitutions in the omega loop (R164-D179) of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase 2 (KPC-2) alter its structure and function and can lead to increased resistance to antibiotics. Accelerated rare-event sampling well-tempered metadynamics simulations have now revealed that in D179 variants of KPC-2 β-lactamase, the N170 side chain can rotate away from the active site, allowing the binding of antibiotics such as moxalactam and ceftazidime.
Na-ion Batteries | Hot Paper
Stress Dissipation Driven by Multi-Interface Built-In Electric Fields and Desert-Rose-Like Structure for Ultrafast and Superior Long-Term Sodium Ion Storage
- First Published: 16 January 2024
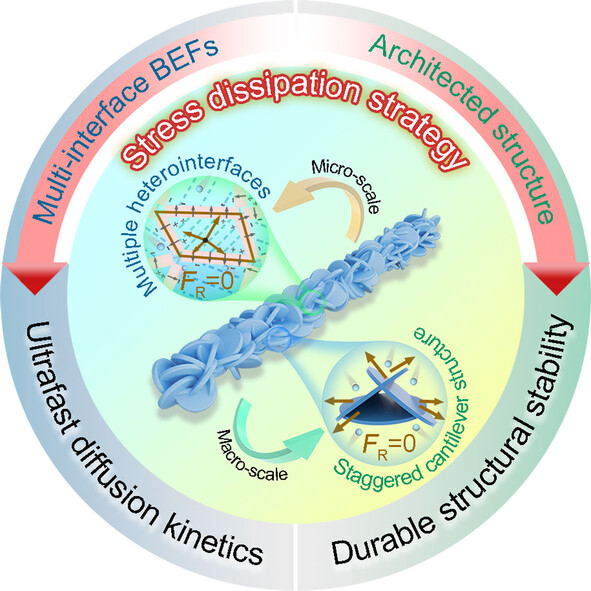
A stress dissipation strategy driven by multi-interface BEFs and architected structure, is proposed to achieve compatibility between fast kinetics and structural stability in an anode. Based on this strategy, desert-rose-like HMI-MFS NRs with multiple interfaces and a staggered cantilever configuration at micro- and macro-scales are fabricated, which display ultrafast and superior long-term sodium ion storage in half/full SIBs.
Ring Expansion Reactions | Very Important Paper
Rhodium-Catalyzed One-Carbon Ring Expansion of Aziridines with Vinyl-N-triftosylhydrazones for the Synthesis of 2-Vinyl Azetidines
- First Published: 28 January 2024
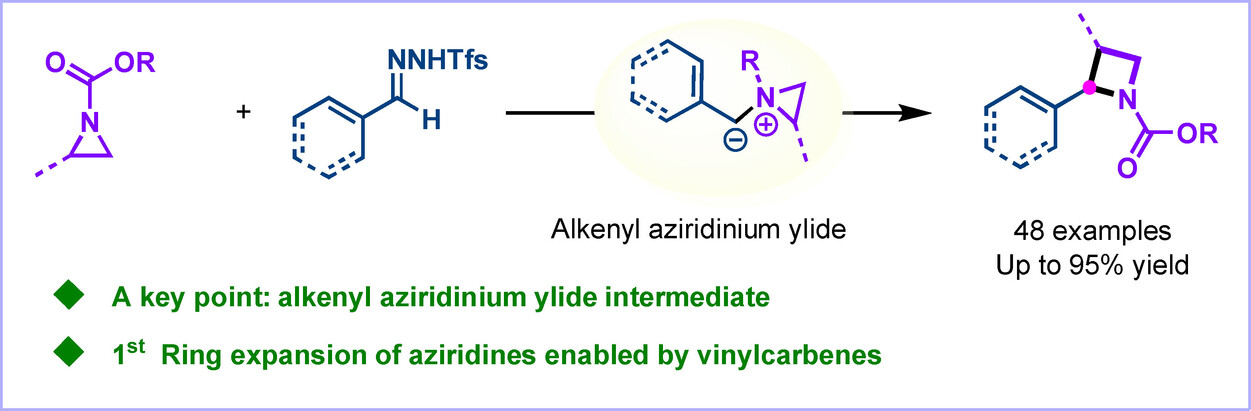
A general skeletal ring expansion strategy for the direct conversion of aziridines into 2-vinyl azetidines via one-carbon insertion using vinyl-N-triftosylhydrazones is described. The method is scalable, tolerates diverse functional groups, and is amenable to the synthesis of medicinally relevant molecules.
Macrocycles
Threading a Linear Molecule Through a Macrocycle Thanks to Boron: Optical Properties of the Threaded Species and Synthesis of a Rotaxane
- First Published: 25 January 2024
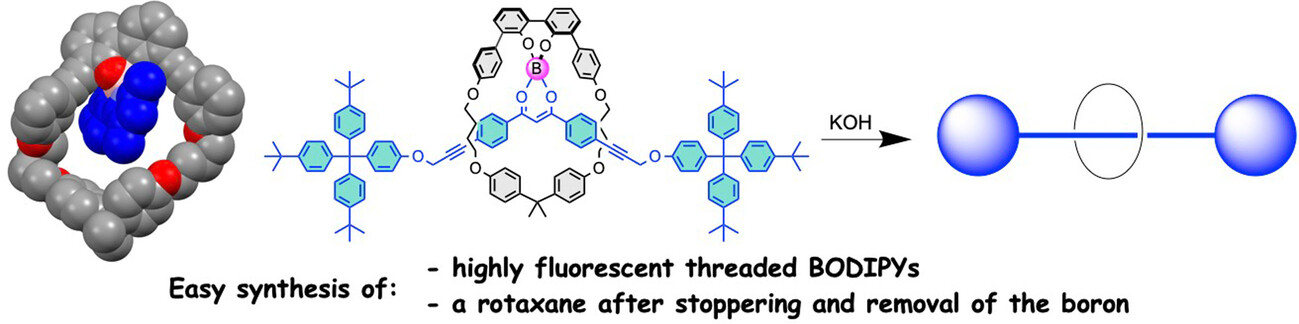
Boron-containing species were threaded through macrocycles bearing a 2,2’-biphenol unit. The new threaded species exhibited interesting fluorescence features with quantum yields up to 91 % and an enhanced photostability. Their properties were rationalized with quantum chemistry to unravel the vibronic contributions. This methodology was used to synthesize a rotaxane.
Luminescent Ag Nanoclusters
Metal-Air Batteries | Hot Paper
Hygroscopic Solutes Enable Non-van der Waals Electrolytes for Fire-Tolerant Dual-Air Batteries
- First Published: 05 January 2024
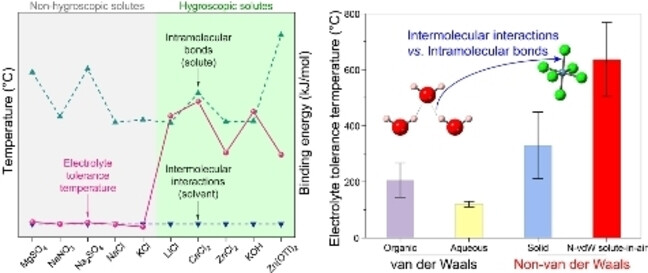
While the irreversible thermal transformation of electrolytes is typically attributed to solvent boiling, which disrupts solvent intermolecular interactions, our research revealed that hygroscopic solutes shift the determining factor to solute decomposition, breaking solute intramolecular bonds. As intramolecular bonds are much stronger, it enables ultrahigh thermal tolerance of non-van der Waals solute-in-air electrolytes.
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Solar Cells
Binary Organic Solar Cells with over 19 % Efficiency and Enhanced Morphology Stability Enabled by Asymmetric Acceptors
- First Published: 30 January 2024
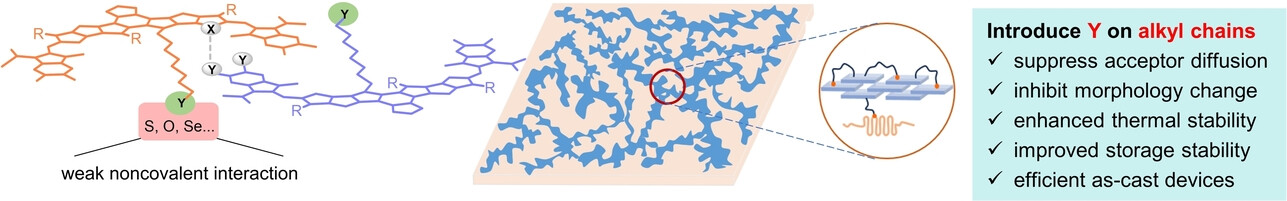
Asymmetric acceptor DT-C8Cl with functional haloalkyl chains was designed and synthesized, where noncovalent interactions induced by haloalkyl chains could effectively optimize the morphology and suppress unfavorable morphology evolutions, leading to simultaneously enhanced efficiency and morphology stability of organic solar cells.
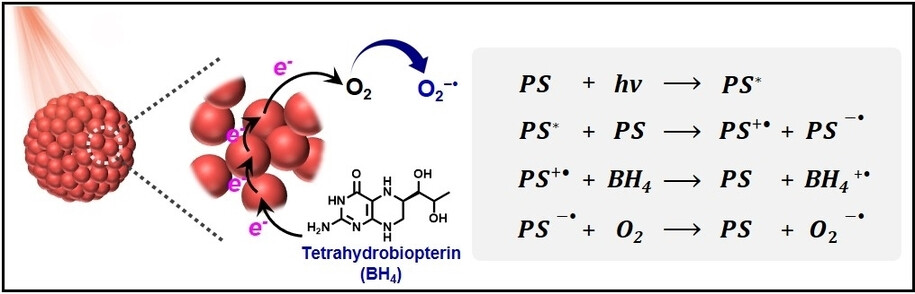
Photodynamic Therapy
Enzymes | Very Important Paper
N-Cyanopiperazines as Specific Covalent Inhibitors of the Deubiquitinating Enzyme UCHL1
- First Published: 19 January 2024
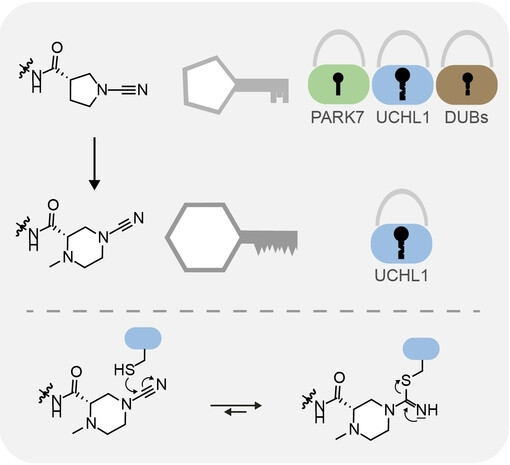
Cyanopiperazines as covalent enzyme inhibitors are disclosed. Extending on cyanopyrrolidines, reported cyanamides made of 6-membered rings display context-dependent reversibility and exquisite specificity for the deubiquitinating enzyme UCHL1 among human DUBs and the protein deglycase DJ-1/PARK7. Their mechanism of specificity is rationalized by a crystal structure, highlighting how protein reactivity of electrophilic compounds can be finetuned.
