Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Achieving Secondary Structural Resolution in Kinetic Measurements of Protein Folding: A Case Study of the Folding Mechanism of Trp-cage (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46/2011)
- Page: 10735
- First Published: 07 September 2011

The folding dynamics of individual structural elements in proteins is studied by a multi-probe and multi-frequency approach. In their Communication on page 10 884 ff., M. R. Bunagan, F. Gai, and co-workers achieve a significantly improved structural resolution in kinetic studies of protein folding using their approach. Application of this approach to the miniprotein Trp-cage provides new insights into the folding mechanism of this extensively studied protein.
Inside Cover
Inside Cover: Solid-State NMR Measurements of Asymmetric Dipolar Couplings Provide Insight into Protein Side-Chain Motion (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46/2011)
- Page: 10736
- First Published: 16 September 2011

Molecular dynamics are generally anisotropic in nature. For the case of a three-site jump motion of a protein side chain (shown for valine), the apparent dipolar coupling tensor (turquoise/red lobes) therefore becomes asymmetric. In their Communication on page 11 005 ff., B. H. Meier, M. Ernst et al. report the first direct measurement of such asymmetric dipolar coupling tensors using isotopic labeling and REDOR solid-state NMR spectroscopy (REDOR data shown in the center).
Back Cover
Back Cover: Tuning Chemoselectivity in Iron-Catalyzed Sonogashira-Type Reactions Using a Bisphosphine Ligand with Peripheral Steric Bulk: Selective Alkynylation of Nonactivated Alkyl Halides (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46/2011)
- Page: 11012
- First Published: 11 October 2011

Iron complexes synthesized from iron salts and a newly developed bisphosphine ligand are described by M. Nakamura et al. in their Communication on page 10 973 ff. These complexes were used to achieve the C -center-selective alkynylation of nonactivated alkyl halides. Thus, this method uses iron complexes to forge substituted alkynes in a new practical synthesis just as the picture shows the forging of a samurai sword from iron.
-center-selective alkynylation of nonactivated alkyl halides. Thus, this method uses iron complexes to forge substituted alkynes in a new practical synthesis just as the picture shows the forging of a samurai sword from iron.
Editorial
Editorial: Scientific Social Responsibility: A Call to Arms
- Pages: 10738-10740
- First Published: 10 October 2011
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46/2011
- Pages: 10742-10756
- First Published: 09 November 2011
Corrigendum
Corrigendum: Asymmetric Allylboration of vic-Tricarbonyl Compounds: Total Synthesis of (+)-Awajanomycin
- Page: 10756
- First Published: 09 November 2011
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46/2011
- Pages: 10758-10760
- First Published: 09 November 2011
Author Profile
News
2011 IUPAC Awards to Distinguished Women in Chemistry and Chemical Engineering
- Pages: 10763-10764
- First Published: 13 October 2011
Book Review
Bioinorganic Medicinal Chemistry. Edited by Enzo Alessio.
- Pages: 10765-10767
- First Published: 21 October 2011
Highlights
Double CH Activation
Nickel-Mediated Cycloaddition by Two Sequential CH Activations†
- Pages: 10768-10769
- First Published: 27 September 2011
Templating Giants
Vernier Templating of Nanoscopic Porphyrin Rings†
- Pages: 10770-10771
- First Published: 07 September 2011
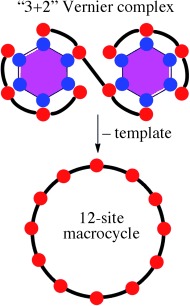
Growing bigger: A versatile approach toward the construction of nanosize π-conjugated macrocycles by Vernier templation has been demonstrated. The use of linear tetranuclear ZnII porprhyrin complexes and a suitable and readily available six-site template leads to formation and isolation of a giant, monodisperse macrocycle in a limited amount of synthetic steps, marking Vernier complex formation a powerful and new tool for the creation of superstructures (see picture).
N-Heterocyclic Nitrenium Ligands
N-Heterocyclic Nitrenium Ligands: A Missing Link Explored†
- Pages: 10772-10774
- First Published: 28 September 2011
Pince me: N-heterocyclic nitrenium cations have been framed into pincer motifs to explore their unprecedented ligand behavior to transition metals. This work fills a long-standing gap in the series of main-group N-heterocyclic carbene(NHC)-type ligands (see picture). Reasonable π-acceptor and weak σ-donor properties of these new ligands are expected to play a pivotal role in many organometallic reactions and in catalysis in the near future.
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2011
Quasicrystals: Sections of Hyperspace
- Pages: 10775-10778
- First Published: 13 October 2011
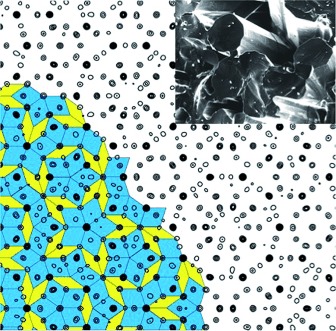
Since the moment Dan Shechtman discovered a material with an ordered but aperiodic (“quasiperiodic”) structure, which was believed to be impossible at the time, he began a long battle to convince his colleagues that his data were real. His efforts were finally rewarded with a Nobel Prize. The picture shows the projected electron density distribution function of decagonal Al-Co-Ni with Penrose tiling as an example of a quasicrystal.
