Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Unprecedented Molecular Architectures by the Controlled Self-Assembly of a β-Peptide Foldamer (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2010)
- Page: 8047
- First Published: 26 August 2010

Windmill-shaped architectures and square rods were formed by the self-assembly of a short helical β peptide in aqueous solution. In their Communication on page 8232 ff., H.-S. Lee and co-workers show how the self-assembly of these exceptional 3D shapes and their intermediate states could be guided and controlled by the addition of a surfactant.
Inside Cover
Inside Cover: Enantioselective Synthesis of Amines: General, Efficient Iron-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Imines (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2010)
- Page: 8048
- First Published: 03 August 2010

Although iron is one of the most abundant metals, its application to catalysis is still in its infancy. In their Communication on page 8121 ff., M. Beller and co-workers present the first iron-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of imines. Iron carbonyl complexes in the presence of a tetradentate P2N2 ligand catalyze the reduction of N-diphenylphosphinylimines with high enantioselectivity (99 %) and good yields (98 %).
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2010
- Pages: 8051-8063
- First Published: 20 October 2010
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2010
- Pages: 8066-8068
- First Published: 20 October 2010
Author Profile
Book Review
Electrochemistry of Functional Supramolecular Systems. Edited by Paola Ceroni, Alberto Credi and Margherita Venturi.
- Pages: 8073-8074
- First Published: 06 October 2010
Highlights
Biological Materials Chemistry
The Iron-Fortified Adhesive System of Marine Mussels†
- Pages: 8076-8078
- First Published: 13 September 2010
Enantioselective Catalysis
A Bimetallic Titanium Catalyst for the Enantioselective Cyanation of Aldehydes Based on Cooperative Catalysis
- Pages: 8079-8081
- First Published: 31 August 2010
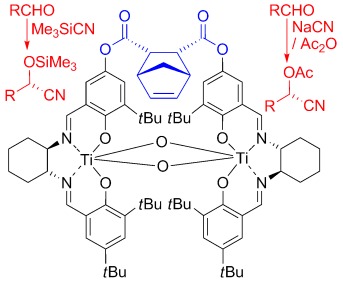
Joined at the hip: By linking two salen ligands together with a strap of appropriate size and shape, the effectiveness of a bimetallic titanium(salen) complex as a catalyst for asymmetric cyanohydrin synthesis can be increased by up to two orders of magnitude. The optimal catalyst is active at a catalyst loading as low as 0.0005 mol % and will accept both trimethylsilyl cyanide and sodium cyanide/acetic anhydride as the cyanide source (see scheme).
Minireview
Small Focused Libraries
Factors Determining the Selection of Organic Reactions by Medicinal Chemists and the Use of These Reactions in Arrays (Small Focused Libraries)
- Pages: 8082-8091
- First Published: 21 September 2010
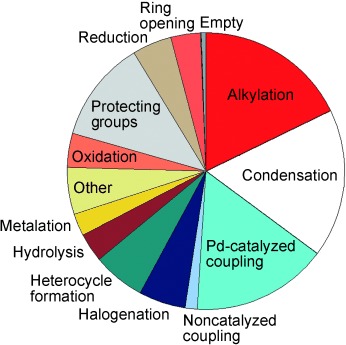
Helping chemists help chemists: What reactions do medicinal chemists use in drug discovery? (The pie chart shows a snapshot from one unit at GlaxoSmith-Kline.) What criteria do they use to select synthetic methodology? Why are arrays (small focused libraries) so powerful in the lead-optimization process? These questions are considered in this Minireview, which also describes attempts to expand the number of robust reactions available to medicinal chemists.
Review
The Ozone Layer
Climate Change and Atmospheric Chemistry: How Will the Stratospheric Ozone Layer Develop?
- Pages: 8092-8102
- First Published: 04 October 2010
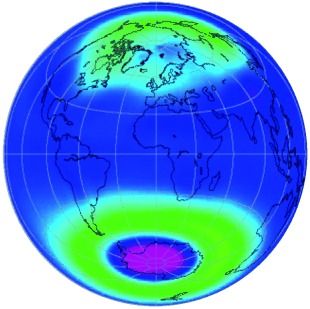
Since the industrial revolution began about 150 years ago, the concentration of greenhouse gases such as CO2 in the atmosphere has increased dramatically, with corresponding consequences for the climate. For over 25 years, destruction of the ozone layer (pink and green regions on the globe), which is caused by chlorofluorocarbons, has also been observed. The future development of the ozone layer and of the climate are closely related to each other.
