Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Harnessing Colloidal Crack Formation by Flow-Enabled Self-Assembly (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2017)
- Page: 4363
- First Published: 06 March 2017

Crack formation in a colloidal nanoparticle film can be harnessed by restricting the drying of the colloidal suspension using a flow-enabled self-assembly (FESA) strategy to yield large-area periodic cracks (i.e., microchannels) with tunable spacing. In their Communication on page 4554 ff., Z. Lin and co-workers also show that these uniform microchannels can be utilized as a template to guide the assembly of Au nanoparticles, forming intriguing nanoparticle threads.
Inside Cover: Germabenzenylpotassium: A Germanium Analogue of a Phenyl Anion (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2017)
- Page: 4364
- First Published: 23 March 2017

A germanium analogue of the phenyl anion was synthesized by the reduction of a stable germabenzene with KC8, under concomitant elimination of the aryl group from the Ge atom. In their Communication on page 4588 ff., N. Tokitoh and co-workers show its ambident character with contributions from aromatic and germylene resonance structures, which was supported experimentally and theoretically.
Inside Back Cover: Precisely Regulated and Efficient Locking of Linear Peptides into Stable Multicyclic Topologies through a One-Pot Reaction (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2017)
- Page: 4629
- First Published: 20 March 2017

Precisely regulated and efficient locking of linear peptides into multicyclic topologies through a one-pot reaction (PROP-locking) is reminiscent of playing with the Kongming lock, a traditional Chinese puzzle game. In their Communication on page 4458 ff., C. Wu et al. report a small phenyl molecule with four isosteric thiolate-reactive groups of sequentially varied reactivity, and how this molecule was used for PROP-locking of linear peptides.
Back Cover: Next-Generation Polymer Shells for Inorganic Nanoparticles are Highly Compact, Ultra-Dense, and Long-Lasting Cyclic Brushes (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2017)
- Page: 4630
- First Published: 16 March 2017

Next-generation shells for inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) are polymeric “shields” designed to last. In their Communication on page 4507 ff., E. M. Benetti et al. have demonstrated that when cyclic polymer ligands are grafted onto inorganic NPs, ultra-dense and highly compact brush shells are generated. Core-cyclic shell NPs are significantly more stable than their linear brush-functionalized counterparts and show full bio-inertness towards serum proteins.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Mesoscale Polarization by Geometric Frustration in Columnar Supramolecular Crystals
- First Published: 04 April 2017

Organic Ferroelectrics In their Communication on page 4432 ff., A. L. Goodwin, H.-W. Schmidt, J. Senker, and co-workers describe how supramolecular chemistry meets geometric frustration in the bulk structures of benzene-1,3,5-trisamides.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2017
- Pages: 4367-4378
- First Published: 04 April 2017
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2017
- Pages: 4380-4383
- First Published: 04 April 2017
Author Profile
Obituary
Highlights
Electrocatalysis
Dinitrogen Reduction: Interfacing the Enzyme Nitrogenase with Electrodes
- Pages: 4388-4390
- First Published: 16 March 2017
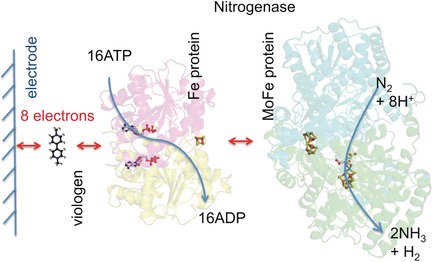
Potential for nitrogenase: Milton, Minteer, and co-workers report the first evidence for the bioelectrochemical reduction of N2 to ammonia by nitrogenase. This complex enzyme could be wired to an electrode by using the soluble mediator methyl viologen; this very simple approach makes it possible to develop a variety of biotechnological devices.
Reviews
Medical Imaging
Label-Free Molecular Imaging of Biological Cells and Tissues by Linear and Nonlinear Raman Spectroscopic Approaches
- Pages: 4392-4430
- First Published: 15 November 2016

