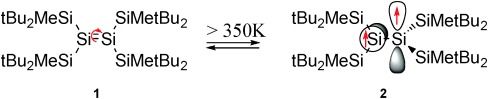Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Self-Assembled DNA Nanoclews for the Efficient Delivery of CRISPR–Cas9 for Genome Editing (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41/2015)
- Page: 11877
- First Published: 21 September 2015

A biologically inspired carrier for the delivery of CRISPR–Cas9 that is based on yarn-like DNA nanoparticles, so-called DNA nanoclews, is described by Z. Gu, C. L. Beisel, and co-workers in their Communication on page 12029 ff. DNA nanoclews (the flying saucers), partially complementary to the single guide RNA (sgRNA), were efficiently loaded with Cas9/sgRNA complexes (the missiles) and delivered the complexes into human cells for genome editing.
Inside Cover: Metallic Single-Unit-Cell Orthorhombic Cobalt Diselenide Atomic Layers: Robust Water-Electrolysis Catalysts (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41/2015)
- Page: 11878
- First Published: 21 August 2015

Single-unit-cell orthorhombic CoSe2 sheets are prepared by thermally exfoliating a lamellar CoSe2–DETA hybrid. As shown by Y. Sun, S. Wei, Y. Xie et al. in their Communication on page 12004 ff., the single-unit-cell thickness means that 66.7 % of the Co2+ ions are exposed on the surface and are low coordinate (coordination numbers of 1.3 and 2.6), leading to a lower Tafel slope (64 mV dec−1) and a higher turnover frequency (745 h−1) in water splitting.
Inside Back Cover: Six-Coordinate Group 13 Complexes: The Role of d Orbitals and Electron-Rich Multi-Center Bonding (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41/2015)
- Page: 12177
- First Published: 02 September 2015

The d or not the d, that is the question that F. M. Bickelhaupt, M. G. Goesten et al. address in their Communication on six-coordinate Group 13 complexes on page 12034 ff. The structural resemblance between the complexes and transition-metal analogues had formerly been suggested to hint at the involvement of the d atomic orbitals of the Group 13 elements. It is now shown that these orbitals play essentially no role, and that the bonding in these six-coordinate complexes is best described in terms of 7-center-12-electron bonds.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Direct Epoxidation of Propylene over Stabilized Cu+ Surface Sites on Titanium-Modified Cu2O
- First Published: 29 September 2015

Propylene Epoxidation Catalysts. Cu+ active sites on a Cu2O surface are stabilized with TiOx. J. G. Chen et al. show in their Communication on page 11946 ff. that the resulting mixed oxide helps form an oxametallacycle intermediate with propylene giving higher selectivity for propylene epoxidation.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41/2015
- Pages: 11881-11895
- First Published: 29 September 2015
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41/2015
- Pages: 11898-11901
- First Published: 29 September 2015
Author Profile
News
Highlight
Iron Catalysis
Hydroaminations of Alkenes: A Radical, Revised, and Expanded Version
- Pages: 11906-11908
- First Published: 11 September 2015
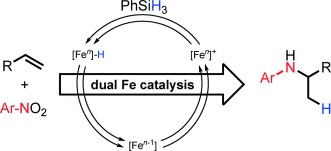
Radical changes: The applicability of alkene hydroamination has recently been significantly expanded by the development of radical variants that are based on initial hydrogen atom transfer to the alkene. This Highlight assesses the current state of the art, focusing on an iron-catalyzed reaction that utilizes stable nitroarenes as the electrophilic N component and is based on the dual catalytic activation of both starting materials.
Essay
1915 Nobel Prize for Chemistry
Richard Willstätter and the 1915 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- Pages: 11910-11916
- First Published: 20 August 2015

One hundred years after his Nobel Prize, Richard Willstätter’s achievements and the fascinating role he played in 20th century chemistry are discussed in this Essay. Several of his discoveries, such as the anthocyanidins, cyclooctatetraene, the ortho-quinones, and the structure of cocaine, will forever be associated with his name.
Minireview
Small-Ring Systems
Cyclobutane and Cyclobutene Synthesis: Catalytic Enantioselective [2+2] Cycloadditions
- Pages: 11918-11928
- First Published: 02 September 2015
![Cyclobutane and Cyclobutene Synthesis: Catalytic Enantioselective [2+2] Cycloadditions](/cms/asset/720713d7-30f2-43a9-afbe-b93fcd09d086/mcontent.jpg)
Squared away: Cyclobutanes and cyclobutenes are important structural motifs found in numerous biologically significant molecules, and they are useful intermediates for chemical synthesis. Consequently, catalytic enantioselective [2+2] cycloadditions to access cyclobutanes and cyclobutenes have emerged as an attractive target for method development. The advances made in catalytic enantioselective [2+2] cycloadditions are described herein.
Review
Expanded Genetic Alphabet
The Expanded Genetic Alphabet
- Pages: 11930-11944
- First Published: 25 August 2015
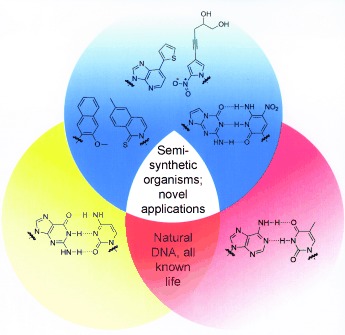
Rule of three: Natural nucleic acids and the genetic information they encode are limited by the use of only four nucleotides that form two base pairs, (d)G-(d)C and d(A)-dT/U. In the past decade, three classes of unnatural base pairs have been developed to a high level of proof-of-concept. This Review summarizes their development and the potentially revolutionary applications that they are now enabling.
