A Highly Selective Mitochondria-Targeting Fluorescent K+ Sensor
Dr. Xiangxing Kong
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Fengyu Su
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Liqiang Zhang
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jordan Yaron
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorFred Lee
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorZhengwei Shi
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Yanqing Tian
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, South University of Science and Technology of China, No. 1088, Xueyuan Rd., Xili, Nanshan District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 (China)
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Deirdre R. Meldrum
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xiangxing Kong
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Fengyu Su
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Liqiang Zhang
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jordan Yaron
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorFred Lee
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorZhengwei Shi
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Yanqing Tian
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, South University of Science and Technology of China, No. 1088, Xueyuan Rd., Xili, Nanshan District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 (China)
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Deirdre R. Meldrum
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)
Center for Biosignatures Discovery Automation, Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, 1001 S. McAlister Ave., P.O. Box 876501, Tempe, AZ 85287 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
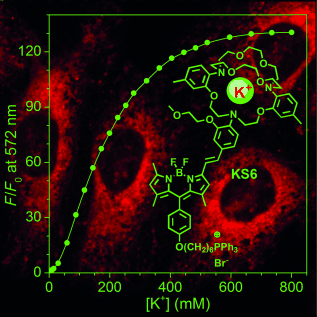
A lamp to light the K: An intracellular mitochondria-specific K+ sensor, KS6, was developed. KS6 shows a K+ response range of 30–500 mM, sensitive fluorescence enhancement (Fmax/F0≈130), high brightness (ϕf=14.4 % at 150 mM of K+), and insensitivity to both pH (in the range 5.5–9.0) and other metal ions under physiological conditions. KS6 is thus the first sensor that can be used for monitoring K+ ion flux in the mitochondria of live cells
Abstract
Regulation of intracellular potassium (K+) concentration plays a key role in metabolic processes. So far, only a few intracellular K+ sensors have been developed. The highly selective fluorescent K+ sensor KS6 for monitoring K+ ion dynamics in mitochondria was produced by coupling triphenylphosphonium, borondipyrromethene (BODIPY), and triazacryptand (TAC). KS6 shows a good response to K+ in the range 30–500 mM, a large dynamic range (Fmax/F0≈130), high brightness (ϕf=14.4 % at 150 mM of K+), and insensitivity to both pH in the range 5.5–9.0 and other metal ions under physiological conditions. Colocalization tests of KS6 with MitoTracker Green confirmed its predominant localization in the mitochondria of HeLa and U87MG cells. K+ efflux/influx in the mitochondria was observed upon stimulation with ionophores, nigericin, or ionomycin. KS6 is thus a highly selective semiquantitative K+ sensor suitable for the study of mitochondrial potassium flux in live cells.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201506038_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf1.9 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1C. Miller, Genome Biol. 2000, 1, reviews 0004.1.
10.1186/gb-2000-1-4-reviews0004 Google Scholar
- 2
- 2aD. Urrego, A. P. Tomczak, F. Zahed, W. Stuhmer, L. A. Pardo, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. B 2014, 369, 20130094;
- 2bI. Szabò, L. Leanza, E. Gulbins, M. Zoratti, Pfluegers Arch. 2012, 463, 231–246;
- 2cD. Malinska, S. R. Mirandola, W. S. Kunz, FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2043–2048;
- 2dV. Pétrilli, S. Papin, C. Dostert, A. Mayor, F. Martinon, J. Tschopp, Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1583–1589.
- 3
- 3aM. Levin, C. G. Stevenson, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 295–323;
- 3bZ. W. Wang, O. Saifee, M. L. Nonet, L. Salkoff, Neuron 2001, 32, 867–881.
- 4
- 4aX. Huang, L. Y. Jan, J. Cell Biol. 2014, 206, 151–162;
- 4bH. Wulff, B. S. Zhorov, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 1744–1773;
- 4cM. P. Mattson, G. Kroemer, Trends Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 196–205;
- 4dP. Rorsman, M. Braun, Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 155–179.
- 5O. B. McManus, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 15, 91–96.
- 6
- 6aD. W. Beacham, T. Blackmer, M. O’Grady, G. T. Hanson, J. Biomol. Screening 2010, 15, 441–446;
- 6bA. P. Wojtovich, D. M. Williams, M. K. Karcz, C. M. B. Lopes, D. A. Gray, K. W. Nehrke, P. S. Brookes, Circul. Res. 2010, 106, 1190–U1138.
- 7S. Rezazadeh, J. C. Hesketh, D. Fedida, J. Biomol. Screening 2004, 9, 588–597.