Communications
Nanoparticles
Photoswitchable Nanoassemblies by Electrostatic Self-Assembly
- Pages: 8104-8108
- First Published: 26 August 2010

Light controls size: A novel type of self-organized supramolecular nanoparticles can change their size upon irradiation with UV light (see picture). The doubly responsive system combines a light-triggered size with a pH-induced switching between nanoscale aggregates and molecular building blocks. The nano-objects form by a combination of ionic and π–π interactions between macro-ions and dye ions.
Synthetic Methods
An Intermolecular Palladium-Catalyzed Diamination of Unactivated Alkenes†
- Pages: 8109-8111
- First Published: 22 September 2010
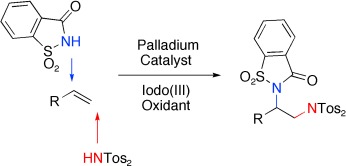
Adding 2Ns: Palladium catalysis introduces two nitrogen groups in a new regio and chemoselective diamination of non-activated alkenes that proceeds under entirely intermolecular reaction control. This palladium-catalyzed reaction employs commercial nitrogen sources in combination with a hypervalent iodo(III) reagent as oxidant (see scheme; Tos=toluenesulfonyl).
Enzymatic CH Activation
Intermediates in the Catalytic Cycle of Methyl Coenzyme M Reductase: Isotope Exchange is Consistent with Formation of a σ-Alkane–Nickel Complex†
- Pages: 8112-8115
- First Published: 20 September 2010
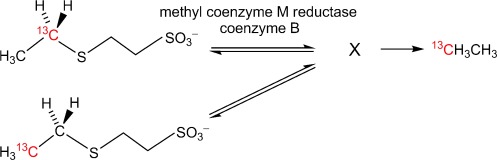
The key nickel enzyme for methanogenesis (MCR) catalyzes the formation of CH3D and CH2D2 in a deuterated medium. CH2D2 is formed by an exchange of deuterium into the S-methyl group of the substrate. Deuterium is incorporated at both carbon atoms of the S-ethyl group of ethyl coenzyme M, and a 13C label is rapidly scrambled within the ethyl group (see scheme). Thus, at least one intermediate is formed and the isotope exchange pattern is consistent with formation of a σ-alkane–nickel complex.
Enzyme Reactions in Microparticles
Enzyme Reaction in the Pores of CaCO3 Particles upon Ultrasound Disruption of Attached Substrate-Filled Liposomes†
- Pages: 8116-8120
- First Published: 21 September 2010
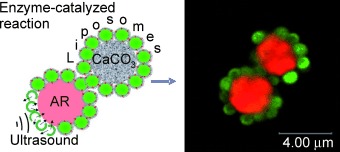
Breaking out: Liposomes that are adsorbed onto porous CaCO3 particles and that contain the peroxidase substrate Amplex Red (AR) are disrupted by ultrasonic treatment. The substrate is released and diffuses into the inner part of the multicompartment containers where the peroxidase enzyme is found, and the enzymatic reaction is triggered. This approach may be useful for the simultaneous delivery of multiple molecules into cells.
Iron Catalysis
Enantioselective Synthesis of Amines: General, Efficient Iron-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Imines†
- Pages: 8121-8125
- First Published: 19 July 2010
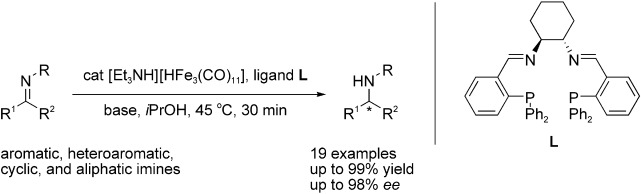
In the iron age: A readily accessible, active iron catalyst serves in the straightforward, catalytic transfer hydrogenation of imines (see scheme). A series of imines are converted into chiral amines in high yields and very good enantioselectivities. This method should find broad application in the search for bioactive chiral amines.
