Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: A Halogen-Bond-Induced Triple Helicate Encapsulates Iodide (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40/2016)
- Page: 12111
- First Published: 11 August 2016

Like Jörmungandr—the World Serpent of Norse mythology that encircled Midgard—arylethynyl oligomers envelop their guests with halogen bonds. In their Communication on page 12398 ff., O. B. Berryman et al. present the first halogen-bond-induced triple helicate to encapsulate iodide in solution and the solid state. Strong and linear halogen bonds promote this intricate and robust self-assembly. Garron Hale (Univ. of Oregon) is gratefully acknowledged for assisting with preparation of the cover artwork.
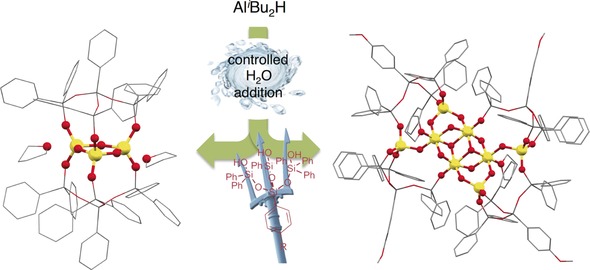
Inside Cover: Trapping Aluminum Hydroxide Clusters with Trisilanols during Speciation in Aluminum(III)–Water Systems: Reproducible, Large Scale Access to Molecular Aluminate Models (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40/2016)
- Page: 12112
- First Published: 28 July 2016

Picking out early aggregates with tripodal trisilanols. In their Communication on page 12325 ff., C. Limberg and co-workers show that tripodal trisilanols stabilize aluminum hydroxide aggregates formed during the hydrolysis of AliBu2H with different sizes dependent on the amount of water added. In the picture, the source of water is the Neptune Fountain in Berlin and the trident of Neptune represents the trident nature of trisilanols employed to trap clusters. Graphic credit: Kapil S. Kalore and Gerd Wallner.
Inside Back Cover: Constructing Interfacial Energy Transfer for Photon Up- and Down-Conversion from Lanthanides in a Core–Shell Nanostructure (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40/2016)
- Page: 12543
- First Published: 11 August 2016

The control of energy transfer at the nanometer length scale leads to the discovery of a new mechanistic strategy for manipulating the photon emission of lanthanides. In their Communication on page 12356 ff., B. Zhou, Q. Y. Zhang, Y. H. Tsang et al. demonstrate the realization of both up- and down-conversion luminescence of lanthanides by using interfacial energy transfer with gadolinium as energy donor in a core–shell nanostructure.
Back Cover: Asymmetric Ring Opening/Cyclization/Retro-Mannich Reaction of Cyclopropyl Ketones with Aryl 1,2-Diamines for the Synthesis of Benzimidazole Derivatives (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40/2016)
- Page: 12544
- First Published: 20 July 2016

The first asymmetric ring-opening/cyclization/retro-Mannich reaction of cyclopropyl ketones with aryl-1,2-diamines is described by X. M. Feng, X. H. Liu and co-workers in their Communication on page 12228 ff. The construction of benzimidazole backbones and establishing the stereochemistry in their side chains are accomplished in only one step in the presence of a N,N′-dioxide/ScIII complex. ‘‘The carp has leaped through the dragon's gate’’ means success in a Chinese saying. The N,N′-dioxide/ScIII complex is the dragon's gate, the reagents are the carp, and the successfully generated product is the dragon.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Photon Energy Becomes the Third Dimension in Crystallographic Texture Analysis
- First Published: 19 September 2016

Crystallographic Texture. H. C. Lichtenegger et al. describe in their Communication on page 12190 ff. a method to determine crystallographic texture. The method is based on energy-dispersive Laue diffraction and enables 3D information to be obtained without sample rotation.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40/2016
- Pages: 12115-12136
- First Published: 19 September 2016
Corrigenda
Corrigendum: Substrate-Controlled Product Divergence: Conversion of CO2 into Heterocyclic Products
- Page: 12136
- First Published: 09 May 2016
Corrigendum: Benzimidazobenzothiazole-based Bipolar Hosts to Harvest Nearly All of the Excitons from Blue Delayed Fluorescence and Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes
- Page: 12136
- First Published: 04 July 2016
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40/2016
- Pages: 12138-12141
- First Published: 19 September 2016
Author Profiles
News
Book Reviews
Handbook of Bibliometric Indicators. Quantitative Tools for Studying and Evaluating Research By Roberto Todeschini and Alberto Baccini.
- Page: 12144
- First Published: 09 September 2016
Highlights
Asymmetric Catalysis
Balancing C=C Functionalization and C=O Reduction in Cu−H Catalysis
- Pages: 12148-12149
- First Published: 04 August 2016
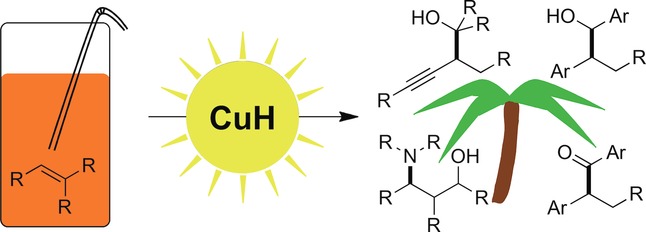
Coppercabana: The copper(I) hydride catalyzed functionalization of unactivated alkenes has been shown to be compatible with conventional carbonyl reduction. Through the combination of both pathways or complete suppression of C=O reduction in favor of C=C functionalization, methods for the stereoselective synthesis of a variety of chiral molecules have been developed.
Minireviews
Sustainable Chemistry
Which Metals are Green for Catalysis? Comparison of the Toxicities of Ni, Cu, Fe, Pd, Pt, Rh, and Au Salts
- Pages: 12150-12162
- First Published: 17 August 2016
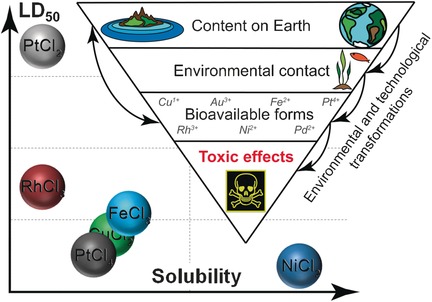
Heavy weights versus the light weights: A comparison of available data on biological activity of metals commonly used in catalysis suggests that the assumption of toxic heavy metals and benign lighter metals should be re-evaluated. The available experimental data are insufficient for accurate evaluation of biological activity of these metals. Therefore, without dedicated experimental measurements, toxicity should not be used as a “selling point” when describing new catalysts.
Reviews
Synthetic Methods
Harnessing the Power of the Water-Gas Shift Reaction for Organic Synthesis
- Pages: 12164-12189
- First Published: 06 September 2016
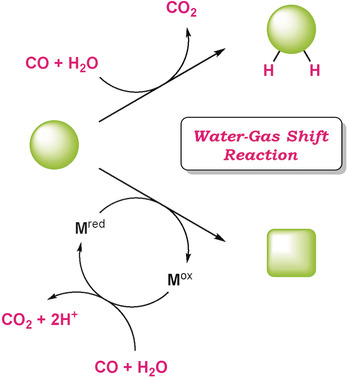
New directions for a classic: In addition to its fundamental role in the production of hydrogen, the water-gas shift reaction has found application in a multitude of reductive transformations in organic synthesis. These include hydrogenation-type reactions, as well as catalytic, overall-reductive processes wherein the CO/H2O couple can act as the terminal reductant.
Communications
Crystallographic Texture
Photon Energy Becomes the Third Dimension in Crystallographic Texture Analysis
- Pages: 12190-12194
- First Published: 02 August 2016
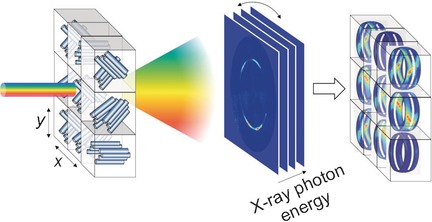
In full view: A new method to determine crystallographic texture based on energy-dispersive Laue diffraction exploits the curvature of the Ewald sphere to obtain 3D information in one shot without sample rotation, which opens up unprecedented spatial resolution. The principle was demonstrated on a complex carbon fiber system as well as the biomineralized exocuticle tissue of the American lobster.
Photochemistry | Hot Paper
Near-Infrared Photoinduced Coupling Reactions Assisted by Upconversion Nanoparticles
- Pages: 12195-12199
- First Published: 25 August 2016
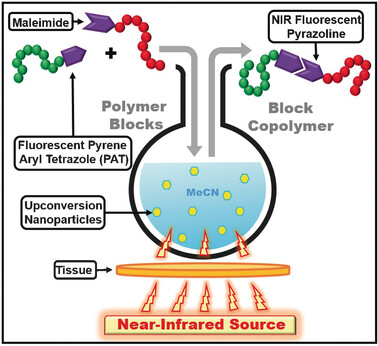
Gently does it: The first example of upconversion photoinduced coupling chemistry based on the established tetrazole–ene cycloaddition system induced by near-infrared light is introduced. The power of the technique, including tissue penetration, is demonstrated for small-molecule ligation, macromolecular end-group modification as well as polymer–polymer ligation.