Photochemistry | Hot Paper
Green Light Promoted Iridium(III)/Copper(I)-Catalyzed Addition of Alkynes to Aziridinoquinoxalines Through the Intermediacy of Azomethine Ylides
- First Published: 24 January 2024
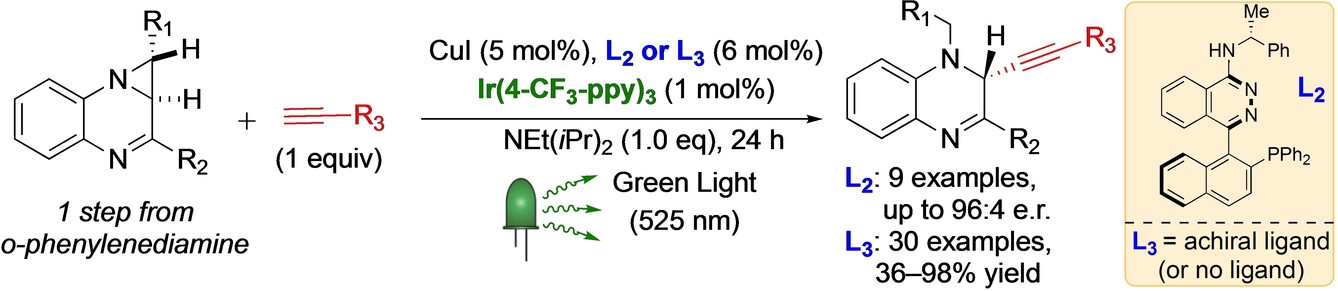
The development of alkyne addition to the aziridine moiety of aziridinoquinoxalines using dual Ir(III)/Cu(I) catalysts under green light-emitting diode (LED) photolysis (λmax=525 nm), is described. The experimental and quantum chemical explorations suggest a triplet energy transfer mechanism followed by a ring-opening reaction ultimately leading to the formation of azomethine ylide intermediates that are trapped with copper(I) acetylides.
Reactive Oxygen Species
Spin-state Conversion by Asymmetrical Orbital Hybridization in Ni-doped Co3O4 to Boost Singlet Oxygen Generation for Microbial Disinfection
- First Published: 25 January 2024
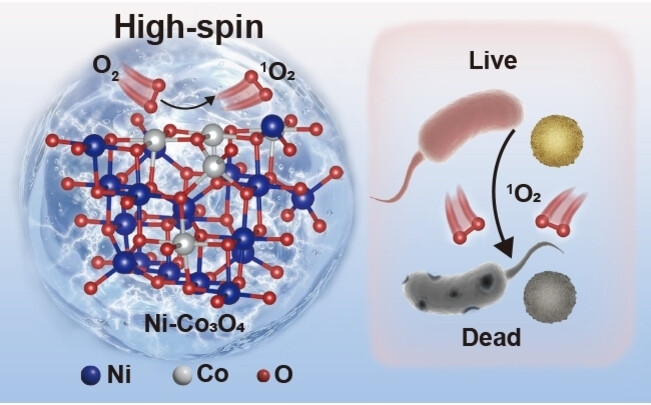
The introduction of Ni into the octahedral site of Co3O4 effectively induced a low-to-high spin-state transition, thereby enhancing the activity of 1O2 generation. We further explored the spin-related charge transfer and orbital interactions between the catalysts and intermediates, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the 1O2 generation. This work deepens the understanding about orbital interactions and spin states.
Protein Engineering | Hot Paper
Controlling Monoterpene Isomerization by Guiding Challenging Carbocation Rearrangement Reactions in Engineered Squalene-Hopene Cyclases
- First Published: 25 January 2024
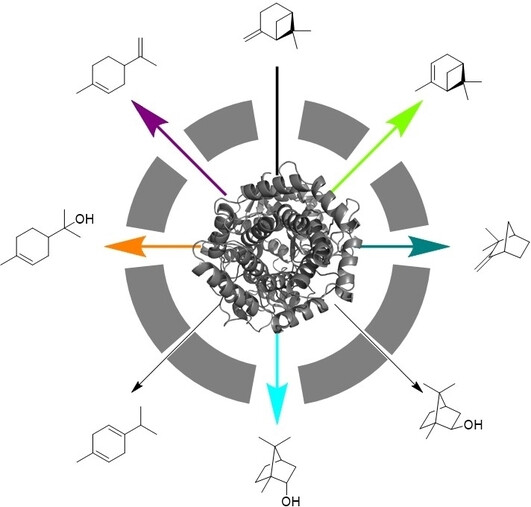
Carbocation-based rearrangements are vital for terpene versatility. AacSHC triterpene cyclase from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius acted as a promiscuous catalyst for multiple monoterpene rearrangements. Tailored AacSHC variants directed the specific isomerization of pinene with exceptional selectivities. Success involved restructuring the aromatic active pocket and reorganizing water clusters to stabilize demanding carbocationic intermediates.
Neurochemistry
A Potentiometric Dual-Channel Microsensor Reveals that Fluctuation of H2S is Less pH-Dependent During Spreading Depolarization in the Rat Brain
- First Published: 25 January 2024
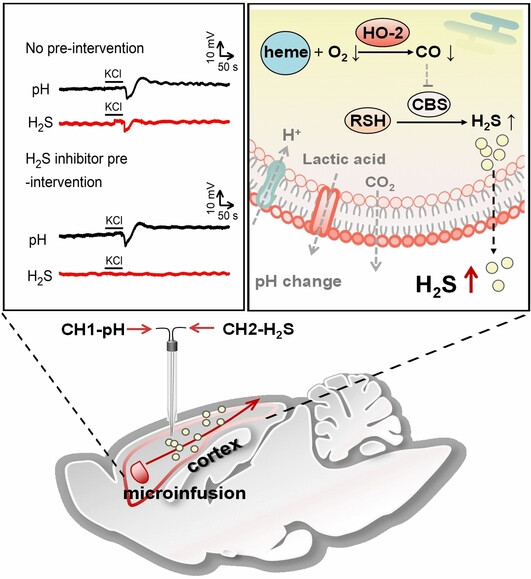
Understanding the mechanism of spreading depolarization (SD) is essential for the therapy of SD associated diseases. We report a potentiometric dual-channel microsensor for simultaneous detection of H2S and pH, enabling the first observation of H2S fluctuation induced by SD in vivo. Our work provides the direct experimental evidence that the H2S release during SD in rat cortex is less pH-dependent, possibly by modulating enzyme-dependent pathways.
Room-Temperature Phosphorescence
Dopants Induce Persistent Room Temperature Phosphorescence in Triarylamine Boronate Esters
- First Published: 26 January 2024
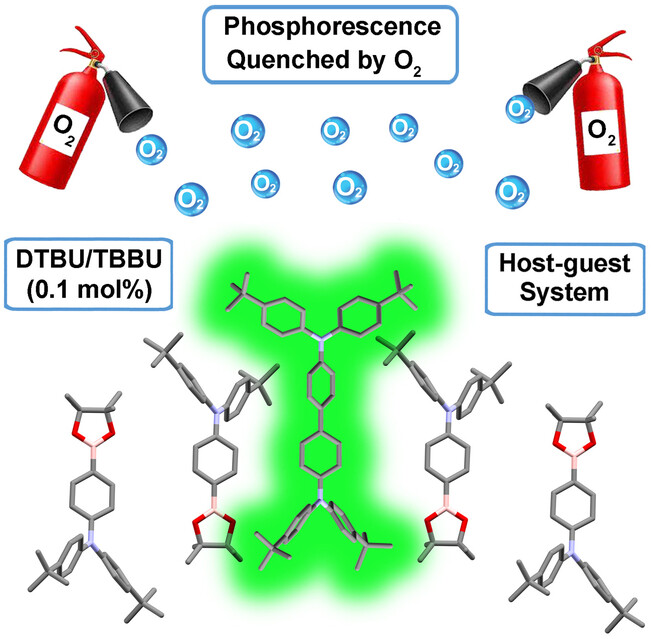
Purely organic luminescent material TBBU does not show room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) in the solid state even under N2. When doped with 0.1 mol % DTBU, a persistent yellowish green afterglow can be observed from this binary system in N2 atmosphere. This induced phosphorescence is quite sensitive to oxygen, making the material a candidate for oxygen sensing.
Asymmetric catalysis
Direct, Stereodivergent, and Catalytic Michael Additions of Thioimides to α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes – Total Synthesis of Tapentadol
- First Published: 17 January 2024

The direct, triisopropy silyl triflate (TIPSOTf)-mediated, regioselective and stereodivergent Michael additions of thioimides to α,β-unsaturated aldehydes catalyzed by chiral nickel complexes give any of the potential syn and anti diastereomers, at will, with good to high yields. The resultant adducts can be easily transformed into a wide array of enantiomerically pure intermediates ready to participate in the asymmetric synthesis of biologically active compounds.