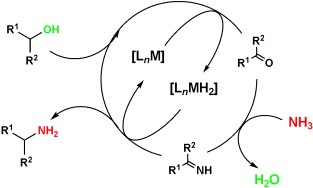
Amination
An Efficient and General Synthesis of Primary Amines by Ruthenium-Catalyzed Amination of Secondary Alcohols with Ammonia†
- Pages: 8126-8129
- First Published: 02 August 2010
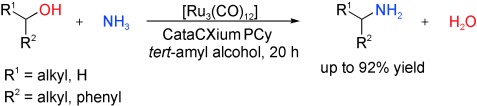
Atom efficiency and selectivity are the key features of the first homogeneously catalyzed amination of secondary alcohols with ammonia to give the corresponding primary amines (see scheme). This novel amination method relies on the commercially available catalyst [Ru3(CO)12]/cataCXium PCy and does not require any additional source of hydrogen.
Direct Amination of Secondary Alcohols Using Ammonia†
- Pages: 8130-8133
- First Published: 29 July 2010
Gold Catalysis
One-Pot Synthesis of Menthol Catalyzed by a Highly Diastereoselective Au/MgF2 Catalyst†
- Pages: 8134-8138
- First Published: 20 September 2010
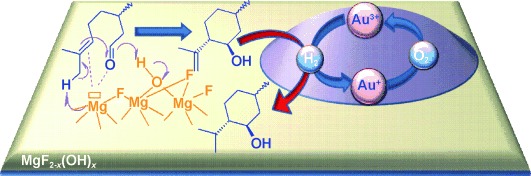
No toxic compounds such as KCN and no thermal activation is required for the preparation of Au/MgF2 complexes by a simple and facile “incipient wetness impregnation” method in which hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (HAuCl4) is the gold precursor. One of the complexes prepared exhibits unique catalytic properties and serves as a heterogeneous catalyst for the highly diastereoselective one-pot synthesis of (±)-menthol from citronellal (see picture).
P,N Compounds
The Reaction of White Phosphorus with NO+/NO2+[Al(ORF)4]−: The [P4NO]+ Cluster Formed by an Unexpected Nitrosonium Insertion†
- Pages: 8139-8143
- First Published: 23 September 2010
![The Reaction of White Phosphorus with NO+/NO2+[Al(ORF)4]−: The [P4NO]+ Cluster Formed by an Unexpected Nitrosonium Insertion](/cms/asset/7d40fd67-62e2-4f7a-abe0-70c11481b85f/mcontent.jpg)
An appealing couple: The unprecedented insertion of the nitrosonium cation into a tetrahedral edge of white phosphorus forms the highly reactive [P4NO]+ cation (see picture). The synthesis, characterization, and applications are discussed, and NO2[Al(OC(CF3)3)4] is presented as an easily synthesized oxidant.
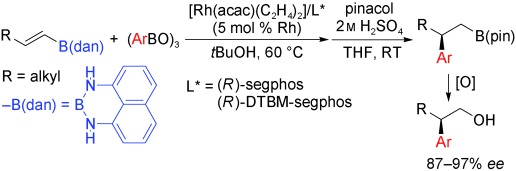
Rhodium Catalysis
Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Conjugate Addition of Arylboroxines to Borylalkenes: Asymmetric Synthesis of β-Arylalkylboranes†
- Pages: 8145-8147
- First Published: 20 September 2010
Photoreduction
Photoinduced Catalytic Reaction by a Fluorescent Active Cryptand Containing an Anthracene Fragment†
- Pages: 8148-8151
- First Published: 20 September 2010
Dendrimers
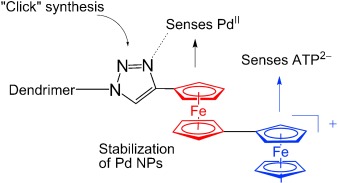
Click Syntheses of 1,2,3-Triazolylbiferrocenyl Dendrimers and the Selective Roles of the Inner and Outer Ferrocenyl Groups in the Redox Recognition of ATP2− and Pd2+†
- Pages: 8152-8156
- First Published: 20 September 2010
Synthetic Methods
Enantioselective and Z/E-Selective Conjugate Addition of α-Substituted Cyanoacetates to Acetylenic Esters Catalyzed by Bifunctional Ruthenium and Iridium Complexes†
- Pages: 8157-8160
- First Published: 20 September 2010
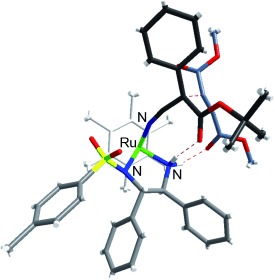
Metal-based catalysts: The title reaction provided the chiral adducts in high yields, excellent enantiomeric excess, and high Z/E selectivity. A combined NMR/DFT study revealed a key intermediate for the stereoselective reaction and a possible reaction mechanism (see the optimized transition-state structure).
