Regulating Cofactor Balance In Vivo with a Synthetic Flavin Analogue
Dr. Zhuotao Tan
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Chenjie Zhu
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJingwen Fu
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaowang Zhang
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ming Li
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wei Zhuang
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Hanjie Ying
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zhuotao Tan
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Chenjie Zhu
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJingwen Fu
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaowang Zhang
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ming Li
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wei Zhuang
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Hanjie Ying
College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 S Puzhu Rd, 211816 Nanjing, China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
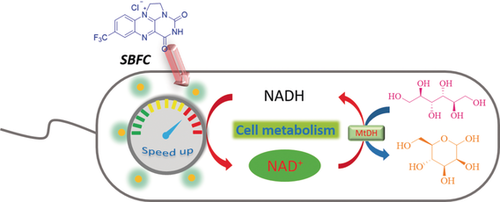
Balancing act: A novel strategy to manipulate the intracellular cofactor balance for whole-cell biotransformations based on a synthetic flavin analogue is reported. The synthetic flavin analogue can directly permeate into E. coli cells and accelerate cellular NAD+ regeneration without requiring cell-membrane modification.
Abstract
A novel strategy to regulate cofactor balance in vivo for whole-cell biotransformation using a synthetic flavin analogue is reported. High efficiency, easy operation, and good applicability were observed for this system. Confocal laser scanning microscopy was employed to verify that the synthetic flavin analogue can directly permeate into Escherichia coli cells without modifying the cell membrane. This work provides a promising intracellular redox regulatory approach to construct more efficient cell factories.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201810881-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.5 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201810881-sup-0001-video1.avi2.3 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aU. T. Bornscheuer, G. W. Huisman, R. J. Kazlauskas, S. Lutz, J. C. Moore, K. Robins, Nature 2012, 485, 185;
- 1bM. T. Reetz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12480;
- 1cG. W. Huisman, S. J. Collier, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 284.
- 2
- 2aM. Wang, B. Chen, Y. Fang, T. Tan, Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 1032;
- 2bX. Chen, S. Li, L. Liu, Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 337;
- 2cY. Wang, K. Y. San, G. N. Bennett, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 994.
- 3
- 3aS. H. Park, H. U. Kim, T. Y. Kim, J. S. Park, S. S. Kim, S. Y. Lee, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4618;
- 3bJ. Liu, S. H. J. Chan, T. Brock-Nannestad, C. Jun, S. Y. Lee, C. Solem, P. R. Jensen, Metab. Eng. 2016, 36, 57.
- 4
- 4aX. Wang, Y. J. Zhou, L. Wang, W. Liu, Y. Liu, C. Peng, Z. K. Zhao, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 692;
- 4bG. N. Vemuri, M. A. Eiteman, E. Altman, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1715.
- 5
- 5aT. S. Reynolds, C. M. Courtney, K. E. Erickson, L. M. Wolfe, A. Chatterjee, P. Nagpal, R. T. Gill, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 2685;
- 5bD. Brekasis, M. S. B. Paget, EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4856.
- 6
- 6aH. Gröger, F. Chamouleau, N. Orologas, C. Rollmann, K. Drauz, W. Hummel, A. Weckbecker, O. May, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5677; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 5806;
- 6bS. Kim, J. S. Hahn, Metab. Eng. 2015, 31, 94.
- 7M. Ask, M. Bettiga, V. Mapelli, L. Olsson, Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 22.
- 8
- 8aS. Brinkmann-Chen, T. Flock, J. K. B. Cahn, C. D. Snow, E. M. Brustad, J. A. McIntosh, P. Meinhold, L. Liang, F. H. Arnold, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10946;
- 8bT. W. Johannes, R. D. Woodyer, H. Zhao, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 96, 18.
- 9
- 9aC. E. Paul, I. W. C. E. Arends, F. Hollmann, ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 788;
- 9bT. Knaus, C. E. Paul, C. W. Levy, S. Vries, F. G. Mutti, F. Hollmann, N. S. Scrutton, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1033;
- 9cA. Geddes, C. E. Paul, S. Hay, F. Hollmann, N. S. Scrutton, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11089;
- 9dC. E. Paul, F. Hollmann, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4773;
- 9eC. Nowak, A. Pick, P. Lommes, V. Sieber, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5202;
- 9fD. Ji, L. Wang, S. Hou, W. Liu, J. Wang, Q. Wang, Z. K. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20857.
- 10L. Wang, D. Ji, Y. Liu, Q. Wang, X. Wang, Y. J. Zhou, Y. Zhang, W. Liu, Z. K. Zhao, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1977.
- 11
- 11aH. Oshikane, M. Watabe, T. Nakaki, Protein Expression Purif. 2018, 148, 40;
- 11bB. Miroux, J. E. Walker, J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 260, 289.
- 12C. Zhu, Q. Li, L. Pu, Z. Tan, K. Guo, H. Ying, P. Ouyang, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 4989.
- 13X. Hu, Y. Shi, P. Zhang, M. Miao, T. Zhang, B. Jiang, Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 773.
- 14M. Rauch, S. Schmidt, I. W. C. E. Arends, K. Oppelt, S. Kara, F. Hollmann, Green Chem. 2017, 19, 376.
- 15
- 15aB. Kaup, S. Bringer-Meyer, H. Sahm, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 69, 397;
- 15bW. Yang, Y. Zhou, Z. K. Zhao, Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 4387.
- 16H. Link, J. M. Buescher, U. Sauer, Methods Microbiol. 2012, 39, 127.
- 17
- 17aW. Chin, K. Lin, C. Liu, K. Tsuge, C. Huang, BMC Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 36;
- 17bJ. A. Imlay, Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 395;
- 17cI. Fridovich, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 97.
- 18J. L. Brumaghim, Y. Li, E. Henle, S. Linn, J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 42495.
- 19
- 19aB. R. Riebel, P. R. Gibbs, W. B. Wellborn, A. S. Bommarius, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2002, 344, 1156;
- 19bZ. Xiao, C. Lv, C. Gao, J. Qin, C. Ma, Z. Liu, P. Liu, L. Li, P. Xu, PloS one 2010, 5, e 8860;
- 19cQ. Han, M. A. Eiteman, Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2017, 106, 106.
- 20G. N. Vemuri, M. A. Eiteman, E. Altman, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 94, 538.
- 21
- 21aA. K. Holm, L. M. Blank, M. Oldiges, A. Schmid, C. Solem, P. R. Jensen, G. N. Vemuri, J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17498;
- 21bY. J. Zhou, W. Yang, L. Wang, Z. Zhu, S. Zhang, Z. K. Zhao, Microb. Cell Fact. 2013, 12, 103.
- 22R. Ciriminna, A. Fidalgo, L. M. Ilharco, M. Pagliaro, ChemistryOpen 2018, 7, 233.