Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Evolved Aliphatic Halogenases Enable Regiocomplementary C−H Functionalization of a Pharmaceutically Relevant Compound (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2019)
- Page: 18299
- First Published: 28 November 2019

Tailored aliphatic halogenases enable the derivatization of unactivated carbon centers in non-native substrates with exquisite stereo- and regioselectivity. In their Communication on page 18535, R. Buller and co-workers report the first evolution of a non-heme iron halogenase, WelO5*, to yield two regiocomplementary variants for the chlorination of a pharmaceutically interesting substrate. The highly evolvable nature of this enzyme underscores the usefulness of this halogenase family for late-stage derivatization.
Inside Cover: Zeolite-Encaged Single-Atom Rhodium Catalysts: Highly-Efficient Hydrogen Generation and Shape-Selective Tandem Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2019)
- Page: 18300
- First Published: 27 November 2019

Single-atom catalysis is emerging as a new frontier in heterogeneous catalysis. In their Research Article page 18570, J. Yu, A. Mayoral, and co-workers report a novel ligand-protected direct H2-reduction method to encapsulate single rhodium atoms within MFI zeolites under in situ hydrothermal conditions. The catalysts exhibit superior catalytic efficiency in ammonia borane (AB) hydrolysis and shape-selective tandem hydrogenation of nitroarenes by coupling with the hydrolysis of AB.
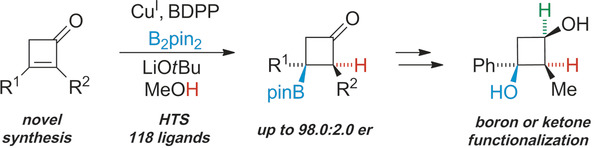
Inside Back Cover: Dynamic Open Coordination Cage from Nonsymmetrical Imidazole–Pyridine Ditopic Ligands for Turn-On/Off Anion Binding (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2019)
- Page: 18717
- First Published: 19 November 2019

Nonsymmetrical ligands are usually not considered building blocks for discrete self-assembled products. In their Communication on page 18424, J. Yuasa and D. Ogata employ a new imidazole/pyridine-based ditopic ligand as a building block for a dynamic Pd2L4 open cage compound that is available for turn-on/off anion binding through stoichiometry-driven structural transitions.
Back Cover: Inverting the Triiodide Formation Reaction by the Synergy between Strong Electrolyte Solvation and Cathode Adsorption for Lithium–Oxygen Batteries (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2019)
- Page: 18718
- First Published: 22 November 2019

Of the Li metal batteries the Li–O2 battery has the highest theoretical specific energy. In their Communication on page 18394, Y.-Y. Sun, T. Zhang, and co-workers find that the synergic effect of the strong binding of RuO2 to I2 and the strong solvation effect of DMSO on I2 could shift the direction of the well-known reaction I−+I2⇄I3− to the left-hand side. A Li–O2 battery with the Li/DMSO+LiI/RuO2 structure had significantly enhanced stability compared to one with TEGDME.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: A Supported Nickel Catalyst Stabilized by a Surface Digging Effect for Efficient Methane Oxidation
- First Published: 09 December 2019

Methane Oxidation In their Communication on page 18388, J. Luo, Y. Li, Y. Wu et al. present Ni NPs that etch and sink into a N-doped carbon support to prevent sintering. The Ni NPs are transformed into metal-defect sites in C−H bond activation for methane oxidation by elevating the temperature.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51/2019
- Pages: 18303-18318
- First Published: 09 December 2019
Author Profile
News
KNCV Gold Medal: I. K. Voets / SBIC Early Career Award: A. Dey / Malcolm McIntosh Prize: E. J. New / ICS Excellent Young Scientist Prize:C. E. Diesendruck
- Page: 18322
- First Published: 06 November 2019
Minireviews
Batteries
Sulfur-Based Electrodes that Function via Multielectron Reactions for Room-Temperature Sodium-Ion Storage
- Pages: 18324-18337
- First Published: 13 May 2019
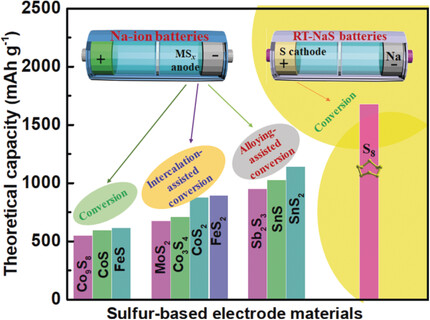
Sulfur-based electrode materials are currently regarded as promising candidates for sodium-storage technologies, especially for sodium-ion (Na-ion) and room-temperature sodium–sulfur (RT-NaS) batteries. In this Minireview on the progress of electrodes based on metal sulfides and elemental sulfur, material design and performance enhancement are highlighted and sodium-storage mechanisms for both battery systems are discussed.
