A Potentiometric Dual-Channel Microsensor Reveals that Fluctuation of H2S is Less pH-Dependent During Spreading Depolarization in the Rat Brain
Rantong Liu
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
College of Petroleum and Environment Engineering, Yan'an University, Shaanxi Yan'an, 716000 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuai Zhang
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui Zeng
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorNan Gao
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongyue Yin
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Meining Zhang
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Lanqun Mao
College of Chemistry, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875 China
Search for more papers by this authorRantong Liu
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
College of Petroleum and Environment Engineering, Yan'an University, Shaanxi Yan'an, 716000 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuai Zhang
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui Zeng
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorNan Gao
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongyue Yin
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Meining Zhang
Key Laboratory of Advanced Light Conversion Materials and Biophotonics, Department of Chemistry, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Lanqun Mao
College of Chemistry, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
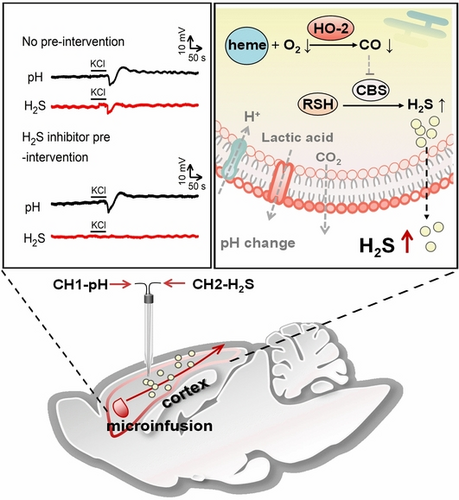
Understanding the mechanism of spreading depolarization (SD) is essential for the therapy of SD associated diseases. We report a potentiometric dual-channel microsensor for simultaneous detection of H2S and pH, enabling the first observation of H2S fluctuation induced by SD in vivo. Our work provides the direct experimental evidence that the H2S release during SD in rat cortex is less pH-dependent, possibly by modulating enzyme-dependent pathways.
Abstract
Spreading depolarization (SD) is one of the most common neuropathologic phenomena in the nervous system, relating to numerous diseases. However, real-time monitoring the rapid chemical changes during SD to probe the molecular mechanism remains a great challenge. We develop a potentiometric dual-channel microsensor for simultaneous monitoring of H2S and pH featuring excellent selectivity and spatiotemporal resolution. Using this microsensor we first observe real time changes of H2S and pH in the rat brain induced by SD. This changes of H2S are completely suppressed when the rat pre-treats with aminooxyacetic acid (AOAA), a blocker to inhibit the H2S-producing enzyme, indicating H2S fluctuation might be related to enzyme-dependent pathway during SD and less pH-dependent. This study provides a new perspective for studying the function of H2S and the molecular basis of SD-associated diseases.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202318973-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf910.8 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aJ. A. Hartings, N. Andaluz, M. R. Bullock, J. M. Hinzman, B. Mathern, C. Pahl, A. Puccio, L. A. Shutter, A. J. Strong, A. Vagal, J. A. Wilson, J. P. Dreier, L. B. Ngwenya, B. Foreman, L. Pahren, H. Lingsma, D. O. Okonkwo, JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 489–499;
- 1bJ. P. Dreier, Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 439–447;
- 1cC. Ayata, M. Lauritzen, Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 953–993;
- 1dD. Pietrobon, M. A. Moskowitz, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 379–393.
- 2
- 2aJ. Jin, W. Ji, L. Li, G. Zhao, W. Wu, H. Wei, F. Ma, Y. Jiang, L. Mao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 19012–19016;
- 2bT. Xiao, Y. Wang, H. Wei, P. Yu, Y. Jiang, L. Mao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6616–6619; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 6618–6691;
- 2cÁ. Menyhárt, A. E. Farkas, D. P. Varga, R. Frank, R. Tóth, A. R. Bálint, P. Makra, J. P. Dreier, F. Bari, I. A. Krizbai, E. Farkas, Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 119, 41–52;
- 2dC. N. Hobbs, G. Holzberg, A. S. Min, R. M. Wightman, ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 2512–2521;
- 2eH. Martins-Ferreira, M. Nedergaard, C. Nicholson, Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 32, 215–234.