Owing to its unique ability to generate spectroscopic fingerprints, Raman spectroscopy is an emerging technique in bioanalysis and biomaterial imaging. The theory behind this method as well as instrumentation and data-processing methods are discussed in this Review, and the progress in medical Raman imaging since 2012 is summarized.
Communications
Organic Ferroelectrics
Mesoscale Polarization by Geometric Frustration in Columnar Supramolecular Crystals
- Pages: 4432-4437
- First Published: 20 March 2017

Supramolecular chemistry meets geometric frustration in axially polar bulk phases of benzene-1,3,5-trisamides (BTAs). The macrodipole moments generated through the formation of supramolecular stacks frustrate during progressive aggregation into hexagonal rod packings. It is shown by total X-ray scattering that the frustration can be utilized to induce spontaneous polarization on the mesoscale.
Magnetic Properties
Large Magnetoelectric Coupling Near Room Temperature in Synthetic Melanostibite Mn2FeSbO6
- Pages: 4438-4442
- First Published: 23 March 2017
DNA Computing
A Molecular Circuit Regenerator to Implement Iterative Strand Displacement Operations
- Pages: 4443-4446
- First Published: 21 March 2017

Regenerating molecular circuit components: Watson–Crick base-pairing imparts a unique structural programmability to DNA, enabling the design of molecular reactions that perform computations. However, many of the current architectures limit devices to a single operational cycle. To overcome this limitation, a device based on coupled enthalpic and entropic reactions that permits the regeneration of molecular circuit components is introduced.
Photochemical Organocatalysis
Enantioselective Formal α-Methylation and α-Benzylation of Aldehydes by Means of Photo-organocatalysis
- Pages: 4447-4451
- First Published: 21 March 2017

Formally achieved: Enantioenriched α-alkylated aldehydes (2) are synthesized by exploiting the ability of chiral enamines (A) to generate radicals from (phenylsulfonyl)alkyl iodides (1) and trap them in a stereoselective fashion. Coupling this step with the simple desulfonylation of 2 provides a method to install either a methyl or a benzyl moiety with high stereoselectivity. SET=single-electron transfer.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Ring Shuttling Controls Macroscopic Motion in a Three-Dimensional Printed Polyrotaxane Monolith
- Pages: 4452-4457
- First Published: 22 March 2017
Peptide Cyclization | Hot Paper
Precisely Regulated and Efficient Locking of Linear Peptides into Stable Multicyclic Topologies through a One-Pot Reaction
- Pages: 4458-4463
- First Published: 27 February 2017

Bioactive tricyclic peptide ligands: A small phenyl molecule with four isosteric thiolate-reactive groups of varied reactivity was discovered. This molecule was used in combination with cysteine/penicillamine thiolate groups of different nucleophilic reactivity for precisely regulated and efficient locking of a linear peptide into multicyclic topologies through a one-pot reaction.
Mass Spectrometry | Hot Paper
Diversity in Gold Finger Structure Elucidated by Traveling-Wave Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry
- Pages: 4464-4467
- First Published: 20 March 2017

A golden opportunity: Traveling-wave ion mobility (TWIM) mass spectrometry (MS) was used to separate isomeric metalated peptide ions derived from gold(I) complexes, enabling the acquisition of distinct product ion spectra for each isomer (blue and red). Measurements of the collision cross-sections showed that the aurated peptide has a slightly more compact structure than the parent zinc finger.
Antibiotic Resistance | Hot Paper
Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms with a Carbapenem-Based Fluorogenic Probe
- Pages: 4468-4472
- First Published: 23 March 2017

