Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Covers
Cover Picture: Tailoring Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Copper by Reactive Ionic Liquid and Native Hydrogen Bond Donors (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1/2024)
- First Published: 23 November 2023
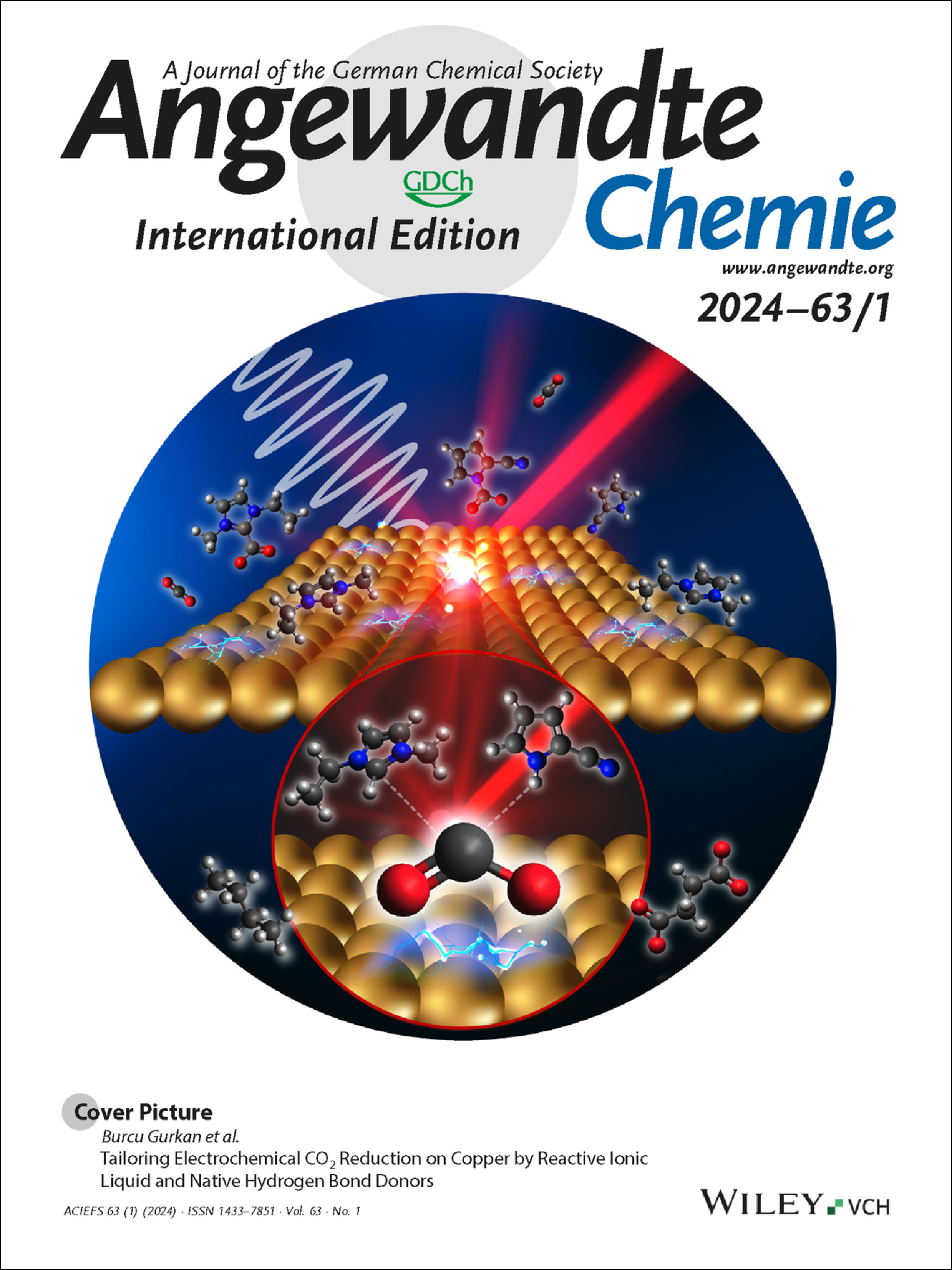
The dynamic interplay between a copper electrode and a reactive ionic liquid is illustrated in the cover picture, showcasing key components in the electrochemical reduction of CO2. The role of the cation in covering the electrode surface and the in-situ generated hydrogen bond donor from CO2 binding to the ionic liquid in enhancing the kinetics were uncovered by in-situ spectroscopy, complemented by electroanalytical and computational methods. Multi-carbon products with reduced reaction energy were obtained, as reported by Burcu Gurkan et al. in their Research Article (e202312163). Cover image credit: Miguel Munoz.
Inside Cover: pH-Responsive Protein Conformation Transistor (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1/2024)
- First Published: 23 November 2023

The successful creation of “core–shell” protein nanocrystals, which demonstrate ultra-rapid crystalline cross-linking behavior at pH levels above 7.6, underpins the concept of a protein conformation proton transistor. As reported by Peng Yang et al. in their Communication (e202310879), this pH-triggered cross-linking can be feasibly accomplished under conditions that resemble physiological environments, highlighting its significant potential in biomedicine, biosensing, and microfluidic chemistry.
Inside Back Cover: Photo-Induced Self-assembly of Copolymer-Capped Nanoparticles into Colloidal Molecules (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1/2024)
- First Published: 20 December 2023

The UV light-induced generation of colloidal molecules with precisely controlled structures is reported by Zhihong Nie, Yutao Sang and co-workers in their Research Article (e202313406). Photolabile copolymer ligands are used to control the self-assembly of complementary copolymer-capped binary nanoparticles A and B into clustered ABx or linear (AB)y structures on demand.
Back Cover: Significant Roles of Surface Hydrides in Enhancing the Performance of Cu/BaTiO2.8H0.2 Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1/2024)
- First Published: 23 November 2023

A BaTiO3 lattice is shown in the background of the cover picture, with the stack of orange balls symbolizing Cu nanoparticles. Pipes delivering the reactants and products have the shapes of H− and e− indicating they are involved in the catalytic hydrogenation of CO2. Lattice O is replaced with hydrides for the enhanced performance in CO2 hydrogenation to methanol, as demonstrated by Zili Wu et al. in their Research Article (e202313389).
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Enzymatic Upcycling of PET Waste to Calcium Terephthalate for Battery Anodes
- First Published: 27 December 2023

Depolymerization. In their Research Article (e202313633), Weiliang Dong, Ren Wei et al. report the enzymatic upcycling of polyethylene terephthalate waste to calcium terephthalate for battery anodes.
Graphical Abstract
Corrigenda
Corrigendum: Highly Efficient Production of Nanoporous Block Copolymers with Arbitrary Structural Characteristics for Advanced Membranes
- First Published: 06 December 2023
Announcement
Classifieds: Jobs and Awards, Products and Services
- First Published: 27 December 2023
Team Profile
A Team for the Low-Temperature Bulk Depolymerization of Polymethacrylates
- First Published: 08 November 2023
“Depolymerization has been on my mind since my PhD and I started seriously thinking about how to approach this topic during my postdoctoral studies… [We] then decided to initiate a collaboration with Lewis [Manring], as he was the world expert in this area—a topic that had not been revisited since the 1990s…” Find out more about the collaborative work in the Anastasaki group.
Introducing …
Kecheng Jie
- First Published: 09 November 2023

“A key experience in my education was a visit to Prof. Andrew I. Cooper's group at the University of Liverpool as an exchange PhD student where I started to learn about porous materials and crystal engineering and then got obsessed… The biggest scientific advance of the last decade was artificial intelligence.” Find out more about Kecheng Jie in his Introducing… Profile.
Minireviews
Radicals
Spin Frustration in Organic Radicals
- First Published: 28 September 2023
Spin frustration has drawn people's attention for its significance in physics and materials science, especially for quantum spin liquids. Organic radical species show a promising potential in building spin-frustrated compounds. This Minireview briefly introduces the reported examples of organic radicals that possess spin frustration and summarizes their related data on frustration properties.
Organic Optoelectronics
Towards Artificial Visual Sensory System: Organic Optoelectronic Synaptic Materials and Devices
- First Published: 02 October 2023
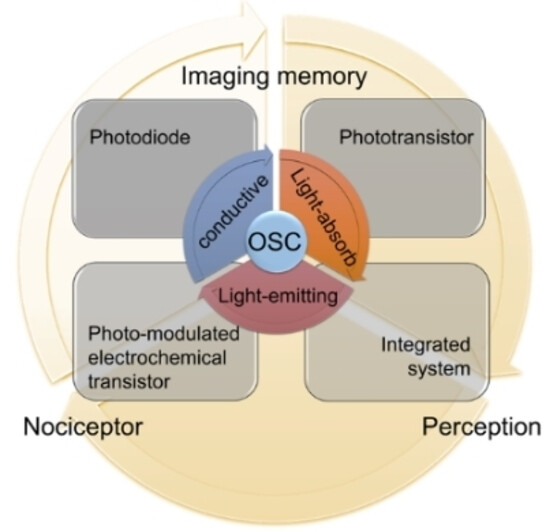
Creating an artificial visual sensory system demands cutting-edge optoelectronic materials and devices capable of emulating the intricate functions of biological synapses. In this concise review, we delve into the latest breakthroughs in organic materials, devices, and applications pertaining to the realm of artificial visual sensory systems. Our comprehensive summary of these developments serves as a vital source of insight, illuminating the path forward for future advancements in this dynamic field.
CO2 Reduction
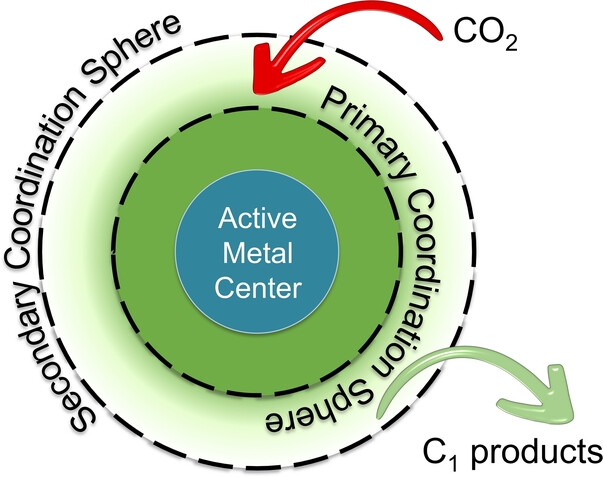
From Biomimicking to Bioinspired Design of Electrocatalysts for CO2 Reduction to C1 Products
- First Published: 05 October 2023
Reviews
Nanostructures
Spatiotemporal Studies of Soluble Inorganic Nanostructures with X-rays and Neutrons
- First Published: 25 September 2023
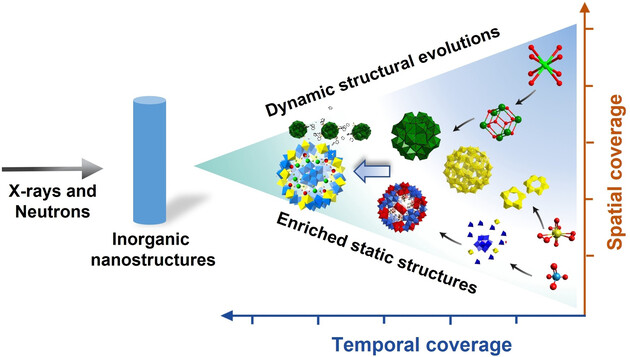
Advanced X-ray scattering and absorption as well as neutron scattering can extract structural information describing assembly and supramolecular assembly of soluble inorganic nanostructures (SoINs). Here we review the use of X-rays and neutrons for SoIN characterization, covering basic principles, practices, data analysis, and recent relevant studies that probe the solution state of materials/inorganic chemistry.
Electrocatalysis
Unlocking Catalytic Potential: Exploring the Impact of Thermal Treatment on Enhanced Electrocatalysis of Nanomaterials
- First Published: 29 September 2023

This review examines the impact of thermal treatments on the optimization of nano-electrocatalysts for electrochemical applications. It focuses on atomic-level structural changes induced by heat and assesses their influence on electrocatalysis. The article also offers tailored approaches to guide researchers in selecting effective techniques and thermal settings, thereby advancing electrochemical research.
Research Articles
Catalysis
Enzymatic Upcycling of PET Waste to Calcium Terephthalate for Battery Anodes
- First Published: 25 October 2023
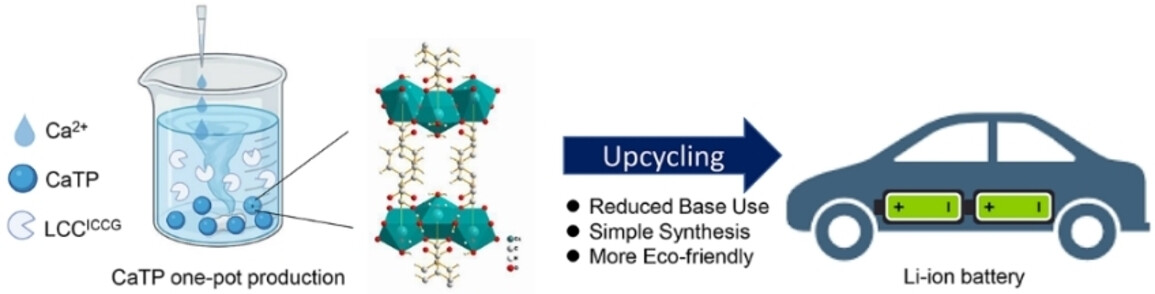
This study successfully demonstrates the one-pot biocatalysis-based production of calcium terephthalate from waste PET. The incorporation of Ca2+ during the production process not only enhanced the efficiency of enzymatic plastic depolymerization but also reduced the base consumption. Consequently, this approach has proven to be a cost-effective and eco-friendly method for upcycling PET into calcium terephthalate.
