Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Biomimetic Amino Acid Functionalized Phenazine Flow Batteries with Long Lifetime at Near-Neutral pH (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2021)
- Page: 4953
- First Published: 04 January 2021

Aqueous organic redox flow batteries (AORFB) are a promising electrochemical technology for large-scale energy storage. In their Research Article on page 5289, Pan Wang, Yunlong Ji et al. report a biomimetic, ultra-stable AORFB utilizing an amino acid functionalized phenazine (AFP), thus demonstrating the importance of molecular engineering of redox-active organics for robust redox-flow batteries.
Inside Cover: Interaction with Ribosomal Proteins Accompanies Stress Induction of the Anticancer Metallodrug BOLD-100/KP1339 in the Endoplasmic Reticulum (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2021)
- Page: 4954
- First Published: 01 February 2021

A multi-omics approach including proteomics, transcriptomics, and imaging was applied to comprehensively investigate the mode of action of the anticancer ruthenium(III) drug candidate BOLD-100. In their Communication on page 5063, Samuel M. Meier-Menches, Christopher Gerner, and co-workers found the ribosomal proteins RPL10, RPL24, and the transcription factor GTF2I as probable protein targets. They are functionally connected to endoplasmic reticulum stress, a key drug effect of BOLD-100.
Inside Back Cover: Seven-Step Synthesis of All-Nitrogenated Sugar Derivatives Using Sequential Overman Rearrangements (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2021)
- Page: 5569
- First Published: 04 January 2021

All-nitrogenated sugars (ANSs), in which all hydroxy groups in a carbohydrate are replaced with amino groups, are anticipated to be privileged structures with useful biological activities. In their Communication on page 5193, Takaaki Sato, Noritaka Chida, and co-workers report the synthesis, transformation, and biological tests of ANS derivatives. The key to success was a seven-step synthesis of ANSs by a sequential Overman rearrangement enabling formal simultaneous substitution of four or five hydroxy groups in monosaccharides with amino groups.
Back Cover: Potent Trivalent Inhibitors of Thrombin through Hybridization of Salivary Sulfopeptides from Hematophagous Arthropods (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2021)
- Page: 5570
- First Published: 04 February 2021

A novel class of trivalent thrombin inhibitor is reported by Pedro José Barbosa Pereira, Richard J. Payne, and co-workers in their Research Article on page 5348. These inhibitors were rationally designed by hybridizing native sulfopeptide thrombin inhibitors from three different invertebrates: variegin from a bont tick, anophelin from the Anopheles mosquito, and TTI from the tsetse fly. When fused using bidirectional peptide synthesis and peptide ligation technologies the resulting hybrid inhibitors exhibited exquisite potency both in vitro, with femtomolar inhibition constants, and in an in vivo model of thrombosis.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Metal-Free Electrochemical Synthesis of Sulfonamides Directly from (Hetero)arenes, SO2, and Amines
- First Published: 22 February 2021

Electrochemical Synthesis In their Communication on page 5056, Siegfried R. Waldvogel et al. report the metal-free electrochemical synthesis of sulfonamides directly from (hetero)arenes, SO2, and amines.
Frontispiece: A MOF-based Ultra-Strong Acetylene Nano-trap for Highly Efficient C2H2/CO2 Separation
- First Published: 22 February 2021
Metal–Organic Frameworks A MOF-based ultra-strong acetylene nano-trap for highly efficient C2H2/CO2 separation is reported by Zheng Niu, Shengqian Ma et al. in their Research Article on page 5283.
Guest Editorial
Circular Economy
Chemistry 2030: A Roadmap for a New Decade
- Pages: 4956-4960
- First Published: 01 February 2021
This new decade poses many new challenges at many different levels. The SIDE vision for Chemistry 2030 gathers the main recommendations from various organizations and initiatives and provides a roadmap for the advancement of chemistry and to respond to increasingly complex and interconnected challenges.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2021
- Pages: 4962-4984
- First Published: 22 February 2021
Minireviews
Biosensors
Binary (Split) Light-up Aptameric Sensors
- Pages: 4988-4999
- First Published: 24 March 2020
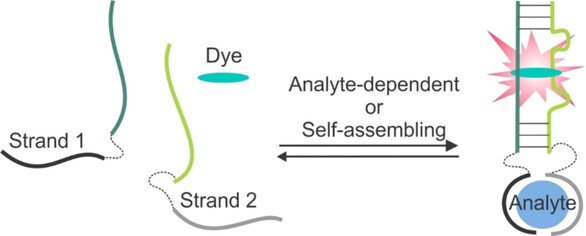
Binary light-up aptameric sensors (BLAS) consist of two RNA or DNA strands and a fluorogenic organic dye added as a buffer component. When associated, the two strands form a dye-binding site, followed by an increase in fluorescence of the aptamer-bound dye. This Minireview summarizes the state of the art in BLAS development and outlines perspectives and applications.
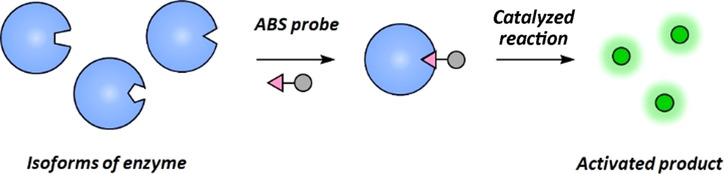
Activity-Based Sensing
Advances in Activity-Based Sensing Probes for Isoform-Selective Imaging of Enzymatic Activity
- Pages: 5000-5009
- First Published: 09 April 2020
Reviews
Metal–Organic Frameworks
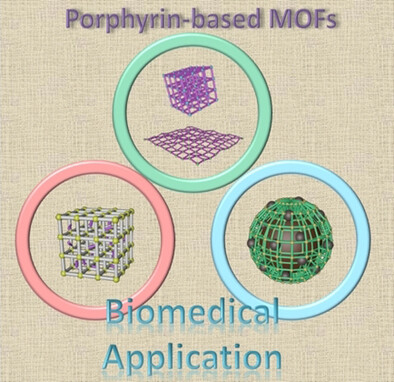
Porphyrin-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Biomedical Applications
- Pages: 5010-5035
- First Published: 27 January 2020
Solar Cells
Performance-Enhancing Approaches for PEDOT:PSS-Si Hybrid Solar Cells
- Pages: 5036-5055
- First Published: 15 December 2019
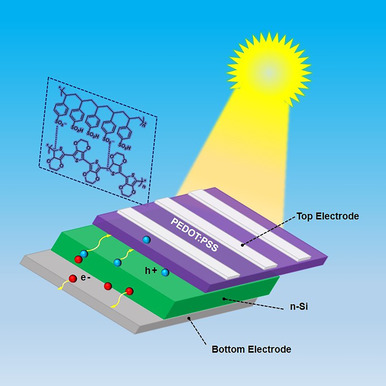
This Review describes approaches to improve the performance of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cells. The main strategies include modifying PEDOT:PSS, optimizing the light-trapping effect, passivating the silicon surface, inserting an interface layer, and improving the back contact and the transparent conductive electrode.
Communications
Electrochemistry | Hot Paper
Metal-Free Electrochemical Synthesis of Sulfonamides Directly from (Hetero)arenes, SO2, and Amines
- Pages: 5056-5062
- First Published: 28 December 2020
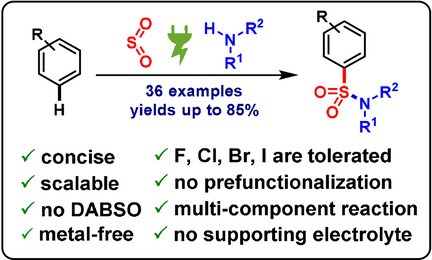
A convergent single-step synthesis of sulfonamides directly from (hetero)arenes, SO2, and amines by electrochemical C−H activation is presented. No prefunctionalization of the aromatic compound is required and halogen substituents are tolerated. The in situ formation of the amidosulfinate species serves a dual role as nucleophile and supporting electrolyte.
Bioinorganic Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Interaction with Ribosomal Proteins Accompanies Stress Induction of the Anticancer Metallodrug BOLD-100/KP1339 in the Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Pages: 5063-5068
- First Published: 25 December 2020
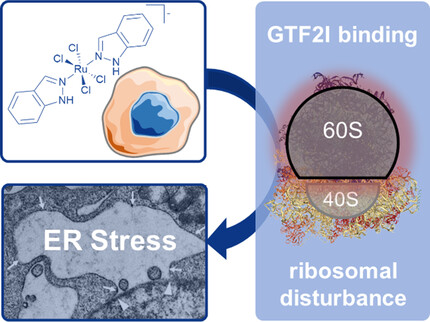
Multi-omics analysis, including affinity proteomics, revealed that the anticancer drug candidate BOLD-100/KP1339 may target the ribosomal proteins RPL10/RPL24 and GTF2I. Swelling of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the observation of polyribosomes using imaging techniques indicate that BOLD-100 treatment may not only inhibit proliferation, but also lead to a functional disturbance of the ER.
Organocatalysis
A Bidentate Iodine(III)-Based Halogen-Bond Donor as a Powerful Organocatalyst
- Pages: 5069-5073
- First Published: 20 November 2020
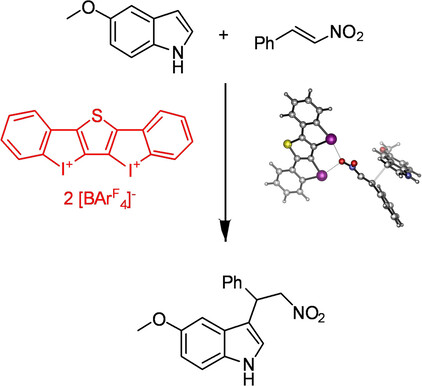
The first application of a bidentate iodine(III)-based halogen bond donor as organocatalyst is presented. In three benchmark reactions, it markedly outperforms “classical” iodine(I)-based noncovalent organocatalysts. The bidentate mode of activation as well as the crucial relevance of halogen bonding are confirmed by comparison experiments.
