Fast Enantio- and Chemoselective Arylation of Ketones with Organoboronic Esters Enabled by Nickel/N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis
Dr. Yuan Cai
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorLin-Xin Ruan
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Abdul Rahman
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Shi-Liang Shi
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yuan Cai
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorLin-Xin Ruan
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Abdul Rahman
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Shi-Liang Shi
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the 70th anniversary of Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry (SIOC)
Graphical Abstract
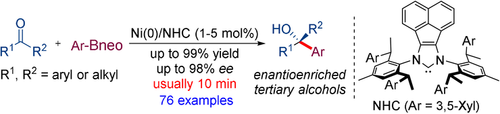
A method for general asymmetric addition of arylborons to simple ketones is reported, which is enabled by nickel/N-heterocyclic carbene catalysis. Chiral tertiary alcohols are furnished with high efficiency and excellent levels of enantio- and chemocontrol, and the method offers a broad substrate scope.
Abstract
A general, efficient, highly enantio- and chemoselective N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)/Ni-catalyzed addition of readily available and stable arylboronic esters to ketones is reported. This protocol provides unexpectedly fast access (usually 10 min) to various chiral tertiary alcohols with exceptionally broad substrate scope and excellent functional group tolerance (76 examples, up to 98 % ee). This process is orthogonal to other known Ni-mediated Suzuki–Miyaura couplings, as it tolerates aryl chlorides, fluorides, ethers, esters, amides, nitriles, and alkyl chlorides. The reaction is applied to late-stage modifications of various densely functionalized medicinally relevant molecules. Preliminary mechanistic studies suggest that a rare enantioselective η2-coordinating activation of ketone carbonyls is involved. This cross-coupling-like mechanism is expected to enable other challenging transformations of ketones.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202015021-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf15.6 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For books, see:
- 1a Quaternary stereocenters, challenges and solutions for organic synthesis (Eds.: J. Christoffers, A. Baro), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005;
10.1002/3527606858 Google Scholar
- 1b Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis (Eds.: E. N. Jacobsen, A. Pfaltz, H. Yamamoto), Springer, Berlin, 1999.
- 2
- 2aL. Chen, X.-P. Yin, C.-H. Wang, J. Zhou, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 6033–6048;
- 2bQ. Zhou, K. M. Cobb, T. Tan, M. P. Watson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12057–12060.
- 3For selected reviews, see:
- 3aM. Shibasaki, M. Kanai, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2853–2873;
- 3bO. Riant, J. Hannedouche, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 873–888;
- 3cD. Leonori, V. K. Aggarwal, Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3174–3183;
- 3dY.-L. Liu, X.-T. Lin, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 876–918.
- 4For selected examples, see:
- 4aJ. L. Stymiest, V. Bagutski, R. M. French, V. K. Aggarwal, Nature 2008, 456, 778–782;
- 4bK. C. Harper, M. S. Sigman, Science 2011, 333, 1875–1878;
- 4cY. Yang, I. B. Perry, G. Lu, P. Liu, S. L. Buchwald, Science 2016, 353, 144–150;
- 4dS.-L. Shi, L.-W. Xu, K. Oisaki, M. Kanai, M. Shibasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6638–6639.
- 5
- 5aR. Noyori, M. Kitamura, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1991, 30, 49–69; Angew. Chem. 1991, 103, 34–55;
- 5bL. Pu, H.-B. Yu, Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 757–824;
- 5cM. Hatano, K. Ishihara, Synthesis 2008, 1647–1675;
- 5dJ. F. Collados, R. Solà, S. R. Harutyunyan, B. Maciá, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1952–1970.
- 6For selected enantioselective examples of organometallic addition to ketones, see: Zn:
- 6aP. I. Dosa, G. C. Fu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 445–446;
- 6bD. J. Ramón, M. Yus, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 284–287; Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 286–289;
- 6cH. Li, C. Garcia, P. J. Walsh, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5425–5427; Al:
- 6dC.-A. Chen, K.-H. Wu, H.-M. Gau, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5373–5376; Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 5469–5472; Ti:
- 6eK.-H. Wu, Y.-Y. Kuo, C.-A. Chen, Y.-L. Huang, H.-M. Gau, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2013, 355, 1001–1008; Mg:
- 6fE. Fernández-Mateos, B. Maciá, M. Yus, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 6519–6526.
- 7A. Suzuki, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6722–6737; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 6854–6869.
