Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Synthesis of C3-Fluorinated Oxindoles through Reagent-Free Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 17/2017)
- Page: 4631
- First Published: 22 March 2017

Electricity was used to charge ferrocene (Cp2Fe) to catalyze the cross-coupling of C−H centers. In their Communication on page 4734 ff., H.-C. Xu and Z.-J. Wu describe an efficient and scalable Cp2Fe-catalyzed electrochemical synthesis of functionalized C3-fluorinated oxindoles from easily available malonate amides through dehydrogenative cross-coupling of C(sp3)–H and C(sp2)–H bonds.
Inside Cover: Reagent- and Metal-Free Anodic C−C Cross-Coupling of Aniline Derivatives (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 17/2017)
- Page: 4632
- First Published: 22 March 2017

The formation of polyanilines is avoided in an anodic coupling of anilines with simple and easily removable carbonyl-based protecting groups. In their Communication on page 4877 ff., S. R. Waldvogel and co-workers present a facile method for the electrolytic synthesis of protected 2,2′-diaminobiaryl derivatives in high yield and excellent selectivity by oxidative cross-coupling. The use of 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol as the solvent allows for clean electrochemical conversion.
Inside Back Cover: Amine-Rich Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanodots as a Platform for Self-Enhancing Electrochemiluminescence (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 17/2017)
- Page: 4891
- First Published: 05 April 2017

Carbon nanodots are the latest member to join the carbon nanomaterial family, thus generating many expectations based on their fascinating properties. In their Communication on page 4757 ff., M. Prato, L. De Cola et al. demonstrate the promising use of amine-rich nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots as co-reactant for Ru(bpy)32+ electrochemiluminescence (ECL). The covalently linked hybrid acts as an ECL self-enhancing system, showing higher emission than the combination of the single components.
Back Cover: Large-Area Elemental Imaging Reveals Van Eyck's Original Paint Layers on the Ghent Altarpiece (1432), Rescoping Its Conservation Treatment (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 17/2017)
- Page: 4892
- First Published: 29 March 2017

Van Eyck's Ghent Altarpiece is considered by many to be the pinnacle of European mediaeval paintxting. In their Communication on page 4797 ff., G. Van der Snickt et al. describe how they used large- and microscale elemental imaging (EI) to obtain compositional maps for the surface of the verso wing panels of the altarpiece, which allowed visualization and assessment of the original paint layers below the overpainting. Thus, EI provided objective arguments supporting the decision for full removal of the overpaint.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Supported Rhodium Catalysts for Ammonia–Borane Hydrolysis: Dependence of the Catalytic Activity on the Highest Occupied State of the Single Rhodium Atoms
- First Published: 07 April 2017

Single-Atom CatalystsIn their Communication on page 4712 ff., Z. Hu, R. Si, J. Zeng et al. show that the activity of a catalyst consisting of isolated Rh atoms dispersed on VO2 nanorods depends on the highest occupied state of the Rh atoms.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 17/2017
- Pages: 4635-4646
- First Published: 07 April 2017
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 17/2017
- Pages: 4648-4651
- First Published: 07 April 2017
Author Profile
News
Book Reviews
Fluorescent Analogs of Biomolecular Building Blocks. Design and Applications Edited by Marcus Wilhelmsson and Yitzhak Tor.
- Page: 4655
- First Published: 27 March 2017
Highlights
Enzymology
Polyketide Synthase Modules Redefined
- Pages: 4658-4660
- First Published: 21 March 2017
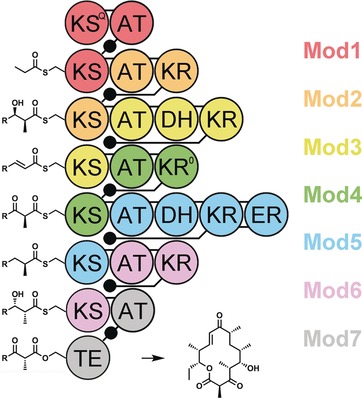
Modular redefinition: A long-standing paradigm in modular polyketide synthase enzymology, namely the definition of a module, has been challenged by Abe and co-workers in their recent study. With this new understanding has emerged renewed hope for engineering these assembly lines to produce new materials and medicines.
Reviews
Water Purification Membranes
Surface Modification of Water Purification Membranes
- Pages: 4662-4711
- First Published: 08 September 2016
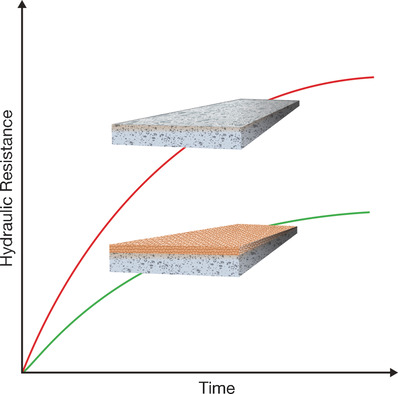
Cleaning up: The efficiency of polymeric water purification membranes, which are capable of removing many impurities from water but frequently suffer from fouling, can be improved by surface modification. Common techniques used to modify membrane surfaces, including grafting, coating, chemical treatment, UV irradiation, plasma treatment, and polydopamine application, are reviewed.