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction | Very Important Paper
[Mo3S13]2− as a Model System for Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis by MoSx: Probing Protonation Sites in the Gas Phase by Infrared Multiple Photon Dissociation Spectroscopy
- Pages: 5074-5077
- First Published: 17 December 2020
![[Mo3S13]2− as a Model System for Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis by MoSx: Probing Protonation Sites in the Gas Phase by Infrared Multiple Photon Dissociation Spectroscopy](/cms/asset/454af020-20ee-4bfd-af59-cdbdd7d1ca69/anie202014449-toc-0001-m.jpg)
The cluster compound [Mo3S13]2− is an interesting model system for hydrogen evolution catalysis. Herein, we probe the protonation site of the cluster by coupling mass spectrometry with infrared action spectroscopy. One distinct band at 2450 cm−1 together with DFT calculations and IRMPD kinetics reveals the nature of this S−H stretching vibration.
Surface Chemistry | Hot Paper
Charge-Promoted Self-Metalation of Porphyrins on an Oxide Surface
- Pages: 5078-5082
- First Published: 27 November 2020
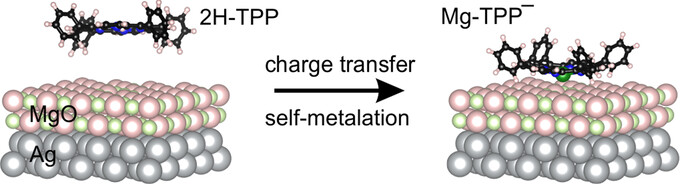
The self-metalation of 2H-tetraphenylporphyrin on the surface of MgO is believed to be feasible only at defect sites. It is shown that this reaction is promoted by charge transfer and does not necessarily require the presence of defects. Using ultrathin MgO films as substrate and tuning its work function allows the charge and metalation state of the adsorbed molecules to be controlled.
Stroke Therapy
Ultrasound Controlled Anti-Inflammatory Polarization of Platelet Decorated Microglia for Targeted Ischemic Stroke Therapy
- Pages: 5083-5090
- First Published: 01 December 2020
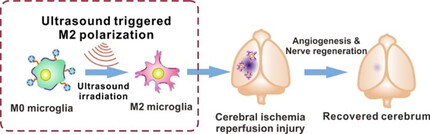
To realize on-demand microglia polarization for controllable ischemic stroke therapy, a sono-sensitive hybrid microglia machine was prepared. Platelet membrane fused microglia have strong accumulation in cerebral vascular injury and can specifically polarize to anti-inflammatory phenotypes, upon external control by ultrasound irradiation, for angiogenesis and nerve regeneration, leading to survival and behavioral improvement of the stroke mice.
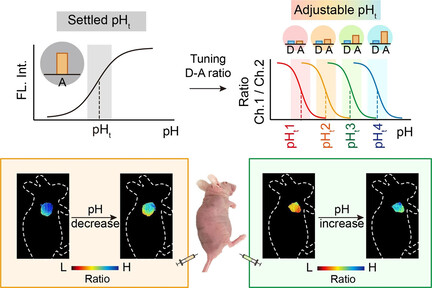
Imaging Agents | Hot Paper
NIR-II pH Sensor with a FRET Adjustable Transition Point for In Situ Dynamic Tumor Microenvironment Visualization
- Pages: 5091-5095
- First Published: 10 December 2020
Organocatalysis | Hot Paper
Enantio- and Diastereoselective Nucleophilic Addition of N-tert-Butylhydrazones to Isoquinolinium Ions through Anion-Binding Catalysis
- Pages: 5096-5101
- First Published: 12 October 2020
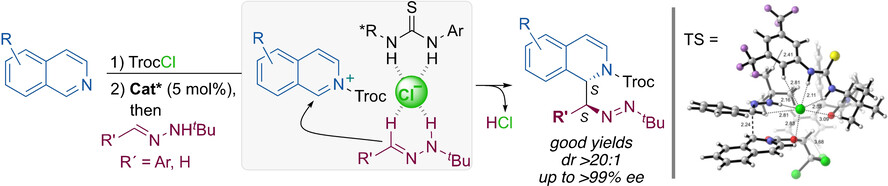
The ability of the chloride anion to simultaneously bind a thiourea catalyst and a hydrazone nucleophile results in a highly ordered termolecular transition structure stabilized by a cooperative set of noncovalent interactions, ultimately resulting in an exquisite stereocontrol in the dearomatization of isoquinolines.
Organocatalysis
N,N-Dialkylhydrazones as Versatile Umpolung Reagents in Enantioselective Anion-Binding Catalysis
- Pages: 5102-5107
- First Published: 11 December 2020
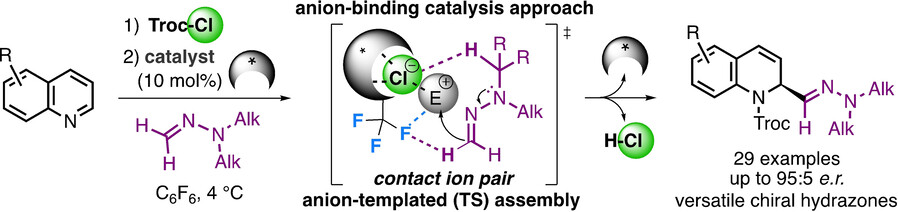
Networking for success: N,N-Dialkylhydrazones have been identified as versatile nucleophiles with multiple-networking ability to enable self-assembled chiral contact ion pair complexation for enantioselective anion-binding catalysis. The resulting network of highly ordered noncovalent interactions with the anion as a central template motif led to high enantiomeric induction in a model Reissert-type reaction with quinolines (see scheme).
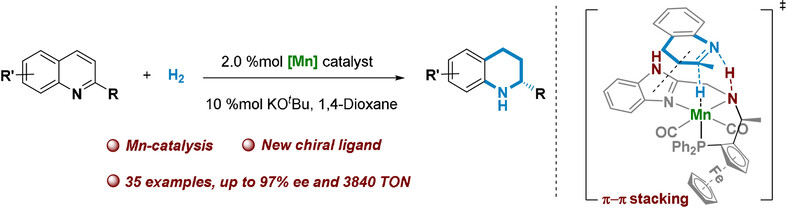
Hydrogenation | Hot Paper
Manganese-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Quinolines Enabled by π–π Interaction
- Pages: 5108-5113
- First Published: 25 November 2020
Sodium Ion Batteries | Hot Paper
MgO-Template Synthesis of Extremely High Capacity Hard Carbon for Na-Ion Battery
- Pages: 5114-5120
- First Published: 09 December 2020
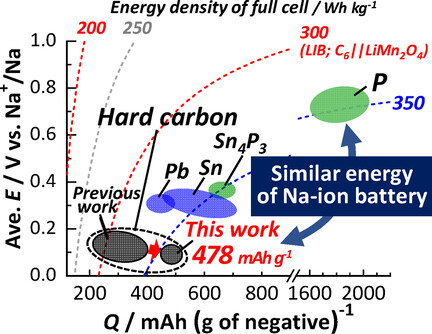
Mg-templated hard carbon as an extremely high capacity negative electrode material for Na-ion batteries is successfully synthesized by heating a freeze-dried mixture of magnesium gluconate and glucose. The hard carbon demonstrates an extraordinarily large reversible capacity of 478 mAh g−1 with a high Coulombic efficiency of 88 % at the first cycle. Owing to the low potential operation, estimated energy density of the full cell is very high.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
Role of Pyridinic Nitrogen in the Mechanism of the Oxygen Reduction Reaction on Carbon Electrocatalysts
- Pages: 5121-5124
- First Published: 10 November 2020
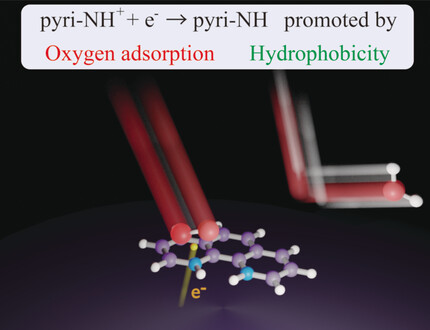
In N-doped carbon catalysts, pyridinic nitrogen (pyri-N) provides active sites for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The roles of pyri-N in the ORR mechanism were investigated using pyri-N-containing molecules as model catalysts. In acidic media, pyri-N species were protonated to pyri-NH+ and then reduced upon the simultaneous thermal adsorption of O2. The reduction was accelerated by hydrophobic environments.
Imaging | Hot Paper
Multimodal Imaging of Autofluorescent Sites Reveals Varied Chemical Speciation in SSZ-13 Crystals
- Pages: 5125-5131
- First Published: 17 December 2020
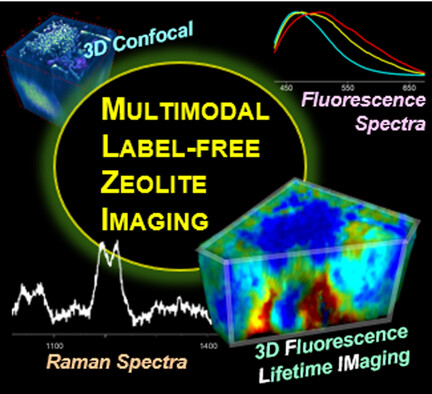
A multimodal imaging study of chabazite is used to analyse emissive deposits. A notable difference is seen in the morphology of agglomerated surface deposits and larger subsurface deposits. Comparison of the distribution of organic residue throughout the crystal volume and XRF mapping is demonstrating that a fluorescence-based technique can also be used to indirectly comment on the compositional chemistry of the inorganic framework.
