Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
SSK1-Loaded Neurotransmitter-Derived Nanoparticles for Alzheimer's Disease Therapy via Clearance of Senescent Cells (Small 26/2024)
- First Published: 26 June 2024

Alzheimer's Disease Therapy
SSK1-NPs efficiently delivered SSK1 into the brain, at where SSK1 is specifically cleaved by β-galactosidase, which in turn induces the apoptosis of senescent cells. Treatment of SSK1-NP induced apoptosis of senescence cells in the brain and improved cognitive function and memory in aged Alzheimer's disease mice. More in article number 2308574, Jian Zhang, Yi Luo, Yan Liu, Jie Gao, You Yin, and co-workers.
Inside Front Cover
Emerging Trends in Electron Transport Layer Development for Stable and Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells (Small 26/2024)
- First Published: 26 June 2024
Perovskite Solar Cells
In article number 2400807, Chunhu Zhao, Jiahua Tao, and co-workers introduce an economical and efficient guideline for electron transport materials (ETMs) in perovskite solar cells (PSCs). They comprehensively discuss significant advancements in ETMs across different systems and address key challenges such as grain structure control, defect passivation, energy level alignment, and interface engineering, all aimed at enhancing the efficiency and stability of PSCs.
Inside Back Cover
High Performance Proprioceptive Fiber Actuators Based on Ag Nanoparticles-Incorporated Hybrid Twisted and Coiled System (Small 26/2024)
- First Published: 26 June 2024
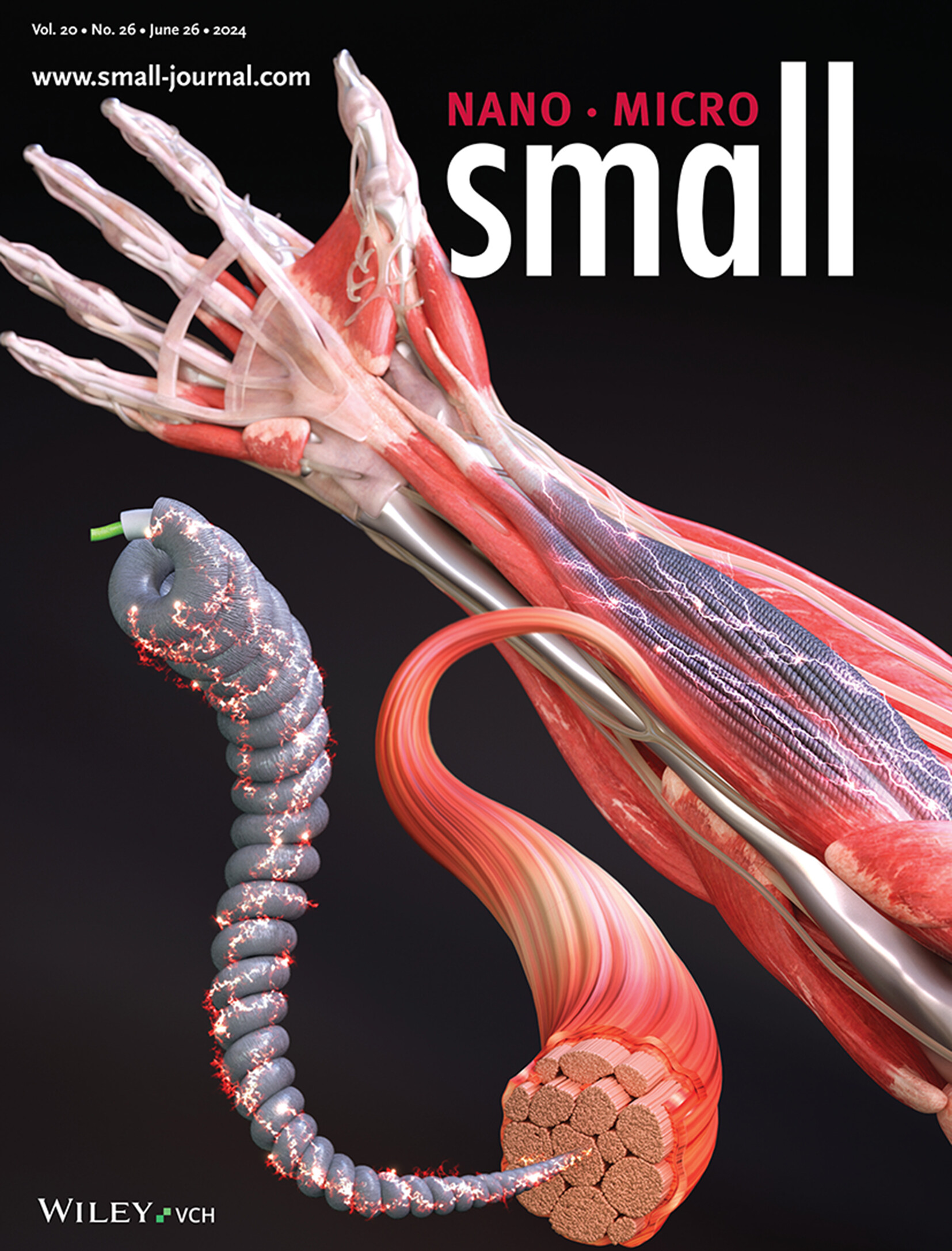
Proprioceptive Fiber Actuators
In article number 2309429, Jaehong Lee and co-workers report on an Ag nanoparticles-based proprioceptive fiber actuator. This fiber actuator demonstrates outstanding performance including high contractile actuation, low operating temperature, fast cooling time, and proprioceptive sensing capability. This study plays a pivotal role in the development of intelligent wearable devices and soft robotic systems.
Back Cover
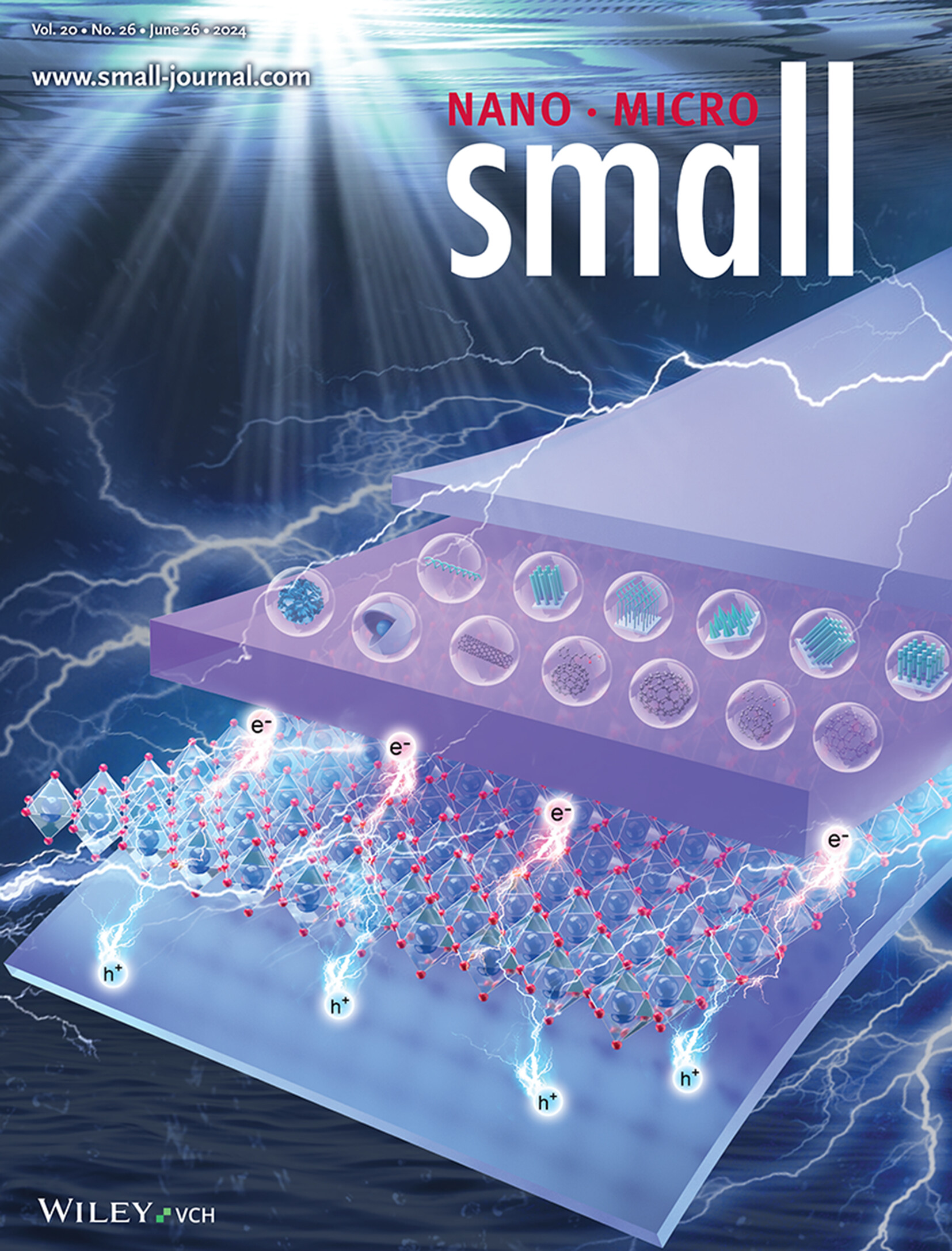
Glass-Like Phonon Dynamics and Thermal Transport in a GeTe Nano-Composite at Low Temperature (Small 26/2024)
- First Published: 26 June 2024
Microelectronics
The landscape represents a GeTe-C nanocomposite, a heterogeneous medium made of materials with different elastic properties, as symbolized by mountains and valleys. A travelling phonon is scattered at the interfaces and strongly attenuated. This strong scattering, like in glasses, modifies phonon properties and leads to a low and weakly temperature dependent thermal conductivity. More in article number 2310209, V. M. Giordano and co-workers.
Masthead
Reviews
Emerging Trends in Electron Transport Layer Development for Stable and Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 04 April 2024
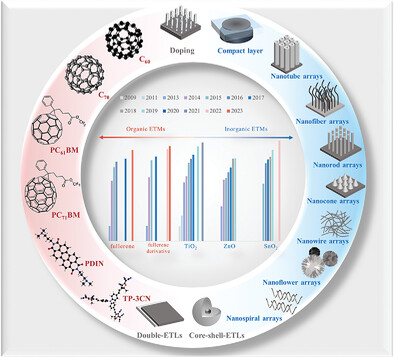
This study provides guidelines for the use of efficient ETMs in PSCs, describes the remarkable progress of ETMs in various perovskite systems, and focuses on the key ETL challenges: regulating grain structure, defect passivation techniques, energy level alignment, and interface engineering. It finishes with a detailed assessment of the most advanced ETMs, focusing on their strategic importance and future challenges.
Gallium-Based Liquid Metals in Rechargeable Batteries: From Properties to Applications
- First Published: 28 January 2024
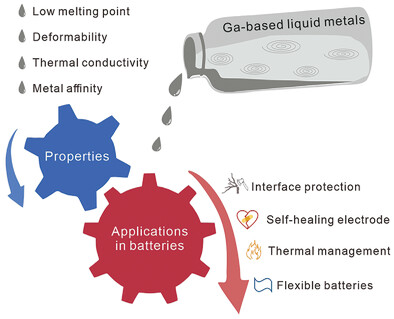
Gallium-based liquid metals exhibit characteristics of both a metal and a liquid, demonstrating favorable qualities such as good deformability, electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and metal affinity at room temperature. Gallium-based liquid metals can be applied in rechargeable batteries, accomplishing dendrite-free and corrosion-free anode, self-healing electrode, keeping away from thermal runaway, and constructing flexible batteries.