- 3
- 3aL. Zhang, T. Xu, W. Ji, X. Wang, S. Cheng, S. Zhang, Y. Zhang, M. Zhang, Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7063–7070;
- 3bC. Pan, F. Wu, J. Mao, W. Wu, G. Zhao, W. Ji, W. Ma, P. Yu, L. Mao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14678–14686;
- 3cG. K. Kolluru, R. E. Shackelford, X. Shen, P. Dominic, C. G. Kevil, Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 20, 109–125;
- 3dG. Yang, L. Wu, B. Jiang, W. Yang, J. Qi, K. Cao, Q. Meng, A. K. Mustafa, W. Mu, S. Zhang, S. H. Snyder, R. Wang, Science, 322, 587–590;
- 3eY. Qian, J. Karpus, O. Kabil, S. Zhang, H. Zhu, R. Banerjee, J. Zhao, C. He, Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 495;
- 3fY. Qian, L. Zhang, S. Ding, X. Deng, C. He, X. Zheng, H. Zhu, J. Zhao, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2920–2923;
- 3gP. Kamoun, Amino Acids 2004, 26, 243–254.
- 4
- 4aM. Ishigami, K. Hiraki, K. Umemura, Y. Ogasawara, K. Ishii, H. Kimura, Antioxid. Redox Signaling 2009, 11, 205–214;
- 4bY. Ogasawara, S. Isoda, S. Tanabe, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 17, 1535–1542;
- 4cK. Abe, H. Kimura, J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1066–1071.
- 5
- 5aR. Wang, Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 791–896;
- 5bM. R. Filipovic, J. Zivanovic, B. Alvarez, R. Banerjee, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1253–1337.
- 6
- 6aK. Hu, K. L. Le Vo, F. Wang, X. Zhang, C. Gu, N. Fang, N. T. N. Phan, A. G. Ewing, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 11499–11503;
- 6bK. Liu, R. Liu, D. Wang, R. Pan, H.-Y. Chen, D. Jiang, CCS Chemistry 2023, 5, 1285–1292;
- 6cM. Shin, B. J. Venton, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207399; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202207399;
- 6dX. Li, L. Ren, J. Dunevall, D. Ye, H. S. White, M. A. Edwards, A. G. Ewing, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3010–3019;
- 6eF. Wu, P. Yu, L. Mao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 62, e202208872; Angew. Chem. 2022, 135, e202208872;
- 6fY. T. Qi, H. Jiang, W. T. Wu, F. L. Zhang, S. Y. Tian, W. T. Fan, Y. L. Liu, C. Amatore, W. H. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9723–9733;
- 6gR. Pan, M. Xu, D. Jiang, J. D. Burgess, H. Y. Chen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11436–11440.
- 7
- 7aH. Cheng, P. Yu, X. Lu, Y. Lin, T. Ohsaka, L. Mao, Analyst 2013, 138, 179–185;
- 7bH. Zhou, J. H. Park, F. R. Fan, A. J. Bard, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13212–13215.
- 8
- 8aF. Zhao, Y. Liu, H. Dong, S. Feng, G. Shi, L. Lin, Y. Tian, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10426–10430; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 10512–10516;
- 8bW. Liu, H. Dong, L. Zhang, Y. Tian, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16328–16332; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 16546–16550;
- 8cJ. Moon, Y. Ha, M. Kim, J. Sim, Y. Lee, M. Suh, Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8942–8948.
- 9T. Xiao, X. Li, H. Wei, W. Ji, Q. Yue, P. Yu, L. Mao, Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13783–13789.