Reviews
Natural Product Synthesis
Tetrodotoxin: History, Biology, and Synthesis
- Pages: 18338-18387
- First Published: 11 March 2019
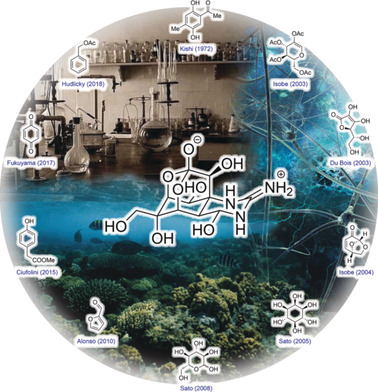
The deadly nature of the puffer fish has been known to mankind since the dawn of civilization. However, the compound responsible for this fatal activity was isolated only in the early 20th century and has been widely known to the scientific community as tetrodotoxin since then. This review traces its history, isolation, structural elucidation, biology, and synthesis. The syntheses of unnatural derivatives are covered as well.
Communications
Methane Oxidation
A Supported Nickel Catalyst Stabilized by a Surface Digging Effect for Efficient Methane Oxidation
- Pages: 18388-18393
- First Published: 06 November 2019
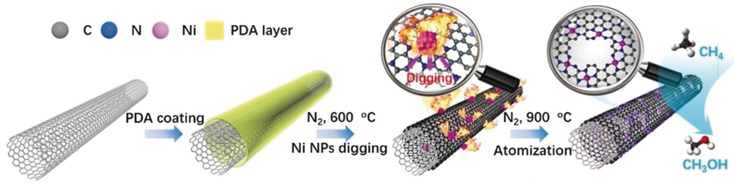
A surface digging effect of supported Ni NPs on an amorphous N-doped carbon is described, during which the surface-loaded Ni NPs etch and sink into the carbon support underneath to prevent sintering. The sinking Ni NPs could be transformed into thermodynamically stable and active metal-defect sites for activation of C−H bonds for methane oxidation by simply elevating temperature.
Li–O2 Batteries | Very Important Paper
Inverting the Triiodide Formation Reaction by the Synergy between Strong Electrolyte Solvation and Cathode Adsorption for Lithium–Oxygen Batteries
- Pages: 18394-18398
- First Published: 18 October 2019
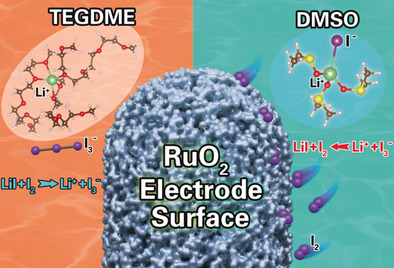
I pod: The synergic effect of the strong binding of RuO2 to I2 and the strong solvation effect of DMSO to I2 is found to invert the direction of the well-known reaction I−+I2⇌I3− to the left-hand side. A Li–O2 battery with the Li/DMSO+LiI/RuO2 structure had enhanced stability compared to one with TEGDME.
Hypergolic Materials
Hypergolic Triggers as Co-crystal Formers: Co-crystallization for Creating New Hypergolic Materials with Tunable Energy Content
- Pages: 18399-18404
- First Published: 14 October 2019

It′s not rocket science: Co-crystallization of a hypergolic decaborane building block designed for hydrogen bonding with energetic but not hypergolic or explosive fuel molecules enables the simple and rapid synthesis of new hypergolic materials with tunable energetic properties and ultrashort ignition delays down to 1 ms.
Asymmetric Catalysis
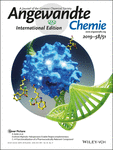
High-Throughput Ligand Screening Enables the Enantioselective Conjugate Borylation of Cyclobutenones to Access Synthetically Versatile Tertiary Cyclobutylboronates
- Pages: 18405-18409
- First Published: 08 October 2019
Organocatalysis
NHC-Catalyzed Chemoselective Reactions of Enals and Aminobenzaldehydes for Access to Chiral Dihydroquinolines
- Pages: 18410-18413
- First Published: 11 October 2019
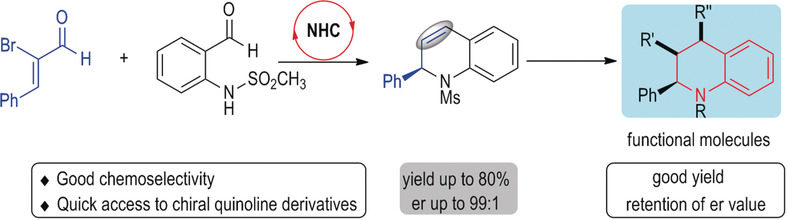
Quick access: An N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)-catalyzed chemoselective reaction of bromoenals and aminobenzaldehydes was developed for quick access to dihydroquinolines with excellent enantioselectivity. The dihydroquinoline products can be readily transformed into a diverse set of functional molecules such as pyridines and chiral piperidines.
Biosynthesis
The Biosynthesis of Norsesquiterpene Aculenes Requires Three Cytochrome P450 Enzymes to Catalyze a Stepwise Demethylation Process
- Pages: 18414-18418
- First Published: 16 October 2019
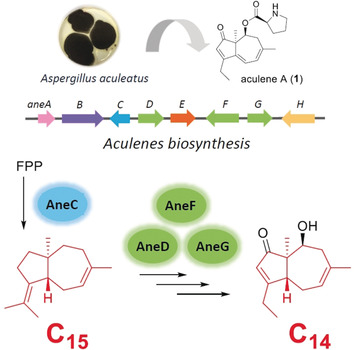
Long time no C: Aculenes are a class of norsesquiterpenes (C14) that are derived from daucane sesquiterpenes (C15), but the biosynthetic basis of the demethylation remained unknown. Three novel P450 monooxygenases were discovered to catalyze a stepwise demethylation process, and a new ent-daucane cyclase was also discovered. This work sheds light on how nature performs enzymatic demethylation and reveals new tools to expand chemical diversity.