Nanoparticles | Very Important Paper
Photo-Induced Self-assembly of Copolymer-Capped Nanoparticles into Colloidal Molecules
- First Published: 06 October 2023
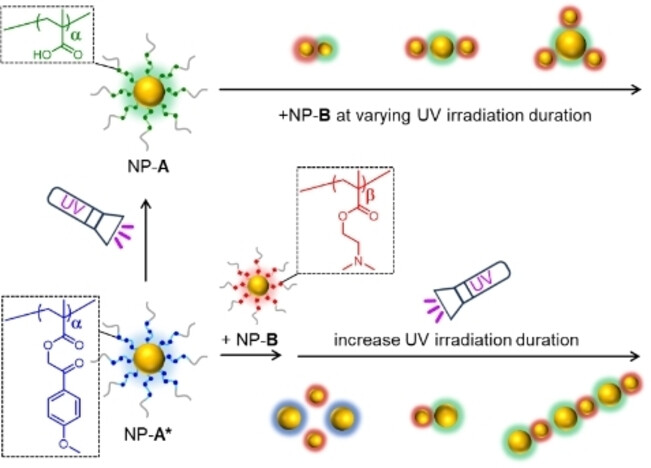
This work describes the photo-induced self-assembly of binary nanoparticles capped with a layer of complementary copolymer ligands into well-defined colloidal molecules. By varying the irradiation duration and the order of mixing and irradiating, the assembly process yields clustered ABx and linear (AB)y structures (x is the coordination number of NP-Bs, and y is the repeating unit number of AB clusters in the linear structure) at high precision and tunability.
Vaccine Adjuvants
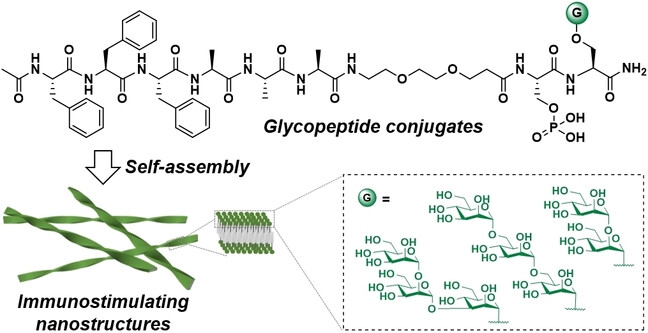
Facile Preparation of Carbohydrate-Containing Adjuvants Based on Self-Assembling Glycopeptide Conjugates
- First Published: 11 November 2023
Multicomponent Reactions | Hot Paper
Diversification of a Novel α-Galactosyl Ceramide Hotspot Boosts the Adjuvant Properties in Parenteral and Mucosal Vaccines
- First Published: 19 October 2023

A previously underexplored α-GalCer chemical space was discovered and diversified to elicit very high antigen-specific humoral and cellular immune responses. The multicomponent derivatization of the new glycolipid hotspot allowed the incorporation either of extra functionalities that enhanced the adjuvant effect or conjugation handles that are useful for the development of self-adjuvanting vaccines.
Artificial Peroxidase | Hot Paper
Spiky Artificial Peroxidases with V−O−Fe Pair Sites for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogens
- First Published: 12 November 2023
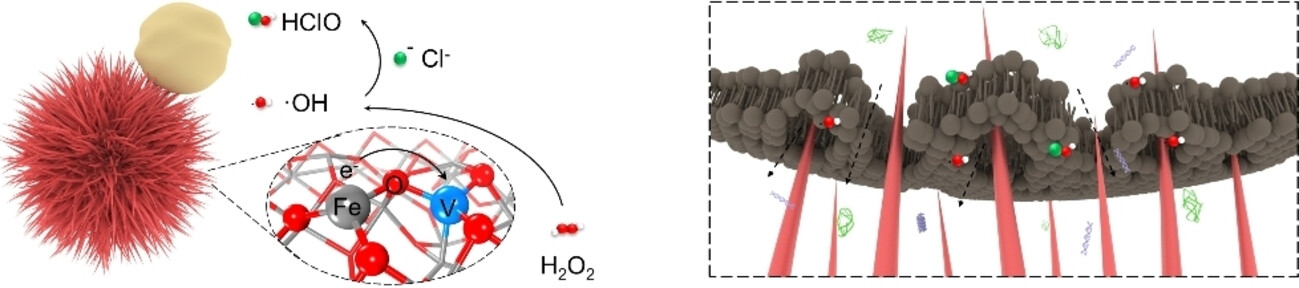
An iron oxide-based spiky artificial peroxidase with V−O−Fe pair sites (V-Fe2O3) for efficient and selective ROS-catalysis has been reported. We demonstrate that the V-Fe2O3 can achieve the localized “capture and killing” bifunction from the spiky morphology and massive ROS (⋅OH and HClO) production, which efficiently eliminate MRSA and accelerate wound recovery without causing noticeable inflammation and toxicity.
Phospholipids
Rapid Formation of Non-canonical Phospholipid Membranes by Chemoselective Amide-Forming Ligations with Hydroxylamines
- First Published: 02 November 2023
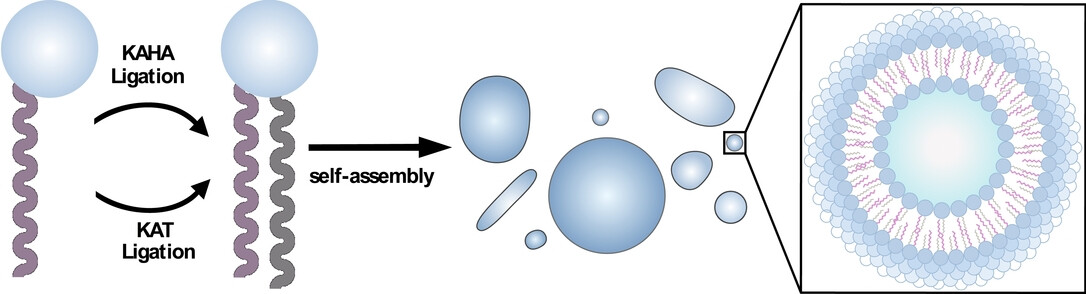
Bioorthogonal de novo phospholipid synthesis utilizing the reactions between hydroxylamine and α-ketoacids (KAs) or potassium acyltrifluoroborates (KATs) enables the rapid formation of biomimetic membranes under physiological pH conditions, using reactant concentrations in the micromolar range. Additionally, these reactions are biocompatible and can be performed in living mammalian cells.
Microgels
Liquid Metal Nanocores Initiated Construction of Smart DNA-Polymer Microgels with Programmable and Regulable Functions and Near-Infrared Light-Driven Locomotion
- First Published: 14 November 2023
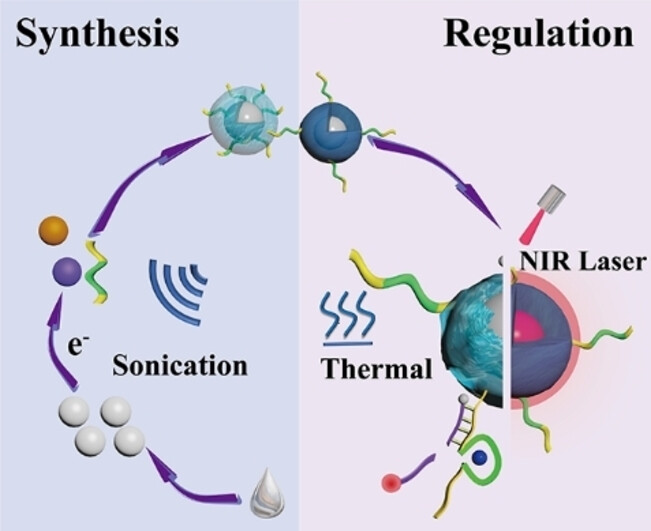
Surface-initiated polymerization reaction of gallium-based liquid metal nanoparticles under sonication allows the construction of smart core/shell microgels. Multifunctional DNA microgels with tunable properties were prepared by introducing different vinyl monomers and functional DNA structures and controlling the polymerization process. The photothermal effect of LM NPs also contributed to the NIR-driven motion of these smart microgels.
CO2 Reduction | Hot Paper
Tailoring Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Copper by Reactive Ionic Liquid and Native Hydrogen Bond Donors
- First Published: 24 October 2023
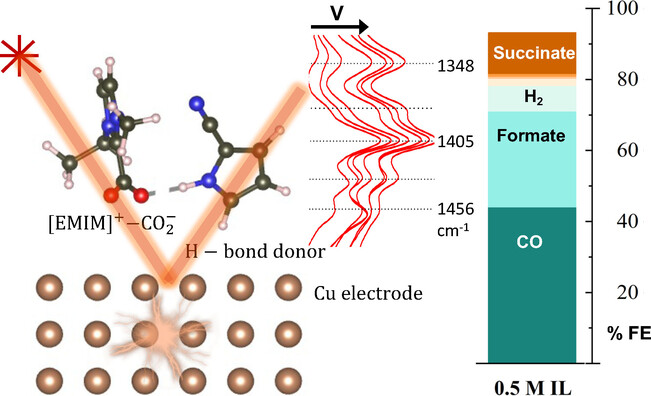
A dynamic exchange of the hydrogen between the CO2 absorbed cation and the anion of a functional ionic liquid modulates the electroreduction of CO2 over copper as examined by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and ab initio calculations. The microenvironment created by the ionic liquid enables conversion products beyond CO with reduced potential requirements, increased current, and product selectivity.
Supramolecular Chemistry
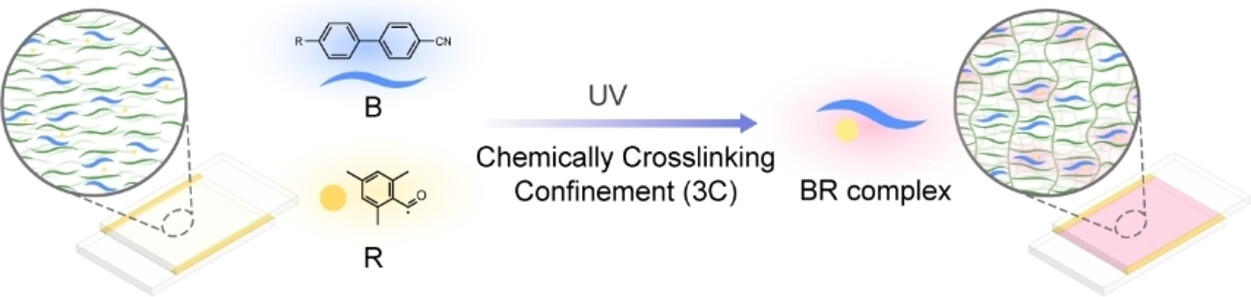
Capturing Doublet Intermediate Emitters by Chemically Crosslinking Confinement towards Spatiotemporal Encryption
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Enzyme Immobilization | Hot Paper
Expanding the Enzymatic Polymerization Landscape by Lipid Mesophase Soft Nanoconfinement
- First Published: 14 November 2023
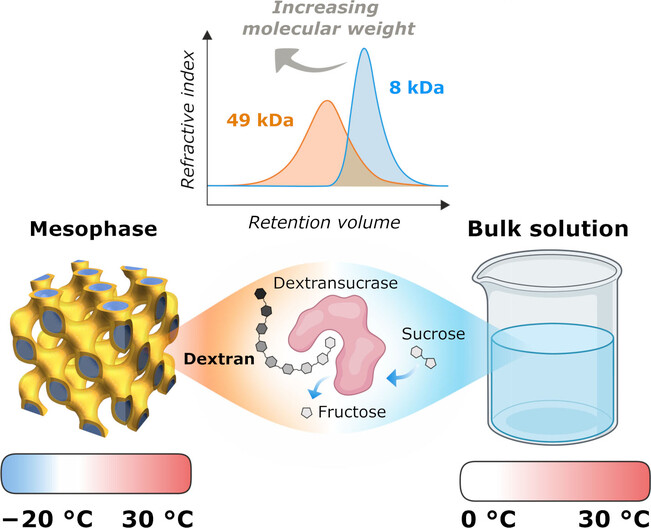
The enzymatic synthesis of dextran in lipidic mesophase catalyzed by the enzyme dextransucrase DSR-M not only yields polymers at 30 °C that are six times longer than in bulk solution at identical concentrations of reactants, but also allows the reaction to be carried out in subzero liquid water at temperatures as low as −20 °C.
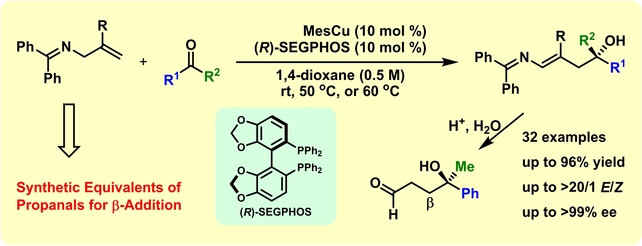
Hydrofunctionalization Reactions
Diphosphine Ligand-Enabled Nickel-Catalyzed Chelate-Assisted Inner-Selective Migratory Hydroarylation of Alkenes
- First Published: 20 November 2023
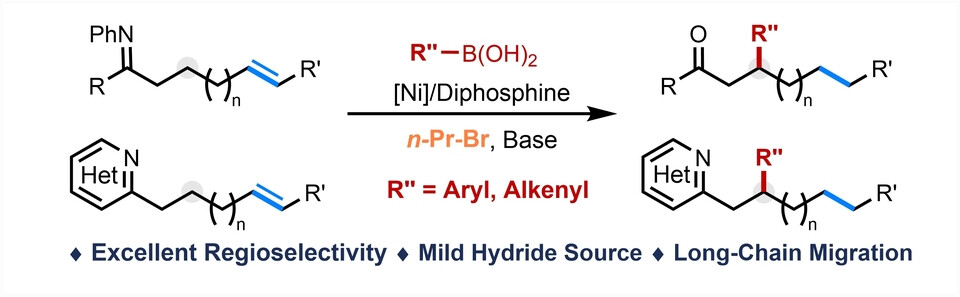
Ni-catalyzed migratory β-selective hydroarylation and hydroalkenylation of alkenyl ketones and alkenyl azahetereoarenes have been realized with aryl boronic acids using alkyl halide as the mild hydride source. This reaction features mild conditions, broad substrate scope and incredible heterocycle compatibility, providing a variety of β-aryl or -alkenyl ketones or heteroarenes in moderate to high yields.
