Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Nitrogen-Doped Titanium Carbide (Ti3C2Tx) MXene Nanosheet Stack For Long-Term Stability and Efficacy in Au and Ag Recovery (Small 48/2023)
- First Published: 28 November 2023

N-Doped MXene Nanosheet Stacks
In article number 2305247, Soon-Yong Kwon, Jae-Woo Choi, and co-workers report an N-doped MXene nanosheet stack with exceptional oxidation stability using a high-energy ball-milling technique. This innovative method offers a novel and efficient solution for the stable incorporation of MXene nanosheets in aqueous environments, particularly showcasing its ability to energy-environmentally efficient way to recovery valuable metals from diverse electronic waste.
Inside Front Cover
Topological Regulating Bismuth Nano-Semiconductor for Immunogenic Cell Death-Mediated Sonocatalytic Hyperthermia Therapy (Small 48/2023)
- First Published: 28 November 2023
Bismuth-Based Semiconductors
Degradable bismuth semiconductor's properties are controlled by topological synthesis, which carries ivermectin under ultrasound and light action to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) and heat, induce tumors to realize immunogenic cell death, and further activate T cells to achieve synergistic immunotherapy. More details can be found in article number 2304032 by Yuhao Li, Lulu Zheng, Yuqing Miao, Dawei Zhang, and co-workers.
Inside Back Cover
Effect of Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Based Confinement Layers on the Performance of Phase-Change Heterostructure Memory (Small 48/2023)
- First Published: 28 November 2023

Phase-Change Heterostructure Memory
In article number 2303659, Tae Geun Kim and co-workers present phase-change heterostructure (PCH) memory devices that control vertical atomic diffusion during operation. The device performance, such as power consumption and thermal stability, is determined by the choice of transition metal dichalcogenide-based confinement materials with different cohesive energies, providing valuable insights for the further engineering and design of PCH devices.
Back Cover
Thermodynamically and Kinetically Controlled Nucleation and Growth of Halide Perovskite Single Crystals (Small 48/2023)
- First Published: 28 November 2023
Halide Perovskite Single Crystals
In article number 2304900, Dong Zhang, Takuya Okamoto, and Vasudevanpillai Biju show size-controlled, monodisperse cubic halide perovskite crystal formation by thermodynamically controlling the nucleation-crystal growth kinetics in inverse temperature crystallization. The concentration of N-cyclohexyl-2-pyrrolidone and the nucleation-growth temperature play central roles in the shape and size of crystals. Controlled growth with the pyrrolidone derivative suppresses the defect density of the crystals, producing uniform samples for optoelectronic and photovoltaic applications.
Masthead
Reviews
Advancement of Engineered Bacteria for Orally Delivered Therapeutics
- First Published: 03 August 2023
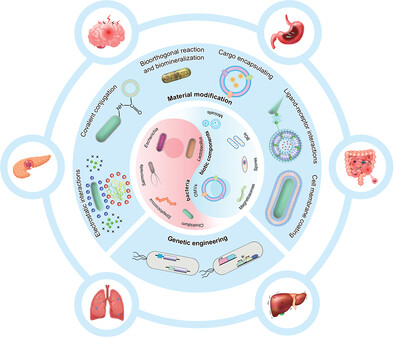
This comprehensive review summarizes the engineering strategies of bacteria and their biotic components for oral delivery and their applications in the biomedicine, especially research progress in the treatment of gastric, intestinal, and respiratory diseases. Finally, this review highlights the current challenges and prospects of bacterial therapeutics that will contribute to the development of next-generation orally delivered bacteriotherapy.
Evolution of Thermoelectric Generators: From Application to Hybridization
- First Published: 06 August 2023
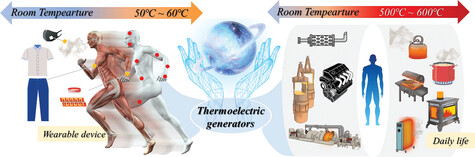
Thermoelectric generators (TEGs), with the ability to continuously convert heat into electricity, is one of the most effective ways to realize heat recovery. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the practical applications of TEGs, mainly in wearable devices, devices for daily life and industry. Meanwhile, the combination of TEGs with other nanogenerators to form hybrid generators is systematically presented.
Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Derivatives-Based Nanostructure with Different Dimensionalities for Supercapacitors
- First Published: 04 August 2023

Recent advances based on metal-organic frameworks and their derivatives in different dimensionalities ranging from nanopowders to nanofilms and aerogels, as well as self-supporting electrodes for supercapacitors are summarized and highlighted. Furthermore, the key challenges and perspectives of metal-organic frameworks and their derivatives-based materials for the practical and sustainable electrochemical energy conversion and storage applications are briefly discussed.
Recent Progress of Covalent Organic Frameworks-Based Materials in Photocatalytic Applications: A Review
- First Published: 04 August 2023
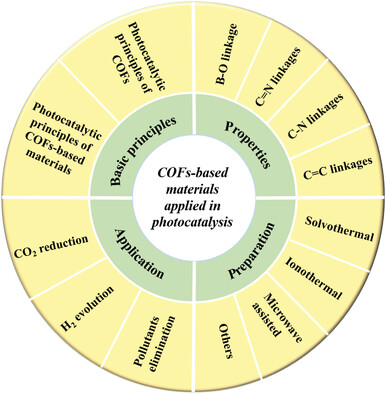
In this review, typical structures and preparation methods of covalent organic framework (COFs) are introduced. Subsequently, the essential principles of photocatalytic reactions over COFs-based materials and the latest research developments in photocatalytic hydrogen production, CO2 reduction, and pollutant elimination are discussed. Finally, challenges and prospects for COFs-based materials applied in photocatalysis are proposed.
Metal Phosphorous Chalcogenide: A Promising Material for Advanced Energy Storage Systems
- First Published: 04 August 2023
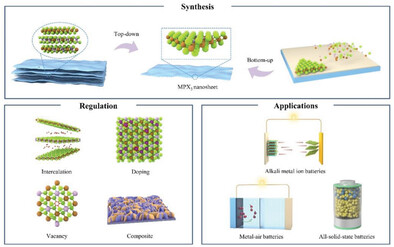
The metal phosphorus chalcogenide (MPX3), has garnered attention in the field of energy storage due to its exceptional electrochemical performance. With high electrical conductivity, relatively large surface area, superb stability, and exceptional energy storage capability, MPX3 presents itself as a promising material. By employing appropriate regulation strategies, it can be applied to energy storage devices such as alkali metal ion batteries, metal-air batteries, and solid-state batteries.
Two Dimensional Ir-Based Catalysts for Acidic OER
- First Published: 03 August 2023
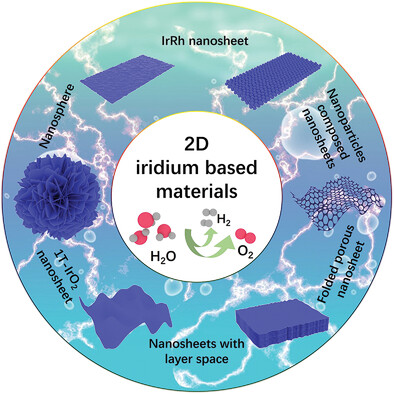
Iridium (Ir)-based materials are one of the few catalysts that can have good oxygen evolution reaction (OER) performance under acidic conditions. Here, this progress report emphasizes the importance of two-dimensional (2D) Ir-based catalysts and significant research progress in designing and synthesizing various electrocatalysts to improve acidic OER performance. Finally, the prospects and challenges of developing 2D Ir-based catalysts are discussed.