Computational Chemistry
Towards J/mol Accuracy for the Cohesive Energy of Solid Argon
- Pages: 12200-12205
- First Published: 04 September 2016
Crystallization
Distinct Short-Range Order Is Inherent to Small Amorphous Calcium Carbonate Clusters (<2 nm)
- Pages: 12206-12209
- First Published: 09 September 2016
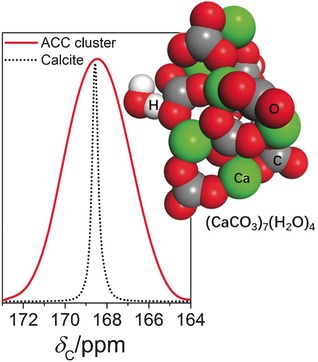
Proto-calcite short-range order was found in ligand-stabilized amorphous calcium carbonate clusters with a very small CaCO3 core 1.4 nm in diameter consisting of only seven CaCO3 units. This supports the notion of a structural link between prenucleation clusters and the postnucleation amorphous phase.
Environmental Chemistry
DNA Nanogels To Snare Carcinogens: A Bioinspired Generic Approach with High Efficiency
- Pages: 12210-12213
- First Published: 01 September 2016
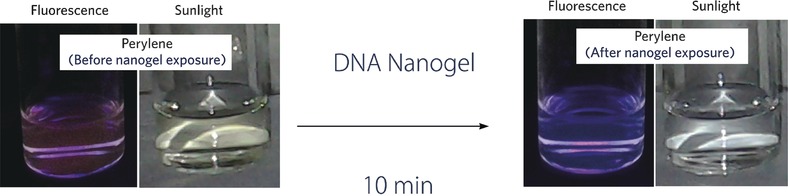
Take it away: DNA nanogels were developed as a biomimetic scavenging agent by exploiting the generic complexation of DNA with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Up to 720 μg of PAH per gram of DNA nanogel are taken up and the uptake is rapid, reaching 50 % loading after 15 minutes. Beyond PAHs, DNA nanogels may be useful for the generic removal of genotoxins from water, since most known molecules that strongly associate with DNA are mutagenic.
Main-Group Chemistry
Metal-Free Activation of Hydrogen, Carbon Dioxide, and Ammonia by the Open-Shell Singlet Biradicaloid [P(μ-NTer)]2
- Pages: 12214-12218
- First Published: 01 September 2016
![Metal-Free Activation of Hydrogen, Carbon Dioxide, and Ammonia by the Open-Shell Singlet Biradicaloid [P(μ-NTer)]2](/cms/asset/453a12a9-18b4-46fc-a31a-ee1a019ad045/anie201606892-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Don't wait for activation: The singlet biradicaloid [P(μ-NTer)]2 readily reacts with H2, CO2, or NH3 at ambient temperature. The addition of H2 is reversible whereas CO2 is reduced to CO with formation of “biradicaloid monoxide”. Activation of ammonia causes the P2N2 scaffold to rearrange to give an azadiphosphiridine.
Dehydrogenation
Frustrated Lewis Pair Catalyzed Dehydrogenative Oxidation of Indolines and Other Heterocycles
- Pages: 12219-12223
- First Published: 05 September 2016
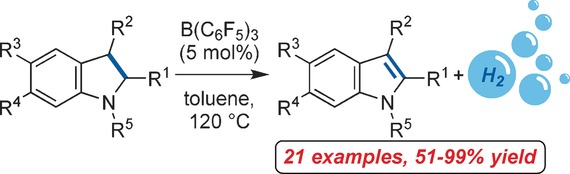
The acceptorless dehydrogenation of N-protected indolines and other heterocycles is catalyzed by frustrated Lewis pairs. Mechanistic as well as quantum-mechanical studies revealed the liberation of molecular hydrogen to be the rate-determining step. The addition of a weaker Lewis acid as a hydride shuttle increased the reaction rate by a factor of 2.28.
Heterocycles
Tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane-Catalyzed Acceptorless Dehydrogenation of N-Heterocycles
- Pages: 12224-12227
- First Published: 19 August 2016
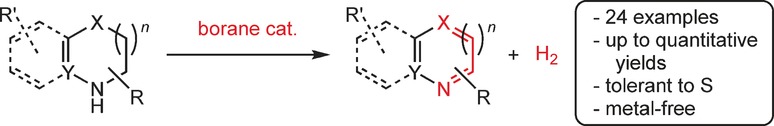
B-side of borane: A metal-free acceptorless dehydrogenation of N-heterocycles was realized by using an electrophilic borane. This protocol affords synthetically important N-heteroarenes in high yield. The borane catalyst exhibits unprecedented chemoselectivity as it is tolerant to sulfur functionalities and demonstrates superior reactivity in the synthesis of benzothiazoles compared to the conventional metal-catalyzed methods.
Heterocycle Synthesis
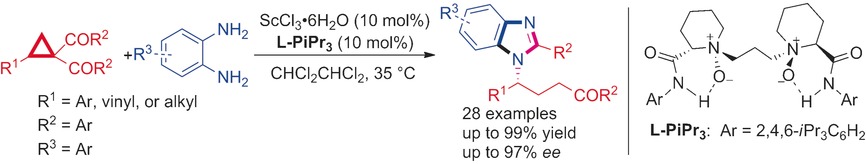
Asymmetric Ring Opening/Cyclization/Retro-Mannich Reaction of Cyclopropyl Ketones with Aryl 1,2-Diamines for the Synthesis of Benzimidazole Derivatives
- Pages: 12228-12232
- First Published: 04 July 2016
Cascade Reactions
GaCl3-Mediated Reactions of Donor–Acceptor Cyclopropanes with Aromatic Aldehydes
- Pages: 12233-12237
- First Published: 30 August 2016
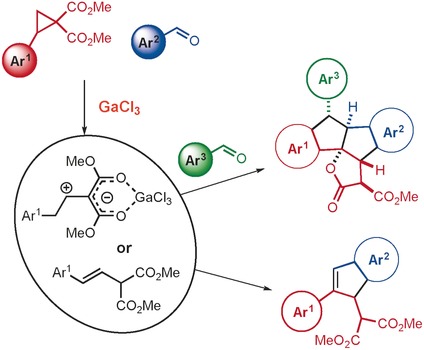
Old reagents, new products: A new strategy for the cascade assembly of substituted indenes and polycyclic lactones based on reactions of donor–acceptor cyclopropanes and styrylmalonates with aromatic aldehydes has been developed. Use of GaCl3 makes it possible to change the direction of the reaction and to perform the process in a multicomponent version (27 examples).
Crystalline Phases
From Sponges to Nanotubes: A Change of Nanocrystal Morphology for Acute-Angle Bent-Core Molecules
- Pages: 12238-12242
- First Published: 05 September 2016
Bioorthogonal Reactions
Vinylboronic Acids as Fast Reacting, Synthetically Accessible, and Stable Bioorthogonal Reactants in the Carboni–Lindsey Reaction
- Pages: 12243-12247
- First Published: 08 September 2016
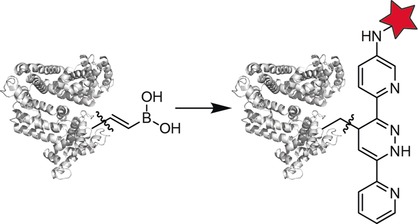
Bioorthogonal iEDDA reagents: Vinylboronic acids (VBAs) were studied as non-strained, synthetically accessible, and water-soluble bioorthogonal reagents in the Carboni–Lindsey reaction with dipyridyl-s-tetrazines. The VBAs were shown to be biocompatible, non-toxic, and highly stable in aqueous media and cell lysate. Furthermore, VBAs were used orthogonally to the strain-promoted alkyne–azide cycloaddition for protein modification.
Enzyme Catalysis
From Alkanes to Carboxylic Acids: Terminal Oxygenation by a Fungal Peroxygenase
- Pages: 12248-12251
- First Published: 30 August 2016
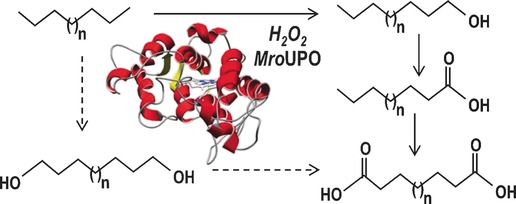
A peroxygenase from the fungus Marasmius rotula was found to catalyze a cascade of mono- and diterminal oxygenation reactions of long-chain n-alkanes to carboxylic acids in the presence of H2O2 as the sole cosubstrate (see scheme). This peroxygenase type has great advantages for the mild activation of alkanes, with its self-sufficient monooxygenase activity and its ability to hydroxylate the most unreactive terminal positions.
