Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: A Microstructured Graphene/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Membrane for Intelligent Solar Water Evaporation (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50/2018)
- Page: 16235
- First Published: 14 November 2018

Solar water evaporation with a leaf-like microstructured graphene/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (mG/PNIPAm) membrane is described by L. Qu and co-workers in their Communication on page 16343 ff. In response to varying sunlight intensities, the water evaporation rate of this leaf-like mG/PNIPAm membrane is tuned through opening and closing of the water transport channels in a process reminiscent of the stomatal opening and closing of leaves. A double-layer membrane variant can further tailor water loss through self-curling.
Inside Cover: Synthesis and Properties of a Highly Congested Tri(9-anthryl)methyl Radical (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50/2018)
- Page: 16236
- First Published: 12 November 2018

A propeller-shaped highly congested mesityl-substituted tri(9-anthryl)methyl radical was synthesized by developing a method that overcomes the challenges posed by the bulky substituents. In their Communication on page 16516 ff., T. Nishiuchi, T. Kubo, and S. Aibara also report on the high persistency, wide-range absorbance, good reversible redox properties, and dimerization behavior of this radical.
Inside Back Cover: A Multi-Ion Strategy towards Rechargeable Sodium-Ion Full Batteries with High Working Voltage and Rate Capability (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50/2018)
- Page: 16569
- First Published: 16 November 2018

A multi-ion strategy can enhance the electrochemical performance of sodium-ion batteries. In their Communication on page 16370 ff., Y. B. Tang et al. report a multi-ion configuration (Na+/Li+/PF6−) for sodium-ion full batteries by combining anion (PF6−) intercalation with a hybrid-ion design (Na+/Li+) electrolyte. The optimized batteries exhibited a high working voltage (ca. 4.0 V), a significantly enhanced rate performance, and superior cycling stability.
Back Cover: Isolation of Tetracyano-Naphthalenediimide and Its Stable Planar Radical Anion (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50/2018)
- Page: 16570
- First Published: 21 November 2018

Tetracyanonaphthalenediimide [NDI(CN)4], an exceptional π-acidic planar molecule and one of the strongest known electron acceptors, has been impossible to isolate, until now. Its remarkably large quadrupole moment (QZZ=+55.5B) and extremely low calculated LUMO of −5.2 eV evoked great interest from academia and industry. In their Communication on page 16318 ff., P. Mukhopadhyay and co-workers report the isolation of [NDI(CN)4] and its ambient-stable radical anion. Structural and spectroscopic elucidation is provided for these long coveted open- and closed-shell π-systems.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Beating Vesicles: Encapsulated Protein Oscillations Cause Dynamic Membrane Deformations
- First Published: 04 December 2018

Synthetic Biology In their Communication on page 16286 ff., P. Schwille et al. report that the encapsulation of Min proteins in giant liposomes leads to oscillatory, spatiotemporal reaction–diffusion patterns on the vesicle membranes and oscillations in the overall shapes of the vesicles.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50/2018
- Pages: 16239-16254
- First Published: 04 December 2018
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50/2018
- Pages: 16256-16260
- First Published: 04 December 2018
Author Profile
News
Highlights
Asymmetric Multicomponent Reactions
The Catalytic Enantioselective Ugi Four-Component Reactions
- Pages: 16266-16268
- First Published: 15 November 2018
Finally stereoselective: Enantioselective variations have been developed for many multicomponent reactions; however, it has been missing for the Ugi four-component reaction. This has now changed with the discovery of an efficient catalytic enantioselective variant for the four-component reaction of isocyanides, primary amines, aldehydes or ketones, and carboxylic acids.
Reviews
Soft Landing of Ions
From Isolated Ions to Multilayer Functional Materials Using Ion Soft Landing
- Pages: 16270-16284
- First Published: 14 May 2018
Communications
Synthetic Biology
Beating Vesicles: Encapsulated Protein Oscillations Cause Dynamic Membrane Deformations
- Pages: 16286-16290
- First Published: 30 September 2018
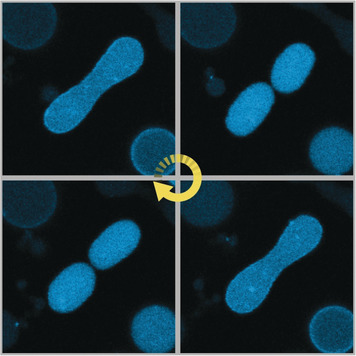
Active vesicles: Min proteins were encapsulated in giant liposomes. This not only caused the proteins to self-organize and form oscillatory, spatiotemporal reaction–diffusion patterns on the vesicle membranes, but also had an unexpected effect on lipid bilayer dynamics: The periodic binding and disassociation of the proteins to and from the membrane induced changes in membrane curvature, leading to oscillations in the overall shape of the vesicles.
Photochemistry | Very Important Paper
Tuning Intramolecular Förster Resonance Energy Transfer and Activating Intramolecular Singlet Fission
- Pages: 16291-16295
- First Published: 19 September 2018
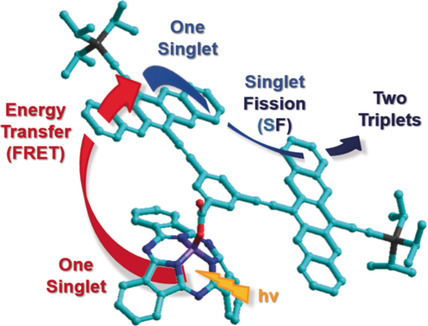
FRETter by design: Three subphthalocyanine (SubPc)/pentacene dimer (Pnc2) conjugates were prepared for the synergy of panchromatic light absorption, energy transfer, and intramolecular singlet fission (SF). Transient absorption measurements confirmed the reaction sequence of light harvesting by the SubPcs, unidirectional Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) from the SubPcs to the Pnc2, and almost quantitative intramolecular SF.
Molecular Recognition
Hydrogen-Bonded Networks: Molecular Recognition of Cyclic Alcohols in Enantiopure Alleno-Acetylenic Cage Receptors
- Pages: 16296-16301
- First Published: 12 November 2018
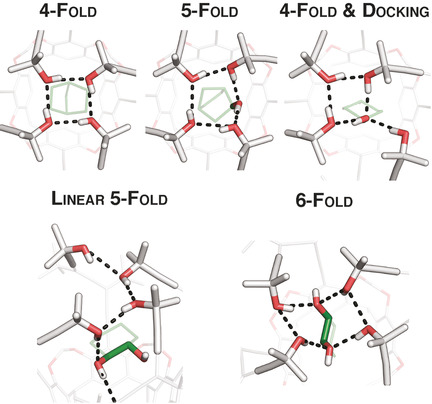
Enantiopure alleno-acetylenic cage receptors display a fourfold circular hydrogen-bonding network of one handedness. Alcohol guests expand the hydrogen-bonding network of the receptor, forming hydrogen-bonding topologies reminiscent of those found in isolated water clusters: circular fourfold & docking, pentagonal, linear fivefold, and boat-shaped hexagonal. The expansion is accompanied by a gain in Gibbs binding energy.