Communications
Epoxidation Catalysis | Hot Paper
Direct Epoxidation of Propylene over Stabilized Cu+ Surface Sites on Titanium-Modified Cu2O
- Pages: 11946-11951
- First Published: 17 July 2015
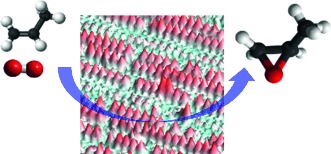
Ti-ed up: Cu+ active sites on a Cu2O surface can be stabilized with TiOx by forming a mixed oxide, TiCuOx. The basicity of the surface-bound oxygen atoms thus decreases which inhibits combustion and promotes the formation of an oxametallacycle intermediate with propylene leading to higher selectivity for propylene epoxidation.
Antibiotics | Hot Paper
An Accurate In Vitro Model of the E. coli Envelope
- Pages: 11952-11955
- First Published: 01 September 2015
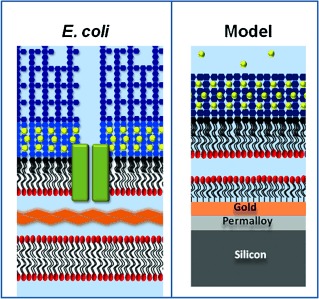
Understanding the outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria is important for the development of new antibacterial compounds. However, their structure and dynamics are poorly understood because of their small in vivo size and inaccurate in vitro models. A stable asymmetric model of the outer membrane that can be analyzed by a range of biophysical techniques and accurately imitates the in vivo behavior of natural outer membranes is presented herein.
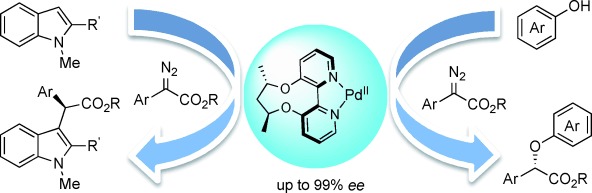
Ligand Design
Enantioselective Palladium-Catalyzed CH Functionalization of Indoles Using an Axially Chiral 2,2′-Bipyridine Ligand
- Pages: 11956-11960
- First Published: 26 August 2015
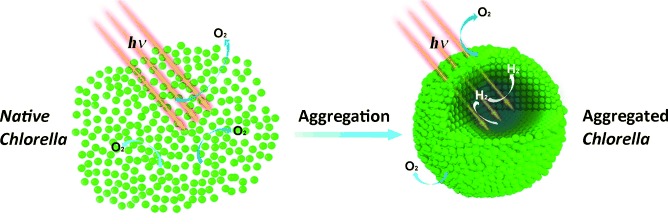
Hydrogen Production
Silicification-Induced Cell Aggregation for the Sustainable Production of H2 under Aerobic Conditions
- Pages: 11961-11965
- First Published: 25 August 2015
Unconventional Retrosynthesis
Final-Stage Site-Selective Acylation for the Total Syntheses of Multifidosides A–C
- Pages: 11966-11970
- First Published: 28 August 2015
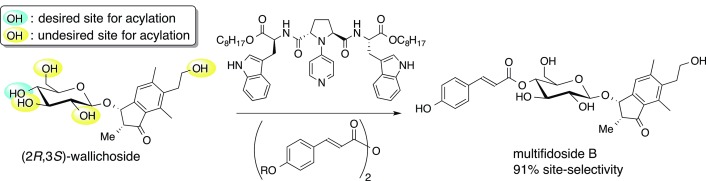
On “site”: A new retrosynthetic route to 4-O-acylated natural and unnatural glycosides is demonstrated. The title reaction of unprotected glycoside precursors, possessing multiple hydroxy groups, was performed successfully. The total syntheses of multifidosides A, B, and C were completed using this acylation strategy.
Organic Semiconductors
Charge and Spin Transport in an Organic Molecular Square
- Pages: 11971-11977
- First Published: 20 August 2015
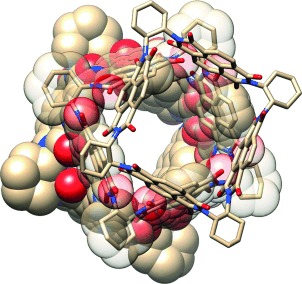
Square dance: A chiral shape-persistent macrocycle comprising four equivalent naphthalene diimide (NDI) subunits, which are almost perpendicular to each other (see figure), can be prepared in a stepwise fashion. EPR and ENDOR spectroscopy on the monoreduced state shows sharing of the unpaired electron over all four NDI subunits, despite the small overlap of the individual π systems.