Nonlinear Optics
Molecular Crystals Constructed by Polar Molecular Cages: A Promising System for Exploring High-performance Infrared Nonlinear Optical Crystals
- First Published: 25 January 2024
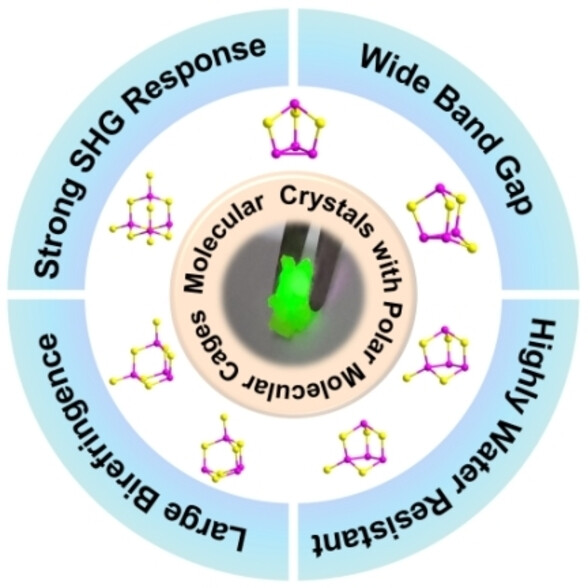
Molecular crystals with polar molecular cages were firstly proposed as a promising system for exploring superior IR NLO materials and a representative system, the binary chalcogenide family P4Sn (n=3–9), is introduced. As a member of the system, α-P4S5 possesses a robust SHG response (1.1×AGS), a broad band gap (3.02 eV), ample birefringence (0.134@2050 nm), a wide optical transmission range (0.41–14.7 μm), and exceptional water-resistance.
Luminescence | Hot Paper
Dual Stimuli-Responsive [2]Rotaxanes with Tunable Vibration-Induced Emission and Switchable Circularly Polarized Luminescence
- First Published: 27 January 2024
Sustainable Chemistry
A New Life For Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber: Co-Harnessing Metathesis And Condensation For Reincorporation Into Bio-Based Materials
- First Published: 31 January 2024
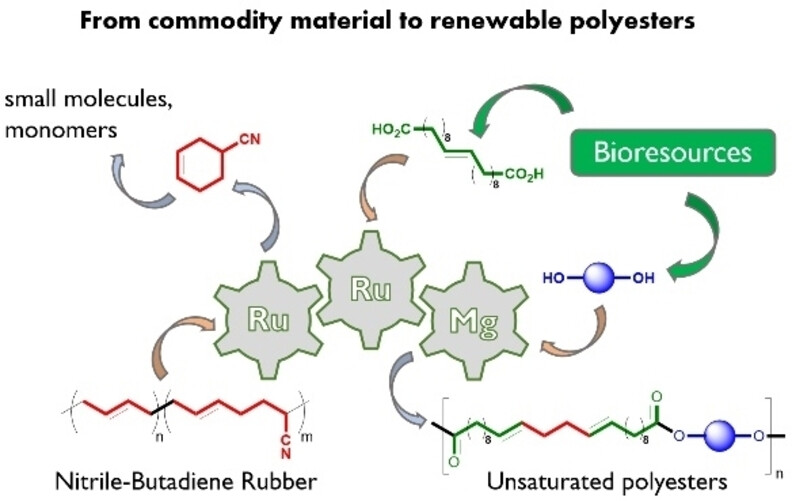
A key polymer material, nitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR), is converted under mild conditions via a one-pot catalytic sequence to bio-based polyesters with highly modulable structure and properties. The overall process operates with high atom-economy, formally redistributing the NBR monomers into new difunctional monomers as well as a single valuable small molecule by-product.
Luminescence | Hot Paper
Dynamically Modulating the Dissymmetry Factor of Circularly Polarized Organic Ultralong Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Soft Helical Superstructures
- First Published: 24 January 2024
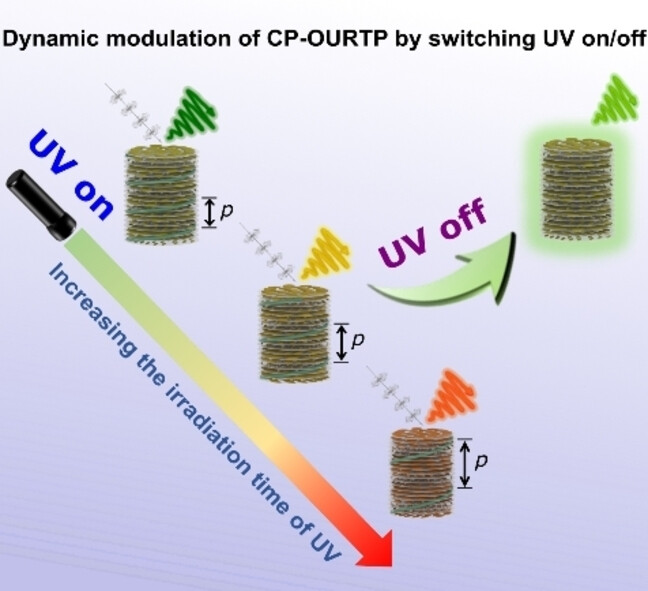
We propose an effective strategy for achieving circularly polarized organic ultralong room-temperature phosphorescence (CP-OURTP) with a high dissymmetry factor based on a bilayered soft helical superstructure doped with a light-driven molecular motor and room-temperature polymer layer. This enables the significant modulation of reflection across a wide spectral range and the dynamic controlling the dissymmetry factor of CP-OURTP from 1.38 to 0.60.
Drug Delivery
Metal–Phenolic-Mediated Assembly of Functional Small Molecules into Nanoparticles: Assembly and Bioapplications
- First Published: 28 January 2024
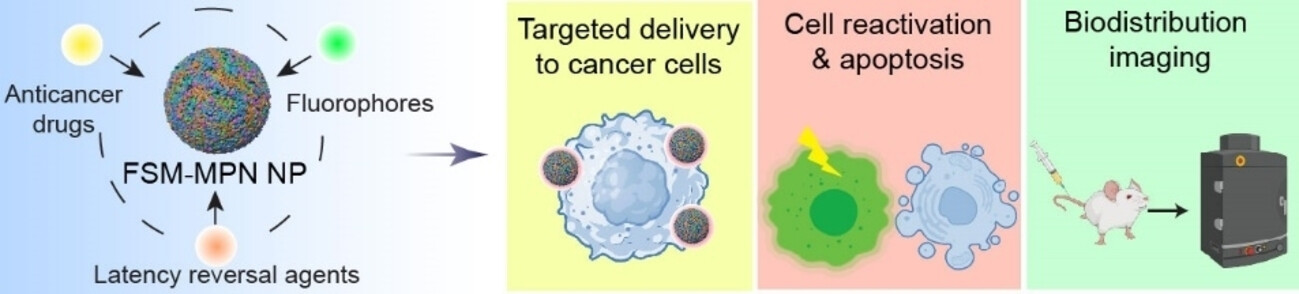
A metal–phenolic-mediated assembly approach is presented whereby a library of functional small molecules, encompassing anticancer drugs, latency reversal agents, and fluorophores, are assembled into functional metal–phenolic network nanoparticles (FSM-MPN NPs) under ambient conditions. These FSM-MPN NPs have potential use in a range of biological applications.
Radical Cation Salts | Very Important Paper
Radical Cation Salts of Hetera-Buckybowls: Polar Crystals, Negative Thermal Expansion and Phase Transition
- First Published: 16 January 2024
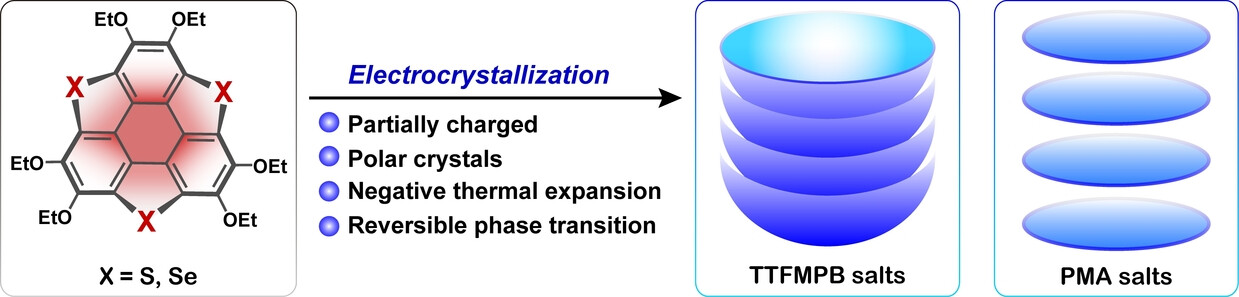
The electrocrystallization of hetera-buckybowl trichalcogenasumanenes (TCSs) has afforded radical cation salts with excellent stability under ambient conditions. The resulting salts are mostly polar crystals, where the TCSs are partially charged and form columnar stacks. A reversible semiconductor-to-semiconductor phase transition is observed, which is caused by a negative thermal expansion of the unit cell.
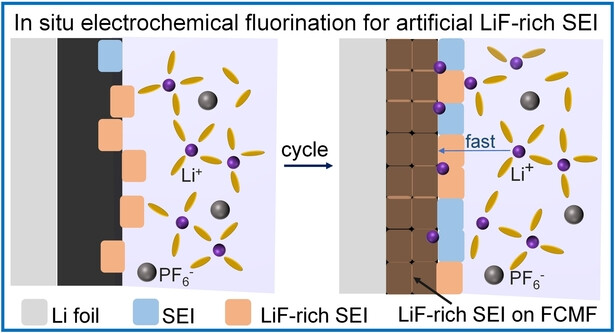
Li Metal Batteries | Hot Paper
Artificial LiF-Rich Interface Enabled by In situ Electrochemical Fluorination for Stable Lithium-Metal Batteries
- First Published: 29 January 2024
Electrochemistry | Hot Paper
Mechanism Behind the Loss of Fast Charging Capability in Nickel-Rich Cathode Materials
- First Published: 31 January 2024
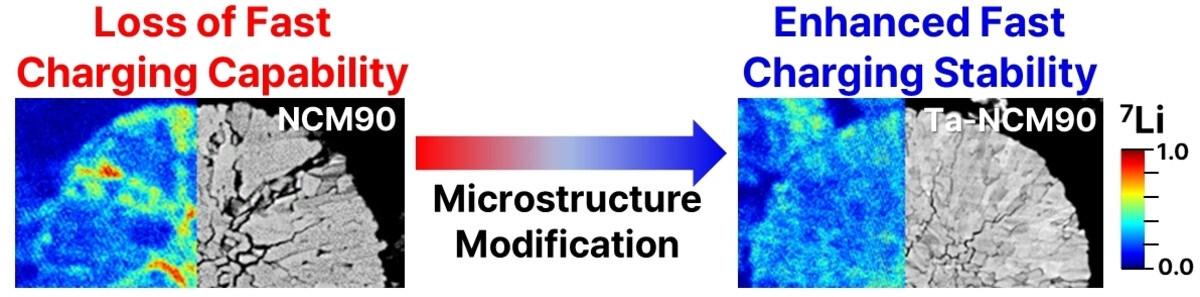
Upon extended cycling, the presence of microcracks and resulting internal degradation lead to the hindered kinetics during the (de)intercalation of Li+ ions. While these issues were not problematic during charging at low currents, fast charging conditions induce electrochemically unreactive regions in the cathodes owing to increased resistance and polarization, which lead to the loss of fast charging.
