Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2002
- Pages: 2857-2869
- First Published: 21 August 2002
From Protein Domains to Drug Candidates—Natural Products as Guiding Principles in the Design and Synthesis of Compound Libraries
- Pages: 2878-2890
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Evolution leads the way: The structure of proteins is based on a limited number of folds (see picture). Natural products have been evolutionarily selected to bind to such protein domains, therefore, they represent biologically validated starting points for the design of combinatorial compound libraries, which allow a higher hit rate despite smaller library sizes.
Macromolecules Containing Bipyridine and Terpyridine Metal Complexes: Towards Metallosupramolecular Polymers
- Pages: 2892-2926
- First Published: 21 August 2002
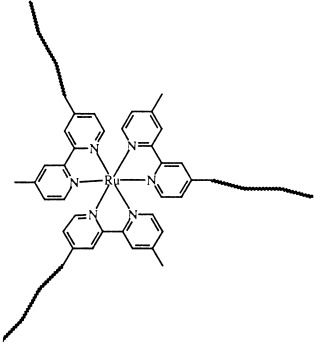
Functional architectures and “intelligent” materials can be constructed from polymer complexes with bipyridine (see picture) and terpyridine ligands, compounds that play an important role in modern macromolecular and supramolecular chemistry. This review provides an overview of the current status of the synthesis, characterization, and application of this class of compounds.
Boron Chemistry Lights the Way: Optical Properties of Molecular and Polymeric Systems†
- Pages: 2927-2931
- First Published: 21 August 2002
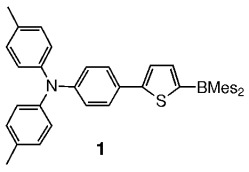
Molecular and polymeric boron-containing systems are proving to display interesting optical and electrooptical properties. Molecules such as thiophene 1 with a donor (4-[bis(4-methylphenyl)amino]phenyl) and an acceptor (dimesitylboryl) substituent, are strongly electroluminescent, and have been incorporated into organic electronic devices.
Enantioselective Synthesis of and with Allenes
- Pages: 2933-2935
- First Published: 21 August 2002
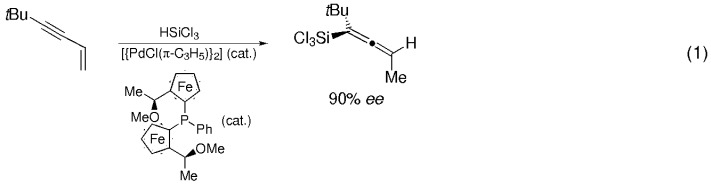
A breakthrough in the catalytic enantioselective synthesis of allenes was recently reported by Hayashi and co-workers: chiral trichlorosilyl allenes were generated with up to 90 % ee by palladium-catalyzed hydrosilylation of but-1-en-3-ynes in the presence of a chiral ferrocenyl phosphane [Eq. (1)]. This transformation, as well as further recent highlights in enantioselective allene synthesis, are summarized in this account.
Remodeling of gp41-C34 Peptide Leads to Highly Effective Inhibitors of the Fusion of HIV-1 with Target Cells†
- Pages: 2937-2940
- First Published: 21 August 2002
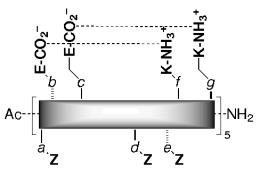
Substitution in the outer surface of the six-helix peptide bundle improved the solubility and enhanced the anti-HIV-1 activity of SC peptides. The E and K residues at positions b, c, f, and g (see scheme) stabilize the α-helix conformation critical to inhibition; the Z residues at positions a, d, and e interact with the inner strand.
Structure–Function Analysis of Urotensin II and Its Use in the Construction of a Ligand–Receptor Working Model
- Pages: 2940-2944
- First Published: 21 August 2002
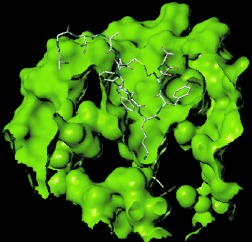
The salient structural features of urotensin II (U II) required for stimulation of its G-protein-coupled receptor were obtained from biological evaluation of synthetic derivatives of U II. This approach led to a plausible U-II–receptor complex (see picture), which inspired the installation of nonnatural amino acids in place of key residues. Notably, replacement of tyrosine with (2-naphthyl)-L-alanine resulted in a sixfold potency improvement compared to U II.
