A Multi-Ion Strategy towards Rechargeable Sodium-Ion Full Batteries with High Working Voltage and Rate Capability
Dr. Chunlei Jiang
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYue Fang
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Physics and Chemistry of the Ministry of Education, Jilin Normal University, Siping, 136000 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWenyong Zhang
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiaohe Song
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jihui Lang
Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Physics and Chemistry of the Ministry of Education, Jilin Normal University, Siping, 136000 China
Search for more papers by this authorLei Shi
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Yongbing Tang
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chunlei Jiang
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYue Fang
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Physics and Chemistry of the Ministry of Education, Jilin Normal University, Siping, 136000 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWenyong Zhang
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiaohe Song
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jihui Lang
Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Physics and Chemistry of the Ministry of Education, Jilin Normal University, Siping, 136000 China
Search for more papers by this authorLei Shi
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Yongbing Tang
Functional Thin Films Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055 China
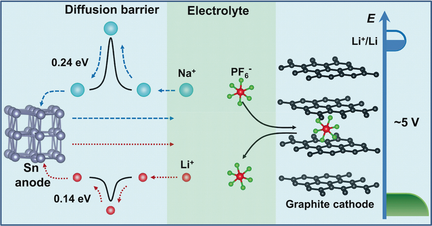
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Two ions in the fire: A multi-ion strategy to improve the electrochemical performance of sodium-ion full batteries is presented. The optimized sodium-ion-based multi-ion battery achieves a high working voltage of about 4.0 V, superior rate capability (up to 30 C; capacity retention: 87 %), and long cycling stability over 500 cycles at 5 C (capacity retention: 95 %).
Abstract
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are a promising alternative for the large-scale energy storage owing to the natural abundance of sodium. However, the practical application of SIBs is still hindered by the low working voltage, poor rate performance, and insufficient cycling stability. A sodium-ion based full battery using a multi-ion design is now presented. The optimized full batteries delivered a high working voltage of about 4.0 V, which is the best result of reported sodium-ion full batteries. Moreover, this multi-ion battery exhibited good rate performance up to 30 C and a high capacity retention of 95 % over 500 cycles at 5 C. Although the electrochemical performance of this multi-ion battery may be further enhanced via optimizing electrolyte and electrode materials for example, the results presented clearly indicate the feasibility of this multi-ion strategy to improve the electrochemical performance of SIBs for possible energy storage applications.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201810575-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf969.9 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aV. Palomares, P. Serras, I. Villaluenga, K. B. Hueso, J. Carretero-González, T. Rojo, Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5884–5901;
- 1bT. Liu, B. Wang, X. Gu, L. Wang, M. Ling, G. Liu, D. Wang, S. Zhang, Nano Energy 2016, 30, 756–761;
- 1cP. K. Nayak, L. Yang, W. Brehm, P. Adelhelm, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 102–120; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 106–126;
- 1dS.-L. Chou, S.-X. Dou, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1705871.
- 2
- 2aD. Larcher, J. M. Tarascon, Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 19–29;
- 2bZ. Hu, Q. Liu, S.-L. Chou, S.-X. Dou, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700606.
- 3W. Ren, Z. Zhu, Q. An, L. Mai, Small 2017, 13, 1604181.
- 4
- 4aY. Xu, Q. Wei, C. Xu, Q. Li, Q. An, P. Zhang, J. Sheng, L. Zhou, L. Mai, Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600389;
- 4bS. Li, J. Qiu, C. Lai, M. Ling, H. Zhao, S. Zhang, Nano Energy 2015, 12, 224–230.
- 5
- 5aD. Kundu, E. Talaie, V. Duffort, L. F. Nazar, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3431–3448; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 3495–3513;
- 5bL. Xu, H. Sitinamaluwa, H. Li, J. Qiu, Y. Wang, C. Yan, H. Li, S. Yuan, S. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2102–2109;
- 5cY. Fang, X.-Y. Yu, X. W. D. Lou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9859–9863; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 10007–10011;
- 5dD. Ma, Y. Li, H. Mi, S. Luo, P. Zhang, Z. Lin, J. Li, H. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8901–8905; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 9039–9043;
- 5eX. Wang, C. Niu, J. Meng, P. Hu, X. Xu, X. Wei, L. Zhou, K. Zhao, W. Luo, M. Yan, L. Mai, Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500716;
- 5fW. Li, C. Han, W. Wang, F. Gebert, S. Chou, H. Liu, X. Zhang, S. Dou, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700274.