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Active Sites in Cr(III)-Based Ethylene Polymerization Catalysts from Machine-Learning-Supported XAS and EPR Spectroscopy
- First Published: 16 November 2023
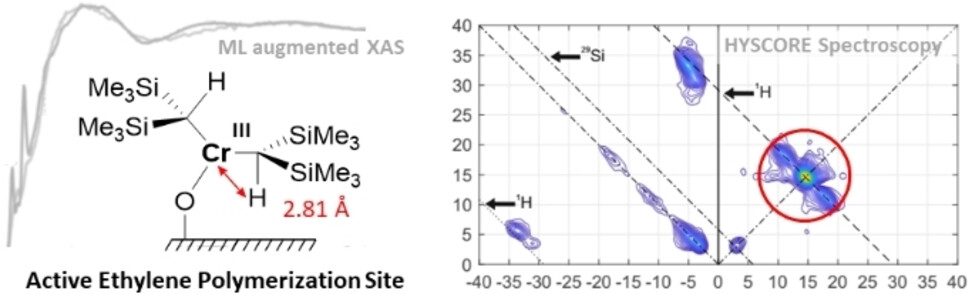
Ethylene polymerization catalyst prepared by grafting Cr[CH(SiMe3)2]3 on SiO2 contains well-defined Cr(III) alkyl surface sites, as shown using a combination of ML-supported-XAS and EPR spectroscopies. Furthermore, it is also possible to show by EPR that Cr(III) alkyl sites are competent for olefin insertion.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Nickel-Catalyzed Asymmetric Propargyl-Aryl Cross-Electrophile Coupling
- First Published: 20 November 2023
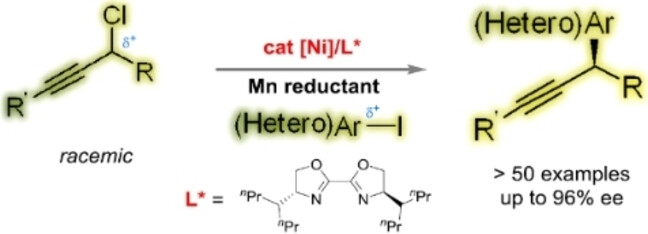
A catalytic enantioselective propargyl-aryl cross-coupling between two electrophiles was achieved for the first time in a stereoconvergent manner. The potential utility of this conversion is demonstrated in the facile construction of stereoenriched bioactive molecule derivatives and medicinal compounds based on the diversity of acetylenic chemistry. Detailed experimental studies have revealed the key mechanistic features of this transformation.
CO2 Hydrogenation | Very Important Paper
Significant Roles of Surface Hydrides in Enhancing the Performance of Cu/BaTiO2.8H0.2 Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol
- First Published: 31 October 2023
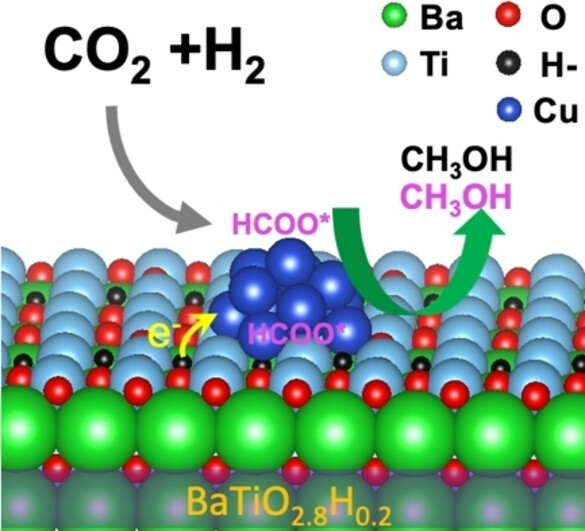
Introducing hydrides into the lattice of BaTiO3 can notably enhance the methanol yield over a supported Cu catalyst in CO2 hydrogenation due to the direct participation of surface hydrides in the reaction and the modified electronic property of the interfacial sites in the Cu/ BaTiO2.8H0.2 catalyst.
Atropisomers
Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydroarylative Cyclization of 1,6-Diynes to Access Atropisomerically Labile Chiral Dienes
- First Published: 16 November 2023
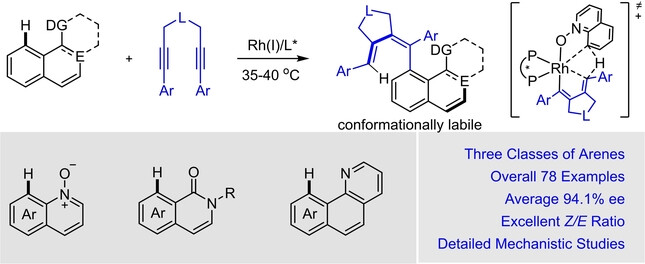
Rhodium(I)-catalyzed hydroarylative cyclization of 1,6-diynes with three distinct classes of arenes has been realized, enabling highly enantioselective synthesis of a broad range of axially chiral 1,3-dienes that are conformationally labile. Detailed mechanistic studies have been explored by experimental and computational methods.
Flow Chemistry
Continuous-Flow Enantioselective Hydroacylations under Heterogeneous Chiral Rhodium Catalysts
- First Published: 22 November 2023
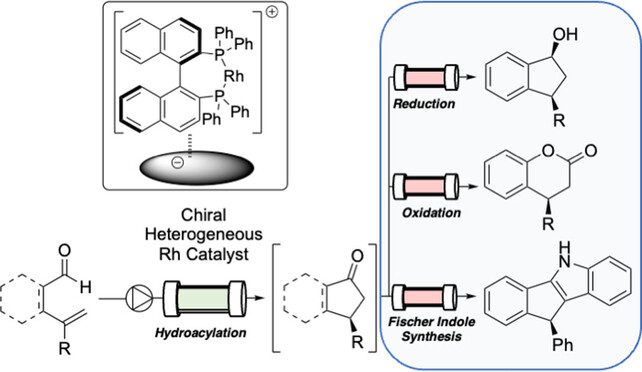
Heterogeneous chiral Rh catalysts were developed for continuous-flow enantioselective hydroacylations. The prepared catalysts exhibited excellent activity and enantioselectivity affording optically active ketones in quantitative yields with 99 % ee's without the leaching of Rh. The catalysts exhibited a wide substrate scope and, in sequential-flow reactions, the flow syntheses of value-added chemicals were demonstrated.
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
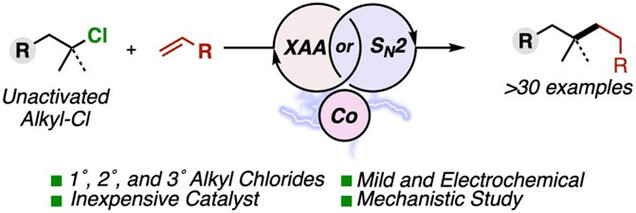
Cobalt-Catalyzed Electroreductive Alkylation of Unactivated Alkyl Chlorides with Conjugated Olefins
- First Published: 14 November 2023
Natural Products | Hot Paper
Analgesic Buxus alkaloids with Enhanced Selectivity for the Low-Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel Cav3.2 over Cav3.1 through a New Binding Mode
- First Published: 23 November 2023
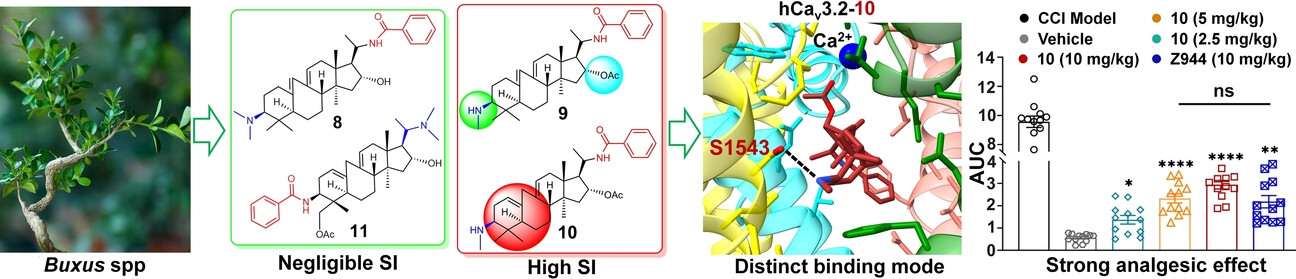
It is important to explore modulators with heightened selectivity index (SI) for a subtype of low-voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (Cav3.1–3.3) for drug development. Among 23 Buxus alkaloids featuring three distinct carbon skeletons, 9(10/19)abeo-artane-type compounds 9 and 10 were identified as a novel type of Cav3.2 inhibitor. With a unique binding mode, they exhibit highly enhanced preference for Cav3.2 over Cav3.1 and robust analgesic effects.
Skeletal Editing | Very Important Paper
Dearomative Insertion of Fluoroalkyl Carbenes into Azoles Leading to Fluoroalkyl Heterocycles with a Quaternary Center
- First Published: 15 November 2023
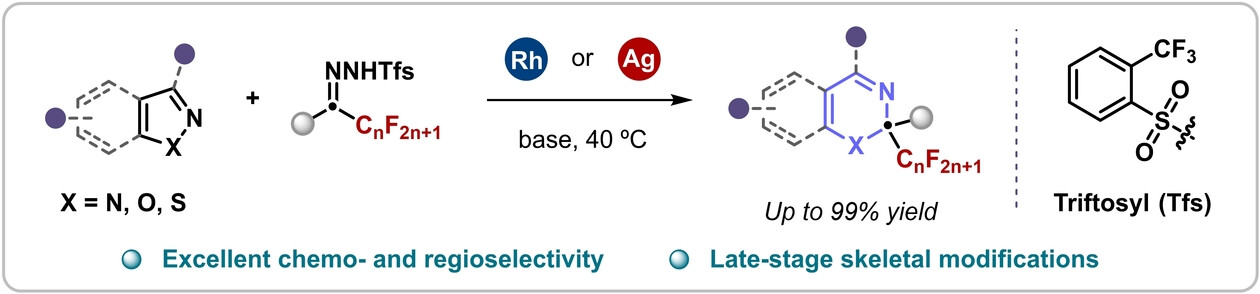
A general skeletal ring expansion strategy was developed for the direct conversion of azoles into various heterocyclic frameworks containing fluoroalkyl-substituted quaternary centers through dearomative one-carbon insertion using fluoroalkyl N-triftosylhydrazones. The method is scalable, tolerates diverse functional groups, and is amenable to the synthesis of medicinally relevant molecules.
Phase Change Materials
Metavalent Bonding in 2D Chalcogenides: Structural Origin and Chemical Mechanisms
- First Published: 20 November 2023
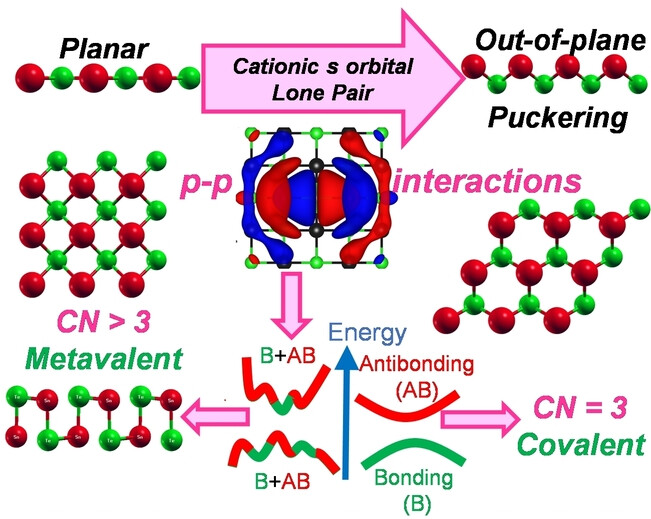
The unique properties of Group IV chalcogenide rocksalt crystals are associated with metavalent bonding (MVB), a recent subject of debate. In this study, we investigate various 2D lattices of chalcogenides to understand MVB. Honeycomb lattices adhere to the 8-N rule and are covalently bonded. Square and orthorhombic structures display in-plane MVB, driven by p-p orbital interactions, with cationic lone pairs inducing out-of-plane puckering.
Radical Reactions
Iron-Catalyzed Asymmetric α-Alkylation of 2-Acylimidazoles via Dehydrogenative Radical Cross-Coupling with Alkanes
- First Published: 20 November 2023
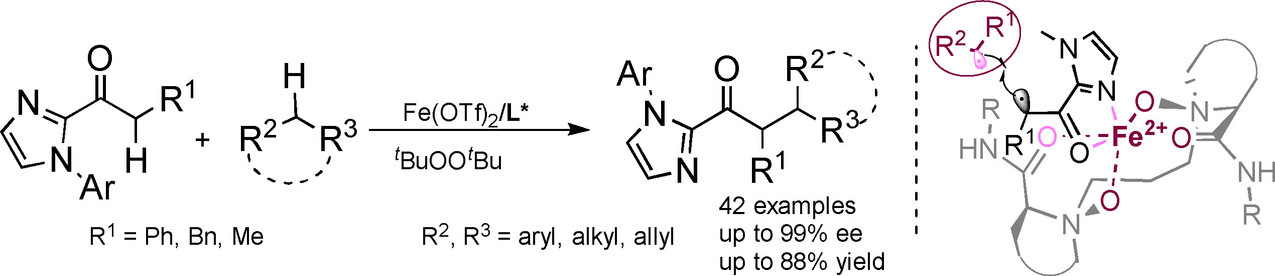
The asymmetric α-alkylation of acyclic carbonyls with hydrocarbons is of substantial interest and challenge. Herein, we achieved the enantioselective oxidative cross-coupling of 2-acylimidazoles with up to 99 % ee in moderate to good yields, thus providing an elegant access to optically active carbonyl compounds. Density functional theory calculations suggest a radical-radical cross-coupling pathway.
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Leveraging the Proximity and Distribution of Cu−Cs Sites for Direct Conversion of Methanol to Esters/Aldehydes
- First Published: 21 November 2023
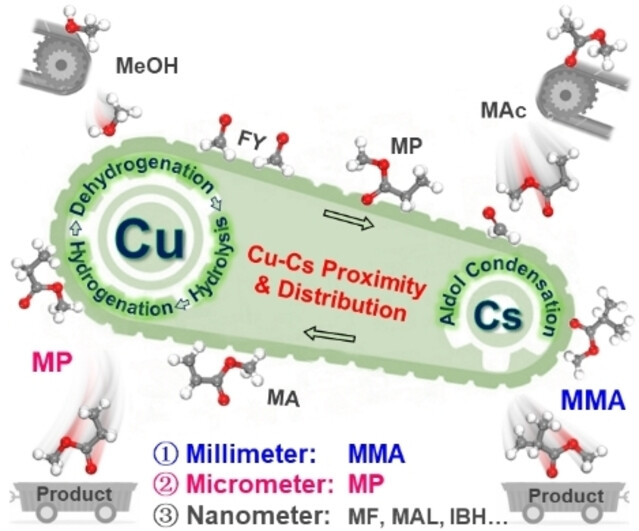
An unprecedented quadruple tandem catalytic production of esters and aldehydes from methanol and methyl acetate/ethanol has been developed, allowing for customized chain length and saturation by leveraging the proximity and distribution of Cu−Cs sites. This approach has the potential to revolutionize the production of value-added methyl methacrylate (MMA), surpassing the current industrial processes to significantly lower the production costs.