Emerging Nanomaterials toward Uranium Extraction from Seawater: Recent Advances and Perspectives
- First Published: 21 January 2024
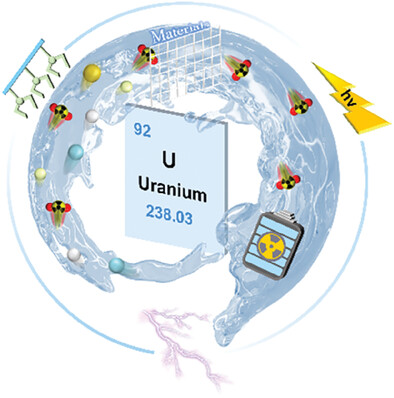
Uranium extraction from seawater (UES) is vital for sustainable nuclear energy and global energy transition. A comprehensive discussion on emerging UES materials presenting the fast-growing progress of this field, focusing on the current UES technologies, the causality between the physiochemical properties of emerging UES materials and UES performances, the relationships of materials-properties-activities and the corresponding mechanisms, is thus highly needed.
Diagnostic, Therapeutic, and Theranostic Multifunctional Microneedles
- First Published: 22 February 2024
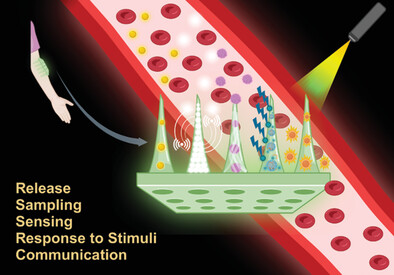
Microneedles have lately evolved into intelligent devices with functions including bodily fluid extraction, biosensing, and drug administration. This paper discusses individual microneedle functions toward the evolution and development of smart and multifunctional microneedles for a variety of applications. The paper examines microneedle constructs that perform multiple functions concurrently, including sensing, drug-molecule release, sampling, response to stimuli and communication.
Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Applications of Layer-Structured Metal Chalcogenides Composites
- First Published: 14 January 2024
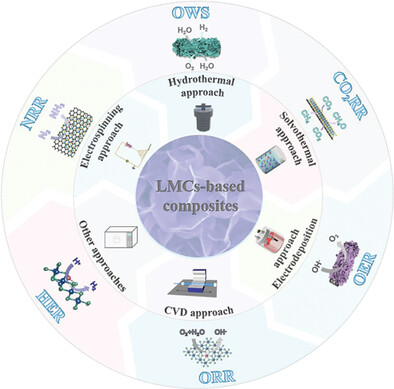
This review summarizes the recent advances in the fabrication approaches and the electrochemical energy conversion applications of LMCs-based electrocatalysts. The potential opportunities and obstacles for the future advancement of LMCs-based composites for energy conversion applications are highlighted.
Self-Assembled Nanocarrier Delivery Systems for Bioactive Compounds
- First Published: 12 January 2024
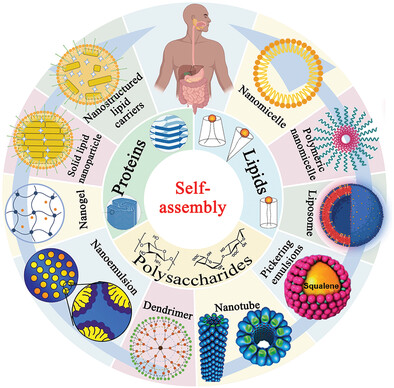
Based on the different self-assembly bases of building blocks (proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids), they can form varieties of structures, including nanomicelles, liposomes, Pickering emulsions, nanotubes, dendrimers, nanoemulsions, nanogels, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers. When nanocarriers are used to deliver bioactive compounds, they can bring many advantages to overcome the deficiencies of bioactive compounds.
Metal Phosphide Anodes in Sodium-Ion Batteries: Latest Applications and Progress
- First Published: 17 January 2024
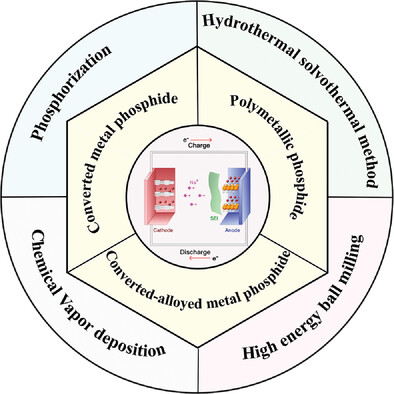
Metal phosphide has a wide application prospect as the anode material of sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). In this paper, the mechanism of sodium storage, the preparation method of metal phosphide, and its latest application in SIBs are reviewed. The current challenges and prospects of metal phosphide are summarized and prospected.
CeO2-Based Frustrated Lewis Pairs via Defective Engineering: Formation Theory, Site Characterization, and Small Molecule Activation
- First Published: 18 January 2024
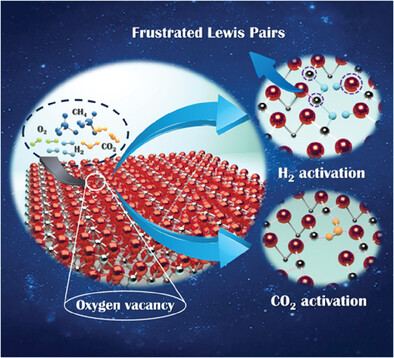
Frustrated Lewis pairs (FLPs) built on the surface of CeO2 show unique advantages in activating small molecules. This review presents the formation theory, characterization methods, regulation strategies, and application in small molecule activation of FLPs. The ideas presented may contribute to further theoretical innovations in FLPs development and environment- and energy-related catalysis.
Frontispiece
Self-healable, Tolerant Superaerophobic Coating for Improving Electrochemical Hydrogen Production (Small 26/2024)
- First Published: 26 June 2024

Electrochemical Hydrogen Production
In article number 2309359, Uttam Manna and co-workers applied a self-healable and superaerophobic hydrogel coating on a porous electrode surface for early release of the generated hydrogen gas bubbles. Eventually, this catalyst-free coating prevents rise in the resistance of the working electrode and significantly improves electrochemical hydrogen evolution performance.
Research Articles
Self-healable, Tolerant Superaerophobic Coating for Improving Electrochemical Hydrogen Production
- First Published: 20 January 2024
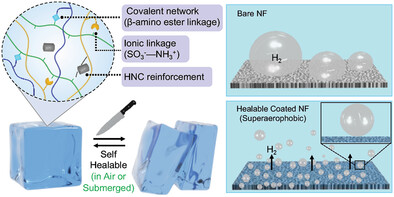
Here, a dual (physical and covalent) cross-linking chemistry and reinforcement of halloysite nano clay are strategically integrated to derive an underwater superaerophobic material with the ultralow force of bubble adhesion, rapid self-healable ability and impeccable chemical tolerance for preventing a rise in resistance of coated electrode through early release of the generated hydrogen gas bubbles. Eventually, this catalyst-free coating is allowed to achieve a significantly improved electrochemical hydrogen evolution performance.
Frontispiece
Microfluidic Impedance Cytometry Enabled One-Step Sample Preparation for Efficient Single-Cell Mass Spectrometry (Small 26/2024)
- First Published: 26 June 2024

Single-Cell Mass Spectrometry
In article number 2310700, Wenhui Wang and co-workers proposed a one-step sample preparation strategy by leveraging label-free microfluidic impedance flow cytometry to solve the problem of simultaneous sorting and desalting of single cells. This strategy enables to flow mixed cell samples into the microfluidic chip, and then collect the target cell samples with desired size and electrical properties from the outlet for direct single cell mass spectrometry analysis.
Research Articles
Microfluidic Impedance Cytometry Enabled One-Step Sample Preparation for Efficient Single-Cell Mass Spectrometry
- First Published: 14 March 2024
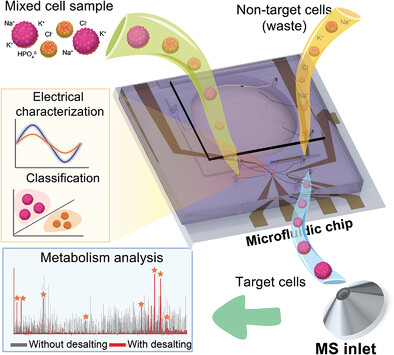
A one-step sample preparation strategy by leveraging label-free impedance flow cytometry (IFC) based microfluidics to solve the problem of simultaneous sorting and desalting of single-cells is proposed. With this strategy, one only needs to flow mixed cell samples into the microfluidic chip, and then get the target cell samples from the outlet for direct single-cell MS analysis.
SSK1-Loaded Neurotransmitter-Derived Nanoparticles for Alzheimer's Disease Therapy via Clearance of Senescent Cells
- First Published: 01 March 2024
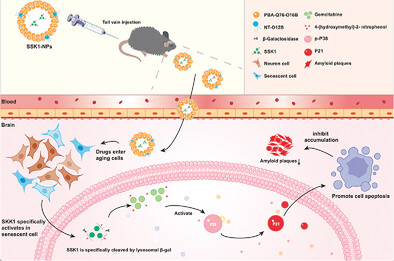
In this study, a novel nanomedicine is generated, SSK1-NPs, that efficiently delivers SSK1 into the brain, at where SSK1 is then specifically cleaved by lysosomal β-gal that is expressed at higher levels in aged cells, followed by the release of its active form, gemcitabine, which in turn induces the apoptosis of senescent cells leading to the reduction of amyloid-beta accumulation and improvement of cognitive function in aged AD mice.
High Performance Proprioceptive Fiber Actuators Based on Ag Nanoparticles-Incorporated Hybrid Twisted and Coiled System
- First Published: 29 March 2024
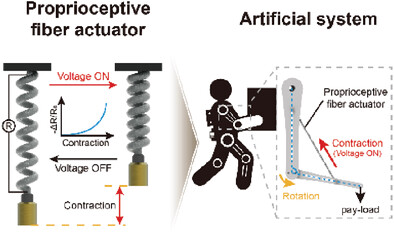
A proprioceptive fiber actuator with high contractile actuation, low operating temperature, and proprioceptive sensing capability is realized by incorporating a large amount of silver nanoparticles into a non-conductive hybrid twisted-coiled actuator. Based on its proprioceptive sensing capability, this study presents several applications, including feedback-controlled systems and artificial arm systems.
Glass-Like Phonon Dynamics and Thermal Transport in a GeTe Nano-Composite at Low Temperature
- First Published: 18 April 2024

An investigation of thermal transport in nanocomposites made of crystalline GeTe and amorphous carbon is reported. The thermal conductivity is low and weakly increasing with temperature, like in glasses. It is shown that this is due to a strong diffusion of the main heat carriers, phonons, at the interfaces, which leads to a glass-like phonon dynamics.
An Automated Single-Cell Droplet-Digital Microfluidic Platform for Monoclonal Antibody Discovery
- First Published: 05 March 2024
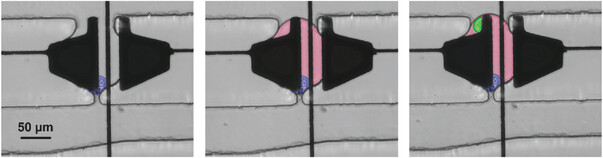
A new microfluidic method for antibody screening that allows for deterministic encapsulation of two cells and for frequent washes with minimal losses in the droplet. This new method is powered by droplet-digital microfluidics, which combines droplet-in-flow techniques with digital microfluidic for the generation and the manipulation of droplets.