Helicenes | Hot Paper
Symmetric, Unsymmetrical, and Asymmetric [7]-, [10]-, and [13]Helicenes
- Pages: 18419-18423
- First Published: 14 October 2019
![Symmetric, Unsymmetrical, and Asymmetric [7]-, [10]-, and [13]Helicenes](/cms/asset/65df8900-3816-4b7d-be71-d17b26a154a2/anie201910214-toc-0001-m.jpg)
All in a twirl: The gram-scale synthesis of a series of azaoxa[7]-, [10]-, and [13]helicenes is described. The synthesis is based on iterative oxidative furan formation between 3,6-dihydroxycarbazoles and/or 2-naphthols. The optically pure [13]helicenes can be synthetically functionalized both at the termini (see picture: blue) and the periphery (red).
Host–Guest Systems | Hot Paper
Dynamic Open Coordination Cage from Nonsymmetrical Imidazole–Pyridine Ditopic Ligands for Turn-On/Off Anion Binding
- Pages: 18424-18428
- First Published: 18 October 2019
Uranyl Peroxide Materials
In Situ Generation of Organic Peroxide to Create a Nanotubular Uranyl Peroxide Phosphate
- Pages: 18429-18433
- First Published: 11 October 2019
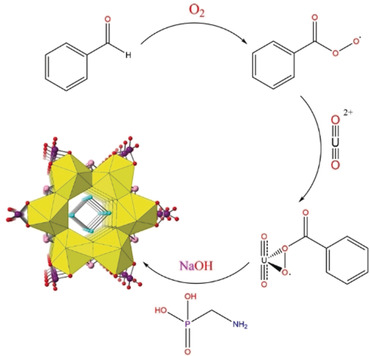
Autoxidation of benzaldehyde in the presence of uranium results in the in situ generation of organic peroxide and the isolation of novel nanotubular uranyl peroxide phases. Owing to the constant low-level production of peroxide, the uranium phase is formed in remarkably high yield and uniform structure.
Supramolecular Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Drawing with Iron on a Gel Containing a Supramolecular Siderophore
- Pages: 18434-18437
- First Published: 16 October 2019
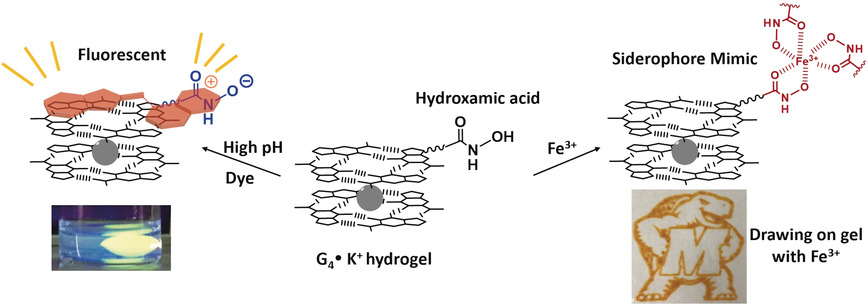
Soft matter, hard shell: pH-responsive hydrogels that can chelate Fe3+ were prepared from guanosine-5′-hydroxamic acid (HA). At high pH, the hydrogel binds thiazole orange, signaled by enhanced fluorescence. The HA units can also act as a supramolecular siderophore to form red complexes with Fe3+, which allowed the patterning of the hydrogel surface with FeCl3.
Relay Catalysis
Asymmetric Synthesis of Oxa-Bridged Oxazocines through a Catalytic RhII/ZnII Relay [4+3] Cycloaddition Reaction
- Pages: 18438-18442
- First Published: 15 October 2019
![Asymmetric Synthesis of Oxa-Bridged Oxazocines through a Catalytic RhII/ZnII Relay [4+3] Cycloaddition Reaction](/cms/asset/d8682e86-9e44-47df-b148-0d766df92541/anie201910898-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A highly efficient asymmetric cascade reaction of β,γ-unsaturated α-ketoesters and diazoimides was realized by using a bimetallic rhodium(II)/chiral N,N′-dioxide-zinc(II) catalytic system. The corresponding oxa-bridged oxazocine products bearing different substituents were obtained in moderate to excellent yields with excellent enantioselectivity under mild reaction conditions.
Room-Temperature Phosphorescence | Hot Paper
Carbon Dots in a Matrix: Energy-Transfer-Enhanced Room-Temperature Red Phosphorescence
- Pages: 18443-18448
- First Published: 09 October 2019
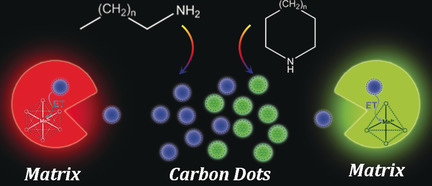
Connecting the dots: Energy transfer (ET) from carbon dots embedded in crystalline Mn-containing open-framework matrices results in high-efficiency red room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) emissions. Varying the carbon dot precursors and the heteroatom coordination geometries enables the emissions to be tuned from red to green/yellow.
