High-nuclearity Luminescent Lanthanide Nanocages for Tumor Drug Delivery
Dr. Shi-Qing Wang
College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Carbon Materials, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, 325035 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yili Wang
Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Tissue Repair Materials, Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wenzhou, 325035 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xiaoping Yang
College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Carbon Materials, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, 325035 China
Search for more papers by this authorYong Liu
Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Tissue Repair Materials, Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wenzhou, 325035 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Huaqiong Li
Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Tissue Repair Materials, Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wenzhou, 325035 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhi Yang
College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Carbon Materials, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, 325035 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Wei-Yin Sun
State Key Laboratory of Coordination Chemistry, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing National Laboratory of Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jonathan L. Sessler
Department of Chemistry, The University of Texas at Austin, 105 E. 24th Street—A5300, Austin, Texas, 78712-1224 United States
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shi-Qing Wang
College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Carbon Materials, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, 325035 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yili Wang
Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Tissue Repair Materials, Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wenzhou, 325035 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xiaoping Yang
College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Carbon Materials, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, 325035 China
Search for more papers by this authorYong Liu
Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Tissue Repair Materials, Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wenzhou, 325035 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Huaqiong Li
Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Tissue Repair Materials, Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wenzhou, 325035 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhi Yang
College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Carbon Materials, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, 325035 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Wei-Yin Sun
State Key Laboratory of Coordination Chemistry, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing National Laboratory of Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jonathan L. Sessler
Department of Chemistry, The University of Texas at Austin, 105 E. 24th Street—A5300, Austin, Texas, 78712-1224 United States
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
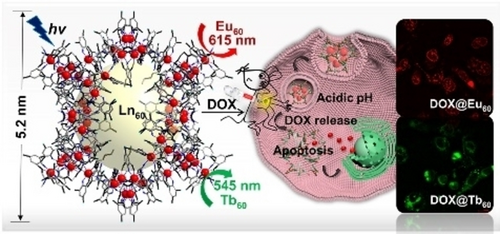
Two 60-metal lanthanide nanocages (Ln60, Ln=Eu and Tb) constructed from Schiff base ligands were used as molecular drug delivery agents (DOX@Ln60, DOX=doxorubicin). They provided for effective tumor therapy in a murine model with negligible side effects. Moreover, DOX@Ln60 proved luminescent and efficiently internalized by breast cancer cells, allowing these cells to be readily visualized.
Abstract
There is an unmet need for easy-to-visualize drug carriers that can deliver therapeutic cargoes deep into solid tumors. Herein, we report the preparation of ultrasmall luminescent imine-based lanthanide nanocages, Eu60 and Tb60 (collectively Ln60), designed to encapsulate anticancer chemotherapeutics for tumor therapy. The as-prepared nanocages possess large cavities suitable for the encapsulation of doxorubicin (DOX), yielding DOX@Ln60 nanocages with diameters around 5 nm. DOX@Ln60 are efficiently internalized by breast cancer cells, allowing the cells to be visualized via the intrinsic luminescent property of Ln(III). Once internalized, the acidic intracellular microenvironment promotes imine bond cleavage and the release of the loaded DOX. DOX@Ln60 inhibits DNA replication and triggers tumor cell apoptosis. In a murine triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) model, DOX@Ln60 was found to inhibit tumor growth with negligible side effects on normal tissues. It proved more effective than various controls, including DOX and Ln60. The present nanocages thus point the way to the development of precise nanomedicines for tumor imaging and therapy.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202317775-sup-0001-Eu60.cif58.8 KB | Supporting Information |
| anie202317775-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf13.7 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202317775-sup-0001-Tb-polymer.cif45.5 KB | Supporting Information |
| anie202317775-sup-0001-Tb3.cif71.1 KB | Supporting Information |
| anie202317775-sup-0001-Tb60.cif58.2 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1WHO report on cancer: setting priorities, investing wisely and providing care for all, World Health Organization. 2020, http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330745.
- 2Q. Sun, X. Hou, J. Yang, M. Zhang, Y. Yang, Y. Liu, W. Shen, D. Yin, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55577–55590.
- 3S. Mallakpour, E. Nikkhoo, C. M. Hussain, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 451, 214262.
- 4S. Senapati, A. K. Mahanta, S. Kumar, P. Maiti, Sig. Transduct Target Ther. 2018, 3, 7.
- 5Y. Li, X. Zheng, Q. Chu, Nano Today 2021, 38, 101134.
- 6J. Matsuno, T. Kanamaru, K. Arai, R. Tanaka, J. H. Lee, R. Takahashi, K. Sakurai, S. Fujii, J. Controlled Release 2020, 324, 405–412.
- 7Y. Xue, H. Bai, B. Peng, T. Tieu, J. Jiang, S. Hao, P. Li, M. Richardson, J. Baell, H. Thissen, A. Cifuentes, L. Li, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2022, 12, 2200076.
- 8S. Zhang, B. Peng, Z. Chen, J. Yu, G. Deng, Y. Bao, C. Ma, F. Du, W. C. Sheu, W. T. Kinberly, J. M. Simard, D. Coman, Q. Chen, F. Hyder, J. Zhou, K. N. Sheth, Bio-act. Mater. 2022, 16, 57–65.
- 9R. Kannan, A. Datta, P. Prabakaran, E. Prasad, V. Muthuvijayan, Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 12695–12698.
- 10C. Wang, B. Wang, S. Zou, B. Wang, G. Liu, F. Zhang, Q. Wang, Q. He, L. Zhang, Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5977–5987.