Lighting up resistance: A fluorogenic probe for the detection of carbapenemase activity has been developed. The utilization of carbapenem as the enzyme recognition motif in this reagent leads to remarkable specificity for carbapenemases over other prevailing β-lactamases, enabling the rapid detection of carbapenemases.
Decontamination with POMs
A Polyoxoniobate–Polyoxovanadate Double-Anion Catalyst for Simultaneous Oxidative and Hydrolytic Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulants
- Pages: 4473-4477
- First Published: 21 March 2017
Synthetic Methods
Synthesis of Complex Phenols Enabled by a Rationally Designed Hydroxide Surrogate
- Pages: 4478-4482
- First Published: 24 March 2017

The conversion of aryl halides to phenols under mild reaction conditions is a longstanding and formidable challenge in organic chemistry. The rational design of a broadly applicable Pd-catalyzed method to prepare phenols with benzaldehyde oxime as a hydroxide surrogate is now reported. These reactions occur under mildly basic conditions and enable the late-stage hydroxylation of functionally dense aryl halides.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Synthesis and Optoelectronic Properties of Hexa-peri-hexabenzoborazinocoronene
- Pages: 4483-4487
- First Published: 21 March 2017

A BN-doped coronene derivative in which the central benzene ring has been replaced by a borazine core is described. UV/Vis absorption, emission, and electrochemical investigations show that the introduction of the central BN core induces a dramatic widening of the HOMO–LUMO gap and an enhancement of the blue-shifted emissive properties with respect to its all-carbon congener.
Electrocatalysis
Highly Branched Metal Alloy Networks with Superior Activities for the Methanol Oxidation Reaction
- Pages: 4488-4493
- First Published: 23 March 2017

Hierarchically structured Ni-Cu alloys composed of 3D network-like microscopic branches with nanoscopic dendritic feelers on each branch were crafted by a facile and efficient hydrogen evolution-assisted electrodeposition approach. The resultant structures showed excellent electrochemical response and electrocatalytic activity towards methanol oxidation.
Gold Nanocatalysis
Surfactant-Assisted Stabilization of Au Colloids on Solids for Heterogeneous Catalysis
- Pages: 4494-4498
- First Published: 22 March 2017
Strained Molecules
Photochemical Generation of Strained Cycloalkynes from Methylenecyclopropanes
- Pages: 4499-4501
- First Published: 21 March 2017

Growing strains: The hydrocarbons 1-cyclopentylidene-1a,9b-dihydro-1H-cyclopropa[l]phenanthrene and 1-cyclobutylidene-1a,9b-dihydro-1H-cyclopropa[l]phenanthrene undergo photolysis in solution at ambient temperature to produce cyclohexyne and cyclopentyne, respectively (see scheme). These strained cycloalkynes, formed via the putative cycloalkylidenecarbenes, were intercepted as Diels–Alder adducts.
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Trimetallic Oxyhydroxide Coralloids for Efficient Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysis
- Pages: 4502-4506
- First Published: 21 March 2017

Coralloid-like W0.5Co0.5−xFex oxyhydroxides with a precisely controlled amount of Fe were directly grown on the conducting substrate in a facile wet-chemical approach. This material exhibits volcano-type oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity as a function of the Fe content, and the optimized variant, W0.5Co0.4Fe0.1 is particularly active and stable towards OER catalysis.
Surface Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Next-Generation Polymer Shells for Inorganic Nanoparticles are Highly Compact, Ultra-Dense, and Long-Lasting Cyclic Brushes
- Pages: 4507-4511
- First Published: 13 March 2017

Shields designed to last: When cyclic polymer ligands are grafted onto inorganic nanoparticles (NPs), ultra-dense and highly compact brush shells are generated. Core-cyclic shell NPs are significantly more stable than their linear brush-functionalized counterparts and show full bio-inertness towards serum proteins.
High-Nitrogen Compounds
A Symmetric Co(N5)2(H2O)4⋅4 H2O High-Nitrogen Compound Formed by Cobalt(II) Cation Trapping of a Cyclo-N5− Anion
- Pages: 4512-4514
- First Published: 22 March 2017