Supramolecular Polymers
One-Dimensionally Arranged Quantum-Dot Superstructures Guided by a Supramolecular Polymer Template
- First Published: 20 November 2023
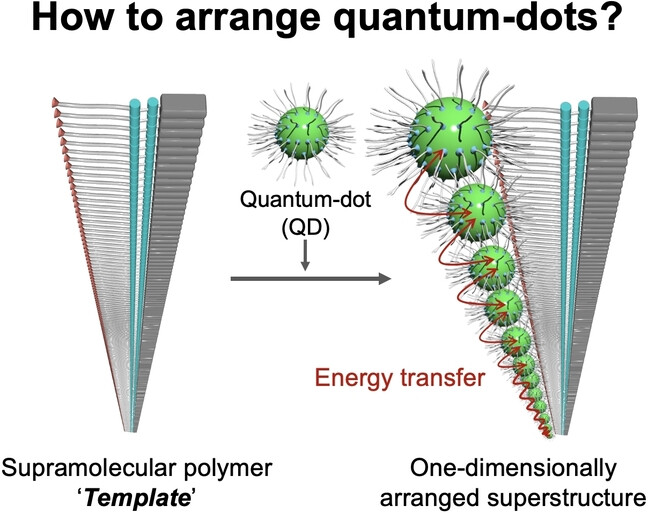
A one-dimensionally arranged quantum-dot superstructure has been created by using a supramolecular polymer template composed of hydrogen-bonded cholesterol derivatives. This superstructure is not obtained by the self-assembly of the quantum dots in the absence of the template. The closely arranged quantum dots allows efficient energy transfer between them.
Nanosheets | Hot Paper
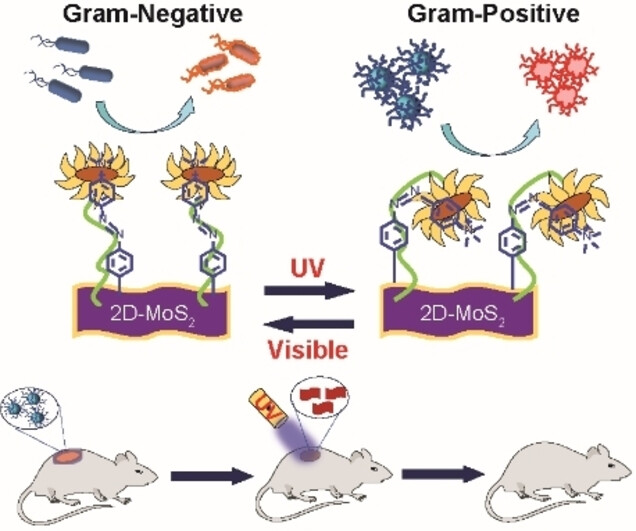
Photo-Controlled Gating of Selective Bacterial Membrane Interaction and Enhanced Antibacterial Activity for Wound Healing
- First Published: 13 November 2023
Single-Atom Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Well-defined N3C1-anchored Single-Metal-Sites for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
- First Published: 22 November 2023
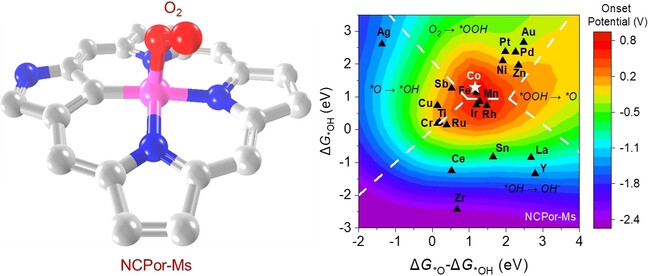
N3C1-anchored single metal sites in well-defined molecules are studied to make up the structure-property correlation study challenge for carbon materials. The established volcano plots and the experimental catalysis results provide possibilities of fundamental understanding of asymmetric single metal active sites for electrochemical catalysis.
Analytical Methods
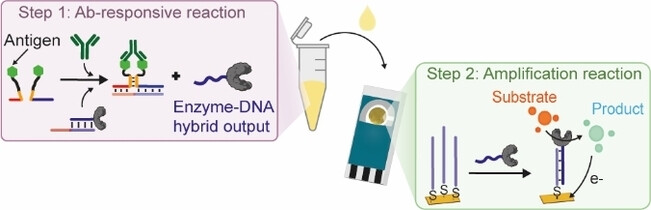
Enzyme-Linked DNA Displacement (ELIDIS) Assay for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection of Antibodies
- First Published: 23 November 2023
Sustainable Chemistry | Very Important Paper
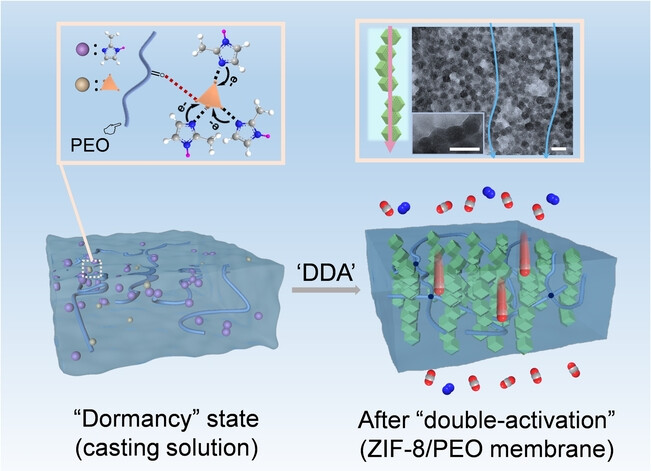
Dormancy and double-activation strategy for construction of high-performance mixed-matrix membranes
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Homogeneous Catalysis
(3+2) Annulation of 4-Acetoxy Allenoate with Aldimine Enabled by AgF-Assisted P(III)/P(V) Catalysis
- First Published: 20 November 2023
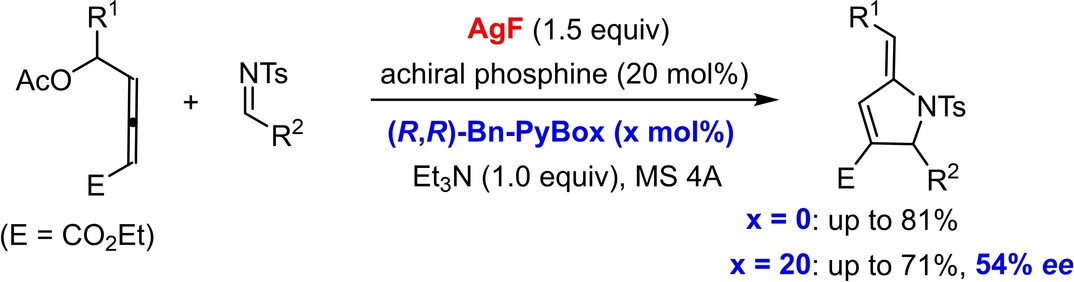
AgF is capable of converting the enolate-phosphonium zwitterion into a novel silver enolate-fluorophosphorane species, which enables the development of (3+2) annulation of 4-acetoxy allenoate and aldimine via P(III)/P(V) catalysis. The proof-of-concept study has demonstrated that the silver enolate moiety offers an alternative approach to realize an asymmetric variant merely by the introduction of an additional chiral PyBox ligand.
Asymmetric Synthesis | Very Important Paper
Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Formal [4+1] Cyclization of Benzyl Alcohols and Benzaldimines: Facile Access to Silicon-Stereogenic Heterocycles
- First Published: 08 November 2023
![Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Formal [4+1] Cyclization of Benzyl Alcohols and Benzaldimines: Facile Access to Silicon-Stereogenic Heterocycles](/cms/asset/6c405a99-9b8d-4dca-baf5-d8c7ab165886/anie202315230-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A rhodium-catalyzed enantioselective formal [4+1] annulation of benzyl alcohols and benzaldimines with secondary silanes has been achieved in excellent enantioselectivity to afford a range of sila-O- and sila-N-heterocycles with silicon-stereogenic centers, where the rhodium catalyst plays a dual role in the O/N-Si and C-Si coupling.
Solar Cells | Very Important Paper
Synchronous Elimination of Excess Photoinstable PbI2 and Interfacial Band Mismatch for Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 22 November 2023
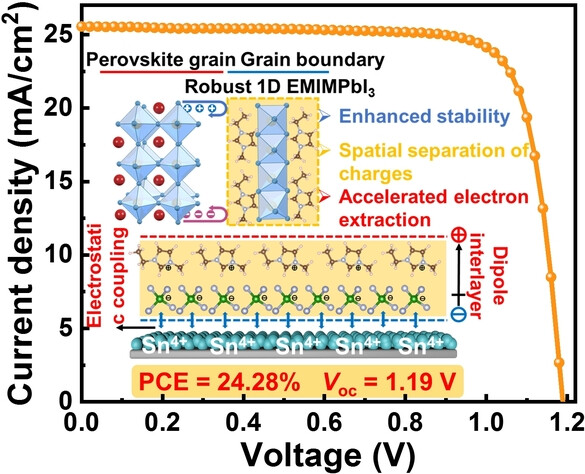
Sufficient conversion of residual photoinstable PbI2 into robust 1D perovskite (EMIMPbI3) can improve device stability, while the formation of an interfacial dipole layer at the SnO2/perovskite interface can reduce the energetic mismatch via a single process. The optimized device delivers an efficiency of 24.28 % and a remarkable open circuit voltage of 1.19 V, accompanied with excellent humidity and operational stability.
Ammonia Synthesis
Gram-level NH3 Electrosynthesis via NOx reduction on a Cu Activated Co Electrode
- First Published: 12 November 2023
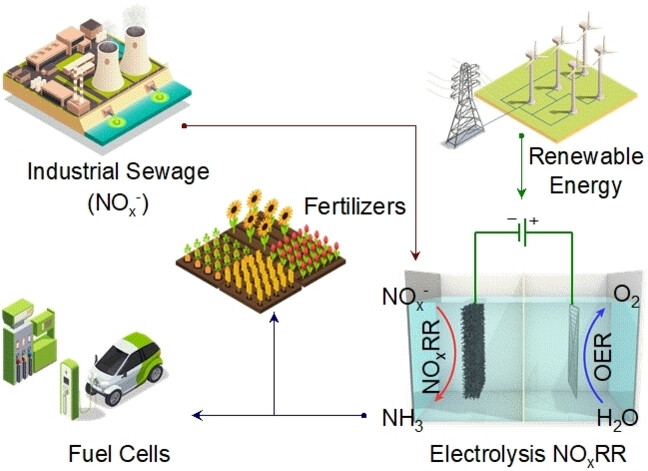
A high-efficiency electrochemical ammonia (NH3) synthesis from NOx on a Cu-activated Co foam electrode was developed as a promising alternative for the Haber–Bosch process. The new synthesis can convert pollutants into elevated value-added NH3 applicable for agriculture, energy storage, etc., imposing a sustainable nitrogen cycle.
Solar Cells
Fully Aromatic Self-Assembled Hole-Selective Layer toward Efficient Inverted Wide-Bandgap Perovskite Solar Cells with Ultraviolet Resistance
- First Published: 21 November 2023
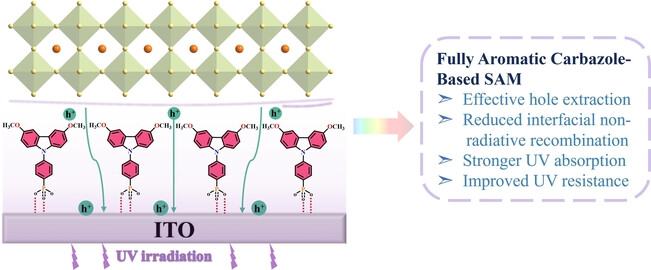
A fully aromatic carbazole-based self-assembled monolayer, denoted as MeO-PhPACz, is employed as a hole-selective layer (HSL) in inverted wide-band gap perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The fully aromatic configuration is crucial in promoting the formation of a dense and highly ordered HSL, improving hole extraction/transport efficiency. The optimized wide-band gap PSCs attain a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 21.10 % and excellent UV resistance.
Batteries
New Reaction Pathway of Superoxide Disproportionation Induced by a Soluble Catalyst in Li-O2 Batteries
- First Published: 27 November 2023
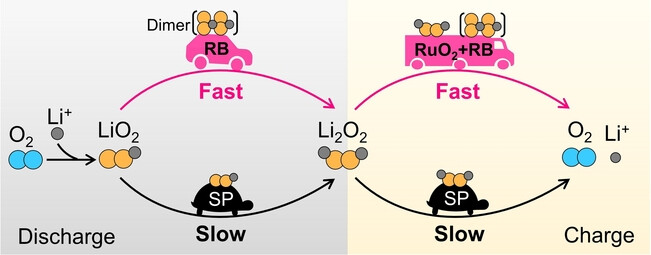
Ruthenium tris(bipyridine) (RB) cations promote the intramolecular charge transfer of O2− dimers and accelerate their disproportionation in discharge and charge processes. This facilitates the reaction kinetics and simultaneously mitigates O2− and 1O2 related side reactions to endow the Li-O2 battery with small overvoltages and prolonged cycling stability.