Communications
Single-Atom Catalysts
Supported Rhodium Catalysts for Ammonia–Borane Hydrolysis: Dependence of the Catalytic Activity on the Highest Occupied State of the Single Rhodium Atoms
- Pages: 4712-4718
- First Published: 30 March 2017
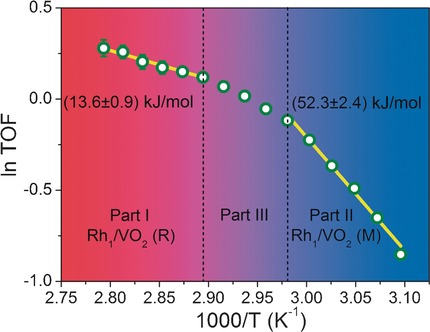
Phase-dependent: When a catalyst consisting of isolated rhodium atoms dispersed on the surface of VO2 nanorods was employed for ammonia–borane hydrolysis, the activation energy changed when the substrate underwent a phase transition. Mechanistic studies indicate that the catalytic performance depends directly on the highest occupied state of the single Rh atoms, which is determined by the band structure of the substrate.
Enzyme Catalysis
Different Structural Origins of the Enantioselectivity of Haloalkane Dehalogenases toward Linear β-Haloalkanes: Open–Solvated versus Occluded–Desolvated Active Sites
- Pages: 4719-4723
- First Published: 23 March 2017
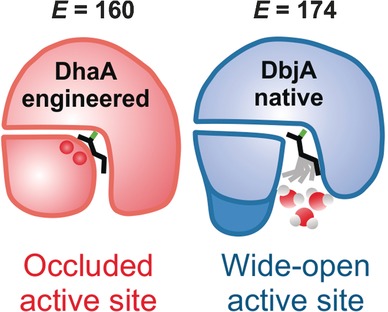
Two recipes for success: Two distinct mechanisms are described for the enantiodiscrimination of 2-bromopentane by haloalkane dehalogenases. Highly enantioselective DbjA has a very open, solvent-accessible active site. The engineered enzyme DhaA31 has a more occluded and less solvated cavity (see picture) but shows similar enantioselectivity as a result of steric hindrance imposed by two specific residues, rather than hydration as in DbjA.
Cell Fixation | Hot Paper
Cell Fixation by Light-Triggered Release of Glutaraldehyde
- Pages: 4724-4728
- First Published: 22 March 2017
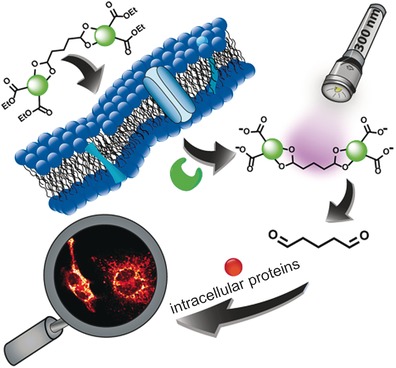
Cellfi-Flash: A new fixative for light microscopy of living cells was obtained by functionalizing glutaraldehyde with a photocleavable protecting group. Ester substituents ensure that the masked compound can enter the cell and accumulate therein after esterase-mediated hydrolysis. Incubated cells are instantly fixed and ready for microscopy upon irradiation, whereas conventional aldehyde fixation is diffusion-controlled.
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis of Modular Ascarosides in C. elegans
- Pages: 4729-4733
- First Published: 28 March 2017
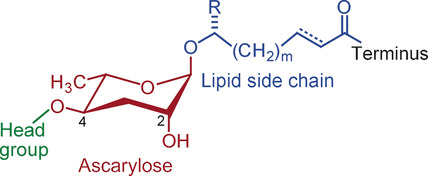
From the waste bin: C. elegans uses simple building blocks from primary metabolism to construct a modular library of signaling molecules, the ascarosides. It is demonstrated that lysosome-related organelles, which are essentially cellular waste-disposal centers, play a major role in the assembly of these compounds, which requires the activation of building blocks by a specific acyl-CoA synthetase.
Cross-Coupling | Very Important Paper
Synthesis of C3-Fluorinated Oxindoles through Reagent-Free Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling
- Pages: 4734-4738
- First Published: 13 March 2017
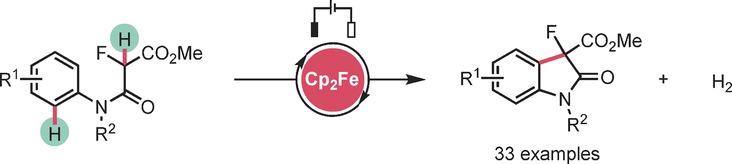
C−H functionalization: A ferrocene-catalyzed electrochemical cross-coupling reaction of C(sp3)-H and C(sp2)-H centers has been developed to give access to C3-fluorinated oxindoles using fluorinated malonate amides. The electrosynthetic method is characterized by mild reaction conditions, broad substrate scope, high functional group tolerance, and easy scalability.