Epigenetics
Discovery of an MLLT1/3 YEATS Domain Chemical Probe
- Pages: 16302-16307
- First Published: 05 October 2018
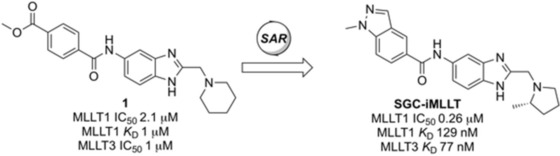
Molecular poetry: YEATS domain (YD) containing proteins are an emerging class of epigenetic protein targets in drug discovery. A screening hit has been developed into the first potent, selective, and cell-active chemical probe for the YD-containing proteins MLLT1 and MLLT3. The probe represents the first inhibitor of its class to explore YD-associated biology and disease links.
Corrinoids
A Nickel(II)-Containing Vitamin B12 Derivative with a Cofactor-F430-type π-System
- Pages: 16308-16312
- First Published: 23 October 2018
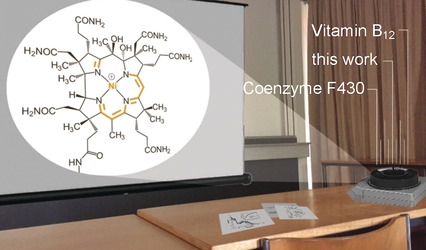
Nickel for cobalt: F430 is a unique enzymatic cofactor in the production and oxidation of methane by strictly anaerobic bacteria. The key enzyme methyl coenzyme M reductase contains a hydroporphinoid nickel complex. A hybrid nickel(II)-containing corrinoid that partly resembles F430 in its structural and spectroscopic features was obtained in a three-step semisynthesis from vitamin B12.
Chemical Crystallography
Rapid Structure Determination of Microcrystalline Molecular Compounds Using Electron Diffraction
- Pages: 16313-16317
- First Published: 16 October 2018
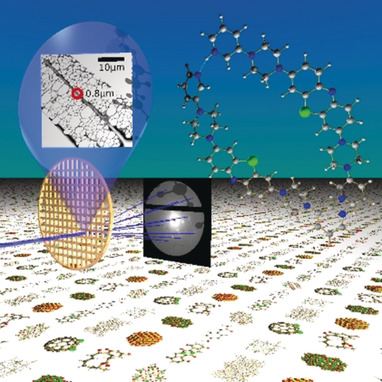
Electrons instead of X-rays: An electron diffractometer was tailored and employed for de novo structure determination from submicrometer-sized crystals. A new methylene blue derivative was analysed together with a microcrystalline extract of an active pharmaceutical ingredient from a pill. The results obtained on submicrometer-sized samples complement X-ray crystallography.
Radicals | Hot Paper
Isolation of Tetracyano-Naphthalenediimide and Its Stable Planar Radical Anion
- Pages: 16318-16322
- First Published: 27 September 2018

An exceptional radical: Tetracyano-naphthalenediimide and its radical anion have been isolated and subjected to structural elucidation through spectroscopic and X-ray diffraction studies. The planar radical anion is supramolecularly stabilized and electrochemical studies confirm its extraordinarily low-lying LUMO (−5.0 eV), rendering it one of the strongest electron-deficient planar π systems to be isolated.
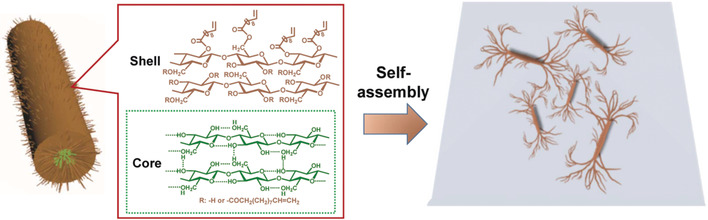
Self-Assembly
Helical Fibers via Evaporation-Driven Self-Assembly of Surface-Acylated Cellulose Nanowhiskers
- Pages: 16323-16328
- First Published: 27 September 2018
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Molecular Mimics of Heterogeneous Metal Phosphides: Thermochemistry, Hydride-Proton Isomerism, and HER Reactivity
- Pages: 16329-16333
- First Published: 12 October 2018
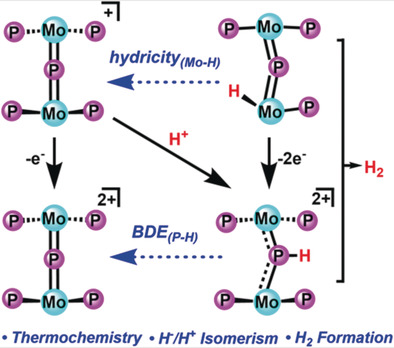
Molecularly precise: A series of reduced dinuclear μ-phosphido complexes have been prepared as models for heterogeneous proton reduction catalysts. These molecular complexes provide insight into elementary reaction steps and thermochemical parameters relevant to their solid-state counterparts. μ-P protonation, Mo-to-P H-migration, and H-atom transfer have all been demonstrated, en route to H2 formation.
Solvation
Imaging the Solvation of a One-Dimensional Solid on the Molecular Scale
- Pages: 16334-16338
- First Published: 11 October 2018
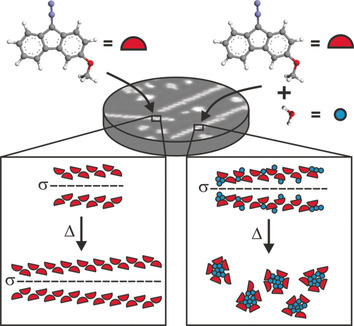
The formation of a one-dimensional solid, its hydration, and its dissolution on a Ag(111) surface were followed by low-temperature scanning tunneling microscopy. The annealing of dry chains results in a simple increase in chain length and number whereas the annealing of water-decorated chains results in a complete loss of order and produces water clusters decorated with the organic molecule.
