Multifunctional Liposome: A Bright AIEgen–Lipid Conjugate with Strong Photosensitization
Graphical Abstract
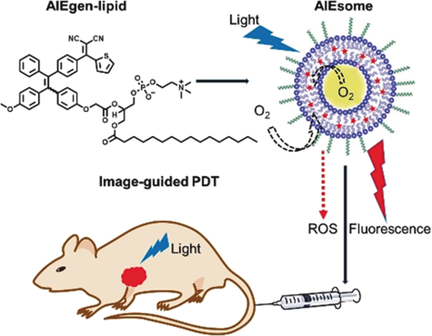
Teamwork: An aggregation-induced emission fluorogen was combined with a liposome to yield an AIEgen–lipid conjugate (“AIEsome”). The AIEsome exhibits bright red fluorescence and strong photosensitization along with great photostability and biocompatibility, and can be used for image-guided photodynamic therapy for in vitro cancer cell ablation and in vivo antitumor therapy. PDT=photodynamic therapy, ROS=reactive oxygen species.
Abstract
Liposomes have been used as popular drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. However, it is difficult to track traditional liposome delivery systems in an efficient and stable fashion to assess their delivery efficacy and biodistribution after administration. Meanwhile, conventional fluorescent liposomes containing optical tracers face the challenge of aggregation-caused quenching. Herein, we report a strategy for the integration of an aggregation-induced emission fluorogen with a liposome to yield an AIEgen–lipid conjugate, termed “AIEsome”. The AIEsome exhibits bright red fluorescence along with great photostability and biocompatibility, and can be used for in vitro cancer cell labeling and in vivo tumor targeting. Meanwhile, benefiting from the excellent photosensitizing ability of the AIEgen and its good oxygen exposure in aqueous media, the AIEsome also performs well in efficient photodynamic therapy (PDT) for both in vitro cancer cell ablation and in vivo antitumor therapy after white light illumination.