Lignocellulosic Biomass-Based Carbon Dots: Synthesis Processes, Properties, and Applications
- First Published: 03 August 2023
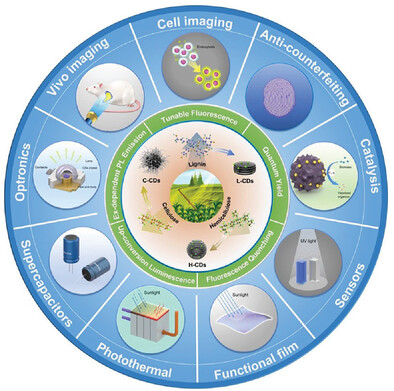
This review provides a summary of the synthesis methods and mechanisms of lignocellulosic biomass based-CDs (LC-CDs). It also covers LC-CDs' properties and advancements in various fields, including optics, energy, and biomedicine. The challenges associated with the development of LC-CDs and their potential advanced applications are also discussed, which is aimed to inspire ongoing research.
Hydrogel Electrolyte Enabled High-Performance Flexible Aqueous Zinc Ion Energy Storage Systems toward Wearable Electronics
- First Published: 02 August 2023
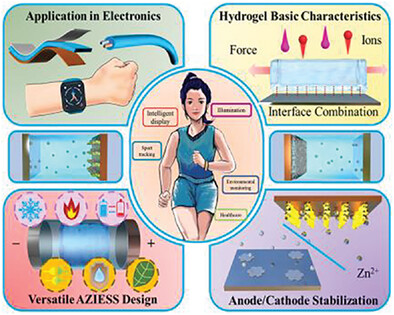
This review focuses on hydrogel electrolytes engineering for high-performance flexible aqueous zinc ion energy storage systems. From basic characteristics, anode and cathode stabilization effects, and functional properties, the corresponding mechanisms of designing desirable hydrogel electrolytes are elaborated. The application of flexible aqueous zinc ion energy storage systems in wearable electronics is also depicted with a bright future.
Recent Advances on Single-Atom Catalysts for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- First Published: 01 August 2023
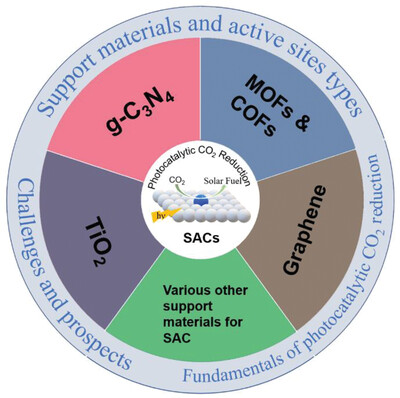
The most current scientific developments, difficulties, and potential applications of single-atom catalysts (SACs) in photocatalytic CO2 reduction are outlined. In this review, the effects of support materials and active site types in SACs on the efficiency of photocatalytic CO2 reduction are evaluated and investigated. On the development of SACs for photocatalytic CO2 reduction, several individual opinions are presented.
Frontispiece
Positron Emission Tomography Studies of the Biodistribution, Translocation, and Fate of Poly Allyl Amine-Based Carriers for Sirna Delivery by Systemic and Intratumoral Administration (Small 48/2023)
- First Published: 28 November 2023

Positron Emission Tomography
Polyplex nanoparticles are prepared by complexation of siRNA and polyamines aimed at gene therapy applications for cancer treatment. The radiolabeled polyplexes are injected intratumorally in lung tumor tissue, resulting in a high retention of the nanoparticles in the malignant tissue. More details can be found in article number 2304326 by Jordi Llop, Sergio E. Moya, and co-workers.
Research Articles
Positron Emission Tomography Studies of the Biodistribution, Translocation, and Fate of Poly Allyl Amine-Based Carriers for Sirna Delivery by Systemic and Intratumoral Administration
- First Published: 03 August 2023
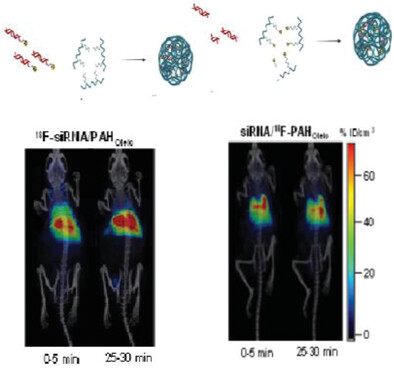
Positron emission tomography is used to study the fate of polyplexes formed by siRNA and modified polyamines. Polyplexes are prepared with either radiolabeled siRNA or radiolabeled polyamines. By comparing biodistribution patterns of labeled siRNA and labeled polyamines conclusions are driven on the stability of the polyplexes in vivo.
Frontispiece
Reticular Chemistry of the Fcu-Type Gd(III)-Doped Metal–Organic Framework for T1-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (Small 48/2023)
- First Published: 28 November 2023

Magnetic Resonance Imaging
The frontispiece represents a reticular chemistry approach to optimize relaxation transfer in the inner-, second- and outer-sphere of the metal cluster underlying the fcu-type metal–organic framework (MOF) for T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and indicates that the metal cluster arranged in the fcu-type MOF matrix surpasses its discrete molecular cluster for in-vitro and in-vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). More details can be found in article number 2303063 by Yun Ling and co-workers.
Research Articles
Reticular Chemistry of the Fcu-Type Gd(III)-Doped Metal–Organic Framework for T1-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- First Published: 07 July 2023
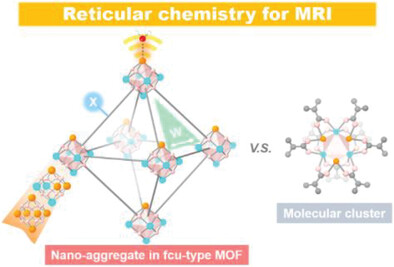
It is not only shown the reticular chemistry approach to optimize relaxation transfer in the inner-, second- and outer-sphere of Gd(III)-doped Zr-oxo cluster underlying the fcu-type metal–organic framework (MOF) for T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging but also confirmed that the Gd(III)-doped cluster aggregated in the MOF matrix surpasses its discrete molecular cluster for in vitro and in vivo T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Frontispiece
Synergistic Effect of Electron Scattering and Space Charge Transfer Enabled Unprecedented Room Temperature NO2 Sensing Response of SnO2 (Small 48/2023)
- First Published: 28 November 2023

NO2 Sensors
In article number 2303631, Wen Zeng, Zaihua Duan, Huiling Tai, and co-workers propose an enhanced gas sensing strategy based on the synergistic effect of electron scattering and space charge transfer, and verify it by designing porous SnO2 nanoparticles assembled from ultra-small grains, achieving unprecedented NO2 gas sensing performance at room temperature. This work provides an innovative approach for developing high-performance and low-power gas sensors.