Light my fire: The metal pentazolate anion complex Co(N5)2(H2O)4⋅4 H2O was obtained by reacting (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl with Co(NO3)2⋅6 H2O in a methanol/water solution at room temperature. Single-crystal X-ray crystallographic characterization and the physical properties of the comburent material are presented.
Circumstellar Chemistry
HACA's Heritage: A Free-Radical Pathway to Phenanthrene in Circumstellar Envelopes of Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars
- Pages: 4515-4519
- First Published: 22 March 2017

HACA quo vadis? Hydrogen-abstraction/acetylene-addition (HACA) has been central to rationalize the origin and the formation routes leading to the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). The detection of phenanthrene in the reaction of ortho-biphenylyl radical with acetylene under combustion-like conditions validates the formation of PAHs beyond naphthalene and provide legitimacy to alternative scenarios such as a vinylacetylene-mediated mechanism.
Heteroarenes
Catalytic Direct-type 1,4-Addition Reactions of Alkylazaarenes
- Pages: 4520-4524
- First Published: 20 March 2017
Supramolecular Chemistry
Hierarchical Corannulene-Based Materials: Energy Transfer and Solid-State Photophysics
- Pages: 4525-4529
- First Published: 23 March 2017

But first, coffee: A rapid ligand-to-ligand energy transfer observed in the first example of a donor–acceptor corannulene-based scaffold is similar to the energy that a cup of coffee could provide. Many components can be added to the corannulene bowl, similar to cream and sugar added to coffee, highlighting the possibility of merging the intrinsic properties of π-bowls with the tunability of hierarchical materials for applications in optoelectronic devices.
Aminocarbonylation
Nitroarenes as the Nitrogen Source in Intermolecular Palladium-Catalyzed Aryl C–H Bond Aminocarbonylation Reactions
- Pages: 4530-4534
- First Published: 29 March 2017

C−H functionalization: A three-component palladium-catalyzed aminocarbonylation of sp2 C−H bonds using nitroarenes as the nitrogen source was achieved using Mo(CO)6 as the reductant and origin of the CO. This intermolecular C−H bond functionalization does not require any exogenous ligand to be added.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Enantioselective Palladium-Catalyzed Carbonylative Carbocyclization of Enallenes via Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling with Terminal Alkynes: Efficient Construction of α-Chirality of Ketones
- Pages: 4535-4539
- First Published: 27 March 2017

From CO to ketones with the introduction of α-chirality: A PdII/Brønsted acid-catalyzed enantioselective carbonylation–carbocyclization of enallenes has been developed, proceeding through an efficient CO and olefin insertion cascade to yield ketones with α-chirality. A number of chiral cyclopentenones could be easily synthesized in good to excellent enantioselectivity and good yields.
Rhodium Catalysis
Asymmetric Synthesis of Spiropyrazolones by Rhodium-Catalyzed C(sp2)−H Functionalization/Annulation Reactions
- Pages: 4540-4544
- First Published: 22 March 2017

Enantioenriched five-membered-ring 4-spiro-5-pyrazolones were synthesized by the rhodium-catalyzed C(sp2)−H functionalization of 4-aryl-5-pyrazolones followed by a [3+2] annulation reaction with alkynes. The use of a chiral SCpRh catalyst (see scheme) led to excellent enantioselectivity, reactivity, and regioselectivity in this cascade process.
Photochemistry
Merging Distal Alkynyl Migration and Photoredox Catalysis for Radical Trifluoromethylative Alkynylation of Unactivated Olefins
- Pages: 4545-4548
- First Published: 20 March 2017

1+1>2: A redox-neutral protocol for the visible-light catalyzed radical alkynylation of unactivated olefins is disclosed. The intramolecular migration of an alkynyl group, by cleaving an inert C−C σ bond, is realized for the first time. A broad range of synthetically useful trifluoroethylated linear alkynes are efficiently produced under mild reaction conditions.
11C-Labeling
Application of Methyl Bisphosphine-Ligated Palladium Complexes for Low Pressure N-11C-Acetylation of Peptides
- Pages: 4549-4553
- First Published: 16 March 2017
Colloidal Microchannel | Very Important Paper
Harnessing Colloidal Crack Formation by Flow-Enabled Self-Assembly
- Pages: 4554-4559
- First Published: 02 March 2017
Polymer Chemistry
Coordination Polymerization of Renewable 3-Methylenecyclopentene with Rare-Earth-Metal Precursors
- Pages: 4560-4564
- First Published: 22 March 2017