Electrocatalysis
Aligned MoOx/MoS2 Core–Shell Nanotubular Structures with a High Density of Reactive Sites Based on Self-Ordered Anodic Molybdenum Oxide Nanotubes
- Pages: 12252-12256
- First Published: 07 September 2016
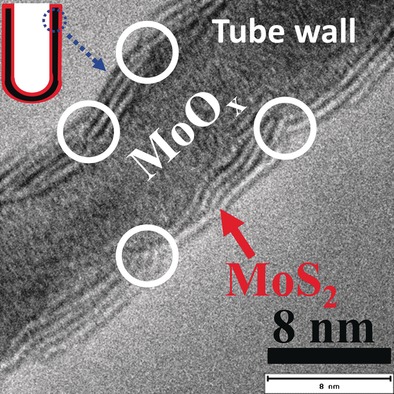
Anodic molybdenum oxide nanotube arrays were formed. These MoOx nanotube layers can be converted into a MoOx/MoS2 nanotubular core–shell structure with bent MoS2 nanosheets consisting of stacks of typically four S-Mo-S layer units, which are discordantly grown on the MoOx substrate, exposing catalytically active end planes to the surrounding. These structures are highly promising for applications in electrocatalysis.
3D Nanomaterials
Facile Synthesis of Three-Dimensional Pt-TiO2 Nano-networks: A Highly Active Catalyst for the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia–Borane
- Pages: 12257-12261
- First Published: 06 September 2016
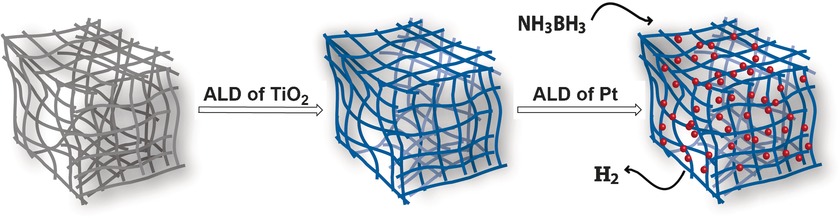
A 3D peptide nanofiber aerogel was coated with TiO2 by atomic layer deposition (ALD) with angstrom-level thickness precision. This nano-network was further decorated with Pt nanoparticles (Pt NPs; see picture; red) using ozone-assisted ALD. The 3D Pt-TiO2 nano-network shows superior catalytic activity in hydrolysis of ammonia–borane, generating 3 equivalents of H2.
Nitrogen Fixation | Hot Paper
Proton-Coupled Reduction of an Iron Cyanide Complex to Methane and Ammonia
- Pages: 12262-12265
- First Published: 08 September 2016
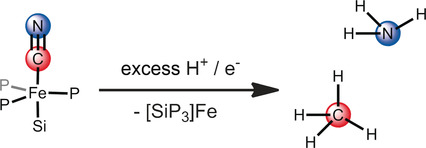
Reductive cleavage of cyanide: A trigonal bipyramidal iron cyanide complex is shown to evolve methane and ammonia upon exposure to proton and electron equivalents at low temperature (see picture). Terminally bound Fe(CNH) and Fe(CNH2) complexes are characterized as possible intermediates in this CN− cleavage reaction.
CO2 Utilization
Ruthenium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Dialkoxymethane Ethers Utilizing Carbon Dioxide and Molecular Hydrogen
- Pages: 12266-12269
- First Published: 01 September 2016
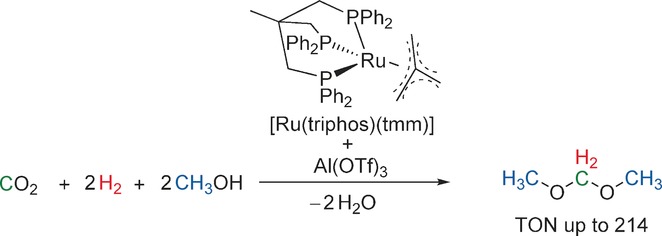
Come together! The molecular catalyst [Ru(triphos)(tmm)] in combination with the Lewis acid Al(OTf)3 enables the synthesis of dimethoxymethane from carbon dioxide, molecular hydrogen and methanol. This new catalytic reaction provides the first synthetic example for the selective conversion of carbon dioxide and hydrogen into the formaldehyde oxidation level, thus opening access to new molecular structures using this important C1 source.
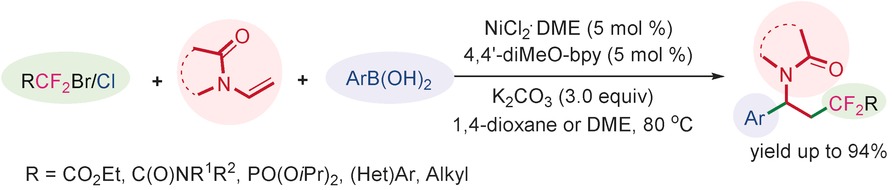
Cross-Coupling
Tandem Difluoroalkylation-Arylation of Enamides Catalyzed by Nickel
- Pages: 12270-12274
- First Published: 08 September 2016
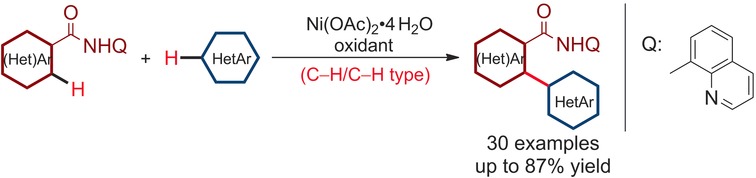
Homogeneous Catalysis
Nickel Catalysis Enables Oxidative C(sp2)–H/C(sp2)–H Cross-Coupling Reactions between Two Heteroarenes
- Pages: 12275-12279
- First Published: 06 September 2016
Heterocycle Synthesis
Enantioselective Nucleophilic β-Carbon-Atom Amination of Enals: Carbene-Catalyzed Formal [3+2] Reactions
- Pages: 12280-12284
- First Published: 06 September 2016
![Enantioselective Nucleophilic β-Carbon-Atom Amination of Enals: Carbene-Catalyzed Formal [3+2] Reactions](/cms/asset/fb7a3d0c-4d8d-4f46-a410-fda0e2544dbc/anie201606571-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Focus on the β-C: The aza-Michael addition of protected hydrazine to a catalytically generated unsaturated acyl azolium intermediate provides a highly efficient approach for enantioselective β-carbon-atom amination of enals. The heterocyclic products, prepared by using this method, are common scaffolds found in bioactive molecules, and can be readily transformed into β3-amino-acid derivatives. NHC=N-heterocyclic carbene.
Alkene Synthesis
Stereospecific Synthesis of Alkenes by Eliminative Cross-Coupling of Enantioenriched sp3-Hybridized Carbenoids
- Pages: 12285-12289
- First Published: 01 September 2016
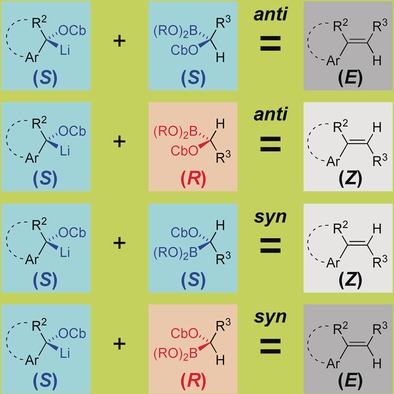
3D to 2D: Stereochemical information encoded in a pair of scalemic carbenoid reagents controls the geometry of the alkene products formed by their eliminative cross-coupling. The configuration of the alkene is determined by the carbenoid stereochemical pairing (like or unlike) and the elimination mechanism (syn or anti ), but not by the nature of the substituents.
CO Cleavage
Facile CO Cleavage by a Multimetallic CsU2 Nitride Complex
- Pages: 12290-12294
- First Published: 06 September 2016
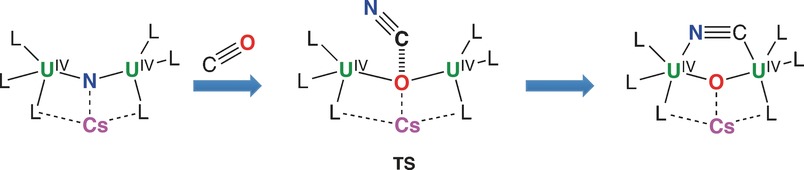
The power of cooperation: A heteropolymetallic uranium nitride with a CsUIV–N–UIV core effected complete cleavage of the strong C≡O bond of carbon monoxide under ambient conditions (see scheme). The reaction led to the formation of a CN− ligand, which could be alkylated readily to afford organic nitriles. The important role of multimetallic cooperativity in these reactions was identified by computation of the reaction mechanisms.