- 8R. Muñoz-Planillo, P. Kuffa, G. Martinez-Colón, B. L. Smith, T. M. Rajendiran, G. Núñez, Immunity 2013, 38, 1142–1153.
- 9J. C. Xu, P. L. Wang, Y. Y. Li, G. Y. Li, L. K. Kaczmarek, Y. L. Wu, P. A. Koni, R. A. Flavell, G. V. Desir, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3112–3117.
- 10D. G. Jackson, J. J. Wang, R. W. Keane, E. Scemes, G. Dahl, Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, srep 04576.
- 11S. Bonnet, S. L. Archer, J. Allalunis-Turner, A. Haromy, C. Beaulieu, R. Thompson, C. T. Lee, G. D. Lopaschuk, L. Puttagunta, S. Bonnet, G. Harry, K. Hashimoto, C. J. Porter, M. A. Andrade, B. Thebaud, E. D. Michelakis, Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 37–51.
- 12M. E. Lidstrom, D. R. Meldrum, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 1, 158–164.
- 13F. Nolin, J. Michel, L. Wortham, P. Tchelidze, G. Balossier, V. Banchet, H. Bobichon, N. Lalun, C. Terryn, D. Ploton, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2383–2394.
- 14B. Alberts, Essential cell biology, 3rd ed., Garland Science, New York, 2010.
- 15
- 15aA. Minta, R. Y. Tsien, J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 19449–19457;
- 15bH. Szmacinski, J. R. Lakowicz, Sens. Actuators B 1999, 60, 8–18.
- 16H. He, M. A. Mortellaro, M. J. P. Leiner, R. J. Fraatz, J. K. Tusa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1468–1469.
- 17
- 17aW. Namkung, P. Padmawar, A. D. Mills, A. S. Verkman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7794–7795
- 17bR. D. Carpenter, A. S. Verkman, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 1242–1248;
- 17cP. Padmawar, X. M. Yao, O. Bloch, G. T. Manley, A. S. Verkman, Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 825–827;
- 17dR. D. Carpenter, A. S. Verkman, Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1160–1163.
- 18
- 18aX. F. Zhou, F. Y. Su, W. M. Gao, Y. Q. Tian, C. Youngbull, R. H. Johnson, D. R. Meldrum, Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8574–8583;
- 18bX. F. Zhou, F. Y. Su, Y. Q. Tian, C. Youngbull, R. H. Johnson, D. R. Meldrum, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18530–18533.
- 19T. Hirata, T. Terai, T. Komatsu, K. Hanaoka, T. Nagano, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6090–6093.
- 20
- 20aM. F. Ross, G. F. Kelso, F. H. Blaikie, A. M. James, H. M. Cocheme, A. Filipovska, T. Da Ros, T. R. Hurd, R. A. J. Smith, M. P. Murphy, Biochemistry 2005, 70, 222–230;
- 20bQ. L. Hu, M. Gao, G. X. Feng, B. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 14225–14229; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 14449–14453;
- 20cK. Krumova, L. E. Greene, G. Cosa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17135–17143;
- 20dC. W. T. Leung, Y. N. Hong, S. J. Chen, E. G. Zhao, J. W. Y. Lam, B. Z. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 62–65.
- 21T. Karstens, K. Kobs, J. Phys. Chem. 1980, 84, 1871–1872.
- 22N. Boens, V. Leen, W. Dehaen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1130–1172.
- 23
- 23aK. Rurack, M. Kollmannsberger, J. Daub, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 385–387;
10.1002/1521-3773(20010119)40:2<385::AID-ANIE385>3.0.CO;2-F CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2001, 113, 396–399;
- 23bM. Baruah, W. W. Qin, C. Flors, J. Hofkens, R. A. L. Vallee, D. Beljonne, M. Van der Auweraer, W. M. De Borggraeve, N. Boens, J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 5998–6009.
- 24K. W. Dunn, M. M. Kamocka, J. H. McDonald, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C 723–C742.
- 25P. Kofuji, E. A. Newman, Neuroscience 2004, 129, 1045–1056.
- 26U. Hopfer, Lehninge. Al, T. E. Thompson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 59, 484–490.
- 27
- 27aK. D. Garlid, P. Paucek, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2003, 1606, 23–41;
- 27bS. Chalmers, J. G. McCarron, J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 75–85;
- 27cS. W. Perry, J. P. Norman, J. Barbieri, E. B. Brown, H. A. Gelbard, BioTechniques 2011, 50, 98–115;
- 27dI. Szabo, M. Zoratti, Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 519–608.