Photoelectrochemistry
Highly Active GaN-Stabilized Ta3N5 Thin-Film Photoanode for Solar Water Oxidation
- Pages: 4739-4743
- First Published: 21 March 2017
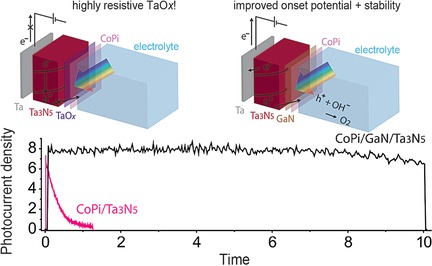
Solar energy conversion: A simple and reliable vapor-phase deposition technique is developed for fabricating GaN/Ta3N5 thin films that achieve state-of-the-art solar water splitting performance and stability. The GaN overcoating strategy is readily applicable to stabilize various promising (oxy)nitrides for practical photo-electrochemical applications.
Halogenation
B(C6F5)3-Catalyzed Selective Chlorination of Hydrosilanes
- Pages: 4744-4748
- First Published: 21 March 2017
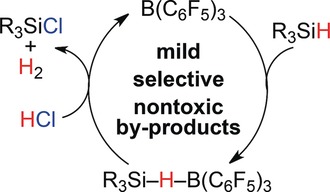
Cl-early a winning combination: Hydrosilanes underwent selective chlorination upon treatment with HCl in the presence of a catalytic amount of B(C6F5)3 with the liberation of H2 (see scheme). For the chlorination of di- and trihydrosilanes, the adduct Et2O⋅B(C6F5)3 was found to be a more selective catalyst.
Biosynthesis
Discovery and Characterization of a New Family of Diterpene Cyclases in Bacteria and Fungi
- Pages: 4749-4752
- First Published: 28 March 2017
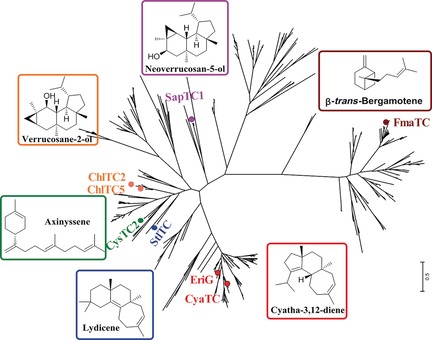
Full circle: EriG, a member of the UbiA superfamily, was identified as the enzyme responsible for the cyclization of the cyathane skeleton in the mushroom Hericium erinaceum. Genome mining using the EriG protein sequence led to the identification of a new family of widespread UbiA-related diterpene cyclase genes in bacteria and fungi.
Sustainability
Fast and Minimal-Solvent Production of Superinsulating Silica Aerogel Granulate
- Pages: 4753-4756
- First Published: 23 March 2017

Solving the solvent problem: Silica aerogels are ideal thermal insulation materials, but are expensive owing to the large solvent consumption during their production. A simplified synthesis combines all reagents in a single step and minimizes the production time, solvent use, and carbon footprint, but retains the outstanding properties associated with silica aerogels.
Electrochemiluminescence
Amine-Rich Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanodots as a Platform for Self-Enhancing Electrochemiluminescence
- Pages: 4757-4761
- First Published: 15 March 2017
On-Surface Synthesis
Highly Selective Synthesis of cis-Enediynes on a Ag(111) Surface
- Pages: 4762-4766
- First Published: 27 March 2017
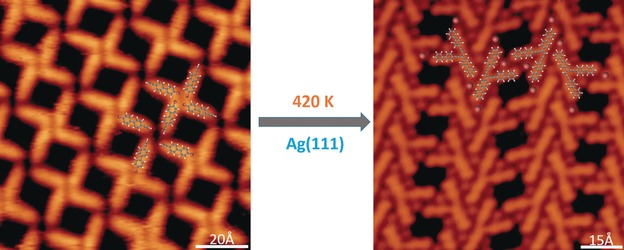
Selective on-surface synthesis of cis-enediyne-type compounds is reported for the first time. Bromide-substituted terminal alkynes transform into cis-enediynes on a Ag(111) surface at 420 K. Coadsorbed bromide ions help the formed cis-enediynes aggregate into close-packed islands through Br⋅⋅⋅H bonds, which impose a high steric barrier to further reaction of cis-enediyne.