Essay
Coordination Chemistry
Alfred Werner’s Coordination Chemistry: New Insights from Old Samples†
- Pages: 10780-10787
- First Published: 11 October 2011

Save your samples! The original compound [Co(en)2(NO2)2]Br prepared by Alfred Werner's student Edith Humphrey around 1900 did not crystallize as a conglomerate, but rather formed twinned crystals of both enantiomorphs. These findings, together with similar results for further samples from the Werner laboratory, provide new insight to the claim that Werner could have proved his coordination theory ten years earlier.
Minireview
Oxidative Carbonylation
Oxidative Carbonylation Reactions: Organometallic Compounds (RM) or Hydrocarbons (RH) as Nucleophiles
- Pages: 10788-10799
- First Published: 23 September 2011

A new option: Classical carbonylation reactions employ organohalides as electrophiles to produce carbonyl compounds. Now a series of carbonylative derivatives can also efficiently synthesized by oxidative carbonylation reactions that have an enriched substrate scope and milder reaction conditions. This Minireview summarizes newly developed oxidative carbonylation reactions employing either RM or RH as the nucleophiles.
Review
Medicinal Chemistry
Biology-Oriented Synthesis
- Pages: 10800-10826
- First Published: 28 October 2011
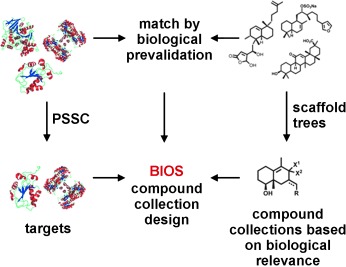
From nature with love! Biological relevance is the key argument in the search for small molecules that enable the chemical-biological analysis of biological systems or modulation of disease states. Biology-oriented synthesis (BIOS) uses this criterion to chart and navigate vast chemical structure space and to identify biologically relevant scaffold structures as guides for the synthesis of compound libraries (see picture).
Communications
Nanocomposites
Investigating the Amorphous–Crystalline Interplay in SiO2/TiO2 Nanocomposites by Total Scattering Methods†
- Pages: 10828-10833
- First Published: 12 September 2011
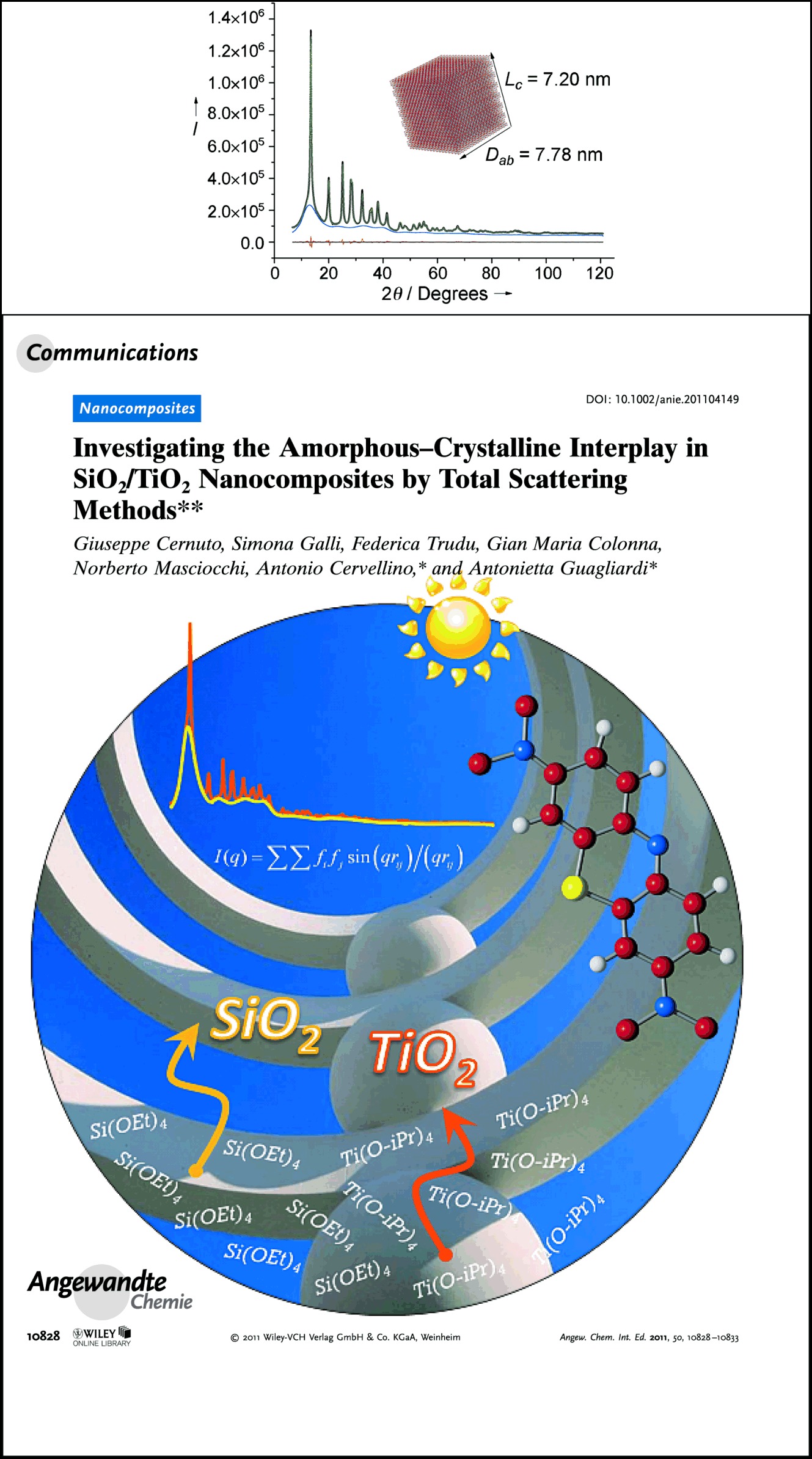
Come together! A combined real- and reciprocal-space total scattering approach was realized by applying Debye and radial distribution functions to nanocrystalline and amorphous fractions within the same experimental pattern. The method allows for the quantitative description of microstructural features induced by the amorphous–crystalline interplay in silica–titania nanocomposites (see picture).