Polyamorous catalysis: Rare-earth-metal precursors supported by moderately bulky ligands mediated polymerization of renewable 3-methylenecyclopentene (MCP) monomers. The rare-earth-metal catalysts were highly active and yielded regiopure 1,4-poly(MCP) with targeted molecular weights across a wide range of polymerization temperatures.
Multicomponent Reactions
One-Pot Multicomponent Synthesis of β-Amino Amides
- Pages: 4565-4568
- First Published: 22 March 2017
Synthetic Methods
Use of a Traceless Activating and Directing Group for the Construction of Trifluoromethylpyrazoles: One-Pot Transformation of Nitroolefins and Trifluorodiazoethane
- Pages: 4569-4574
- First Published: 22 March 2017

Leaves discreetly when the job is done: A one-pot reaction of trifluorodiazoethane and higher perfluorinated homologues with various nitroolefins takes advantage of the nitro group as a traceless activating and directing group that is released in the aromatization step to produce 4-substituted 3-perfluoroalkyl pyrazoles with complete regioselectivity (see scheme). The method was applied to the synthesis of the fungicide penthiopyrad.
Heterocycles
Synthesis and Properties of Aza-ullazines
- Pages: 4575-4578
- First Published: 23 March 2017

Ring, ring: Aza-ullazines, which represent a new heterocyclic core structure, were synthesized through a four-step reaction, including a Sonogashira reaction and metal-free cyclization promoted by p-toluenesulfonic acid. The optical and electrochemical properties of selected derivatives were investigated, and they were found to have similar absorption and emission spectra but a higher oxidation potential than the parent ullazine core.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Benzo[b]thiophene 1,1-Dioxides
- Pages: 4579-4582
- First Published: 23 March 2017
![Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Benzo[b]thiophene 1,1-Dioxides](/cms/asset/b682c025-0c3d-468d-9eed-9af82bb38982/anie201701409-toc-0001-m.jpg)
(Sul)fone a friend: The iridium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of benzothiophene 1,1-dioxides provided access to highly enantiomerically enriched sulfones with substituents at the 2- and 3-position (see scheme). Sulfones of this type are of interest as core structures of agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. They can also be further reduced to chiral 2,3-dihydrobenzothiophenes, which are not always directly accessible by asymmetric hydrogenation.
Organocatalysis
Catalytic Asymmetric N-Alkylation of Indoles and Carbazoles through 1,6-Conjugate Addition of Aza-para-quinone Methides
- Pages: 4583-4587
- First Published: 23 March 2017

An organocatalytic strategy for the asymmetric N-alkylation of indoles and carbazoles was developed in which in situ generated aza-para-quinone methides are employed as the alkylating reagent. With the proper choice of a chiral phosphoric acid and N-protective group (P), the intermolecular C−N bond formation with various indole and carbazole nucleophiles proceeds under mild conditions with excellent efficiency and enantioselectivity.
Organogermanium Compounds | Very Important Paper
Germabenzenylpotassium: A Germanium Analogue of a Phenyl Anion
- Pages: 4588-4592
- First Published: 08 March 2017

Ge is not C: Reduction of a stable germabenzene with KC8 resulted in the formation of the germanium analogue of phenylpotassium, under concomitant elimination of the aryl group from the Ge atom. Its ambident character with contributions from aromatic and germylene resonance structures was supported experimentally and theoretically.
Borasilenes
An Isolable Potassium Salt of a Borasilene–Chloride Adduct
- Pages: 4593-4597
- First Published: 22 March 2017