Piezofluorochromism
Piezofluorochromism in Hierarchical Porous π-stacked Supermolecular Spring Frameworks from Aromatic Chiral Cages
- First Published: 01 February 2024
Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
Deciphering Structure-Activity Relationship Towards CO2 Electroreduction over SnO2 by A Standard Research Paradigm
- First Published: 29 January 2024
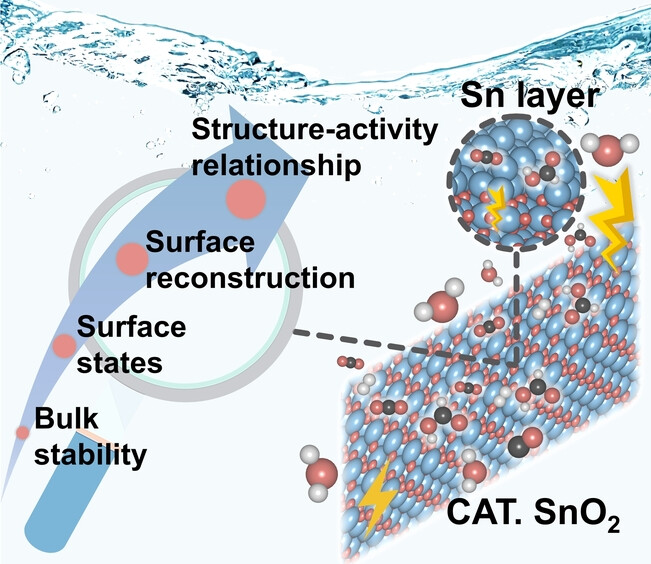
Standard research paradigm proposed to uncover the structure-property-activity relationships for the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) over SnO2, illustrating the surface reconstruction induced by oxygen vacancies (1/1 ML coverage) and surface-active species (Sn layer) accountable for selective HCOOH production. This proposed methodology validated by the experimental CO2RR is appliable to other electrocatalytic systems.
Peptides Modification
N-Terminal-Specific Dual Modification of Peptides through Copper-Catalyzed [3+2] Cycloaddition
- First Published: 28 January 2024
![N-Terminal-Specific Dual Modification of Peptides through Copper-Catalyzed [3+2] Cycloaddition](/cms/asset/8d7cb5f7-d751-442f-81c1-7d07feb33914/anie202320012-toc-0001-m.jpg)
We developed a method for the N-terminal-specific dual modification of peptides through a three-component [3+2] cycloaddition with aldehydes and maleimides under mild copper catalysis. This approach enables exclusive functionalization at the glycine N-terminus of peptides, regardless of the presence of lysine ϵ-amine, affording the chemically robust pyrrolidine ring in excellent yields with complete exo-diastereoselectivity.
Drug Discovery
A Semisynthesis Platform for the Efficient Production and Exploration of Didemnin-Based Drugs
- First Published: 30 January 2024
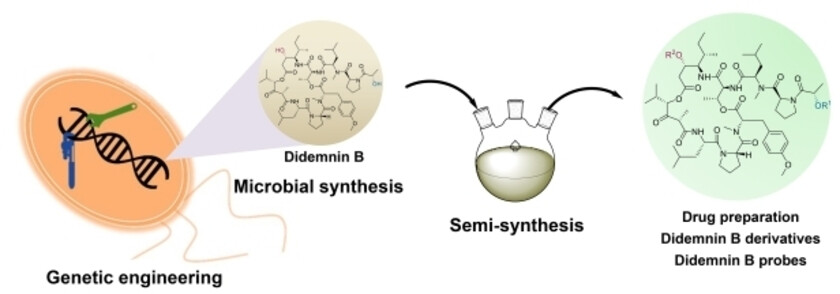
A platform has been established for the exploration of didemnin-based drugs, combining microbial synthesis of didemnin B through genetic engineering of Tistrella mobilis and semisynthesis for the production of plitidepsin for drug purposes, didemnin derivatives for studying structure–activity relationships, and didemnin B probes for targeted protein profiling. This sustainable approach holds potential for investigating other marine natural products.
Na–S Batteries | Hot Paper
Tailoring Na+ Solvation Environment and Electrode-Electrolyte Interphases with Sn(OTf)2 Additive in Non-flammable Phosphate Electrolytes towards Safe and Efficient Na-S Batteries
- First Published: 29 January 2024
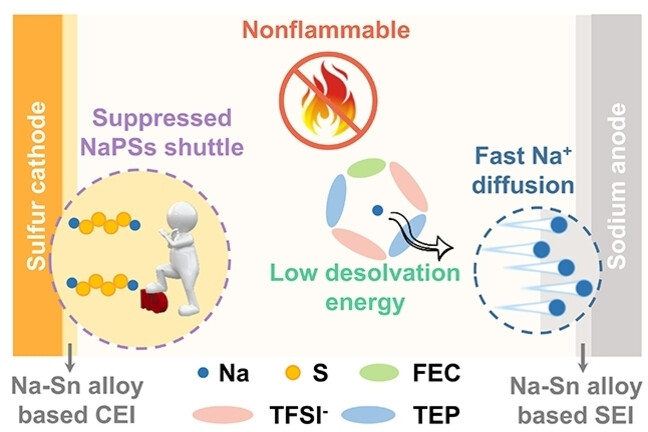
A multifunctional additive, tin trifluoromethanesulfonate (Sn(OTf)2), is proposed to engineer a non-flammable triethyl phosphate (TEP)-based electrolyte, aiming to regulate the solvation environment of Na+, facilitate uniform Na deposition, and suppress the shuttling of sodium polysulfides for safe and efficient room-temperature sodium-sulfur (RT Na-S) batteries.
1D COFs
1D Covalent Organic Frameworks Triggering Highly Efficient Photosynthesis of H2O2 via Controllable Modular Design
- First Published: 01 February 2024
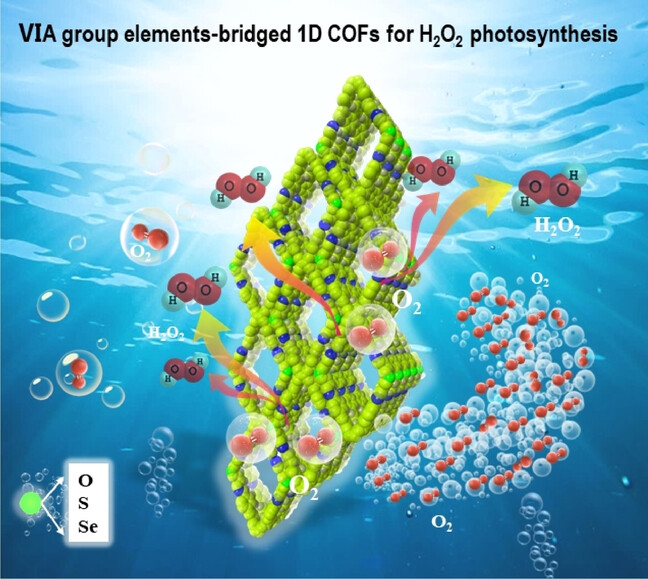
A sequence of novel VIA group elements (O, S, Se)-bridged 1D COFs with typical 4-c sql topology were synthesized and applied as catalysts in the photosynthesis of H2O2. Thanks to their 1D configurations, more active sites are accessible, the proton interlaminar shuttle are accelerated, and the directional transfer of electrons is also improved. The bridge-atoms (O, S, Se) in the 1D COFs play a crucial role for the catalytic activity and selectivity.
DNAzyme
A Programmable DNAzyme for the Sensitive Detection of Nucleic Acids
- First Published: 30 January 2024
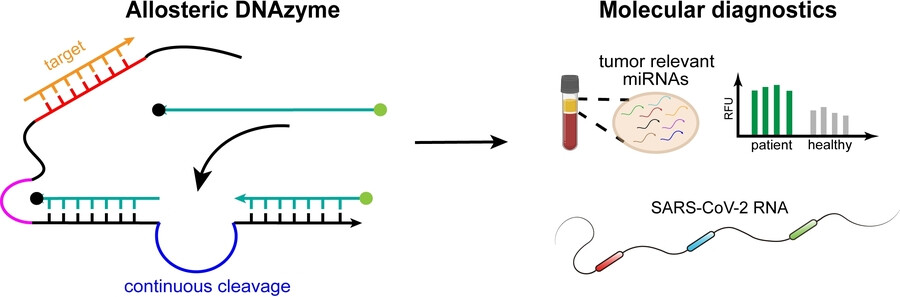
A unimolecular self-locked allosteric DNAzyme biosensor (named SPOT) is developed to enable sensitive detection (LOD: fM-aM) of low-abundance nucleic acids in a one-pot, one-step, preamplification-free, isothermal detection manner. SPOT exhibits potent performance on miRNA-based detection for cancer diagnostics and viral RNA-based detection for SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnostics.
Electrocatalysis
2D Metal/Graphene and 2D Metal/Graphene/Metal Systems for Electrocatalytic Conversion of CO2 to Formic Acid
- First Published: 25 January 2024
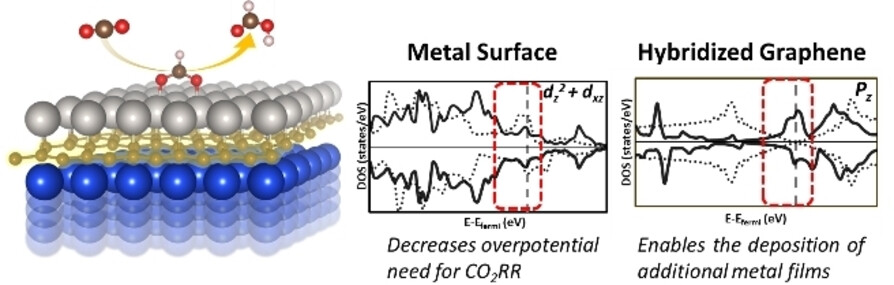
Strong covalent bonding between metal monolayer and graphene driven by the sp and d orbital hybridization, 2D metal/graphene (M/G) system is investigated. The charge transfer from metal to graphene allows for the electrodeposition of another metal film, thus forming metal/graphene/metal (M/G/M) system. These 2D hybrid systems exhibit excellent activity and selectivity toward formic acid production over competitive hydrogen evolution reaction.