Electrochemical Cytometry
Quantitative Measurement of Transmitters in Individual Vesicles in the Cytoplasm of Single Cells with Nanotip Electrodes
- Pages: 11978-11982
- First Published: 12 August 2015
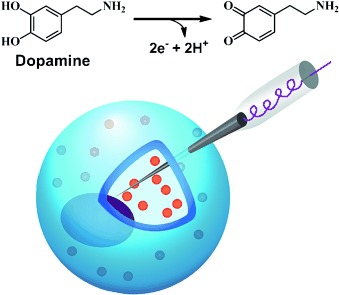
Tiny but tip-top: Nanotip conical carbon-fiber microelectrodes were used for the intracellular quantification of vesicular transmitter content in single cells by a method introduced as intracellular vesicle electrochemical cytometry. It was shown that vesicular levels of catecholamines, such as dopamine (see scheme), can be altered by pharmacological manipulation, and that only partial release of neurotransmitters occurs during normal exocytosis.
Neuronal Differentiation
Induction of Stem-Cell-Derived Functional Neurons by NanoScript-Based Gene Repression
- Pages: 11983-11988
- First Published: 20 August 2015
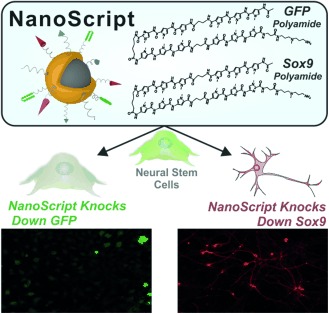
It will knock you down: A functionalized nanoparticle, termed “NanoScript”, is the key component in a platform designed to knock down transcriptional gene expression in stem cells. The tunable and non-viral NanoScript platform, which is functionalized with specific small molecules, effectively knocks down GFP in GFP-labeled neural stem cells (NSCs), and represses Sox9 expression in NSCs to induce differentiation into functional neurons.
Electrocatalysis
Blending Cr2O3 into a NiO–Ni Electrocatalyst for Sustained Water Splitting
- Pages: 11989-11993
- First Published: 24 August 2015
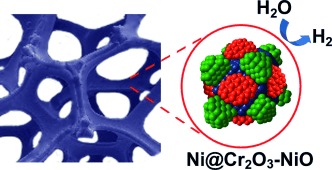
A triphase electrocatalyst composed of a Cr2O3-blended NiO coating on Ni nanocores (CrNN catalyst) synthesized on metal-foam substrates showed superior activity and stability for the hydrogen-evolution reaction in basic solutions. Using the CrNN catalyst, sustained electrolysis of water was achieved at a voltage lower than 1.5 V for at least 500 hours.
Green Chemistry
Nanonickel-Catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Couplings in Water
- Pages: 11994-11998
- First Published: 25 August 2015
Mesoporous Materials | Hot Paper
Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica with Molecular-Scale Ordering Self-Assembled by Hydrogen Bonds
- Pages: 11999-12003
- First Published: 27 August 2015
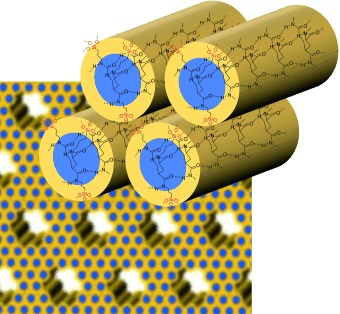
Host–guest systems: Self-assembly of an organosilane precursor by hydrogen bonding is the key to construction of a new class of crystal-like periodic mesoporous organosilicas (see picture). The present mesoporous materials can stably accomodate silane-free H-bonding guest molecules within the pore walls, which is applicable to non-covalent modification of organosilica hybrids.
Water Splitting | Hot Paper
Metallic Single-Unit-Cell Orthorhombic Cobalt Diselenide Atomic Layers: Robust Water-Electrolysis Catalysts
- Pages: 12004-12008
- First Published: 29 July 2015
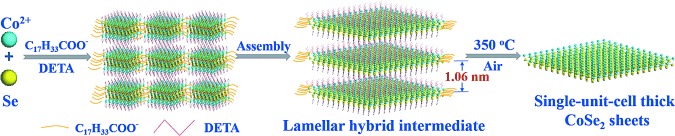
The shape of thins to come: Atomic layers bring better catalytic properties as shown by thermally exfoliating a lamellar CoSe2–DETA hybrid to give single-unit-cell orthorhombic CoSe2 sheets. The single-unit-cell thickness means that 66.7 % of the Co2+ ions are exposed on the surface and are low coordinate leading to a lower Tafel slope and higher turnover frequency in water splitting.
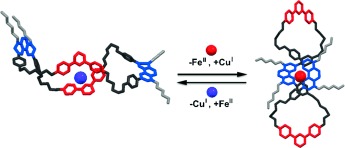
Iron Clusters
Synthesis of Well-Defined Bicapped Octahedral Iron Clusters [(trenL)2Fe8(PMe2Ph)2]n (n=0, −1)
- Pages: 12009-12013
- First Published: 19 August 2015
![Synthesis of Well-Defined Bicapped Octahedral Iron Clusters [(trenL)2Fe8(PMe2Ph)2]n (n=0, −1)](/cms/asset/657cca14-e05b-4da6-89b3-ff4d8b752ba6/mcontent.jpg)
Expanding the nuclearity: Octairon clusters with a bicapped octahedral cluster core employing a polynucleating heptaamine ligand have been synthesized and isolated. This cluster core geometry is unprecedented for first-row transition metals. The design principles used to obtain these clusters may be extended to other transition metals or generalized to synthesize even larger clusters. Atom colors: Fe=orange; N=blue; P=purple; C=gray.