Research Articles
Synergistic Effect of Electron Scattering and Space Charge Transfer Enabled Unprecedented Room Temperature NO2 Sensing Response of SnO2
- First Published: 04 July 2023
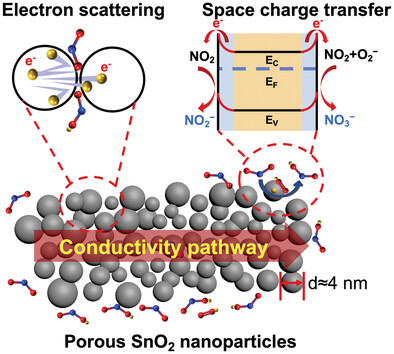
To develop the room temperature NO2 sensor with high response, fast recovery, and exceptional selectivity, porous SnO2 nanoparticles with rich oxygen vacancies are synthesized via acetylacetone-assisted solvent evaporation followed by N2 and air calcinations. The fascinating sensing properties are mainly attributed to the unique synergistic effect of electron scattering and space charge transfer.
Nitrogen-Doped Titanium Carbide (Ti3C2Tx) MXene Nanosheet Stack For Long-Term Stability and Efficacy in Au and Ag Recovery
- First Published: 30 July 2023
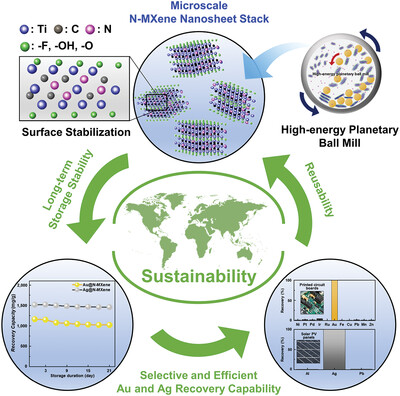
We describe an N-doped MXene nanosheet stack produced by a high-energy planetary ball milling under N2-purged conditions. This process effectively stabilizes defective vacancies of MXene nanosheets while forming a macroscale MXene nanosheet stack, making it easy to recover after use in the aqueous environments. MXene nanosheet stack shows its long-term storability, selective and efficient precious metal recovery capability, and reusability.
Topological Regulating Bismuth Nano-Semiconductor for Immunogenic Cell Death-Mediated Sonocatalytic Hyperthermia Therapy
- First Published: 02 August 2023
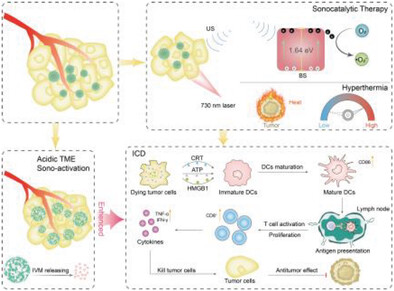
A bismuth-based nano-semiconductor is constructed by topology synthesis strategy and loaded with ivermectin to form a sono/photo-activated bismuth nanoagonist for realizing immunogenic cell death (ICD)-mediated tumor synergistic therapy. The proposed hyperthermia/sonocatalytic therapy strategy will pay the way for the synergetic enhancement of tumor treatment efficacy and provide a feasible idea for controllable induction of ICD.
Effect of Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Based Confinement Layers on the Performance of Phase-Change Heterostructure Memory
- First Published: 23 July 2023
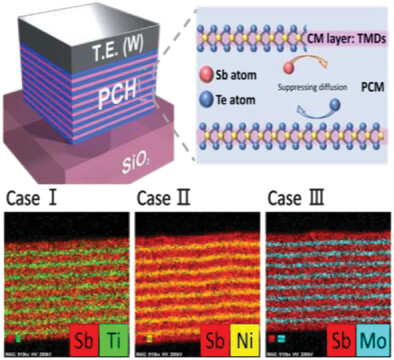
To prevent long-range atomic diffusion in phase change materials (PCMs– Sb2Te3), transition metal dichalcogenide-based confinement materials (TiTe2, NiTe2, and MoTe2) are inserted between PCMs to fabricate phase change heterostructure memory devices. The device performance is then investigated with each other and analysed based on their different electrical resistivity and cohesive energy.
Thermodynamically and Kinetically Controlled Nucleation and Growth of Halide Perovskite Single Crystals
- First Published: 25 July 2023
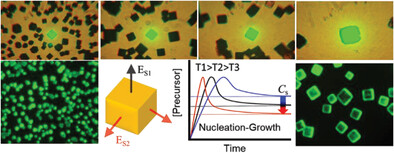
Halide perovskite) single crystals are promising for electro-optical and photovoltaic devices. The challenging size- and shape-controlled single-crystal synthesis is demonstrated by separating and optimizing the crystal nucleation-growth processe . The cuboid single-crystals with controlled size show optimal photoluminescence and minimal defects. This method offers a route to synthesize high-quality perovskite single crystals with size- and shape-control for devices.
Efficient Photocatalytic H2O2 Production Ability of a Novel Graphitic Carbon Nitride/Carbon Composites under Visible Light
- First Published: 28 July 2023
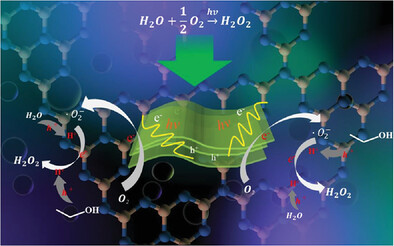
Novel graphitic-carbon nitride/carbon (g-C3N4/C) composites are synthesized by one-step thermal polycondensation. The starting materials are potassium hydroxide (KOH), microplastics, and melamine mixture in air atmosphere. Under visible-light irradiation, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production-rate over CN-K5M7 reaches 6.14 mmol g-1h-1, while H2O2 selectivity is 99.5%. The KOH modification creates a large number of N vacancies and defects caused by cyano-groups in g-C3N4.
Temperature Effects on Electrochemical Energy-Storage Materials: A Case Study of Yttrium Niobate Porous Microspheres
- First Published: 28 July 2023
The temperature effects on electrode materials are fully revealed through intensively investigating a novel yttrium niobate (Y0.5Nb24.5O62) model material with a large interlayer spacing and porous-microspherical morphology. It is found that the operation temperature plays vital roles in electrolyte decomposition on electrode-material surfaces (initial Coulombic efficiency), electrochemical kinetics (reversible capacity, rate capability, and working potential), and crystal-structure evolution (cyclic stability).
Pickering Emulsion Templated 3D Cylindrical Open Porous Aerogel for Highly Efficient Solar Steam Generation
- First Published: 28 July 2023
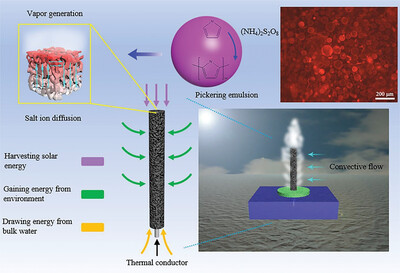
A three-dimensional (3D) cylindrical opened-porous aerogel is fabricated via a Pickering emulsion-mediated polymerization route. All-cold solar evaporation with zero energy loss and significantly increased extra energy harvest is achieved. Vapor diffusion is enhanced, and inner evaporation surfaces are activated via external convective flow. The evaporator can deliver stable vapor generation for highly concentrated salt solution (20 wt.% NaCl).