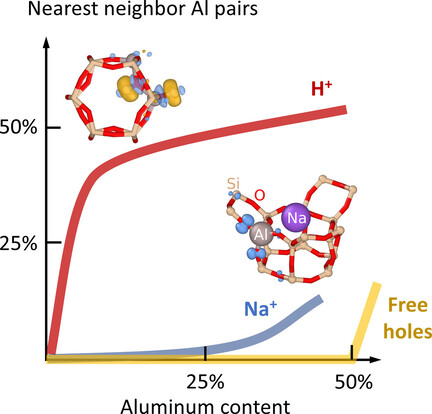
Catalysis | Hot Paper
To Every Rule There is an Exception: A Rational Extension of Loewenstein's Rule
- Pages: 5132-5135
- First Published: 14 December 2020
C−H Activation | Hot Paper
Enantioselective Pd0-Catalyzed C(sp2)–H Arylation for the Synthesis of Chiral Warped Molecules
- Pages: 5136-5140
- First Published: 27 November 2020
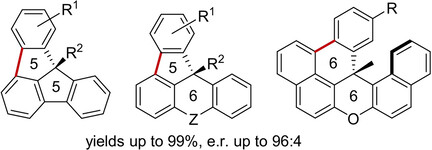
Enantioselective Pd0-catalyzed C(sp2)−H arylation allows the synthesis of warped molecules possessing congested stereocenters. The polycyclic compounds were obtained in high yields and with good to excellent enantioselectivities using chiral bifunctional ligands and could serve to the bottom-up construction of chiral polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Natural Products | Hot Paper
A Concise Total Synthesis of (−)-Berkelic Acid
- Pages: 5141-5146
- First Published: 30 November 2020
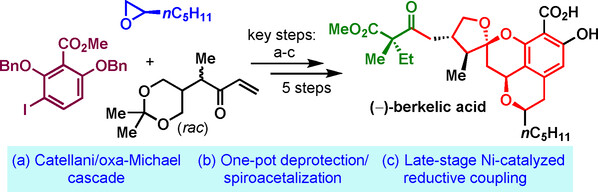
A concise total synthesis of (−)-berkelic acid in eight linear steps was developed. This synthesis features a Catellani reaction/oxa-Michael cascade for the construction of the isochroman scaffold, a one-pot deprotection/spiroacetalization operation for the formation of tetracyclic core structure, and a late-stage Ni-catalyzed reductive coupling for the introduction of the lateral chain.
Multicomponent Reactions | Hot Paper
Triazenyl Alkynes as Versatile Building Blocks in Multicomponent Reactions: Diastereoselective Synthesis of β-Amino Amides
- Pages: 5147-5151
- First Published: 07 December 2020
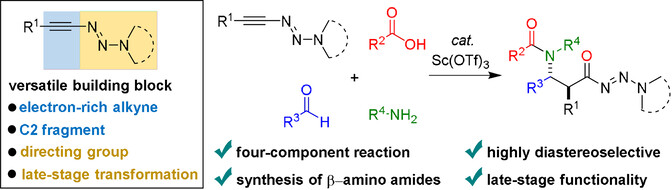
Triazenyl alkynes serve as versatile building blocks in multicomponent reactions for diastereoselective synthesis of β-amino amides. The alkyne moiety acts as C2 fragment and the triazene group serves as directing group to modulate the transition state thus to achieve both chemical reactivity and diastereoselectivity. The triazene group also enables late-stage transformation. Diverse β-amino amides were rapidly assembled in an operationally simple and atom-economic process.
Optoelectronic Materials
Cationic Boron Formazanate Dyes
- Pages: 5152-5156
- First Published: 20 November 2020
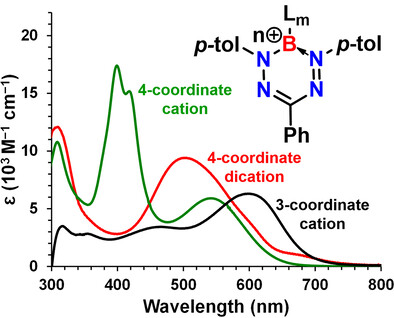
Optoelectronic properties of boron formazanate dyes are usually tuned by varying the substituents of the formazan moiety. We show that the wavelength and type of the lowest-energy electronic excitation of these compounds can also be modulated through variation of the charge, coordination number, and supporting ligands at the cationic boron atom.
Nanomedicine
High-Preservation Single-Cell Operation through a Photo-responsive Hydrogel-Nanopipette System
- Pages: 5157-5161
- First Published: 26 November 2020
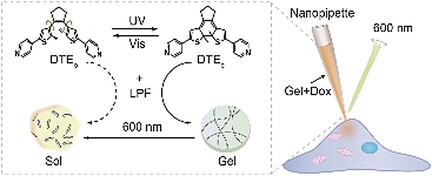
The fabrication of photo-responsive hydrogel-nanopipette system ensures both precision single-cell operation and high cell preservation. Upon light-controlled, non-invasive operation, a high cell viability over 90 % as well as precise quantification of injection are obtained. Hence, a single-cell precise-dosing is achieved with a minimum lethal dose of 163–217 fg cell−1.
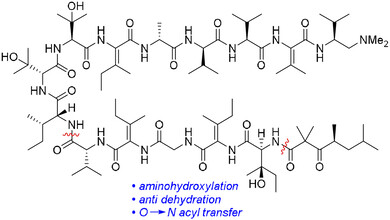
Peptide Synthesis
Dyes
A Fluorinated Carbanionic Substituent for Improving Water Solubility and Lipophilicity of Fluorescent Dyes
- Pages: 5168-5172
- First Published: 27 November 2020

A fluorinated carbanionic substituent enhanced both water solubility and lipophilicity of organic fluorescence dyes, including BODIPYs, fluorescein, and aminocoumarin, without impairing the photophysical properties of the parent fluorophores. Considering that incorporation of conventional ionic substituents reduces the lipophilicity, the present carbanion structure is a new and promising candidate to tune such macroscopic properties.
Protein Aggregation
Photoresponsive Prion-Mimic Foldamer to Induce Controlled Protein Aggregation
- Pages: 5173-5178
- First Published: 12 November 2020
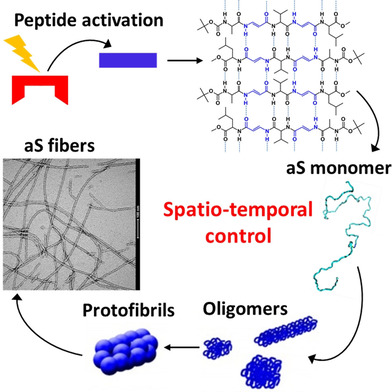
A photo-responsive prion-like foldamer is designed to act as spatio-temporal molecular template, which can be activated by selective photo-irradiation without changing other experimental conditions. It is able to induce a fast transition to the β-sheet conformation for aS monomers that undergo fibrillar polymerization. This method allows the study of protein aggregation relevant to misfolding diseases.
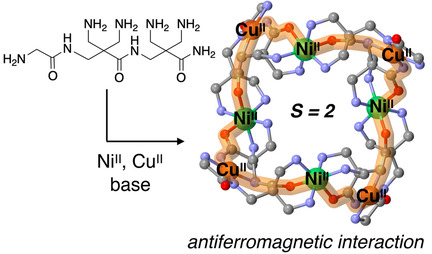
Heterometallic Complexes
Cyclic Heterometallic Interactions formed from a Flexible Tripeptide Complex Showing Effective Antiferromagnetic Spin Coupling
- Pages: 5179-5183
- First Published: 18 November 2020
Perovskites
Chemical Control of Spin-Orbit Coupling and Charge Transfer in Vacancy-Ordered Ruthenium(IV) Halide Perovskites
- Pages: 5184-5188
- First Published: 27 November 2020
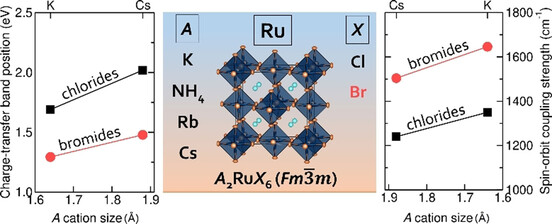
Vacancy-ordered double perovskites, A2RuCl6 and A2RuBr6, were studied. The synthesis, crystal structures, and optical and magnetic properties of the materials were determined. Differences in the halide and the A cation size influence the charge-transfer spectra. On the basis of temperature-dependent magnetic moments, accurate values were estimated for the spin-orbit coupling constants of the RuIV d4 ion.
C–H Activation
Palladium-Catalyzed Site-Selective [3+2] Annulation via Benzylic and meta C−H Bond Activation
- Pages: 5189-5192
- First Published: 25 November 2020
Sugar Chemistry | Hot Paper
Seven-Step Synthesis of All-Nitrogenated Sugar Derivatives Using Sequential Overman Rearrangements
- Pages: 5193-5198
- First Published: 30 November 2020
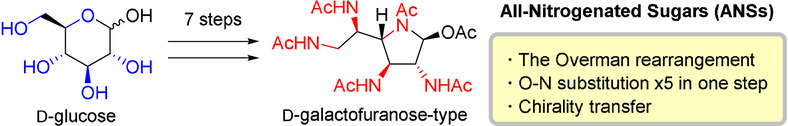
Concise synthesis of all-nitrogenated sugar derivatives was achieved in seven steps from commercially available monosaccharides. The sequential Overman rearrangement enabled formal simultaneous substitution of four or five hydroxy groups in the monosaccharides with amino groups. A variety of ANSs were available by the same synthetic route starting from different carbohydrates. Transformation and biological activities of ANS derivatives were also reported.