Ion Transport in ZIFs
Insight into Ion Transfer through the Sub-Nanometer Channels in Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks
- Pages: 4767-4771
- First Published: 27 March 2017
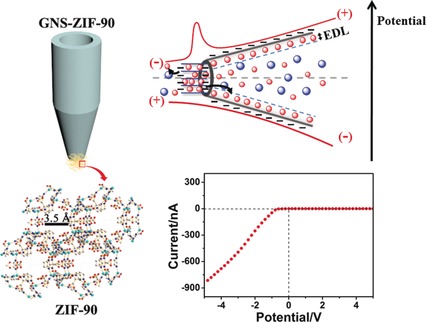
Tipping the balance: By coating the tip of a nanopipette with crystalline zeolitic imidazolate framework-90 (ZIF-90), super-high ionic rectification was detected. The rectification results from the interaction between the sub-nanometer channels of the glass-nanopipette-supported ZIF-90 (GNS-ZIF-90) and the ions in solution.
Oxygen Atom Transfer
Accelerated Oxygen Atom Transfer and C−H Bond Oxygenation by Remote Redox Changes in Fe3Mn-Iodosobenzene Adducts
- Pages: 4772-4776
- First Published: 24 March 2017

Rare finding: Iodosobenzene adducts LFe3(PhPz)3OMn(sPhIO)][OTf]x (x=2 or 3; PhPz=phenylpyrazolate) on multinuclear scaffolds were synthesized and characterized. The reactivity of these rare adducts was investigated in light of remote redox state changes in a triiron core (FeIII2FeIIMnII vs. FeIII3MnII), thereby highlighting significant reactivity differences (>102) in oxygen atom transfer and C−H bond oxygenation.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Palladium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Synthesis of 2-Aryl Cyclohex-2-enone Atropisomers: Platform Molecules for the Divergent Synthesis of Axially Chiral Biaryl Compounds
- Pages: 4777-4781
- First Published: 24 March 2017
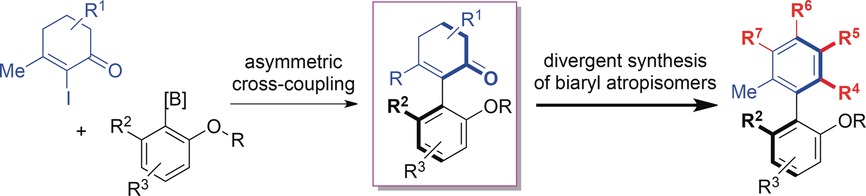
A platform to improve the outlook: The palladium-catalyzed asymmetric coupling of 2-iodo-3-methylcyclohex-2-enones and aryl boronic acids provided axially chiral enone–arene systems with several potential sites for further transformation (see scheme). In particular, these cyclohexenone-based atropisomers serve as a valuable platform for the synthesis of biaryl atropisomers with different ortho substituents.
Biosynthesis
A Cascade of Redox Reactions Generates Complexity in the Biosynthesis of the Protein Phosphatase-2 Inhibitor Rubratoxin A
- Pages: 4782-4786
- First Published: 28 March 2017
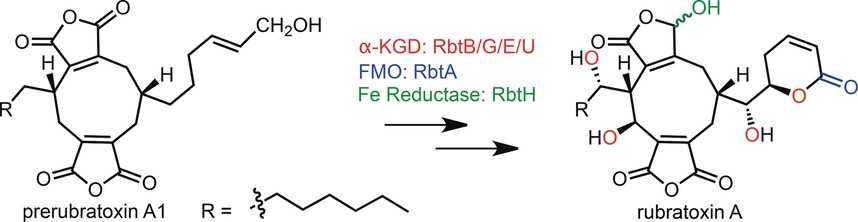
Hit for six: Four α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases (red) that hydroxylate sp3 carbon atoms, a flavin-dependent dehydrogenase (blue) that forms the unsaturated lactone, and the highly unusual ferric-reductase-like enzyme RbtH (green) are involved in the biosynthesis of rubratoxin A. RbtH regioselectively reduces one of the maleic anhydride moieties in the intermediate rubratoxin B to the γ-hydroxybutenolide group that is critical for the biological activity.
Natural Product Synthesis
Total Syntheses of Sesterterpenoid Ansellones A and B, and Phorbadione
- Pages: 4787-4791
- First Published: 28 March 2017
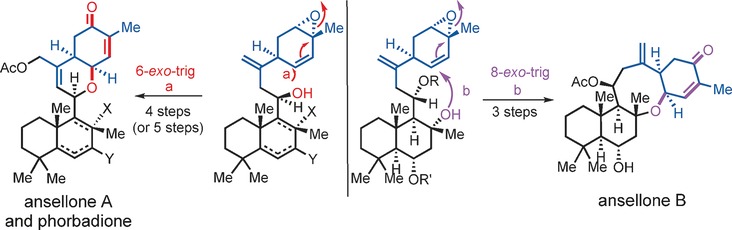
Minding manners: Unusual regioselective intramolecular cyclization of 1,3-cyclohexadiene epoxides with alcohol nucleophiles in a 1,4-addition manner enabled the first asymmetric total syntheses of (−)-ansellones A and B and (+)-phorbadione in 16–23 steps from (+)-sclareolide. This strategy is expected to be applicable to the synthesis of other ansellane sesterterpenoids.