- 10
- 10aH. Wei, L. Li, J. Jin, F. Wu, P. Yu, F. Ma, L. Mao, Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10177–10182;
- 10bX. Liu, T. Xiao, F. Wu, M. Y. Shen, M. Zhang, H. H. Yu, L. Mao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11802–11806; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 11964–11968;
- 10cM. J. Russo, M. Han, P. E. Desroches, C. S. Manasa, J. Dennaoui, A. F. Quigley, R. M. I. Kapsa, S. E. Moulton, R. M. Guijt, G. W. Greene, S. M. Silva, ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1482–1507;
- 10dY. Li, R. Han, M. Chen, X. Yang, Y. Zhan, L. Wang, X. Luo, Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14351–14357.
- 11
- 11aE. Zdrachek, E. Bakker, Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7591–7599;
- 11bL. Zhao, Y. Jiang, H. Wei, Y. Jiang, W. Ma, W. Zheng, A. M. Cao, L. Mao, Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4421–4428;
- 11cL. Zhao, Y. Jiang, J. Hao, H. Wei, W. Zheng, L. Mao, Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 1414–1420;
- 11dE. Zdrachek, T. Forrest, E. Bakker, Anal. Chem. 2021, 94, 612–617.
- 12
- 12aM. R. Filipovic, J. Zivanovic, B. Alvarez, R. Banerjee, R. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1253–1337;
- 12bM. S. Vandiver, B. D. Paul, R. Xu, S. Karuppagounder, F. Rao, A. M. Snowman, H. S. Ko, Y. I. Lee, V. L. Dawson, T. M. Dawson, N. Sen, S. H. Snyder, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1626.
- 13
- 13aT. Feng, W. Ji, Y. Zhang, F. Wu, Q. Tang, H. Wei, L. Mao, M. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 23445–23449; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 23651–23655;
- 13bA. Balabiyev, N. P. Podolnikova, J. A. Kilbourne, D. P. Baluch, D. Lowry, A. Zare, R. Ros, M. J. Flick, T. P. Ugarova, Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121087;
- 13cY. Yin, H. Zeng, H. Wang, M. Zhang, Langmuir 2023, 39, 1719–1729.
- 14L. Zhang, J. Sha, R. Chen, Q. Liu, J. Liu, J. Yu, H. Zhang, C. Lin, W. Zhou, J. Wang, Appl. Catal. B. 2020, 271, 118920.
- 15G. G. Somjen, Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1065–1096.
- 16A. Shatillo, R. A. Salo, R. Giniatullin, O. H. Grohn, Neuropharmacology 2015, 93, 164–170.
- 17
- 17aS. S. El-Sayed, R. M. Shahin, A. Fahmy, S. M. Elshazly, Life Sci. 2021, 287, 120144;
- 17bM. Adel, H. R. H. Elsayed, M. El-Nablaway, S. Hamed, A. Eladl, S. Fouad, E. M. El Nashar, M. L. Al-Otaibi, M. R. Rabei, Cells 2022, 11, 2500;
- 17cT. Morikawa, M. Kajimura, T. Nakamura, T. Hishiki, T. Nakanishi, Y. Yukutake, Y. Nagahata, M. Ishikawa, K. Hattori, T. Takenouchi, T. Takahashi, I. Ishii, K. Matsubara, Y. Kabe, S. Uchiyama, E. Nagata, M. M. Gadalla, S. H. Snyder, M. Suematsu, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 1293–1298.
- 18N. Zhou, R. L. Rungta, A. Malik, H. Han, D. C. Wu, B. A. MacVicar, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1582–1594.
- 19
- 19aK. R. Olson, Antioxid. Redox Signaling 2015, 22, 377–397;
- 19bK. R. Olson, R. A. Dombkowski, M. J. Russell, M. M. Doellman, S. K. Head, N. L. Whitfield, J. A. Madden, J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 4011–4023.
- 20
- 20aR. E. Carter, I. Aiba, R. M. Dietz, C. T. Sheline, C. W. Shuttleworth, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 31, 1073–1084;
- 20bM. Lauritzen, J. P. Dreier, M. Fabricius, J. A. Hartings, R. Graf, A. J. Strong, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 31, 17–35;
- 20cK. Zuhra, F. Augsburger, T. Majtan, C. Szabo, Biomol. Eng. 2020, 10, 697;
- 20dC. Szabo, A. Papapetropoulos, E. H. Ohlstein, Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 497–564.