Hydrosilylation
An Easily Accessed Nickel Nanoparticle Catalyst for Alkene Hydrosilylation with Tertiary Silanes
- Pages: 12295-12299
- First Published: 09 September 2016
Enzyme Labeling
Activity-Based Probes for 15-Lipoxygenase-1
- Pages: 12300-12305
- First Published: 09 September 2016
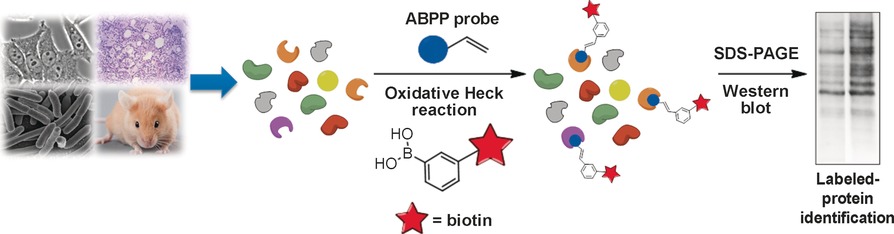
A villain meets its match: An activity-based probe was developed for human 15-lipoxygenase-1 (15-LOX-1), which plays an important role in various diseases. The probe mimicked the natural enzyme substrate and was able to bind covalently to the active enzyme. It included a terminal alkene as a chemical reporter for the bioorthogonal linkage of a detectable functionality by the oxidative Heck reaction (see scheme).
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
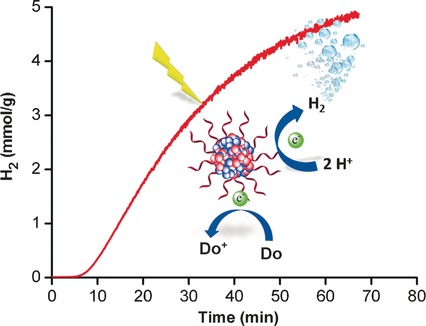
Organic Polymer Dots as Photocatalysts for Visible Light-Driven Hydrogen Generation
- Pages: 12306-12310
- First Published: 08 September 2016
Porphyrinoids | Hot Paper
Fusing Porphyrins and Phospholes: Synthesis and Analysis of a Phosphorus-Containing Porphyrin
- Pages: 12311-12315
- First Published: 09 September 2016
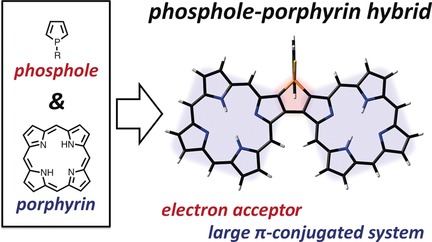
A phosphole-fused porphyrin dimer as a representative of a new class of phosphorus-containing porphyrins was synthesized. This structure exhibits remarkably broadened absorption as well as unique optoelectronic properties and is a good electron acceptor owing to the unique phosphole-fused structure.
Nitrogen Fixation | Hot Paper
Conversion of Dinitrogen to Nitriles at a Multinuclear Titanium Framework
- Pages: 12316-12320
- First Published: 09 September 2016
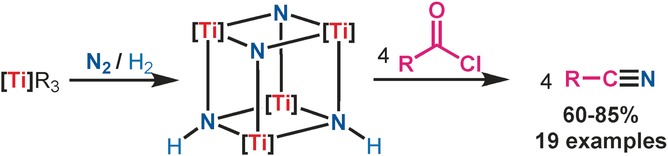
Activation and functionalization of N2: A mixed diimide/dinitride tetranuclear titanium complex formed by activation of dinitrogen served as a unique platform for the synthesis of nitriles (see picture). Functional groups such as aromatic C−X (X=Cl, Br, I) bonds, nitro groups, and ammonia-sensitive aldehyde and chloromethyl moieties were compatible with the synthetic method.
Reaction Mechanisms | Very Important Paper
Stereo- and Regioselective Alkyne Hydrometallation with Gold(III) Hydrides
- Pages: 12321-12324
- First Published: 04 September 2016
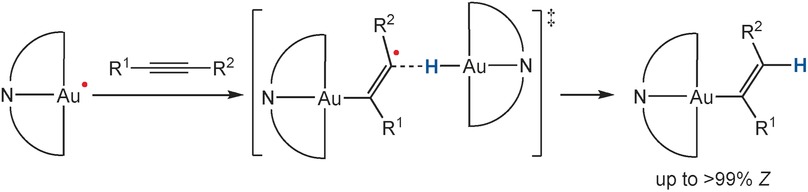
Gold(II) provides a helping hand: Gold(III) pincer complexes overcome their lack of substrate binding sites by participating in a radical-mediated bimolecular pathway. Gold(III) hydrides react with acetylenes in the presence of a radical source in a kinetically controlled reaction to give trans-hydroauration products with high regio- and stereoselectivity.
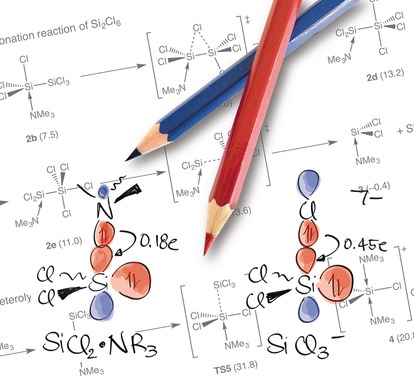
Aluminate Models | Hot Paper
Trapping Aluminum Hydroxide Clusters with Trisilanols during Speciation in Aluminum(III)–Water Systems: Reproducible, Large Scale Access to Molecular Aluminate Models
- Pages: 12325-12329
- First Published: 06 July 2016
Epimerases
A Lanthipeptide-like N-Terminal Leader Region Guides Peptide Epimerization by Radical SAM Epimerases: Implications for RiPP Evolution
- Pages: 12330-12333
- First Published: 01 September 2016
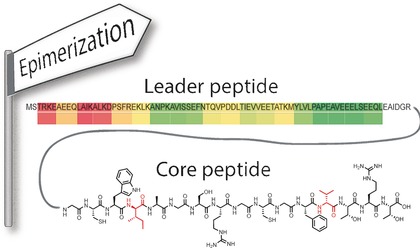
To guide an epimerase: Radical S-adenosyl-methionine peptide epimerases from proteusin biosynthetic pathways introduce d-amino acids into ribosomal peptides. A region in proteusin peptide precursors is identified that is important for epimerization. This region and other shared features in precursors of proteusins, lanthipeptides, and other peptide classes suggest a common evolutionary origin with nitrile hydratase-like enzymes as ancestors.
Solar Cells
An Organic Dyad Composed of Diathiafulvalene-Functionalized Diketopyrrolopyrrole–Fullerene for Single-Component High-Efficiency Organic Solar Cells
- Pages: 12334-12337
- First Published: 30 August 2016
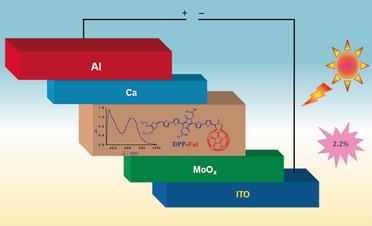
Climbing alone: The combination of dithiafulvalene-functionalized diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) as donor with fullerene (Ful) as acceptor has been successfully explored. Its utilization in single-component organic solar cells (SC-OSCs) was investigated, and it was shown to have a record power-conversion efficiency. ITO=indium tin oxide.
Siderophore Conjugates
Facile and Versatile Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Enterobactin Analogues and Applications in Bacterial Detection
- Pages: 12338-12342
- First Published: 01 September 2016
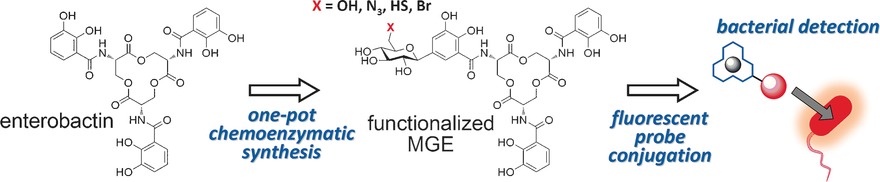
Siderophore-based bacteria labeling: A one-pot chemoenzymatic synthesis approach that is capable of functionalizing enterobactin with different reactive groups is developed. The functionalized enterobactin can be further conjugated with fluorophores to perform specific detection of bacteria. This strategy can serve as a convenient way to deliver cargos into bacteria with selectivity.