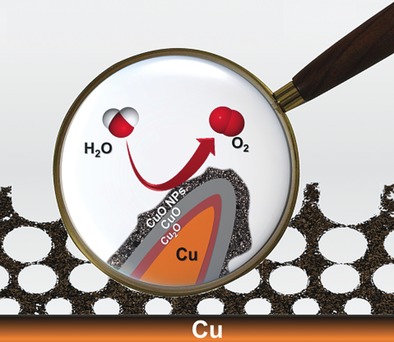
Electrocatalysis
A Dendritic Nanostructured Copper Oxide Electrocatalyst for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 4792-4796
- First Published: 04 April 2017
Analytical Methods
Large-Area Elemental Imaging Reveals Van Eyck's Original Paint Layers on the Ghent Altarpiece (1432), Rescoping Its Conservation Treatment
- Pages: 4797-4801
- First Published: 22 March 2017

Ghent what it used to be: A combination of large- and microscale chemical/elemental imaging supplied compositional information for the entire paint surface of the verso wing panels of van Eyck's Ghent Altarpiece. MA-XRF scanning allowed visualization and assessment of the original paint layers hidden below the overpainted surface. In this way, elemental imaging provided objective arguments supporting the decision for full removal of the overpaint.
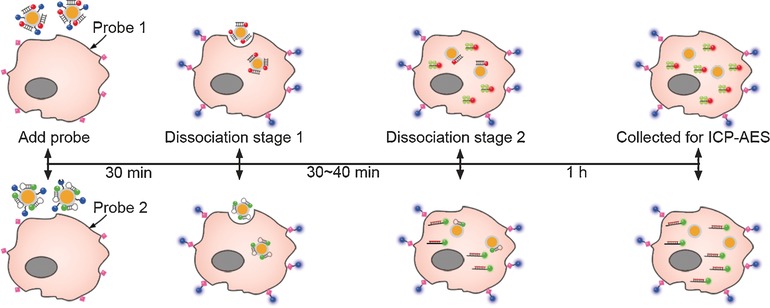
Intracellular Disassembly
A Two-Stage Dissociation System for Multilayer Imaging of Cancer Biomarker-Synergic Networks in Single Cells
- Pages: 4802-4805
- First Published: 28 March 2017
B,P,N Compounds
Li47B3P14N42—A Lithium Nitridoborophosphate with [P3N9]12−, [P4N10]10−, and the Unprecedented [B3P3N13]15− Ion
- Pages: 4806-4809
- First Published: 29 March 2017
![Li47B3P14N42—A Lithium Nitridoborophosphate with [P3N9]12−, [P4N10]10−, and the Unprecedented [B3P3N13]15− Ion](/cms/asset/82301c22-e9fd-45bd-be21-03d86fe59a1e/anie201701084-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Triple salt: The first lithium nitridoborophosphate Li47B3P14N42 was synthesized by two different approaches using a Li3N flux. It consists of noncondensed [P4N10]10−, [P3N9]12−, and [B3P3N13]15− ions in a matrix of Li+ ions. The formation of the novel [B3P3N13]15− ion suggests a great potential of the Li3N flux method for synthesis of unprecedented anion topologies.
Post-Synthetic Modification
Increased Synthetic Control—Gaining Access to Predicted Mg2Si5N8 and β-Ca2Si5N8
- Pages: 4810-4813
- First Published: 27 March 2017
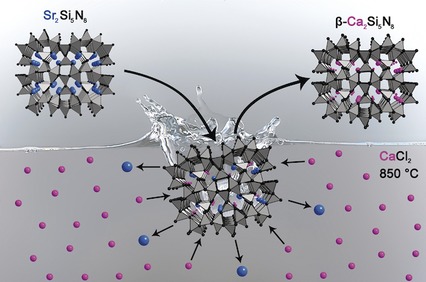
An exchange is as good as a rest: Nitridosilicates are solid-state materials consisting of cations embedded in highly condensed anionic tetrahedra networks. A new synthetic method enables the exchange of cations, while the networks remain preserved. This route gives a significant increase in synthetic control, thus providing the possibility of synthesis planning in nitridosilicate chemistry. The predicted compounds Mg2Si5N8 and β-Ca2Si5N8 were prepared using this route.
Main-Group Compounds
The Lightest Element Phosphoranylidene: NHC-Supported Cyclic Borylidene–Phosphorane with Significant B=P Character
- Pages: 4814-4818
- First Published: 28 March 2017
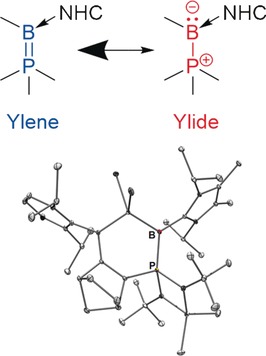
Opposites attract: A phosphorus bora-ylide stabilized by an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand was synthesized. Experimental electron density analysis and DFT calculations indicate enhanced phosphorane character (rather than ylide character) with an exceptionally strong B→P π-back bonding compared to related compounds; this is due to the electronegativity difference between boron and phosphorus atoms.