Photosensitizers
Highly Efficient N-Heterocyclic Carbene/Pyridine-Based Ruthenium Sensitizers: Complexes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells†
- Pages: 8161-8164
- First Published: 20 September 2010
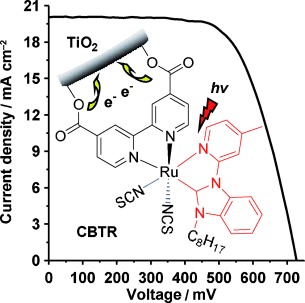
A new generation: The incorporation of N-heterocyclic carbene/pyridine-based ruthenium sensitizers derived from benzimidazolium salts into dye-sensitized solar cells results in superior current densities, cell voltages, and photoelectric conversion efficiencies. The performance of a solar cell sensitized with CBTR (see picture) exceeded that of the traditional N719 cell.
Nanostructures
A Sinter-Resistant Catalytic System Based on Platinum Nanoparticles Supported on TiO2 Nanofibers and Covered by Porous Silica†
- Pages: 8165-8168
- First Published: 24 September 2010
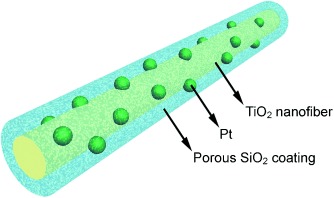
Holey support: The generation of a porous coating of SiO2 on Pt-decorated TiO2 nanofibers enables the preparation of a sinter-resistant catalytic system (see picture). The Pt nanoparticles could resist sintering at temperatures up to 750 °C in air, as the SiO2 coating acts as a physical barrier that slows down surface migration, but the system remained catalytically active because of the porous nature of the coating.
Asymmetric Catalysis
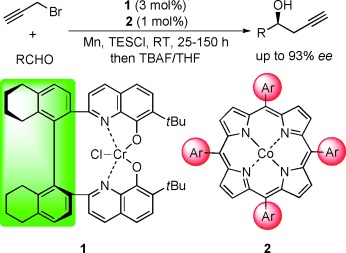
Asymmetric Nozaki–Hiyama Propargylation of Aldehydes: Enhancement of Enantioselectivity by Cobalt Co-Catalysis†
- Pages: 8169-8172
- First Published: 21 September 2010
Molecular Recognition
Small-Molecule Sensing: A Direct Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Monosaccharide Kdo
- Pages: 8173-8176
- First Published: 20 September 2010
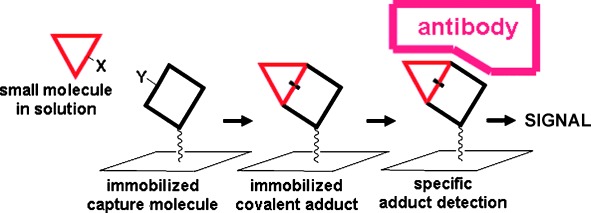
Captured and bound! Kdo, a monosaccharide, and an immobilized capture molecule form a covalent adduct that can be detected by adduct-specific antibodies (see scheme). The recognition yields a signal that is proportional to the amount of Kdo present in solution. This small-molecule sensor should be applicable for any small molecule that can react to give an immunogenic adduct.