CO2 Reduction
Reaction Mechanisms of Well-Defined Metal–N4 Sites in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- Pages: 16339-16342
- First Published: 12 October 2018
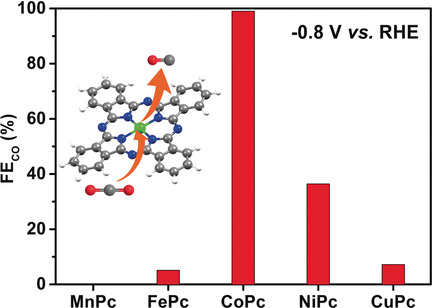
To the “CO2RR”: Metal phthalocyanines (MePcs) with well-defined metal–N4 structures were used as model catalysts to study the active centers and reaction mechanisms for the electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR). Theoretical and experimental studies identify CoPc as the optimum catalyst for the selective electrocatalytic CO2RR to deliver CO. The Co site serves as the active center for achieving a Faradaic efficiency (FE) of up to 99 % with long-term stability.
Membranes
A Microstructured Graphene/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Membrane for Intelligent Solar Water Evaporation
- Pages: 16343-16347
- First Published: 23 October 2018
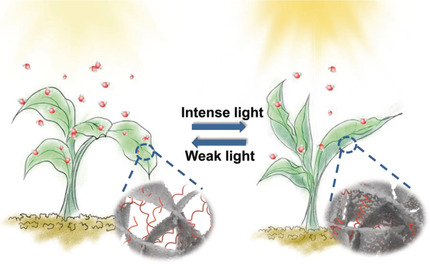
A thermally responsive and microstructured graphene/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (mG/PNIPAm) membrane was used for intelligent solar water evaporation. In response to varying sunlight intensities, the water evaporation rate of this leaf-like mG/PNIPAm membrane is tuned through opening and closing the water transport channels in a process similar to the stomatal opening/closing of leaves.
Macrocycle Chemistry
Strain-Promoted Reactivity of Alkyne-Containing Cycloparaphenylenes
- Pages: 16348-16353
- First Published: 15 October 2018
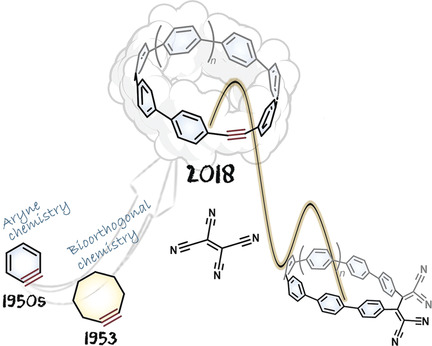
Poised to react: Macrocyclic cycloparaphenylenes with built-in alkynes are presented and the impact of strain on the structural/electronic properties of the alkyne investigated. The angle-strained alkynes demonstrate a size-dependent reactivity profile that permits [2+2]cycloaddition-retrocyclization and copper-free azide–alkyne coupling reactions under mild conditions.
Photodynamic Therapy
Enhancing the Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy through a Porphyrin/POSS Alternating Copolymer
- Pages: 16354-16358
- First Published: 14 October 2018
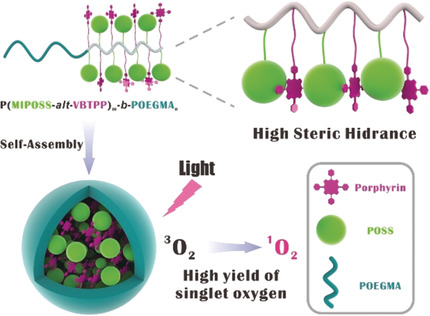
Nanoparticles formed by self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers were investigated for their potential application in photodynamic therapy. The porphyrin-containing polymeric nanoparticles display high photochemical yield and phototoxicity in vitro and in vivo, thus providing a novel strategy to enhance the PDT efficacy.
Polymer Electrodes | Hot Paper
A Long-Cycle-Life Self-Doped Polyaniline Cathode for Rechargeable Aqueous Zinc Batteries
- Pages: 16359-16363
- First Published: 11 October 2018
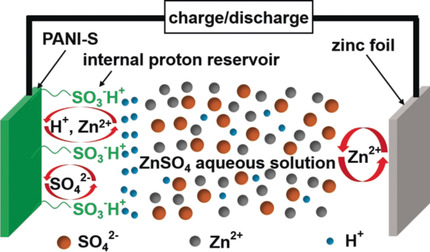
Staying active: A sulfo self-dopant of polyaniline (PANI) functioned as an internal proton reservoir, so that the electrochemical activity of the polymer was preserved in weakly acidic ZnSO4 aqueous electrolyte (see picture). In a full zinc cell, the self-doped polyaniline cathode showed a high capacity of 180 mAh g−1, excellent rate capability, and a long cycle life of over 2000 cycles with almost 100 % coulombic efficiency.
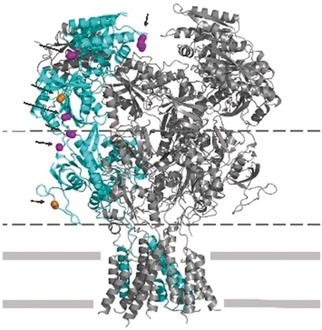
Super-Resolution Imaging
Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry Enables Site-specific Fluorescence Labeling of Functional NMDA Receptors for Super-Resolution Imaging
- Pages: 16364-16369
- First Published: 22 October 2018
Batteries | Very Important Paper
A Multi-Ion Strategy towards Rechargeable Sodium-Ion Full Batteries with High Working Voltage and Rate Capability
- Pages: 16370-16374
- First Published: 15 October 2018
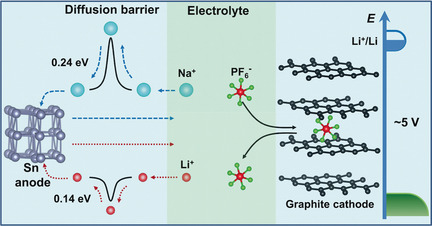
Two ions in the fire: A multi-ion strategy to improve the electrochemical performance of sodium-ion full batteries is presented. The optimized sodium-ion-based multi-ion battery achieves a high working voltage of about 4.0 V, superior rate capability (up to 30 C; capacity retention: 87 %), and long cycling stability over 500 cycles at 5 C (capacity retention: 95 %).