Organocatalysis
Chiral Tertiary Sulfonium Salts as Effective Catalysts for Asymmetric Base-Free Neutral Phase-Transfer Reactions
- Pages: 4819-4823
- First Published: 28 March 2017
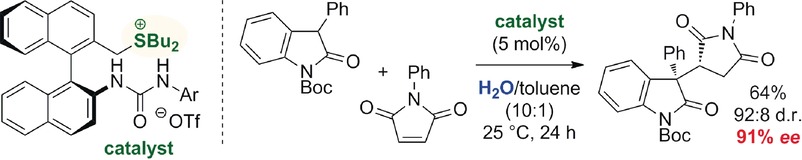
Sulfonium catalyst: Whereas chiral quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts are commonly used for asymmetric organocatalysis, chiral tertiary sulfonium salts have not been employed for such purposes. It is now shown that chiral bifunctional trialkylsulfonium salts catalyze the enantioselective conjugate addition of 3-substituted oxindoles to maleimides under base-free neutral phase-transfer conditions.
Heterocycles
Copper-Catalyzed [2+2+2] Modular Synthesis of Multisubstituted Pyridines: Alkenylation of Nitriles with Vinyliodonium Salts
- Pages: 4824-4828
- First Published: 28 March 2017
![Copper-Catalyzed [2+2+2] Modular Synthesis of Multisubstituted Pyridines: Alkenylation of Nitriles with Vinyliodonium Salts](/cms/asset/d7c5c2ef-db07-4d88-b42e-819bd04b365e/anie201700696-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Three to one! A [2+2+2] modular synthesis of multisubstituted pyridines with excellent regioselectivity has been realized by copper catalysis and involves three distinct components: vinyliodonium salts, nitriles, and alkynes. The reactions proceeded with the facile formation of an aza-butadienylium intermediate by alkenylation of the nitrile with a vinyliodonium salt.
Asymmetric Allylboration
Chiral Amino Alcohol Accelerated and Stereocontrolled Allylboration of Iminoisatins: Highly Efficient Construction of Adjacent Quaternary Stereogenic Centers
- Pages: 4829-4833
- First Published: 24 March 2017
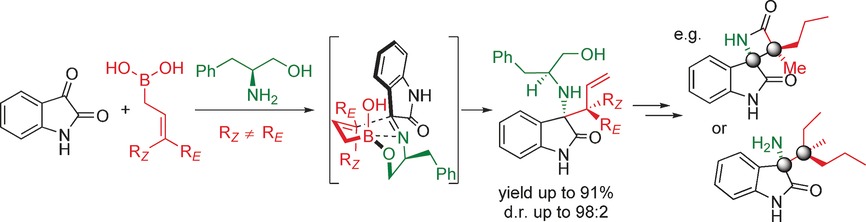
Collect the full set of four! A chiral amino alcohol was used as the directing group for the asymmetric allylboration of ketimines with nonchiral γ,γ-disubstituted allylboronic acids (see scheme). The amino alcohol not only serves as a cheap source of nitrogen and chirality, but also dramatically enhances reactivity. This versatile method can be used to access all four stereoisomers of a product with respect to the adjacent quaternary carbon centers.
Bowl-Shaped Aromatic Systems
Synthesis of Rationally Halogenated Buckybowls by Chemoselective Aromatic C−F Bond Activation
- Pages: 4834-4838
- First Published: 24 March 2017
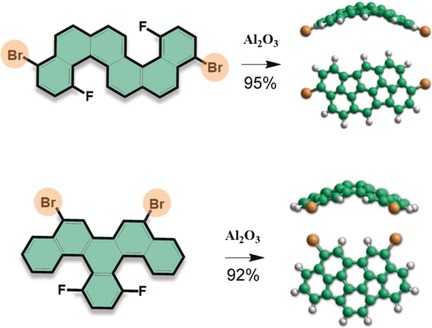
Efficiency that will bowl you over: The activation of aromatic C−F bonds in the presence of more labile C−Br and C−Cl bonds enabled the fully controlled synthesis of halogenated bowl-shaped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons through intramolecular aryl–aryl coupling (see picture). Besides its simplicity and high reproducibility, the technique provides access to halogenated bowl-shaped systems that are not accessible by other methods.
Quinodimethanes | Very Important Paper
Zirconacyclopentadiene-Annulated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- Pages: 4839-4844
- First Published: 23 March 2017
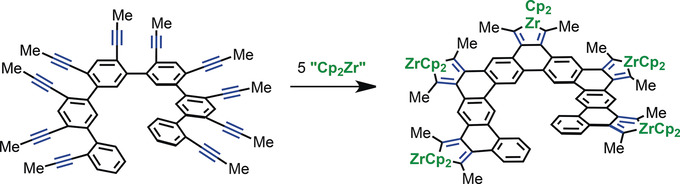
Zirconocene zipper: An efficient fivefold reductive cyclization demonstrates the promise of a new strategy for the construction of graphene nanostructures. Protodemetalation of the resulting zirconacyclopentadiene-annulated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons provides a conceptually unique means for the generation of valuable ortho-quinodimethane structures.