Multiple Magneto-Optical Microrobotic Collectives with Selective Control in Three Dimensions Under Water
- First Published: 23 January 2024
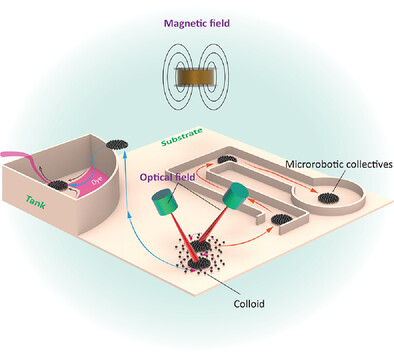
The proposed strategy that combines magnetic and optical fields to achieve independent position control and task execution of multiple microrobotic collectives in 3D space. The magnetic field excites the self-assembly of colloids and maintains the self-assembled microrobotic collectives without disassembly, while the optical field drives selected microrobotic collectives to perform different tasks.
Encapsulation of Titanium Disulfide into MOF-Derived N,S-Doped Carbon Nanotablets Toward Suppressed Shuttle Effect and Enhanced Sodium Storage Performance
- First Published: 14 January 2024
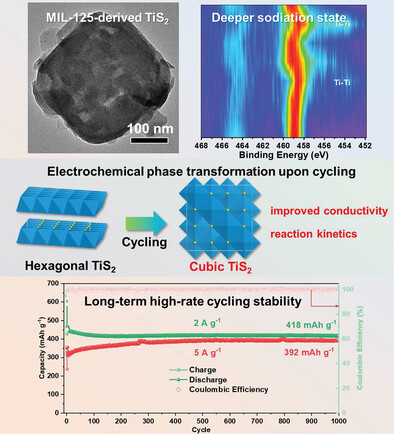
TiS2@N,S co-doped C (TiS2@NSC) nanotablets are fabricated through sulfidation of Ti-based metal–organic framework (NH2-MIL-125) using CS2, in which the polar bonds (C─N and C─S bonds) synergistically suppress the shuttle effect of polysulfides. Ex situ characterizations reveal that TiS2 undergoes a deeper sodiation state upon cycling, and the pristine hexagonal TiS2 is electrochemically transformed into cubic rock-salt TiS2 as a reversible phase with enhanced reaction kinetics.
Platinum–Ruthenium Dual-Atomic Sites Dispersed in Nanoporous Ni0.85Se Enabling Ampere-Level Current Density Hydrogen Production
- First Published: 15 January 2024
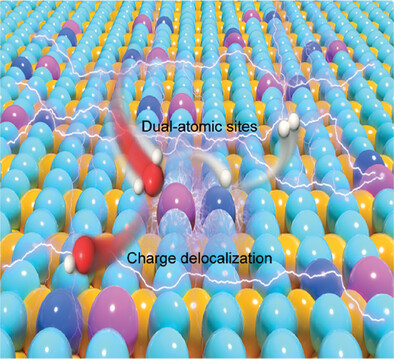
In this paper, Pt-Ru dual-atomic-sites co-embedded in nanoporous nickel selenides are developed through a rapid melt-quenching approach and chemical etching method. The strong intracrystal electronic metal-support interaction (IEMSI) between Pt-Se-Ru sites and Ni0.85Se support greatly enlarge the charge redistribution density, which enables the highly-efficient hydrogen production under an industrial-level current density.
Highly Solubilized Urea as Effective Proton Donor-Acceptors for Durable Zinc-Ion Storage Beyond Single-Anion Selection Criteria
- First Published: 24 January 2024

A dual-anion urea-based (DAU) electrolyte is proposed. The composition of dual-Zn salts in a urea-H2O mixture contributes to a stable electric double-layer construction and in situ organic/inorganic SEI formation for the practical Zn energy storage application. The cheap, antifreezing, and non-flammable DAU electrolyte system directs the battery technology development in commercialization.
Cobalt Nitride Nanoparticles Encapsulated in N-Doped Carbon Nanotubes Modified Separator of Li–S Battery Achieving the Synergistic Effect of Restriction-Adsorption-Catalysis of Polysulfides
- First Published: 18 January 2024
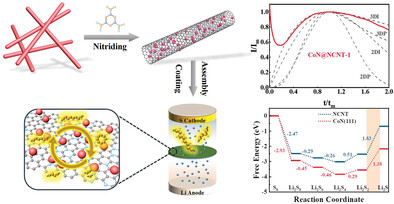
The cobalt nitride nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped carbon nanotube (CoN@NCNT) catalysts are rationally designed as a separator modifier for Li–S battery. Owing to the synergistic effect of the confinement of CNT, the adsorption capacity of N-doping, and the catalytic ability of CoN nanoparticles, the modified separator can significantly achieve excellent performance both in rate capability and long-cycle durability.
Protein Binding Leads to Reduced Stability and Solvated Disorder in the Polystyrene Nanoparticle Corona
- First Published: 21 January 2024
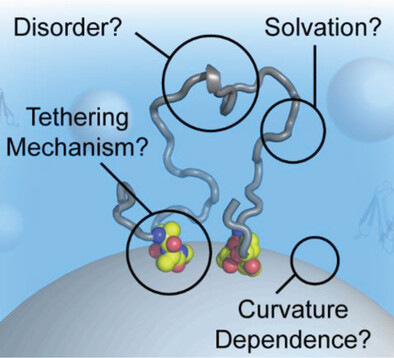
Proteins experience destabilization when bound to polystyrene nanoparticle surfaces. This leads to highly solvated protein conformations separated by tethering regions, termed “adsorbotopes.” Nanoparticle curvature influences the amount of protein disorder as well as the degree of protein destabilization. Identifying the tethering regions and intervening structure has implications for how living systems respond to therapeutic nanoparticles.
GO-PEG Represses the Progression of Liver Inflammation via Regulating the M1/M2 Polarization of Kupffer Cells
- First Published: 17 January 2024
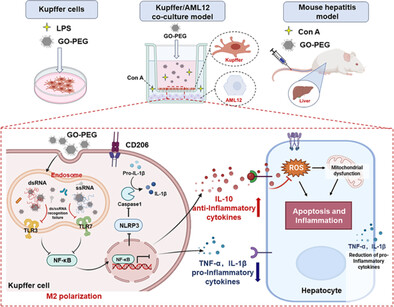
At both cellular and animal levels, Polyethylene glycol-modified graphene oxide accumulated in endosomes interferes with TLR3/7 activation by adsorbing ds/ssRNA, thereby regulating the immune response of liver macrophages and promoting alternative activation (M2). The corresponding inflammatory mediators further alleviate the progression of liver inflammation through the crosstalk between liver macrophages and hepatocytes.
Capsaicin Enhanced the Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy Against Osteosarcoma via a Pro-Death Strategy by Inducing Ferroptosis and Alleviating Hypoxia
- First Published: 14 January 2024
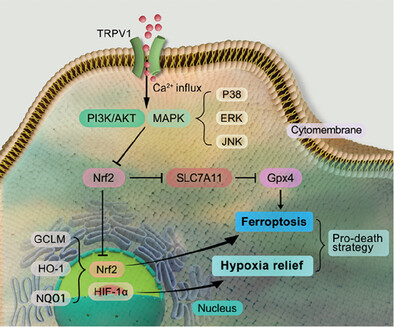
Using a “pro-death” strategy, CI@HSA NPs are engineered to induce ferroptosis and alleviate hypoxia against OS (osteosarcoma) by releasing CAP (capsaicin), accompanied by increased TRPV1 (transient receptor potential vanilloid 1)/Ca2+ levels and inactivation of Gpx4 (glutathione peroxidase 4), and inhibited HIF-1α (hypoxia-inducible factor-1α), amplifying PDT (photodynamic therapy) efficiency under NIR (near-infrared) irradiation and FL (fluorescence) imaging guidance.
Adaptive Laboratory Evolution of Probiotics toward Oxidative Stress Using a Microfluidic-Based Platform
- First Published: 21 January 2024
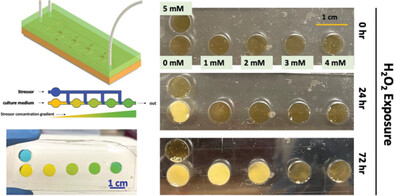
A microfluidic platform is developed as an alternative to large batch scale adaptive laboratory evolution cultures. The microfluidic Evolution on a Chip design progressively drives microbial cells from areas of lower H2O2 concentration to areas of higher concentration. The adaptive strains have different morphology and gene expression compared to wild type, and genome sequencing revealed a single nucleotide mutation.
Doping-Induced Surface and Grain Boundary Effects in Ni-Rich Layered Cathode Materials
- First Published: 23 January 2024
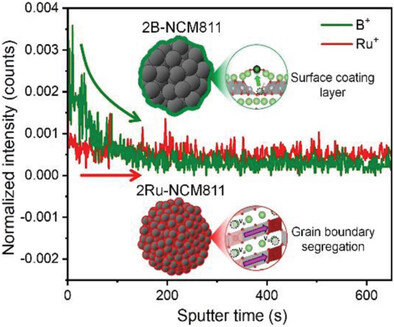
A small amount of dopant can considerably change the performance of layered oxide Ni-rich LiNixCoyMn1x−yO2 (NCM) cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Depending on its size and oxidation state, a dopant can modify the atomistic structure of agglomerate surface and/or grain boundaries, and thereby, influence the capacity and cyclability of NCM cathodes.
High-Index NiO Particle Synthesis in Alkali Chloride Salts: Nonclassical Crystallization Pathways and Thermally-Induced Surface Restructuring
- First Published: 06 February 2024
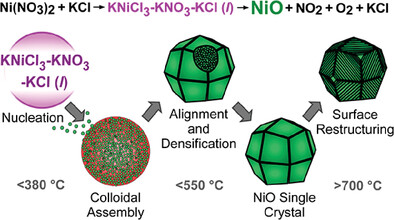
The synthesis of NiO in alkali halide molten salts occurs by a nonclassical mechanism involving colloidal assembly and ripening/densification from the exterior to the interior of the crystal. The (311) facets generated in KCl growth media undergo restructuring at temperatures much higher than those used to synthesize the metal oxide.
Hydrophilic 1T-WS2 Nanosheet Arrays toward Conductive Textiles for High-Efficient and Continuous Hydroelectric Generation and Storage
- First Published: 14 January 2024
Through constructing 2D nanosheet arrays and moisture-induced primary battery system, a high-performance and flexible hydroelectric generator is developed with a sustained open-circuit voltage of 0.65 V, and an excellent short-circuitcurrent of 0.51 mA. Moreover, these prepared flexible hydroelectric generators can be used in the wearable self-powered field.
Tuning the Selectivity of Nitrate Reduction via Fine Composition Control of RuPdNP Catalysts
- First Published: 07 February 2024
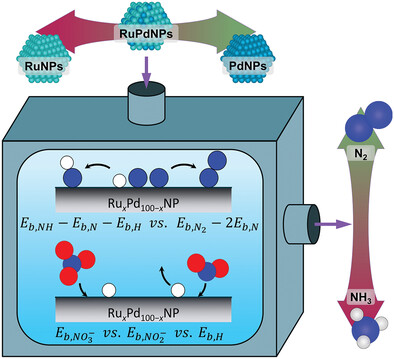
Randomly alloyed RuPdNPs are used to examine the mechanisms that influence selectivity during aqueous nitrate (NO3−) reduction to form either ammonium (NH4+) or N2. Experimental results starting with either nitrate, nitrite (NO2−), or NO combined with density functional theory (DFT) calculations demonstrate that the end-product selectivity is determined both by the binding energies of the initial reactants and the formation energies of important intermediate species.
A Novel Multifunctional Photonic Film for Colored Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling and Energy Harvesting
- First Published: 23 January 2024
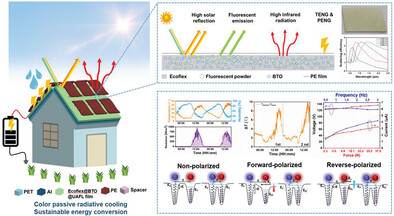
A novel fluorescent luminescence color passive radiative cooling photonic film (Ecoflex@BTO@UAFL) is synthesized by filling the dielectric BTO particles and UAFL powder into Ecoflex matrix, which is expected to realize high-performance color PDRC and highly effective sustainable energies conservation. The BTO nanoparticles can simultaneously enhance the solar reflectance of the composite film and promote the electric outputs of the nanogenerator.
