Enhancing the Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy through a Porphyrin/POSS Alternating Copolymer
Jianqiu Jin
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry, Key Laboratory for Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology of the Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYucheng Zhu
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry, Key Laboratory for Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology of the Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zhenghe Zhang
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry, Key Laboratory for Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology of the Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Weian Zhang
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry, Key Laboratory for Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology of the Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorJianqiu Jin
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry, Key Laboratory for Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology of the Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYucheng Zhu
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry, Key Laboratory for Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology of the Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zhenghe Zhang
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry, Key Laboratory for Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology of the Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Weian Zhang
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Chemistry, Key Laboratory for Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology of the Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
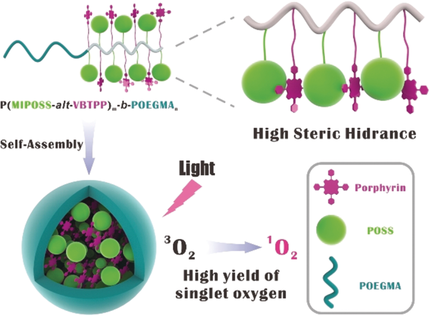
Nanoparticles formed by self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers were investigated for their potential application in photodynamic therapy. The porphyrin-containing polymeric nanoparticles display high photochemical yield and phototoxicity in vitro and in vivo, thus providing a novel strategy to enhance the PDT efficacy.
Abstract
Aggregation-induced quenching (AIQ) of photosensitizers greatly reduces the quantum yield of singlet oxygen generation and mitigates the efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT). We have prepared an alternating copolymer starting from 4-vinylbenzyl-terminated tetraphenylporphyrin (VBTPP) and maleimide isobutyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (MIPOSS), via alternating reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. Porphyrin and POSS are installed on the amphiphilic block copolymers backbone in an alternating fashion and POSS completely inhibits the aggregation of porphyrin units via stacking. The amphiphilic block copolymer can self-assemble into nanoparticles and its application in PDT treatment was tested. These porphyrin-containing polymeric nanoparticles display high photochemical yield and phototoxicity in vitro and in vivo, providing a novel strategy to enhance the PDT efficacy.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201808811-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aD. E. Dolmans, D. Fukumura, R. K. Jain, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387;
- 1bW. Sun, S. Li, B. Haupler, J. Liu, S. Jin, W. Steffen, U. S. Schubert, H. J. Butt, X. J. Liang, S. Wu, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603702.
- 2
- 2aY. Huang, F. Qiu, L. Shen, D. Chen, Y. Su, C. Yang, B. Li, D. Yan, X. Zhu, ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10489–10499;
- 2bH. Chen, L. Xiao, Y. Anraku, P. Mi, X. Liu, H. Cabral, A. Inoue, T. Nomoto, A. Kishimura, N. Nishiyama, K. Kataoka, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 157–163;
- 2cS. Chakrabortty, B. K. Agrawalla, A. Stumper, N. M. Vegi, S. Fischer, C. Reichardt, M. Kögler, B. Dietzek, M. Feuring-Buske, C. Buske, S. Rau, T. Weil, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2512–2519;
- 2dC. Zhang, K. Zhao, W. Bu, D. Ni, Y. Liu, J. Feng, J. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1770–1774; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 1790–1794;
- 2eY. Yuan, C. J. Zhang, M. Gao, R. Zhang, B. Z. Tang, B. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1780–1786; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 1800–1806;
- 2fY. Liu, Y. Liu, W. Bu, C. Cheng, C. Zuo, Q. Xiao, Y. Sun, D. Ni, C. Zhang, J. Liu, J. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8105–8109; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 8223–8227;
- 2gW. Wu, D. Mao, F. Hu, S. Xu, C. Chen, C.-J. Zhang, X. Cheng, Y. Yuan, D. Ding, D. Kong, B. Liu, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700548;
- 2hC. Ji, Q. Gao, X. Dong, W. Yin, Z. Gu, Z. Gan, Y. Zhao, M. Yin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11384–11388; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 11554–11558;
- 2iA. Galstyan, R. Schiller, U. Dobrindt, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10362–10366; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 10498–10502.
- 3
- 3aJ. P. Celli, B. Q. Spring, I. Rizvi, C. L. Evans, K. S. Samkoe, S. Verma, B. W. Pogue, T. Hasan, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2795–2838;
- 3bA. L. Wirotius, E. Ibarboure, L. Scarpantonio, M. Schappacher, N. D. McClenaghan, A. Deffieux, Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 1903–1912.