207Pb NMR Spectroscopy
Probing a Homoleptic PbS3 Coordination Environment in a Designed Peptide Using 207Pb NMR Spectroscopy: Implications for Understanding the Molecular Basis of Lead Toxicity†
- Pages: 8177-8180
- First Published: 21 September 2010
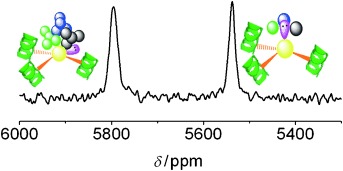
The lead-inhibited active site of a zinc-binding metalloenzyme in a thiol-rich coordination environment (PbS3) has been modeled by homoleptic three-strand coiled-coil peptides and characterized using natural-abundance 207Pb NMR spectroscopy (see picture: 207Pb NMR signals from two binding sites of the same protein). 207Pb NMR spectroscopy could thus be used to identify and characterize important human proteins associated with lead toxicity.
CH Activation
syn-Selective Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed Allylations of Ketimines Proceeding through a Directed CH Activation/Allene Addition Sequence†
- Pages: 8181-8184
- First Published: 23 September 2010
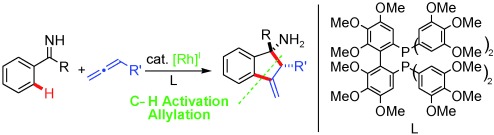
On a Rh-oll: Rhodium(I)-catalyzed CH activations of ketimines and subsequent carborhodation of an allene led to an allyl metal species, which then allylated the imine directing group to give highly functionalized methylene dihydroindenyl amines (see scheme) with excellent regio- and diastereoselectivity.
Fast Proteolysis
Efficient Tryptic Proteolysis Accelerated by Laser Radiation for Peptide Mapping in Proteome Analysis†
- Pages: 8185-8189
- First Published: 24 September 2010
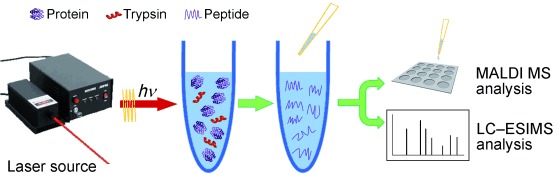
Back to basics: Coupled with MALDI-TOF MS, laser-assisted proteolysis (see schematic illustration) enabled rapid protein digestion and peptide mapping without the need for enzyme immobilization to increase the efficiency of tryptic digestion. Protein solutions containing trypsin were digested in less than a minute upon irradiation at 808 nm with a laser.
Enzyme Models
Water as an Oxygen Source: Synthesis, Characterization, and Reactivity Studies of a Mononuclear Nonheme Manganese(IV) Oxo Complex†
- Pages: 8190-8194
- First Published: 21 September 2010
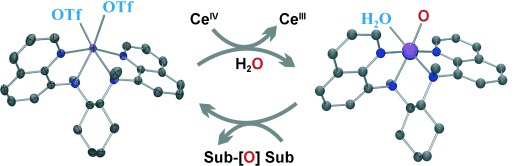
The source of the problem: Experiments with isotopically labeled water can be used to unambiguously assign the source of oxygen in a nonheme manganese(IV) oxo complex. The complex, which was generated using water as an oxygen source and cerium(IV) as an oxidant (see picture), shows reactivities in the activation of CH bonds of alkyl-functionalized aromatic molecules and the oxidation of aromatic substrates (sub) and benzyl alcohol.
Glycan Imaging
Noninvasive Imaging of Dendrimer-Type N-Glycan Clusters: In Vivo Dynamics Dependence on Oligosaccharide Structure†
- Pages: 8195-8200
- First Published: 20 September 2010
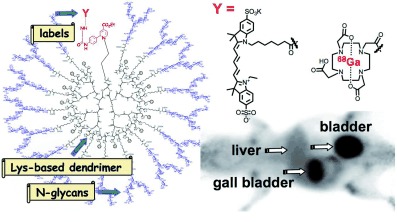
Body image: Self-activating Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition and 6π azaelectrocyclization of lysine-based dendrimers (see picture) enable the in vivo dynamics and organ-specific accumulation of N-glycans to be visualized. The sugar structure and glycosyl bond linkages of N-glycans control the whole-body trafficking of the clusters in nude mice and a cancer model.