Achieving Fast and Stable Sodium Storage in Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) via Entropy Engineering
- First Published: 17 January 2024
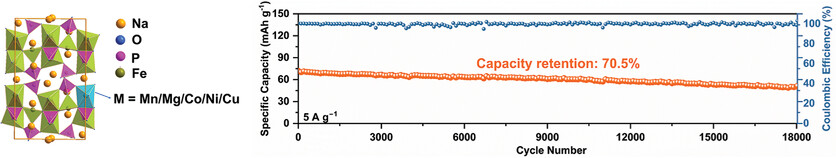
In this work, an entropy engineering strategy is employed in Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) to both improve the electronic/ionic conductivity and structural stability. Based on this strategy, the as-obtained Na4Fe2.5Mn0.1Mg0.1Co0.1Ni0.1Mg0.1(PO4)2(P2O7) (HE-NFPP) can deliver an excellent rate capacity of 55 mAh g−1 at 10 A g−1. Strikingly, the HE-NFPP exhibits an ultra-long cycling durability of over 18 000 cycles, transcending the most cutting-edge reports about NFPP-based cathode.
A Sandwich Structure Ag/MgFe2O4-Deposited Surface Carbonized Wood for Integrated Solar Steam Generation and Photoreduction of Cr(VI)
- First Published: 14 January 2024
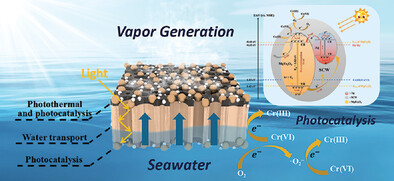
This study demonstrates a bifunctional Ag/MgFe2O4@SCW reactor with sandwich structure, which can be used for efficient SSG and Cr(VI) reduction. An ultra-high evaporation rate of 1.55 kg m−2 h−1 is achieved under 1 sun. High antibacterial activity, desalination capability, and water-harvesting capacity are exhibited. More importantly, the Ag/MgFe2O4@SCW photocatalyst can remove up to 96.1% of Cr(VI) after 180-min illumination.
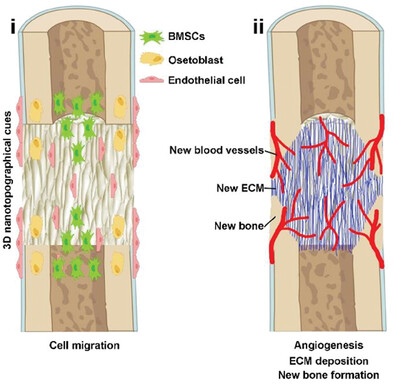
Hierarchically Assembled Nanofiber Scaffold Guides Long Bone Regeneration by Promoting Osteogenic/Chondrogenic Differentiation of Endogenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- First Published: 23 January 2024
Novel Heterostructure-Based CoFe and Cobalt Oxysulfide Nanocubes for Effective Bifunctional Electrocatalytic Water and Urea Oxidation
- First Published: 14 January 2024
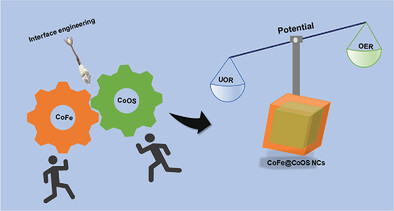
A CoFe-LDH and CoOS 3D nanocubes heterostructure is prepared via a hydrothermal route for effective electrocatalytic water and urea oxidation. During sulfidation process, the divalent sulfur ions react with Co-precursors and lead to the transformation of CoOH nanorods into CoOS nanocubes. The obtained heterostructure required a cell voltage of 1.63 and 1.56 V for overall water and urea-splitting alkaline electrolyzer.
Designing Tough Hydrogel Shells for Glucose Sensing
- First Published: 16 January 2024
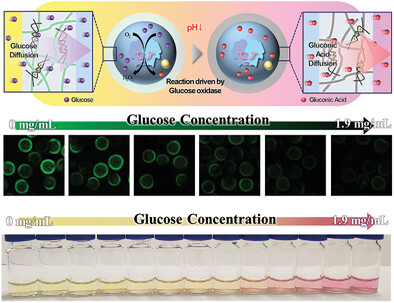
Hydrogel shells are created with double-network hydrogel using triple-emulsion template. The shells provide high mechanical stability, optical transparency, and well-defined permeation threshold, serving as a promising platform for enzyme-based microsensors. A fluorometric glucose sensor is demonstrated by encapsulating glucose oxidase in the core and pH-responsive dye in the shell, which exhibits excellent stability against mechanical stress, drying, and proteolysis.
Effect of Surface Modification on the Luminescence of Individual Upconversion Nanoparticles
- First Published: 17 January 2024
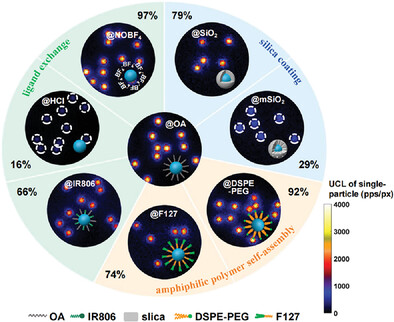
A comprehensive study is conducted to elucidate the impacts of surface modification on upconversion luminescence of individual nanoparticles. Commonly used modification approaches are employed, including ligand exchange, silica coating, and amphiphilic polymer self-assembly. The study reveals that treatments with NOBF4 and the amphiphilic polymer DSPE-PEG resulted in minimal luminescence quenching, preserving 97% and 92% of the original single-particle brightness, respectively.
Bacterial Surface Appendages Modulate the Antimicrobial Activity Induced by Nanoflake Surfaces on Titanium
- First Published: 17 January 2024
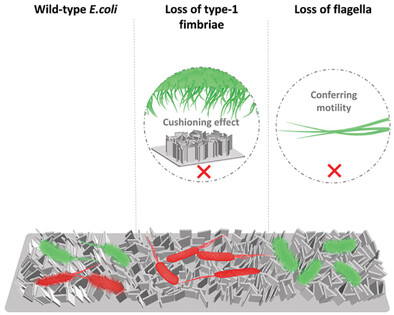
Nanoflakes generated on pure titanium surfaces are shown to mediate antibiofouling, bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects against bacterium Escherichia. coli. This indicates the potential for nanoflake surfaces to be exploited for medical applications such as implants. Furthermore, two bacterial surface appendages, type-1 fimbriae and flagella, affect the susceptibility of the bacteria to these nanoflakes, conferring protective or damaging effects, respectively.
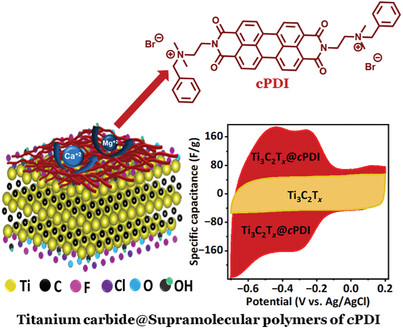
Supramolecular Engineering of Ti3C2Tx MXene -Perylene Diimide Hybrid Electrodes for the Pseudocapacitive Electrochemical Storage of Calcium Ions
- First Published: 23 January 2024
Methamphetamine Removal from Aquatic Environments by Magnetic Microrobots with Cyclodextrin Chiral Recognition Elements
- First Published: 18 January 2024

The study explores the use of magnetic cyclodextrin (CD) functionalized microrobots for cleaning water contaminated with drug residues, specifically methamphetamine. These microrobots, with a hematite/magnetite core and CD surface, enhance pollutant removal due to their combined magnetic movement and hydrophobic cavities of CDs on microrobot surfaces. The design emphasizes autonomous movement, improved mass transfer, and targeted functionalization for effective remediation.
Promoted Overall Water Splitting Catalytic Activity and Durability of Ni3Fe Alloy by Designing N-Doped Carbon Encapsulation
- First Published: 23 January 2024
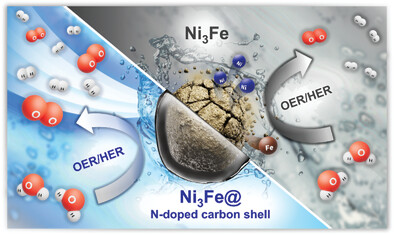
Forming N-doped carbon shells on the catalyst surface is a promising method to improve the stability of electrochemical catalysts. Additionally, the carbon shell suppresses the phase change of the transition metal catalyst, significantly reducing the amount of catalyst dissolved in the electrolyte. This study demonstrates the role of the carbon shell as a strategy to maintain durability and catalytic properties.
High-Temperature Melt Stamping of Polymers Using Polymer/Nanoporous Gold Composite Stamps
- First Published: 23 January 2024
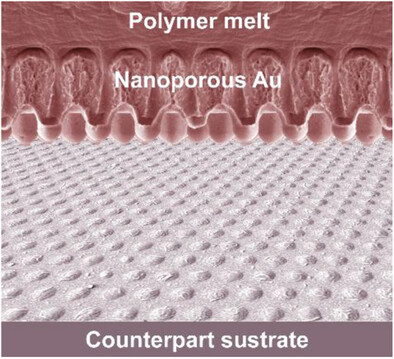
Composite stamps for the solvent-free high-temperature capillary stamping of polymer melts consisting of thin nanoporous gold layers attached bulk molten polymer reservoirs are reported. The nanoporous gold layer stabilizes the topographically patterned contact surface and the polymer melt supports the nanoporous gold layer; polymer microstructures may be produced without ink depletion and problems related to the presence of solvents.
Boosting Bulk Oxygen Transport with Accessible Electrode Nanostructure in Low Pt Loading PEMFCs
- First Published: 11 February 2024
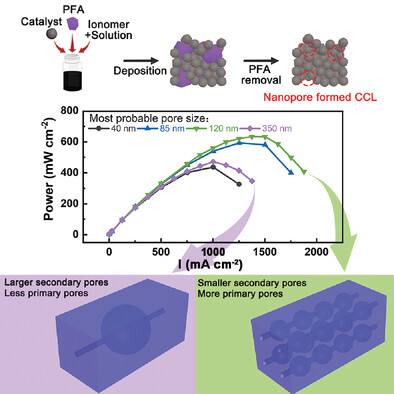
The nanopore structure in CCLs is controlled with pore forming technology, leading to a 3.6-fold increase in effective oxygen diffusivity and a 45% improvement in peak power density of ultralow Pt MEA. A “sphere-pipe” model is proposed to describe the practical oxygen transport in CCLs, which benefits further investigation of nanostructure of gas diffusion electrode and scale-up of MEA manufacture.
An Ultrasound-Triggered STING Pathway Nanoagonist for Enhanced Chemotherapy-Induced Immunogenic Cell Death
- First Published: 15 January 2024
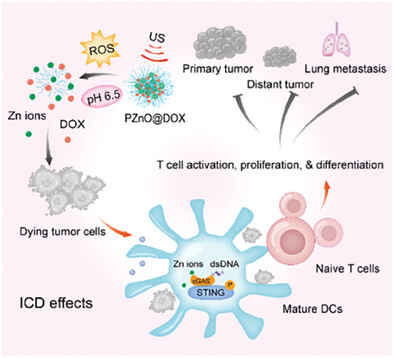
The PZnO@DOX nanoparticles can release zinc ions and doxorubicin in the tumor microenvironment with controllable ultrasound and demonstrate substantial antitumor capacity by enhancing immunogenic cell death effects through stimulation of the interferon genes pathway. This combination strategy involving chemotherapy, sonodynamic therapy, and immunotherapy significantly inhibits tumor growth, metastasis, and recurrence both in vitro and in vivo.