Structural Virology | Hot Paper
Attachment of Norovirus to Histo Blood Group Antigens: A Cooperative Multistep Process
- Pages: 12014-12019
- First Published: 19 August 2015
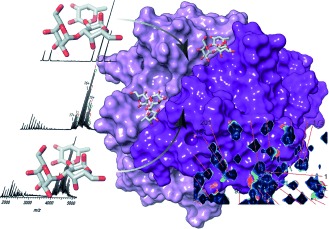
More than binding: Attachment of noroviruses to histo blood group antigens is a complex and cooperative process. This is in contrast to current perception conveying simple one-site binding. NMR spectroscopy and native mass spectrometry independently confirm this new paradigm of virus–carbohydrate interaction.
Drug Delivery | Hot Paper
Enzymatic Prenylation and Oxime Ligation for the Synthesis of Stable and Homogeneous Protein–Drug Conjugates for Targeted Therapy
- Pages: 12020-12024
- First Published: 28 August 2015
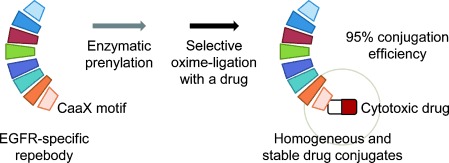
A chemoenzymatic conjugation method that is based on enzymatic prenylation and oxime ligation is a simple and efficient means for generating highly stable and homogeneous protein–drug conjugates in a site-specific manner. It can be generally applied to the conjugation of drugs to a wide range of protein binders, facilitating the development of targeted therapies with high efficacies and low off-target effects.
Molecular Biomimetics
Modular Architecture of Protein Binding Units for Designing Properties of Cellulose Nanomaterials
- Pages: 12025-12028
- First Published: 25 August 2015
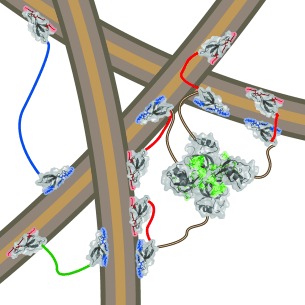
Better together: Engineered proteins were combined with nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC; gray/brown fibres) to show how a multimodular architecture leads to tuned properties. Two cellulose-binding modules (red and blue structures) were separated by 12-, 24-, or 48-mer linkers (red, green, and blue lines), with an optional multimerizing domain (green structure). The linkers significantly affect the interaction between protein and NFC in the wet colloidal and dry film states.
Drug Delivery | Hot Paper
Self-Assembled DNA Nanoclews for the Efficient Delivery of CRISPR–Cas9 for Genome Editing
- Pages: 12029-12033
- First Published: 27 August 2015
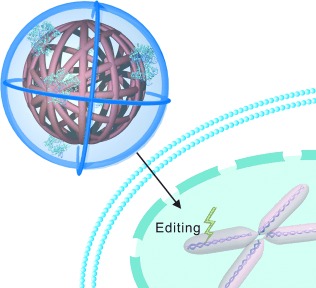
All rolled into one: A biologically inspired delivery vehicle for CRISPR–Cas9 is based on yarn-like DNA nanoparticles that are synthesized by rolling circle amplification. The DNA nanoclews were efficiently loaded with Cas9 protein/single guide RNA complexes and delivered them into human cells, enabling targeted gene disruption.
Main Group Chemistry
Six-Coordinate Group 13 Complexes: The Role of d Orbitals and Electron-Rich Multi-Center Bonding
- Pages: 12034-12038
- First Published: 12 August 2015
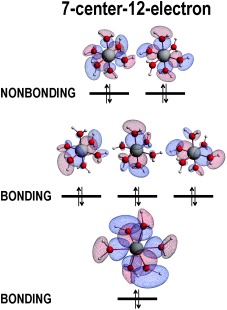
According to molecular orbital theory and relativistic Kohn–Sham density functional theory, six-coordinate clusters based on Group 13 elements bind through an electron-rich 7-center-12-electron pattern instead of using d orbitals. Strongly polar bonding and an affinity towards small anions are thus predicted, properties that are indeed associated with materials and molecules based on such clusters.
Biosensors | Hot Paper
Site-Directed, On-Surface Assembly of DNA Nanostructures
- Pages: 12039-12043
- First Published: 26 August 2015
Alkaloid Synthesis
Synthesis of ent-Ketorfanol via a C–H Alkenylation/Torquoselective 6π Electrocyclization Cascade
- Pages: 12044-12048
- First Published: 17 August 2015
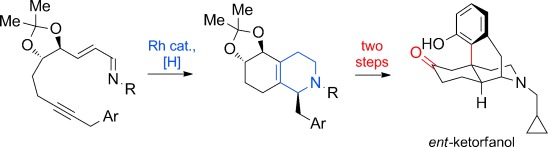
The asymmetric synthesis of ent-ketorfanol from simple and commercially available precursors is reported. A RhI-catalyzed intramolecular CH alkenylation/torquoselective 6π electrocyclization cascade provides a fused bicyclic 1,2-dihydropyridine as a key intermediate. The ketone functionality and final ring are introduced in a single step through a redox-neutral acid-catalyzed rearrangement of a vicinal diol followed by intramolecular Friedel–Crafts alkylation.