Rotaxanes
A Twin-Axial Hetero[7]rotaxane†
- Pages: 10834-10838
- First Published: 20 September 2011
![A Twin-Axial Hetero[7]rotaxane](/cms/asset/020de021-49c0-450a-838d-6392a7950b91/mcontent.jpg)
Two in one: Two pseudorotaxanes can be combined to form a twin-axial hetero[7]rotaxane (see picture) by using the copper-catalyzed alkyne–azide “click” reaction. The synthetic route, in which twin-axial and single-axial rotaxanes are formed, combines self-assembly and the formation of covalent bonds to ensure the correct positioning of the two types of rings in the final product.
Inorganic Graphene Analogues
A Mixed-Solvent Strategy for Efficient Exfoliation of Inorganic Graphene Analogues†
- Pages: 10839-10842
- First Published: 27 September 2011
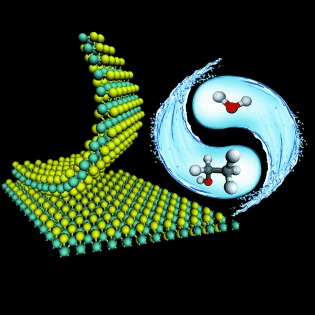
Two are better than one: A mixed-solvent method for liquid exfoliation of MoS2, WS2, and BN nanosheets is presented. Although ethanol and water are both poor solvents for this process, ethanol/water mixtures of appropriate composition, which can be predicted on the basis of Hansen solubility parameters, result in efficient exfoliation (see schematic) to give highly stable suspensions.
Enzymatic Reaction Dynamics
Is There a Dynamic Protein Contribution to the Substrate Trigger in Coenzyme B12-Dependent Ethanolamine Ammonia Lyase?†
- Pages: 10843-10846
- First Published: 22 September 2011
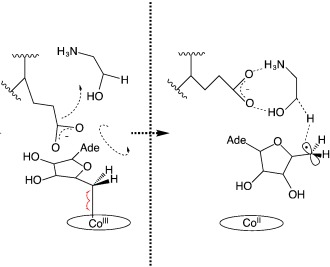
“Cohort-ry” in motion: The chemistry following CoC bond homolysis in coenzyme B12-dependent ethanolamine ammonia lyase is known to favor dissociation, but what of the protein contribution? Experiments reveal the radical pair reaction dynamics to be coupled to the ps–ns protein dynamics in B12 photolysis. This raises the possibility of a subtle, dynamic contribution to homolysis, which acts in cohort with electrostatics and H-abstraction from the substrate.
NIR Dyes
Halochromic Phenolate Perylene Bisimides with Unprecedented NIR Spectroscopic Properties
- Pages: 10847-10850
- First Published: 23 September 2011
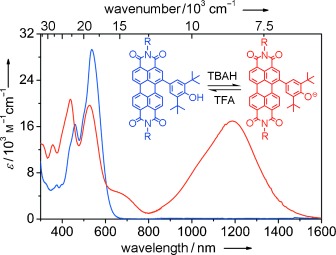
CC coupling of 1,7-dibromoperylene bisimide with sterically hindered 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol by a carbon nucleophilic substitution reaction in the absence of transition-metal catalysts gave novel halochromic perylene bisimides (see picture). The corresponding phenolate ions of these compounds exhibit unprecedented NIR spectroscopic properties including strong absorption with maxima at around 1200 nm.
DNA-Directed Chemistry
DNA-Programmed Glaser–Eglinton Reactions for the Synthesis of Conjugated Molecular Wires†
- Pages: 10851-10854
- First Published: 22 September 2011
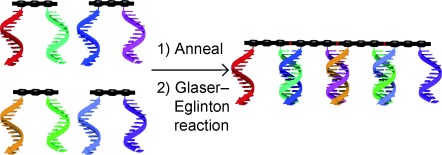
Wire self-assembly: Short oligo(phenylene ethynylene) modules (black structures, see picture) are assembled by attached DNA strands, which also direct the formation of 1,3-diyne linkages between the modules by the Cu-mediated Glaser–Eglinton reaction to selectively form dimer, trimer, and tetramer conjugated wires of up to 8 nm in length.
Nanostructures
Regulated Oxidation of Nickel in Multisegmented Nickel–Platinum Nanowires: An Entry to Wavy Nanopeapods†
- Pages: 10855-10858
- First Published: 26 September 2011
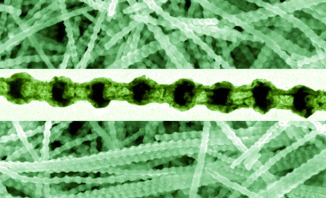
Split peas: Nanopeapods consisting of highly ordered, wavy NiO nanopods embedded with equally spaced Pt nanopeas were fabricated by the oxidation of multisegmented Ni/Pt nanowires at low temperatures. The Ni/Pt interface is an efficient platform for enhancing the outward diffusion of Ni during oxidation and for manipulating the nucleation of vacancies in Ni, which intrinsically behaves in an uncontrolled manner.