Triple Synergism Effect of Ammonium Nitrilotriacetate on the Chemical Mechanical Polishing Performance of Ruthenium Barrier Layers
- First Published: 21 January 2024
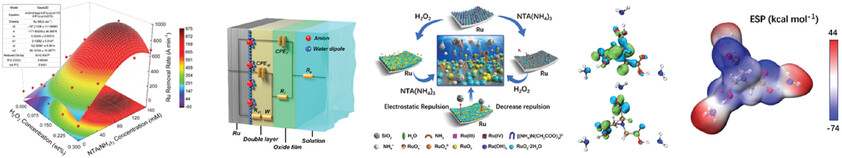
The core mechanism of NTA(NH4)3 in promoting ruthenium (Ru) removal involves a triple synergistic effect: 1) interaction of in NTA(NH4)3 with silica abrasives; 2) chelation effect of [(NH4)N(CH2COO)3]2− in NTA(NH4)3 on Ru and its oxides; 3) ammoniation and chelation effect of in NTA(NH4)3 on Ru and its oxides. This triple synergistic removal mechanism simultaneously achieves a high removal rate and low surface defects, providing a new perspective in the field of barrier layer CMP.
Injectable Hydrogel System Incorporating Black Phosphorus Nanosheets and Tazarotene Drug for Enhanced Vascular and Nerve Regeneration in Spinal Cord Injury Repair
- First Published: 26 January 2024
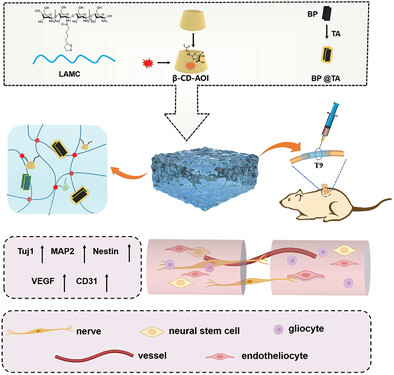
This study explores an innovative injectable hydrogel system for spinal cord injury treatment. Incorporating conductive black phosphorus (BP) nanosheets and tazarotene into a lipoic acid-modified chitosan matrix, the hydrogel demonstrates enhanced conductivity and angiogenic potential. In a rat SCI model, the LAMC/BP@TA hydrogel significantly promotes motor function recovery, fostering endogenous angiogenesis and neurogenesis at the injury site.
Polysulfide Anions [Sx]2− (x = 2, 3, 4, 5): Promising Functional Building Units for Infrared Nonlinear Optical Materials
- First Published: 23 January 2024
![Polysulfide Anions [Sx]2− (x = 2, 3, 4, 5): Promising Functional Building Units for Infrared Nonlinear Optical Materials](/cms/asset/24eccbb0-bee6-40d6-b6dc-d8165ad307af/smll202310423-gra-0001-m.jpg)
The authors have investigated all binary chalcogenides with ordered non-centrosymmetric structures collected in the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database and selected 14 crystals including polysulfide anions to research NLO-related properties and structure-performance relationships. This work provides a full exploration of chalcogenides containing [Sx]2− (x = 2, 3, 4, 5) units as NLO materials and obtains excellent candidates for further development.
Ni Single-Atom Dual Catalytic Electrodes for Long Life and High Energy Efficiency Zinc-Iodine Batteries
- First Published: 17 January 2024
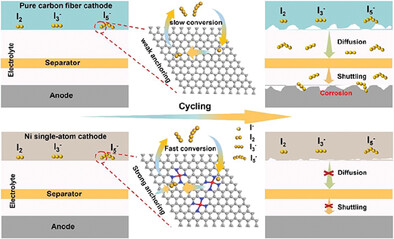
Ni single atoms highly dispersed on carbon fibers is designed and synthesized as iodine anchoring sites and dual catalysts for Zn-I2 batteries, and successfully inhibit the iodine species shuttling and boost dual reaction kinetics. Consequently, the high-rate performance (180 mAh g−1 at 3 A g−1), cycling stability (capacity retention of 74% after 5900 cycles) and high energy efficiency (90% at 3 A g−1) are achieved.
Benzoquinone-Lubricated Intercalation in Manganese Oxide for High-Capacity and High-Rate Aqueous Aluminum-Ion Battery
- First Published: 17 January 2024
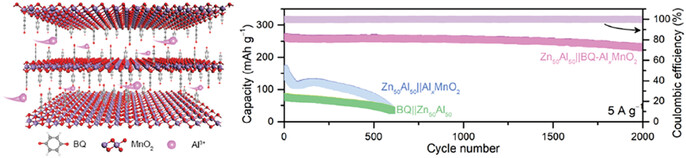
An organic–inorganic hybrid material of manganese oxide pre-intercalated with benzoquinone-coordinated aluminum ions is developed as a cathode material of an aqueous aluminum-ion battery. Owing to the coordination of flexible benzoquinone with Al3+ ions to extend interlayer spacing and weaken the electrostatic field of Al3+, it exhibits reversible Al3+ intercalation/extraction behaviors, with high capacity and rate capability, and long-term stability.
High-Throughput Miniaturized Synthesis of PROTAC-Like Molecules
- First Published: 22 January 2024
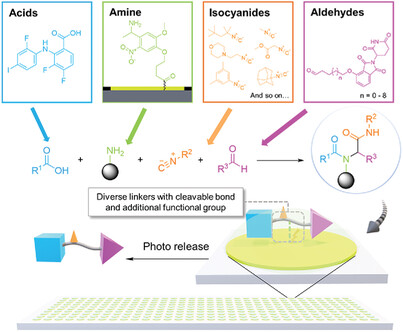
In this study, an approach for miniaturized high-throughput synthesis of PROTAC-like molecules on droplet microarray using one-step four-component Ugi reaction is presented. The platform integrates direct combinatorial solid-phase synthesis, structure characterization, and biological screening on the chip, laying the groundwork for accelerated drug discovery.
Unveiling Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Graphite and Boron Nitride Using Fluorescent Dyes Through Combined Experiments and Simulations
- First Published: 24 January 2024
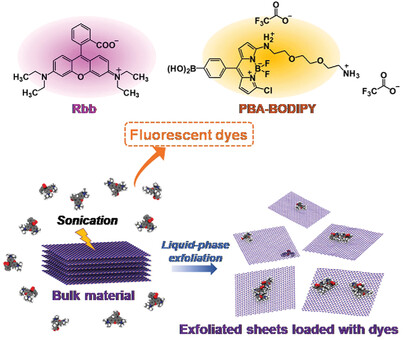
Liquid-phase exfoliation is a powerful methodology to produce 2D materials. The use of rhodamine B base and PBA-BODIPY dispersants has allowed generating few-layer graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) through a sonication-assisted exfoliation. The exfoliated graphene and hBN with a high loading of dispersants exhibit good dispersibility and low defect content. Moreover, atomistic simulations are exploited to understand the interaction between the nanosheets and the two dispersant molecules.
Devastating the Supply Wagons: Multifaceted Liposomes Capable of Exhausting Tumor to Death via Triple Energy Depletion
- First Published: 19 February 2024
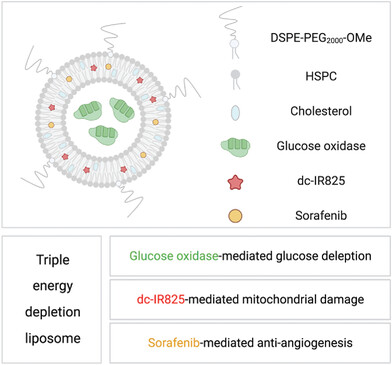
A glucose oxidase (GOx)-, dc-IR825-, and sorafenib-containing liposome is designed for triple energy depletion-based tumor therapy. GOx continuously consumes glucose in the tumor. dc-IR825 precisely targets and destroys mitochondria upon laser irradiation. Sorafenib inhibits tumor vessel growth to block energy and nutrition supply from blood. Such a multifaceted liposome can effectively exhaust energy in a tumor and starve the tumor to death.
Deep Cracking of Bulky Hydrocarbons into Light Products via Tandem Catalysis over Uniform Interconnected ZSM-5@AlSBA-15 Composites
- First Published: 17 January 2024
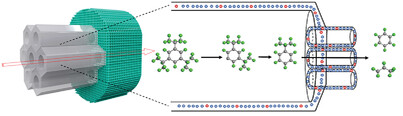
Intimate ZSM-5@AlSBA-15 composites containing an AlSBA-15 matrix and isolated ZSM-5 nanoparticles are synthesized via rapid aerosol-confined assembly. The two components in the composites are uniformly mixed with chemically bonded walls and interconnected pores. They show superior performance in tandem cracking of 1,3,5-triisopropylbenzene with ≈100% conversion, > 60% mass selectivity to benzene and propylene, and excellent long-term stability.
Self-Assembled Preparation of Porous Nickel Phosphide Superparticles with Tunable Phase and Porosity for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 16 January 2024
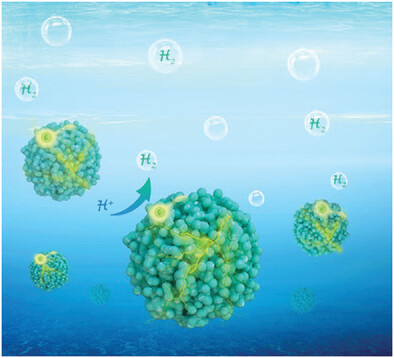
Porous nickel phosphide (Ni3P and Ni12P5) superparticles are prepared via an emulsion self-assembly method. The phase structure and porosity of the superparticle can be adjusted by the assembly parameters. The porous superparticles exhibit significantly enhanced specific surface area, and can be applied as cathode catalysts that can effectively drive the hydrogen evolution reaction under acidic conditions.
Synergistic Effects of PtRhNiFeCu High Entropy Alloy Nanocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution and Oxygen Reduction Reactions
- First Published: 17 January 2024
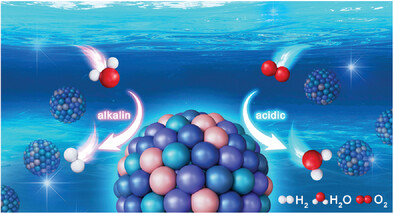
Under the synergistic effect of up to five atoms, the surface electronic structure and coordination environment of ultrasmall high entropy alloy PtRhNiFeCu nanoparticles are optimized, exhibiting high oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reaction performance in acidic and alkaline environments, respectively.
How to Stabilize the Current of Efficient Inverted Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells at the Maximum Power Point
- First Published: 18 January 2024
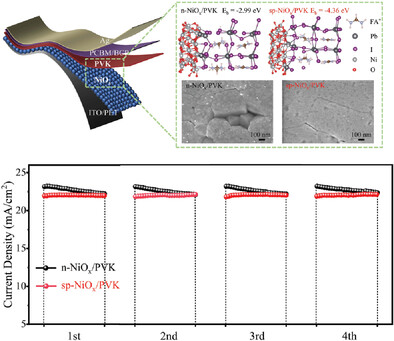
A larger adsorption energy between the NiOx surface and the PbI6 species in the perovskite precursor solution promotes the perovskite film's buried surface by retarding the crystallization, resulting in a stabilized steady–state photocurrent and high performance of inverted flexible perovskite solar cells.