Homogeneous Catalysis
Iron(II)-Catalyzed Hydrophosphination of Isocyanates
- Pages: 4845-4848
- First Published: 24 March 2017
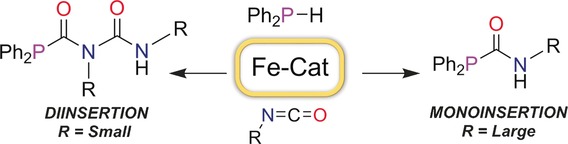
Seeing double: Low-coordinate iron(II) complexes have been used in the hydrophosphination of isocyanates to produce, by mono- and/or diinsertion, phosphinocarboxamides, a new family of derivatized organophosphorus compounds. Small changes in reaction conditions drastically alter the product selectivity.
Click Chemistry
Palladium-Catalyzed Fluorosulfonylvinylation of Organic Iodides
- Pages: 4849-4852
- First Published: 29 March 2017
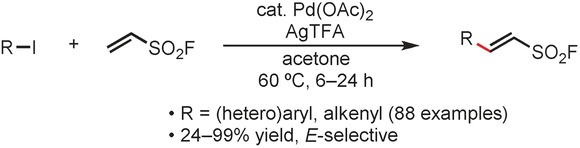
Adding a fluorosulfonylvinyl group: Catalytic Pd(OAc)2 with a stoichiometric amount of silver(I) trifluoroacetate enables the coupling process between either an (hetero)aryl or alkenyl iodide with ethenesulfonyl fluoride. The method is demonstrated in the successful syntheses of eighty-eight otherwise difficult to access compounds, in up to 99 % yields. The method does not require base, phosphine ligand, anhydrous solvent, or an inert atmosphere.
C−H Borylation Reactions | Hot Paper
para-Selective C−H Borylation of (Hetero)Arenes by Cooperative Iridium/Aluminum Catalysis
- Pages: 4853-4857
- First Published: 27 March 2017
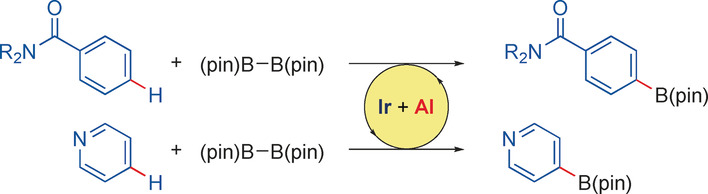
Collect. Select. Reflect: para-Selective C−H borylation of benzamide and pyridine adducts is controlled by a combination of iridium and bulky aluminum-based Lewis acid catalysts. Variously substituted (hetero)arylboronates were prepared, which are versatile synthetic intermediates for complex multi-substituted aromatic compounds.
Electrocatalysis
Oxygen-Containing Amorphous Cobalt Sulfide Porous Nanocubes as High-Activity Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction in an Alkaline/Neutral Medium
- Pages: 4858-4861
- First Published: 27 March 2017
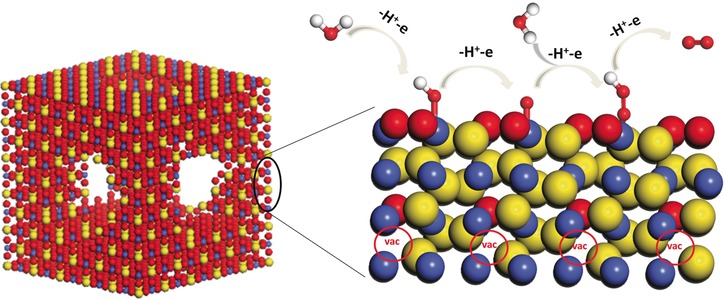
Oxygen-containing amorphous cobalt sulfide porous nanocubes with Co−S dangling bands, a distorted CoS4.6O0.6 octahedral structure, and incorporated oxygen in the CoSx have been prepared. The material shows outstanding electrocatalytic activity for water oxidation in alkaline and neutral electrolytes. vac=vacancy; Co blue, S yellow, O red, H white.
Polymer Chemistry | Hot Paper
Completely Recyclable Monomers and Polycarbonate: Approach to Sustainable Polymers
- Pages: 4862-4866
- First Published: 28 March 2017
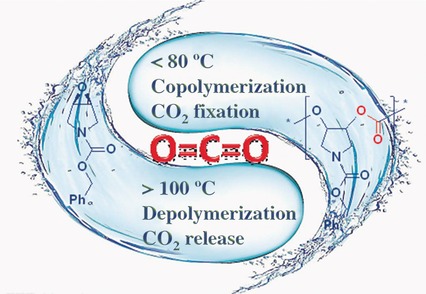
A sustainable plastic was synthesized by dinuclear chromium-complex-mediated copolymerization of CO2 with an epoxide that could be recycled back into the monomer in quantitative yield under mild conditions. Temperature was used as a reversible switch in the recycle process. These characteristics are in accordance with the concept of perfectly sustainable polymers.