Heterocycles
Catalyst-Free Synthesis of O-Heteroacenes by Ladderization of Fluorinated Oligophenylenes
- Pages: 5199-5203
- First Published: 13 September 2020
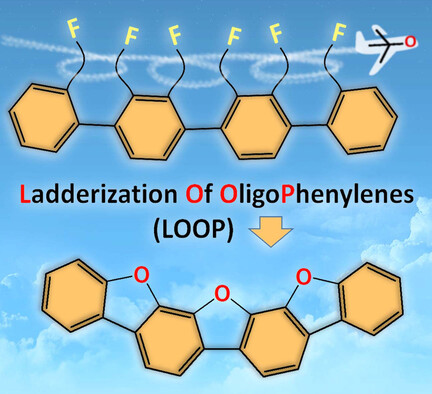
O-heteroacenes are now available by a one-step LOOP reaction by SET-induced SNAr-radical de-tert-butylation-SNAr. tBuOK serves as a reliable oxygen atom source and O2− synthon, enabling synthesis of dibenzofuran, benzoxanthenes, and benzooxepines, and a range of longer ladder-type O-heteroacenes from fluorinated oligophenylenes.
H2 Production
Hydrogen Purification through a Highly Stable Dual-Phase Oxygen-Permeable Membrane
- Pages: 5204-5208
- First Published: 14 September 2020
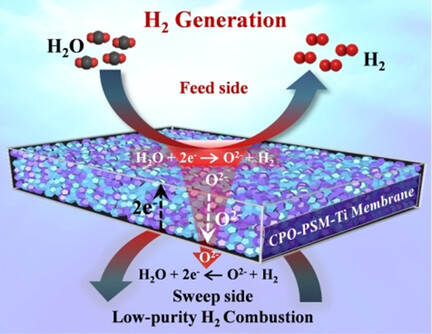
By taking advantages of the high chemical stability and moderate reduction of Ti and Ce ions under reducing atmosphere, a novel Ti-based dual-phase oxygen-permeable membrane was developed for H2 purification. The Ce0.9Pr0.1O2−δ/Pr0.1Sr0.9Mg0.1Ti0.9O3−δ (CPO-PSM-Ti) membrane has excellent chemical stability and mixed oxygen ionic-electronic conductivity under reducing atmospheres.
Biocatalysis
In Vitro Production of Ergothioneine Isotopologues
- Pages: 5209-5212
- First Published: 30 September 2020
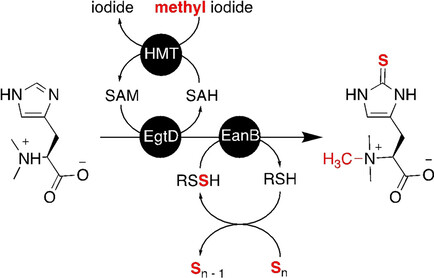
In an enzyme-based approach involving commercial isotope reagents, ergothioneine isotopologues with programmable 2H, 15N, 13C, 34S, and 33S isotope patterns were synthesized (see scheme). Such isotope-labeled ergothioneine derivatives are expected to be useful for deciphering the distribution, function, and metabolism of this compound in vivo. The labeling method is directly applicable to the synthesis of radio-isotopologues.
OLEDs
Multi-Layer π-Stacked Molecules as Efficient Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitters
- Pages: 5213-5219
- First Published: 22 November 2020
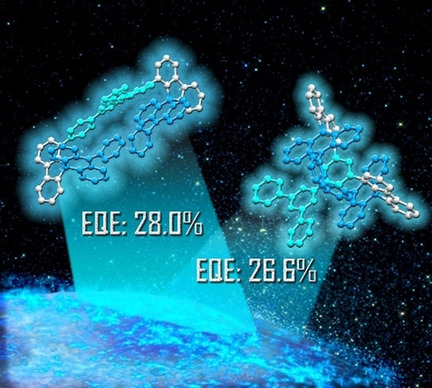
Multi-Layer π-stacked molecules are designed to realize efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescence. Spatially confined molecules with stereochemical structures are constructed in donor/acceptor/donor architectures with different conformations. Their organic light-emitting diode (OLED) devices exhibit high external quantum efficiencies (EQEs) of 28.0 %/26.6 %, respectively.
Photoresponsive Catalysis
A Photoregulated Racemase Mimic
- Pages: 5220-5224
- First Published: 12 November 2020
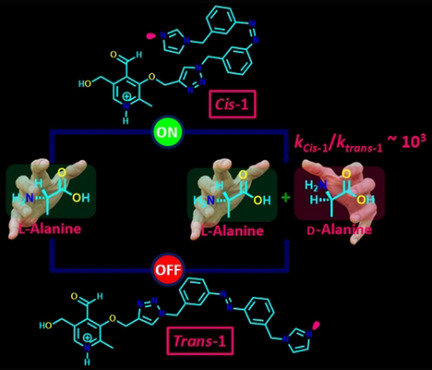
The cis isomer of an azobenzene-based artificial pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) racemase effectively deprotonates and racemizes L-alanine. A histidinyl unit bearing an imidazole group in close proximity to the racemizable Cα-H of the L-alanine aldimine residue is responsible for racemization using light as the stimulus. The trans isomer is less effective in terms of deprotonation and racemization.
Gold Clusters
Atomically Precise Preorganization of Open Metal Sites on Gold Nanoclusters with High Catalytic Performance
- Pages: 5225-5229
- First Published: 01 December 2020
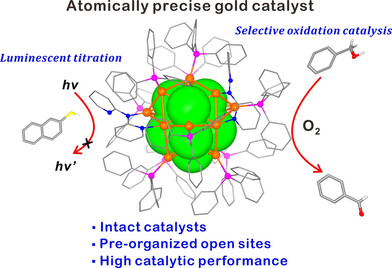
A stable Au23 nanocluster with preorganized open sites has been conducted through surface geometric mismatch strategy. The 35 % accessibility of Au23 was confirmed by luminescent titration with 2-naphthalenethiol. The preorganized open sites make intact Au23 a high-performance catalyst for aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol.
Homogeneous Catalysis
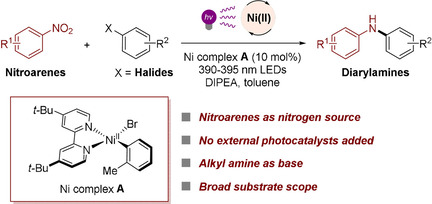
Light-Promoted C–N Coupling of Aryl Halides with Nitroarenes
- Pages: 5230-5234
- First Published: 12 November 2020
Surfactants
Behavior of Smart Surfactants in Stabilizing pH-Responsive Emulsions
- Pages: 5235-5239
- First Published: 30 November 2020
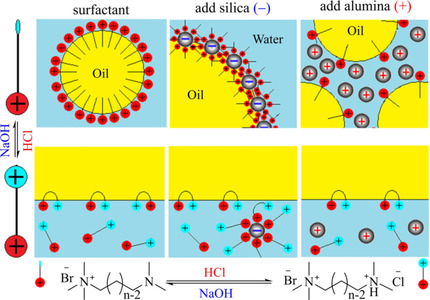
Newly structured smart surfactants, N+-(n)-N, were synthesized with a tertiary amine group at the end of the hydrophobic chain. At neutral and alkaline pH they behave as a cationic surfactant and can stabilize oil-in-water emulsions alone or, together with charged nanoparticles, conventional Pickering, or oil-in-dispersion emulsions. In acidic media they turn to the Bola form, resulting in demulsification, returning into the aqueous phase which is then recycled when triggered by pH change.
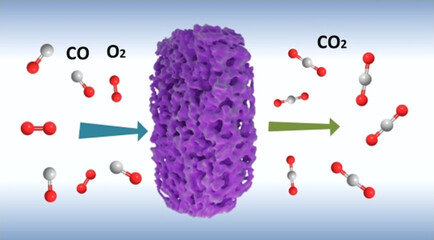
Surface Chemistry
Activating Lattice Oxygen at the Twisted Surface in a Mesoporous CeO2 Single Crystal for Efficient and Durable Catalytic CO Oxidation
- Pages: 5240-5244
- First Published: 27 November 2020
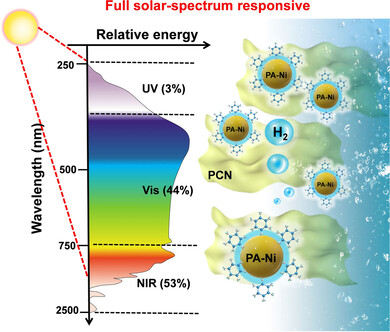
Hydrogen Production
A NIR-Responsive Phytic Acid Nickel Biomimetic Complex Anchored on Carbon Nitride for Highly Efficient Solar Hydrogen Production
- Pages: 5245-5249
- First Published: 27 November 2020
Noble Gas Uptake
Kinetic Barriers and Microscopic Mechanisms of Noble Gas Adsorption by Nanoporous γ-Mg(BH4)2 Obtained by Means of Sub-Second X-Ray Diffraction
- Pages: 5250-5256
- First Published: 16 November 2020
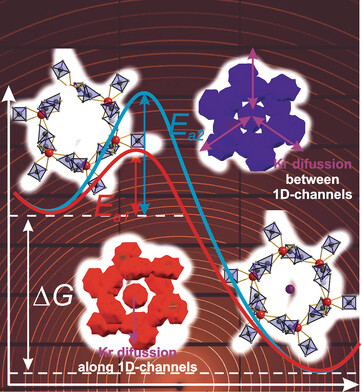
The sub-second crystal structure analysis of noble gas uptake by nanoporous γ-Mg(BH4)2 sheds light on its diffusion mechanisms and activation barriers. It resolves two kinetic barriers for noble gas adsorption: one with diffusion along the 1D channels and the other by diffusion between the channels via a smaller aperture.
