Identification of Intermediates in the Biosynthesis of PR Toxin by Penicillium roqueforti
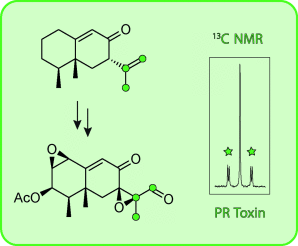
Graphical Abstract
The sesquiterpenoid 7-epi-neopetasone was synthesized and shown to be identical to a previously tentatively identified headspace constituent of the fungus Penicillium roqueforti. Feeding with (11,12,13-13C3)-7-epi-neopetasone revealed that the compound is a pathway intermediate for PR toxin, while feeding with 13C-labeled isotopomers of mevalonolactone gave additional insight into a double-bond isomerization/oxidation sequence along the pathway.
Abstract
The sesquiterpenoid 7-epi-neopetasone was synthesized via the Wieland–Miescher ketone. The compound was identical to a previously tentatively identified headspace constituent of Penicillium roqueforti. Feeding experiments with 13C-labeled mevalonolactone isotopomers demonstrated that oxidation at C12 and an isomerization of the C11C12 to a C7C11 double bond must occur independently and not via a C7-C11-C12 allyl radical in one step. Feeding with (11,12,13-13C3)-7-epi-neopetasone resulted in labelling of the PR toxin, thus establishing this compound as a newly identified pathway intermediate.