The potassium salt of a borasilene–chloride adduct was synthesized and isolated. Its reactivity and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis revealed the double-bond character of its Si=B bond and reduced Lewis acidity. This adduct provides a cyclic product by formal intramolecular C−H insertion across the Si=B bond, possibly via the corresponding base-free borasilene.
Supramolecular Organization | Very Important Paper
Shape-Assisted Self-Organization in Highly Disordered Liquid Crystal Phases
- Pages: 4598-4602
- First Published: 22 March 2017

The heart of the crystal: A dumbbell-shaped molecule R−C6H10−CH=CH−C6H4−CH=CH−C6H10−R (R=nC5H11) generates a liquid crystal phase (X phase) between two N phases. The X phase was investigated by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy and molecular dynamics simulation. A self-organization mechanism is postulated for formation of the layered structure.
Polysaccharide Structure
Unravelling a Direct Role for Polysaccharide β-Strands in the Higher Order Structure of Physical Hydrogels
- Pages: 4603-4607
- First Published: 23 March 2017

Agarose hydrogels are stiff but chemical carboxylation of the polysaccharide backbone leads to formation of soft gels. Carboxyl groups prevent interchain organization of the polysaccharide into double helices, thereby promoting a β-strand conformation instead. Raman optical activity was used to identify and quantify the higher order polysaccharide structure directly in the gel phase.
Photobiochemistry | Hot Paper
Green-Light-Induced Inactivation of Receptor Signaling Using Cobalamin-Binding Domains
- Pages: 4608-4611
- First Published: 20 March 2017

When green means stop: The fusion of a bacterial cobalamin (vitamin B12) binding domain (CBD) and a mammalian kinase domain (KD) results in constitutively active signaling in the dark. Signaling leads to developmental defects in zebrafish that can be avoided by green-light illumination to permit normal development (AdoCbl=5′-deoxyadenosylcobalamin, MYR=myristoylation membrane anchor).
Synthetic Methods
Preparation and Application of Solid, Salt-Stabilized Zinc Amide Enolates with Enhanced Air and Moisture Stability
- Pages: 4612-4616
- First Published: 22 March 2017

Solid chemistry: A convenient method for the preparation of solid zinc enolates with enhanced air and moisture stability is described. These enolates undergo Pd- and Cu-catalyzed cross-couplings. The reactive N-morpholino amides can be readily converted into aldehydes or various ketones. These new zinc enolates were employed in the short synthesis of a 3-formylindole derivative that is a potent inhibitor of tubulin polymerization.
Protein Structures | Hot Paper
Structural Adaptation of a Protein to Increased Metal Stress: NMR Structure of a Marine Snail Metallothionein with an Additional Domain
- Pages: 4617-4622
- First Published: 23 March 2017

A heavy hitter: Metallothioneins are small proteins that are capable of binding heavy metals through Cys residues, thereby forming distinct metal clusters. It is demonstrated that the MT from the snail Littorina littorea displays a novel three-domain structure that increases its metal-loading capacity. This biologically significant feature may help the organism to survive in environments polluted with heavy metals.
Biofabrication
Control of Nanoparticle Release Kinetics from 3D Printed Hydrogel Scaffolds
- Pages: 4623-4628
- First Published: 22 March 2017

Released in print: Formulations of positively and negatively charged mesoporous silica nanoparticles or spherical gold nanoparticles with a hydrogel bioink were used for biofabrication. Negatively charged nanoparticles are released rapidly and positively charged nanoparticles slowly. This generic principle may allow nanoparticles to be used in biofabrication for spatiotemporal control of drug release.









 ) is found to show a massive non-linear magnetoelectric coupling at 260 K, breaking local symmetry through the cationic off-centering under the application of an external magnetic field.
) is found to show a massive non-linear magnetoelectric coupling at 260 K, breaking local symmetry through the cationic off-centering under the application of an external magnetic field.