Tungsten–Iron–Ruthenium Ternary Alloy Immobilized into the Inner Nickel Foam for High-Current-Density Water Oxidation
- First Published: 22 January 2024
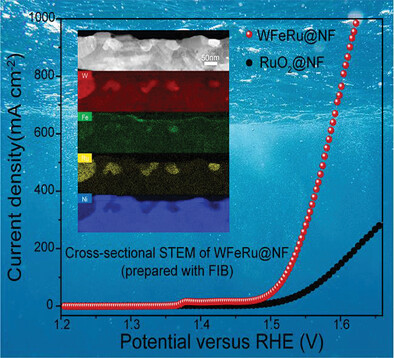
Self-standing WFeRu@NF alloying catalyst is deliberately designed by the diffusion of W, Fe, and Ru atoms into the inner layer of nickel foam. Thanks to the high intrinsic OER activity of WFeRu alloy and the surrounded-compression bringing robust protection environment, the as-obtained WFeRu@NF composite catalyst shows a superior high-current-density water oxidation process.
Engineering High-Performance Hypergolic Propellant by Synergistic Contribution of Metal–Organic Framework Shell and Aluminum Core
- First Published: 20 January 2024

A core–shell Al@MOF heterostructure is constructed as solid hypergolic propellant. The hypergolic Ag-MOF shell initiates the ignition upon contact with specific oxidizer, and the efficient shell-to-core heat transfer induces the reliable combustion of Al. Importantly, the co-contribution of energetic Ag-MOF and metal fuel results in significantly improved Isp over a wide range of O/F ratios.
Industrial Waste Derived Separators for Zn-Ion Batteries Achieve Homogeneous Zn(002) Deposition Through Low Chemical Affinity Effects
- First Published: 17 January 2024
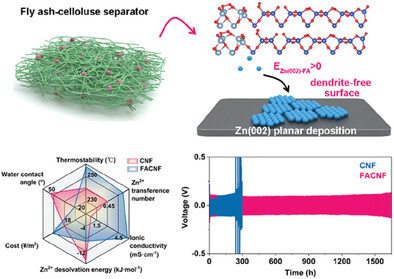
Fly ash particles as industrial waste are introduced into cellulose separators to adjust chemical affinity toward Zn(002) plane and expedite crystallographic homogeneity of Zn anode. The resultant separator can greatly optimize ion transportation kinetics and Zn2+ desolvation energy and realize dendrite-free Zn deposition and thus prolong cycling lifespan of symmetric and full cells.
Exceptional Optical Anisotropy Enhancement Achieved Through Dual-Ions Cosubstitution Strategy in Novel Hybrid Bismuth Halides
- First Published: 17 January 2024
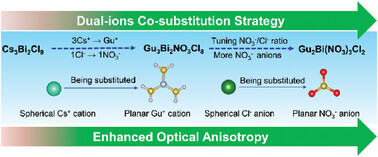
In this study, two optically anisotropic hybrid bismuth halides, Gu3Bi2NO3Cl8 and Gu2Bi(NO3)3Cl2, are designed and synthesized using a dual-ions cosubstitution strategy based on the known Cs3Bi2Cl9. Notably, the incorporation of superior anisotropic Gu+ and [NO3]− in these two crystals resulted in remarkably enhanced birefringence, surpassing the values of the initial Cs3Bi2Cl9 crystal by more than 1 order of magnitude.
Lipid Monolayer on Cell Surface Protein Templates Functional Extracellular Lipid Assembly
- First Published: 20 January 2024
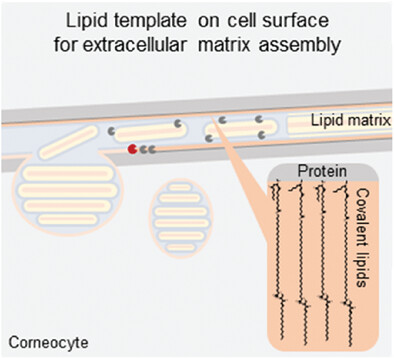
The barriers of organisms to water loss are provided by extracellular lipids, but the mechanisms that sculpt these rather rigid lipid layers are not fully understood. In human skin, covalently bound ultra-long ceramides on the surface of corneocytes, the corneocyte lipid envelope, fluidize and rearrange neighboring extracellular matrix lipids, ensuring their malleability into a functional protective barrier against the environment.
Cu2WS4-PEG Nanozyme as Multifunctional Sensitizers for Enhancing Immuno-Radiotherapy by Inducing Ferroptosis
- First Published: 07 February 2024
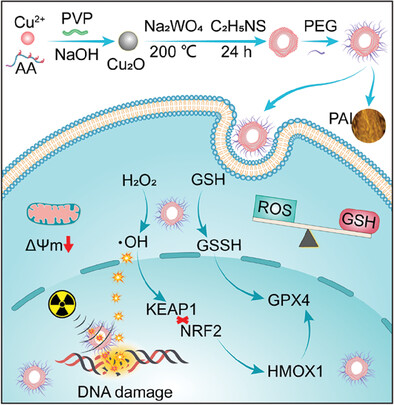
The unavoidable damage to normal tissues near the tumor and microenvironment resistance makes it challenging to eradicate breast carcinoma through traditional radiotherapy. Owing to its multiple enzymatic activities, high-atomic W elements, nucleus-penetrating, and ferroptosis-inducing capacities, PEGylated Cu2WS4 nanozyme effectively improved the efficiency of radiotherapy triggering immunogenic cell death cooperate with immunotherapy for breast carcinoma.
Bio-Inspired Superhydrophilic Self-Assembled Coronavirus-Like Pt-WC/CNT for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 23 January 2024
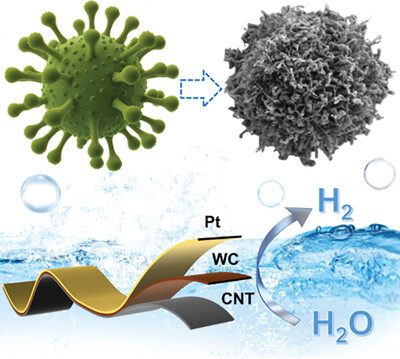
Pt-WC/CNT, coronavirus-like structures, and self-assembly produced by one-step gas–solid reaction and galvanic replacement reaction are reported. Pt-based catalysts that are inspired by biomimicry and achieved through self-assembly, enabling them to adapt to gas-involved reactions. This discovery opens a door to the synthesis of a large number of other Pt based composites materials.
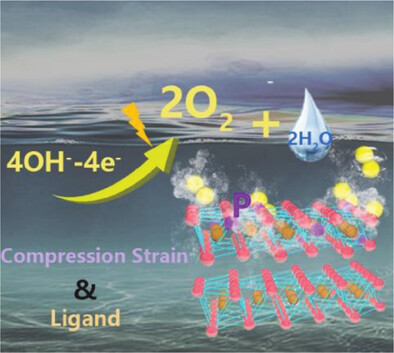
Ligand and Strain Synergistic Effect in NiFeP0.32 LDH for Triggering Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 23 January 2024
Full-Spectrum Utilization of ZIF-67/Ag NPs/NaYF4:Yb,Er Photocatalysts for Efficient Degradation of Sulfadiazine: Upconversion Mechanism and DFT Calculation
- First Published: 26 January 2024
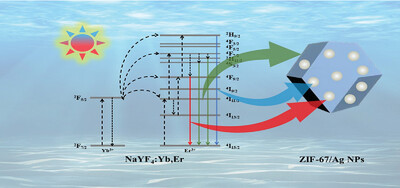
In this work, novel ternary composite ZIF-67/Ag NPs/NaYF4:Yb,Er is synthesized for the first time. It has the high degradation efficiency of ≈95.4% for sulfadiazine (SDZ) under 180 min xenon illumination. It is attributed to the adsorption of broad spectra of the simulated sunlight, the localized surface plasmon resonance effect and the high charge separation efficiency.
3D Pathways Enabling Highly-Efficient Lithium Reservoir for Fast-Charging Batteries
- First Published: 20 January 2024
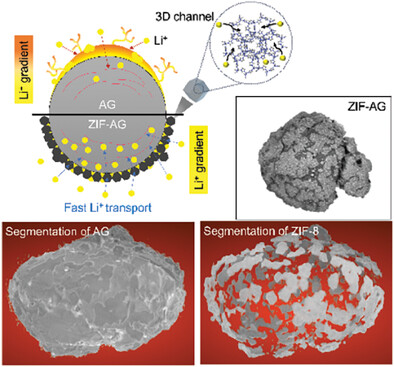
A biphasic zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF)-artificial graphite (AG) composite as an anode material for a fast-charging lithium-ion battery is proposed by directly growing ZIF nanoparticles on the artificial AG surface. The ZIF-derived carbon nanoparticles act as promoters, facilitating Li+ transport through 3D amorphous carbon channels, thereby improving fast-charging capabilities and long-term cycling performance.
Tumor-Targeting Multiple Metabolic Regulations for Bursting Antitumor Efficacy of Chemodynamic Therapy
- First Published: 17 January 2024
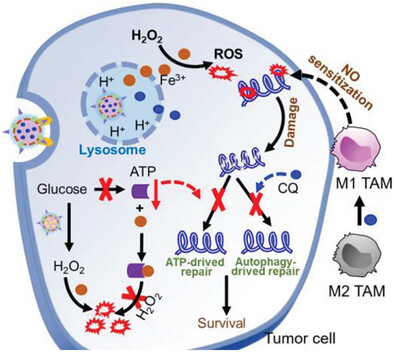
The tumor-targeting multiple metabolic regulations are performed by the CQ@MIL-GOX@PB nanosystem to achieve effective antitumor chemodynamic therapy (CDT). By promoting the NO anabolism of tumor-associated macrophages, and inhibiting energy metabolism and autophagy of tumor cells, the CDT effect of CQ@MIL-GOX@PB is burst via the multiple sensitization mechanisms.
Ultrahigh Degree of Cationic Disorder, Configurational Entropy in New Type of High-Entropy Pseudobrookite Phase
- First Published: 22 January 2024
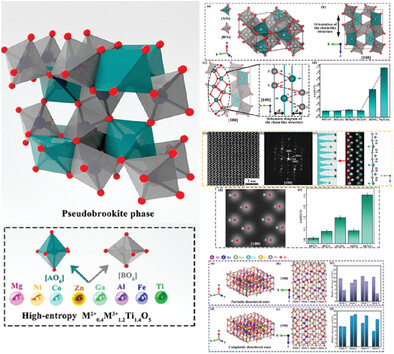
New high-entropy ceramics (M2+0.4M3+1.2)Ti1.4O5 with multi-principal cations sharing two different cationic lattice sites together are synthesized. The degree of cationic disorder and the configurational entropy are analyzed and compared by constructing the crystal structure models, quantifying the atomic column positions in the STEM images, and the density functional theory simulations.
Sustained Release-Driven Interface Engineering Enables Fast Charging Lithium Metal Batteries
- First Published: 21 January 2024
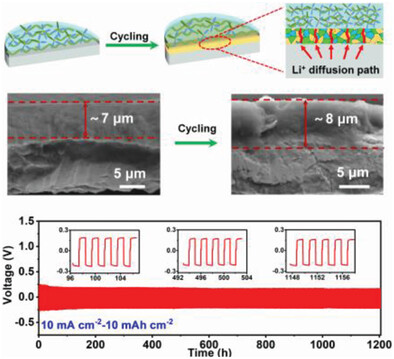
Artificial inorganic/organic composite SEI layers consisted of LiNO3 and PMMA are designed for Li metal anode. The SEI layer (referred as PML) showed significant advantages in homogenizing the Li+ flux, improving the ionic conductivity, and achieving uniform Li deposition. Assisted by PML protective layer, PML-Li exhibits stable and long-term Li deposition/exfoliation behavior at ultra-high current densities and large area capacity.