Mesoporous Materials
Chitin–Silica Nanocomposites by Self-Assembly†
- Pages: 8201-8204
- First Published: 23 September 2010
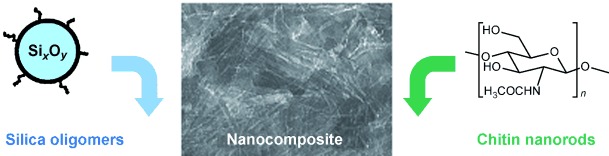
A new family of chitin–silica nanocomposites has been synthesized by using a versatile colloid-based combination of self-assembly and sol–gel chemistry (see picture). Various textures and morphologies can be obtained by adjusting the evaporation-based processes or by applying external fields. After calcination, textures and birefringence are preserved in the resulting mesoporous silicas.
Cyclophanes
Preparation and Characterization of N-Anisyl-Substituted Hexaaza[16]paracyclophane†
- Pages: 8205-8208
- First Published: 21 September 2010
![Preparation and Characterization of N-Anisyl-Substituted Hexaaza[16]paracyclophane](/cms/asset/b1dbc702-357c-46ca-97af-7b2c4c5199db/mcontent.jpg)
Localized or delocalized? For the first time, a cyclic oligoaniline, hexaaza[16]paracyclophane, has been prepared (see picture; carbon: gray; nitrogen: blue; hydrogen: light gray). The macrocycle exhibits a high electron-donating ability, and furthermore, the spin of the corresponding radical cation was delocalized over the macrocyclic molecular backbone.
Heteroarenes
1,5,9-Triazacoronenes: A Family of Polycyclic Heteroarenes Synthesized by a Threefold Pictet–Spengler Reaction†
- Pages: 8209-8213
- First Published: 23 September 2010
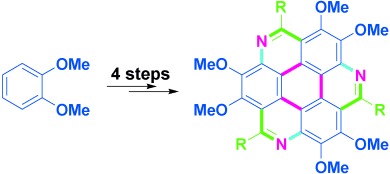
We are family: Triazacoronene derivatives have been synthesized in four steps from veratrole by using a threefold Pictet–Spengler reaction as the key step (see picture). They have good photophysical and electronical properties, thermal stability, and solubility, thus rendering them promising candidates as electron-transport materials.
Drug Delivery
Intracellular pH-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Controlled Release of Anticancer Chemotherapeutics†
- Pages: 8214-8219
- First Published: 23 September 2010
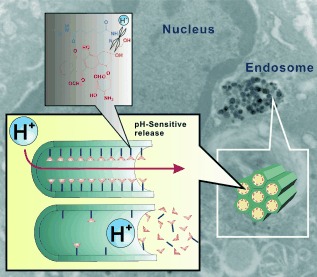
Cut here to cure: Doxorubicin attached to pH-sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN-hydrazone-Dox) shows potential in the chemotherapeutic treatment of liver cancer. Hydrolysis of the pH-sensitive hydrazone bond in the acidic environment of endosomes/lysosomes (see picture) releases Dox intracellularly from the MSN nanochannels, resulting in highly efficient apoptotic cell death.
Micelles
Pointed-Oval-Shaped Micelles from Crystalline-Coil Block Copolymers by Crystallization-Driven Living Self-Assembly†
- Pages: 8220-8223
- First Published: 21 September 2010
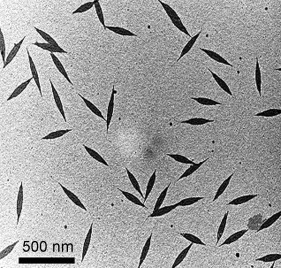
Getting in shape: Stable pointed-oval-shaped micelles of uniform size and shape (see TEM image) were prepared by extending the crystallization-driven living self-assembly method to crystalline core-forming polyferrocenylsilane diblock copolymers with corona-forming coblocks of poly(2-vinylpyridine) and polyphosphazene. The pointed-oval-shaped micelles were subsequently used as precursors to hierarchical micelle architectures.