Hydrogen Evolution | Hot Paper
Substantial Impact of Built-in Electric Field and Electrode Potential on the Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Reaction of Ru−CoP Urchin Arrays
- First Published: 29 January 2024
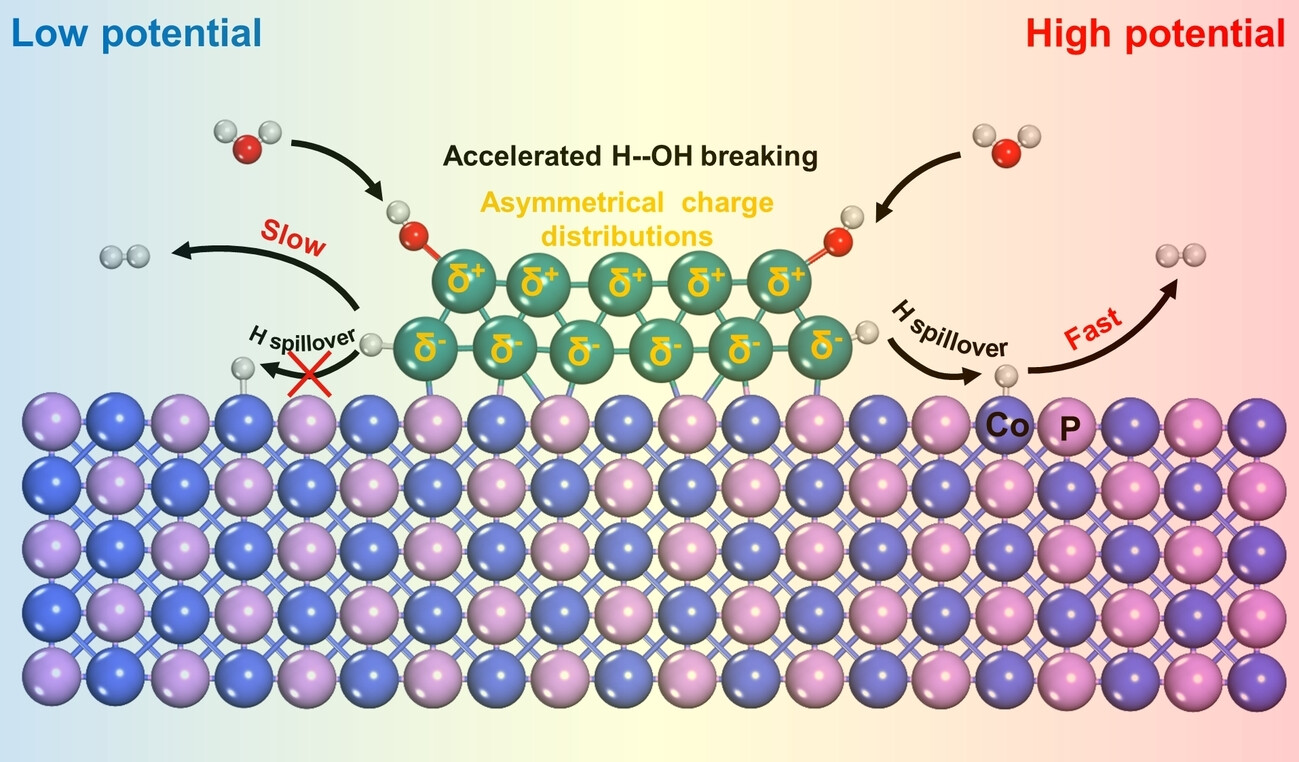
A strong built-in electric field (BIEF) resulted in a strong asymmetrical charge distribution on the Ru cluster, which accelerated water dissociation. However, strong hydrogen adsorption on the interfacial Ru atoms created a high energy barrier for hydrogen desorption and spillover, resulting in unsatisfactory activity at low potentials. As the potential became more negative, the barrier for hydrogen spillover from the interfacial Ru to the Co site, which had a near-zero hydrogen adsorption energy, significantly decreased, thus accelerating the entire alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) process.
OLEDs
Switching from Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence in Single Crystals for Low-Threshold Laser to Room-temperature Phosphorescence in Amorphous-Film for Highly Efficient OLEDs
- First Published: 25 January 2024
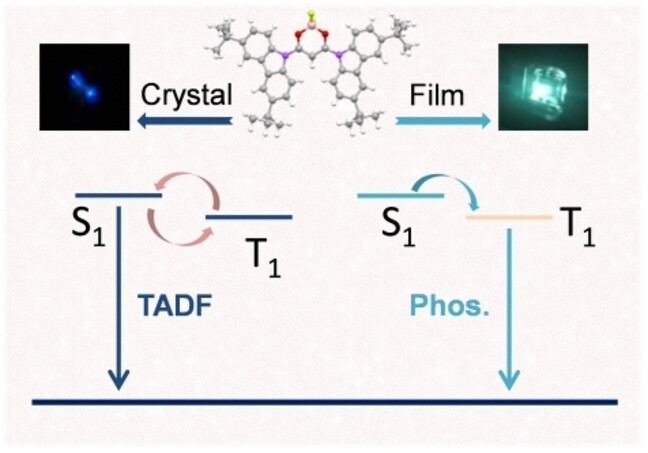
Tightly packed and well-faceted single-crystal microwires of tert-butylcarbazole difluoroboron β-diketonate (DtCzBF2) enabled thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) and low-threshold microlasers. In contrast, its guest-host amorphous thin-films exhibited organic room-temperature phosphorescence (ORTP) with a PLQY up to 61 %, leading to solution-processed OLEDs with external quantum efficiency approaching 18.6 %. This study opens possibilities of low-cost ORTP emitters for high performance OLEDs and future low-threshold electrically injected organic semiconductor lasers (OSLs).
Porous Materials | Hot Paper
Orthogonal Postsynthetic Copolymerization of Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Frameworks into a PolyHOF Membrane
- First Published: 01 February 2024
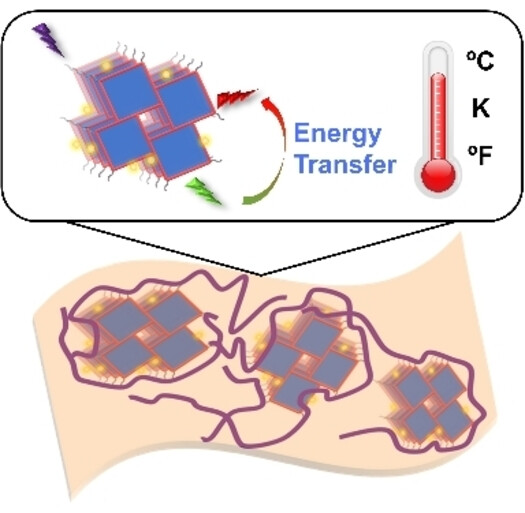
PolyHOF membrane, constructed via covalently copolymerizing nanoscale HOFs into polymeric network, not only exhibits customizable mechanical properties, but also shows excellent functional compatibility, proven by the benchmark luminescent temperature sensing behavior of lanthanide anchored polyHOF membrane even under harsh conditions.
PROTACs
Photoswitchable PROTACs for Reversible and Spatiotemporal Regulation of NAMPT and NAD+
- First Published: 28 January 2024
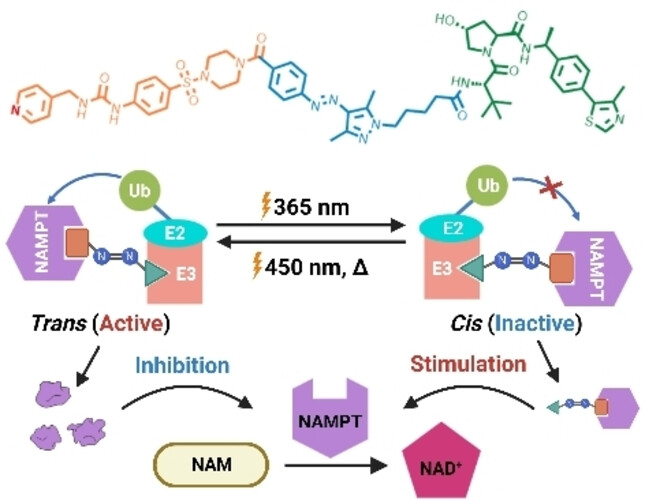
The first activator-based photoswitchable proteolysis-targeting chimera (PS-PROTAC) was developed for the optical control of NAMPT and NAD+ in biological systems. The novel PS-PROTAC enabled the reversible regulation of NAMPT and NAD+, resulting in a significant reduction in target-related toxicity compared to conventional NAMPT degraders or inhibitors. Furthermore, PS-PROTAC allowed for the in vivo optical manipulation of antitumor activity, NAMPT, and NAD+.
Communications
All-Solid-State Batteries | Very Important Paper
Dynamic Monkey Bar Mechanism of Superionic Li-ion Transport in LiTaCl6
- First Published: 11 December 2023
Cascade Catalysis
Cascade Electrocatalytic and Thermocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to Propionaldehyde
- First Published: 17 January 2024
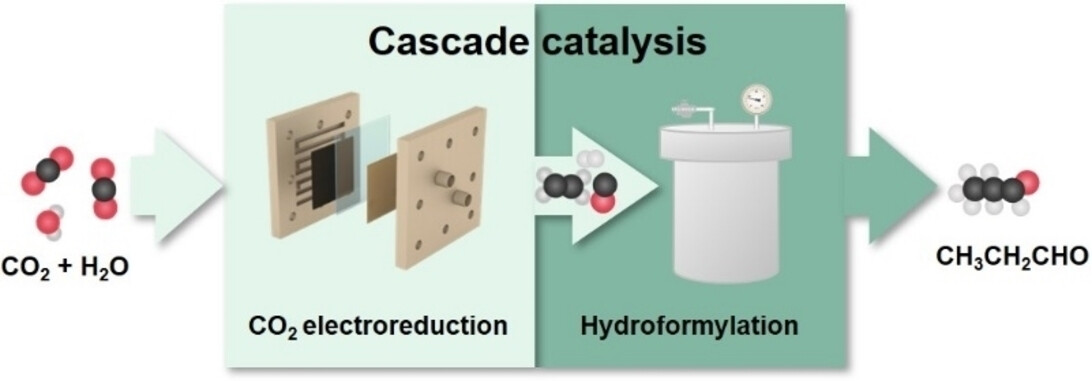
A cascade electrocatalytic and thermocatalytic reaction Scheme is demonstrated to convert CO2 to propionaldehyde. By individually optimizing and efficiently coupling the upstream and downstream processes, this hybrid system achieves a propionaldehyde selectivity of ~38 %, considerably higher than the best electrochemical systems alone or other hybrid systems reported earlier.