Stability of Ni–Fe-Layered Double Hydroxide Under Long-Term Operation in AEM Water Electrolysis
- First Published: 25 January 2024
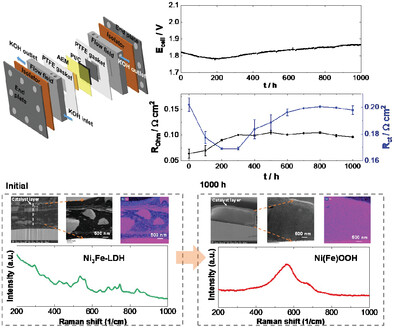
Transitioning industrial processes toward renewable energy is vital for decarbonization. Green hydrogen, generated via anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) offers cost-effective, efficient hydrogen production. While recent research has improved AEMWE components, long-term durability and comprehensive electrode studies are lacking. This study investigates a Ni3Fe-LDH-based single-cell's 1000 h operation, tracking anode degradation, and establishing correlations with overall cell stability.
Self-Assembly of Delta-Formamidinium Lead Iodide Nanoparticles to Nanorods: Study of Memristor Properties and Resistive Switching Mechanism
- First Published: 20 January 2024
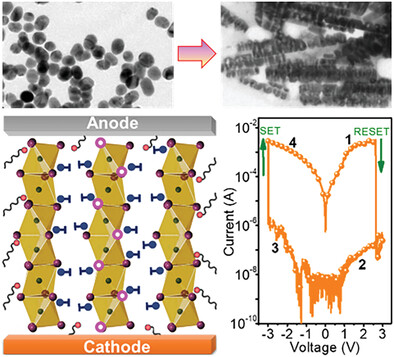
Novel, environmentally stable hexagonal δ-FAPbI3 nanoparticles are prepared using a single-step hot-injection method. At higher concentrations, the nanoparticles self-assembled to form their corresponding nanorods. Resistive random-access memory devices fabricated using these nanorods show an excellent on/off ratio due to reduced halide vacancies, low dimensionality, and parallel orientation toward the electrodes.
Organization of Carotenoid Aggregates in Membranes Studied Selectively using Resonance Raman Optical Activity
- First Published: 21 January 2024
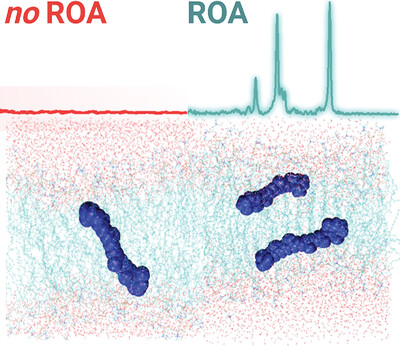
Resonance Raman Optical Activity (RROA) spectra of carotenoids embedded in liposomes provide selective information solely about aggregates and not monomers. Experimental spectra supported by computations provide rich data about the organization of molecules in formed aggregates, their orientation, and stability. Overall, this research opens new perspectives for using RROA as a new tool in studies of compounds embedded in membranes.
Strong Interface Coupling Enables Stability of Amorphous Meta-Stable State in CoS/Ni3S2 for Efficient Oxygen Evolution
- First Published: 05 February 2024
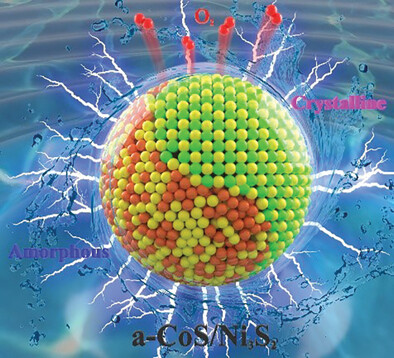
In this work, a novel amorphous/crystalline heterostructure (a-CoS/Ni3S2) is fabricated, which possesses strong interface coupling between the amorphous phase (a-CoS) and crystalline phase (Ni3S2). XPS results and theoretical calculations prove such strong interface coupling. In alkaline conditions, it has an ultralow overpotential of 192 mV at 10 mA cm−2 for OER. This strong interface coupling improves the stability of amorphous CoS.
Rapid, Tough, and Trigger-Detachable Hydrogel Adhesion Enabled by Formation of Nanoparticles In Situ
- First Published: 21 January 2024
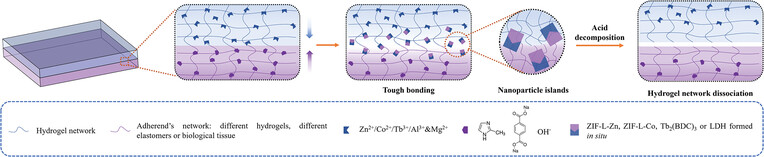
A universally applicable and straightforward strategy is presented for establishing a robust interfacial adhesion between hydrogels and diverse adherends through the in situ nanoparticle formation. This method is versatile across both wet and dry surfaces and notably permits the removal of the adhesive layer upon exposure to acidic solutions.
Unleashing the Power of Osmotic Energy: Metal Hydroxide-Organic Framework Membranes for Efficient Conversion
- First Published: 01 February 2024
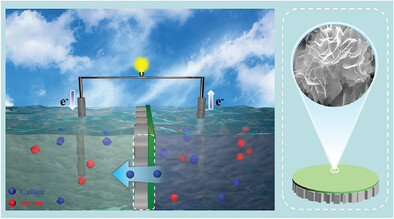
Osmotic energy is a renewable clean energy with huge energy density that has received widespread attention in the past decades. Herein, a simple hydrothermal method to prepare metal hydroxide-organic framework (MHOF) composite membranes for capturing osmotic energy is used. The maximum output power density of 5.65 W m−2 is achieved at a 50-fold KCl concentration gradient, exceeding the commercial benchmark.
Ion-Exchange Enabled Dual-Functional Swarms with Reconfigurability and Magnetic Controllability
- First Published: 23 January 2024
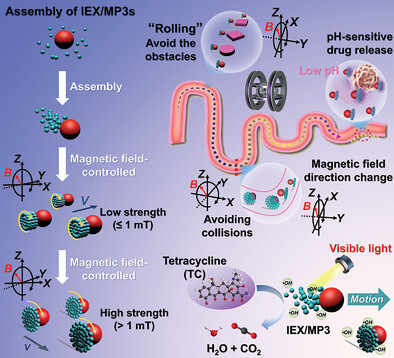
Dual-functional leader-follower-like hierarchical swarms are assembled from ion-exchange particles and the magnetic microspheres, which are controllable and reconfigurable under external magnetic fields to navigate in confined and complex environments. The swarm can load, transport, and release drugs in a pH-enhanced manner, as well as effectively degrade antibiotics via light-enhanced Fenton-like reaction in polluted water.
P-Incorporation Induced Enhancement of Lattice Oxygen Participation in Double Perovskite Oxides to Boost Water Oxidation
- First Published: 21 January 2024
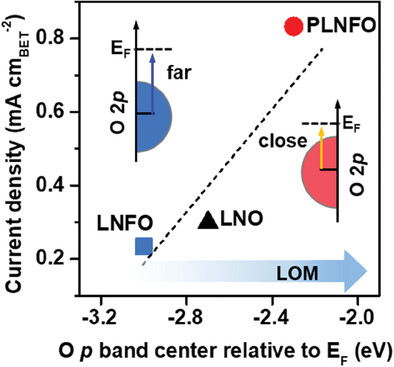
This study reports the enhanced lattice oxygen participation in P-incorporated double perovskite oxides LaNi0.58Fe0.38P0.07O3-σ (PLNFO) for boosting water oxidation. The substitution of P upshifts the O p band center and enhances the hybridization, making the electronic states near the Fermi level with substantial O 2p character, which aggravate the lattice oxygen participation mechanism (LOM) pathway, and thus accelerate the oxygen-evoluting kinetics.
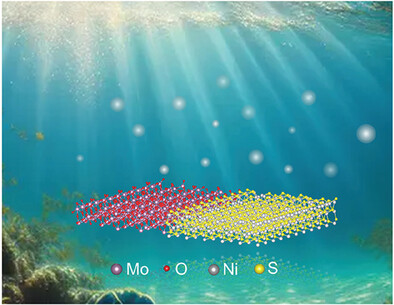
Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-Doped Carbon-Coated Ni3S2/MoO2 Nanowires as Bifunctional Catalysts for Alkaline Seawater Electrolysis
- First Published: 20 January 2024
Strong Oxidizing Molten Salts for Strengthening Structural Restoration Enabling Direct Regeneration of Spent Layered Cathode
- First Published: 18 January 2024
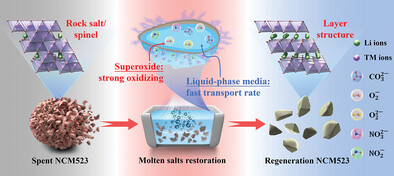
For the existence of rock salt/spinel phase of spent LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode, a ternary-component molten salt system (LiOH-Li2CO3-LiNO3) is proposed for direct regeneration. It shows a low eutectic temperature and strong oxidative capability, and the liquid-phase molten salt medium can accelerate the transport of superoxide, demonstrating a synergistic effect that strengthens the complete restoration of the rock salt/spinel phase.
MOF Derivatives with Gradient Structure Anchored on Carbon Foam for High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorption
- First Published: 20 January 2024
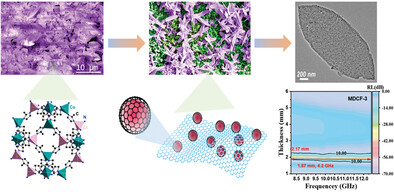
A gradient composite via MOF derivatives anchored on carbon foam matrix (MDCF) is prepared, and the micro-mechanism is thoroughly investigated to illustrate the importance of structural design in EM wave absorption. This study guides composite with gradient structure for achieving high-performance EM wave absorption and yields a novel insight into cooperate impedance matching and attenuation capability.
Construction of Nickel Molybdenum Sulfide/Black Phosphorous 3D Hierarchical Structure Toward High Performance Supercapacitor Electrodes
- First Published: 26 January 2024
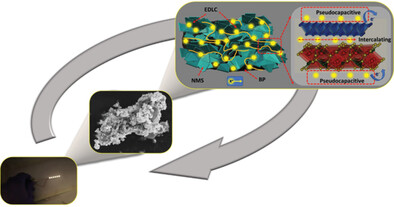
This work highlights the significance of the NiMo3S4/BP hybrid nanostructure for energy storage applications. The hybrid nanostrucure is synthesized via a straightforward hydrothermal method. The hybrid enables multiple ion transfer channels to avoid self-stacking by enabling electrochemical reactions to redox-active sites. Consequently, the charge storage capabilities of active electrodes have been examined in addition to real-time applications.
Dual-Stimuli-Responsive Modulation Organic Afterglow Based on N─H Proton Migration Mechanism
- First Published: 02 February 2024
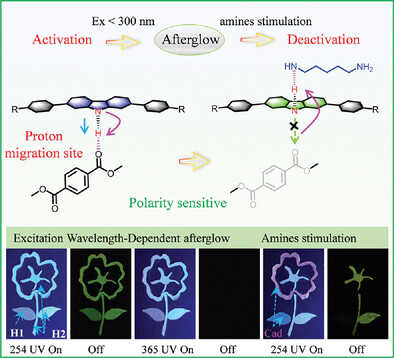
The migration direction of N-H protons on two Hs compounds can be regulated by altering the excitation wavelength (Ex) or amine stimulation, thereby achieving dual-stimuli-responsive modulation of organic afterglow emission, displaying well dynamic information anti-counterfeiting applications. Furthermore, it provides deep insights into the stimuli-responsive mechanism and enriching effective afterglow material design strategies.