Photoisomerization
Switching of a Single Boryl Center in π-Conjugated Photochromic Polyboryl Compounds and Its Impact on Fluorescence Quenching†
- Pages: 8224-8227
- First Published: 20 September 2010
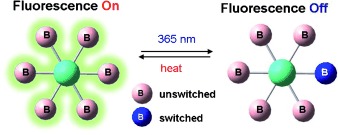
All for one and one for all: Molecules with multiple conjugated photochromic boryl units undergo photoisomerization on a single boryl unit only. This single boryl switching causes fluorescence quenching of the entire molecule, which is greatly amplified with increasing numbers of switchable boryl units in the molecule.
Chemical Biology
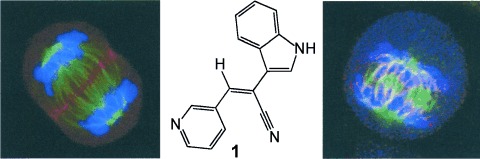
Relocation of Aurora B and Survivin from Centromeres to the Central Spindle Impaired by a Kinesin-Specific MKLP-2 Inhibitor†
- Pages: 8228-8231
- First Published: 20 September 2010
Self-Assembly
Unprecedented Molecular Architectures by the Controlled Self-Assembly of a β-Peptide Foldamer†
- Pages: 8232-8236
- First Published: 23 August 2010
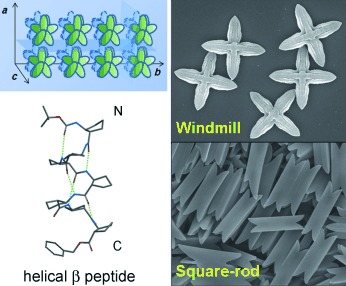
Fighting against windmills: Highly homogeneous, well-defined, and finite “windmill”- and square-rod-shaped supramolecular architectures were formed by the self-assembly of a short helical β peptide in aqueous solution (see picture). The reproducible formation of the unprecedented 3D shapes could be controlled by the use of a surfactant of different concentrations.
Surface Analysis
Mesoscopic Arrays from Supramolecular Self-Assembly†
- Pages: 8237-8239
- First Published: 21 September 2010
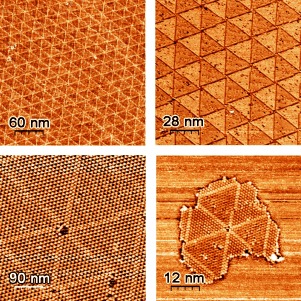
Well-ordered superarrays of exceptionally large period (22 nm) and involving a substantial number of hexahydroxytriphenylene molecules (20×20 superlattice) form on a Ag(111) surface. The superstructure (see picture; triangular pattern) is an intrinsic property of the system and, remarkably, it does not depend on global surface coverage (lower right: partial structure).
Cell-Penetrating Compounds
A Straightforward Approach for Cellular-Uptake Quantification†
- Pages: 8240-8243
- First Published: 23 September 2010

Putting a number on it: MALDI-TOF MS enabled direct quantification of the cellular uptake of cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) by MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. This sensitive general strategy (see schematic representation), which requires no purification or separation steps, relies on the enhancement and discrimination of the MS signals of an α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid tag in a neutral α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic methyl ester matrix.
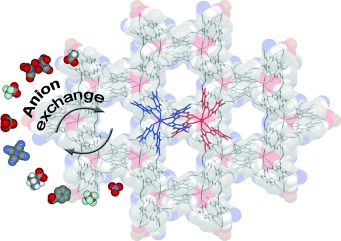
Metal–Organic Frameworks
Single-Crystal to Single-Crystal Cross-Linking of an Interpenetrating Chiral Metal–Organic Framework and Implications in Asymmetric Catalysis†
- Pages: 8244-8248
- First Published: 21 September 2010
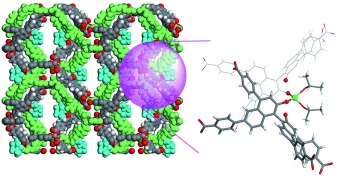
Support framework: Post-synthesis modification of an interpenetrating Zn-based chiral metal–organic framework with Ti(OiPr)4 results in a Lewis acidic catalyst (see picture; gray C, white H, red O, green Ti) with modest enantioselectivity in the asymmetric addition of diethylzinc to aldehydes. The Ti(OiPr)4-treated framework contains single-crystal to single-crystal cross-linking of the two interpenetrating networks.