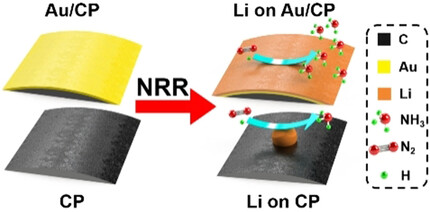
Electrocatalysis
Domino Effect: Gold Electrocatalyzing Lithium Reduction to Accelerate Nitrogen Fixation
- Pages: 5257-5261
- First Published: 29 November 2020
Arylation Reactions | Hot Paper
Fast Enantio- and Chemoselective Arylation of Ketones with Organoboronic Esters Enabled by Nickel/N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis
- Pages: 5262-5267
- First Published: 26 November 2020
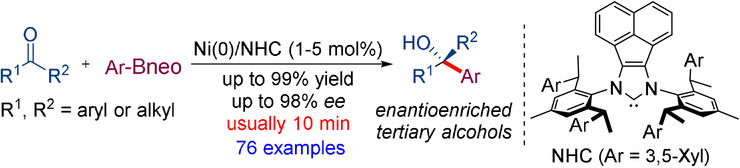
A method for general asymmetric addition of arylborons to simple ketones is reported, which is enabled by nickel/N-heterocyclic carbene catalysis. Chiral tertiary alcohols are furnished with high efficiency and excellent levels of enantio- and chemocontrol, and the method offers a broad substrate scope.
Asymmetric Organocatalysis
Asymmetric Synthesis of Hydroquinolines with α,α-Disubstitution through Organocatalyzed Kinetic Resolution
- Pages: 5268-5272
- First Published: 04 December 2020
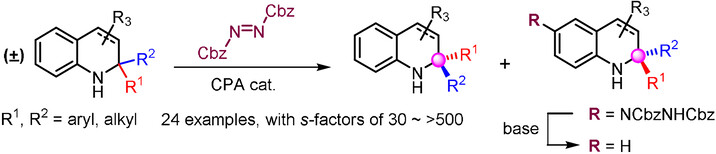
The first kinetic resolution of hydroquinoline derivatives with α,α-disubstitution was realized through organocatalyzed asymmetric remote aminations with azodicarboxylates, which represents a powerful protocol for asymmetric synthesis of N-heterocycles with α-quaternary stereocenters. Mechanistic studies elucidate the reaction mechanisms and highlighted the role of attractive non-covalent interactions between the substrate and catalyst.
Nickel Catalysis
Synthesis of Indanones and Spiroindanones by Diastereoselective Annulation Based on a Hydrogen Autotransfer Strategy
- Pages: 5273-5278
- First Published: 17 November 2020
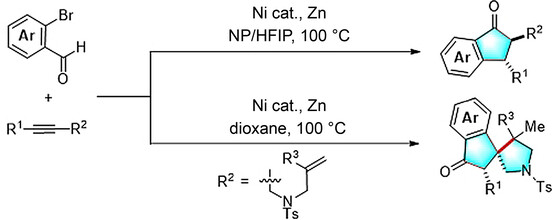
A nickel-catalyzed domino reductive cyclization of alkynes and o-bromoaryl aldehydes provided straightforward access to biologically significant indanones and spiroindanone pyrrolidine derivatives (see scheme). The reaction was found to be tolerant of a variety of functional groups and proceeded in good yields with excellent regio- and diastereoselectivity.
Enantiopure Medicines
Combining Incompatible Processes for Deracemization of a Praziquantel Derivative under Flow Conditions
- Pages: 5279-5282
- First Published: 26 November 2020
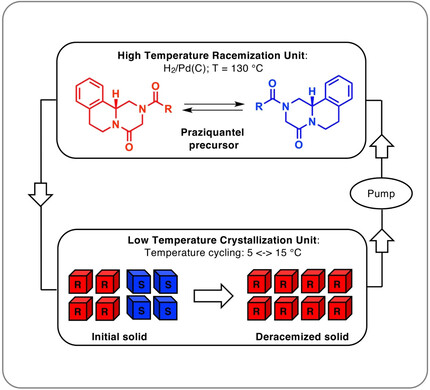
The (R) enantiomer of Praziquantel is more active against schistosomiasis (bilharzia, snail fever). The cheaper, commonly used, racemate can be deracemized via a conglomerate derivative to this enantiomer, which is obtained in 98 % ee using a flow system in which Pd-catalyzed high-temperature racemization is coupled to low-temperature cycled crystallization.
Research Articles
Gas Separation | Hot Paper
A MOF-based Ultra-Strong Acetylene Nano-trap for Highly Efficient C2H2/CO2 Separation
- Pages: 5283-5288
- First Published: 06 January 2021

A new type of ultra-strong C2H2 nano-trap featuring the synergistic effect of multiple open metal sites has been proposed for separating C2H2/CO2 mixture gas. The unique C2H2 nano-trap shows the strongest binding interaction with C2H2 and a benchmark for C2H2/CO2 separation. The binding mechanism for C2H2 was studied through single-crystal X-ray diffraction experiments and molecular simulation studies.
Batteries | Hot Paper
Biomimetic Amino Acid Functionalized Phenazine Flow Batteries with Long Lifetime at Near-Neutral pH
- Pages: 5289-5298
- First Published: 28 November 2020
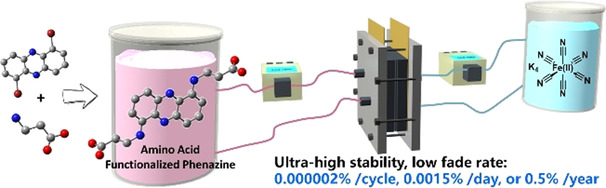
A series of amino acid functionalized phenazines for AORFB negolytes have been synthesized and studied. The 3,3′-(phenazine-1,6-diylbis(azanediyl))dipropionic acid (1,6-DPAP) full cell against a ferrocyanide posolyte with 1.0 M electron concentration has an OCV of 1.15 V and an extremely low capacity fade rate of 0.5 % per year.
Single-Molecule Magnets | Hot Paper
Opening Magnetic Hysteresis by Axial Ferromagnetic Coupling: From Mono-Decker to Double-Decker Metallacrown
- Pages: 5299-5306
- First Published: 20 November 2020
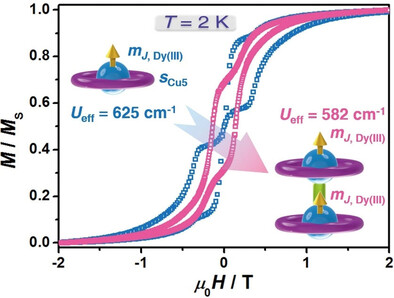
The magnetic hysteresis of a metallacrown magnet opens after introducing axial ferromagnetic by linking two mono-decker Dy[15-MCCu-5] units with a single hydroxide bridge to give the double-decker {Dy[15-MCCu-5]}2 single-molecule magnet in which the anisotropy axes of the two DyIII ions are nearly collinear and the magnetic relaxation times are approximately 200 000 times slower than for the mono-decker unit.
Viruses | Hot Paper
Simultaneous Dual-Gene Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Based on CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Lateral Flow Assay
- Pages: 5307-5315
- First Published: 09 December 2020
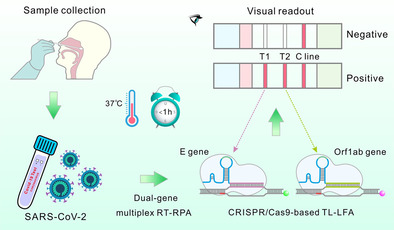
A CRISPR/Cas9-mediated triple-line lateral flow assay was developed and combined with multiplex reverse transcription-recombinase polymerase amplification (RT-RPA) for simultaneous dual-gene diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2. With this platform, the cell-cultured SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA standards, and nasopharyngeal swab clinical samples could be sensitively and specifically detected.
Natural Products Synthesis
Collective Total Synthesis of Casbane Diterpenes: One Strategy, Multiple Targets
- Pages: 5316-5322
- First Published: 08 December 2020

A cornucopia: Sessile soft corals as well as certain higher plants produce a multitude of casbane diterpenes with different oxygenation patterns. A new synthetic approach to this family of natural products (see structural framework) was designed that allows a large subset to be encompassed, yet is short, efficient, and selective. Key to success was a combination of catalytic cyclopropanation, alkyne metathesis, and trans-hydrometalation chemistry.
Structure Elucidation
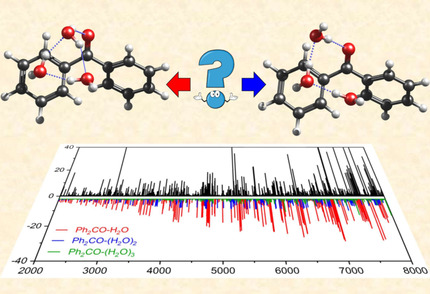
Unlocking the Water Trimer Loop: Isotopic Study of Benzophenone-(H2O)1–3 Clusters with Rotational Spectroscopy
- Pages: 5323-5330
- First Published: 02 December 2020
Cycloaddition | Hot Paper
1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition between Dehydroalanines and C,N-Cyclic Azomethine Imines: Application to Late-Stage Peptide Modification
- Pages: 5331-5338
- First Published: 12 November 2020
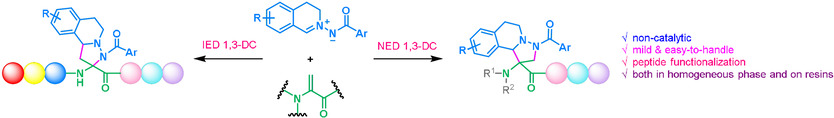
A non-catalytic, mild, and easy-to-handle protecting group switching normal-electron-demand or inverse-electron-demand 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between bi- or mono-N-protected Dha and C,N-cyclic azomethine imines is disclosed and applied in the late-stage peptide modification, labeling, and peptide–drug conjugation.