- 4
- 4aC. S. Jin, J. F. Lovell, J. Chen, G. Zheng, ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2541–2550;
- 4bM. H. Lee, E. J. Kim, H. Lee, H. M. Kim, M. J. Chang, S. Y. Park, K. S. Hong, J. S. Kim, J. L. Sessler, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16380–16387;
- 4cC. Qian, P. Feng, J. Yu, Y. Chen, Q. Hu, W. Sun, X. Xiao, X. Hu, A. Bellotti, Q.-D. Shen, Z. Gu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2588–2593; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 2632–2637;
- 4dK. Liu, R. Xing, Q. Zou, G. Ma, H. Möhwald, X. Yan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3036–3039; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 3088–3091;
- 4eH. Fan, G. Yan, Z. Zhao, X. Hu, W. Zhang, H. Liu, X. Fu, T. Fu, X.-B. Zhang, W. Tan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5477–5482; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 5567–5572;
- 4fJ. Schmitt, V. Heitz, A. Sour, F. Bolze, H. Ftouni, J.-F. Nicoud, L. Flamigni, B. Ventura, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 169–173; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 171–175;
- 4gS.-J. Park, W. Park, K. Na, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3472–3482;
- 4hY. Li, G. Liu, X. Wang, J. Hu, S. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1760–1764; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 1792–1796;
- 4iL. Yin, Z. Song, Q. Qu, K. H. Kim, N. Zheng, C. Yao, I. Chaudhury, H. Tang, N. P. Gabrielson, F. M. Uckun, J. Cheng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5757–5761; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 5869–5873.
- 5
- 5aF. Helmich, C. C. Lee, M. M. L. Nieuwenhuizen, J. C. Gielen, P. C. M. Christianen, A. Larsen, G. Fytas, P. E. L. G. Leclere, A. P. H. J. Schenning, E. W. Meijer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3939–3942; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 4031–4034;
- 5bC. Escudero, J. Crusats, I. Diez-Perez, Z. El-Hachemi, J. M. Ribo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 8032–8035; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 8200–8203.
- 6
- 6aZ. Yu, W. Pan, N. Li, B. Tang, Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 4237–4244;
- 6bP. Huang, X. Qian, Y. Chen, L. Yu, H. Lin, L. Wang, Y. Zhu, J. Shi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1275–1284;
- 6cS. Xu, X. Zhu, C. Zhang, W. Huang, Y. Zhou, D. Yan, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2052.
- 7K. Kano, K. Fukuda, H. Wakami, R. Nishiyabu, R. F. Pasternack, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 7494–7502.
- 8
- 8aK. Lu, C. He, W. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16712–16715;
- 8bS. Y. Li, H. Cheng, B. R. Xie, W. X. Qiu, J. Y. Zeng, C. X. Li, S. S. Wan, L. Zhang, W. L. Liu, X. Z. Zhang, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7006–7018.
- 9
- 9aC.-S. Lee, W. Park, Y. U. Jo, K. Na, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4354–4357;
- 9bL. Xu, L. Liu, F. Liu, H. Cai, W. Zhang, Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 2945–2954;
- 9cY. Liu, S. Pujals, P. J. M. Stals, T. Paulohrl, S. I. Presolski, E. W. Meijer, L. Alhertazzi, A. R. A. Palmans, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3423–3433;
- 9dL. Shen, Y. Huang, D. Chen, F. Qiu, C. Ma, X. Jin, X. Zhu, G. Zhou, Z. Zhang, Theranostics 2017, 7, 4537–4550.
- 10D. B. Cordes, P. D. Lickiss, F. Rataboul, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2081–2173.
- 11
- 11aW. B. Zhang, X. F. Yu, C. L. Wang, H. J. Sun, I. F. Hsieh, Y. W. Li, X. H. Dong, K. Yue, R. Van Horn, S. Z. D. Cheng, Macromolecules 2014, 47, 1221–1239;
- 11bW. A. Zhang, A. H. E. Muller, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1121–1162;
- 11cS. W. Kuo, F. C. Chang, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1649–1696.
- 12
- 12aF. F. Du, J. Tian, H. Wang, B. Liu, B. K. Jin, R. K. Bai, Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3086–3093;
- 12bW. A. Zhang, B. Fang, A. Walther, A. H. E. Muller, Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2563–2569;
- 12cZ. H. Zhang, L. Z. Hong, Y. Gao, W. A. Zhang, Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 4534–4541.
- 13K. Li, Y. T. Liu, K. Y. Pu, S. S. Feng, R. Y. Zhan, B. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 287–294.
- 14
- 14aE. A. Sykes, J. Chen, G. Zheng, W. C. Chan, ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5696–5706;
- 14bH. Jin, D. A. Heller, R. Sharma, M. S. Strano, ACS Nano 2009, 3, 149–158.