Electrocatalytic H2 Evolution
Multi-d Electron Synergy in LaNi1-xCoxRu Intermetallics Boosts Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 20 November 2023
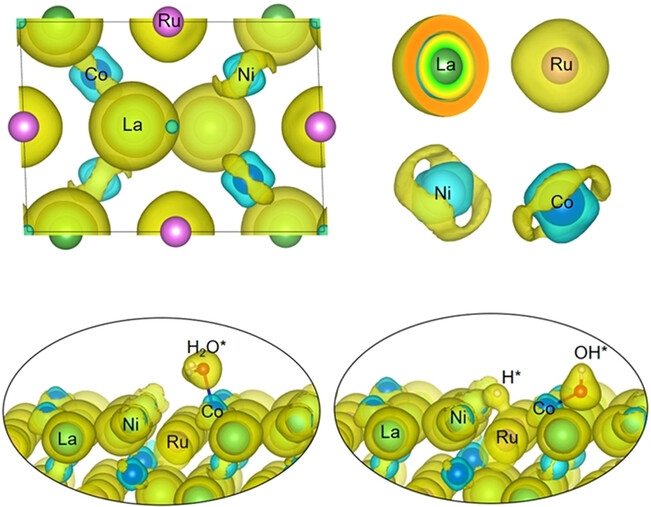
Novel LaNi1-xCoxRu intermetallics were prepared. In these compounds, the 5d orbital of La transfers electrons to the 4d orbital of Ru, which provides adsorption sites for H*. The 3d orbitals of Ni and Co interact with the 5d and 4d orbitals to generate an anisotropic electron distribution, which facilitates the adsorption and desorption of OH*. The synergistic effect of multi-d electrons ensures efficient catalytic activity.
Sustainable Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Ultrapermeable Gel Membranes Enabling Superior Carbon Capture
- First Published: 20 November 2023
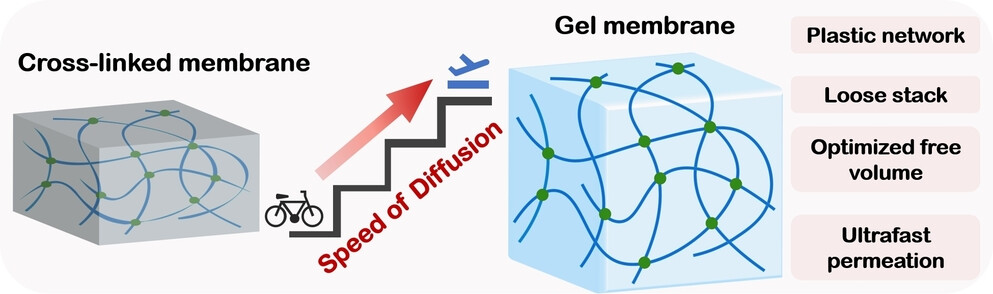
Gel membranes integrate the structural benefits of solid and liquid phases, culminating in the plasticization of cross-linked structure. This results in a decrease in the density of chain segment stacking and enhances the free volume within the separation membrane. Consequently, these gel membranes exhibit exceptional gas permeability, setting new records in performance.
Solar Cells | Very Important Paper
Cesium Cyclopropane Acid-Aided Crystal Growth Enables Efficient Inorganic Perovskite Solar Cells with a High Moisture Tolerance
- First Published: 22 November 2023
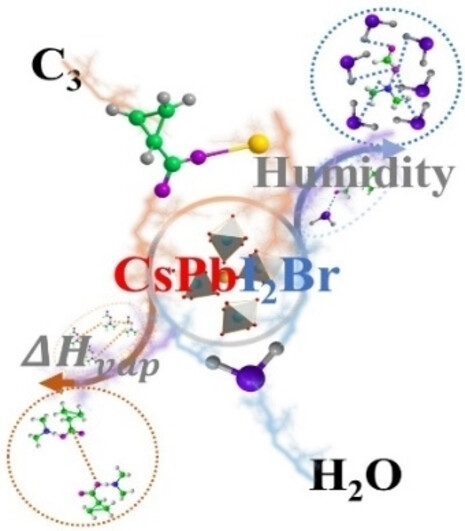
Using cesium cyclopropane acids (C3) gives high crystallization quality in an all-inorganic perovskite CsPbI2Br prepared in a wide ambient moisture window (RH: 25–65 %). The resultant CsPbI2Br solar cells exhibit a high efficiency (>17 %) and excellent environmental stability. The vaporization enthalpy of the side product DMA-acid (adjustable by C3 loads) modifies the perovskite crystallization and device performance under different humidity.
Enzyme Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Reconstitution of the Final Steps in the Biosynthesis of Valanimycin Reveals the Origin of Its Characteristic Azoxy Moiety
- First Published: 14 November 2023
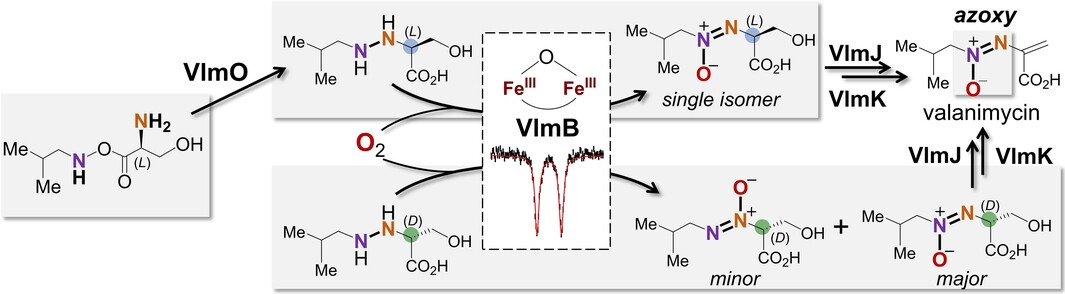
The final steps of valanimycin biosynthesis have been reconstituted in vitro. The oxidation of a dialkyl hydrazine intermediate to the characteristic azoxy moiety in valanimycin is catalyzed by VlmB, which is a non-heme diiron enzyme. The VlmB-catalyzed four-electron oxidation may commence with a resting μ-oxo diferric complex without prior reduction.
Solid-state Li Batteries
Achieving the High Capacity and High Stability of Li-Rich Oxide Cathode in Garnet-Based Solid-State Battery
- First Published: 20 November 2023
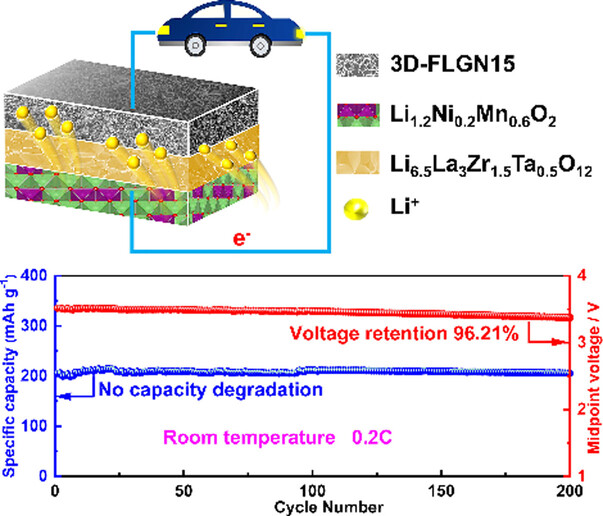
We successfully constructed a high-performance solid-state battery based on Li-rich Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 cathode, Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 solid electrolyte and GaN-modified Li anode. The assembled Li symmetric cell shows quite low interfacial resistance and great interfacial stability, and the full battery shows a high initial capacity, a high capacity retention, a high rate capability and a significantly mitigated voltage decay demonstrating a great potential in high energy density solid-state battery.
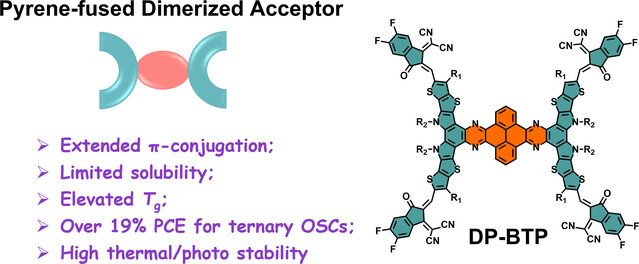
Solar Cells
A Pyrene-Fused Dimerized Acceptor for Ternary Organic Solar Cells with 19% Efficiency and High Thermal Stability
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Electrocatalysis
Perovskite Oxide as A New Platform for Efficient Electrocatalytic Nitrogen Oxidation
- First Published: 20 November 2023
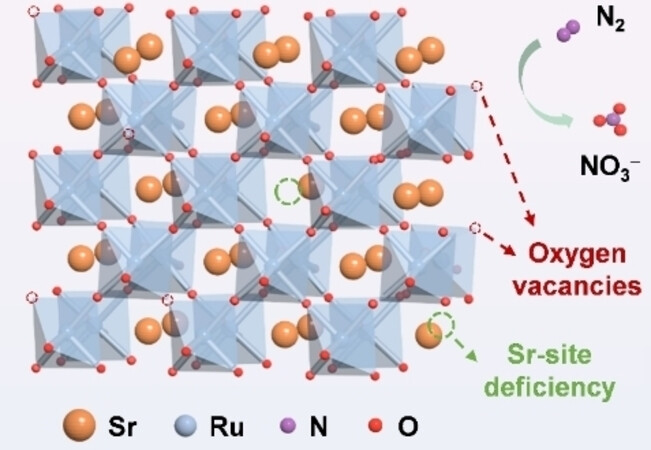
An oxygen-vacancy-enriched Sr and Ru perovskite oxide is constructed by modulating the Sr-site deficiency, thus exhibiting high Faradaic efficiency (38.6 %) and high NO3− yield rate (17.9 μmol mg−1 h−1) in the electrocatalytic nitrogen oxidation reaction (NOR). The Ru active sites along with their adjacent oxygen vacancies in the perovskite oxide enhance the adsorption/activation of N2 molecules and decrease the thermodynamic barrier towards NOR.
Porous Carbon
Room-Temperature Salt Template Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped 3D Porous Carbon for Fast Metal-Ion Storage
- First Published: 20 November 2023
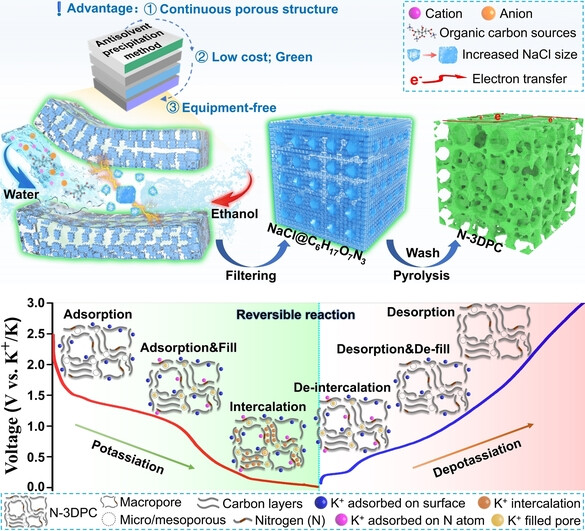
By combining experimental and theoretical approaches, a facile and green recyclability room-temperature salt template antisolvent precipitation strategy is developed to prepare nitrogen-doped 3D pore carbon (N-3DPC). In situ Raman and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analyses reveal that N-3DPC has highly reversible adsorption, fill, and intercalation reaction mechanisms, resulting in superior alkali metal-ion storage performance.
Fluorescent Probes
Thiolation for Enhancing Photostability of Fluorophores at the Single-Molecule Level
- First Published: 17 November 2023
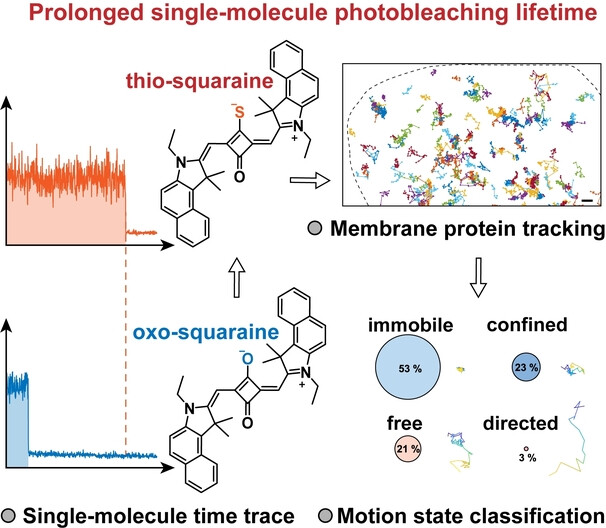
Single-molecule imaging can elucidate the intricate biomolecular dynamics in vivo. We present a straightforward thiolation of squaraine that enhances its photobleaching lifetime by approximately fivefold at the single molecule level. This advancement allows for extended single-molecule tracking of the membrane protein CD56 in live cells, effectively tripling the duration of our observations.
Li Organic Batteries | Very Important Paper
Dendritic sp Carbon-Conjugated Benzothiadiazole-Based Polymers with Synergistic Multi-Active Groups for High-Performance Lithium Organic Batteries
- First Published: 21 November 2023
Natural Products
Bent π-Conjugation within a Macrocycle: Asymmetric Total Syntheses of Spirohexenolides A and B
- First Published: 21 November 2023
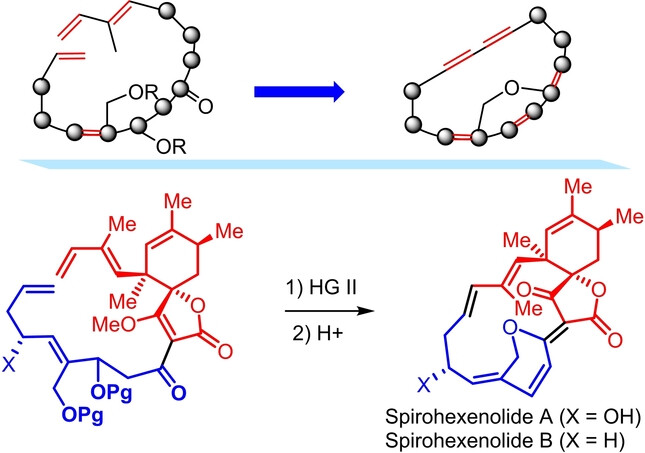
The first asymmetric total synthesis of spirotetronate polyketides spirohexenolides A and B is reported. This synthesis features a ring-closing metathesis macrocyclization followed by double dehydration to achieve the C15 macrocycle with the unprecedented deformed nonplanar 1,3,5-triene conjugation.