Cell-Free Synthesis | Hot Paper
Dimer Organization of Membrane-Associated NS5A of Hepatitis C Virus as Determined by Highly Sensitive 1H-Detected Solid-State NMR
- Pages: 5339-5347
- First Published: 18 November 2020
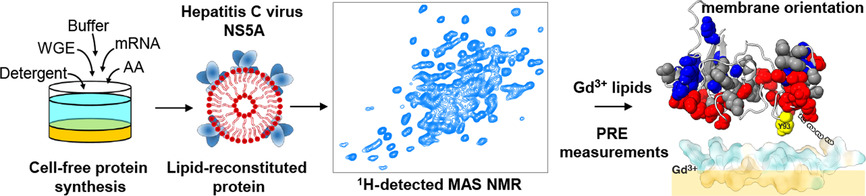
The membrane orientation of the hepatitis C virus NS5A protein was assessed by combining a cell-free protein synthesis approach with highly sensitive 1H-detected solid-state NMR. Insertion of lipids chelated with a paramagnetic Gd3+ ion allowed to orient the protein with respect to its membrane anchor using PRE. This information allowed to propose a model for the interaction of NS5A with a direct acting antiviral.
Peptide Engineering | Hot Paper
Potent Trivalent Inhibitors of Thrombin through Hybridization of Salivary Sulfopeptides from Hematophagous Arthropods
- Pages: 5348-5356
- First Published: 20 December 2020
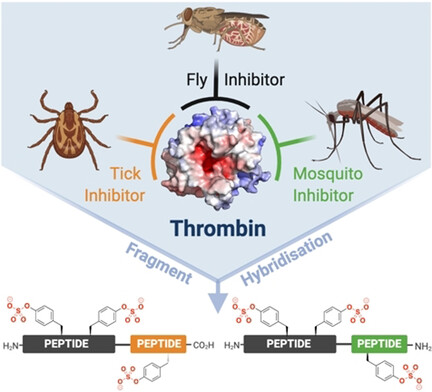
The rational design of a novel class of trivalent thrombin inhibitors is described through the hybridization of natural sulfopeptides produced by blood feeding organisms. The hybrid sulfopeptides were rapidly assembled using peptide ligation chemistry and shown to exhibit femtomolar inhibition constants against thrombin. A lead inhibitor also showed potent inhibition of thrombin generation and platelet aggregation in vitro, as well as antithrombotic effects in a murine model.
Asymmetric Radical Chemistry | Hot Paper
A General Organocatalytic System for Enantioselective Radical Conjugate Additions to Enals
- Pages: 5357-5362
- First Published: 07 December 2020
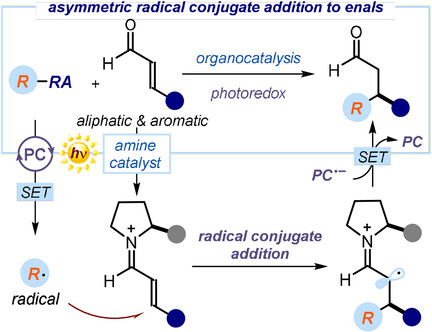
An organocatalytic method for the enantioselective conjugate addition of carbon radicals to aliphatic and aromatic enals is reported. The system imparts consistently high stereoselectivity for the interception of a wide variety of radicals, including highly reactive primary radicals. The protocol also serves to develop radical cascade processes leading to stereochemically dense chiral products in one-step.
Selective Adsorption | Hot Paper
Polymorphism of 2D Imine Covalent Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 5363-5369
- First Published: 27 November 2020
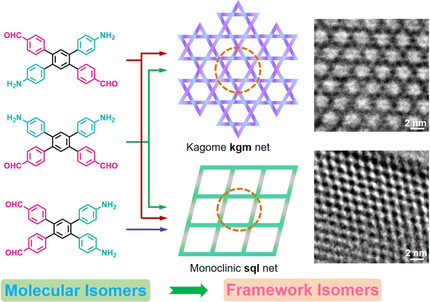
A strategy was developed for selective growth of isomeric covalent organic frameworks by designing monomer isomers and tuning reaction conditions. Three A2B2 type tetraphenyl benzene monomers (p-, m-, and o-TetPB) afford five different 2D TetPB-COF isomers that exhibit selective adsorption of vitamin B12 owing to a great difference in their pore shape and size.
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
Photocatalytic Aerobic Oxidative Ring Expansion of Cyclic Ketones to Macrolactones by Cerium and Cyanoanthracene Catalysis
- Pages: 5370-5376
- First Published: 01 December 2020
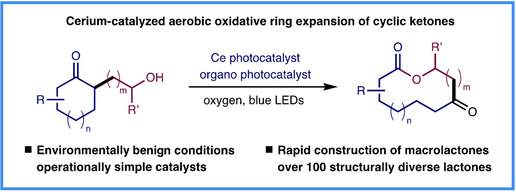
Challenging macrolactones can now be modularly assembled through a photocatalytic aerobic oxidative ring expansion of cyclic ketones. With the assistance of an organophotocatalyst, α-alkoxyketones can be transformed into macrolactones with 20 min of blue LED irradiation, ultimately enabling the rapid assembly of a large collection of structurally diverse lactones.
Nanomedicine | Hot Paper
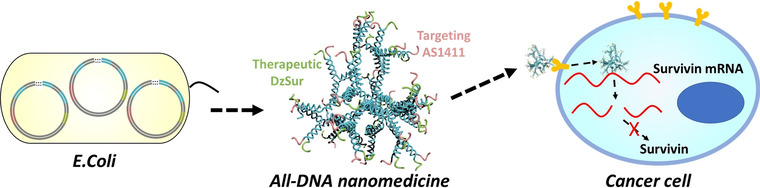
Genetically Encoded and Biologically Produced All-DNA Nanomedicine Based on One-Pot Assembly of DNA Dendrimers for Targeted Gene Regulation
- Pages: 5377-5385
- First Published: 23 November 2020
Photodynamic Immunotherapy | Hot Paper
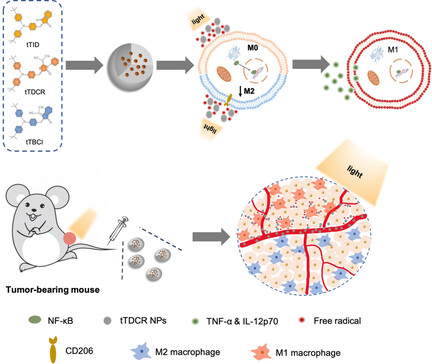
Acceptor Engineering for Optimized ROS Generation Facilitates Reprogramming Macrophages to M1 Phenotype in Photodynamic Immunotherapy
- Pages: 5386-5393
- First Published: 25 November 2020
Cancer Therapy
Bile Acid Tethered Docetaxel-Based Nanomicelles Mitigate Tumor Progression through Epigenetic Changes
- Pages: 5394-5399
- First Published: 30 November 2020
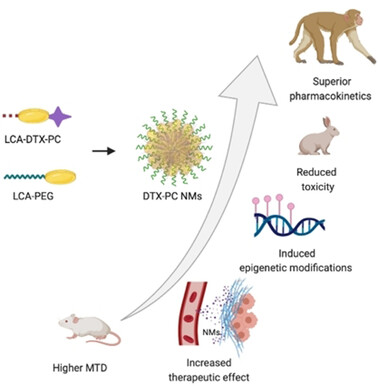
Phosphocholine derivative of docetaxel-conjugated lithocholic acid can form stable sub-100 nm nanomicelles (DTX-PC NMs). DTX-PC NMs exhibit superior tolerance and pharmacokinetics over FDA-approved formulation. DTX-PC NMs can retard tumor progression in murine models and induce upregulation of tumor suppressor genes. Superior pharmacokinetic profiling in non-human primates makes them an ideal platform for clinical applications.
π-Clusters
Synthesis of Anthracene-Based Cyclic π-Clusters and Elucidation of their Properties Originating from Congested Aromatic Planes
- Pages: 5400-5406
- First Published: 20 November 2020
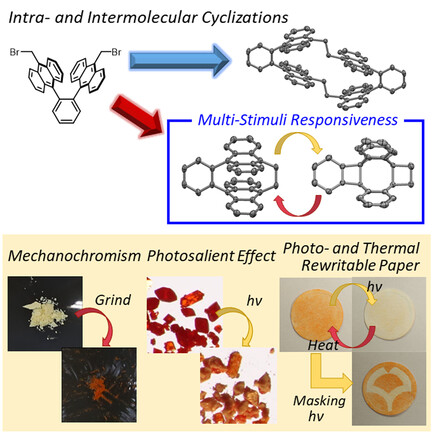
Anthracene-based π-congested cyclic dimer and tetramer were obtained using Ni(cod)2. These cyclic π-clusters exhibit narrow HOMO–LUMO gaps, reflecting the face-to-face distance between the anthracene units. This π-congestion endows the cyclic anthracene dimer with multi-stimuli responsiveness such as photoisomerization and thermal reversion, accompanied by chromism, mechanochromism, and the photosalient effect.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Solvent-Driven Supramolecular Wrapping of Self-Assembled Structures
- Pages: 5407-5413
- First Published: 27 November 2020
Biosynthesis
A Dual Role Reductase from Phytosterols Catabolism Enables the Efficient Production of Valuable Steroid Precursors
- Pages: 5414-5420
- First Published: 30 November 2020
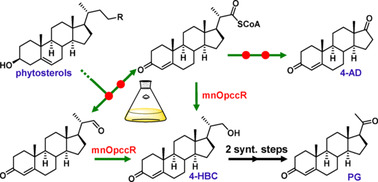
An unusual reductase (mnOpccR) in phytosterol catabolism is found to catalyze the formation of 4-HBC through two different routes. Inactivation or overexpression of mnOpccR leads to exclusive production of 4-androstenedione (4-AD) and 4-HBC from phytosterols. By a two-step synthesis, 4-HBC can be further efficiently converted into progesterone (PG). This work provides two green and economical methods for 4-AD and PG manufacturing.