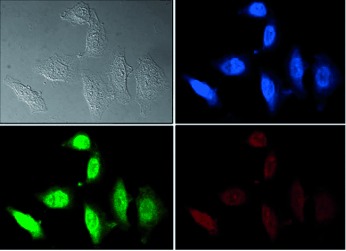
Peptide Structure
A Membrane-Bound Antiparallel Dimer of Rat Islet Amyloid Polypeptide†
- Pages: 10859-10862
- First Published: 22 September 2011
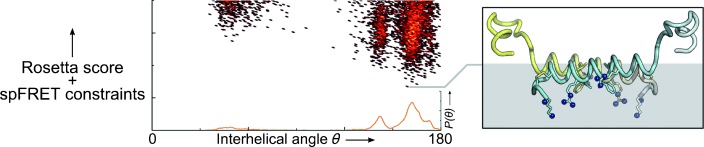
Gaining recognition: The structure of a previously unrecognized antiparallel dimer of rat islet amyloid polypeptide bound to anionic membrane nanodiscs was examined by using a combination of single-pair FRET and Rosetta model refinement. Models of the dimer showed a likely interface for lipid binding and suggest key interactions may also occur in the human isoform, thereby providing possible insights into fibril formation in type II diabetes.
Artificial Metalloenzymes
OsO4⋅Streptavidin: A Tunable Hybrid Catalyst for the Enantioselective cis-Dihydroxylation of Olefins†
- Pages: 10863-10866
- First Published: 21 September 2011
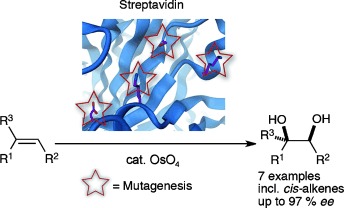
Taking control: Selective catalysts for olefin dihydroxylation have been generated by the combination of apo-streptavidin and OsO4. Site-directed mutagenesis allows improvement of enantioselectivity and even inversion of enantiopreference in certain cases. Notably allyl phenyl sulfide and cis-β-methylstyrene were converted with unprecedented enantiomeric excess.
Nonlinear Optics
Strongly Nonlinear Optical Chalcogenide Thin Films of APSe6 (A=K, Rb) from Spin-Coating†
- Pages: 10867-10870
- First Published: 20 September 2011
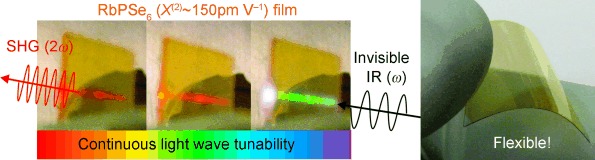
The first example of solution-based deposition of strongly nonlinear optical inorganic thin films at low temperatures of 125–250 °C is presented. The obtained glassy and crystalline films of highly nonlinear APSe6 compounds (A=K, Rb; χ(2)≈150 pm V−1) exhibit strong, inherent second harmonic and difference frequency generation (SHG and DFG) in the visible and near-IR spectral region at room temperature without the need of poling (see picture).
Surface Chemistry
Facile and Efficient Control of Bioadhesion on Poly(dimethylsiloxane) by Using a Biomimetic Approach†
- Pages: 10871-10874
- First Published: 21 September 2011
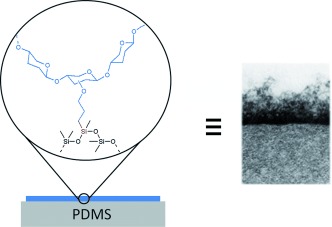
An antiadhesive nanofilm has been designed and prepared in one step in water onto commercial poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) by mimicking the external region of cell membranes. The resulting biomimetic surfaces are effective in suppressing protein adsorption as well as bacterial and mammalian cell adhesion.
Microengines
Light-Controlled Propulsion of Catalytic Microengines†
- Pages: 10875-10878
- First Published: 20 September 2011
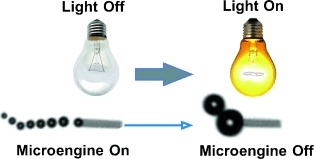
Turn off the light: A white-light source is used to control the propulsion of catalytic microengines powered by the local decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water. The influence of the wavelength of the light and intensity on the fuel conditions provides a remote control over the power of the self-propelled microengines (see picture).
Thermochromism
A Functional Nitroxide Radical Displaying Unique Thermochromism and Magnetic Phase Transition†
- Pages: 10879-10883
- First Published: 22 September 2011
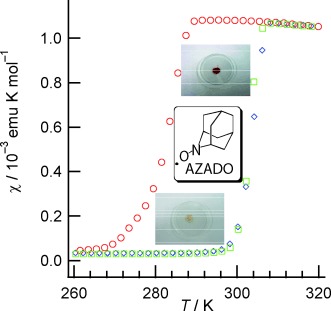
Thermochromic nitroxide: A nitroxide radical (AZADO) exhibits thermochromism with a structural change from a dimer at low temperature (4 °C) to paired monomers with large antiferromagnetic interaction at high temperature (35 °C). An hysteresis loop is observed in the magnetic data of this compound, revealing it to exhibit a first-order phase transition with room-temperature magnetic bistability.
Protein Folding
Achieving Secondary Structural Resolution in Kinetic Measurements of Protein Folding: A Case Study of the Folding Mechanism of Trp-cage†
- Pages: 10884-10887
- First Published: 29 September 2011
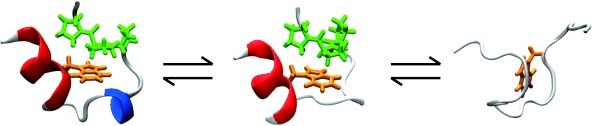
A new twist: A multi-probe and multi-frequency approach is shown for dissecting the folding dynamics of individual protein structural elements. In response to a temperature jump the 310-helix (blue in the picture) of the miniprotein Trp-cage unfolds before the global unfolding of the protein, whereas the formation of the cage structure depends on the folding of the α-helix (red).