Polymer Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Supramolecular Complexation of Metal Oxide Cluster and Non-Fluorinated Polymer for Large-Scale Fabrication of Proton Exchange Membranes for High-Power-Density Fuel Cells
- First Published: 24 January 2024
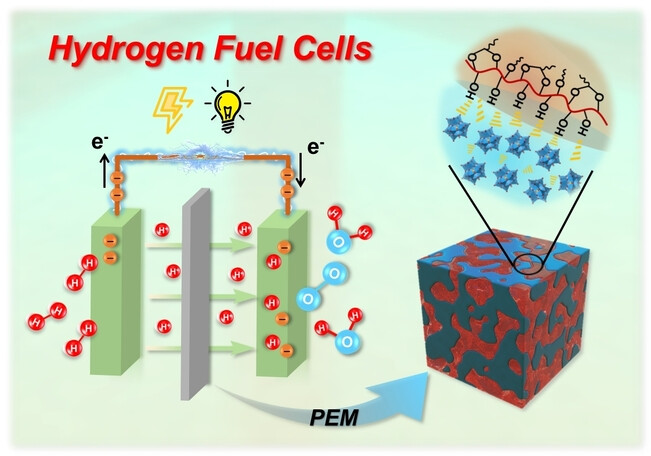
The facile and cost-effective hybridization strategy for proton exchange membranes (PEMs) design by blending 1 nm metal oxide clusters and polyvinyl butyral. The fuel cells equipped with the PEM show promising power densities and excellent durability that is on par with Nafion® and surpass the previously reported non-fluorinated PEMs.
Enantioselective Synthesis
Benzo-fused Nitrogen Heterocycles by Asymmetric Ring Expansion and Stereochemically Retentive Re-contraction of Cyclic Ureas
- First Published: 23 January 2024
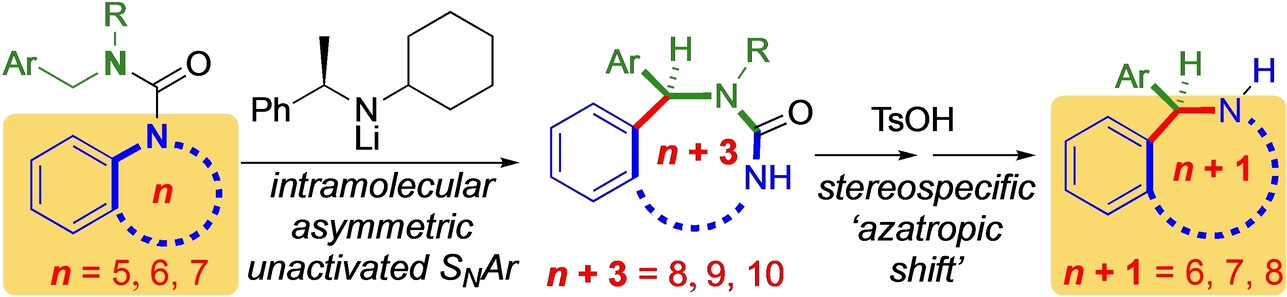
Asymmetric deprotonation of N-benzyl urea derivatives of nitrogen heterocycles leads to enantioselective insertion of the benzylic substituent into an aromatic C−N bond. Treatment of the ring-expanded products induces a stereospecific ring-contraction that results in an overall asymmetric enantioselective one-carbon enlargement of the heterocycle.
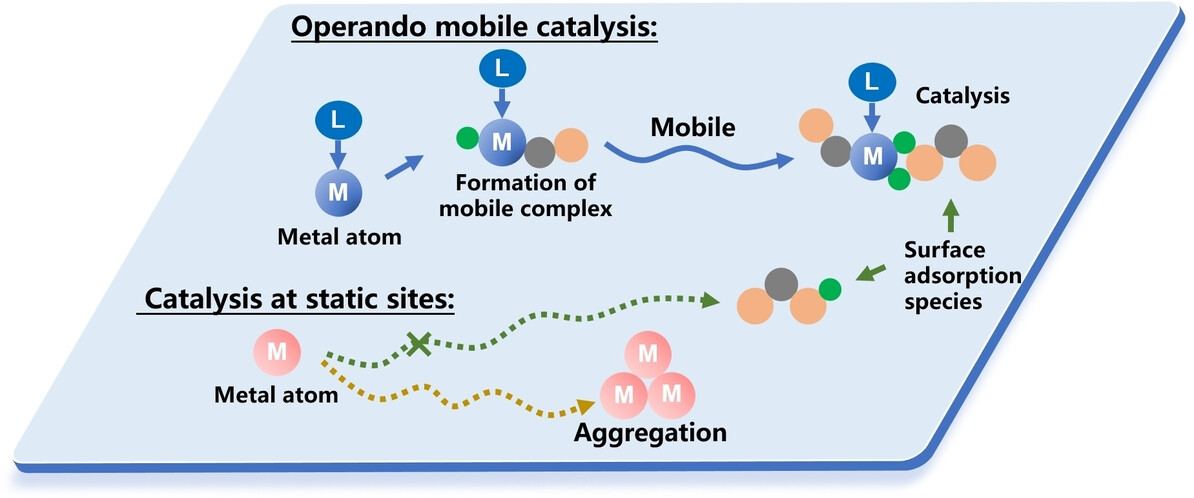
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Converting Glycerol into Valuable Trioses by Cuδ+-Single-Atom-Decorated WO3 under Visible Light
- First Published: 01 February 2024
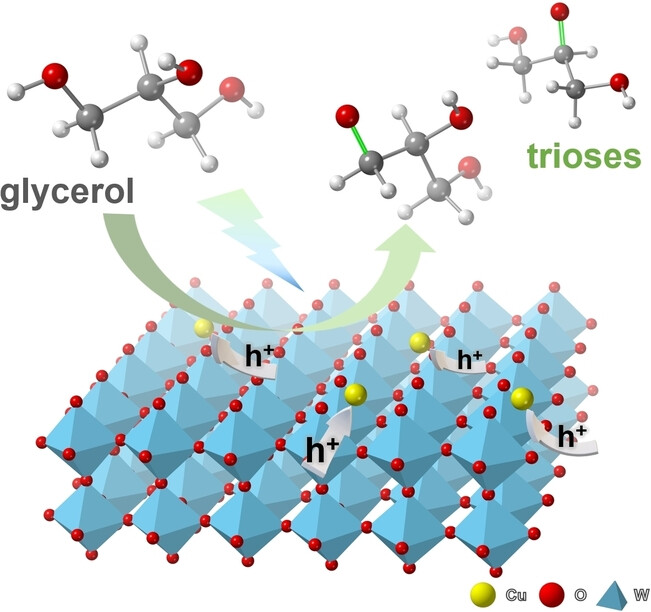
A single-atom Cu-decorated WO3 photocatalyst has achieved a high conversion rate and excellent selectivity in the process of visible light-driven oxidation of glycerol to trioses. The critical role of single Cu atoms is to attract photogenerated holes, thereby improving charge transfer and activating glycerol molecules.
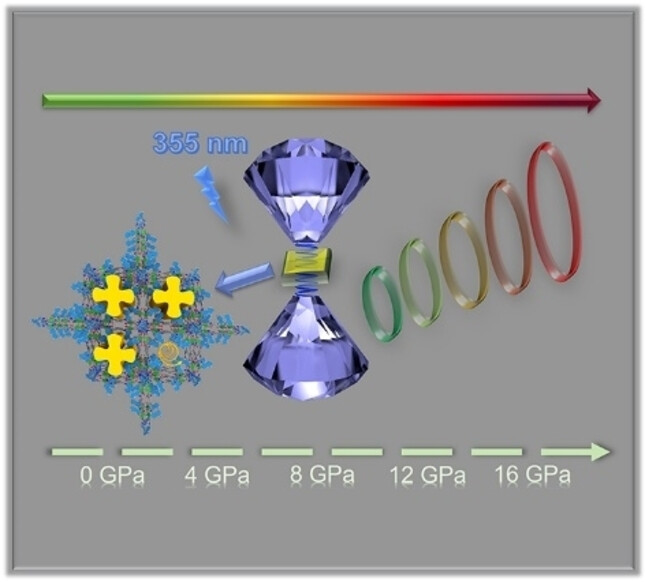
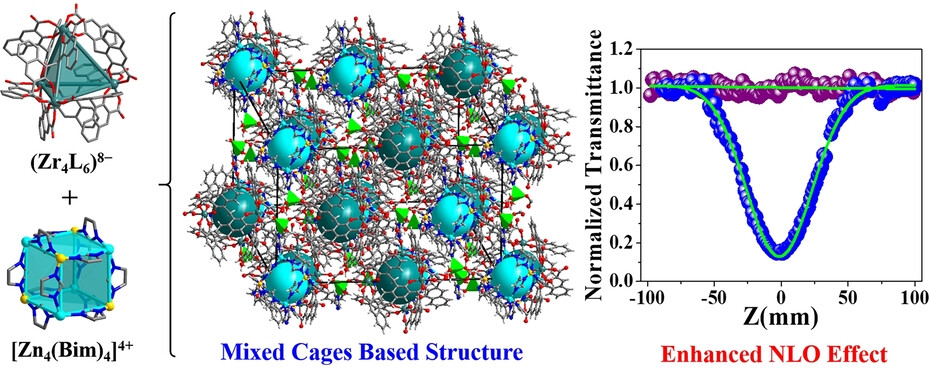
Nonlinear Optics
Integrated Anionic Zirconium-Organic Cage and Cationic Boron-Imidazolate Cage for Synergetic Optical Limiting
- First Published: 26 January 2024
Polymer Chemistry
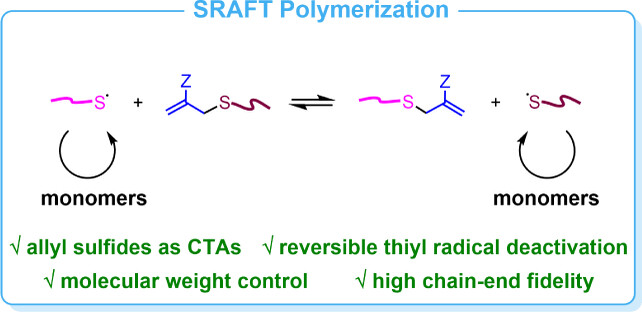
Reversible Thiyl Radical Addition−Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization
- First Published: 29 January 2024
Synthetic Methods | Hot Paper
Amino-λ3-iodane-Enabled Electrophilic Amination of Arylboronic Acid Derivatives
- First Published: 25 January 2024
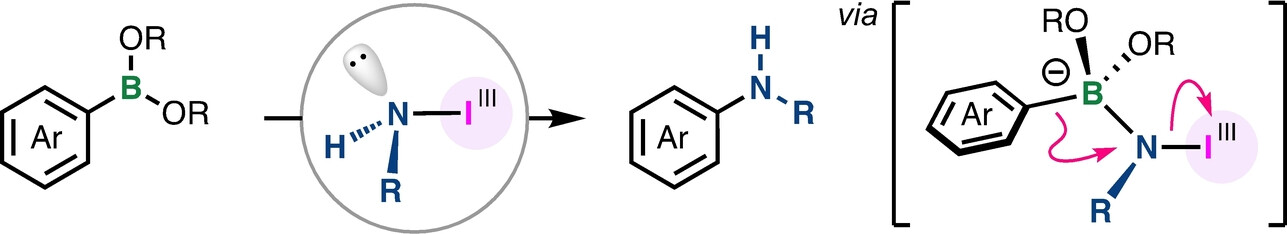
Amino-λ3-iodanes enable the electrophilic amination of arylboronic acids and boronates. Iodine(III) reagents with transferable amino groups, including one with an NH2 group, were synthesized and used in the amination, allowing the synthesis of a wide range of primary and secondary (hetero)arylamines.
