Ultrasound Controlled Anti-Inflammatory Polarization of Platelet Decorated Microglia for Targeted Ischemic Stroke Therapy
Graphical Abstract
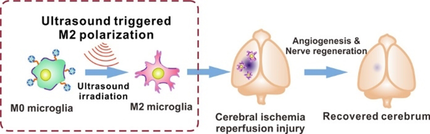
To realize on-demand microglia polarization for controllable ischemic stroke therapy, a sono-sensitive hybrid microglia machine was prepared. Platelet membrane fused microglia have strong accumulation in cerebral vascular injury and can specifically polarize to anti-inflammatory phenotypes, upon external control by ultrasound irradiation, for angiogenesis and nerve regeneration, leading to survival and behavioral improvement of the stroke mice.
Abstract
Stroke is a lethal cerebral disease with severe sequelae and high mortality. Microglia, the main immune cell in the cerebrum, possess therapeutic potential for strokes as its specific anti-inflammatory phenotype can reduce inflammation and promote neuron regeneration. However, the on-demand anti-inflammatory polarization of microglia at the stroke site is uncontrollable for therapeutic application. Here, we develop a platelet hybrid microglia platform which can specifically polarize to the anti-inflammatory phenotype by ultrasound irradiation for targeted cerebrum repair after stroke. The engineered microglia have strong adherence to the injured cerebral vessels with platelet membrane fusion and realize on-demand anti-inflammatory polarization with ultrasound-responsive IL-4 liposome decoration. The intravenously injected microglia platform showed anti-inflammatory polarization at the stroke site with insonation, and accelerated the M2-type polarization of endogenous microglia for long-term stroke recovery. Satisfied prognoses were achieved with reduced apoptosis, promoted neurogenesis, and functional recovery, indicating the implications of the microglia platform for stroke therapy.