Olefin Metathesis
Tandem Ring-Opening–Ring-Closing Metathesis for Functional Metathesis Catalysts
- Pages: 12343-12346
- First Published: 05 September 2016
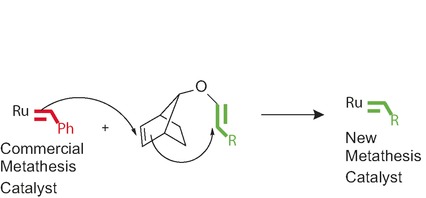
The preferred reaction of a commercial ruthenium benzylidene complex with a highly strained norbornene, followed by a fast intramolecular cyclization, yields new ruthenium carbene complexes in excellent yields. These complexes are ready for functional initiation of polymerization reactions without the need of purification.
Metal–Ammonia Solutions
Metal Transition in Sodium–Ammonia Nanodroplets
- Pages: 12347-12350
- First Published: 29 August 2016
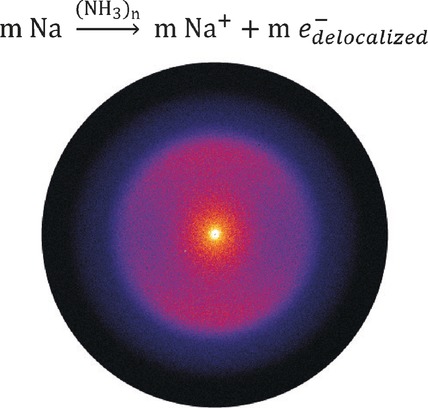
When is a metal not a metal? For more than a century, chemists have been struggling for a detailed understanding of the intriguing concentration-dependent color change of metal–ammonia solutions from deep blue to copper-gold. Indications for the underlying nonmetal-to-metal transition have now been found in photoelectron images of sodium–ammonia nanodroplets, paving the way for an atomistic description.
Coordination Polymers
A PCP Pincer Ligand for Coordination Polymers with Versatile Chemical Reactivity: Selective Activation of CO2 Gas over CO Gas in the Solid State
- Pages: 12351-12355
- First Published: 17 August 2016
Up- and Down-Conversion
Constructing Interfacial Energy Transfer for Photon Up- and Down-Conversion from Lanthanides in a Core–Shell Nanostructure
- Pages: 12356-12360
- First Published: 05 July 2016
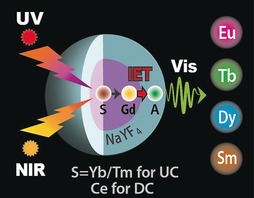
Up, down, flying around: Photon up- and down-conversion (UC and DC, respectively) have been realized through Gd3+-mediated interfacial energy transfer (IET) in a core–shell nanoarchitecture. This finding offers a simple, efficient approach for photon management, and enables a fundamental understanding of the interactions between lanthanide ions at nanometer length scale.
C−H Activation
Cobalt-Catalyzed sp2-C−H Activation: Intermolecular Heterocyclization with Allenes at Room Temperature
- Pages: 12361-12365
- First Published: 01 September 2016
Surface Functionalization
Site-Targeted Interfacial Solid-Phase Chemistry: Surface Functionalization of Organic Monolayers via Chemical Transformations Locally Induced at the Boundary between Two Solids
- Pages: 12366-12371
- First Published: 09 September 2016
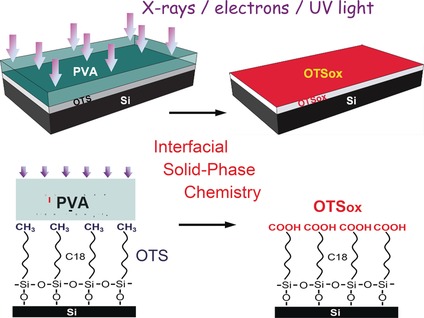
Novel interfacial chemistry is induced by electromagnetic radiation or electrons at the boundary between two solid materials, one of which acts as a removable thin film reagent/catalyst. This approach offers a variety of viable routes for nondestructive surface functionalization and patterning over length scales extending from centimeters to nanometers.
Laboratory Evolution | Hot Paper
Aptamers against Cells Overexpressing Glypican 3 from Expanded Genetic Systems Combined with Cell Engineering and Laboratory Evolution
- Pages: 12372-12375
- First Published: 07 September 2016
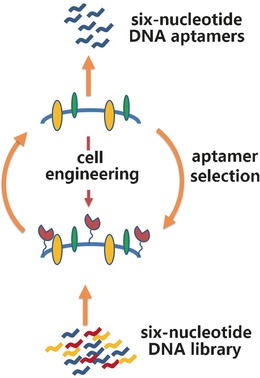
Six nucleobases: An expanded genetic information system and laboratory in vitro evolution were used to generate six-nucleotide aptamers that target cells engineered to overexpress a particular cell-surface protein. These aptamers could be used to distinguish cells that display that protein from those that do not.
Peptides
Protonation-Driven Membrane Insertion of a pH-Low Insertion Peptide
- Pages: 12376-12381
- First Published: 31 August 2016
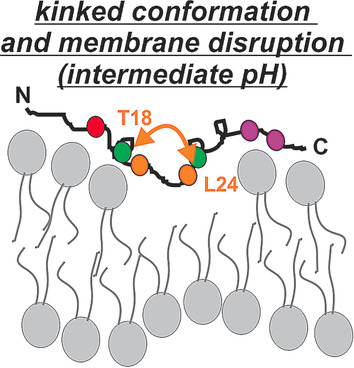
Showing backbone: The pH-low insertion peptide (pHLIP) inserts into membranes and forms a transmembrane (TM) α-helix in response to acidity changes. Tracing backbone conformations revealed that the TM helix spans from A10 to D33 with a break at T19 to P20. Residue-specific pKa values of D31, D33, D25, and D14 were determined to be 6.5, 6.3, 6.1, and 5.8, respectively, and define the sequence of protonations which lead to insertion. Furthermore, possible intermediate states which disrupt membranes at pH 6.4 are proposed.
Polymer Chemistry
Clickable Poly(ionic liquids): A Materials Platform for Transfection
- Pages: 12382-12386
- First Published: 31 August 2016
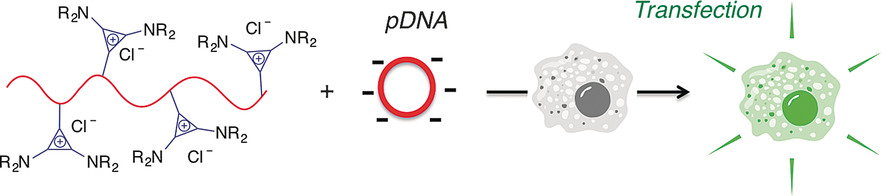
They just clicked: A stable bis(dialkylamino)cyclopropenium chloride salt can efficiently react with polymers containing secondary amines to yield cationic polyelectrolytes. The dialkylamino groups in this click transformation can be modulated to yield various polyelectrolytes bearing soft cationic moieties. Some of these cyclopropenium-based polymers give high transfection efficiencies and are less cytotoxic than linear polyethyleneimine (PEI).
Supramolecular Chemistry
Symbiotic Control in Mechanical Bond Formation
- Pages: 12387-12392
- First Published: 08 September 2016
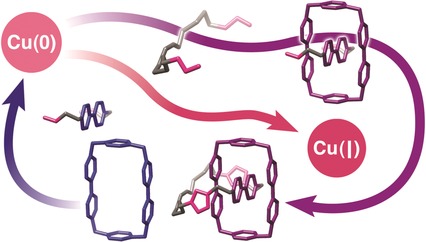
A user-friendly technique for the construction of positively charged catenanes and rotaxanes, templated by radical-pairing interactions in a convenient and efficient manner, has been conceived and implemented. This method opens up the possibility of producing integrated systems with Coulombically challenged catenanes and rotaxanes and of fabricating devices based on these systems.
Molecular Electronics
Molecular Conductance through a Quadruple-Hydrogen-Bond-Bridged Supramolecular Junction
- Pages: 12393-12397
- First Published: 31 August 2016
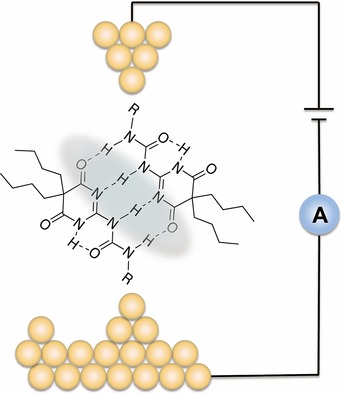
Electron transport through multiple hydrogen bonds: Supramolecular junctions bridged with quadruple hydrogen bonds have been constructed and characterized using the scanning tunneling microscopy break junction method. This noncovalent interaction exhibits conductivity comparable to that of covalently conjugated molecular devices and can also be manipulated by the polarity of the solvent environment.