CO2-Selective Adsorption
Selective Adsorption of CO2 from Light Gas Mixtures by Using a Structurally Dynamic Porous Coordination Polymer†
- Pages: 10888-10892
- First Published: 23 September 2011
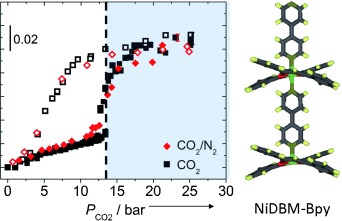
Flexibility provides selectivity: The selective adsorption of CO2 from mixtures with N2, CH4, and N2O in a dynamic porous coordination polymer (see monomer structure) was evaluated by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy, GC, and SANS. All three techniques indicate highly selective adsorption of CO2 from CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 mixtures at 30 °C, with no selectivity observed for the CO2/N2O system.
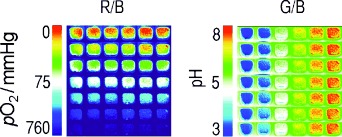
Tissue Imaging
Simultaneous Photographing of Oxygen and pH In Vivo Using Sensor Films†
- Pages: 10893-10896
- First Published: 27 September 2011
Reaction Mechanisms
The Molecular Mechanism of Enzymatic Glycosyl Transfer with Retention of Configuration: Evidence for a Short-Lived Oxocarbenium-Like Species†
- Pages: 10897-10901
- First Published: 26 September 2011
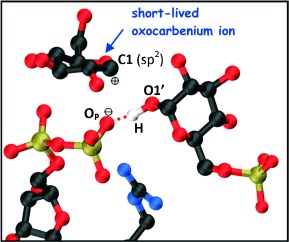
A quantum leap: By means of quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics metadynamics simulations, a front-face SNi-type reaction for glycosyl transfer with retention of the anomeric configuration is shown to be feasible. A short-lived oxocarbenium-like species (see picture; O red, P gold, N blue, C black) is identified and provides the complete itinerary of this long sought after molecular mechanism.
Organic Materials
Coupling Tetracyanoquinodimethane to Tetrathiafulvalene: A Fused TCNQ–TTF–TCNQ Triad†
- Pages: 10902-10906
- First Published: 26 September 2011
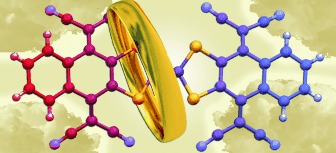
Happy marriage: For the first time, a fused TCNQ–TTF–TCNQ triad has been synthesized and structurally characterized. Strong bending is observed in both the TTF bridge and the benzo-TCNQ moieties, which prevents good packing for intermolecular charge transfer. The Vis/NIR and VT-EPR studies of the mixed-valence derivative of the triad indicate that the electrons are moving from one acceptor moiety to the other through the donor TTF bridge.
Dendritic Solar Concentrators
Towards Unimolecular Luminescent Solar Concentrators: Bodipy-Based Dendritic Energy-Transfer Cascade with Panchromatic Absorption and Monochromatized Emission†
- Pages: 10907-10912
- First Published: 22 September 2011
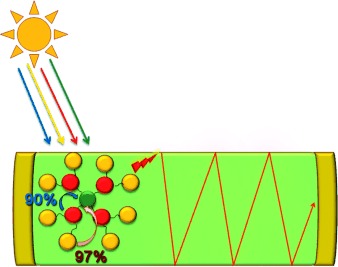
A polymer-embedded dendritic, bodipy-based panchromatic absorber with a built-in energy gradient concentrates incident solar radiation at a terminal chromophore, resulting in a monochromatized emission directed to the sides of the polymer waveguide (see picture). This particular design minimizes self-absorption losses from the peripheral antenna units with an impressive S factor of 10 000.
Arene Functionalization
Friedel–Crafts Benzylation of Activated and Deactivated Arenes†
- Pages: 10913-10916
- First Published: 22 September 2011
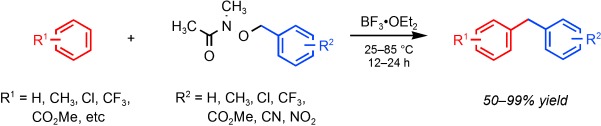
NO going back makes possible facile Friedel–Crafts benzylations with moderate reaction temperatures, simple reaction workups, and improved substrate scope for the formation of synthetically important diarylmethanes (see scheme). Upon complexation with BF3⋅OEt2, hydroxamates serve as reversible leaving groups that stabilize highly reactive carbocations. Even deactivated arenes and electron-deficient benzylhydroxamates react cleanly under these conditions.
Fulvene Synthesis
Catalytic [2+2+1] Cross-Cyclotrimerization of Silylacetylenes and Two Alkynyl Esters To Produce Substituted Silylfulvenes†
- Pages: 10917-10921
- First Published: 16 September 2011
![Catalytic [2+2+1] Cross-Cyclotrimerization of Silylacetylenes and Two Alkynyl Esters To Produce Substituted Silylfulvenes](/cms/asset/78c57d20-f39b-400d-a033-3cde288d5655/mcontent.jpg)
Three become one: The cationic rhodium(I) complex [Rh(cod)2]BF4 catalyzes the [2+2+1] cross-cyclotrimerization of silylacetylenes and two alkynyl esters, leading to substituted silylfulvenes (see scheme; cod=1,5-cyclooctadiene). The reductive complexation of the silylfulvene product with RhCl3 in EtOH furnished the corresponding dinuclear electron-deficient cyclopentadienyl rhodium(III) complex.