Protein Counting
A Set of Homo-Oligomeric Standards Allows Accurate Protein Counting
- Pages: 12049-12052
- First Published: 20 August 2015
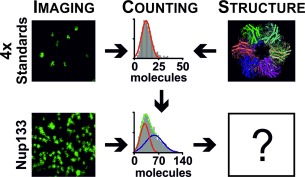
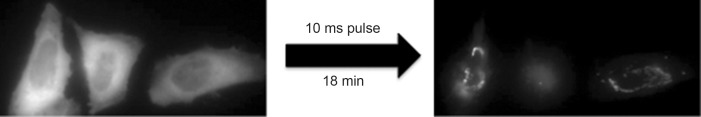
You can count on it: Quantitative fluorescence microscopy requires calibration standards. A set of four protein standards was developed that enables the robust quantification of unknown protein complexes. This versatile method is compatible with various microscopy techniques and was demonstrated with confocal microscopy and super-resolution imaging to quantify the number of Nup133-containing subunits in the nuclear-pore complex.
Fluorescent Probes
A Highly Selective Mitochondria-Targeting Fluorescent K+ Sensor
- Pages: 12053-12057
- First Published: 21 August 2015
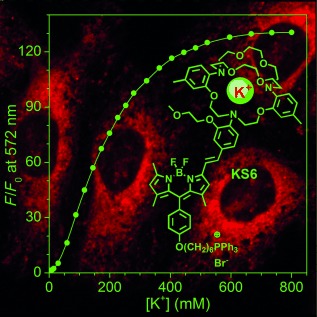
A lamp to light the K: An intracellular mitochondria-specific K+ sensor, KS6, was developed. KS6 shows a K+ response range of 30–500 mM, sensitive fluorescence enhancement (Fmax/F0≈130), high brightness (ϕf=14.4 % at 150 mM of K+), and insensitivity to both pH (in the range 5.5–9.0) and other metal ions under physiological conditions. KS6 is thus the first sensor that can be used for monitoring K+ ion flux in the mitochondria of live cells
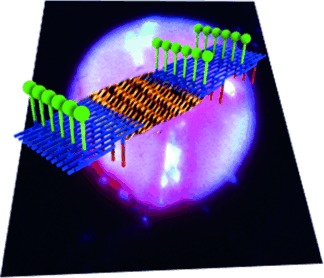
Nanostructures | Hot Paper
Large-Area, Free-Standing, Two-Dimensional Supramolecular Polymer Single-Layer Sheets for Highly Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- Pages: 12058-12063
- First Published: 26 August 2015
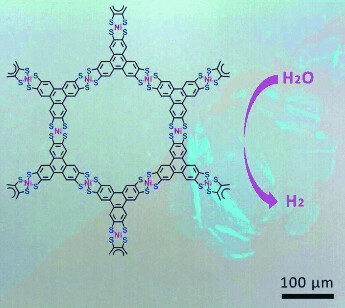
Standing up: The Langmuir–Blodgett method can be used to prepare two-dimensional supramolecular polymer (2DSP) sheets from nickel bis(dithiolene) complexes at the air–water interface (see figure). These free-standing single-layer sheets, which are 0.7–0.9 nm thick and square millimeters in area, showed excellent electrocatalytic activities in the hydrogen evolution reaction from water.
Apoptosis
Optogenetic Apoptosis: Light-Triggered Cell Death
- Pages: 12064-12068
- First Published: 25 August 2015
Perovskite Phases
Giant Magnetoresistance in the Half-Metallic Double-Perovskite Ferrimagnet Mn2FeReO6
- Pages: 12069-12073
- First Published: 31 July 2015
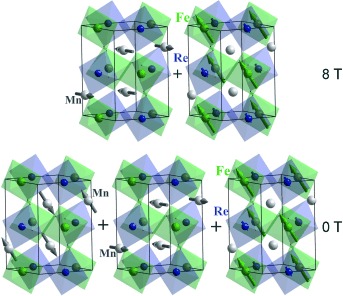
The first transition-metal-only double perovskite, Mn2+2Fe3+Re5+O6, displays ferrimagnetic ordering up to 520 K and a giant positive magnetoresistance of up to 220 % at 5 K and 8 T. These properties result from the ferrimagnetically coupled Fe and Re sublattice and are affected by a two-to-one magnetic-structure transition of the Mn sublattice when a magnetic field is applied.
Large Magnetization and Frustration Switching of Magnetoresistance in the Double-Perovskite Ferrimagnet Mn2FeReO6
- Pages: 12074-12077
- First Published: 26 August 2015
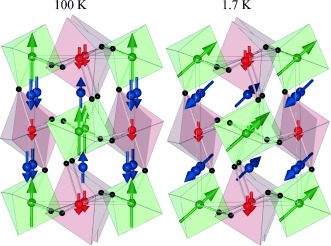
Double-perovskite magnetism: The double perovskite Mn2FeReO6 synthesized at high pressure has magnetic transition-metal cations at all sites. High-spin Mn2+ cations lead to record magnetizations for double-perovskite ferrimagnets and their frustrated magnetic order at 75 K switches magnetoresistance from negative to large positive values at low temperatures.