CO2 Reduction
Effect of Feature Shape and Dimension of a Confinement Geometry on Selectivity of Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- First Published: 20 November 2023
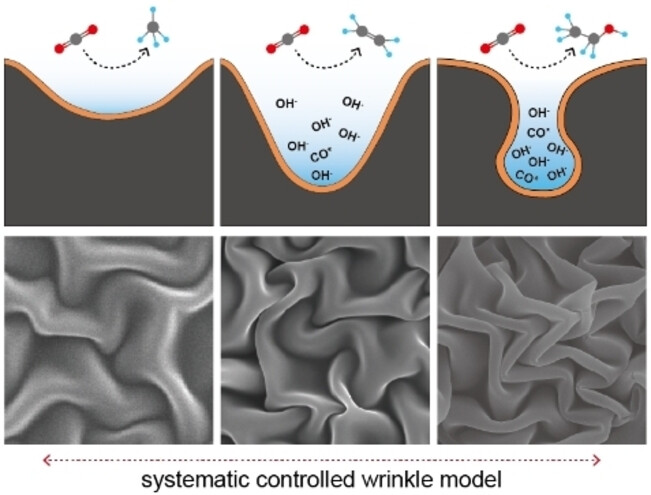
To investigate the relationship between confined space and product selectivity, a wrinkle structure was used as a model for confined spaces. The shape and dimension of the wrinkle can be systematically controlled at nano- to micro-scale. The systematic control of the wrinkle model has revealed that the selectivities for CH4, C2H4, and EtOH are influenced differently by the shape and dimension of the confined space.
Oxygen Reduction Reaction | Hot Paper
Engineering Electronic Structure of Nitrogen-Carbon Sites by sp3-Hybridized Carbon and Incorporating Chlorine to Boost Oxygen Reduction Activity
- First Published: 30 November 2023
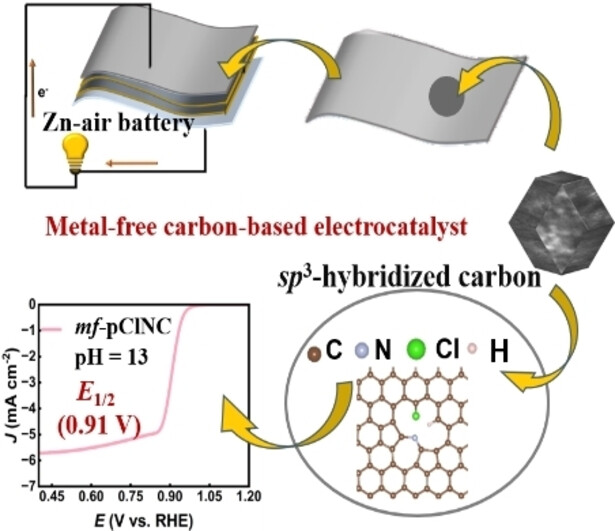
A heteroatom-doped metal-free carbon-based electrocatalyst exhibits a high oxygen reduction reaction activity in alkaline electrolyte. Liquid rechargeable Zn-air battery (ZAB) using the mf-pClNC electrocatalyst as the cathode has a good performance, and more importantly, the assembled flexible quasi-solid-state rechargeable ZAB demonstrates a high power densities and charging/discharging stability at low, room, and high temperatures.
Luminescent Materials
Pressure-Induced Free Exciton Emission in a Quasi-Zero-Dimensional Hybrid Lead Halide
- First Published: 16 November 2023
Membranes | Hot Paper
High Gas Permeability in Aged Superglassy Membranes with Nanosized UiO-66−NH2/cPIM-1 Network Fillers
- First Published: 20 November 2023
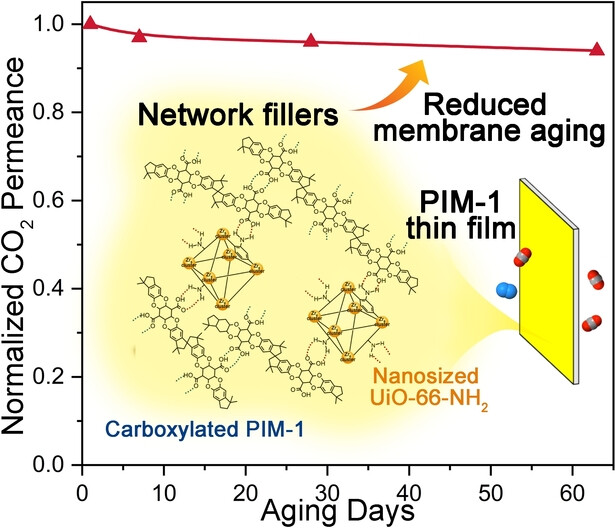
A novel network filler, composed of nanosized UiO-66−NH2 (≈10 nm) and carboxylated PIM-1 (cPIM-1) was prepared and was introduced into PIM-1 thin film nanocomposite membranes (TFN). Unlike conventional fillers, which interact with the polymer only via the surface, the UiO-66−NH2/cPIM-1 forms a stable three-dimensional (3D) network intertwining with the polymer chains, being very effective to impede chain relaxation and physical aging.
Polymer Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Low-Hysteresis and High-Toughness Hydrogels Regulated by Porous Cationic Polymers: the Effect of Counteranions
- First Published: 23 November 2023
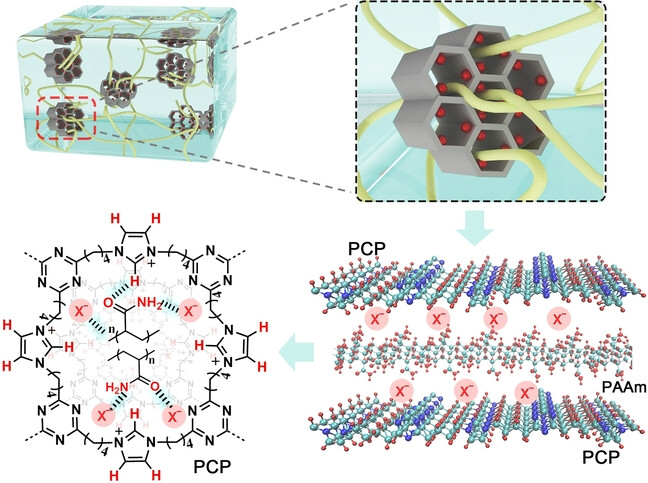
Low-hysteresis and high-toughness hydrogels were developed through controllable interactions of porous cationic polymers (PCPs) with adjustable counteranions. This strategy reduces chain segment slippage under load, endowing the PCP-based hydrogels (PCP-gels) with good elasticity under large deformations (7 % hysteresis at a strain ratio of 40).
Photocatalysis | Very Important Paper
Structure and Defect Engineering Synergistically Boost High Solar-to-Chemical Conversion Efficiency of Cerium oxide/Au Hollow Nanomushrooms for Nitrogen Photofixation
- First Published: 27 November 2023
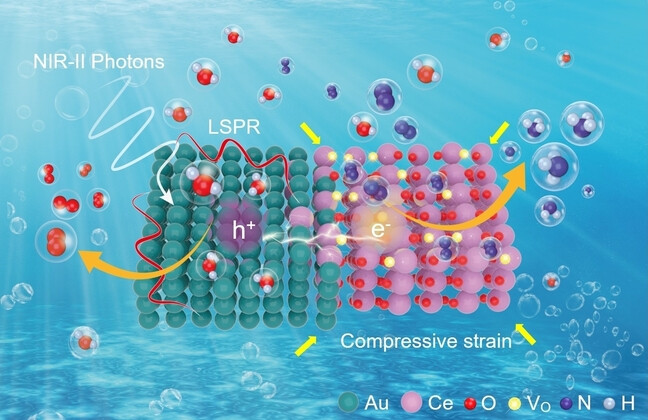
Cerium oxide nanosheets with abundant strain-VO defects were anchored on Au hollow nanomushroom through atomically sharp interfaces to construct a novel semiconductor/plasmonic metal hollow nanomushroom-like heterostructure (cerium oxide-AD/Au) for N2 photofixation. Benefitting from judicious structural and defect engineering, the cerium oxide-AD/Au exhibit great nitrogen photofixation performance with a SCC efficiency of 0.1 %.
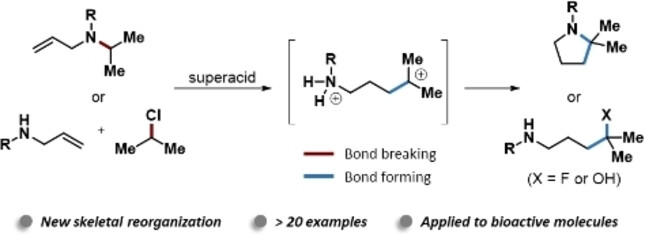
Superacid Chemistry
Exploring Superacid-Promoted Skeletal Reorganization of Aliphatic Nitrogen-Containing Compounds
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Seawater Splitting
Carbon Oxyanion Self-Transformation on NiFe Oxalates Enables Long-Term Ampere-Level Current Density Seawater Oxidation
- First Published: 23 November 2023
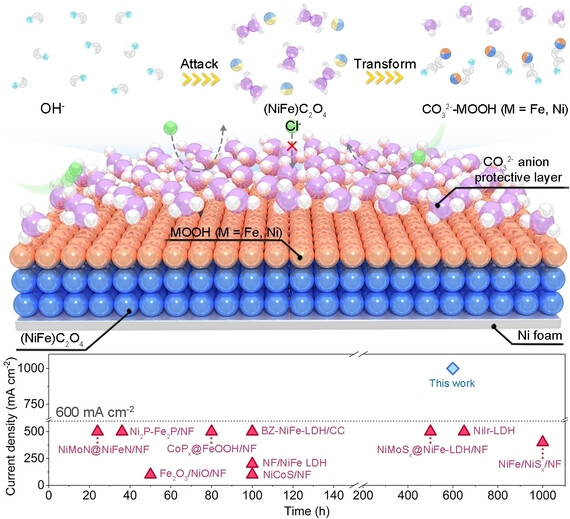
In situ carbon transformation (from C2O42− to CO32−) not only facilitates the generation of active sites but also defends the key active oxyhydroxides against surface chlorine chemistry during oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline seawater. Moreover, NiFe oxalates on Ni foam ((NiFe)C2O4/NF) outperforms reported catalysts by achieving 600-h operation at 1 A cm−2 with minimal potential losses.
Phosphorescent Carbon Dots
Enabling Carbonized Polymer Dots with Color-tunable Time-dependent Room Temperature Phosphorescence through Confining Carboxyl Dimer Association
- First Published: 20 November 2023
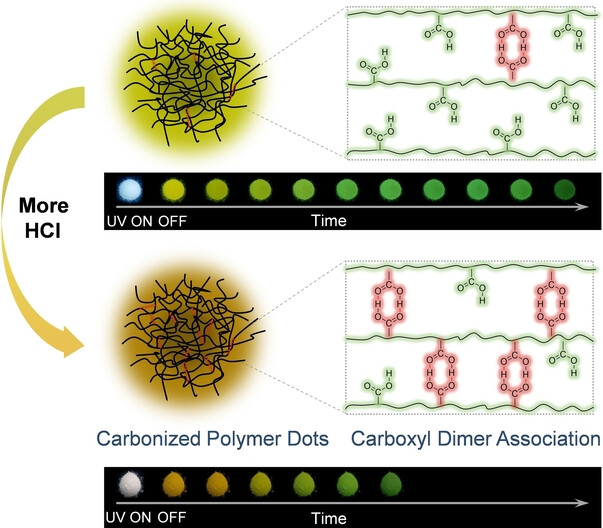
Through confining carboxyl dimer association into carbonized polymer dots, its red room temperature phosphorescence was observed, which provides a brand-new non-conjugated red phosphorescence unit. By hydrochloric acid inhibiting the dissociation of carboxyl groups and promoting the formation of carboxyl dimer association, we realized the fine-tuning of phosphorescence color from yellow to green to orange to green.
CO2 Reduction
Anchoring of Metal Complexes on Au25 Nanocluster for Enhanced Photocoupled Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- First Published: 21 November 2023
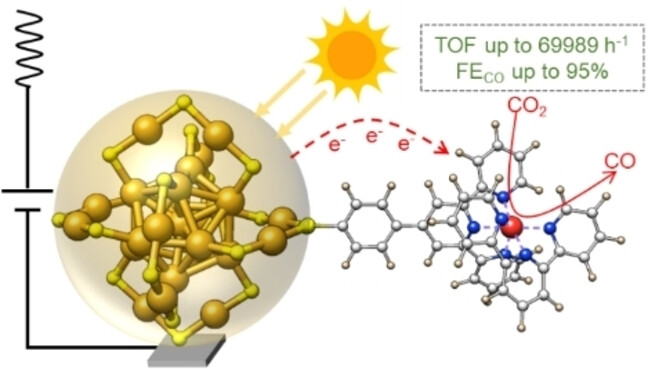
Anchoring of metal complexes on an atomically precise Au25 nanocluster (NC) via a ligand exchange reaction provides an efficient electron-transfer pathway to improve the CO2 reduction activity and selectivity to CO in a wide potential range. Upon illumination, the current density could further be enhanced, and the hybrid system improves the stability of Au NCs by removing the excitation from the Au NCs under light.
Redox Reactions
Domino-Redox Reaction Induced by An Electrochemically Triggered Conformational Change
- First Published: 16 November 2023
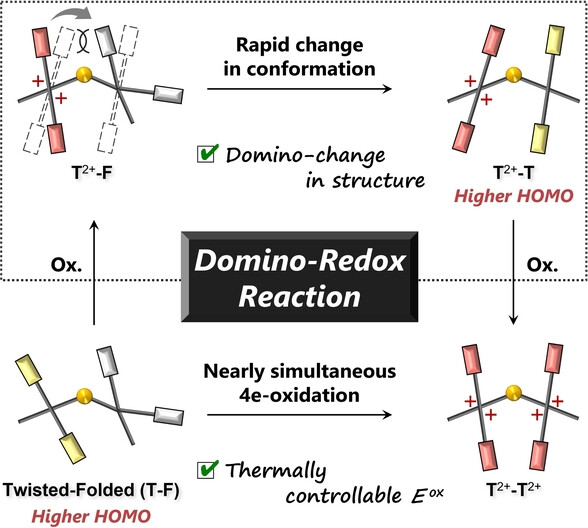
A thermally activated twisted-folded (T-F) form of bisquinodimethane with a dithiin skeleton (SS-BQD) undergoes a facile apparent 2e-transfer (trigger). Furthermore, in the resulting dication, the steric repulsion and interelectrophore interaction cause a facile and rapid change in the structure from the as-generated T2+-F form to the T2+-T form (domino), which facilitates the subsequent oxidation to the tetracation (domino).