Supramolecular Chemistry
A Halogen-Bond-Induced Triple Helicate Encapsulates Iodide
- Pages: 12398-12402
- First Published: 14 July 2016
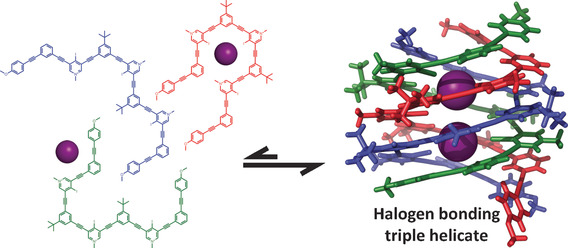
Bond, halogen bond: Three tricationic arylethynyl strands self-assemble to form a tubular anion channel lined with nine halogen-bond donors in solution and the solid state. Eight strong iodine⋅⋅⋅iodide halogen bonds and numerous buried π-surfaces endow the triplex with remarkable stability, even at elevated temperatures. The stringent linearity of halogen bonding could be a powerful tool for the synthesis of multi-strand anion helicates.
Nitric Oxide Chemistry
Mechanistic Insight into the Nitric Oxide Dioxygenation Reaction of Nonheme Iron(III)–Superoxo and Manganese(IV)–Peroxo Complexes
- Pages: 12403-12407
- First Published: 04 September 2016
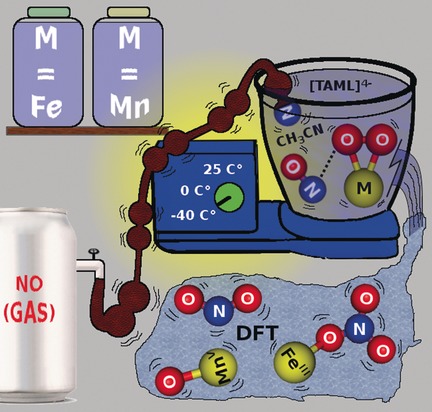
By NO means: Reactions of nonheme FeIII–superoxo and MnIV–peroxo complexes bearing a common tetraamido macrocyclic ligand (TAML), namely [(TAML)FeIII(O2)]2− and [(TAML)MnIV(O2)]2−, with nitric oxide (NO) afford the FeIII–NO3 complex [(TAML)FeIII(NO3)]2− and the MnV–oxo complex [(TAML)MnV(O)]− plus NO2−, respectively.
Natural Products
Deorphaning the Macromolecular Targets of the Natural Anticancer Compound Doliculide
- Pages: 12408-12411
- First Published: 08 September 2016
Pressure and Temperature
Hydrostatic Pressure Increases the Catalytic Activity of Amyloid Fibril Enzymes
- Pages: 12412-12416
- First Published: 30 August 2016
Negative+positive=better catalysis: Studying the combined effects of pressure and temperature on the hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate catalyzed by designed amyloid fibrils using high-pressure stopped-flow techniques with rapid UV/Vis absorbance detection showed that both pressure and temperature effectively enhance the catalysis as a consequence of a negative activation volume and a positive activation energy.
Analytical Chemistry
Ultraviolet Photodissociation Induced by Light-Emitting Diodes in a Planar Ion Trap
- Pages: 12417-12421
- First Published: 08 September 2016
Heterocycles
A Copper-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Amination/Hydroamination Sequence: Switchable Synthesis of Functionalized Indoles
- Pages: 12422-12426
- First Published: 04 September 2016

Switch-hitter: This work describes a copper-catalyzed decarboxylative amination/hydroamination sequential reaction. The one-pot treatment of an indoline intermediate with either an acid or a base enables the switchable synthesis of two types of functionalized indoles in generally high yields and with complete chemoselectivities (36 examples and up to 99 % yield).
Nanoparticle Morphology
In Situ Observation of Hydrogen-Induced Surface Faceting for Palladium–Copper Nanocrystals at Atmospheric Pressure
- Pages: 12427-12430
- First Published: 04 September 2016
Single-Cell Analysis
Detection of Isoforms Differing by a Single Charge Unit in Individual Cells
- Pages: 12431-12435
- First Published: 06 September 2016
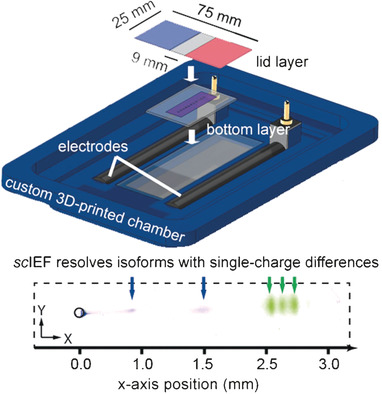
Electrophoretic cytometry: A multilayer, patterned hydrogel device supports isoelectric focusing to separate protein isoforms from single cells (scIEF). All preparative and analytical steps, including cell isolation, lysis, protein separation, UV-actuated blotting, and immunoprobing, are performed on the device. Protein isoforms with single-charge differences are resolved, blotted, and detected by immunoprobing.
Recovery of Gold
A Simple Primary Amide for the Selective Recovery of Gold from Secondary Resources
- Pages: 12436-12439
- First Published: 24 August 2016
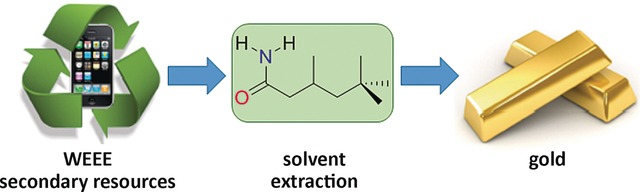
Going for gold: A simple primary amide is shown to be an effective reagent for the selective recovery of gold by solvent extraction from a mixture of metals representative of those in waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). The recovery is achieved through the formation of dynamically assembled hydrogen-bonded amide/AuCl4 clusters.
Gene Technology | Hot Paper
Development of Light-Activated CRISPR Using Guide RNAs with Photocleavable Protectors
- Pages: 12440-12444
- First Published: 24 August 2016
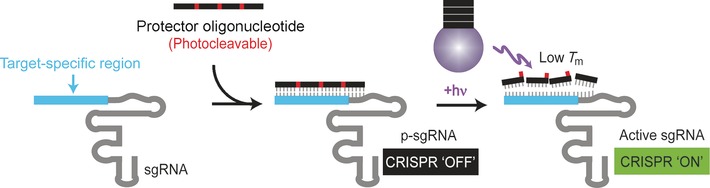
Turn “ON” CRISPR with light: CRISPR can be brought under the control of light simply by hybridizing a single chimeric guide RNA (sgRNA) with a complementary oligonucleotide containing photocleavable groups (protector oligonucleotide). The protected sgRNA (p-sgRNA) remains inactive, blocking CRISPR activity, until the protector oligonucleotide is cleaved with a remote light trigger.
DNA Recognition
Aminopyridinyl–Pseudodeoxycytidine Derivatives Selectively Stabilize Antiparallel Triplex DNA with Multiple CG Inversion Sites
- Pages: 12445-12449
- First Published: 31 August 2016
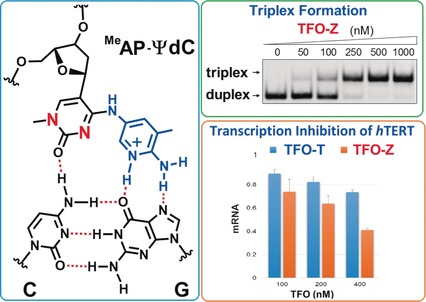
Pseudo-deoxycytidine (ΨdC) derivatives were developed for the selective recognition of the CG base pair to expand the triplex-forming sequence. The ΨdCs formed a stable triplex with the promoter of the hTERT gene containing four CG inversion sites, and effectively inhibited its transcription in human cancer cells, and may lead to the development of new triplex-forming oligonucleotides.
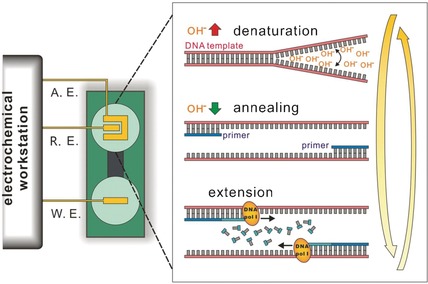
DNA Replication
Ion-Mediated Polymerase Chain Reactions Performed with an Electronically Driven Microfluidic Device
- Pages: 12450-12454
- First Published: 09 September 2016
C−H Activation
Manganese(I)-Catalyzed C−H Activation: The Key Role of a 7-Membered Manganacycle in H-Transfer and Reductive Elimination
- Pages: 12455-12459
- First Published: 07 September 2016
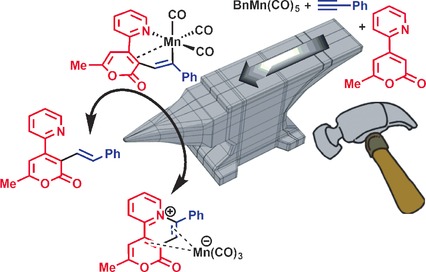
Look left, look right: A highly reactive seven-membered manganese(I) intermediate has been detected and characterized that is effective for H-transfer or reductive elimination to deliver alkenylated or pyridinium products, respectively. The two pathways are determined at MnI by judicious choice of an electron-deficient 2-pyrone substrate containing a 2-pyridyl directing group, which undergoes regioselective C−H activation.