FeN3S1─OH Single-Atom Sites Anchored on Hollow Porous Carbon for Highly Efficient pH-Universal Oxygen Reduction Reaction
- First Published: 06 February 2024
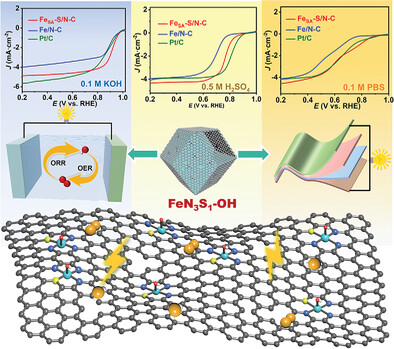
A hollow hierarchical porous FeSA-S/N-C catalyst with unique asymmetric FeN3S1─OH moieties is constructed via a combined approach following the order of electrostatic absorption, polymer coating, and pyrolysis, showing superior pH-Universal oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activities. The homemade liquid and flexible solid-state zinc–air batteries demonstrate excellent performance in terms of open-circuit voltage, discharging specific capacity, and long-term durability.
Biocompatible Silica-Coated Europium-Doped CsPbBr3 Nanoparticles with Luminescence in Water for Zebrafish Bioimaging
- First Published: 24 January 2024
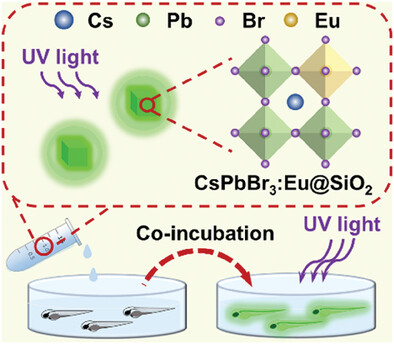
A stable perovskite nanomaterial with good bioimaging activity is developed by incorporating europium (Eu) in CsPbX3 NCs followed by the surface coating of silica (SiO2) shell (CsPbX3:Eu@SiO2). The obtained nanoparticles show efficient luminescence in water and good biocompatibility to achieve cell and zebrafish imaging.
Achieving Long-Lived Charge Separated State through Ultrafast Interfacial Hole Transfer in Redox Sites-Isolated CdS Nanorods for Enhanced Photocatalysis
- First Published: 31 January 2024
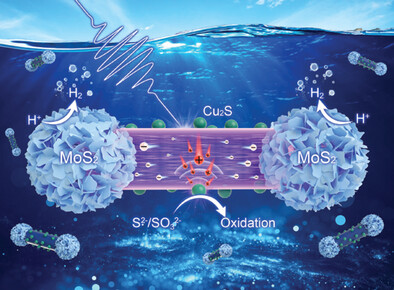
A barbell-shaped ternary heterostructure with spatially isolated redox active sites facilitates efficient charge separation by effectively withdrawing electrons through molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) at both ends and holes via copper sulfide (Cu2S) on the sidewall of cadmium sulfide (CdS) nanorod, resulting in a long-lived charge separated state and thereby enhancing photocatalysis.
Electrochemiluminescence Enhancement and Passivation Mitigation in Carbon Nitride Semiconductors via an Integrated Ternary Heterostructure Strategy
- First Published: 28 January 2024
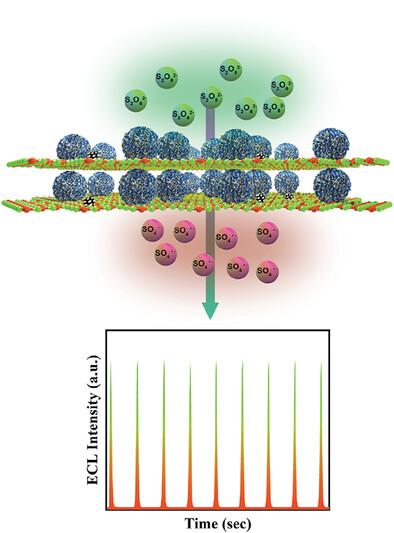
The CN/MoS2-Ni (CNMS-Ni) is synthesized using ultrasound-assisted precipitation method. (1) By applying an internal electric field, electrons are accelerated from CN to the conduction band of MoS2. (2) The introduction of Ni nanoparticles as catalytic active sites promotes the decomposition of K2S2O8. This enhances the stability and intensity of the electrochemiluminescence (ECL) emission.
Biomineralization-Inspired Synthesis of Hybrid COF Nanosheets toward Efficient Desalination Membranes
- First Published: 28 January 2024
Gelatin-Encapsulated Tetrahedral DNA Nanostructure Enhances Cellular Internalization for Treating Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
- First Published: 08 February 2024
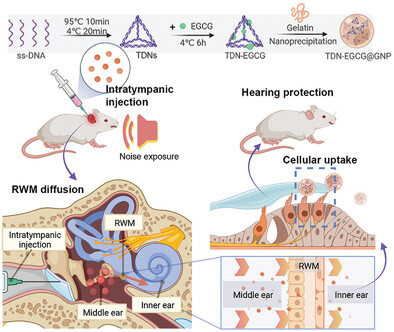
An inner ear drug delivery nanosystem integrating tetrahedral DNA nanostructures with gelatin nanoparticles is presented for efficient otoprotective therapy. The rationally engineered nanocomplex features superior permeability to the biological barrier and cell membrane, enabling efficient drug delivery in target cells. The therapeutic efficacy of combating noise-induced hearing loss is systematically confirmed by functional and histological analysis.
Solvent-Triggered, Ultra-Adhesive, Conductive, and Biocompatible Transition Gels for Wearable Devices
- First Published: 21 January 2024
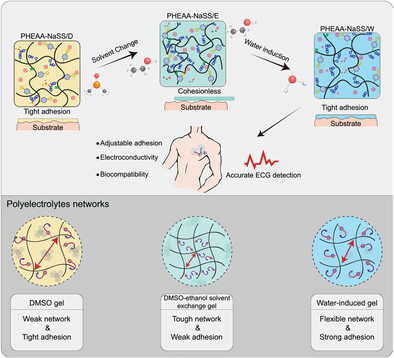
Explore groundbreaking solvent-triggered transition gels (PHEAA-NaSS/W) designs for human-artificial interfaces and electronic devices. Witness their exceptional features, such as an adaptable adhesion, a suitable operation window and a high signal-to-noise ratio for capturing ECG signals under static and dynamic conditions. This method extends its applicability to diverse polyelectrolyte networks, promising versatile applications across scientific disciplines.
A Versatile Nanozyme-Based NADH Circulating Oxidation Reactor for Tumor Therapy through Triple Cellular Metabolism Disruption
- First Published: 23 January 2024
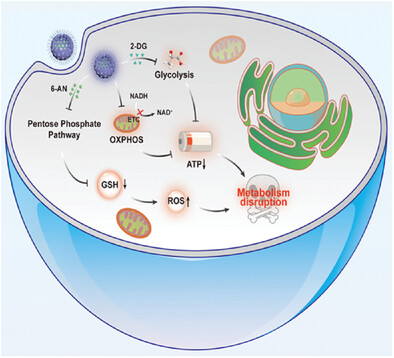
The current efficacy of nanozyme-based metabolism regulation for tumor therapy is limited by the restricted concentration of endogenous substrates and the metabolic plasticity of tumors. To overcome this constraint, a versatile NADH circulating oxidation reactor Co-HCS/D/A is developed for tumor therapy via triple cellular metabolism disruption.
Synchronous Regulation Strategy of Pyrrolidinium Thiocyanate Enables Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells and Self-Powered Photodetectors
- First Published: 01 February 2024
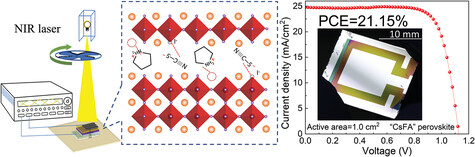
By integrating pyrrolidinium thiocyanate (PySCN) into the perovskite precursor, a synchronous regulation strategy is developed to refine film crystallization and minimize trap defects. Utilizing vacuum flash evaporation for perovskite film deposition, large-area perovskite solar cells can achieve an efficiency of 21.15% with increased stability and the self-powered photodetector demonstrates extremely low dark current and superior detection rate.
Tailored Polypyrrole Nanofibers as Ion-to-Electron Transduction Membranes for Wearable K+ Sensors
- First Published: 23 January 2024
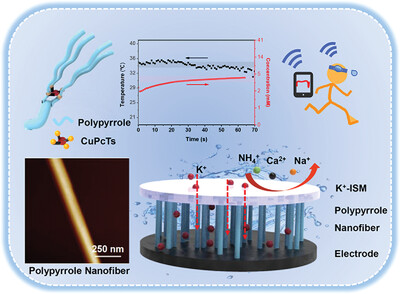
The polypyrrole (PPy) nanostructures are tailored from nanospheres to nanofibers via controlling the supramolecular assembly process, which is utilized as the ion-to-electron conductive layer. Resultantly, the ion-to-electron transduction efficiency and active surface area are significantly enhanced, accompanied by minimized water layer formation. The optimal PPy nanofiber-based potassium ion (K+) sensor achieved a high sensitivity of 62 mV decade−1, good selectivity, and solid stability.
High Polymer Molecular Weight Yields Solar Cells with Simultaneously Improved Performance and Thermal Stability
- First Published: 26 January 2024
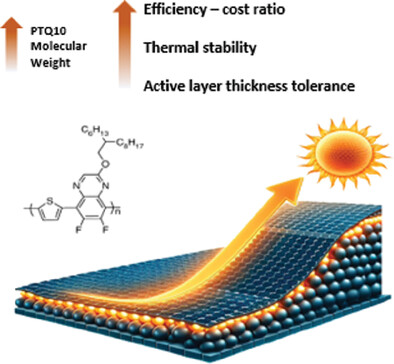
This work shows how increasing the molecular weight of a low synthetic complexity polymer, PTQ10, when paired with different acceptors yielded a notable threefold enhancement in power conversion efficiency. These high-efficiency blends show good thickness tolerance, and exhibited both improved stability and efficiency, underscoring the potential of cost-effective organic solar cells.
Image-Guided Photothermal and Immune Therapy of Tumors via Melanin-Producing Genetically Engineered Bacteria
- First Published: 17 February 2024
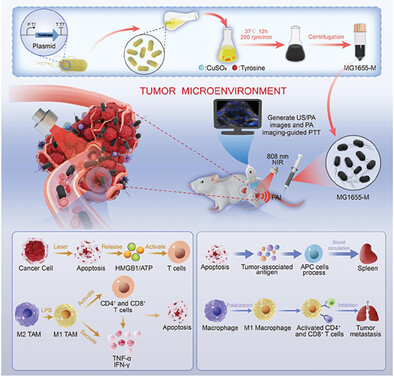
After systemic administration of MG1655-M with melanin nanoparticles, these genetically engineered bacteria accumulate in the tumor owing to their tumor-targeting ability. Subsequently, the tumor is exposed to an 808 nm laser. MG1655-M combined with laser can increase apoptosis of tumor cells, release HMGB1, and ATP, and stimulate the polarization of macrophages, secretion of cytokines, and the activation of T-cells, thereby resulting in the growth inhibition of tumor metastasis and recurrence.
Multi-Functional Regulation on Buried Interface for Achieving Efficient Triple-Cation Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 22 January 2024
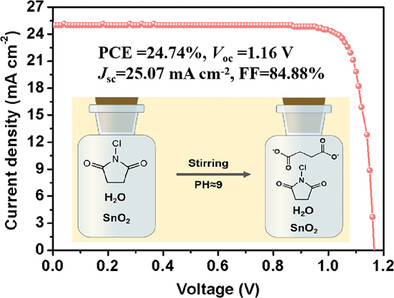
A hydrolysis reaction regulation strategy is proposed to achieve multifunctional modification of the buried interface of perovskite films by introducing N-chlorosuccinimide (NCS) into SnO2 solution. The device based on CsFAMA triple cation perovskite achieved a champion power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 24.74% with an ultra-high fill factor, and showed an excellent long-term stability performance.