Synthesis of Free-Standing Tin Phosphide/Phosphate Carbon Composite Nanofibers as Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries with Improved Low-Temperature Performance
- First Published: 28 July 2023
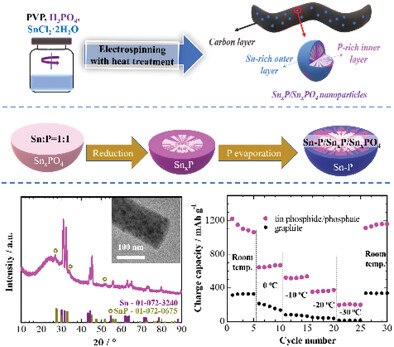
Tin phosphide/phosphate nanoparticles uniformly distributed within thecarbon nanofiber matrix have been designed by electrospinning with carbothermal reduction of phosphate-containing precursors. Designed material of unique nanostructure and composition exhibits outstanding electrochemical properties at low temperatures as an anode for lithium-ion batteries, retaining 580 mAh g−1 capacity after 100 cycles at −20 °C using commercial electrolyte without any additives.
Open-Mouthed Hollow Carbons: Systematic Studies as Cobalt- and Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
- First Published: 30 July 2023
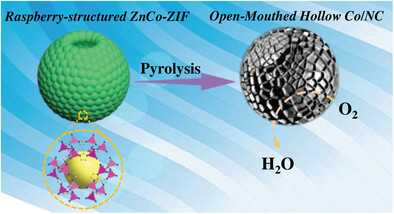
An open-mouthed hollow cobalt/nitrogen-doped carbon with mesoporous shells (OMH-Co/NC) is synthesized using the self-conglobation effect of metal sulfate in methanol, followed by pyrolysis. The incorporation of open holes in the structure enhances the accessibility of both the inner and outer surfaces. As a result, the OMH-Co/NC exhibits superior activity in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and improve mass transfer efficiency.
Rheology Engineering for Dry-Spinning Robust N-Doped MXene Sediment Fibers toward Efficient Charge Storage
- First Published: 30 July 2023
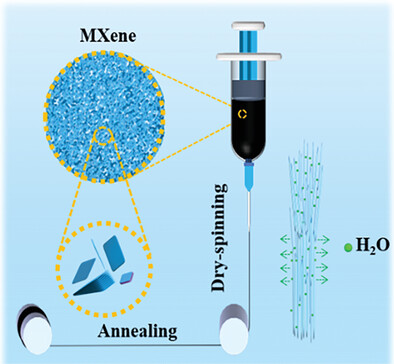
A dry-spinning strategy is proposed to fabricate flexible MXene fibers (MFs) for wearable supercapacitors by engineering the rheological behavior of Ti3C2Tx sediment. The parameters affecting the dry spinning process, the mechanical and electrochemical properties of the as-prepared MFs are studied in detail.
Rapid Detection and Selective Extraction of Au(III) from Electronic Waste Using an Oxime Functionalized MOF-on-MOF Heterostructure
- First Published: 28 July 2023
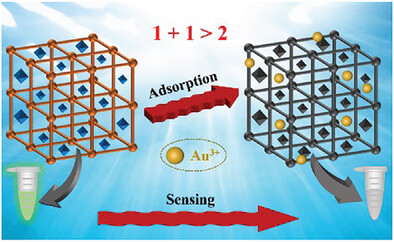
A hybrid MOF-on-MOF heterostructure is first reported for the rapid detection and selective capture of gold. Due to the strong interaction between the framework and Au3+, an ultra-fast fluorescence response time (3.6s) and ultra-high adsorption capacity (1575 mg g−1) are observed on MOF-808@ZIF-90-XE.
Sequentially Controlled Recognition of Different Proteins Using Programmable Protein Imprinted Nanospheres
- First Published: 30 July 2023
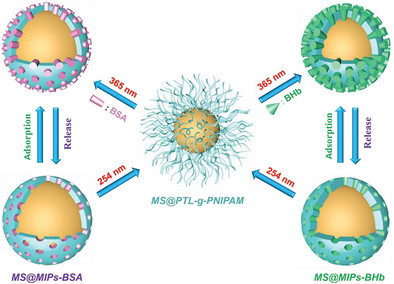
This study designs a programmable protein imprinted nanosphere by dynamically reversible cross-linking/de-cross-linking of the temperature- and pH-responsive polymeric surface under different wavelengths of UV light. The nanosphere can be repeatedly programmed toward a variety of proteins, thereby achieving the selective separation of different proteins from real biological samples in sequential.
Capacitive and Diffusive Contributions in Supercapacitors and Batteries: A Critique of b-Value and the ν–ν1/2 Model
- First Published: 28 July 2023

The ν −ν1/2 model and the b-value, widely used in energy storage literature, have serious shortcomings: the latter is highly subjective, while the former assumes a linear response which is often not present. Consequently, electrodes are frequently wrongly evaluated, and the deconvoluted capacitive and diffusive contributions are often in error. The corrected model proposed here seeks to remedy this state of affairs.
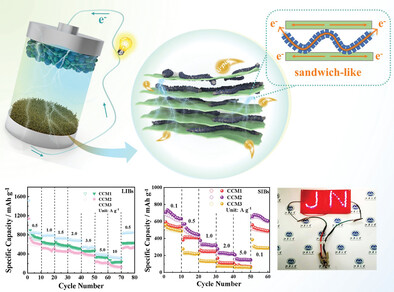
Multi-Pleated Alkalized Ti3C2Tx MXene-Based Sandwich-Like Structure Composite Nanofibers for High-Performance Sodium/Lithium Storage
- First Published: 30 July 2023
Extremely Large Response of Phonon Coherence in Twisted Penta-NiN2 Bilayer
- First Published: 31 July 2023
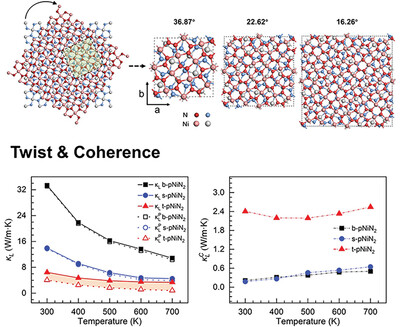
Interlayer twist can manipulate phonon coherence in the 2D bilayers. Through extensive simulations and analysis, the distinctive phonon properties of twisted anharmonic sheets are demonstrated, particularly the pronounced response of phonon coherence to twisting in penta-NiN2 bilayers. These findings highlight the potential applications of 2D twisted systems in phonon-based devices.
Tight Binding and Dual Encapsulation Enabled Stable Thick Silicon/Carbon Anode with Ultrahigh Volumetric Capacity for Lithium Storage
- First Published: 31 July 2023
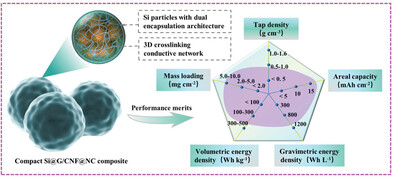
The compact micron-sized Si@G/CNF@NC composite features a tightly bonded and dual encapsulated structure, which endows it with excellent conductivity and deformation resistance, demonstrating a range of comprehensive advantages in lithium-ion batteries, including high tap density, high mass loading, outstanding areal capacity, and excellent gravimetric and volumetric energy density.