- 6
- 6aB. L. Ellis, L. F. Nazar, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2012, 16, 168–177;
- 6bS.-W. Kim, D.-H. Seo, X. Ma, G. Ceder, K. Kang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 710–721;
- 6cM. D. Slater, D. Kim, E. Lee, C. S. Johnson, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 947–958;
- 6dN. Yabuuchi, K. Kubota, M. Dahbi, S. Komaba, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11636–11682.
- 7
- 7aF. Li, Z. Zhou, Small 2018, 14, 1702961;
- 7bY. Qi, L. Mu, J. Zhao, Y. S. Hu, H. Liu, S. Dai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9911–9916; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 10049–10054.
- 8
- 8aJ. Barker, R. K. B. Gover, P. Burns, A. J. Bryan, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2006, 9, A 190–A192;
- 8bY. Cheng, H. J. Chang, H. Dong, D. Choi, V. L. Sprenkle, J. Liu, Y. Yao, G. Li, J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 3125–3141;
- 8cT. Gao, F. Han, Y. Zhu, L. Suo, C. Luo, K. Xu, C. Wang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401507;
- 8dY. Ju, Y. Meng, Y. Wei, X. Bian, Q. Pang, Y. Gao, F. Du, B. Liu, G. Chen, Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 18073–18079;
- 8eW. Song, X. Ji, C. Pan, Y. Zhu, Q. Chen, C. E. Banks, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 14357–14363;
- 8fH.-R. Yao, Y. You, Y.-X. Yin, L.-J. Wan, Y.-G. Guo, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 9326–9333.
- 9
- 9aC. Jiang, Y. Fang, J. Lang, Y. Tang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700913;
- 9bM. Wang, C. Jiang, S. Zhang, X. Song, Y. Tang, H. M. Cheng, Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 667–672;
- 9cX. Zhang, Y. Tang, F. Zhang, C.-S. Lee, Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502588.
- 10
- 10aH. Gao, J. B. Goodenough, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12768–12772; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 12960–12964;
- 10bJ. Z. Guo, P. F. Wang, X. L. Wu, X. H. Zhang, Q. Yan, H. Chen, J. P. Zhang, Y. G. Guo, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701968;
- 10cJ. Y. Hwang, S. M. Oh, S. T. Myung, K. Y. Chung, I. Belharouak, Y. K. Sun, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6865;
- 10dH. Li, L. Peng, Y. Zhu, D. Chen, X. Zhang, G. Yu, Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3399–3405;
- 10eY. Wang, R. Xiao, Y. S. Hu, M. Avdeev, L. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6954.
- 11S. T. Senthilkumar, H. Bae, J. Han, Y. Kim, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5335–5339; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5433–5437.
- 12M. Noel, R. Santhanam, J. Power Sources 1998, 72, 53–65.
- 13V. Eshkenazi, E. Peled, L. Burstein, D. Golodnitsky, Solid State Ionics 2004, 170, 83–91.
- 14
- 14aG. Henkelman, A. Arnaldsson, H. Jónsson, Comput. Mater. Sci. 2006, 36, 354–360;
- 14bM. Yu, D. R. Trinkle, J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 064111.
- 15
- 15aS. P. Kowalczyk, L. Ley, F. R. McFeely, R. A. Pollak, D. A. Shirley, Phys. Rev. B 1973, 8, 3583–3585;
- 15bX. Zhang, Q. Zhang, X. G. Wang, C. Wang, Y. N. Chen, Z. Xie, Z. Zhou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12814–12818; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 12996–13000.
- 16
- 16aJ. Cabana, L. Monconduit, D. Larcher, M. R. Palacin, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, E 170–192;
- 16bC. K. Chan, H. Peng, G. Liu, K. McIlwrath, X. F. Zhang, R. A. Huggins, Y. Cui, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 31–35.
- 17J. A. Read, J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 8438–8446.
- 18G. Henkelman, B. P. Uberuaga, H. Jónsson, J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 9901–9904.