Gelation versus Crystallization
Stoichiometric Sensing to Opt between Gelation and Crystallization
- Pages: 12078-12082
- First Published: 21 August 2015
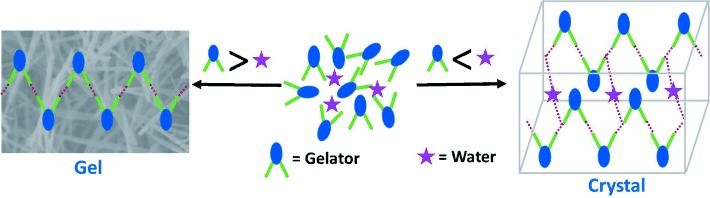
To gel or not to gel: A new class of organogelators having a cyclohexanediol motif uses molecular quorum sensing to make a definite choice between two competing modes of self-assembly: gelation or crystallization. When the concentration of gelator is less than that of adventitious water present in the system, the gelator molecules undergoes crystallization; when its concentration is more than water, it congeals the solvent to form a stable organogel.
Ring Expansion
1,2-Phosphaborines: Hybrid Inorganic/Organic P–B Analogues of Benzene
- Pages: 12083-12086
- First Published: 28 August 2015
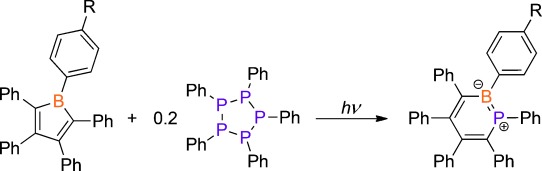
Jamming PB into benzene: 1,2-Phosphaborines were synthesized by the ring expansion reaction of boroles with the cyclic phosphine [PPh]5 under UV irradiation. The products were structurally characterized revealing a planar central ring. The nature of the bonding was analyzed computationally and indicated that the heterocycle had appreciable aromatic character.
Nucleophilic Substitution
Participation of Alkoxy Groups in Reactions of Acetals: Violation of the Reactivity/Selectivity Principle in a Curtin–Hammett Kinetic Scenario†
- Pages: 12087-12090
- First Published: 19 August 2015
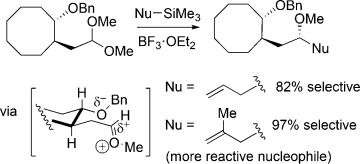
On principle: Nucleophilic substitution reactions of acetals having benzyloxy groups four carbon atoms away can be highly diastereoselective. The selectivity in several cases increased as the reactivity of the nucleophile increased, in violation of the reactivity/selectivity principle. The increase in selectivity with reactivity suggests that multiple conformational isomers of reactive intermediates can give rise to the products.
Core/Shell Nanoparticles
Precisely Size-Tunable Magnetic/Plasmonic Core/Shell Nanoparticles with Controlled Optical Properties
- Pages: 12091-12096
- First Published: 31 August 2015
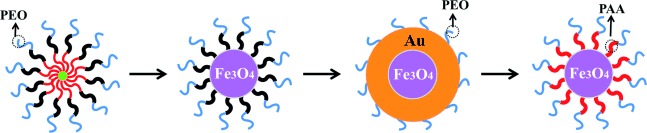
Star-like amphiphilic triblock copolymers with narrow molecular weight distributions were synthesized by combining two sequential atom-transfer radical polymerizations with a click reaction. A family of uniform magnetic/plasmonic core/shell nanoparticles with precisely controllable core diameters and shell thicknesses were then obtained by capitalizing on these triblock copolymers as nanoreactors [PAA=poly(acrylic acid), PEO=poly(ethylene oxide)].
Synthetic Methods
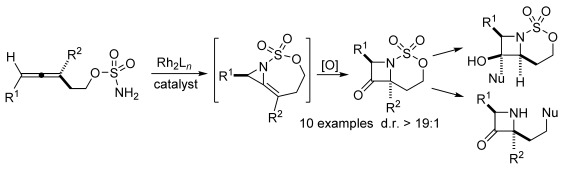
Oxidative Allene Amination for the Synthesis of Azetidin-3-ones
- Pages: 12097-12101
- First Published: 19 August 2015
Asymmetric Catalysis
Carbamate-Catalyzed Enantioselective Bromolactamization
- Pages: 12102-12106
- First Published: 28 August 2015
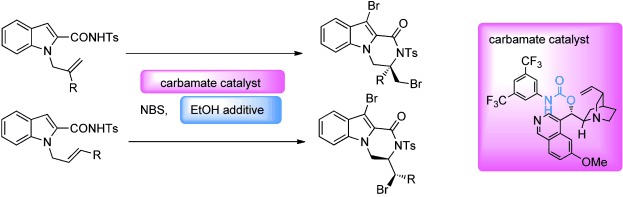
A splash of EtOH: A highly facile, efficient, and enantioselective bromolactamization of olefinic amides was effected by a carbamate catalyst and ethanol additive. The amide substrates undergo N-cyclization predominantly to give a diverse range of enantioenriched bromolactam products which contain up to two chiral centers. Ts=4-toluenesulfonyl.