- 11J. He, T. Peng, Y. Peng, L. Ai, Z. Deng, X.-Q. Wang, W. Tan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2699–2703.
- 12P. Moharil, Z. Wan, A. Pardeshi, L. Li, H. Huang, Z. Luo, S. Rathod, Z. Zhang, B. Chen, N. Zhang, C. A. Fernandez, J. Sun, S. Li, Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 12, 1148–1162.
- 13A. Pluen, Y. Boucher, S. Ramanujan, T. D. McKee, T. Gohongi, E. D. Tomaso, E. B. Brown, Y. Izumi, R. B. Campbell, D. A. Berk, R. K. Jain, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4628–4633.
- 14M. C. Heffern, L. M. Matosziuk, T. J. Meade, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4496–4539.
- 15D. T. Thielemann, A. T. Wagner, E. Rösch, D. K. Kölmel, J. G. Heck, B. Rudat, M. Neumaier, C. Feldmann, U. Schepers, S. Bräse, P. W. Roesky, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7454–7457.
- 16X. Yu, K. Yue, I.-F. Hsieh, Y. Li, X.-H. Dong, C. Liu, Y. Xin, H.-F. Wang, A.-C. Shi, G. R. Newkome, R.-M. Ho, E.-Q. Chen, W.-B. Zhang, S. Z. D. Cheng, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10078–10083.
- 17Z.-R. Luo, H.-L. Wang, Z.-H. Zhu, T. Liu, X.-F. Ma, H.-F. Wang, H.-H. Zou, F.-P. Liang, Nat. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 30.
- 18I. Colliard, M. Nyman, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7308–7315.
- 19X.-Y. Li, H.-F. Su, Q.-W. Li, R. Feng, H.-Y. Bai, J. Xu, X.-H. Bu, Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 10290–10294.
- 20L. Qin, G.-J. Zhou, Y.-Z. Yu, H. Nojiri, C. Schröder, R. E. P. Winpenny, Y.-Z. Zheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16405–16411.
- 21X.-Y. Zheng, Y.-H. Jiang, G.-L. Zhuang, D.-P. Liu, H.-G. Liao, X.-J. Kong, L.-S. Zheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18178–18181.
- 22D. Chen, Q. Tang, J. Zou, X. Yang, W. Huang, Q. Zhang, J. Shao, X. Dong, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018, 7, 1701272.
- 23C. D. Phung, T. H. Tran, Y.-Y. Choi, J.-H. Jeong, S. K. Ku, C.-S. Yong, J.-O. Kim, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5999–6010.
- 24X. Yang, S. Wang, Y. Zhang, G. Liang, T. Zhu, L. Zhang, S. Huang, D. Schipper, R. A. Jones, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4630–4637.
- 25K. A. Brown, X. Yang, D. Schipper, J. W. Hall, L. J. DePue, A. J. Gnanam, J. F. Arambula, J. N. Jones, J. Swaminathan, Y. Dieye, J. Vadivelu, D. J. Chandler, E. M. Marcotte, J. L. Sessler, L. I. R. Ehrlichd, R. A. Jones, Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 2667–2675.
- 26X. Yang, D. Schipper, R. A. Jones, L. A. Lytwak, B. J. Holliday, S. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8468–8471.
- 27X. Yang, R. A. Jones, S. Huang, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 273, 63–75.
- 28J. C. G. Bünzli, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2729–2755.
- 29C. Piguet, J. C. G. Bünzli, Chem. Soc. Rev. 1999, 28, 347–358.
- 30J. W. Kang, H. J. Cho, H. J. Lee, H. E. Jin, H. J. Maeng, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 61–71.
- 31X. Sun, G. He, C. Xiong, C. Wang, X. Lian, L. Hu, Z. Li, S. J. Dalgarno, Y.-W. Yang, J. Tian, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 3679–3693.
- 32L. Liu, C. Kong, M. Huo, C. Liu, L. Peng, T. Zhao, Y. Wei, F. Qian, J. Yuan, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 9190–9193.
- 33D. Chen, D. Yang, C. A. Dougherty, W. Lu, H. Wu, X. He, T. Cai, M. E. V. Dort, B. D. Ross, H. Hong, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4315–4327.
- 34H. Peng, X. Zhang, P. Yang, J. Zhao, W. Zhang, N. Feng, W. Yang, J. Tang, Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 1–11.
- 35V. T. Banala, S. Urandur, S. Sharma, M. Sharma, R. P. Shukla, D. Marwaha, S. Gautam, M. Dwivedi, P. R. Mishra, Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2889–2906.
- 36A. Upadhyay, R. Kandi, C. P. Rao, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3321–3330.
- 37D. K. Dey, S. C. Kang, Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 196, 111497.
- 38Y.-C. Yang, Z.-L. Li, T.-Y. Huang, K.-W. Su, C.-Y. Lin, C.-H. Huang, H.-Y. Chen, M.-C. Lu, H.-M. Huang, S.-Y. Lee, J. W. Peng, H.-Y. Lin, P. J. Davis, K. Wang, Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 688607.
- 39C. Qiao, X. Wang, G. Liu, Z. Yang, Q. Jia, L. Wang, R. Zhang, Y. Xia, Z. Wang, Y. Yang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2107791.
- 40D. Wang, D. Wang, I.-W. He, J. Liu, D. Jana, Y. Wu, X. Zhang, C. Qian, Y. Guo, X. Chen, A. K. Bindra, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 26254–26259.
- 41Deposition numbers 2201788 (for Eu60), 2201789 (for Tb60), 2201790 (for Tb3), and 2201791 (for 2D−Tb) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service.