Dynamic Electronic and Ionic Transport Actuated by Cobalt-Doped MoSe2/rGO for Superior Potassium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 31 July 2023
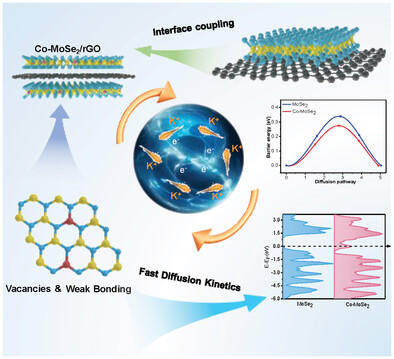
Co-induced engineering is proposed to enhance electron conduction and ion diffusion of MoSe2 nanosheets anchored on reduced graphene oxide. The as-prepared Co-MoSe2/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) anode possesses remarkable reversible capacity, superior rate capability, and stable long-term cyclability for potassium-ion batteries, as well as high energy/power density for potassium-ion hybrid capacitors.
CDs Regulated Sulfur-Based Flexible Electrode with Range pH Values for Efficient and Durable Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 31 July 2023
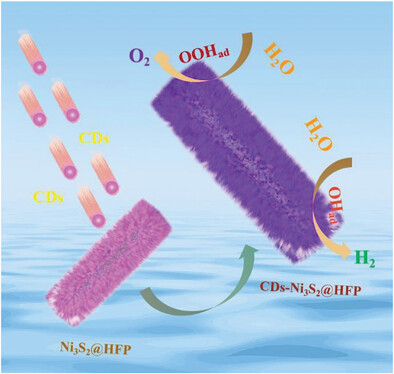
This work creatively proposes to prepare industrial-grade catalytic electrodes with high efficiency and stability at high current density through carbon quantum dots (CDs) modification nickel sulfide on hydrophilic flexible filter paper via one-step mild chemical plating (denoted as CDs-Ni3S2@HFP), which achieves over 500 h for efficient and stable catalysis at industrial high current density (500 mA cm−2) in 1 m KOH, simulated seawater (1 m KOH + 0.5 m NaCl), and neutral electrolyte (0.5 m PBS).
Two Birds with One Stone: Micro/Nanostructured SiOxCy Composites for Stable Li-Ion and Li Metal Anodes
- First Published: 31 July 2023
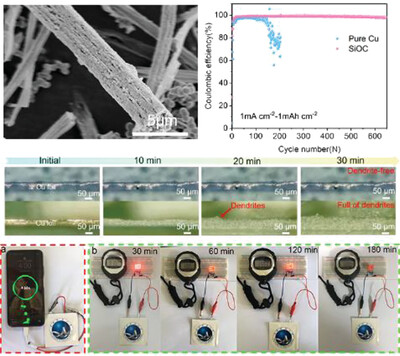
The micro/nanostructured SiOxCy composites are synthesized by chemical vapor deposition strategy. The SiOxCy composites are not only capable of being used in lithium-ion battery anodes, but can also be employed as a substrate for lithium metal uniform deposition in Li metal anode. This work provides a new perspective for the simultaneous development of practical SiOxCy and dendrite-free lithium metal anodes.
Bimetallic MOF-Derived Solar-Triggered Monolithic Adsorbent for Enhanced Atmospheric Water Harvesting
- First Published: 28 July 2023
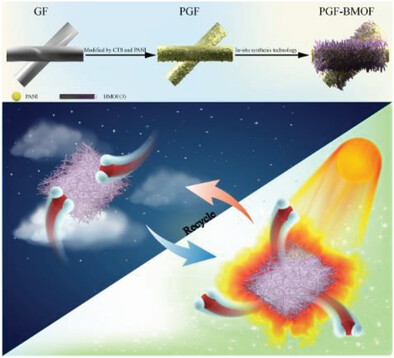
A solar-triggered monolithic adsorbent is constructed from hydrophilic bimetallic metal-organic framework (BMOF) skeletons and photothermal layers on a glass fiber support to generate safe freshwater from atmospheric air. The open hybridized BMOF skeleton can efficiently capture and store moisture during the night. The polymeric photothermal layer relies on its high photothermal conversion capacity in sunlight to automatically release the adsorbed water.
A “Win–Win” Strategy to Modify Co/C Foam with Carbon Microspheres for Enhanced Dielectric Loss and Microwave Absorption Characteristics
- First Published: 01 August 2023
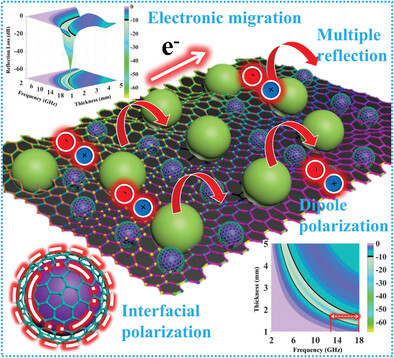
The construction of 3D Co/C foam and its surface decoration with carbon microspheres are synchronously achieved by a “win–win” strategy. Both Co nanoparticles and carbon microspheres display good dispersity, which improves the graphitization degree of carbon framework and creates abundant heterogeneous interfaces. As a result, the Co/C foam decorated with carbon microspheres gains enhanced dielectric property and microwave absorption performance.
Phase Engineering of W-Doped MoS2 by Magneto-Hydrothermal Synthesis for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 01 August 2023
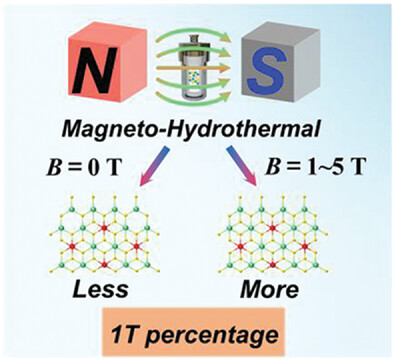
A feasible method is reported to synthesize ambient-stable molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) with high concentration 1T phase under low magnetic fields. Owing to the synergistic effect of magnetic free energy and microstrain, the 1T phase proportion can be as high as 80% and the synthesized MoS2 is ambient-stable for more than one year with excellent hydrogen evolution reaction(HER)performances.
Terephthalic Acid Intercalated CoNi-LDH Materials for Improved Li–O2 Battery
- First Published: 02 August 2023
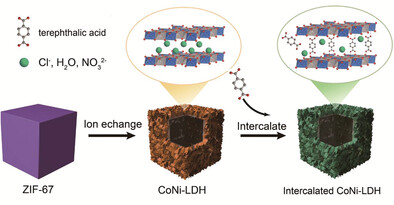
Hollow nano-cage layered CoNi double hydroxides (CoNi-LDH) were obtained by Ni ion etching of ZIF-67 (Zeolitic imidazolate framework-67). By adjusting the amount of terephthalic acid, the intercalated CoNi-LDH-2 (with 0.02 mmol terephthalic acid intercalated) was not easy to collapse after 209 cycles and showed the best electrochemical performance in Li–O2 battery.
Polycrystalline Diamond Micro-Hotplates
- First Published: 02 August 2023
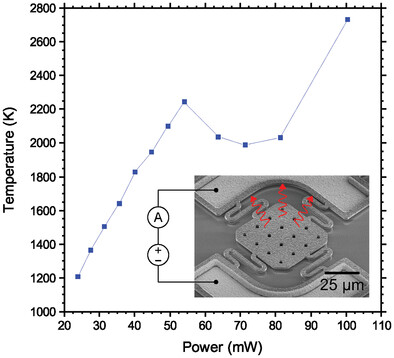
Micro-hotplate structures composed of boron-doped polycrystalline diamond are fabricated and comprehensively characterized. Through constructing the devices from a single layer of low coefficient of thermal expansion diamond, stress issues that plague traditional multi-layered structures are averted, allowing the resulting devices to operate up to 2731 K and far beyond the current 1600 K limit of conventional structures.