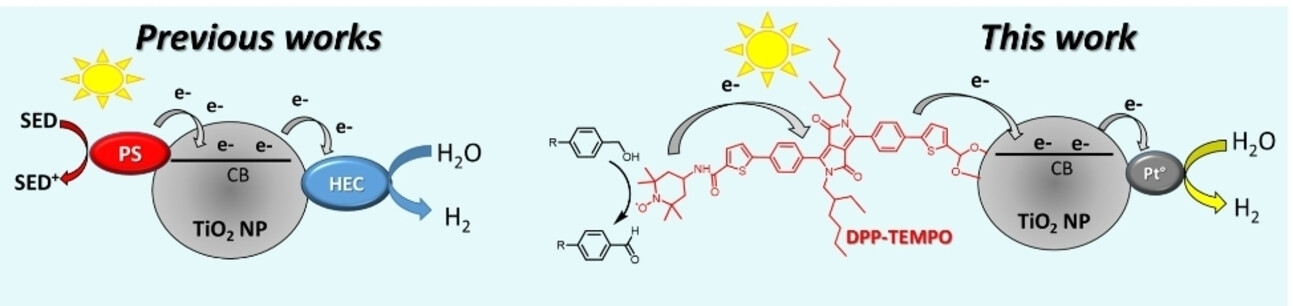
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
Dye-Sensitized Photocatalysis: Hydrogen Evolution and Alcohol-to-Aldehyde Oxidation without Sacrifical Electron Donor
- First Published: 16 January 2024
Chemoenzymatic Cascades | Hot Paper
Peptide and Enzyme Catalysts Work in Concert in Stereoselective Cascade Reactions—Oxidation followed by Conjugate Addition
- First Published: 18 January 2024
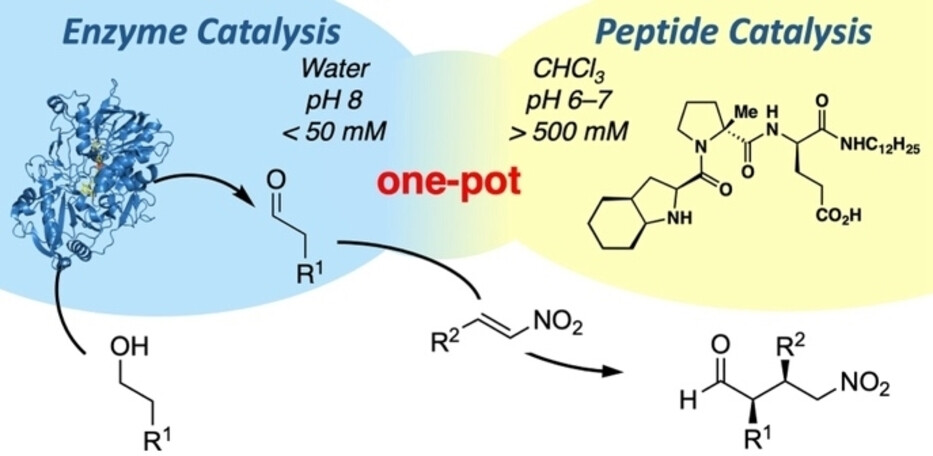
An enzyme and a peptide catalyze—in an aqueous buffer—a two-step cascade reaction with high chemo- and stereoselectivity in one pot. The optimization of the modular peptide catalyst and the identification of common reaction conditions were key for bringing the two worlds of enzyme and peptide catalysis together.
Fuel Cells
Symmetry-Broken Ru Nanoparticles with Parasitic Ru-Co Dual-Single Atoms Overcome the Volmer Step of Alkaline Hydrogen Oxidation
- First Published: 29 January 2024
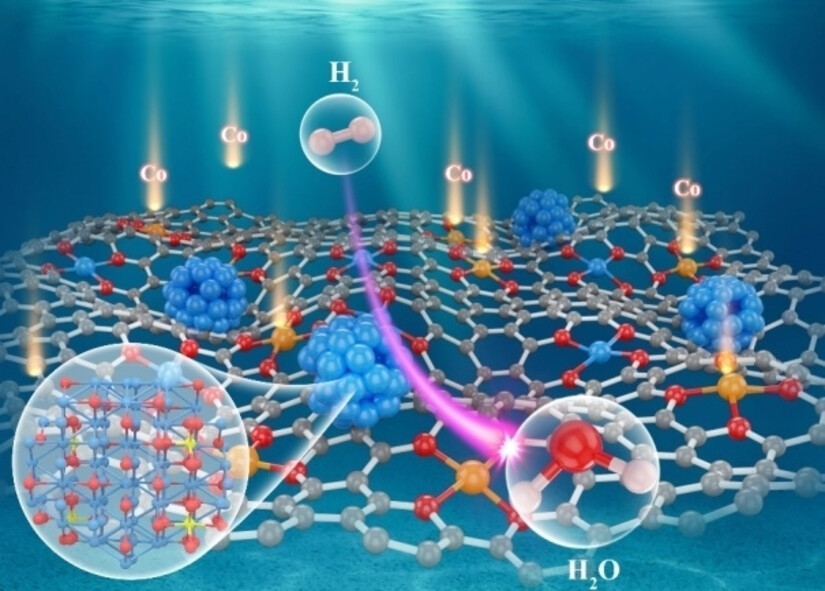
The symmetry of ultrasmall Ru nanoparticles is compromised by embedding Co single atoms, leading to the release of Ru single atoms and the formation of a Co1Ru1,n/rGO structure, which regulates the interaction between active sites and enhances the hydrogen oxidation reaction kinetics, mass activity and excellent durability.
Deuteration
Palladium-Catalyzed Deuteration of Arylketone Oxime Ethers
- First Published: 27 January 2024
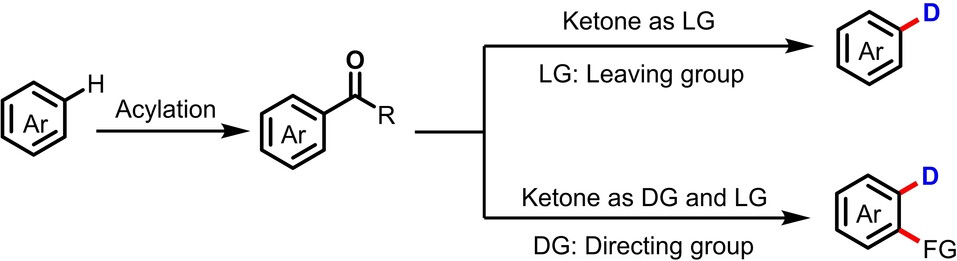
A palladium-catalyzed deuteration of arylketone oxime ethers has been realized. Regioselective deuteration of some biologically important drugs and natural products is showcased via Friedel–Crafts acylation and subsequent deacylative deuteration. Vicinal difunctionalization of electro-rich arenes is achieved by using the ketone as both directing group and leaving group.
N Heterocycles
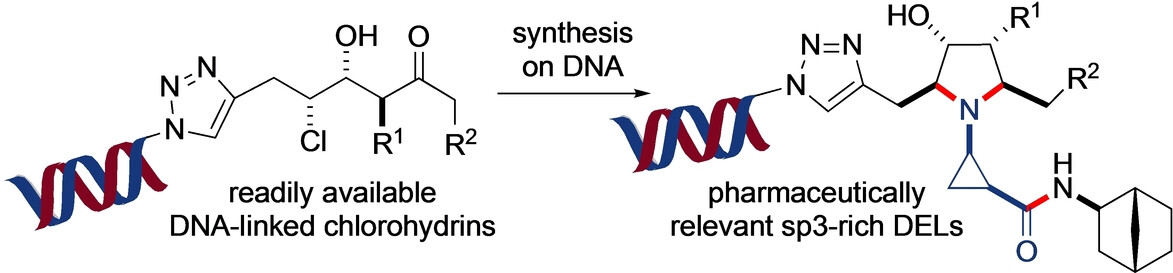
sp3-Rich Heterocycle Synthesis on DNA: Application to DNA-Encoded Library Production
- First Published: 08 February 2024
Enzyme Identification | Hot Paper
Mining the Metabolic Capacity of Clostridium sporogenes Aided by Machine Learning
- First Published: 29 January 2024
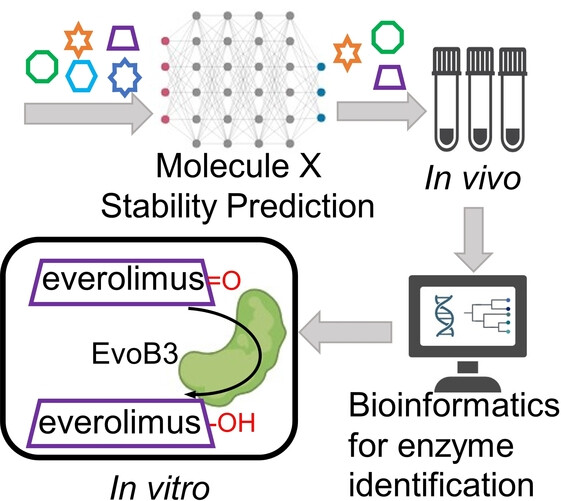
The metabolic capacity of Clostridium sporogenes ATCC 15579 against small molecules was predicted by using an in silico machine learning platform, MoleculeX, followed by experimental evaluation in vivo. Bioinformatics and in vitro biochemical assays were further utilized to identify an enzyme EvoB3 for everolimus modification through ketoreduction.