Nitrogen Reduction Reaction
Greatly Improving Electrochemical N2 Reduction over TiO2 Nanoparticles by Iron Doping
- Pages: 18449-18453
- First Published: 23 September 2019
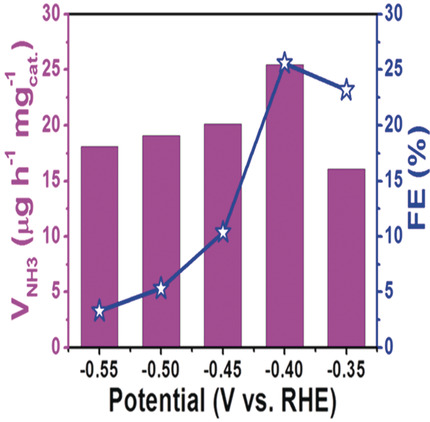
Strike while the iron is hot: Iron doping greatly improves electrochemical N2 reduction over TiO2 nanoparticle for ambient N2-to-NH3 fixation with excellent selectivity. The Fe-TiO2 catalyst attains a high Faradaic efficiency of 25.6 % and a large NH3 yield of 25.47 μg h−1 mgcat−1 at −0.40 V in 0.5 m LiClO4 versus a reversible hydrogen electrode. The synergistic effect of bi-Ti3+ sites and oxygen vacancies are responsible for the superior activity.
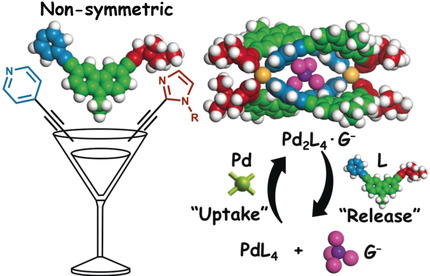
Chirality
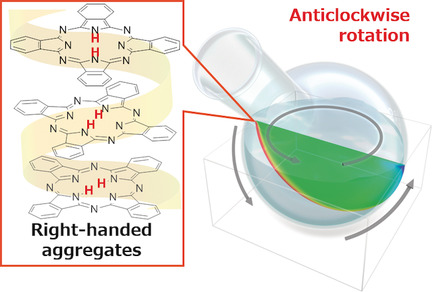
Chiral Supramolecular Nanoarchitectures from Macroscopic Mechanical Rotations: Effects on Enantioselective Aggregation Behavior of Phthalocyanines
- Pages: 18454-18459
- First Published: 29 September 2019
Perovskite Solar Cells
Enhanced Lifetime and Photostability with Low-Temperature Mesoporous ZnTiO3/Compact SnO2 Electrodes in Perovskite Solar Cells
- Pages: 18460-18465
- First Published: 13 October 2019
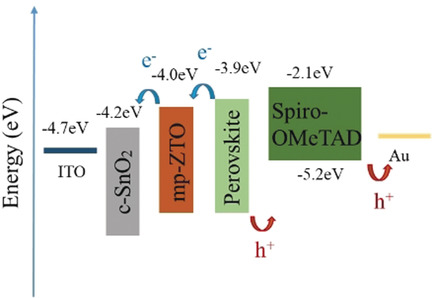
Low-temperature-processed, UV-inert ZnTiO3 as a mesoporous layer was introduced in SnO2-based planar perovskite solar cells. The application of ZnTiO3 modified the interface of SnO2/perovskite, and significantly improve the UV stability and lifetime of devices. The low-temperature mesoporous structure expands the choice for transmission layer and electrode materials.
Lithium | Hot Paper
Flexible Amalgam Film Enables Stable Lithium Metal Anodes with High Capacities
- Pages: 18466-18470
- First Published: 08 October 2019
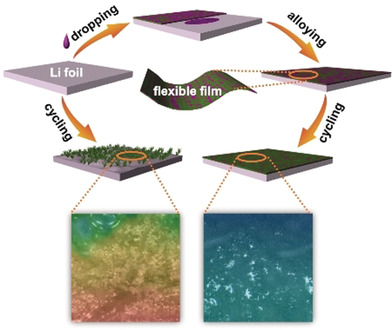
Protective coating: Li amalgam was studied for Li protection. The rational design of a Li anode with such a protective layer affords much improved cycling performance at practically high currents and capacities. Coupled with high-loading cathodes, the protected hybrid anodes demonstrate significantly improved cell stability, indicating its reliability for practical development of Li metal batteries.