[2+2+2] Cross-Trimerization
Rhodium-Catalyzed Intermolecular [2+2+2] Cross-Trimerization of Aryl Ethynyl Ethers and Carbonyl Compounds To Produce Dienyl Esters†
- Pages: 10922-10926
- First Published: 21 September 2011
![Rhodium-Catalyzed Intermolecular [2+2+2] Cross-Trimerization of Aryl Ethynyl Ethers and Carbonyl Compounds To Produce Dienyl Esters](/cms/asset/2bb59355-d1af-4f73-b4e5-bf2170d8bcc1/mcontent.jpg)
Positive thinking: A cationic rhodium(I)/H8-binap complex catalyzes the chemo-, regio-, and stereoselective completely intermolecular [2+2+2] cross-trimerization of two aryl ethynyl ethers with both electron-deficient and electron-rich carbonyl compounds (see scheme; cod=1,5-cyclooctadiene). This reaction proceeded at room temperature to give aryloxy-substituted dienyl esters in good yields.
CH activation
PdII-Catalyzed CH Olefination of N-(2-Pyridyl)sulfonyl Anilines and Arylalkylamines†
- Pages: 10927-10931
- First Published: 22 September 2011
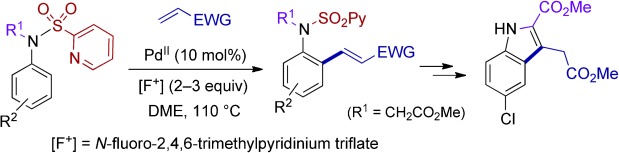
Flexible friend: The N-(2-pyridyl)sulfonyl group acts as a removable directing group in the PdII-catalyzed aryl CH ortho alkenylation of N-alkyl aniline, benzylamine, and phenethylamine derivatives with electron-poor alkenes. The products were obtained in high yields (70–90 %) and with complete regiocontrol. The mild reductive N-sulfonyl removal enables the construction of a variety of nitrogen heterocycles. EWG=electron-withdrawing group.
Polyketone Synthesis
Morphology Control of Polymer Particles in Ethylene/Carbon Monoxide Copolymerization†
- Pages: 10932-10935
- First Published: 23 September 2011

Partial to particular particles: The morphology of the polymer particles can be controlled in ethylene/CO copolymerization by pressurizing catalyst-containing 1-octanol droplets dispersed in water. The palladium catalyst should be harnessed with lipophilic long alkyl chains. Polymer particles of 0.5–1.0 mm size (see micrographs) with bulk densities of 0.2–0.3 g mL−1 are produced without reactor fouling.
Dioxygen Activation
Directing Protons to the Dioxygen Ligand of a Ruthenium(II) Complex with Pendent Amines in the Second Coordination Sphere†
- Pages: 10936-10939
- First Published: 26 September 2011

Proton relay: A side-on Ru–O2 complex with pendent amines in the ligand backbone has been synthesized to model proton delivery in O2 reduction (see scheme and structure; red O, purple Ru, blue N, yellow P). Protonation occurs at the amine near the O2 ligand, forming a hydrogen bond between the ammonium ion and the O2 ligand, leading to a small increase in OO bond length.
Heterocyclic Compounds
Synthesis of 1-Phospha-2-boraacenaphthenes: Reductive 1,2-Aryl Migration of 1-Diarylboryl-8-dichlorophosphinonaphthalenes†
- Pages: 10940-10943
- First Published: 21 September 2011
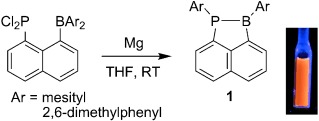
On the move: The title compounds 1, which are unique heterocyclic systems containing a PB bond, have been synthesized by the reduction of 1-diarylboryl-8-dichlorophosphinonaphthalene derivatives (see scheme). Both experimental and theoretical results for 1 revealed an effective interaction between the phosphorus atom, boron atom, and naphthyl moiety. Furthermore, 1 exhibits orange fluorescence in solution.
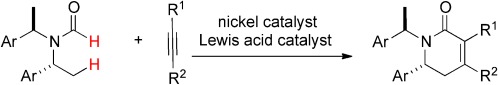
Dynamic Kinetic Resolution
Ionic-Surfactant-Coated Burkholderia cepacia Lipase as a Highly Active and Enantioselective Catalyst for the Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Secondary Alcohols†
- Pages: 10944-10948
- First Published: 27 September 2011
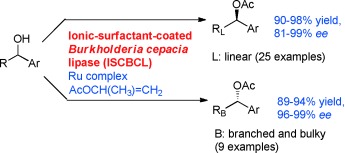
With a coat for activity: A highly active enzyme was prepared by coating Burkholderia cepacia lipase with an ionic surfactant for use in dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR). Important features of this enzyme include: the fastest DKR of 1-phenylethanol, the highly enantioselective DKR of a wide range of secondary alcohols (RCH(OH)Ar), and the switching of lipase enantioselectivity in DKR depending on the shape of the aliphatic chain (R).