Asymmetric Catalysis | Hot Paper
Chiral CpxRhodium(III)-Catalyzed Enantioselective Aziridination of Unactivated Terminal Alkenes
- First Published: 27 January 2024
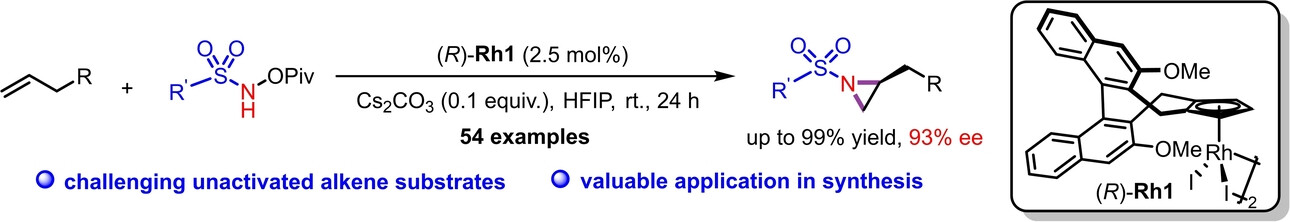
A chiral cyclopentadienyl-rhodium(III) catalyzed highly enantioselective aziridination of challenging unactivated terminal alkenes and N-pivalolyloxy sulfonamides has been developed. This catalytic system demonstrated outstanding catalytic activity and broad functional group tolerance, yielding synthetically important and highly valuable chiral aziridines with good to excellent yields and enantioselectivities (up to 99% yields, 93% ee).
NMR Spectroscopy
A Straightforward Method for the Generation of Hyperpolarized Orthohydrogen with a Partially Negative Line
- First Published: 20 September 2023
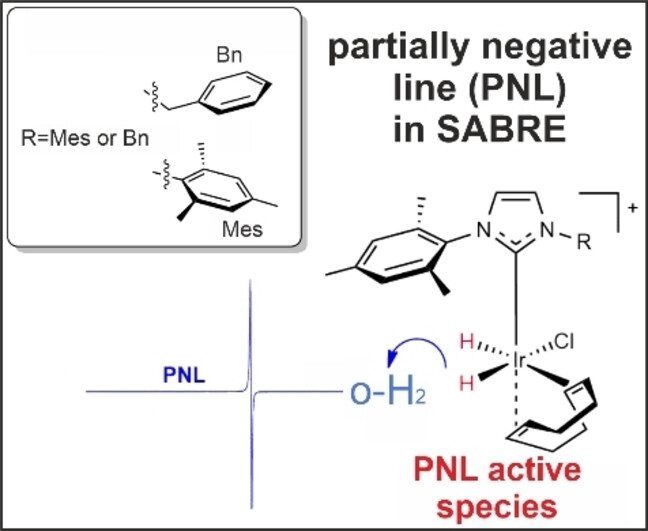
The conditions under which orthohydrogen with a unique Partial Negative Line (PNL) can be observed were determined by one of the essential Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) hyperpolarization methods, called Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange (SABRE). A transient species exists during the preliminary SABRE activation processes, and is responsible for the generation of PNL.
Electrosynthesis
Electrochemical Ni-Catalyzed Decarboxylative C(sp3)−N Cross-Electrophile Coupling
- First Published: 01 February 2024
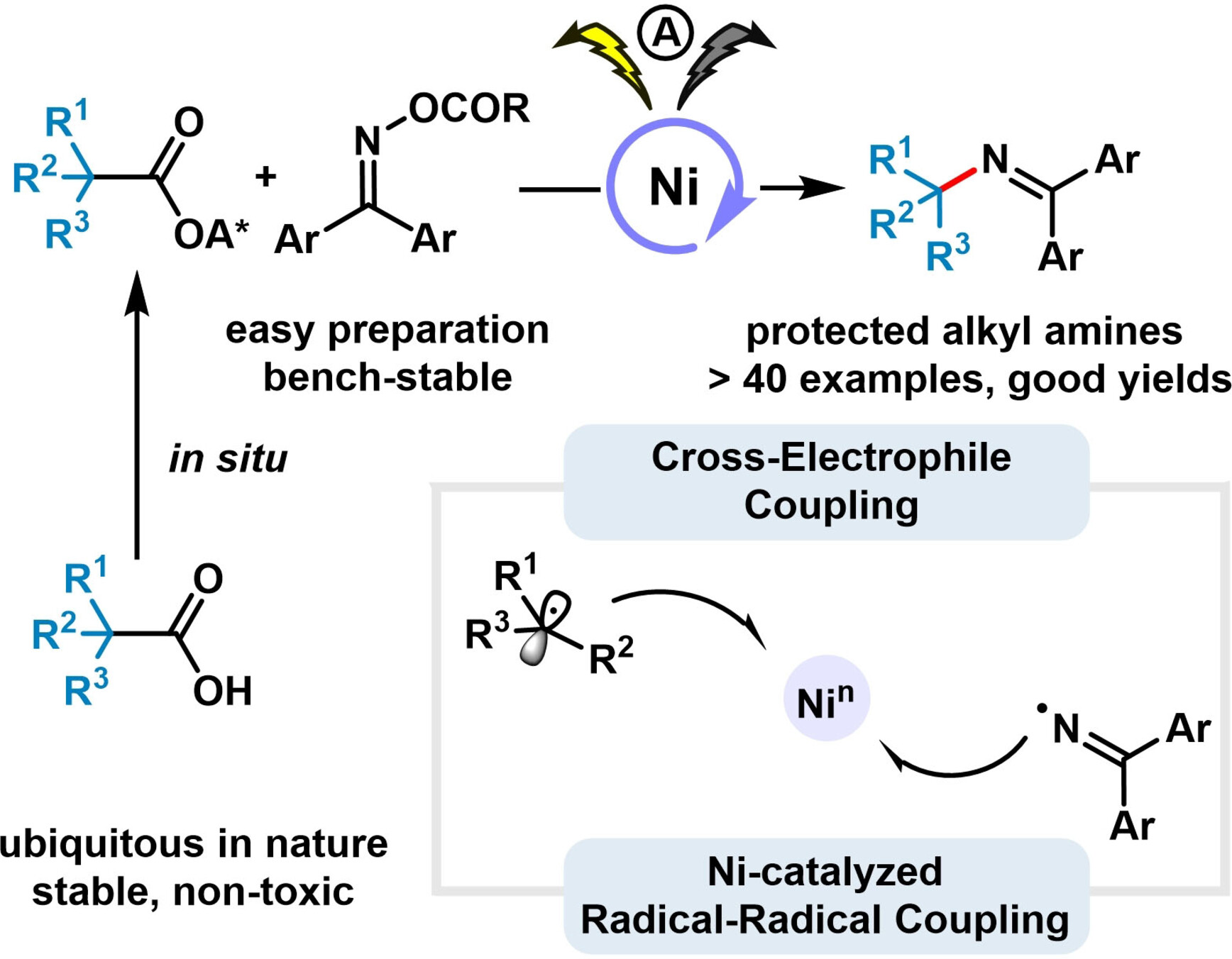
Ni-catalyzed decarboxylative C(sp3)−N cross-coupling of redox active ester and oxime esters was realized through electrochemical cathodic reduction. Mechanistic studies unveil a high-valent nickel species-driven reductive elimination pathway, rather than direct radical-radical coupling. The utility of this methodology was demonstrated through a broad scope (1°, 2°, 3° carboxylic acids) and late-stage functionalization of complex molecules.
C−H Activation | Hot Paper
Stereoselective Synthesis of Complex Polyenes through Sequential α-/β-C−H Functionalization of trans-Styrenes
- First Published: 13 January 2024
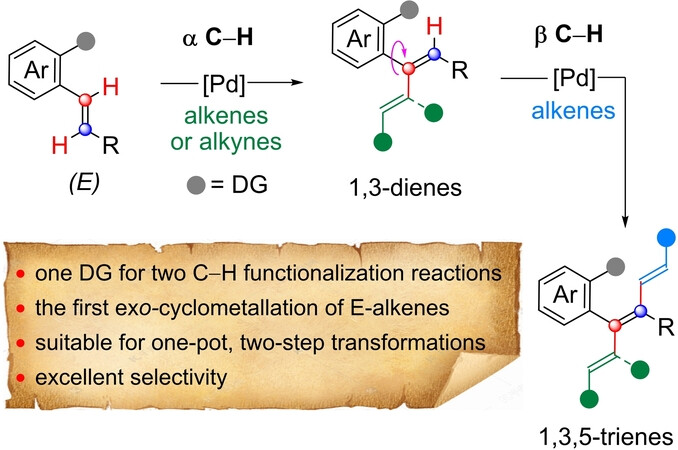
The α-/β-C−H functionalization of E styrenes with simple alkenes and alkynes is presented. The process involves α C−H functionalization via a six-membered exo-palladacycle to afford tri- and tetrasubstituted 1,3-dienes and β C−H functionalization via a seven-membered endo-palladacycle to produce tetra- and pentasubstituted 1,3,5-trienes, both enabled by the chelation assistance of pyrazinamide.






![Dual Stimuli-Responsive [2]Rotaxanes with Tunable Vibration-Induced Emission and Switchable Circularly Polarized Luminescence](/cms/asset/cf5f743a-1d5b-4445-8371-0b756ecb9fc0/anie202319502-toc-0001-m.jpg)