Bioinorganic Chemistry
A {Cu2S}2+ Mixed-Valent Core Featuring a CuCu Bond†
- Pages: 8249-8252
- First Published: 17 September 2010
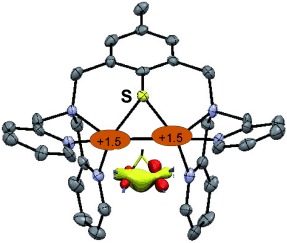
Not so far away from me: Reductive cleavage of a disulfide ligand with CuI leads to the formation of a new mixed-valent CuIICuI complex (see picture). Combined X-ray and theoretical investigations highlight the presence of a striking Cu2S core containing a CuCu bond, and solution studies also indicate a high degree of delocalization.
Nanostructures
Layered Cobalt Hydroxide Nanocones: Microwave-Assisted Synthesis, Exfoliation, and Structural Modification†
- Pages: 8253-8256
- First Published: 20 September 2010
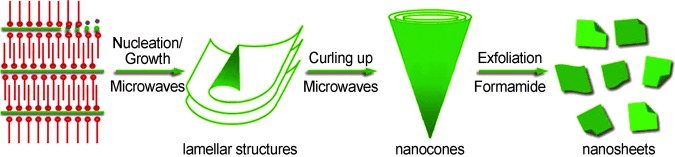
Layered cobalt hydroxide nanocones intercalated with dodecyl sulfate (DS) ions (see scheme; OH− blue, Co green dots, DS ions red) could be synthesized by the microwave-assisted rolling of lamellar structures. The cones could be exfoliated into cobalt hydroxide nanosheets and converted into CoOOH and Co3O4 nanocones.
CO2 Activation
Selective Formic Acid Synthesis from Nanoscale Electrochemistry†
- Pages: 8257-8259
- First Published: 21 September 2010
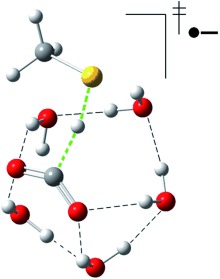
Hydrogen-atom transfer from a thiol group to the CO2 radical anion is a fast and selective downhill process in a gas-phase water cluster. This suggests that placing a thiol group near the site of electron transfer to CO2 in a nanostructured electrochemical environment allows the selective formation of formic acid (see picture; dark gray C, light gray H, red O, yellow S).
Self-Assembly
Mechanical Bond Formation by Radical Templation†
- Pages: 8260-8265
- First Published: 23 September 2010
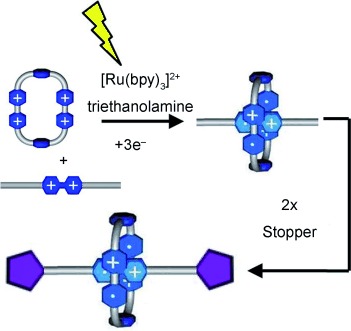
A radical interaction has been employed as the recognition motif in the template-directed synthesis of a [2]rotaxane composed of cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) and a viologen derivative. The ruthenium tris(bipyridine)/triethanolamine system is used as the electron-transfer photocatalyst to generate the necessary radical cation components that result in the formation of an inclusion complex. A stoppering reaction follows to form the mechanical bond.
Mechanochemistry
Solid-State Conversion of the Solvated Dimer [{tBuZn(μ-OtBu)(thf)}2] into a Long Overlooked Trimeric [{tBuZnOtBu}3] Species†
- Pages: 8266-8269
- First Published: 20 September 2010
![Solid-State Conversion of the Solvated Dimer [{tBuZn(μ-OtBu)(thf)}2] into a Long Overlooked Trimeric [{tBuZnOtBu}3] Species](/cms/asset/e8a9727f-3be9-4354-bdd9-b917c72a8d75/mcontent.jpg)
Zinc links: Solid-state desolvation of the dimeric alkoxide [{tBuZn(μ-OtBu)(thf)}2] leads to a trimer [{tBuZnOtBu}3] with a unique core structure; subsequent grinding affords the tetrameric cubane [{tBuZnOtBu}4]. This approach demonstrates a new direction in the generation of metal alkoxide clusters.