A Cluster Rearrangement of an Open Cubane (Cu4Br4) to a Prismane (Cu6Br6) in a Copper(I)–Olefin Network†
- Pages: 2944-2946
- First Published: 21 August 2002
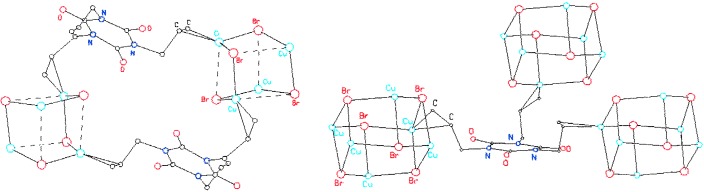
Temperature determines the product: The reaction of triallyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-(1H,3H,5H)-trione with CuBr at 60°C affords a copper(I)–olefin coordination polymer with a Cu4Br4 open cubane (left) as a connecting node; when the reaction is repeated at 90°C a Cu6Br6 prismane unit is formed in a coordination polymer (right).
Molecular Recognition of Carbohydrates through Directional Hydrogen Bonds by Urea-Appended Porphyrins in Organic Media †
- Pages: 2947-2950
- First Published: 21 August 2002
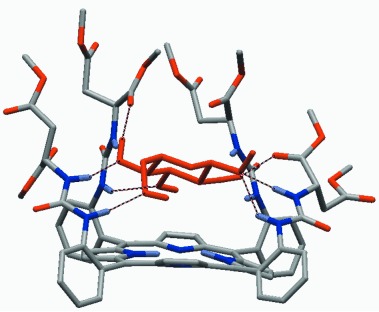
Sugar receptors: Urea-appended porphyrins were the most effective binding agent for pyranosides in chloroform and still very effective even in the presence of hydroxylic cosolvents. The combination of a rigid porphyrin skeleton and acyclic, flexible, yet preorganized polar urea groups aligned in a rigid platform (see picture) enabled three-dimensional recognition of carbohydrates.
Micelles and Hollow Nanospheres Based on ε-Caprolactone-Containing Polymers in Aqueous Media†
- Pages: 2950-2953
- First Published: 21 August 2002
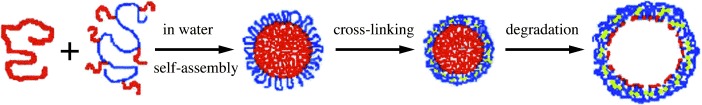
A block-copolymer-free strategy has been used to form micelles by the self-assembly of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and a graftlike copolymer which has a hydrophilic backbone and short PCL side-chains (see schematic representation). Affinity between the PCL homopolymer and the PCL short branches appears to stabilize the micelles. The hydrophobic polyester core can be selectively hydrolyzed by lipase to give hollow spheres, as shown by transmission electron microscopy.
An Efficient and Highly Enantio- and Diastereoselective Cyclopropanation of Olefins Catalyzed by Schiff-Base Ruthenium(II) Complexes†
- Pages: 2953-2956
- First Published: 21 August 2002
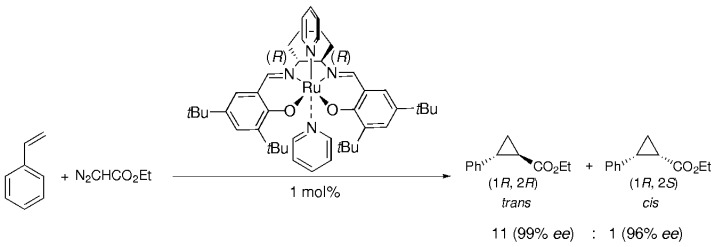
Both electron-rich and electron-deficient olefins—such as styrene and methyl methacrylate—undergo efficient (yields >90 %) cyclopropanation with ethyl diazoacetate as the carbene source to give predominantly trans products with exceptionally high enantioselectivity when the (salen)Ru catalyst shown is used (see scheme).
Supramolecular Organization of Oligopeptides, through Complexation with Surfactants†
- Pages: 2957-2960
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Ionic self-assembly: Oligopeptides with a small number of charged sites can be precipitated from water by complexation with oppositely charged surfactants, as exemplified here with oxidized glutathione, GSSG. These complexes are well-defined 1:1 species, dissolve in organic solvents, and form highly organized supramolecular aggregates (solution; see schematic representation) or mesophases (solid-state films). This ionic self-assembly with surfactants represents a simple access to new peptide superstructures with structural features on the nanometer scale.