Hierarchical 3D Electrode Design with High Mass Loading Enabling High-Energy-Density Flexible Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 02 August 2023
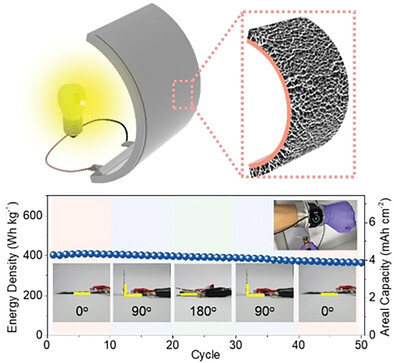
A hierarchical 3D electrode design with high mass loading enables the realization of high-energy-density flexible batteries. The electrode demonstrates outstanding mechanical flexibility, while the bicontinuous network facilitates efficient Li-ion conduction, resulting in enhanced cycle stability and rate performance. As a result, the hierarchical 3D electrode allows to achieve high-energy-density of flexible LIBs in a pouch-type cell (438.6 Wh kg−1/20.4 mWh cm−2).
Virus-Like Magnetic Heterostructure: an Outstanding Metal-Complex Active Platform Enables High-Efficiency Separation and Catalysis
- First Published: 03 August 2023
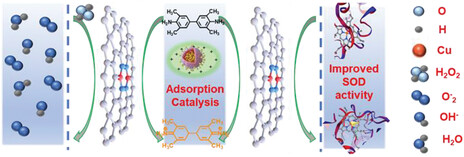
Here, the study describes an easy-to-execute strategy to fabricate magnetic heterostructure as a multifunctional delivery system. first-row transition metal copper and nitroso/amino ligand as modules to assemble around Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles by excessed mild stimuli and fabricate the magnetic heterostructure materials is utilized. The Fe3O4@ TACN NPs can effectively isolate Cyt-c from complex biological samples (pork heart). Importantly, the Fe3O4@ TACN NPs coordinated with heme-structure, induced methionine 80 disassociates from heme prosthetic group, and contributed to peroxidase-like activities increasing.
Yolk–Shell Structured ST@Al2O3 Enables Functional PE Separator with Enhanced Lewis Acid Sites for High-Performance Lithium Metal Batteries
- First Published: 03 August 2023
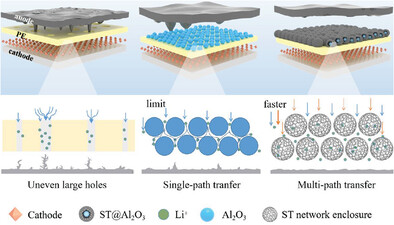
Benefiting from the spherical yolk–shell structure of Ti–doped SiO2@Al2O3 (ST@Al2O3), Li+ can diffuse through the porous shell and hollow interior. Moreover, Lewis acid sites may reduce the solvation effect of Li+, and the bilayer shell with abundant Lewis acid sites can effectively trap anions by charge attraction, thus creating an anion shield.
Positional Isomers of Covalent Organic Frameworks for Indoor Humidity Regulation
- First Published: 03 August 2023
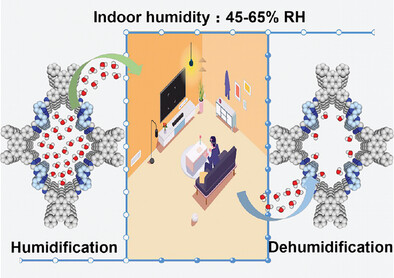
Covalent organic frameworks (o-COF) for indoor humidity regulation was constructed by adjusting the difference of water adsorption sites in positional isomers. o-COF exhibits a steep adsorption isotherm in the range of 45–65% RH with a suitable hysteresis range. Both laboratory experiment and real environment experiment confirm that o-COF is a new generation of indoor humidity regulation material.
Pt-Loaded Nb─W Metal Composite Oxide for Selective Cleavage of Secondary C─O Bonds
- First Published: 03 August 2023
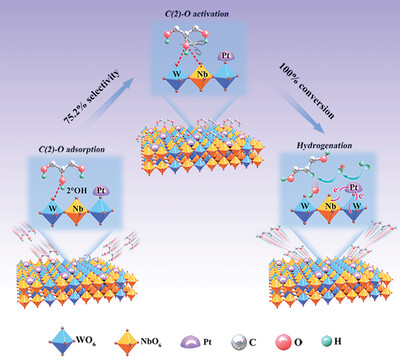
A uniform Pt/Nb14W3O44 catalyst with crystallographic shear structure is developed for the extremely efficient and selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1,3-propanedio with excellent stability, reaching an exceptional 75.2% yield of 1,3-propanediol. Strong interaction between Nb14W3O44 and Pt can coordinate the precise adsorption and activation of the secondary C─O bond, simultaneously triggering subsequent hydrogenation.
Building Atomic Scale and Dense Fe─N4 Edge Sites of Highly Efficient Fe─N─C Oxygen Reduction Catalysts Using a Sacrificial Bimetallic Pyrolysis Strategy
- First Published: 03 August 2023
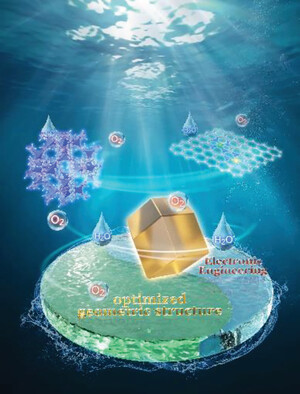
A sacrificial bimetallic pyrolysis strategy is applied to synthesize a Fe/N/C catalyst with excellent oxygen reduction reaction performances in acidic media. As a result, the Fe(Cd)─N─C catalyst performs with ≈8 higher site utilization efficiency than the Fe─N─C catalyst, which is also higher than most Fe/N/C catalysts prepared by wet-chemistry synthesis methods.
Modulating Photoinduced Electron Transfer between Photosensitive MOF and Co(II) Proton Reduction Sites for Boosting Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production
- First Published: 03 August 2023
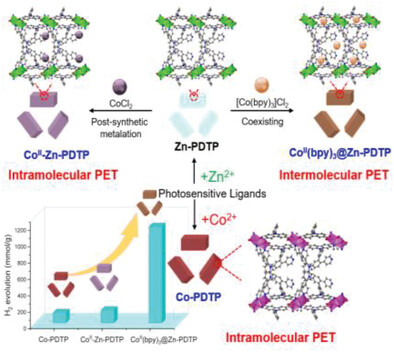
Three photoactive metal–organic framework systems having two different photoinduced electron transfer (PET) processes to drive photocatalytic H2 production are reported, wherein, CoII(bpy)3@Zn-PDTP system using [Co(bpy)3]Cl2 as a cocatalyst with the intermolecular PET process extremely enhances the photocatalytic activity to 7.5 and 9.3 times the value afforded by CoII-Zn-PDTP system and bare Co-PDTP, respectively.