Biocatalysis
Hierarchically Porous Biocatalytic MOF Microreactor as a Versatile Platform towards Enhanced Multienzyme and Cofactor-Dependent Biocatalysis
- Pages: 5421-5428
- First Published: 30 November 2020
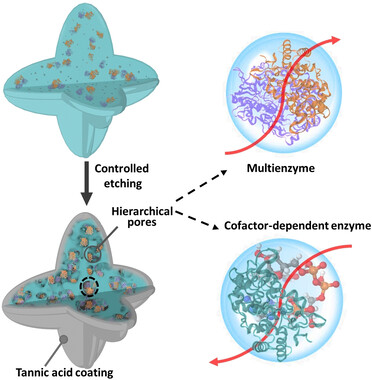
Hierarchically porous biocatalytic MOFs provide sufficient space for accommodation of enzymes to reorientate and spread in their lower surface energy state as well as to decrease the inherent barriers to accelerate the diffusion of reactants and intermediates. The promoted intermolecular correlation of enzymes and MOFs, and polyphenol coating, safeguards the enzymes from inactivation, showcasing their promise for diverse biotechnological applications.
Protein Delivery
Hierarchical Self-assembly of Discrete Metal–Organic Cages into Supramolecular Nanoparticles for Intracellular Protein Delivery
- Pages: 5429-5435
- First Published: 27 November 2020
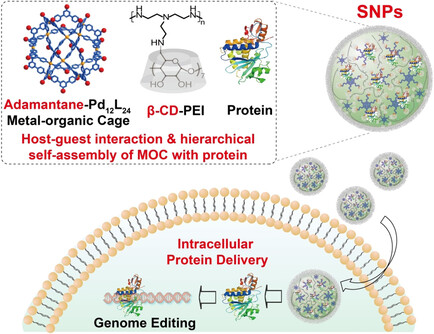
Self-assembly of Ada-MOC and host–guest interaction with β-cyclodextrin-conjugated polyethylenimine (PEI-βCD) affords supramolecular nanoparticles. Hierarchical self-assembly of Ada-MOC and PEI-βCD maintains high efficiency and orthogonality in the presence of protein, enabling protein encapsulation into nanoparticles for intracellular protein delivery for therapeutic application and CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing.
GCase Activators
Novel β-Glucocerebrosidase Activators That Bind to a New Pocket at a Dimer Interface and Induce Dimerization
- Pages: 5436-5442
- First Published: 25 November 2020
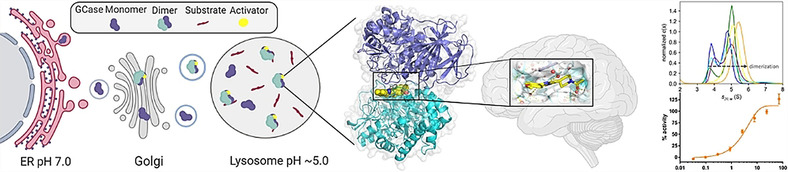
A first crystal structure for a novel GCase activator is obtained and a novel non-inhibitory binding mode at a dimer interface, rationalizing the observed structure–activity relationship, is identified. Mechanistic insights and key information for future drug discovery efforts towards GCase activation are provided.
Batteries
High-Energy Aqueous Magnesium Hybrid Full Batteries Enabled by Carrier-Hosting Potential Compensation
- Pages: 5443-5452
- First Published: 22 November 2020
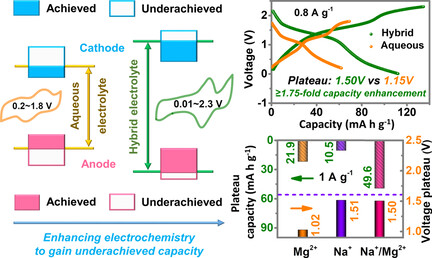
High-energy magnesium hybrid full batteries were built by coupling a Mg1.5VCr(PO4)3 cathode with an FeVO4 anode in an aqueous/organic Mg2+/Na+ hybrid electrolyte. Benefiting from enhanced electrochemistry and carrier-hosting potential compensation, the batteries delivered a high voltage plateau and a capacity that is ≥1.75-fold higher than those in conventional aqueous electrolytes.
Biosensors
DNA Triplex and Quadruplex Assembled Nanosensors for Correlating K+ and pH in Lysosomes
- Pages: 5453-5458
- First Published: 26 November 2020
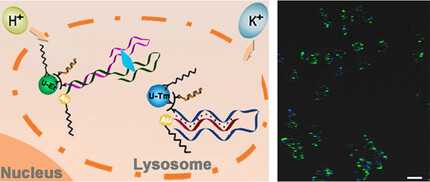
DNA quadruplex and triplex nanosensors are designed for simultaneously monitoring of K+ and pH by assembling upconversion nanoparticle luminophores and gold nanoparticle quenchers. Co-delivery of the two sensors with ATP stimulation indicates lysosomal acidification is accompanied with the efflux of K+.
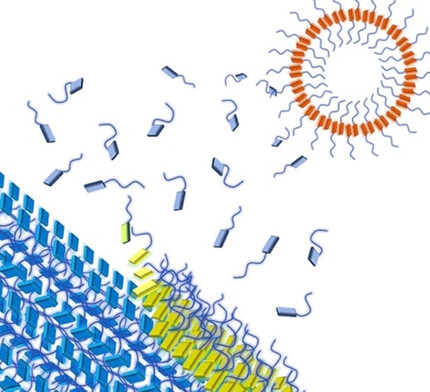
Supramolecular Polymers
Supramolecular Depolymerization in the Mixture of Two Poor Solvents: Mechanistic Insights and Modulation of Supramolecular Polymerization of Ionic π-Systems
- Pages: 5459-5466
- First Published: 28 November 2020
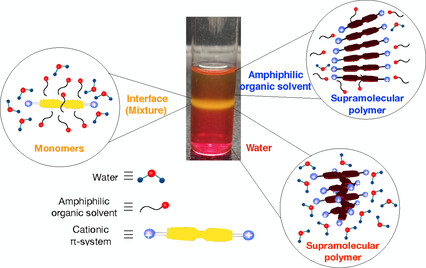
Mixtures of poor solvents are always not poor. Water and amphiphilic organic solvents (poor solvents), that individually promote the supramolecular polymerization of cationic π-systems, readily depolymerize them into monomers in their mixtures (good solvent). Segregation of water and organic solvents around the molecular surface of the π-system is the key for this surprising phenomenon.
Radical–Polar Crossover
Direct C(sp3)−H Trifluoromethylation of Unactivated Alkanes Enabled by Multifunctional Trifluoromethyl Copper Complexes
- Pages: 5467-5474
- First Published: 17 November 2020
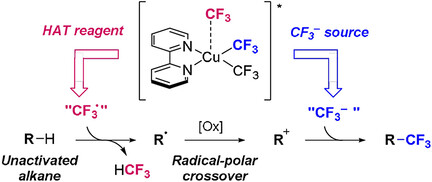
A photoinduced C(sp3)−H trifluoromethylation reaction of alkanes was developed by employing bpyCu(CF3)3 as a multifunctional reagent: photoinduced-reaction initiator, precursor of the hydrogen-atom-transfer reagent, and trifluoromethyl anion source (see scheme). The operatively simple reaction enables the direct, late-stage trifluoromethylation of complex molecules under mild reaction conditions.
Cycloaddition
Low-Temperature Intramolecular [4+2] Cycloaddition of Allenes with Arenes for the Synthesis of Diene Ligands
- Pages: 5475-5481
- First Published: 20 November 2020
![Low-Temperature Intramolecular [4+2] Cycloaddition of Allenes with Arenes for the Synthesis of Diene Ligands](/cms/asset/5ac22815-048d-419e-9472-35c259276c7b/anie202012299-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A highly efficient strategy for the rapid assembly of bicyclooctadienes starting from simple diazo esters and EBX reagents through a one-pot sequential oxyalkynylation/ [4+2] allene-arene cycloaddition reaction at low temperature (23–90 °C) is reported. The obtained products are good chiral ligands for rhodium-catalyzed conjugate addition.
Oxidation | Hot Paper
Oxidation Under Reductive Conditions: From Benzylic Ethers to Acetals with Perfect Atom-Economy by Titanocene(III) Catalysis
- Pages: 5482-5488
- First Published: 27 November 2020
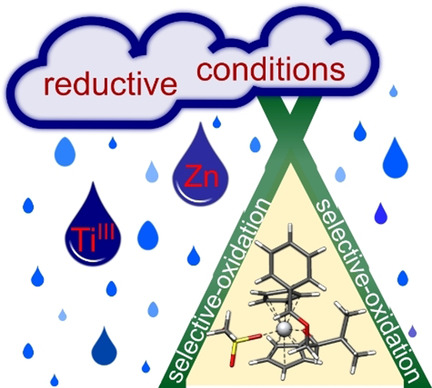
Oxidations with reducing agents? Fact and not fiction in a reaction featuring titanocene(III) catalysis, H-atom transfer, and an organometallic oxygen rebound. Acetals and hemiaminals can be readily prepared from benzylic ethers and amines, respectively, under mild reaction conditions and in high yields. The structures of the radical intermediates were elucidated by the CREST program.