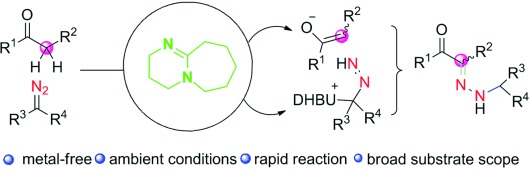
Diazo Compounds
Activation of α-Diazocarbonyls by Organic Catalysts: Diazo Group Acting as a Strong N-Terminal Electrophile
- Pages: 12107-12111
- First Published: 28 August 2015
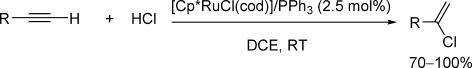
Halogenation
Selective Ruthenium-Catalyzed Hydrochlorination of Alkynes: One-Step Synthesis of Vinylchlorides
- Pages: 12112-12115
- First Published: 24 August 2015
CO2 Activation | Hot Paper
Hydrophosphination of CO2 and Subsequent Formate Transfer in the 1,3,2-Diazaphospholene-Catalyzed N-Formylation of Amines
- Pages: 12116-12120
- First Published: 14 August 2015
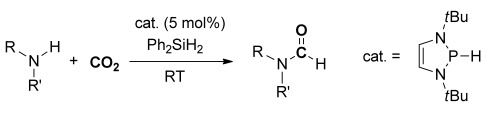
Formate formation: Hydrophosphination of CO2 with 2-H-1,3,2-diazaphospholene afforded phosphorus formate, from which transfer of the formate to Ph2SiH2 produced Ph2Si(OCHO)2. These elementary reactions were applied to the metal-free catalytic N-formylation of various amine derivatives with CO2 in a one-pot approach at room temperature.
CH Activation
Redox-Neutral Rhodium-Catalyzed CH Functionalization of Arylamine N-Oxides with Diazo Compounds: Primary C(sp3)H/C(sp2)H Activation and Oxygen-Atom Transfer
- Pages: 12121-12126
- First Published: 26 August 2015
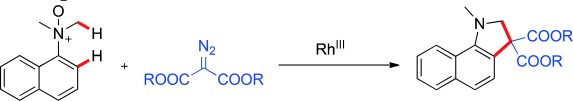
Untapped reactivity: The title reaction affords 1H-benzo[g]indolines under mild reaction conditions and external oxidants are not required. The only by-products are dinitrogen and water. This reaction represents the first example of dual functionalization of unactivated primary C(sp3)H and C(sp2)H bonds with diazocarbonyl compounds. Moreover, a method to access various aminomandelic acid derivatives by an O-atom-transfer strategy is described.
Polymer Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Conductive Elastomers with Autonomic Self-Healing Properties
- Pages: 12127-12133
- First Published: 25 August 2015
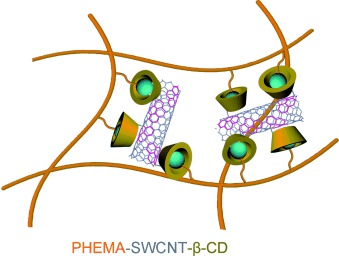
Candidates for smart robotics: Self-healing conductive composites were prepared by connecting single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) to a polymer network through host–guest interactions (see picture). The poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)–SWCNT composite combines bulk electrical conductivity, proximity sensitivity, humidity sensitivity, and autonomic self-healing properties.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Copper-Catalyzed Enantioselective 1,6-Boration of para-Quinone Methides and Efficient Transformation of gem-Diarylmethine Boronates to Triarylmethanes
- Pages: 12134-12138
- First Published: 28 August 2015
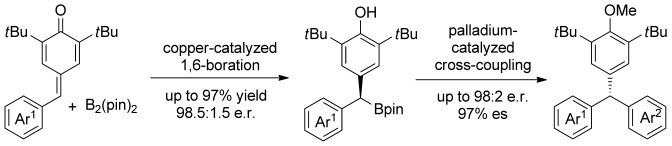
Quite a gem: The first enantioselective copper-catalyzed 1,6-conjugate addition of bis(pinacolato)diboron to para-quinone methides is presented. It proceeds with excellent yields and good to excellent enantioselectivities, and provides an attractive approach for the construction of optically active gem-diarylmethine boronic esters, which can be converted into triarylmethanes with highly enantiospecificity.
Small-Ring Compounds
Zinc-Catalyzed Alkene Cyclopropanation through Zinc Vinyl Carbenoids Generated from Cyclopropenes
- Pages: 12139-12143
- First Published: 25 August 2015
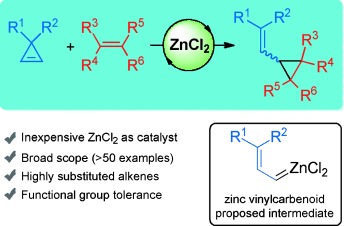
Open and close! The title reaction provides a convenient and general route to relevant vinylcyclopropane derivatives. Mechanistic studies support the participation of a zinc vinylcarbene intermediate, which may be subsequently involved in a concerted cyclopropanation reaction. This method represents a step towards identifying suitable precursors for the catalytic generation of zinc carbenoids.