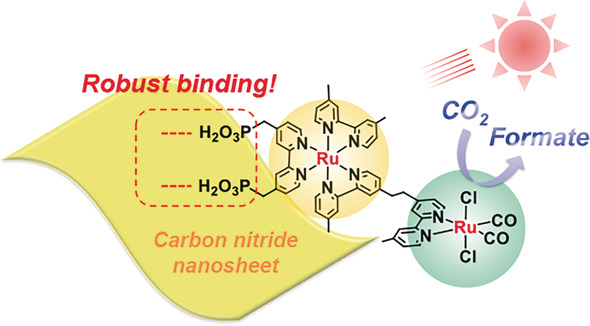
CO2 Fixation | Hot Paper
Robust Binding between Carbon Nitride Nanosheets and a Binuclear Ruthenium(II) Complex Enabling Durable, Selective CO2 Reduction under Visible Light in Aqueous Solution
- Pages: 4867-4871
- First Published: 07 April 2017
Molecular Photoswitches
Photochromism and Dual-Color Fluorescence in a Polyoxometalate–Benzospiropyran Molecular Switch
- Pages: 4872-4876
- First Published: 24 March 2017
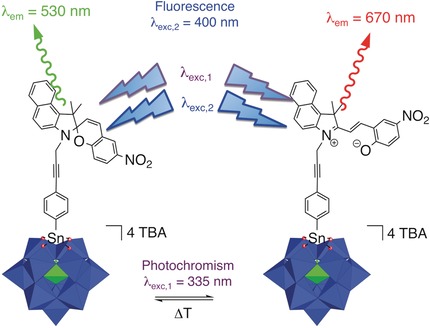
Small cause, big effect: A covalent polyoxometalate (POM)–benzospiropyran (BSPR) dyad is an unprecedented example of an organic–inorganic molecular switch that displays a specific fluorescence feature in each photochromic form. The fluorescence of the BSPR unit of the POM-based hybrid is considerably enhanced compared to BSPR reference compounds, which is attributed to a more easily accessible emitting state in the hybrid.
Electrosynthesis | Very Important Paper
Reagent- and Metal-Free Anodic C−C Cross-Coupling of Aniline Derivatives
- Pages: 4877-4881
- First Published: 02 March 2017
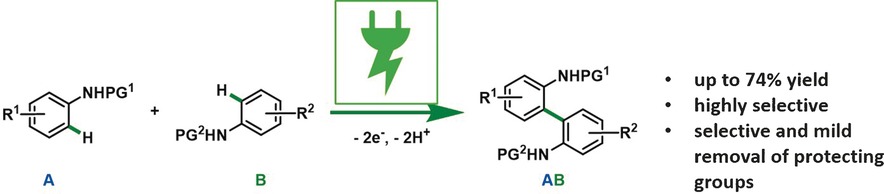
Cross-couplings under electrochemical conditions selectively provide protected 2,2′-diaminobiaryl derivatives. For clean conversion, 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP) and glassy carbon should be used as the electrolyte and anode material, respectively. Easily removable protecting groups enable the stepwise and selective liberation of the amine functional groups.
Iron–Sulfur Clusters | Hot Paper
Ligand Rearrangements at Fe/S Cofactors: Slow Isomerization of a Biomimetic [2Fe-2S] Cluster
- Pages: 4882-4886
- First Published: 30 March 2017
Protonation
Charges Shift Protonation: Neutron Diffraction Reveals that Aniline and 2-Aminopyridine Become Protonated Upon Binding to Trypsin
- Pages: 4887-4890
- First Published: 28 March 2017
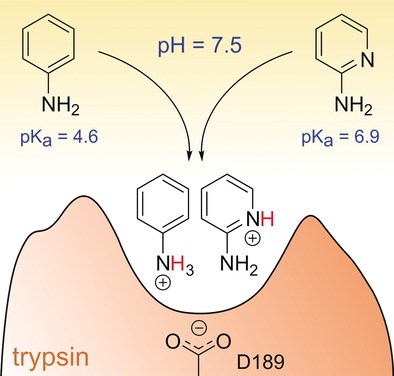
Where are the protons? Hydrogen atoms are usually difficult to visualize experimentally but are key for a proper understanding of protein–ligand recognition. Using neutron crystallography, it was found that, despite its low pKa, the amino group of aniline picks up a proton upon binding to the archetypical serine protease trypsin. In contrast, 2-aminopyridine becomes protonated at the pyridine nitrogen atom to give the more stable tautomer of this molecule.










![Ligand Rearrangements at Fe/S Cofactors: Slow Isomerization of a Biomimetic [2Fe-2S] Cluster](/cms/asset/b44811cc-8e67-4124-95da-4d5c81b0396c/anie201612621-toc-0001-m.jpg)