- 8For selected examples on metal-catalyzed asymmetric arylboration of aldehyde, see: Rh:
- 8aM. Sakai, M. Ueda, N. Miyaura, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 3279–3281;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19981217)37:23<3279::AID-ANIE3279>3.0.CO;2-M CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 1998, 110, 3475–3477;10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(19981204)110:23<3475::AID-ANGE3475>3.0.CO;2-W Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 8bH.-F. Duan, J.-H. Xie, W.-J. Shi, Q. Zhang, Q.-L. Zhou, Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 1479–1481;
- 8cT. Nishimura, H. Kumamoto, M. Nagaosa, T. Hayashi, Chem. Commun. 2009, 5713–5715; Ru:
- 8dY. Yamamoto, K. Kurihara, N. Miyaura, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4414–4416; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4478–4480; Cu:
- 8eD. Tomita, M. Kanai, M. Shibasaki, Chem. Asian J. 2006, 1, 161–166; Ni:
- 8fT. Arao, K. Kondo, T. Aoyama, Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 4115–4117; Co:
- 8gJ. Karthikeyan, M. Jeganmohan, C.-H. Cheng, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8989–8992; For amino- or iminoalcohol-catalyzed asymmetric aldehyde arylation via boron-to-zinc transmetalation, see:
- 8hC. Bolm, J. Rudolph, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14850–14851.
- 9For additions to α-keto esters, see:
- 9aH.-F. Duan, J.-H. Xie, X.-C. Qiao, L.-X. Wang, Q.-L. Zhou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4351–4353; Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 4423–4425;
- 9bF. Cai, X. Pu, X. Qi, V. Lynch, A. Radha, J. M. Ready, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18066–18069;
- 9cY. Yamamoto, T. Shirai, M. Watanabe, K. Kurihara, N. Miyaura, Molecules 2011, 16, 5020–5034;
- 9dT.-S. Zhu, S.-S. Jin, M.-H. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 780–783; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 804–807; For additions to trifluoromethyl ketones, see:
- 9eS. L. X. Martina, R. B. C. Jagt, J. G. de Vries, B. L. Feringa, A. J. Minnaard, Chem. Commun. 2006, 4093–4095;
- 9fR. Li, K. Luo, Y. Hu, W. Tang, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2013, 355, 1297–1302; For additions to isatins, see:
- 9gR. Shintani, M. Inoue, T. Hayashi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3353–3356; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 3431–3434;
- 9hZ. Liu, P. Gu, M. Shi, P. McDowell, G. Li, Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2314–2317.
- 10Intramolecular additions:
- 10aG. Liu, X. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16504–16505;
- 10bG. Liu, X. Lu, Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 7324–7330;
- 10cD. Tomita, K. Yamatsugu, M. Kanai, M. Shibasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6946–6948;
- 10dR. Sarpong, G. L. Gallego, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1338–1342;
- 10eD. W. Low, G. Pattison, M. D. Wieczysty, G. H. Churchill, H. W. Lam, Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 2548–2551;
- 10fD.-X. Zhu, W.-W. Chen, M.-H. Xu, Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 2637–2642;
- 10gC. Ni, J. Gao, X. Fang, Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2654–2657.
- 11
- 11aJ. Bouffard, K. Itami, Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4410–4413;
- 11bY.-X. Liao, C.-H. Xing, Q.-S. Hu, Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1544–1547;
- 11cT. Korenaga, A. Ko, K. Uotani, Y. Tanaka, T. Sakai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10703–10707; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 10891–10895.
- 12L. Huang, J. Zhu, G. Jiao, Z. Wang, X. Yu, W.-P. Deng, W. Tang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4527–4531; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 4603–4607.
- 13
- 13aD. Janssen-Müller, C. Schlepphorst, F. Glorius, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4845–4854;
- 13bF. Wang, L.-J. Liu, W. Wang, S. Li, M. Shi, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 804–853.
- 14
- 14aY. Cai, X.-T. Yang, S.-Q. Zhang, F. Li, Y.-Q. Li, L.-X. Ruan, X. Hong, S.-L. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1376–1380; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 1390–1394;
- 14bY. Cai, J.-W. Zhang, F. Li, J.-M. Liu, S.-L. Shi, ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1–6;
- 14cW.-B. Zhang, X.-T. Yang, J.-B. Ma, Z.-M. Su, S.-L. Shi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5628–5634;
- 14dD. Shen, Y. Xu, S.-L. Shi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14938–14945;
- 14eY. Cai, X. Ye, S. Liu, S.-L. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13433–13437; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 13567–13571;
- 14fD. Shen, W.-B. Zhang, Z. Li, S.-L. Shi, Y. Xu, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 1125–1130; For a concomitant development of ligands, see:
- 14gJ. Diesel, A. M. Finogenova, N. Cramer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4489–4493;
- 14hJ. Diesel, D. Grosheva, S. Kodama, N. Cramer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 11044–11048; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 11160–11164.
- 15F.-S. Han, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5270–5298.
- 16
- 16aY. Hoshimoto, M. Ohashi, S. Ogoshi, Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1746–1755;
- 16bJ. Montgomery, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3890–3908; Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 3980–3998;
- 16cE. A. Standley, S. Z. Tasker, K. L. Jensen, T. F. Jamison, Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1503–1514.
- 17
- 17aR. Kumar, Y. Hoshimoto, H. Yabuki, M. Ohashi, S. Ogoshi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11838–11845;
- 17bK. Hirano, H. Yorimitsu, K. Oshima, Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 4689–4691;
- 17cC. Lei, Y. J. Yip, J. S. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6086–6089;
- 17dD. K. Nielsen, A. G. Doyle, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6056–6059; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 6180–6183. Also, see refs. [11a], [8f].