Batteries
Revealing the CO2 Conversion at Electrode/Electrolyte Interfaces in Li–CO2 Batteries via Nanoscale Visualization Methods
- First Published: 13 November 2023
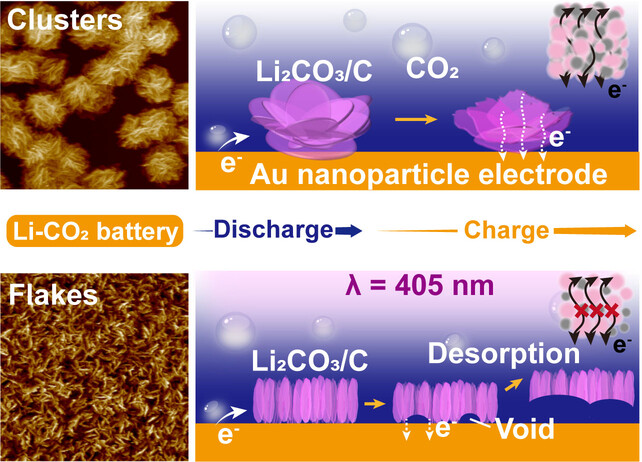
Using in situ atomic force microscopy, laser confocal microscopy-differential interference contrast microscopy and Raman spectroscopy, we explored the electrode/electrolyte interfacial evolution in Li–CO2 batteries. The results indicate that the laser alters the reaction pathways of the CO2 reduction processes, which changes the morphological evolution of the discharge products at the interfaces, and in turn, affects the cell performance.
Radical Polymerization
Umpolung Isomerization in Radical Copolymerization of Benzyl Vinyl Ether with Pentafluorophenylacrylate Leading to Degradable AAB Periodic Copolymers
- First Published: 16 November 2023
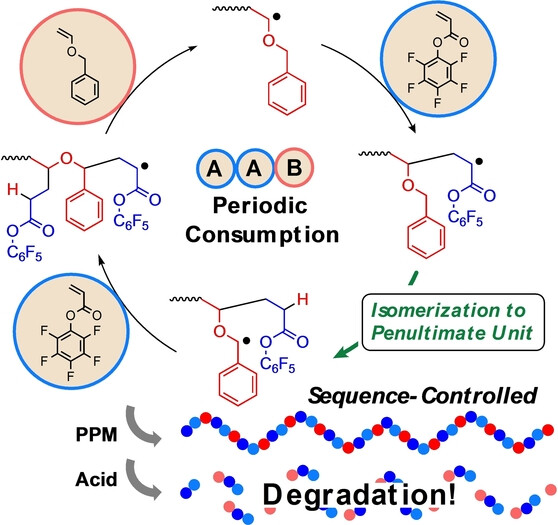
The radical copolymerzation of benzyl vinyl ether (BnVE; A) with the highly electron-deficient acrylate monomer pentafluorophenylacrylate (PFA; B) progressed with unique backward isomerization to the penultimate BnVE unit. The isomerization caused the umpolung of the growing species, leading to a periodic consumption in the order AAB, and consequently the copolymer resulting after post-polymerization modification (PPM) was degradable under acidic conditions.
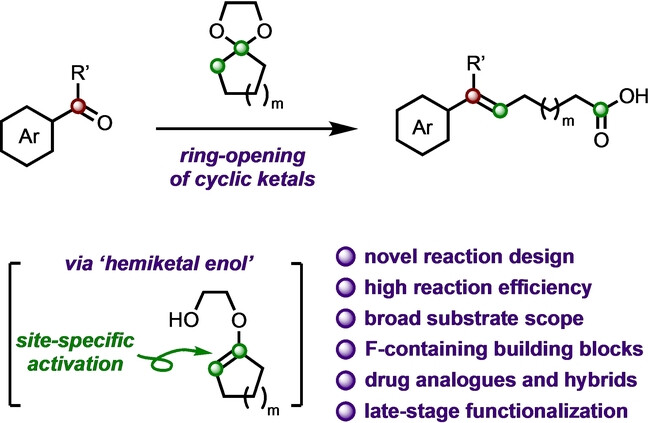
Organic Chemistry | Hot Paper
Olefination of Aromatic Carbonyls via Site-Specific Activation of Cycloalkanone Ketals
- First Published: 23 November 2023
COFs for Gold Recovery | Hot Paper
Modulating Skeletons of Covalent Organic Framework for High-Efficiency Gold Recovery
- First Published: 20 November 2023

Skeleton engineering was used to form covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with diarylamine derivatives and ionized skeletons, thus overcoming the weak binding ability of Au ions, giving gold adsorbents with high selectivity and uptakes. Experiments and theoretical calculations show that the transition of binding sites from C=N bonds to ionic amine sites, thereby avoiding the protonation process, contributed to enhanced absorbing kinetics.
Communications
Quantum Chemistry
Tipping the Balance Between the bcc and fcc Phase Within the Alkali and Coinage Metal Groups
- First Published: 25 October 2023
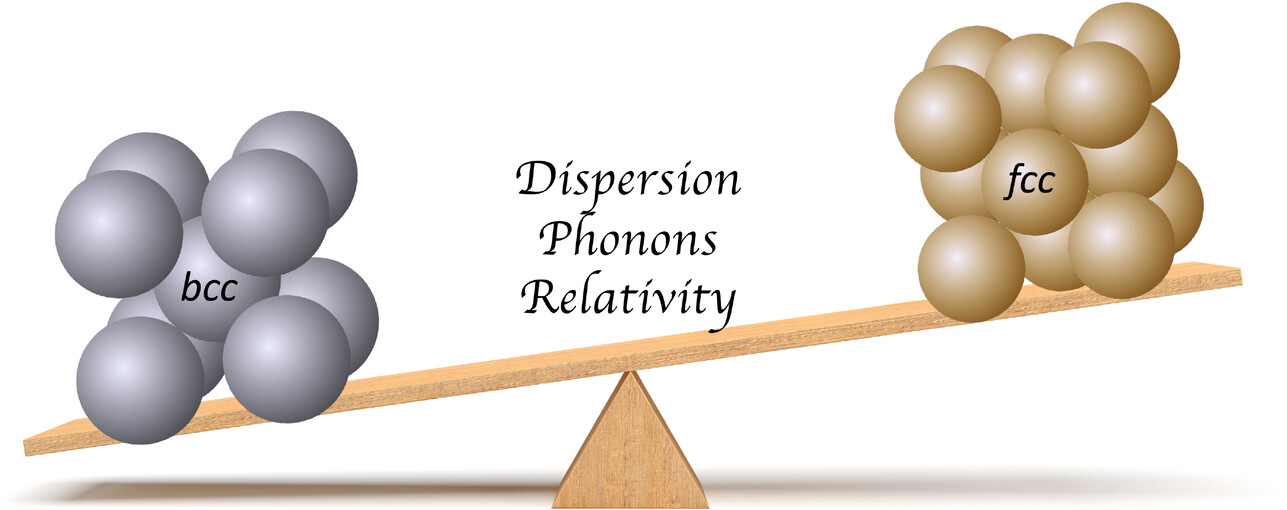
Relativistic density functional calculations for the cuboidal phase transition show that small effects such as dispersion interactions and phonon contributions can tip the balance between the body-centered and face-centered cubic structures shedding light into the difference between the Groups 1 and 11 elements in the Periodic Table.
Nanocrystals
pH-Responsive Protein Conformation Transistor
- First Published: 08 October 2023
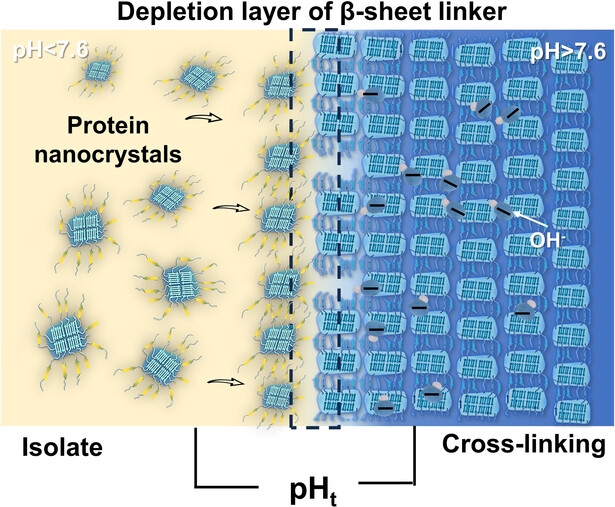
The successful acquisition of “core–shell” structural protein nanocrystals that undergo ultrafast cross-linking behavior in response to pH levels above 7.6 illustrate the concept of a protein conformation proton transistor. This pH-responsive cross-linking can be conveniently achieved under near physiological conditions, highlighting the great potential in biomedicine, biosensing, and microfluidic chemistry.
Biocatalysis
Enzymatic Fluoromethylation as a Tool for ATP-Independent Ligation
- First Published: 13 November 2023
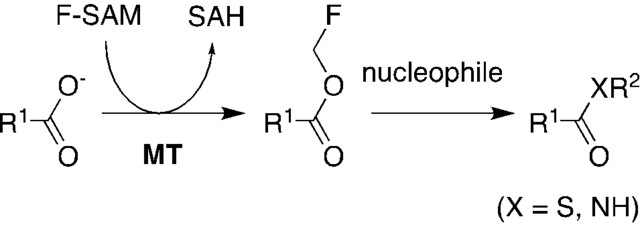
This report shows that methyltransferase-mediated fluoromethylation can activate small and large carboxylate substrates for conjugation to thiols, hydrazine, hydroxylamine or amines. This methodology to produce anhydrides offers an alternative to the much more common ATP-dependent processes observed in nature and utilized in biocatalysis.
Amine Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Alicyclic-Amine-Derived Imine-BF3 Complexes: Easy-to-Make Building Blocks for the Synthesis of Valuable α-Functionalized Azacycles
- First Published: 01 November 2023
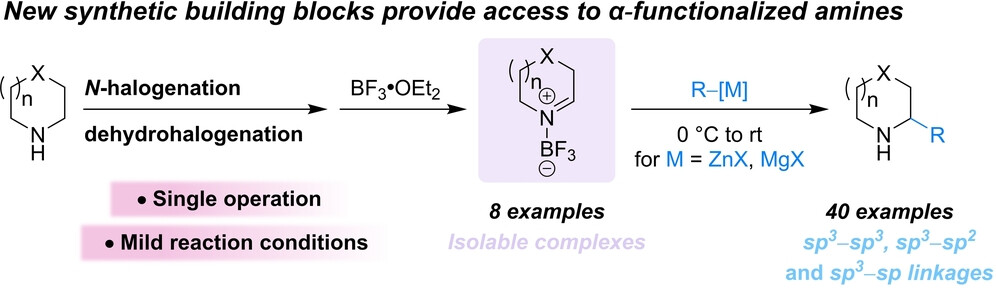
Imine-BF3 complexes derived from alicyclic amines represent novel building blocks that are readily prepared in a single synthetic operation. These complexes engage with a wide range of organometallic nucleophiles to afford α-functionalized azacycles, typically under non-cryogenic conditions. The in situ preparation of imine-BF3 complexes provides access to α-functionalized morpholines and piperazines directly from their parent amines.
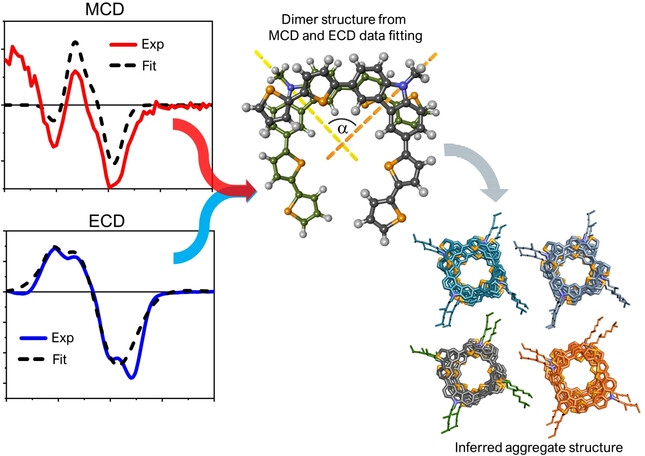
Supramolecular Chemistry
Magnetic Circular Dichroism Elucidates Molecular Interactions in Aggregated Chiral Organic Materials
- First Published: 14 November 2023
Phosphorescence
Acquiring Charge-Transfer-Featured Single-Molecule Ultralong Organic Room Temperature Phosphorescence via Through-Space Electronic Coupling
- First Published: 15 November 2023
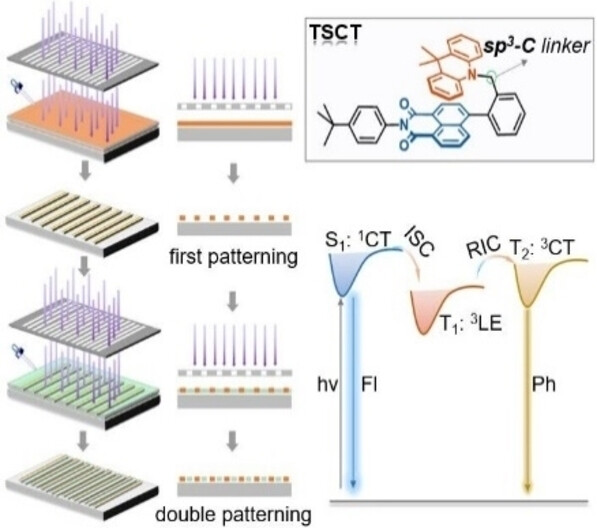
A rational design strategy for high energy level and long-lived triplet charge transfer (3CT)-featured single-molecule phosphorescence materials was proposed. Through this strategy, a robust phosphor, NIC-DMAC, was constructed with a long lifetime (τ3CT) exceeding 210 ms and a 3CT energy level (E3CT) as high as 2.50 eV. Thanks to its long-lived 3CT state and high E3CT, NIC-DMAC was successfully applied in photolithography as a photoinitiator and achieved double patterning.