Metal–Organic Frameworks
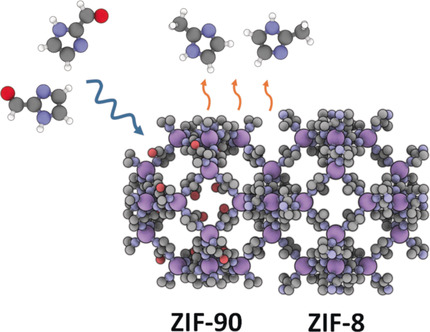
Vapor-Phase Linker Exchange of the Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-8: A Solvent-Free Approach to Post-synthetic Modification
- Pages: 18471-18475
- First Published: 08 October 2019
Hydrogenation
Mechanistic Divergence in the Hydrogenative Synthesis of Furans and Butenolides: Ruthenium Carbenes Formed by gem-Hydrogenation or through Carbophilic Activation of Alkynes
- Pages: 18476-18481
- First Published: 14 October 2019
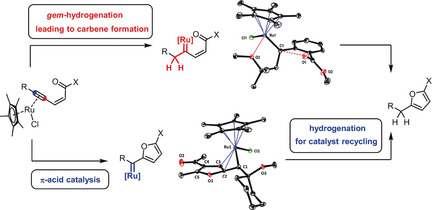
One way or the other: Enynes bearing a tethered carbonyl group are transformed into furans upon catalytic hydrogenation using a ruthenium catalyst. Strikingly though, the reaction can follow two distinct pathways, each of which involves discrete metal carbene intermediates. They differ in that the hydrogenation and carbene formation are either synchronized (gem-hydrogenation) or fully uncoupled.
Nanocrystals
Effect of Temperature on the Nucleation and Growth of Precious Metal Nanocrystals
- Pages: 18482-18486
- First Published: 08 October 2019
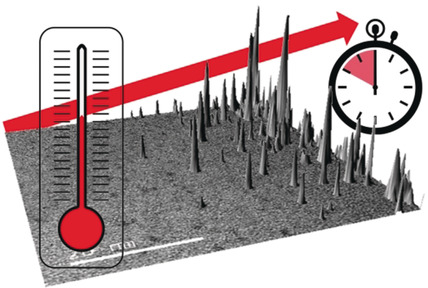
The dynamics of the nucleation of precious metal nanocrystals were studied at three different temperatures (20, 50, and 100 °C) by aberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy. A fast, and apparently linear, acceleration of the rate of nucleation was observed against increasing temperature (78.8, 117.7, and 176.5 pm min−1, respectively).
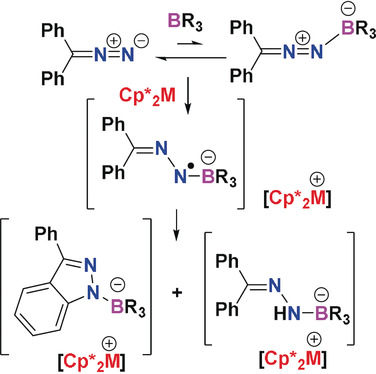
Radical Chemistry
Single Electron Transfer to Diazomethane–Borane Adducts Prompts C−H Bond Activations
- Pages: 18487-18491
- First Published: 07 October 2019
Polymers
Cellulose-Derived Functional Polyacetal by Cationic Ring-Opening Polymerization of Levoglucosenyl Methyl Ether
- Pages: 18492-18495
- First Published: 11 September 2019
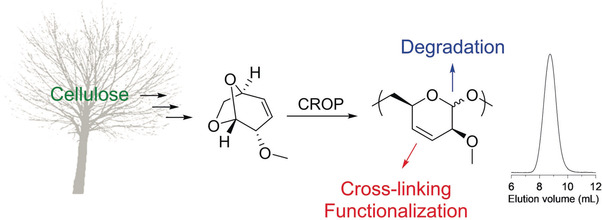
From crops to CROP: Cationic ring-opening polymerization (CROP) of biomass-derived levoglucosenyl methyl ether yields a semicrystalline thermoplastic unsaturated polyacetal. The double bonds can undergo hydrogenation and thiol–ene reactions as well as crosslinking, thus making this polyacetal potentially interesting as a reactive functional material.
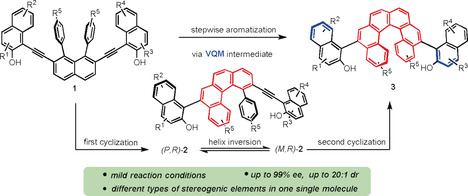
Organocatalysis
Enantioselective Control of Both Helical and Axial Stereogenic Elements though an Organocatalytic Approach
- Pages: 18496-18501
- First Published: 14 October 2019
C−H Activation
Carboxy Group as a Remote and Selective Chelating Group for C−H Activation of Arenes
- Pages: 18502-18507
- First Published: 09 October 2019
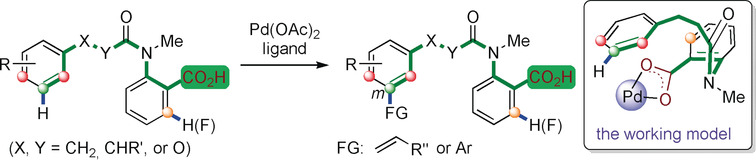
Coordination mode matters: The first example of carboxy group assisted, remote-selective meta-C(sp2)−H activation through a possible κ2 coordination has been developed, thus suppressing the ortho-C−H activation thorugh κ1 coordination. Besides meta-C−H olefination, direct meta-arylation of hydrocinnamic acid derivatives with low-cost aryl iodides has been achieved for the first time. These findings may motivate the exploration of novel selectivities and reactivities for carboxyl assisted C−H activation reactions.