Use of Enzymes Deactivated by Site-Directed Mutagenesis for the Preparation of Enantioselective Membranes†
- Pages: 2960-2962
- First Published: 21 August 2002
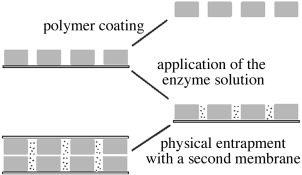
The conversion of enzymes into enantioselective receptors by mutagenesis opens the way for resolution of racemates by using enantioselective membranes: the transport of one enantiomer is accelerated through the membrane, while the other enantiomer diffuses across much more slowly. As an example, histidine ammonia lyase and phenylalanine ammonia lyase were rendered catalytically inactive and incorporated in artificial membranes (see figure). The facilitated transport of L-histidine and L-phenylalanine resulted in a maximum 14-fold enantiomeric enrichment.
Copper-Catalyzed Oxidative Heterocyclization by Atmospheric Oxygen
- Pages: 2962-2965
- First Published: 21 August 2002

Starting from Schiff bases 1, a wide variety of heterobicycles, which can be applied as pharmaceuticals or as ligands for catalysts, is accessible by copper-catalyzed oxidation with atmospheric oxygen. The scheme shows, for example, the synthesis of imidazo[1,5-a]pyridines 2 (R1=2-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl, tBu, 2-hydroxyphenyl, 2-aminophenyl; R2=2-pyridyl, Me, phenyl).
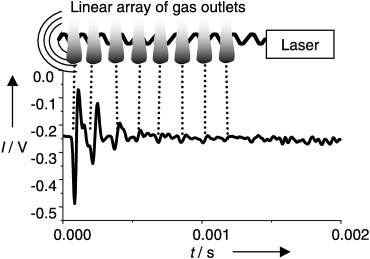
Real-Time Photoacoustic Parallel Detection of Products from Catalyst Libraries†
- Pages: 2966-2968
- First Published: 21 August 2002
1,2,3,5-Tetrahydro-1,2,3-methenopentalene, a Valence Isomer of Isoindene: Synthesis and Diels–Alder Reactions†
- Pages: 2969-2971
- First Published: 21 August 2002
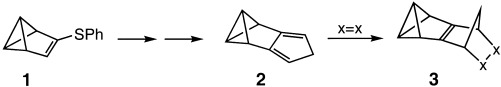
A strong pyramidalization of the double bond in the Diels–Alder adducts 3, as suggested by quantum-chemical calculations and NMR spectroscopic data, is probably the reason why these very reactive compounds are observable at best at low temperatures. The title compound 2, required for preparation of 3, was prepared in five steps from benzvalene 1.
Stereoselective Synthesis of β-D-Mannopyranosides with Reactive Mannopyranosyl Donors Possessing a Neighboring Electron-Withdrawing Group†
- Pages: 2972-2974
- First Published: 21 August 2002
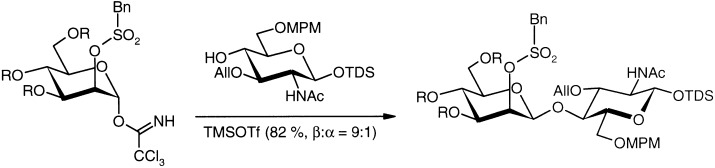
An electron-withdrawing protecting group at the O-2 atom and a good anomeric leaving group at the mannopyranosyl donor are required for a new, practical approach to the production of β-linked mannopyranoside units (see scheme, MPM=para-methoxybenzyl, TDS=thexylmethysilyl, TMS=trimethylsilyl, All=β-D-allose, OTf=trifluoromethanesulfonate). Many attempts to solve this problem in a direct manner have failed. β-Mannopyranoside units are found, for instance, in N-glycopeptides.
ULTRA Loaded Resins Based on the Cross-Linking of Linear Poly(ethylene imine). Improving the Atom Economy of Polymer-Supported Chemistry†
- Pages: 2975-2978
- First Published: 21 August 2002
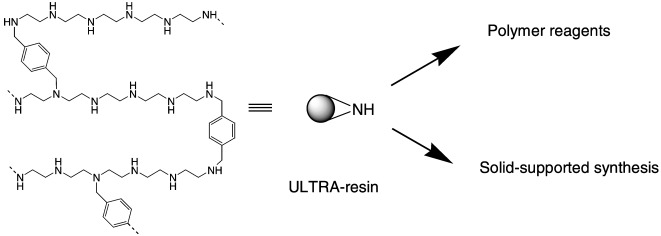
ULTRA resins (see picture), useful for making polymer reagents, heterocycles, and peptides, were prepared by thermodynamically controlled cross-linking of linear poly(ethylene imine)s with a loading of up to 15 mmol g−1. During characterization, the secondary amines in the resin backbone of the novel carriers were found to be very accessible to chemical modification.