Polymerization Catalysts | Very Important Paper
Porphyrinic Zirconium Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) as Heterogeneous Photocatalysts for PET-RAFT Polymerization and Stereolithography
- Pages: 5489-5496
- First Published: 11 November 2020
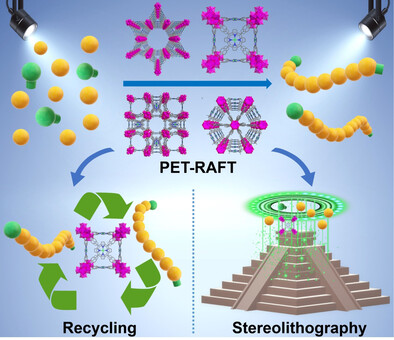
Porphyrinic zirconium MOFs act as heterogeneous photocatalysts for photoinduced electron transfer-reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (PET-RAFT) polymerization of various monomers under a broad range of wavelengths, producing polymers with high monomer conversions, narrow molecular weight distributions, low dispersity and good chain-end fidelity
Energetic Materials | Hot Paper
1,3,4-Oxadiazole Bridges: A Strategy to Improve Energetics at the Molecular Level
- Pages: 5497-5504
- First Published: 04 December 2020
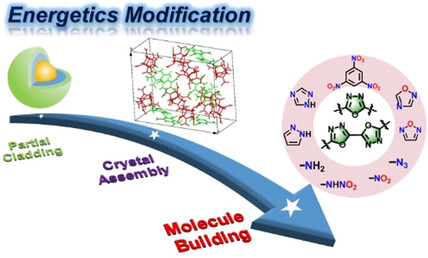
A series of 1,3,4-oxadiazole-bridged furazans was prepared. The thermal stability, friction sensitivity, impact sensitivity, detonation velocity, and detonation pressure were evaluated. The hydroxylammonium salt 8 shows great potential as a high-performance insensitive explosive. The synthetic method for introducing 1,3,4-oxadiazole and the systematic study of 1,3,4-oxadiazole-bridged compounds provide a theoretical basis for future energetics design.
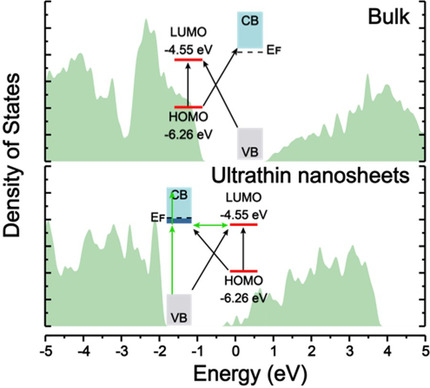
Ultrathin Nanosheets
Ultrathin Two-Dimensional Nanostructures: Surface Defects for Morphology-Driven Enhanced Semiconductor SERS
- Pages: 5505-5511
- First Published: 30 November 2020
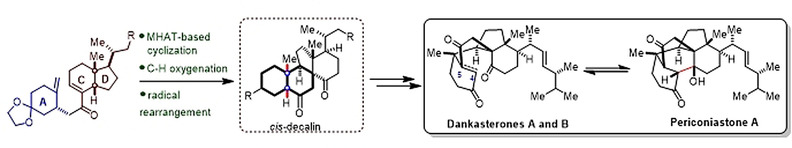
Total Synthesis
Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Dankasterones A and B and Periconiastone A Through Radical Cyclization
- Pages: 5512-5518
- First Published: 18 November 2020
Metal–Organic Frameworks
Energy Efficient Ultrahigh Flux Separation of Oily Pollutants from Water with Superhydrophilic Nanoscale Metal–Organic Framework Architectures
- Pages: 5519-5526
- First Published: 05 October 2020
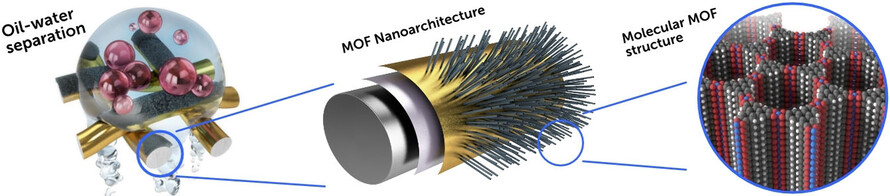
In this work we introduce the synthesis of a pillar-like Co-CAT-1 MOF nanoarchitecture on gold-coated woven stainless steel meshes. These nanostructured mesh surfaces feature extreme superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic wetting properties, allowing for gravity-driven, highly efficient oil–water separation with ultra-high flux of up to nearly one million L m−2 h−1.
Plastic Recycling | Hot Paper
Towards the Circular Economy: Converting Aromatic Plastic Waste Back to Arenes over a Ru/Nb2O5 Catalyst
- Pages: 5527-5535
- First Published: 02 December 2020
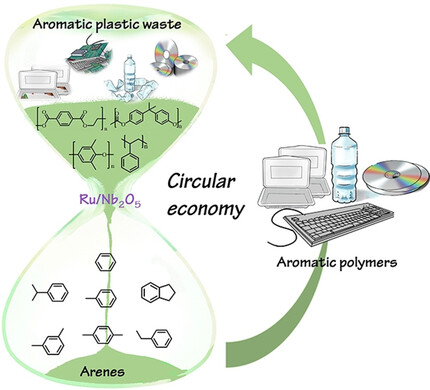
While plastic waste upcycling has attracted increasing worldwide concern, catalytic routes capable to convert a mixture of plastics selectively and effectively into useful chemicals remain exceedingly rare. Here, we report a salient example of the catalytic upgrading of various aromatic plastic waste to simple arenes in high yield via the selective cleavage of interunit C−O and C−C linkages.
Liquid Crystal Elastomers
4D-Printing of Photoswitchable Actuators
- Pages: 5536-5543
- First Published: 20 November 2020
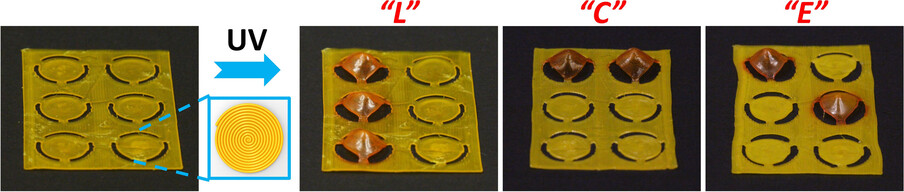
Shape-switching liquid crystal elastomers are formulated where light is used to trigger a shape change which is then stable indefinitely. The original shape can be recovered on heating. These materials can be 4D printed into reconfigurable Braille-like actuators capable of displaying letters “L”, “C” and “E” by switching the shape-morphing of the Archimedean chord patterns with UV light and heating.
Cooperative Catalysis
Highly Active Cooperative Lewis Acid—Ammonium Salt Catalyst for the Enantioselective Hydroboration of Ketones
- Pages: 5544-5553
- First Published: 19 November 2020
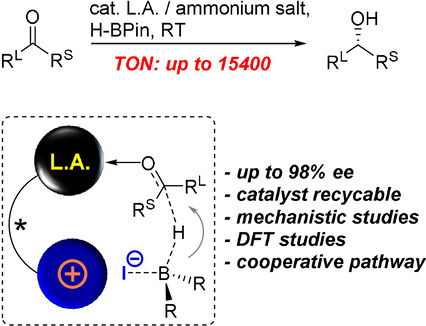
A new concept for asymmetric hydroboration of ketones is shown, in which an ammonium halide initiates a hydride transfer to a Lewis acid activated ketone. Advantages of the bifunctional catalyst include remarkable turnover numbers (up to 15 400, 50 ppm catalyst) and high enantioselectivity. The catalyst was recycled 10 times still providing high efficiency. Mechanistic and DFT studies confirm the cooperative mechanism.
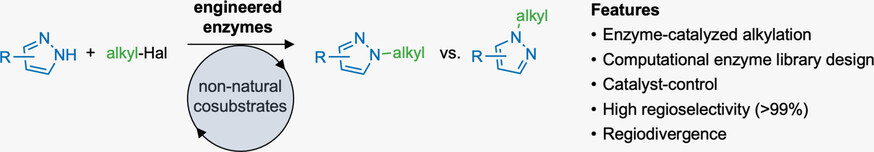
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Engineered Enzymes Enable Selective N-Alkylation of Pyrazoles With Simple Haloalkanes
- Pages: 5554-5560
- First Published: 10 December 2020
Prebiotic Chemistry | Hot Paper
Prebiotic Peptide Synthesis and Spontaneous Amyloid Formation Inside a Proto-Cellular Compartment
- Pages: 5561-5568
- First Published: 16 December 2020
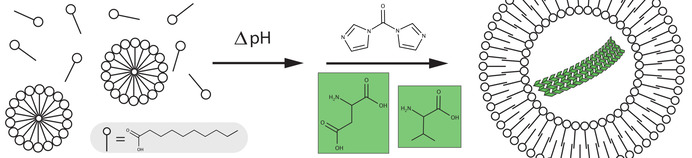
Self-organization in a system of fatty acids and activated amino acids leads to vesicle-encapsulated amyloids. The fatty-acid vesicles act both as a filter, allowing the selective passage of activated amino acids, and as a barrier, blocking the diffusion of the amyloidogenic peptides that form spontaneously inside the vesicles. Hence, a simple mixture of prebiotically plausible starting materials leads to organizationally complex structures.





![Palladium-Catalyzed Site-Selective [3+2] Annulation via Benzylic and meta C−H Bond Activation](/cms/asset/da745ff0-a082-41db-ae54-1463ed776304/anie202015054-toc-0001-m.jpg)