Polymer Microspheres
Polymer and Mesoporous Silica Microspheres with Chiral Nematic Order from Cellulose Nanocrystals
- Pages: 12460-12464
- First Published: 01 September 2016
Direct Urea Fuel Cells
Metallic Nickel Hydroxide Nanosheets Give Superior Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Urea for Fuel Cells
- Pages: 12465-12469
- First Published: 30 August 2016
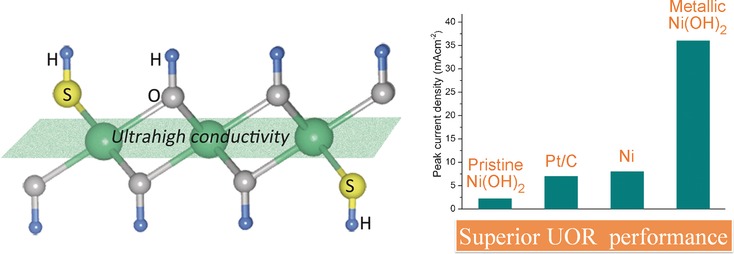
Metal as anything: Surface sulfur incorporation into β-Ni(OH)2 nanosheets gives the first metallic configuration of a transition-metal hydroxide. The resulting metallic Ni(OH)2 nanosheets have more exposed active sites and metallic electrical conductivity, giving rise to greatly enhanced performance for the urea oxidation reaction (UOR) for direct urea fuel cells.
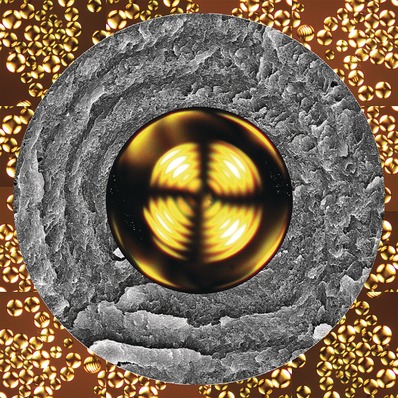
Electrocatalysis
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Metal–Polyphenol Coordination Crystals and Their Derived Metal/N-doped Carbon Composites for Oxygen Electrocatalysis
- Pages: 12470-12474
- First Published: 01 September 2016
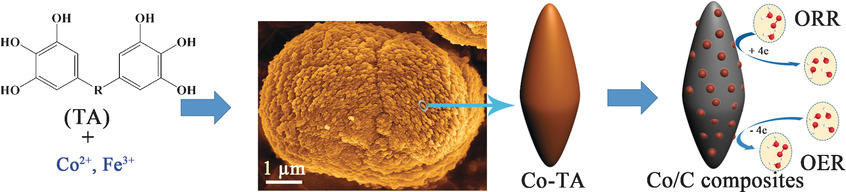
Coordination crystals (see SEM image) obtained from a polyphenol (tannic acid; TA) and cobalt or iron were synthesized by a hydrothermal synthesis route. The crystals are a renewable source for the fabrication of metal/carbon composites as a nonprecious metal catalyst for the oxygen reduction and evolution reactions.
Protein Engineering
Multifunctional Antibody Agonists Targeting Glucagon-like Peptide-1, Glucagon, and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptors
- Pages: 12475-12478
- First Published: 06 September 2016
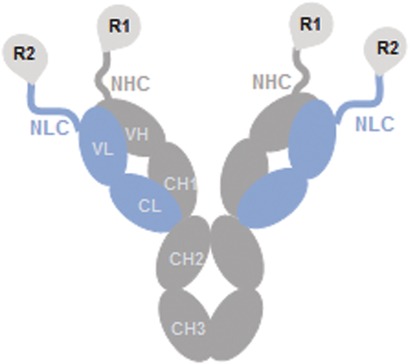
Mono- and multifunctional antibody agonists of the receptors GLP-1R, GCGR, and GIPR were generated by N-terminal fusion of the exendin-4, glucagon-like peptide-1, glucagon, GIP, and ZP peptides to the heavy chains (HC) and/or light chains (LC) of the humanized monoclonal antibody Synagis. The resulting antibody fusions show excellent activity in sustaining blood glucose control and reducing body weight in rodent models.
Drug Discovery
Partially Saturated Bicyclic Heteroaromatics as an sp3-Enriched Fragment Collection
- Pages: 12479-12483
- First Published: 06 September 2016
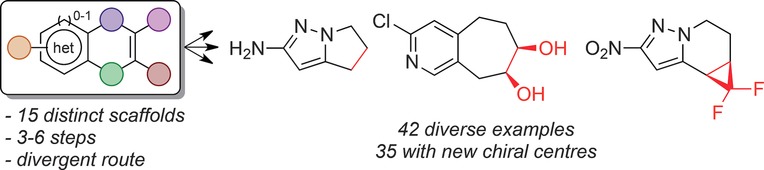
2D or not 2D: A collection of partially saturated bicyclic pyridine- and pyrazole-based fragments, derived from a diverse set of readily accessible branch-point scaffolds, is presented. Their enhanced sp3 content, compared to typical fragment libraries, allows excellent control of 3D growth vectors in drug development applications.
Iodine Adducts
Modification of σ-Donor Properties of Terminal Carbide Ligands Investigated Through Carbide–Iodine Adduct Formation
- Pages: 12484-12487
- First Published: 09 September 2016
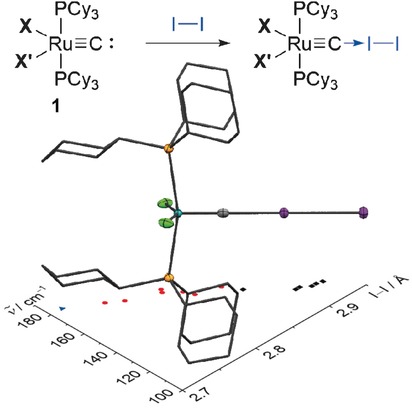
To give and take: terminal ruthenium carbide complexes [(Cy3P)2X2Ru≡C] (1; X=halide or pseudohalide), form charge-transfer adducts with I2 exhibiting large variation in bond lengths and stretching frequencies. This shows that the auxiliary ligand sphere on ruthenium enables control over the σ-donor properties of carbide ligands, elucidating their isolobal relationship with carbon monoxide.
Supramolecular Chemistry
A Kinetic Self-Sorting Approach to Heterocircuit [3]Rotaxanes
- Pages: 12488-12493
- First Published: 07 September 2016
![A Kinetic Self-Sorting Approach to Heterocircuit [3]Rotaxanes](/cms/asset/0ddc60d0-8437-4e1a-9897-b41cb4ac1c46/anie201606640-toc-0001-m.jpg)
If at first you don't succeed, fall apart: A novel self-sorting approach is described in which the kinetic stability of the desired [3]rotaxane isomer determines the reaction outcome. All other threaded structures derived from the larger ring are kinetically unstable, allowing the yield of the target to be amplified at the expense of other possible products.
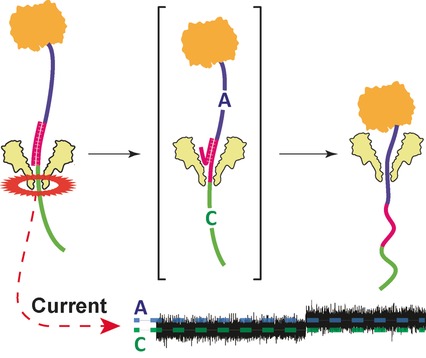
Biosensors
Alpha-Helical Fragaceatoxin C Nanopore Engineered for Double-Stranded and Single-Stranded Nucleic Acid Analysis
- Pages: 12494-12498
- First Published: 08 September 2016
Radical Cyclization
Selective Synthesis of Cyclooctanoids by Radical Cyclization of Seven-Membered Lactones: Neutron Diffraction Study of the Stereoselective Deuteration of a Chiral Organosamarium Intermediate
- Pages: 12499-12502
- First Published: 07 September 2016
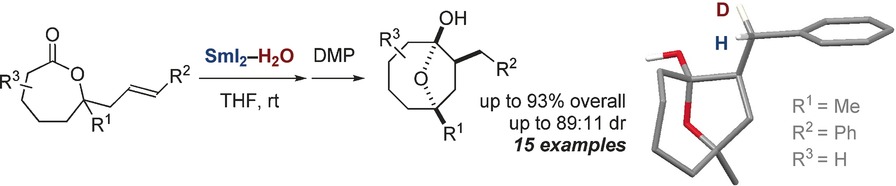
Seven-membered lactones undergo selective SmI2–H2O-promoted radical cyclization to form substituted cyclooctanols. The products arise from an exo-mode of cyclization rather than the usual endo-attack. A labeling experiment and neutron diffraction study have been used for the first time to probe the configuration and highly diastereoselective deuteration of a chiral organosamarium intermediate.