A Model Nucleoside for Electron Injection into DNA: 5-Pyrenyl-2′-Deoxyribose†
- Pages: 2978-2980
- First Published: 21 August 2002
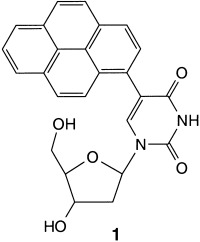
Ultrafast intramolecular electron transfer results from the excitation of the pyrene-modified nucleoside 1. The dynamics and pH dependence of this process were investigated by steady-state fluorescence and femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopy. These studies suggest that reductive electron transfer through DNA is not coupled to protonation.
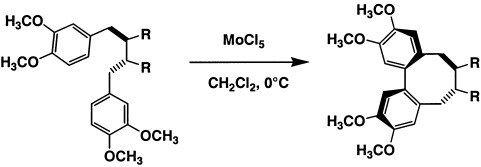
Highly Selective Formation of Eight-Membered-Ring Systems by Oxidative Cyclization with Molybdenum Pentachloride—An Environmentally Friendly and Inexpensive Access to 2,2′-Cyclolignans†
- Pages: 2981-2982
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Rhenium(VII) Oxo Complexes as Extremely Active Catalysts in the Dehydration of Primary Amides and Aldoximes to Nitriles
- Pages: 2983-2986
- First Published: 21 August 2002
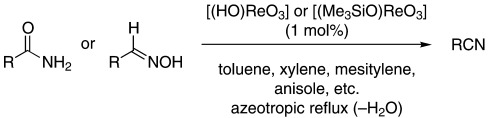
An economical and environmentally benign process for the preparation of nitriles by the dehydration of primary amides and aldoximes is catalyzed by rhenium(VII) oxo complexes such as perrhenic acid and trimethylsilylperrhenate (see scheme). The reaction proceeds at azeotropic reflux (with the removal of water) under essentially neutral conditions.
Lewis Acid Promoted, O-Selective, Nucleophilic Addition of Silyl Enol Ethers to NO bonds†
- Pages: 2986-2988
- First Published: 21 August 2002
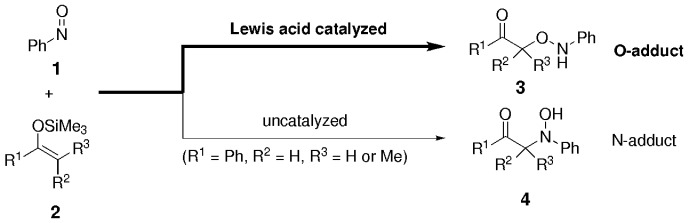
Not N-adduct but O-adduct is formed in the Lewis acid catalyzed nucleophilic addition of silyl enol ethers 2 to the NO bond of nitrosobenzene (1). Various Lewis acids (e.g. alkylsilyl triflates) efficiently catalyze the formation of the aminooxy ketone (O-adduct 3) rather than of the hydroxyamino ketone (N-adduct 4), which is the product of the uncatalyzed reaction.
Chiral Templating of Silica–Lipid Lamellar Mesophase with Helical Tubular Architecture†
- Pages: 2988-2991
- First Published: 21 August 2002
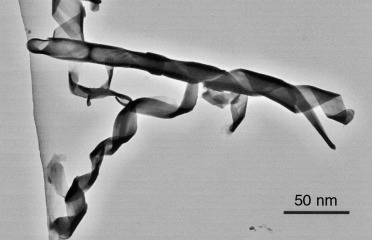
A lamellar hybrid mesostructure containing polymerizable diacetylinic groups is coassembled in the in situ synthesis of silica by acid hydrolysis and condensation of tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in the presence of 1,2-bis(10,12-tricosadiyonyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (DC8,9PC) lipid molecules. This mesostructure is subsequently twisted into high aspect-ratio tubules and ribbons with helical architecture (see picture). Interactions between the silica and lipid headgroups promote diacetylenic polymerization under conditions at which the unmineralized lipid microstructures show little or no activity.