N-Doping Induced Lattice Expansion of 1D Template Confined Ultrathin MoS2 Sheets to Significantly Enhance Lithium Polysulfides Redox Kinetics for Li–S Battery
- First Published: 15 August 2023
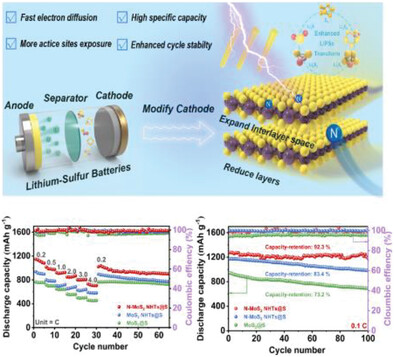
Preparing MoS2-based materials with reasonable structure and catalytic activity to enhance the lithium polysulfides conversion is significant for Li–S batteries (LSBs) but still faces challenges. Hence, hollow nanotubes composing N-doped MoS2 nanosheets (N-MoS2 NHTs) are fabricated as cathode for LSBs by using CdS nanorods as a sacrifice template, and the batteries with the N-MoS2 NHTs cathode show excellent performance.
Morphology Dictated Immune Activation with Framework Nucleic Acids
- First Published: 09 August 2023
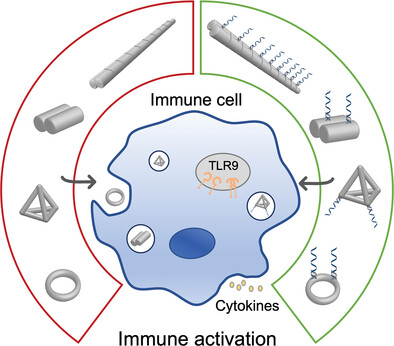
The innate immunological response of framework nucleic acids (FNAs) is primarily dependent on both dose and morphology. A low-dose FNA with minimal immune activation and higher cellular uptake is recommended as a carrier for biomolecule delivery. Moreover, the immune activity of cytosine-phosphate-guanine oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG ODNs) can be programmed through FNA-mediated spatial distance, which can be tuned by morphology.
Fabrication of Optical Fourier Surface by Multiple-Frequency Vibration Cutting for Structural True Coloration
- First Published: 04 August 2023
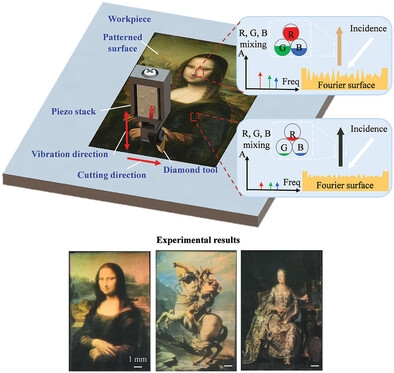
This study presents a simple yet powerful approach, multi-frequency vibration cutting, to enable the high-efficiency fabrication of optical Fourier surfaces. Due to the capacity of multicomponent gratings in coupling red, green, and blue lights, the RGB true color is prepared on the metallic surface. The additive and subtractive principles of mixing the three primary colors are demonstrated.
Quantifying the Efficacy of Magnetic Nanoparticles for MRI and Hyperthermia Applications via Machine Learning Methods
- First Published: 10 August 2023
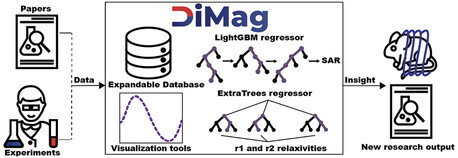
A machine learning-based approach is demonstrated for prediction of the specific absorption rate for hyperthermia and r1/r2 relaxivities in magnetic resonance imagining (MRI), with descriptors including parameters of nanoparticles and experimental conditions. DiMag, an open access resource, is developed to guide the synthesis of novel nanosized magnets for MRI and hyperthermia treatment to boost the development of new biomedical agents.
Multifunctional Asymmetric Bacterial Cellulose Membrane with Enhanced Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities for Promoting Infected Wound Healing
- First Published: 11 August 2023
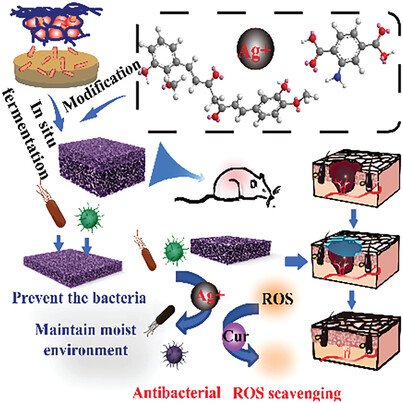
An asymmetric bacterial cellulose membrane is fabricated through microbial fermentation, serving as the foundation for the development of multifunctional wound dressings. The wound dressing can provide an ideal moist environment for wound healing and inhibit the growth of bacteria on infected wounds while releasing Cur in a controlled manner, scavenging ROS, and promoting the production of epithelium and granulation.
Electrochemical Enhancement of Lithium-Ion Diffusion in Polypyrrole-Modified Sulfurized Polyacrylonitrile Nanotubes for Solid-to-Solid Free-Standing Lithium–Sulfur Cathodes
- First Published: 06 August 2023
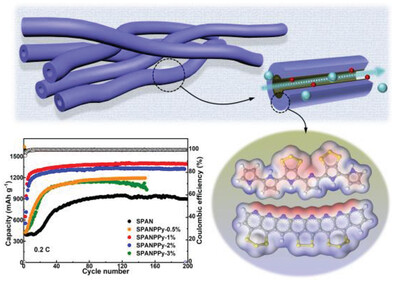
Polypyrrole is used as an electrochemically active additive to introduce hollow channels into polyacrylonitrile nanotubes, creating a free-standing Li-S cathode based on solid-phase conversion. This not only increases the sulfur loading but also significantly enhances charge transport. Consequently, the charge-transfer kinetics and interfacial compatibility are significantly enhanced for superior electrochemical properties.
Synergistic Promotion of the Photocatalytic Preparation of Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) from Oxygen by Benzoxazine and Si─O─Ti Bond
- First Published: 11 August 2023
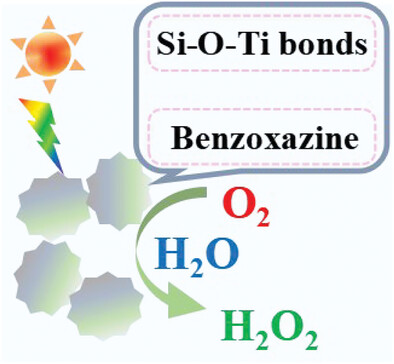
A nanoparticles based benzoxazine containing a Si─O─Ti bond photocatalyst is developed for photocatalytic preparation of H2O2. Compared to traditional nanocatalysts for catalytic preparation of H2O2, the photocatalyst exhibits superior photocatalytic efficiency and excellent hydrolysis resistance, enabling its repeated use with minimal loss.
The Linkage-Moderated Covalent Organic Frameworks with C=N and NN on Charge Transfer Kinetics Towards the Robust Photocatalytic Hydrogen Activity
- First Published: 11 August 2023
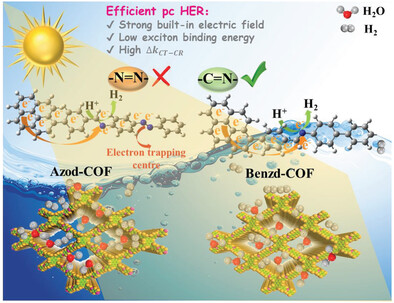
Charge transfer kinetics is discussed in −C=N− linked COFs, with high ΔkCT CR. Low ΔkCT CR is obtained for additional −N=N− linkage case, since it acts as electron trapping centers for inefficient charge transfer process. The ΔkCT CR value can be one important indicator for photocatalysts design at a molecular level.
