Silicification-Induced Cell Aggregation for the Sustainable Production of H2 under Aerobic Conditions
Wei Xiong
Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorXiaohong Zhao
College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorGenxing Zhu
Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorChangyu Shao
Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorYaling Li
Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Weimin Ma
College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Weimin Ma, College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Xurong Xu, Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Ruikang Tang, Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xurong Xu
Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Weimin Ma, College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Xurong Xu, Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Ruikang Tang, Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Ruikang Tang
Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Weimin Ma, College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Xurong Xu, Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Ruikang Tang, Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorWei Xiong
Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorXiaohong Zhao
College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorGenxing Zhu
Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorChangyu Shao
Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorYaling Li
Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Weimin Ma
College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Weimin Ma, College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Xurong Xu, Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Ruikang Tang, Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xurong Xu
Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Weimin Ma, College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Xurong Xu, Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Ruikang Tang, Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Ruikang Tang
Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Weimin Ma, College of Life and Environmental Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 (China)
Xurong Xu, Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies and State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Ruikang Tang, Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
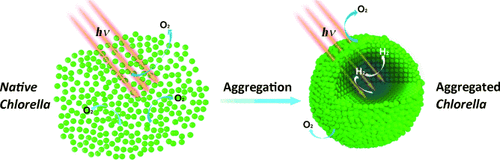
Photobiological hydrogen production is of great importance because of its promise for generating clean renewable energy. In nature, green algae cannot produce hydrogen as a result of the extreme sensitivity of hydrogenase to oxygen. However, we find that silicification-induced green algae aggregates can achieve sustainable photobiological hydrogen production even under natural aerobic conditions. The core–shell structure of the green algae aggregates creates a balance between photosynthetic electron generation and hydrogenase activity, thus allowing the production of hydrogen. This finding provides a viable pathway for the solar-driven splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen to develop green energy alternatives by using rationally designed cell–material complexes.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201504634_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf938.7 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aO. Kruse, B. Hankamer, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 238–243;
- 1bK. Srirangan, M. E. Pyne, C. P. Chou, Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8589–8604.
- 2
- 2aJ. A. Turner, Science 1999, 285, 687–689;
- 2bJ. R. Bartels, M. B. Pate, N. K. Olson, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 8371–8384.
- 3S. J. Burgess, B. Tamburic, F. Zemichael, K. Hellgardt, P. J. Nixon, Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 75, 71–110.
- 4
- 4aA. Hemschemeier, T. Happe, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2011, 1807, 919–926;
- 4bS. Grewe, M. Ballottari, M. Alcocer, C. D’Andrea, O. Blifernez-Klassen, B. Hankamer, J. H. Mussgnug, R. Bassi, O. Kruse, Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1598–1611.
- 5H. Gaffron, J. Rubin, J. Gen. Physiol. 1942, 26, 219–240.
- 6S. T. Stripp, G. Goldet, C. Brandmayr, O. Sanganas, K. A. Vincent, M. Haumann, F. A. Armstrong, T. Happe, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17331–17336.
- 7
- 7aA. Melis, L. Zhang, M. Forestier, M. L. Ghirardi, M. Seibert, Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 127–133;
- 7bM. L. Ghirardi, L. Zhang, J. W. Lee, T. Flynn, M. Seibert, E. Greenbaum, A. Melis, Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 506–511.
- 8E. Eroglu, A. Melis, Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8403–8413.
- 9aA. Bandyopadhyay, J. Stöckel, H. Min, L. A. Sherman, H. B. Pakrasi, Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 139;
- 9bJ.-H. Hwang, H. C. Kim, J.-A. Choi, R. A. I. A. -Shanab, B. A. Dempsey, J. M. Regan, J. R. Kim, H. Song, I.-H. Nam, S.-N. Kim, W. Lee, D. Park, Y. Kim, J. Choi, M.-K. Ji, W. Jung, B. H. Jeon, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3234;
- 9cM. L. Ghirardi, J. Cohen, P. King, K. Schulten, K. Kim, M. Seibert, Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2006, 6340, U 257–U262.
- 10
- 10aT. K. Antal, T. E. Krendeleva, T. V. Laurinavichene, V. V. Makarova, M. L. Ghirardi, A. B. Rubin, A. A. Tsygankov, M. Seibert, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2003, 1607, 153–160;
- 10bA. A. Volgusheva, V. E. Zagidullin, T. K. Antal, B. N. Korvatovsky, T. E. Krendeleva, V. Z. Paschenko, A. B. Rubin, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 559–564.
- 11
- 11aC. E. Hamm, R. Merkel, O. Springer, P. Jurkojc, C. Maier, K. Prechtel, V. Smetacek, Nature 2003, 421, 841–843;
- 11bF. Nudelman, N. A. J. M. Sommerdijk, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6582–6596; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 6686–6700;
- 11cE. Bäuerlein, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 614–641; Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 636–664.
- 12
- 12aB. Wang, P. Liu, W. Jiang, H. Pan, X. Xu, R. Tang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3560–3564; Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 3616–3620;
- 12bS. H. Yang, K.-B. Lee, B. Kong, J.-H. Kim, H.-S. Kim, I. S. Choi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9160–9163; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 9324–9327;
- 12cE. H. Ko, Y. Yoon, J. H. Park, S. H. Yang, D. Hong, K.-B. Lee, H. K. Shon, T. G. Lee, I. S. Choi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12279–12282; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 12505–12508;
- 12dG. Wang, X. Li, L. Mo, Z. Song, W. Chen, Y. Deng, H. Zhao, E. Qin, C. Qin, R. Tang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10576–10579; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10728–10731;
- 12eW. Xiong, Z. Yang, H. Zhai, G. Wang, X. Xu, W. Ma, R. Tang, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7525–7527.
- 13T. Hübert, L. Boon-Brett, G. Black, U. Banach, Sens. Actuators B 2011, 157, 329–352.
- 14L. J. Iwuchukwu, M. Vaughn, N. Myers, H. O’Neill, P. Frymier, B. D. Bruce, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 5, 73–79.
- 15M. L. Ghirardi, S. Kosourov, A. Tsygankov, M. Seiber-t, Proceedings of the 2000 DOE Hydrogen Program Review (San Ramon, CA) 2000, pp. 1–13. NREL/CP-570-28890.
- 16F. Rappaport, B. A. Diner, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 259–272.
- 17A. Volgusheva, S. Styring, F. Mamedov, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7223–7228.
- 18G. Goldet, A. F. Wait, J. A. Cracknell, K. A. Vincent, M. Ludwig, O. Lenz, B. Friedrich, F. A. Armstrong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11106–11113.