Protein Structural Analysis
Fast Magic-Angle Spinning 19F NMR Spectroscopy of HIV-1 Capsid Protein Assemblies
- Pages: 16375-16379
- First Published: 17 September 2018
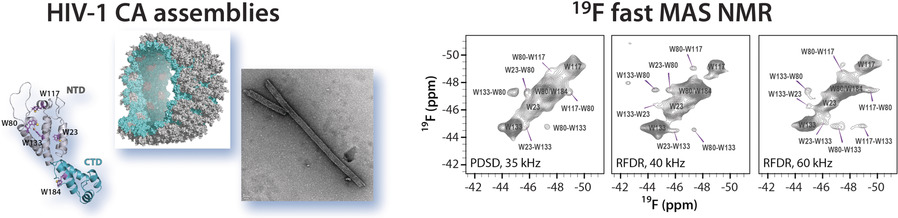
Think big: The structural characterization of large biological systems is a challenge by conventional techniques. Fast MAS 19F NMR spectroscopy was found to be an attractive means for investigating protein assemblies (see picture). In the investigation of HIV-1 capsid protein assemblies, high spectral resolution was attained in 19F–19F correlation spectra, permitting the detection of nanometer distances of the order of 20 Å.
Polymerization
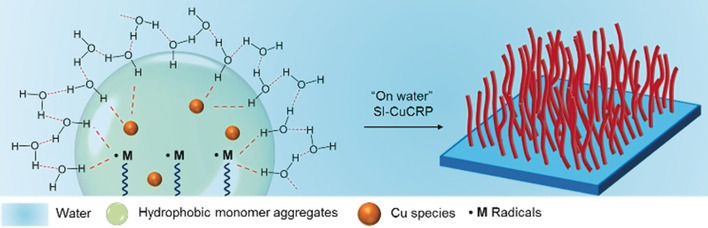
“On Water” Surface-initiated Polymerization of Hydrophobic Monomers
- Pages: 16380-16384
- First Published: 09 October 2018
Polymers
Tracking Local Mechanical Impact in Heterogeneous Polymers with Direct Optical Imaging
- Pages: 16385-16390
- First Published: 05 September 2018
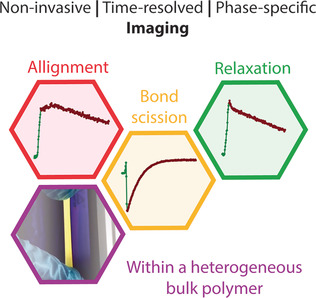
One probe to see them all: complex behavior of discrete phases of a heterogeneous polymer can be directly imaged by robust phosphorescent mechanophores. Hard phase rearrangement, breakdown, and crystallization were shown to have distinct optical response patterns that makes it possible to track and identify these diverse deformation mechanisms.
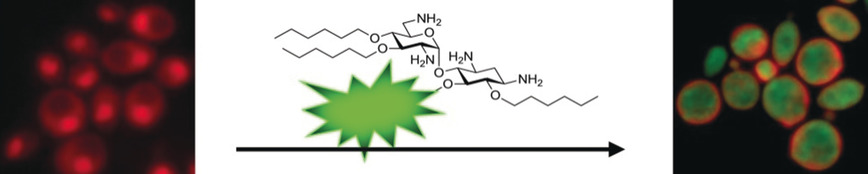
Antifungal Agents | Hot Paper
Cationic Amphiphiles Induce Macromolecule Denaturation and Organelle Decomposition in Pathogenic Yeast
- Pages: 16391-16395
- First Published: 11 October 2018
Photodynamic Therapy
Multifunctional Liposome: A Bright AIEgen–Lipid Conjugate with Strong Photosensitization
- Pages: 16396-16400
- First Published: 20 October 2018
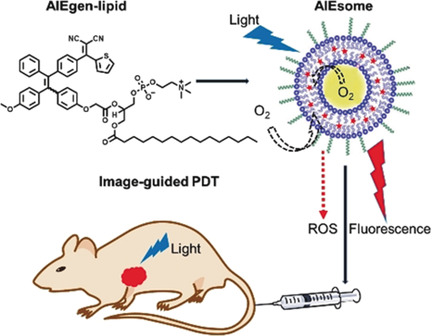
Teamwork: An aggregation-induced emission fluorogen was combined with a liposome to yield an AIEgen–lipid conjugate (“AIEsome”). The AIEsome exhibits bright red fluorescence and strong photosensitization along with great photostability and biocompatibility, and can be used for image-guided photodynamic therapy for in vitro cancer cell ablation and in vivo antitumor therapy. PDT=photodynamic therapy, ROS=reactive oxygen species.
Halogenated Contaminants
Hundreds of Unrecognized Halogenated Contaminants Discovered in Polar Bear Serum
- Pages: 16401-16406
- First Published: 30 October 2018
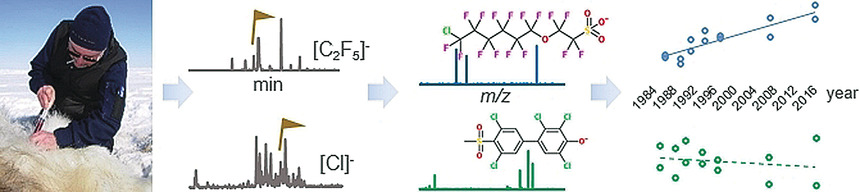
Alarming trend: High resolution mass spectrometry revealed hundreds of previously unknown halogenated contaminants in polar bear serum. A mouse study confirmed the 5 new PCB metabolite classes. Stable time-trends of PCB metabolites and increasing fluoroalkyl contaminants in polar bear serum between the mid-1980s and 2016 make toxicological studies on these new contaminants warranted.
Phosphorescence
Intramolecular Charge Transfer Controls Switching Between Room Temperature Phosphorescence and Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence
- Pages: 16407-16411
- First Published: 19 October 2018
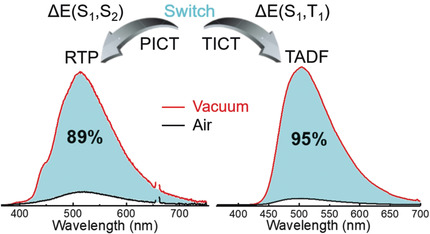
Rapid and efficient utilization of triplet states to generate room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) or highly efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) is achieved by structural modification to give a planar or twisted intramolecular charge transfer (PICT or TICT) geometry, respectively.