General Synthesis of Single-Crystal Spinel Cathodes with the Tailored Orientation of Exposed Crystal Planes for Advanced Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 11 August 2023
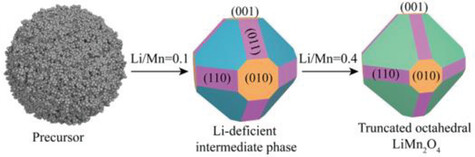
Single-crystal truncated octahedral LiMn2O4 with exposed {111}, {100}, and {110} facets is proposed to decelerate the disproportionation and Jahn–Teller distortion for advanced lithium-ion batteries. The cycling stability of spinel LiMn2O4 cathode is remarkably enhanced, obtaining an outstanding capacity retention of 84.3% after 2000 cycles.
Polyoxometalates@Metal-Organic Frameworks Derived Bimetallic Co/Mo2C Nanoparticles Embedded in Carbon Nanotube-Interwoven Hierarchically Porous Carbon Polyhedron Composite as a High-Efficiency Electrocatalyst for Al–S Batteries
- First Published: 04 August 2023
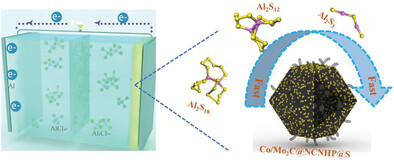
Polyoxometalates@Metal-Organic frameworks derived bimetallic cobalt clusters with Mo2C nanostructures embedded in carbon nanotubes interlaced layered porous carbon (Co/Mo2C@NCNHP) not only can effectively promote the electron transport within the cathode and confine the shuttle effect of aluminum polysulfides (AlPSs) by physical confinement and chemical adsorption, but also can catalyze the reversible kinetics of aluminum polysulfide conversion in Al–S battery (ASB).
3D Hollow Hierarchical Porous Carbon with Fe-N4-OH Single-Atom Sites for High-Performance Zn-Air Batteries
- First Published: 18 August 2023
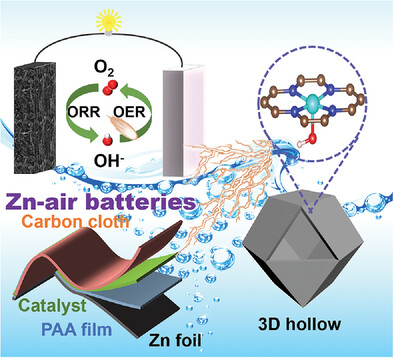
A hollow hierarchical porous ZIF8@FePMPDA-920 catalyst with unique asymmetric Fe-N4-OH moieties is constructed via a combined approach following the order of polymer coating, electrostatic absorption, and pyrolysis, showing superior oxygen reduction reaction and oxygen evolution reaction activities. The homemade liquid and flexible solid-state zinc-air batteries demonstrate excellent performance in terms of desirable open-circuit voltage, discharging specific capacity, and long-term durability.
SERS Sensing of Dopamine with Fe(III)-Sensitized Nanogaps in Recleanable AuNP Monolayer Films
- First Published: 21 August 2023
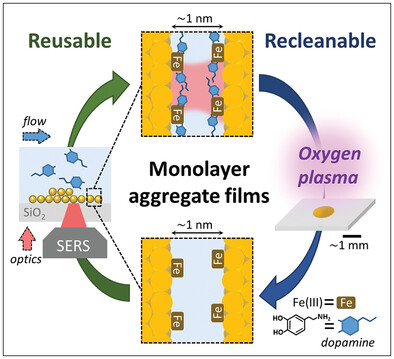
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) sensing of dopamine down to nm concentration is demonstrated using self-assembled monolayers of plasmonic Au nanoparticles sensitized with Fe(III) for multiplicative SERS enhancement. Since they are deposited onto glass, this configuration allows for double-sided access, enabling simultaneous flow and optical sensing. The repeated reusability after analyte sensing is demonstrated through oxygen plasma cleaning protocols.
Bone Homeostasis Modulating Orthopedic Adhesive for the Closed-Loop Management of Osteoporotic Fractures
- First Published: 21 August 2023
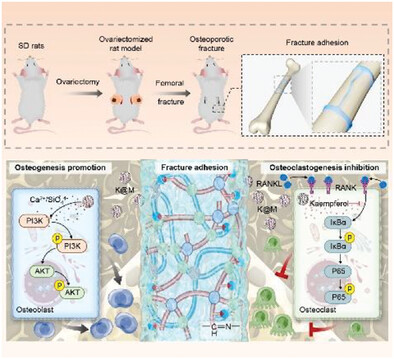
The orthopedic GMOS/K@M adhesive excels in splicing fracture fragments and facilitating osteoporotic fracture fixation using a non-invasive approach. GMOS/K@M adhesive, doped with mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles (MBGNs) and loaded with kaempferol, effectively treats osteoporotic fractures in a closed-loop management by restoring bone homeostasis through pro-osteogenic and anti-osteoclastic effects.
Biosynthesis of Multifunctional Transformable Peptides for Inducing Tumor Cell Apoptosis
- First Published: 21 August 2023

A biosynthesized protein-based material is fabricated by non-pathogenic Escherichia coli (E. coli). The self-assembled nanoparticles of P1 could transform into nanofibers in situ, which could lead to efficient anticancer activity. Furthermore, a spatiotemporally controllable anticancer system is constructed by coating P1-expressing E. coli with cationic conjugated polyelectrolytes to release the peptides in situ under light irradiation.
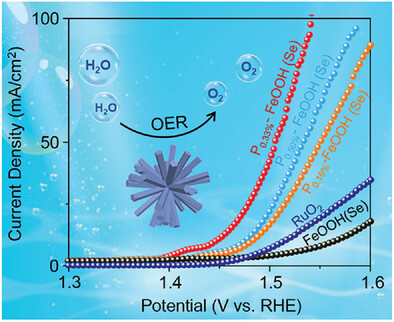
Electronic Structure Regulation and Surface Reconstruction of Iron Diselenide for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Activity
- First Published: 18 August 2023
Hydrophobic and Homogeneous Conductive Carbon Matrix for High-Rate Non-Alkaline Zinc-Air Batteries
- First Published: 21 August 2023
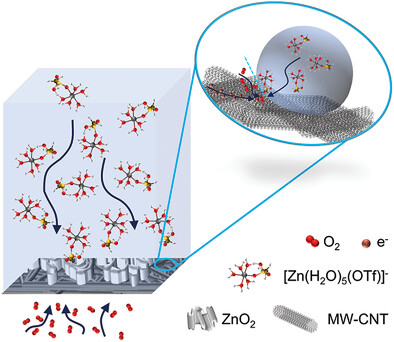
MW-CNTs cathodes demonstrate unique structures, superior hydrophobicity, and uniform electronic conductibility, thus benefit the gas–liquid–solid three-phase reaction interfaces in the non-alkaline electrolyte. And as a result, the non-alkaline zinc-air batteries using MW-CNTs cathodes display a high specific capacity with high zinc utilization ratio, superior rate performance, excellent cycling stability, and negligible self-discharge.