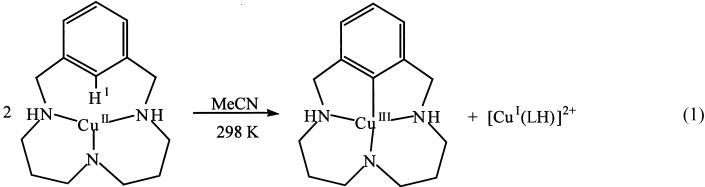
Aryl CH Activation by CuII To Form an Organometallic Aryl–CuIII Species: A Novel Twist on Copper Disproportionation†
- Pages: 2991-2994
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Migration of a Phosphane Ligand between the Two Metal Centers in Diruthenium Hydrido Complexes†
- Pages: 2994-2997
- First Published: 21 August 2002
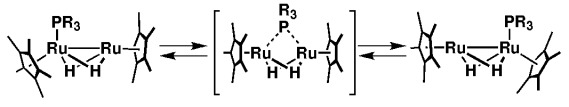
On the move! Novel diruthenium dihydrido [{(η5-C5Me5)Ru}2(PR3)(μ-H)2] complexes, which were synthesized in the reaction of [{(η5-C5Me5)Ru}2(μ-H)4] with a phosphorus ligand containing no aryl substituents, undergo intramolecular migration of the phosphorus ligand between the two ruthenium centers (see scheme). Support for this result is derived from variable temperature NMR spectroscopic studies and preliminary DFT calculations.
A Combined Effect of Molecular Electrostatic Potential and N7 Accessibility Explains Sequence-Dependent Binding of cis-[Pt(NH3)2(H2O)2]2+ to DNA Duplexes†
- Pages: 2998-3001
- First Published: 21 August 2002
![A Combined Effect of Molecular Electrostatic Potential and N7 Accessibility Explains Sequence-Dependent Binding of cis-[Pt(NH3)2(H2O)2]2+ to DNA Duplexes](/cms/asset/d9dda590-ca36-4c60-b1cc-a04c525adb2b/mcontent.jpg)
The main factor determining the sequence-selective binding of platinum complexes to DNA is the accessibility of the N7 atom of guanine (G). The rate constants observed for the reactions of cis-[Pt(NH3)2(H2O)2]2+ with DNA G residues in various sequences can be accounted for by a mathematical formula compatible with the kinetic model shown in the scheme, where the association constant K is determined by the molecular electrostatic potential and the rate constant k by the accessible area of the N7 van der Waals sphere.
Two [Nb6Cl9O3(CN)6]5− Isomer Anions in Two Nb6 Cluster Oxyhalides: Cs5[Nb6Cl9O3(CN)6]⋅4 H2O and (Me4N)5[Nb6Cl9O3(CN)6]⋅5 H2O†
- Pages: 3002-3004
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Trifluoroacetophenone Derivatives as Amino Acid Selective Ionophores for the Potentiometric Determination of Phenylalanine†
- Pages: 3005-3007
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Selective sensors: Trifluoroacetophenone derivatives were synthesized with a hexasubstituted benzene ring as a preorganized spacer (see scheme) and their characteristics as ionophores were examined for use in ion-selective electrodes. The electrode membranes based on these neutral carriers combined with a cationic additive showed a monoanionic Nernstian response to underivatized phenylalanine, with excellent selectivity towards other essential amino acids and inorganic anions.
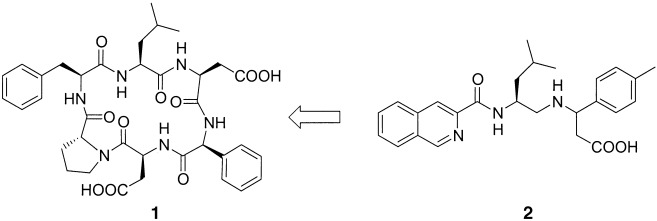
Combinatorial and Rational Strategies To Develop Nonpeptidic α4β7-Integrin Antagonists from Cyclic Peptides
- Pages: 3007-3011
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Tetraiodobutatriene: A New Cumulenic Carbon Iodide†
- Pages: 3011-3014
- First Published: 21 August 2002

In how many different ways can carbon and iodine combine to form a stable molecule? Here is a new possibility: the first reported iodocumulene. Tetraiodobutatriene (C4I4; see picture) is formed spontaneously and in good yield from diiodobutadiyne (C4I2). In solution, however, C4I4 disproportionates to give hexaiodobutadiene (C4I6) and unknown carbon-rich by-products.
Atom-Transfer Tandem Radical Cyclization Reactions Promoted by Lewis Acids†
- Pages: 3014-3017
- First Published: 21 August 2002
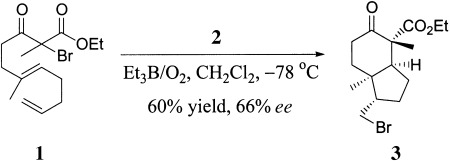
Various polycyclic ring skeletons (e.g. 3) are formed from unsaturated α-bromo β-keto esters (e.g. 1) in a Lewis acid catalyzed atom-transfer tandem radical-cyclization reaction in moderate to good yields and with excellent stereoselectivities. Furthermore, in the presence of chiral complexes such as [Yb(Ph-pybox)(OTf)3] (2), the enantioselective cyclization gave up to 84 % ee. OTf = trifluoromethanesulfonate, pybox = 2,6-bis(2-oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine.