Biomimetic Self-Organization
Mimicking Primitive Photobacteria: Sustainable Hydrogen Evolution Based on Peptide–Porphyrin Co-Assemblies with a Self-Mineralized Reaction Center
- Pages: 12503-12507
- First Published: 01 September 2016
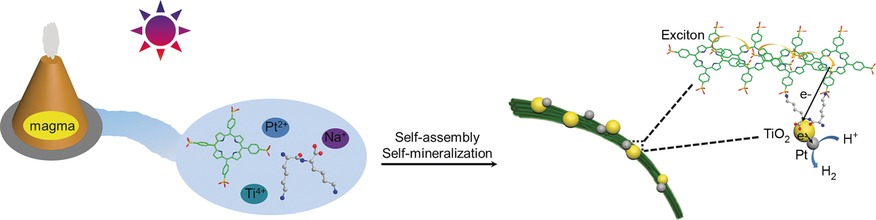
Mimicking primitive photosystems: Self-organization, dynamic evolution, and sustainable utilization of components in a “prebiotic soup” are conceptually and experimentally validated through simple but well-functioning peptide–porphyrin co-assemblies, which support a new type of primitive hydrogen producing photobacteria model.
G-Quadruplexes
NMR Structure of a Triangulenium-Based Long-Lived Fluorescence Probe Bound to a G-Quadruplex
- Pages: 12508-12511
- First Published: 31 August 2016
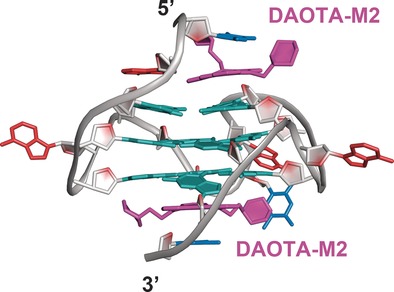
Playing the triangle in a quartet: A small-molecule optical probe (DAOTA-M2) based on a triangulenium core binds to G-quadruplexes in a 1:2 stoichiometry. Binding of DAOTA-M2 occurs mainly through π–π stacking between the triangulenium core and the guanine residues of the outer G-quartets. Interestingly, the binding affinities of DAOTA-M2 for the two outer G-quartets differ by a factor of two.
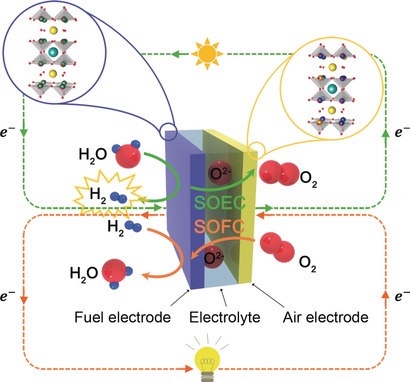
Hydrogen Productions | Hot Paper
Achieving High Efficiency and Eliminating Degradation in Solid Oxide Electrochemical Cells Using High Oxygen-Capacity Perovskite
- Pages: 12512-12515
- First Published: 08 September 2016
Conducting Polymers | Hot Paper
Two-Dimensional Mesoscale-Ordered Conducting Polymers
- Pages: 12516-12521
- First Published: 07 September 2016
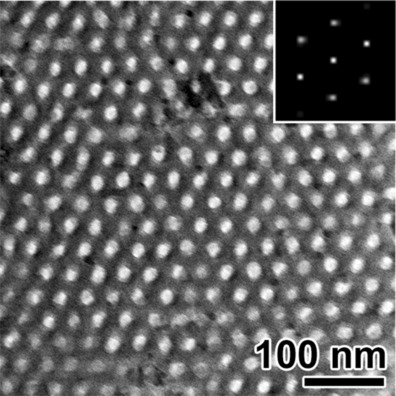
Ultrathin conducting polymer nanosheets were achieved by synergistically manipulating the self-assembly of perfluorocarboxylic acids and polystyrene-b-poly(ethylene oxide) diblock copolymers. The nanosheets feature mesoscale-ordered hexagonal pore arrays, tunable morphologies and pore sizes, large specific surface area as well as anisotropic and record-high electrical conductivity.
Hierarchical Assembly
Hierarchical Nanowires Synthesized by Supramolecular Stepwise Polymerization
- Pages: 12522-12527
- First Published: 08 September 2016
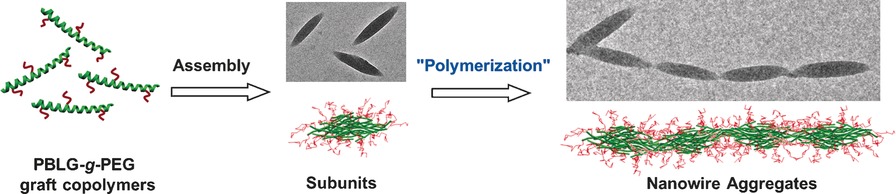
Connect the dots: Anisotropic spindle-like micelles, self-assembled from polypeptide graft copolymers with rigid backbones, can serve as ideal pre-assembled subunits for constructing hierarchical nanowires. The growth of the nanowires follows a hierarchical process that resembles step polymerization.
Energy Storage | Hot Paper
Oxocarbon Salts for Fast Rechargeable Batteries
- Pages: 12528-12532
- First Published: 08 September 2016
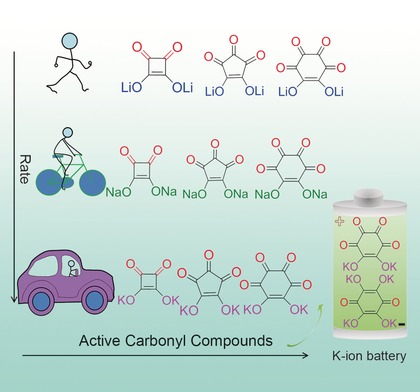
Organic electrode material: Oxocarbon salts (M2(CO)n) with different metal ions (M=Li, Na, K) and frameworks (n=4, 5, 6) were rationally designed and used as electrodes for rechargeable Li, Na, and K-ion batteries. A first example of a renewable and sustainable K-ion battery based on K2C6O6 and K4C6O6 with a rocking-chair reaction mechanism is shown.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Rotationally Active Ligands: Dialing-Up the Co-conformations of a [2]Rotaxane for Metal Ion Binding
- Pages: 12533-12537
- First Published: 04 September 2016
![Rotationally Active Ligands: Dialing-Up the Co-conformations of a [2]Rotaxane for Metal Ion Binding](/cms/asset/2c3517b6-11ea-4764-b037-c968c326b1c8/anie201607281-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A rigid, H-shaped [2]rotaxane ligand with different sets of donor atoms on the axle and wheel components was prepared. The dynamics of the rotaxane and the orthogonal arrangement of the donors allows access to different co-conformations by simple rotation of the wheel about the axle. Three different rotational isomers were observed and structurally characterized for the neutral ligand and coordination complexes with Li+ and Cu+ ions.
Batteries | Hot Paper
Lithium Ion Pathway within Li7La3Zr2O12-Polyethylene Oxide Composite Electrolytes
- Pages: 12538-12542
- First Published: 09 September 2016
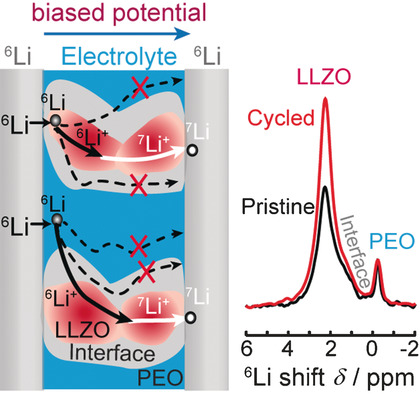
Where do they go? The first experimental evidence was obtained for lithium ions diffusing through composite ceramic electrolytes (LLZO and PEO) in an all-solid-state battery. Lithium ion diffusion was determined using 6,7Li NMR and isotope exchange, and indicated that Li ions mainly pass through the LLZO ceramic phase instead of the LLZO-PEO interface or the PEO phase.