Oxidation
Aerobic Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation Catalyzed by a Flavin-Containing Enzyme Mimic in Water
- Pages: 16412-16415
- First Published: 24 October 2018
Catalysis
An Iron-Containing Metal–Organic Framework as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Ozone Decomposition
- Pages: 16416-16420
- First Published: 17 October 2018
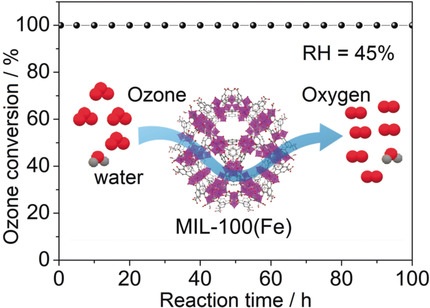
Ozone overthrown: The iron containing metal–organic framework MIL-100(Fe) exhibits a long-lasting ozone conversion efficiency of 100 % for over 100 h under 45 % relative humidity, which is well beyond the performance of most porous or metal catalysts such as activated carbon and α-MnO2. MIL-100(Fe) has also been incorporated into air filters for efficient protection against ozone under humid conditions.
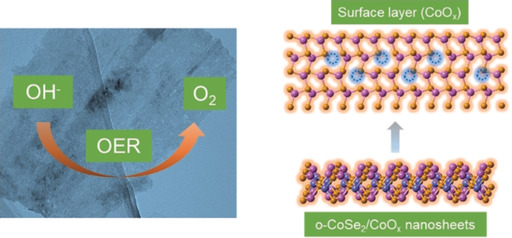
Surface Oxidation | Hot Paper
Plasma-Triggered Synergy of Exfoliation, Phase Transformation, and Surface Engineering in Cobalt Diselenide for Enhanced Water Oxidation
- Pages: 16421-16425
- First Published: 17 October 2018
Metathesis
Wavelength-Controlled Dynamic Metathesis: A Light-Driven Exchange Reaction between Disulfide and Diselenide Bonds
- Pages: 16426-16430
- First Published: 21 October 2018
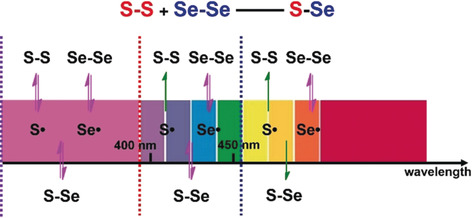
Controlled metathesis: Metathesis between disulfide and diselenide bonds was realized under irradiation, and the conversion of the exchange reaction could be controlled by modulating the wavelength of the light. This chemistry was applied to polymer materials to control the cleavage of polymers from a distance.
Difluorination
Enantioselective, Catalytic Vicinal Difluorination of Alkenes
- Pages: 16431-16435
- First Published: 26 September 2018
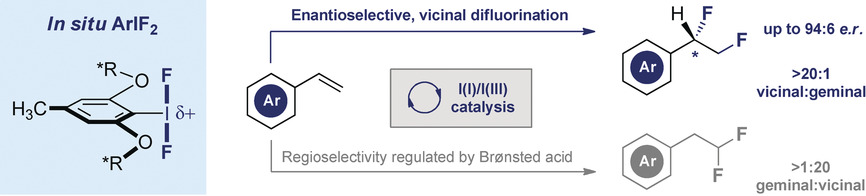
A C2-symmetric resorcinol derivative was used in the enantioselective, catalytic vicinal difluorination of alkenes by II/IIII catalysis. The HF:amine ratio employed in this process provides a handle for regioselective orthogonality as a function of Brønsted acidity. Selectivity reversal from the 1,1-difluorination pathway (geminal) to the desired 1,2-difluorination (vicinal) is disclosed.
Nanosheets
Topochemical Synthesis of 2D Carbon Hybrids through Self-Boosting Catalytic Carbonization of a Metal–Polymer Framework
- Pages: 16436-16441
- First Published: 17 October 2018
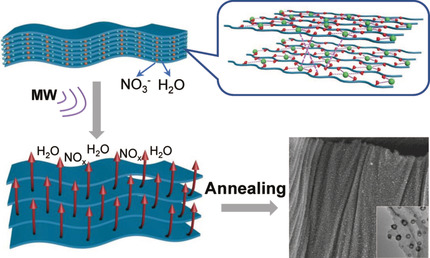
Superdrying: Microwave-enabled fast evaporation of water and decomposition of nitrate converted a metal–agarose framework into a 2D nanosheet structure. Using this approach, hybrids such as hollow Fe3C nanoparticles, Ni/Co nanoparticles, and hollow FeOx nanoparticles uniformly embedded in 2D graphitic carbon nanosheets could be obtained after annealing.
Coordination Chemistry
Low Heat of Adsorption of Ethylene Achieved by Major Solid-State Structural Rearrangement of a Discrete Copper(I) Complex
- Pages: 16442-16446
- First Published: 17 October 2018
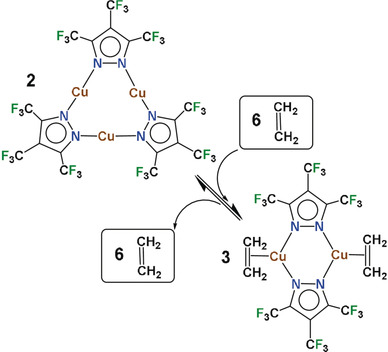
Three's a crowd: A polyfluorinated, trinuclear copper complex absorbs ethylene and undergoes a major structural rearrangement leading to a dinuclear copper–ethylene complex. Upon removal of ethylene it reverts back to the trinuclear species. This process occurs both in solution and in the solid state.
Photocatalysis
Enabling Visible-Light-Driven Selective CO2 Reduction by Doping Quantum Dots: Trapping Electrons and Suppressing H2 Evolution
- Pages: 16447-16451
- First Published: 23 October 2018
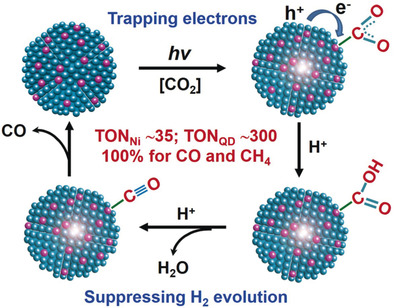
Quantum dots (QDs), a class of promising nanoparticles for visible-light harvesting, commonly possess low activity and selectivity towards photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Doping CdS QDs with transition-metal cations, which can trap photoexcited electrons and suppress H2 evolution, provides an approach to visible-light-driven highly selective CO2 reduction with excellent durability.
Nanorods
Tuning the Morphology and Chiroptical Properties of Discrete Gold Nanorods with Amino Acids
- Pages: 16452-16457
- First Published: 30 October 2018
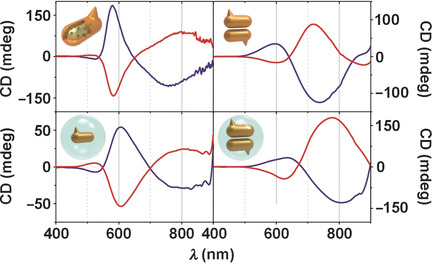
Discrete gold nanorods (Au NRs) with strong chiroptical responses in the visible and near infrared region were synthesized by a seed-mediated approach in the presence of l- or d-cysteine. The chiral Au NRs can be further stabilized by a silica coating (lower pictures). Assembly of the chiral Au NRs (right pictures) with glutathione further improved the g factor.