Total Synthesis of the Natural Enantiomer of (−)-Lepadiformine and Determination of Its Absolute Stereochemistry†
- Pages: 3017-3020
- First Published: 21 August 2002
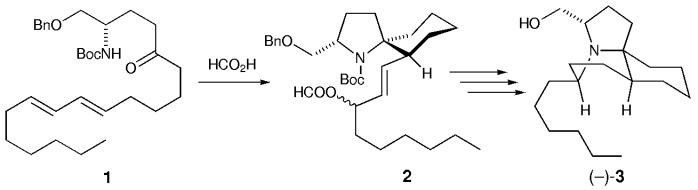
A short synthesis: The naturally occurring (−)-lepadiformine ((−)-3) was prepared in nine steps in 31.4 % overall yield. The key step involved the formation of 2 by the spirocyclization of the N-acyliminium ion generated from 1. Furthermore, HPLC analysis of the synthetic material and the natural product established the absolute configuration of 3 as 3S,5R,7aS,11aS. Bn=benzyl, Boc=tert-butoxycarbonyl.
“Molecular” Molecular Sieves: Lid-Free Decamethylcucurbit[5]uril Absorbs and Desorbs Gases Selectively†
- Pages: 3020-3023
- First Published: 21 August 2002
![“Molecular” Molecular Sieves: Lid-Free Decamethylcucurbit[5]uril Absorbs and Desorbs Gases Selectively](/cms/asset/b61247ed-8b99-45ed-b7e0-95c3f96b45dc/mcontent.jpg)
Miniature gas jars with lids: Salt-free decamethylcucurbit[5]uril (MeCuc5) powder, absorbs N2, O2, Ar, N2O, NO, CO, and CO2 selectively at room temperature and desorbs at 110°C, this process can be carried out repeatedly. In contrast, all noble gases from He to Xe were encapsulated inside MeCuc5 in solution and the crystal structures of the gas inclusion complexes were determined (see picture for Xe complex).
Efficient and General Synthetic Approach to Pentasubstituted Conjugated Dienes Using Site-Selective Coupling of Cuprates with 1,4-Diiodo-1,3-alkadienes as the Key Reaction†
- Pages: 3023-3025
- First Published: 21 August 2002
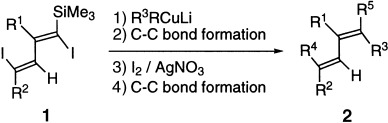
Taking advantage of the presence of a silyl group at the α position in 1, carbon–carbon bonds are formed regioselectively by the reaction of 1 with organocuprate compounds. This method is a practical and efficient approach to molecules of type 2 (R1–R5=alkyl, aryl) with a variety of substitution patterns.
Reaction of “[MnII(CH2tBu)2]” with Bidentate Diimine Ligands: From Simple Base Adducts to CC Activation of the Ligand†
- Pages: 3025-3027
- First Published: 21 August 2002
![Reaction of “[MnII(CH2tBu)2]” with Bidentate Diimine Ligands: From Simple Base Adducts to C<span class='icomoon'></span>C Activation of the Ligand](/cms/asset/1479fca5-3363-423d-87eb-61605b495b78/mcontent.jpg)
Ligand transformations that depend on the substitution patterns of the diimine ligands occur upon their complexation with MnII dialkyl complexes. For example the 1,3-migration of the neopentyl unit from Mn to a carbon atom and the 1,2-migration of the methyl in the putative intermediate 1 give the product 2.
Facile Oxidation of Alcohols to Carbonyl Compounds Using a Tris(2-methylphenyl)bismuth Dichloride–DBU Binary System†
- Pages: 3028-3031
- First Published: 21 August 2002

High efficiency and chemoselectivity as well as the facile isolation of the carbonyl products by simple workup procedures characterize a new method of alcohol oxidation. A variety of primary and secondary alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes and ketones by the combined use of tris(2-methylphenyl)bismuth dichloride and 1,8-diazabicyclo[5,4,0]undec-7-ene (DBU) under mild conditions [Eq. (1)].