Photoredox Catalysis
Hydrotrifluoromethylthiolation of Unactivated Alkenes and Alkynes with Trifluoromethanesulfonic Anhydride through Deoxygenative Reduction and Photoredox Radical Processes
- Pages: 18508-18512
- First Published: 14 October 2019
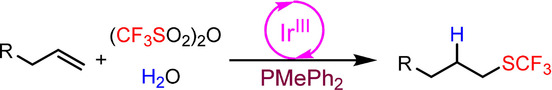
A practical anti-Markovnikov hydrotrifluoromethylthiolation of unactivated alkenes using (CF3SO2)2O and H2O as the SCF3 and H sources was achieved through deoxygenative reduction with PMePh2 and photoredox radical processes. This reaction is the first example of using (CF3SO2)2O as a trifluoromethylthiolating reagent and provides a new strategy for radical trifluoromethylthiolation.
Fused Ring Systems
Arene Trifunctionalization with Highly Fused Ring Systems through a Domino Aryne Nucleophilic and Diels–Alder Cascade
- Pages: 18513-18518
- First Published: 09 October 2019

3 in 1: A convenient and efficient domino aryne process was developed under transition-metal-free conditions to afford tetra- and pentacyclic ring systems. Chemoselective control at both the 1,2-aryne and 2,3-aryne stages enabled three new chemical bonds, namely one C−N and two C−C bonds, and two benzofused rings to be constructed concomitantly.
Heterocycles
Ligand-Controlled Regiodivergent Hydroalkylation of Pyrrolines
- Pages: 18519-18523
- First Published: 23 October 2019
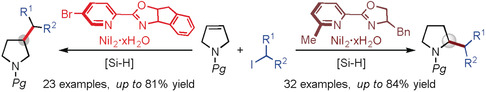
A weak moment: By employing ligand control and a weak directing group as key design elements, an efficient and diversity-oriented method for the synthesis of C-alkylated pyrrolidines has been developed. This nickel hydride catalyzed hydroalkylation achieves two different regioselectivites of the same substrates to yield both 2- and 3-alkylated pyrrolidines.
Membranes | Very Important Paper
Elucidating Ultrafast Molecular Permeation through Well-Defined 2D Nanochannels of Lamellar Membranes
- Pages: 18524-18529
- First Published: 15 October 2019
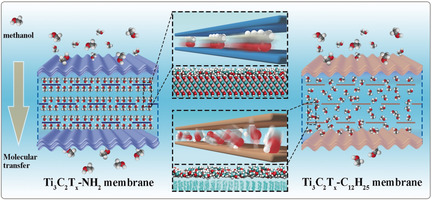
MXene Ti3C2Tx nanosheets were functionalized by hydrophilic or hydrophobic groups to tune the size and wettability of 2D nanochannels for elucidating the molecular transport mechanism of lamellar membranes. Hydrophilic nanochannels induce ordered alignment of polar molecules, which contributes to their fast transport, and thus their permeance is much higher than that in hydrophobic nanochannels with disordered molecular configuration.
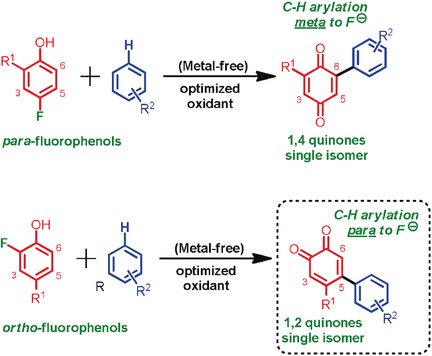
Regioselective Arylation
Regioselective Oxidative Arylation of Fluorophenols
- Pages: 18530-18534
- First Published: 04 October 2019
Biocatalysis
Evolved Aliphatic Halogenases Enable Regiocomplementary C−H Functionalization of a Pharmaceutically Relevant Compound
- Pages: 18535-18539
- First Published: 07 October 2019
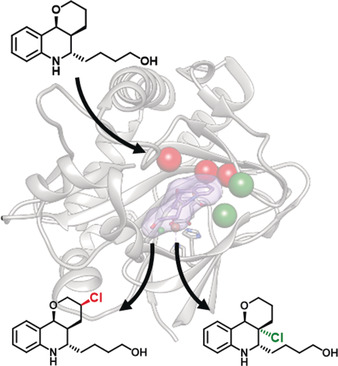
Beyond natural: A protein catalyst was engineered to perform selective halogenation of a fragment of martinelline, a pharmaceutically relevant non-native substrate. Directed evolution of non-heme iron halogenase WelO5* afforded a variant with an up to 400-fold higher apparent kcat and a 290-fold higher TTN for this target substrate than the wildtype enzyme while achieving high stereo- and regioselectivity (>99 %).
Polymers
Loading-Dependent Structural Model of Polymeric Micelles Encapsulating Curcumin by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 18540-18546
- First Published: 17 September 2019
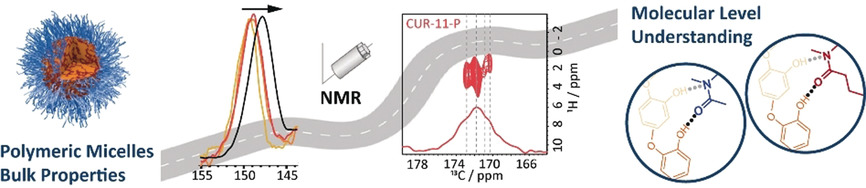
From bulk properties to a molecular level understanding: Solid-state NMR spectroscopy complemented by X-ray diffraction data and calculations gives insights into the loading-dependent structure of micelles formed by amphiphilic triblock copolymers. As coordination sites in the core become saturated, stabilization of higher loadings requires coordination by the hydrophilic corona, which compromises dissolution.