Mechanochemistry
Allylation of C-, N-, and O-Nucleophiles via a Mechanochemically-Driven Tsuji–Trost Reaction Suitable for Late-Stage Modification of Bioactive Molecules
- First Published: 06 November 2023
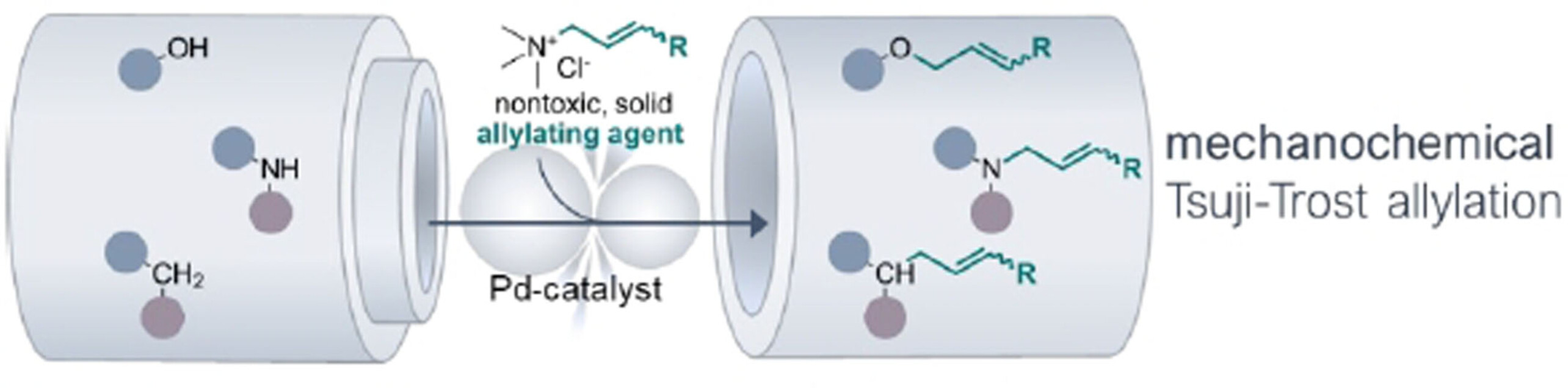
A mechanochemical, solvent-free protocol for Tsuji–Trost allylation of O-, N-, and C-Nucleophiles using nontoxic, solid allyl trimethylammonium chloride as alternative allylating agent is presented. This method features fast reaction kinetics, very low catalyst loadings, high yields, mild conditions, and high functional group tolerance. Its potential for late-stage modifications of bioactive compounds is demonstrated through multiple examples.
Heterocyclic Chemistry
Enantioselective Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Desymmetrizative Coupling of 7-Azabenzonorbornadienes with Alkynylanilines
- First Published: 09 November 2023
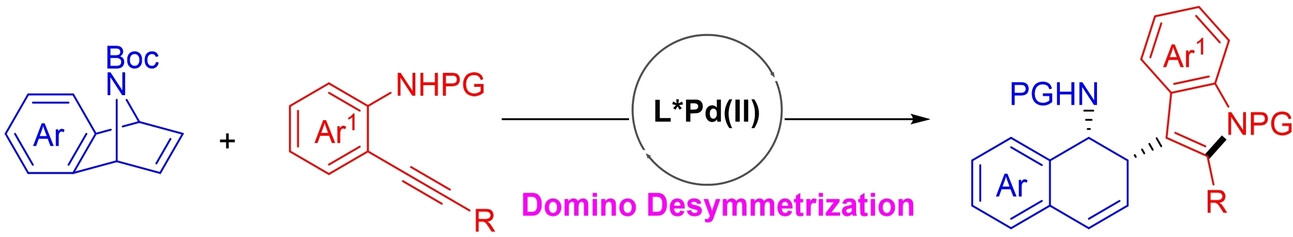
A palladium-catalyzed enantioselective desymmetrizative coupling of prochiral 7-azabenzonorbornadienes with readily available alkynylanilines afforded dihydronaphthalenes via concomitant generation of three covalent bonds. The methods also allows to build two stereocenters and an indole motif in a highly diastereo- and enantioselective as well as atom-economic manner.
Natural Products Synthesis
Total Synthesis of (+)-Discorhabdin V
- First Published: 13 November 2023
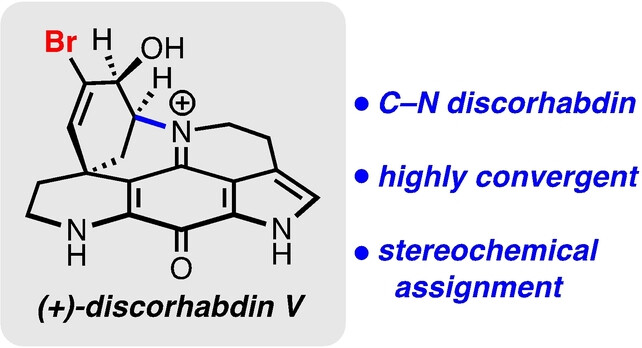
The first total synthesis and full stereochemical assignment of (+)-discorhabdin V was accomplished through a highly convergent strategy enabled by scalable access to the two key components. This highly selective asymmetric approach to nitrogen-bridged discorhabdins lays the foundation for access to this class of natural products.
Asymmetric Allylation Reactions | Hot Paper
Copper(I)-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylation of Ketones with 2-Aza-1,4-Dienes
- First Published: 13 November 2023
Photocatalysis
Tuning the Aggregates of Thiophene-based Trimers by Methyl Side-chain Engineering for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 23 November 2023
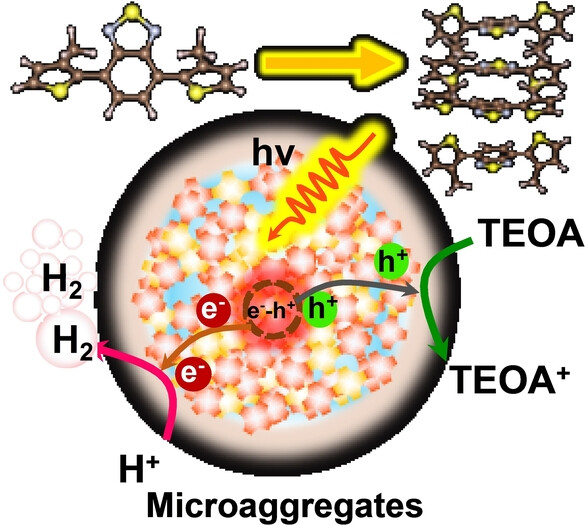
The relationship between the aggregation of 4,7-bis(thiophen-2-yl) benzothiadiazole (TBT)-based conjugated trimers and their photocatalytic activity was systematically investigated by methyl side-chain engineering. TBT-3 with the smallest size of aggregates and highest crystallinity exhibit the highest photocatalytic H2 evolution activity, which is due to the shorter charge carrier transport distance and solid long-range order.
Cage Compounds
Self-Assembly of an [M8L24]16+ Intertwined Cube and a Giant [M12L16]24+ Orthobicupola
- First Published: 20 November 2023
![Self-Assembly of an [M8L24]16+ Intertwined Cube and a Giant [M12L16]24+ Orthobicupola](/cms/asset/be420dd4-d21f-4e47-b07e-e647a4a4bd5f/anie202315572-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Coordination-driven self-assembly has been used to create a giant orthobicupola and an intertwined “A-type cube”. The concept of generating intricate structures through the use of flexibility in the form of an elongated, flexible terphenyl-based tetratopic ligand (L2) in combination with a cis-blocked Pd(II) metal counterpart led to the formation of this uncommon water-soluble intertwined “A-type” cube.
Fluorescent Probes
Prediction of Early Atherosclerotic Plaques Using a Sequence-Activated Fluorescence Probe for the Simultaneous Detection of γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase and Hypobromous Acid
- First Published: 20 November 2023
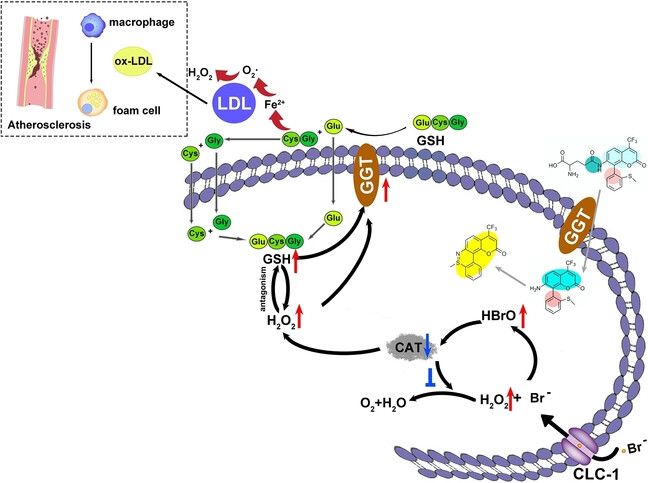
To avoid false-positive diagnoses caused by a single disease biomarker, a two-photon fluorescence probe which is turned on sequentially by γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) and HBrO was designed to predict early atherosclerotic plaques. The voltage-gated chloride channel (CLC-1)-HBrO-catalase (CAT)-GGT signaling pathway was confirmed at the cellular level, demonstrating that both GGT and HBrO can be applied as biomarkers of atherosclerosis.
C−H Activation
Methylene C(sp3)−H Arylation Enables the Stereoselective Synthesis and Structure Revision of Indidene Natural Products
- First Published: 23 November 2023
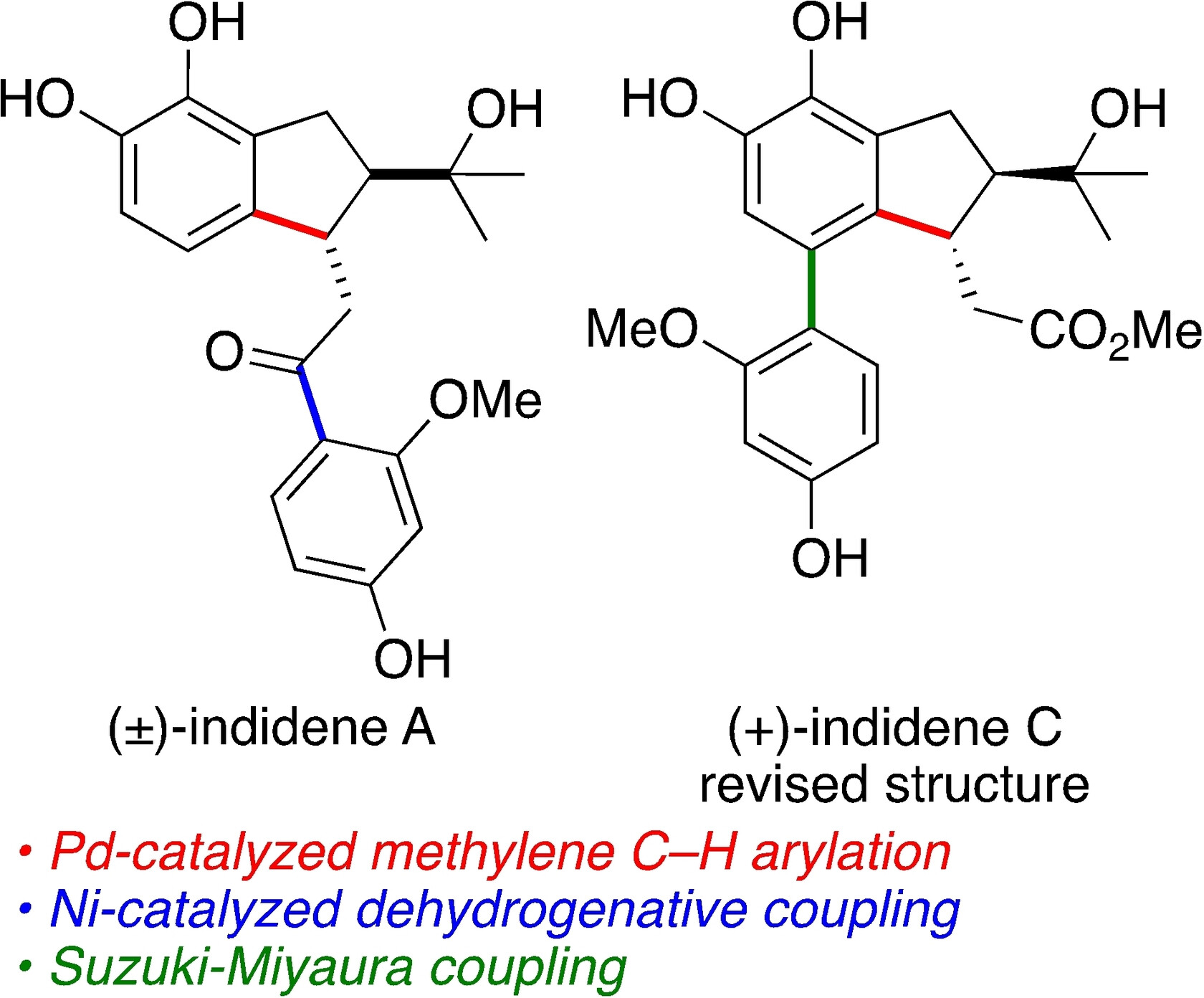
The indane polyketides indidenes A and C were synthesized from a common intermediate through nickel-catalyzed dehydrogenative coupling and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling, respectively. The common diol intermediate was obtained by palladium-catalyzed methylene C−H arylation, which was performed in both racemic and enantioselective modes. This study led to the revision of the absolute configuration of indidene C.
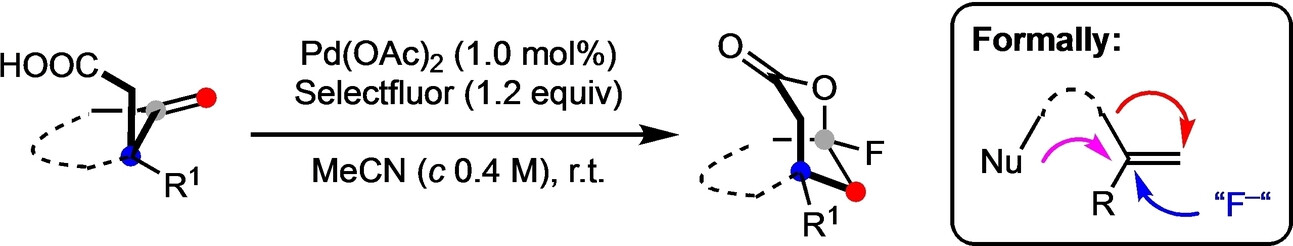
Rearrangement | Very Important Paper
Palladium-Based Dyotropic Rearrangement Enables A Triple Functionalization of Gem-Disubstituted Alkenes: An Unusual Fluorolactonization Reaction
- First Published: 20 November 2023