Organodisilenes | Very Important Paper
Observation of a Thermally Accessible Triplet State Resulting from Rotation around a Main-Group π Bond
- Pages: 12144-12148
- First Published: 20 August 2015
Asymmetric Catalysis
Chiral Cyclopentadienyl Iridium(III) Complexes Promote Enantioselective Cycloisomerizations Giving Fused Cyclopropanes
- Pages: 12149-12152
- First Published: 27 August 2015
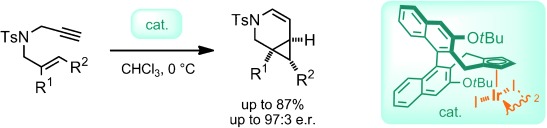
Be selective! A set of chiral CpxIrIII complexes (Cpx=chiral cyclopentadienyl) based on atropchiral cyclopentadienyl ligands are presented. The complexes, in particular the tert-butoxy-substituted derivative (see picture), are shown to promote the asymmetric cycloisomerization of enynes to form fused cyclopropanes with high enantioselectivities.
Radical Cyclization
Synthesis of Bridged Diketopiperazines by Using the Persistent Radical Effect and a Formal Synthesis of Bicyclomycin
- Pages: 12153-12157
- First Published: 25 August 2015
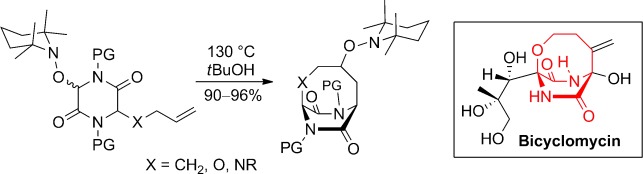
Persistent cyclization: A unified radical approach to diverse bridged diketopiperazines was developed by taking advantage of the persistent radical effect. The method allows rapid access to three-dimensional heterocyclic architectures and was applied to a formal synthesis of the antibiotic bicyclomycin.
Transfer Hydrogenation
B(C6F5)3-Catalyzed Transfer of Dihydrogen from One Unsaturated Hydrocarbon to Another
- Pages: 12158-12162
- First Published: 26 August 2015
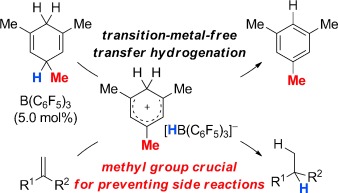
Well balanced: Wheland complexes that were generated by B(C6F5)3-mediated hydride abstraction from cyclohexa-1,4-dienes engage in the transfer hydrogenation of alkenes. Problems arising from the involvement of carbenium ion intermediates, resulting in cationic hetero- or homodimerization, are overcome by sterically shielding the hydridic C3 position of the dihydrogen surrogate (see scheme). The mechanism was analyzed by quantum-chemical calculations.
Organomagnesium Reagents
Direct Transformation of Esters into Arenes with 1,5-Bifunctional Organomagnesium Reagents
- Pages: 12163-12166
- First Published: 20 August 2015
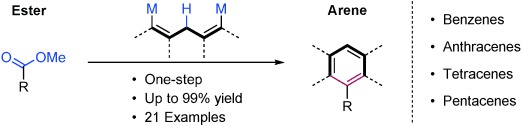
Almost replaced: A direct transformation of carboxylic acid esters into benzenes, anthracenes, tetracenes, and pentacenes is described. Utilizing 1,5-bifunctional organomagnesium reagents, the reaction integrates the ester carbon atom into the newly formed aromatic ring. The method enables the transformation of different esters into arenes in yields of up to 99 %.
Terpene Biosynthesis
Identification of Intermediates in the Biosynthesis of PR Toxin by Penicillium roqueforti
- Pages: 12167-12170
- First Published: 12 August 2015
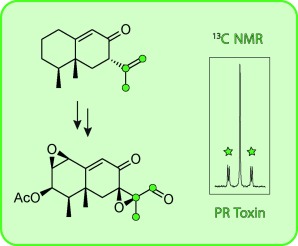
The sesquiterpenoid 7-epi-neopetasone was synthesized and shown to be identical to a previously tentatively identified headspace constituent of the fungus Penicillium roqueforti. Feeding with (11,12,13-13C3)-7-epi-neopetasone revealed that the compound is a pathway intermediate for PR toxin, while feeding with 13C-labeled isotopomers of mevalonolactone gave additional insight into a double-bond isomerization/oxidation sequence along the pathway.
Strontium Guanidinate | Hot Paper
Synthesis, Structure, and Properties of SrC(NH)3, a Nitrogen-Based Carbonate Analogue with the Trinacria Motif
- Pages: 12171-12175
- First Published: 26 August 2015
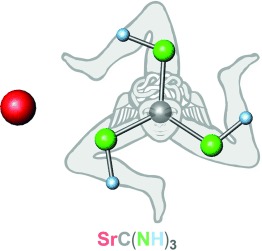
Keeping an ion guanidinate: Strontium guanidinate, SrC(NH)3, the first compound with a doubly deprotonated guanidine unit, was synthesized, and its properties investigated using X-ray and neutron powder diffraction as well as IR spectroscopy. Combined with quantum-theoretical calculations, this allows a qualitative and quantitative discussion of some first insights into the structure of the anionic guanidine unit.