Mesoporous Materials
A Generic Method for Preparing Hollow Mesoporous Silica Catalytic Nanoreactors with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles inside Their Cavities
- Pages: 16458-16463
- First Published: 22 October 2018
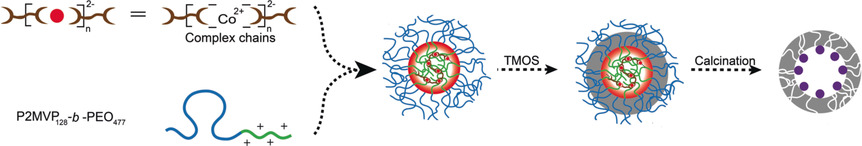
Nanoparticles in nanoreactors: Hollow mesoporous silica nanoreactors with small metal oxide nanoparticles inside their cavities were obtained by deposition of silica onto metal-containing polymer micelles and subsequent calcination. The CoxOy-containing mesoporous silica nanoreactors were used as catalysts for the degradation of methylene blue and new coccine with hydrogen peroxide.
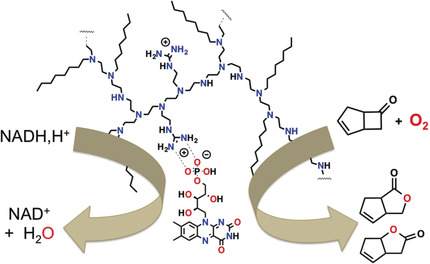
Whole-Cell Biocatalysis
Regulating Cofactor Balance In Vivo with a Synthetic Flavin Analogue
- Pages: 16464-16468
- First Published: 20 October 2018
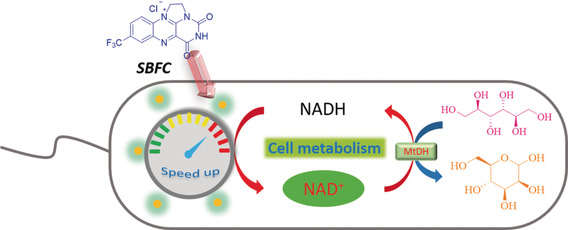
Balancing act: A novel strategy to manipulate the intracellular cofactor balance for whole-cell biotransformations based on a synthetic flavin analogue is reported. The synthetic flavin analogue can directly permeate into E. coli cells and accelerate cellular NAD+ regeneration without requiring cell-membrane modification.
Cooperative Catalysis
Substrate-Induced Self-Assembly of Cooperative Catalysts
- Pages: 16469-16474
- First Published: 10 October 2018
Selenium Compounds | Hot Paper
AISeC2H (AI=K, Rb, Cs): Crystalline Compounds with the Elusive −Se-C≡C-H Anion
- Pages: 16475-16479
- First Published: 22 October 2018
CO2 Reduction
Dinuclear Metal Synergistic Catalysis Boosts Photochemical CO2-to-CO Conversion
- Pages: 16480-16485
- First Published: 25 October 2018
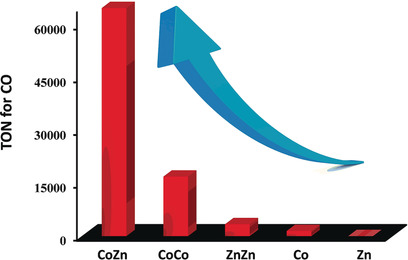
In sync with zinc: A dinuclear heterometallic CoZn catalyst shows much higher photocatalytic activity than the corresponding dinuclear homometallic CoCo and ZnZn catalysts, or the mononuclear Co and Zn catalysts for CO2 reduction under the same conditions. The high performance of the CoZn catalyst is due to the enhanced dinuclear metal synergistic catalysis (DMSC) effect between ZnII and CoII.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Dynamic Covalent Self-Assembly Based on Oxime Condensation
- Pages: 16486-16490
- First Published: 18 October 2018
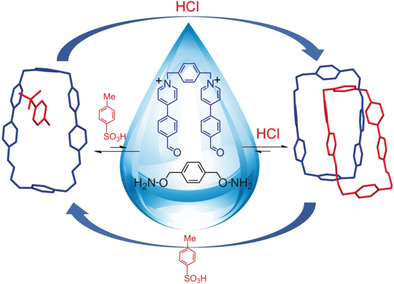
An off and on relationship: In strongly acidic aqueous solutions, the oxime bond is dynamic and allows both a catenane and a macrocycle to self-assemble in relatively high yields. The dynamic nature of oxime linkage could be turned OFF almost fully in neutral conditions, making the self-assembled catenane kinetically inert in both solid state and solution at elevated temperatures or during chromatography and counteranion exchange.
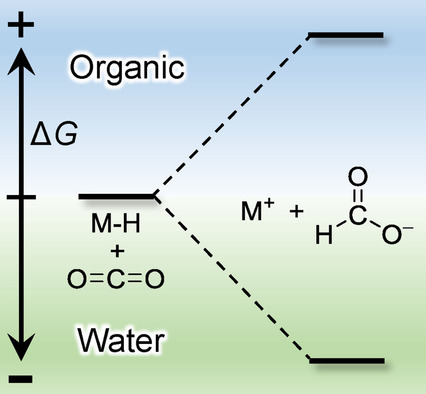
Electrocatalysis
Selective CO2 Splitting by Doubly Reduced Aryl Boranes to Give CO and [CO3]2−
- Pages: 16491-16495
- First Published: 15 October 2018
Noncovalent Interactions
Noncovalent Carbon-Bonding Interactions in Proteins
- Pages: 16496-16500
- First Published: 22 October 2018
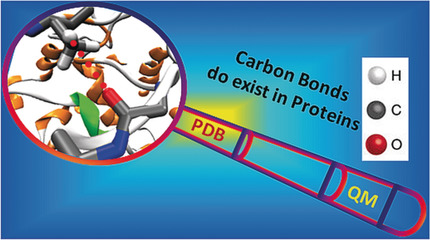
Present and correct: A detailed protein data bank analysis in combination with quantum calculations showed that a significant number of carbon bonds (C-bonds) are present in proteins. These C-bonds contribute enthalpically to the overall hydrophobic interaction and play a significant role in the photodissociation mechanism of myoglobin and the binding of nucleobases to proteins.