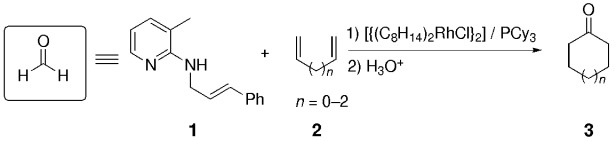
Synthesis of Cycloalkanones from Dienes and Allylamines through CH and CC Bond Activation Catalyzed by a Rhodium(I) Complex†
- Pages: 3031-3033
- First Published: 21 August 2002
An Analogue of Cymantrene [(η5-C5H5)Mn(CO)3] That Contains a Dimetalladithiacyclopentadienyl ring†
- Pages: 3034-3036
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Highly Enantioselective and Practical Cinchona-Derived Phase-Transfer Catalysts for the Synthesis of α-Amino Acids†
- Pages: 3036-3038
- First Published: 21 August 2002
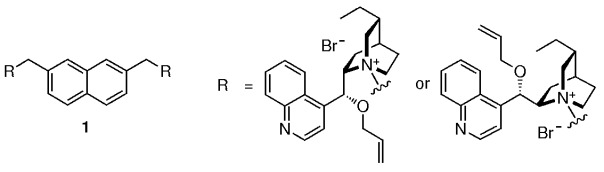
A new class of naphthalene-based dimeric cinchona alkaloids 1 are very efficient and practical phase-transfer catalysts in the alkylation of a glycine derivative. The mild reaction conditions and the high catalytic efficiency (high yields and ee values) could make these alkaloids practical catalysts in the industrial synthetic process for natural and nonnatural chiral α-amino acids.
Facile Syntheses of Copper(I) Alkynyl Clusters Stabilized by Hexafluoroacetylacetonate (hfac) Ligands: The Structure of [Cu26(hfac)11(1-pentynyl)15]†
- Pages: 3038-3041
- First Published: 21 August 2002
![Facile Syntheses of Copper(I) Alkynyl Clusters Stabilized by Hexafluoroacetylacetonate (hfac) Ligands: The Structure of [Cu26(hfac)11(1-pentynyl)15]](/cms/asset/2bad0364-942d-40e2-b108-3576bb31bbfb/mcontent.jpg)
A remarkably anisotropic structure is exhibited by [Cu26(hfac)11(1-pentynyl)15] (hfac=hexafluoroacetylacetone), the largest CuI cluster to have been isolated (see picture). A variety of copper–alkynyl bridging modes are found within the disc-shaped cluster, with all but one of the 26 Cu atoms being located in either of two “layers”. Many short CuI⋅⋅⋅CuI interactions can be discerned within the cluster.
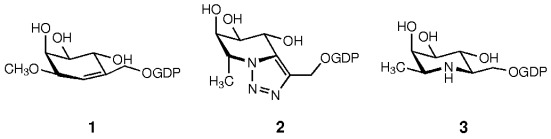
Synthesis and Evaluation of Transition-State Analogue Inhibitors of α-1,3-Fucosyltransferase†
- Pages: 3041-3044
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Cyanoethynylethenes: A Class of Powerful Electron Acceptors for Molecular Scaffolding†
- Pages: 3044-3047
- First Published: 21 August 2002
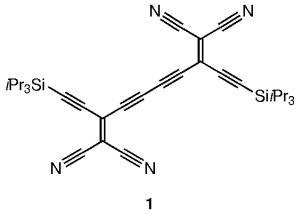
Extended π-electron acceptors, such as 1, have been constructed by the acetylenic scaffolding of a series of novel cyanoethynylethenes. Electrochemical analysis shows that acceptor strength is a function of π-electron conjugation length, and that a linear correlation exists between the electron affinities (B3LYP, 3-21G) and their first reduction potential.
A Structural and Functional Model of Galactose Oxidase: Control of the One-Electron Oxidized Active Form through Two Differentiated Phenolic Arms in a Tripodal Ligand
- Pages: 3047-3050
- First Published: 21 August 2002
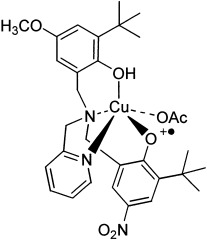
The axial phenol group is protonated and the equatorial phenoxyl group antiferromagnetically coupled to the cupric center in the complex [CuII(LH)(OAc)].+ (see picture), which can be considered as both a structural and functional model of galactose oxidase. This complex reproduces the features of the enzyme chemistry. The phenoxyl radical position (equatorial versus axial) is dictated by protonation.