Diazo Compounds
A Terminal Iron Nitrilimine Complex: Accessing the Terminal Nitride through Diazo N−N Bond Cleavage
- Pages: 18547-18551
- First Published: 17 September 2019
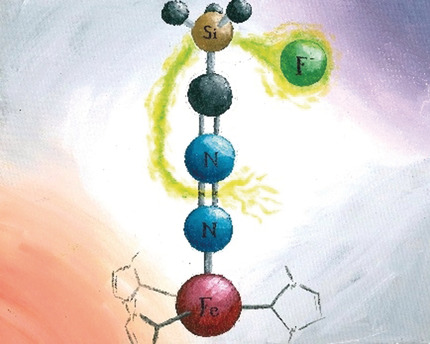
Chain reaction: A fluoride salt cleaves the N–N bond of an iron trimethylsilyl nitrilimine complex and generates the terminal nitride, fluorotrimethylsilane, and cyanide. The complementary reactivity of nitrilimine and azido ligands provides a new approach for the synthesis of metal terminal nitrido complexes.
Dispersion Interactions
Exploring London Dispersion and Solvent Interactions at Alkyl–Alkyl Interfaces Using Azobenzene Switches
- Pages: 18552-18556
- First Published: 26 September 2019
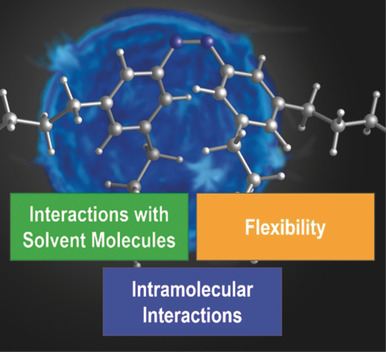
An azobenzene setup was used to examine London dispersion in conjunction with solvent interactions between linear alkyl chains. 1H NOESY NMR analysis indicated additional long-range interactions with the opposite phenyl core in the Z-isomer. This work provides rare insight into the stabilizing contributions of highly flexible groups in an intra- as well as an intermolecular setting.
Energetic Properties
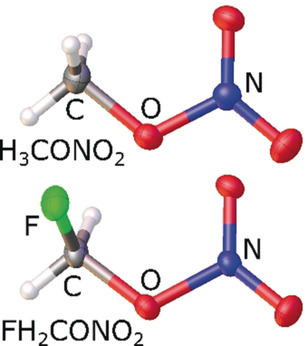
Solid-State and Gas-Phase Structures and Energetic Properties of the Dangerous Methyl and Fluoromethyl Nitrates
- Pages: 18557-18561
- First Published: 01 October 2019
Research Articles
Self-Assembly
Ion-Specific Assembly of Strong, Tough, and Stiff Biofibers
- Pages: 18562-18569
- First Published: 10 October 2019
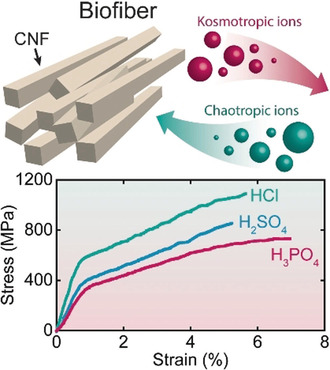
A hydrodynamics-based approach for the organization and assembly of fibrillar building blocks into hierarchical macrostructures with multiscale control over the nanostructure leads to exceptional mechanical properties. For the first time, structure–property relationships are understood depending on specific ion effects for wet and dry nanofibrillar systems.
Single-Atom Catalysts | Hot Paper
Zeolite-Encaged Single-Atom Rhodium Catalysts: Highly-Efficient Hydrogen Generation and Shape-Selective Tandem Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes
- Pages: 18570-18576
- First Published: 28 October 2019
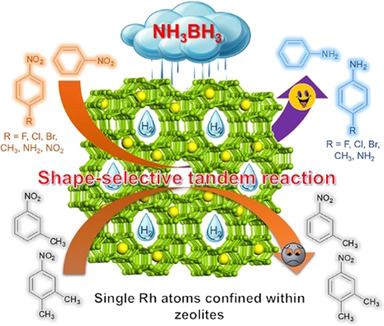
Together alone: Single Rh atoms were encapsulated within MFI zeolites under in situ hydrothermal conditions and a ligand-protected direct H2 reduction. The catalyst gave a high turnover frequency of 699 mol (molRh)−1 min−1 at 298 K for ammonia borane (AB) hydrolysis and exhibited superior catalytic efficiency in shape-selective tandem hydrogenation of nitroarenes by coupling with the hydrolysis of AB.
(molRh)−1 min−1 at 298 K for ammonia borane (AB) hydrolysis and exhibited superior catalytic efficiency in shape-selective tandem hydrogenation of nitroarenes by coupling with the hydrolysis of AB.