Metal–Organic Frameworks
Solid-State Structural Transformations from 2D Interdigitated Layers to 3D Interpenetrated Structures†
- Pages: 10949-10952
- First Published: 28 September 2011
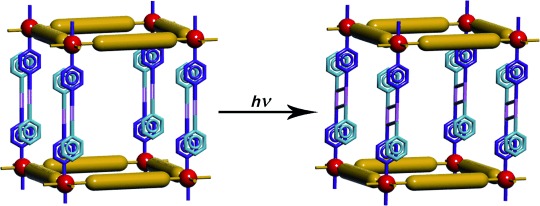
Construction by shining light! A [2+2] cycloaddition reaction in a 2D coordination polymer accompanied by single-crystal-to-single-crystal structural transformation to a 3D structure highlights the retrosynthesis of a 3D structure from a 2D layer compound (see scheme, Zn red, 4-styrylpyridine blue/turquoise).
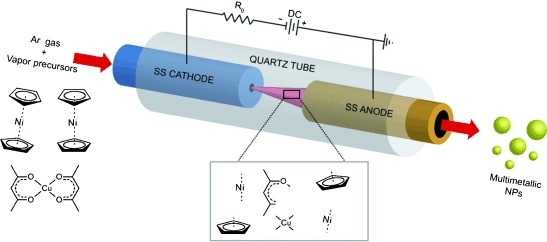
Nanotechnology
Plasma-Assisted Dissociation of Organometallic Vapors for Continuous, Gas-Phase Preparation of Multimetallic Nanoparticles†
- Pages: 10953-10956
- First Published: 22 September 2011
Amino Acids as Nitrogen Sources
Amino Acid-Based Reoxidants for Aminohydroxylation: Application to the Construction of Amino Acid–Amino Alcohol Conjugates†
- Pages: 10957-10960
- First Published: 23 September 2011
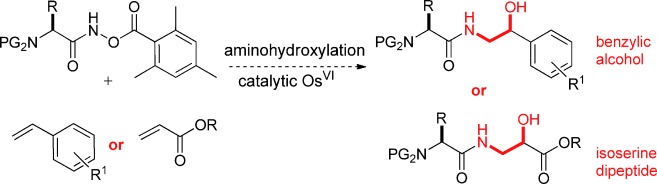
A viable nitrogen source for the aminohydroxylation reaction of terminal alkenes: By adding a N-O based reoxidant onto an amino acid acyl carbon atom, compounds were obtained that facilitated catalytic turnover and also promoted the conjugation of an amino acid with an alkene. High levels of regioselectivity were observed, as well as good stereoselectivity induced by catalytic amounts of a chiral ligand.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Asymmetric Reduction of Ketones by Phosphoric Acid Derived Catalysts†
- Pages: 10961-10964
- First Published: 22 September 2011
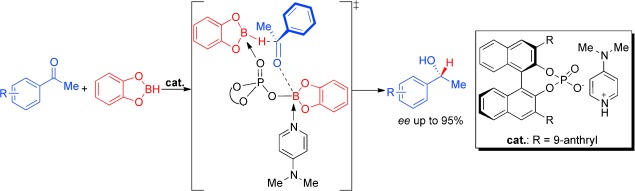
A new path to chiral alcohols: Asymmetric reduction of ketones was achieved utilizing a chiral Brønsted acid as precatalyst for the first time. Using catecholborane as the reducing agent, a highly enantioselective formation of chiral secondary alcohols was found with a broad substrate scope. Mechanistic studies indicate that phosphoryl catechol borate derived from the reaction of the Brønsted acid with catecholborane produced the active catalyst (see scheme).
Hydrogen Bonds
Structural Characterization, Infrared Spectroscopy, and Theoretical Calculations for B(C6F5)3-Stabilized Benzene–Ammonia and Benzene–Water Complexes†
- Pages: 10965-10968
- First Published: 22 September 2011
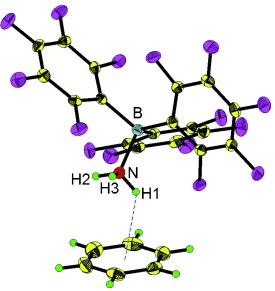
O/NH⋅⋅⋅π hydrogen bonds: Water–benzene and ammonia–benzene complexes are stabilized by the Lewis acid B(C6F5)3 and provide rare structural (X-ray) and infrared spectroscopic data for water–benzene and ammonia–benzene complexes in the solid state (see picture). The infrared spectra of the complexes showed that the OH and NH stretching frequencies decrease significantly on benzene complexation.
Oxygen Reduction
Co1−xS–Graphene Hybrid: A High-Performance Metal Chalcogenide Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction†
- Pages: 10969-10972
- First Published: 23 September 2011
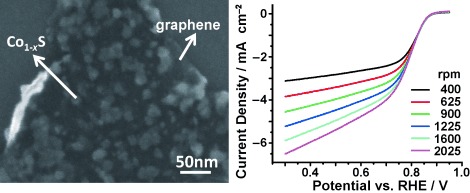
A hybrid electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), consisting of Co1−xS nanoparticles directly nucleated and grown on sheets of reduced graphene oxide (RGO; see SEM image), was prepared by a mild solution-phase reaction followed by an annealing step. The Co1−xS–RGO hybrid has the highest catalytic performance of all cobalt chalcogenide based ORR catalysts, as revealed inter alia by measurements with a rotating-disk electrode (see picture; RHE = reversible hydrogen electrode).