Experimental Detection of the Pentaazacyclopentadienide (Pentazolate) Anion, cyclo-N5−†
- Pages: 3051-3054
- First Published: 21 August 2002
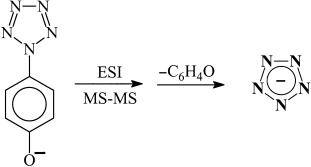
The long-sought pentazolate anion, cyclo-N5−, the isoelectronic polynitrogen counterpart of the cyclopentadienide anion, has been experimentally detected for the first time. Using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and carefully selected collision voltages, the aryl substituent in the para-pentazolylphenolate anion can be removed selectively without breaking the nitrogen–nitrogen bonds of the pentazolate anion (see scheme), thus delineating a synthetic method for the bulk synthesis of N5−.
First Synthesis of Optically Pure Propargylic N-Hydroxylamines by Direct, Highly Diastereoselective Addition of Terminal Alkynes to Nitrones†
- Pages: 3054-3056
- First Published: 21 August 2002
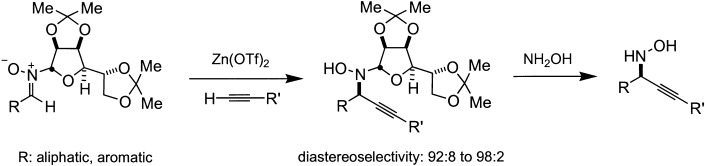
In situ generation of nucleophilic alkynilides by using substoichiometric amounts of Zn(OTf)2 (OTf = trifluoromethanesulfonate) followed by removal of the chiral auxiliary enables the direct use of a wide range of terminal acetylenes in the synthesis of optically pure propargylic N-hydroxylamines (see scheme).
A Stoichiometric Aromatic CH Borylation Catalyzed by Iridium(I)/2,2′-Bipyridine Complexes at Room Temperature
- Pages: 3056-3058
- First Published: 21 August 2002
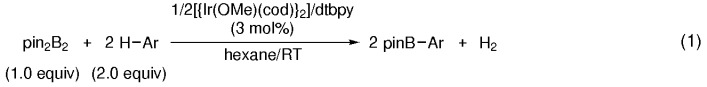
Room-temperature CH borylation using a stoichiometric amount of arenes and bis(pinacolato)diboron (pin2B2) is efficiently catalyzed by iridium(I) complexes generated from [{Ir(OMe)(cod)}2] (cod=1,5-cyclooctadiene) and 4,4′-di-tert-butyl-2,2′-bipyridine (dtbpy) in hexane, and provides the corresponding arylboronates in excellent yields [Eq. (1)].
Highly Enantioselective Inverse-Electron-Demand Hetero-Diels–Alder Reactions of α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes†
- Pages: 3059-3061
- First Published: 21 August 2002
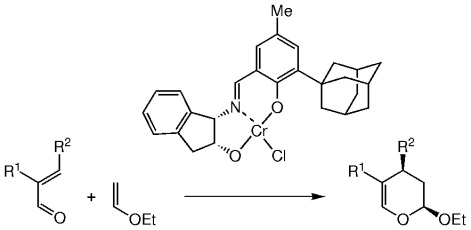
Straightforward access to useful synthetic intermediates is provided by this new method. Simple, α,β-unsaturated aldehydes are excellent substrates in the hetero-Diels–Alder reaction with inverse electron demand, catalyzed by CrIII–Schiff base complexes (see scheme; R1, R2=alkyl or aryl) in the presence of 4-Å molecular sieves and no solvent. The resulting dihydropyrans are obtained in high enantio- (89–98 % ee) and diastereoselectivity (>95 % de) and yield (40–95 %).
Book Review: Molecular Fluorescence. Principles and Applications. By Bernard Valeur
- Pages: 3063-3064
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Book Review: Chemical and Biological Warfare. A Comprehensive Survey for the Concerned Citizen. By Eric Croddy, Clarisa Perez-Armendariz and John Hart
- Page: 3064
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Book Review: Science, Truth, and Democracy. By Philip Kitcher
- Pages: 3064-3066
- First Published: 21 August 2002
Book Review: Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation for Organic Synthesis. By Shigeo Nishimura
- Page: 3066
- First Published: 21 August 2002




41:16<>1.0.co;2-7.cover.gif)
![Two [Nb6Cl9O3(CN)6]5− Isomer Anions in Two Nb6 Cluster Oxyhalides: Cs5[Nb6Cl9O3(CN)6]⋅4 H2O and (Me4N)5[Nb6Cl9O3(CN)6]⋅5 H2O](/cms/asset/ee2d2c36-d1c8-4b4b-8cb9-64aae96fa2ff/mcontent.jpg)
![An Analogue of Cymantrene [(η5-C5H5)Mn(CO)3] That Contains a Dimetalladithiacyclopentadienyl ring](/cms/asset/1a89fd43-35f9-4686-9015-40d8f147a882/mcontent.jpg)