COF Films
Flexible Films of Covalent Organic Frameworks with Ultralow Dielectric Constants under High Humidity
- Pages: 16501-16505
- First Published: 17 October 2018
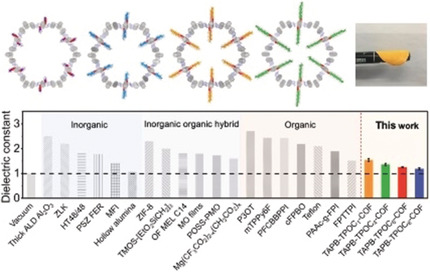
Constant improvement: Covalent organic framework films with ultralow dielectric constants have been prepared by interfacial polymerization. These films feature thermal robustness, good flexibility, tunable dielectric constant, and high resistance to moisture and bending, providing great potential in portable electronic devices.
Fluorescent Probes
Dynamically Monitoring Cell Viability in a Dual-Color Mode: Construction of an Aggregation/Monomer-Based Probe Capable of Reversible Mitochondria-Nucleus Migration
- Pages: 16506-16510
- First Published: 29 October 2018
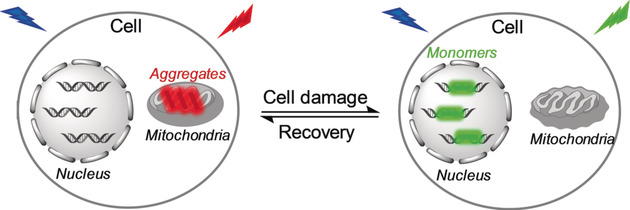
Visualizing cell viability: A fluorescent probe capable of reversible migration between mitochondria and nucleus dependent on cell viability and labelling the two organelles in dual colors has been developed. With the probe, mitochondria and nucleus can be visualized in dual emission channels, and cell viability could be evaluated by intracellular emission color and probe localization.
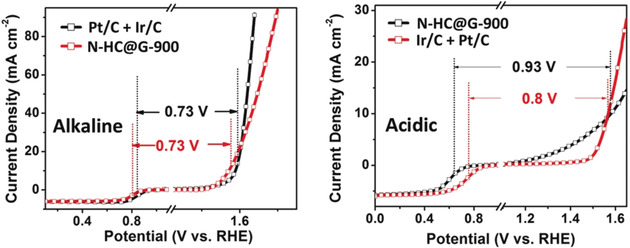
Electrocatalysis | Very Important Paper
Ultrathin Nitrogen-Doped Holey Carbon@Graphene Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions in Alkaline and Acidic Media
- Pages: 16511-16515
- First Published: 30 October 2018
Anthracene π-Clusters | Very Important Paper
Synthesis and Properties of a Highly Congested Tri(9-anthryl)methyl Radical
- Pages: 16516-16519
- First Published: 29 October 2018
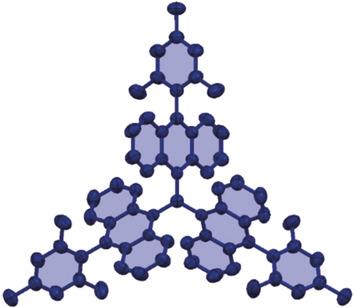
A highly congested tri(9-anthryl)methyl radical was successfully synthesized by circumventing the steric hindrance imposed by the bulky groups surrounding the central methyl carbon atom. Owing to its congested structure, the mesityl-substituted tri(9-anthryl)methyl radical is remarkably stable, which facilitates its handling under ambient conditions.
Synthetic Methods
Umpolung of Carbonyl Groups as Alkyl Organometallic Reagent Surrogates for Palladium-Catalyzed Allylic Alkylation
- Pages: 16520-16524
- First Published: 23 October 2018
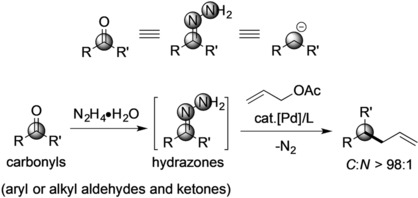
Surrogates: A highly chemo- and regioselective direct palladium-catalyzed C-allylation of hydrazones was developed using umpolung carbonyls as a source of unstabilized alkyl carbanions and surrogates of highly reactive alkyl organometallic reagents. The method requires only a catalytic amount of both metal and ligand, delivers products in high yields, is easily scaled-up, and demonstrates wide substrate scope and good functional-group compatibility.
Nanoparticle Catalysis
The Chemical Properties of Hydrogen Atoms Adsorbed on M0-Nanoparticles Suspended in Aqueous Solutions: The Case of Ag0-NPs and Au0-NPs Reduced by BD4−
- Pages: 16525-16528
- First Published: 15 October 2018
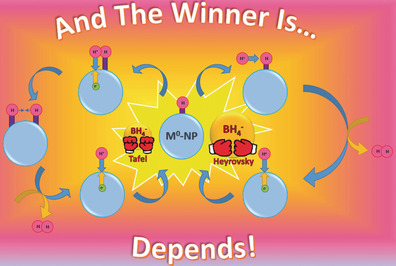
The nature of H-atoms adsorbed on metal nanoparticles (NPs) is of major importance in many catalyzed reduction processes. The H-atoms of the transient {(M0-NP)-Hn}n− behave mainly as hydrides when n is large (the Heyrovsky mechanism), and as atoms when n is small (the Tafel mechanism). The relative contributions of the two mechanisms differ considerably for Au and Ag-NPs.
DNA Nanotechnology
Modulating Self-Assembly of DNA Crystals with Rationally Designed Agents
- Pages: 16529-16532
- First Published: 21 September 2018

Sustainable growth: A strategy for controlling the crystallization kinetics and improving the quality of engineered self-assembled 3D DNA crystals is reported. By using a rationally designed agent to modulate the crystallization process, fewer, but larger, crystals that yield diffraction patterns with modestly higher resolution are produced.