Cross-Coupling
Tuning Chemoselectivity in Iron-Catalyzed Sonogashira-Type Reactions Using a Bisphosphine Ligand with Peripheral Steric Bulk: Selective Alkynylation of Nonactivated Alkyl Halides†
- Pages: 10973-10976
- First Published: 01 September 2011
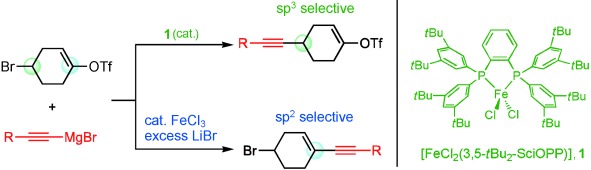
The incredible bulk: A highly C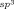 -center-selective alkynylation of nonactivated alkyl halides with the corresponding Grignard reagents is achieved by using the iron-phosphine complex 1. Primary and secondary alkyl iodides, bromides, and chlorides take part in the reaction to give the substituted alkynes in good to excellent yields. Sequential cyclization/cross-coupling reactions are also demonstrated.
-center-selective alkynylation of nonactivated alkyl halides with the corresponding Grignard reagents is achieved by using the iron-phosphine complex 1. Primary and secondary alkyl iodides, bromides, and chlorides take part in the reaction to give the substituted alkynes in good to excellent yields. Sequential cyclization/cross-coupling reactions are also demonstrated.
Lithography
Patterning Materials through Viscoelastic Flow and Phase Separation†
- Pages: 10977-10980
- First Published: 26 September 2011
Going with the flow: Patterning of various inorganic materials was achieved by phase separation between the nanomaterials and a polymer melt as well as concentrating the nanomaterials in defined areas by a polymer melt flow. This technique generated micro- and nanostructured patterns of metals and semiconductors (see picture).
Synthetic Methods
Using Nazarov Electrocyclization to Stage Chemoselective [1,2]-Migrations: Stereoselective Synthesis of Functionalized Cyclopentenones†
- Pages: 10981-10985
- First Published: 26 September 2011
![Using Nazarov Electrocyclization to Stage Chemoselective [1,2]-Migrations: Stereoselective Synthesis of Functionalized Cyclopentenones](/cms/asset/f584d282-199e-4786-9dc9-77c709ea61c0/mcontent.jpg)
Highly functionalized cyclopentenones have been prepared stereospecifically through a chemoselective copper(II)-mediated Nazarov/Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement sequence. After the initial 4π electrocyclization, this reaction involves two sequential [1,2]-migrations depending upon both migratory ability and steric bulk of the substituents at C1 and C5 (see scheme). The proposed mechanism of the reaction is supported by DFT studies.
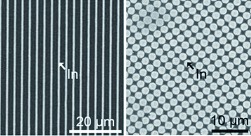
Photochromism
Unprecedented Stability of a Photochromic Bisthienylethene Based on Benzobisthiadiazole as an Ethene Bridge†
- Pages: 10986-10990
- First Published: 23 September 2011
An open and closed case: The photochromic bisthienylethene BTTE based on benzobisthiadiazole exhibits excellent photochromic performance in both solution and single crystals (see picture). BTTE shows excellent thermal stability, which is comparable to the widely known five-membered hexafluorocyclopentene-based counterpart.
Chiral Nanomaterials
Chiral Nematic Mesoporous Carbon Derived From Nanocrystalline Cellulose†
- Pages: 10991-10995
- First Published: 23 September 2011

Twisted organization: Pyrolysis of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC)/silica composite films leads to mesoporous carbon materials with long-range chiral organization (see picture). The NCC acts as a template and the resulting mesoporous carbon has a high specific surface area (>1400 m2 g−1) and accurately replicates the left-handed helical structure of the chiral nematic NCC films.
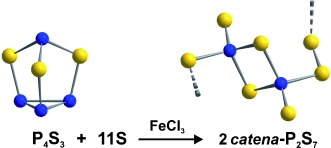
Phosphorus Polysulfides
Rational Syntheses and Structural Characterization of Sulfur-Rich Phosphorus Polysulfides: α-P2S7 and β-P2S7†
- Pages: 10996-11000
- First Published: 26 September 2011
Heterooligomeric Complexes
Vibralactone as a Tool to Study the Activity and Structure of the ClpP1P2 Complex from Listeria monocytogenes†
- Pages: 11001-11004
- First Published: 22 September 2011
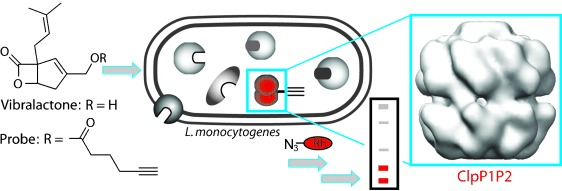
The Clp proteolytic machinery has important functions in many bacteria such as L. monocytogenes. Some organisms encode for two uncharacterized ClpP isoforms. Vibralactone was used to study the activity and assembly of ClpP1 and ClpP2 subunits in a hetero-oligomeric complex. Electron microscopic images reveal that the tetradecameric assembly is made up of two stacked homoheptameric ClpP1 and ClpP2 rings.
Protein NMR Spectroscopy
Solid-State NMR Measurements of Asymmetric Dipolar Couplings Provide Insight into Protein Side-Chain Motion†
- Pages: 11005-11009
- First Published: 14 September 2011

Nonsymmetric motion: Solid-state NMR measurements of dipolar coupling tensors provide insight into protein dynamics. The hitherto ignored asymmetry of the dipolar coupling tensor contains valuable information about motional asymmetry, which was used in the first direct site-resolved measurement of such tensors. Important motions such as rotamer jumps can now be directly detected in the solid state.
Preview
Preview: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47/2011
- Page: 11011
- First Published: 09 November 2011