Chemical Protein Synthesis
Triple Function of 4-Mercaptophenylacetic Acid Promotes One-Pot Multiple Peptide Ligation
- Pages: 16533-16537
- First Published: 22 October 2018
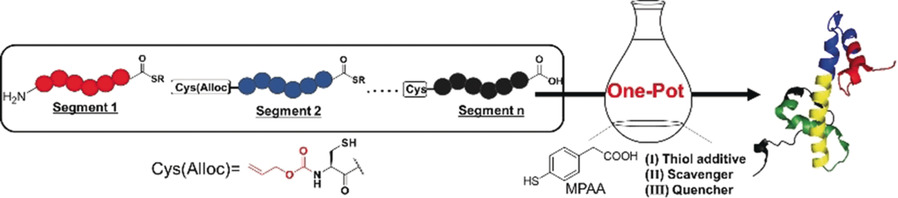
Three in one: Efficient one-pot multiple peptide ligation through repetitive native chemical ligation (NCL) and the removal of allyloxycarbonyl (Alloc) groups with a palladium complex was facilitated by 4-mercaptophenylacetic acid (MPAA; see scheme). This thiol additive for NCL also functioned as a scavenger for π-allyl palladium complexes and quencher of the resulting palladium(0) complexes.
Polymers | Very Important Paper
Investigation of the Locked-Unlocked Mechanism in Living Anionic Polymerization Realized with 1-(Tri-isopropoxymethylsilylphenyl)-1-phenylethylene
- Pages: 16538-16543
- First Published: 26 October 2018

Locked in: An intriguing advance in living anionic polymerization (LAP) by a “locked-unlocked” mechanism was investigated. The living anionic species can be quantitatively locked by end-capping with 1-(tri-isopropoxymethylsilylphenyl)-1-phenylethylene (DPE-Si(O-iPr)3) and can be unlocked by adding the key, sodium 2,3-dimethylpentan-3-olate (NaODP).
Synthetic Methods
gem-Difluorination of Alkenyl N-methyliminodiacetyl Boronates: Synthesis of α- and β-Difluorinated Alkylborons
- Pages: 16544-16548
- First Published: 24 October 2018
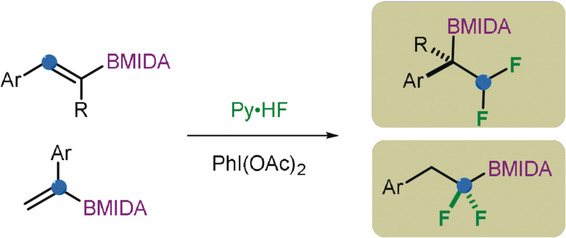
On the move: A migratory geminal difluorination of aryl-substituted alkenyl N-methyliminodiacetyl (MIDA) boronates using commercially available Py⋅HF as the fluorine source is reported. The protocol offers an unprecedented opportunity for the synthesis of α- and β-difluorinated alkylboron compounds. Mild reaction conditions, broad substrate scope, good functional-group tolerance, and moderate to good yields were observed.
One-Pot Synthesis
Gold(III)-Catalyzed Site-Selective and Divergent Synthesis of 2-Aminopyrroles and Quinoline-Based Polyazaheterocycles
- Pages: 16549-16553
- First Published: 11 October 2018
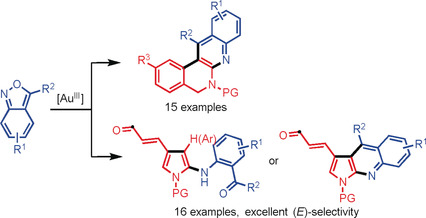
One-pot strategy: A simple gold(III) catalyst enables the construction of 2-aminopyrroles and quinoline-fused polyazaheterocycles from ynamides and anthranils under mild reaction conditions. This strategy uses readily available starting materials, proceeds in a highly step- and atom-economical manner, with broad substrate scope and scale-up potential.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Bimetallic Rhodium(II)/Indium(III) Relay Catalysis for Tandem Insertion/Asymmetric Claisen Rearrangement
- Pages: 16554-16558
- First Published: 20 October 2018
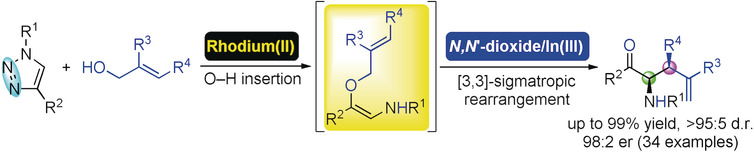
A highly efficient asymmetric tandem reaction of N-sulfonyl-1,2,3-triazoles with two types of allyl alcohol esters was achieved by using a bimetallic rhodium(II)/chiral N,N′-dioxide–indium(III) complex catalyst. A series of β/γ-amino acid derivatives bearing different substituents were obtained in a good to excellent diastereo- and enantioselective manner.
N-Heterocyclic Imines
Successive Protonation of an N-Heterocyclic Imine Derived Carbonyl: Superelectrophilic Dication Versus Masked Acylium Ion
- Pages: 16559-16563
- First Published: 24 October 2018
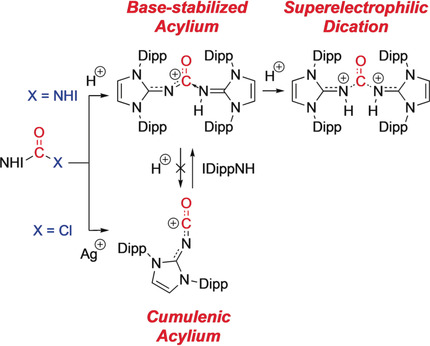
Superelectrophilic dications formed by the double protonation of heteroatom functionalized carbonyl compounds were introduced conceptually and studied in situ in the seminal work of Olah. By employing sterically demanding and strongly electron-releasing N-heterocyclic iminato substituents, the first such example, [(IDippNH)2CO]2+, has been structurally characterized.
Alkynes | Hot Paper
CuI-Mediated Bromoalkynylation and Hydroalkynylation Reactions of Unsymmetrical Benzynes: Complementary Modes of Addition
- Pages: 16564-16568
- First Published: 03 November 2018
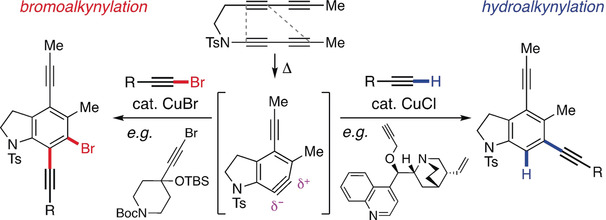
Two mechanistically distinct modes of reaction—Cu-catalyzed bromo- and hydroalkynylations—are described for unsymmetrical arynes. These reactions are efficient, broad in scope, and give complementary alkynylation products. Mechanisms are proposed and potential for synthetic elaboration is demonstrated.







![Selective CO2 Splitting by Doubly Reduced Aryl Boranes to Give CO and [CO3]2−](/cms/asset/9e69b702-4c50-4944-8609-413551c1015c/anie201811135-toc-0001-m.jpg)