Oligosaccharides
Expedient Synthesis of Core Disaccharide Building Blocks from Natural Polysaccharides for Heparan Sulfate Oligosaccharide Assembly
- Pages: 18577-18583
- First Published: 25 September 2019
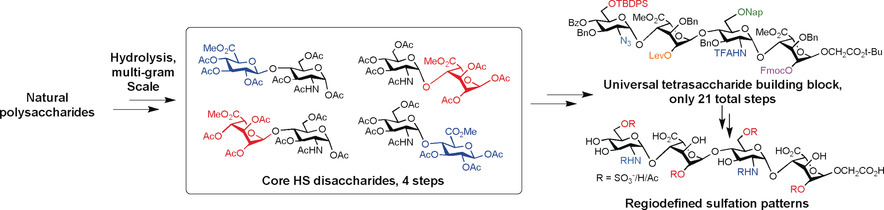
The four core disaccharides required for heparan sulfate (HS)/heparin oligosaccharide synthesis were efficiently generated from natural polysaccharides. Rapid access to these key building blocks will greatly facilitate the generation of comprehensive libraries of HS oligosaccharides for unlocking the sulfation code and understanding the roles of glycosaminoglycans in physiology and disease.
Coordination Compounds
Functionalization of Pentaphosphorus Cations by Complexation
- Pages: 18584-18590
- First Published: 26 September 2019
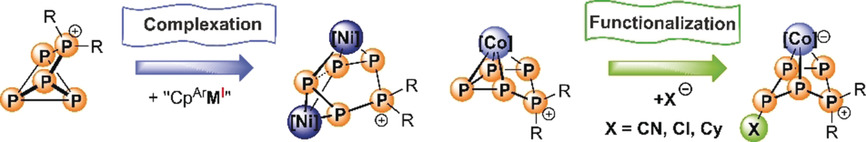
Functionalization of P ligands: The first metal complexes of diorganopentaphosphorus cations [P5R2]+ (R=Cy, iPr) have been prepared from tetrachlorogallate salts [P5R2]GaCl4 and cyclopentadienyl cobalt and nickel complexes (CpAr=C5(C6H4-4-Et)5). The installation of additional chloro, cyano, and cyclohexyl groups on the pentaphosphorus scaffold illustrates a useful strategy to access highly functionalized polyphosphorus ligands.
On-Surface Synthesis | Hot Paper
Strain-Induced Isomerization in One-Dimensional Metal–Organic Chains
- Pages: 18591-18597
- First Published: 13 October 2019
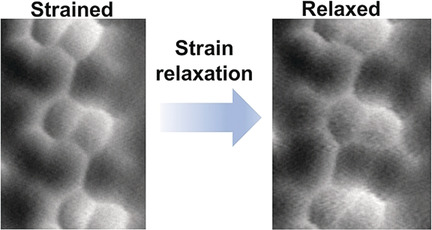
Skeletal rearrangement of 1D metal–organic chains (MOCs) occurs via a concurrent atom shift and bond cleavage on Cu(111) at room temperature. Cu-catalyzed debromination of organic monomers generates 1,5-dimethylnaphthalene diradicals that coordinate to Cu adatoms to form MOCs. Bond-resolved atomic force microscopy and DFT reveal that a relief of internal strain drives skeletal rearrangement.
Porphyrinoids
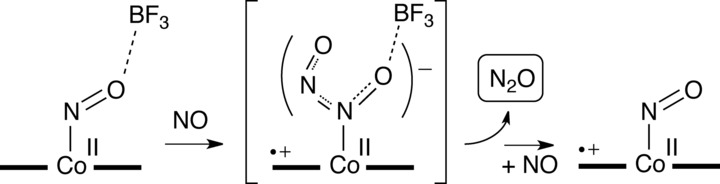
Not Limited to Iron: A Cobalt Heme–NO Model Facilitates N–N Coupling with External NO in the Presence of a Lewis Acid to Generate N2O
- Pages: 18598-18603
- First Published: 07 October 2019
Nanocatalysis
Tuning the Electron Localization of Gold Enables the Control of Nitrogen-to-Ammonia Fixation
- Pages: 18604-18609
- First Published: 18 September 2019
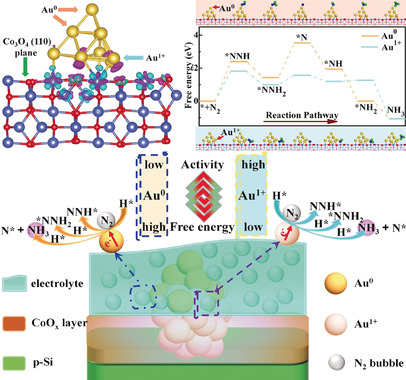
The fix is N: Tuning the local electronic structure of Au nanoparticles with positive valence sites can boost conversion of N2 to NH3 by controlling N2 adsorption and the concomitant energy barrier of NRR. The introduction of a metal with local electronic structure can offer a new direction for the fabrication of highly efficient catalysts for the N2 reduction reaction (NRR).
Halogen Bonds | Very Important Paper
Strong N−X⋅⋅⋅O−N Halogen Bonds: A Comprehensive Study on N-Halosaccharin Pyridine N-Oxide Complexes
- Pages: 18610-18618
- First Published: 15 October 2019
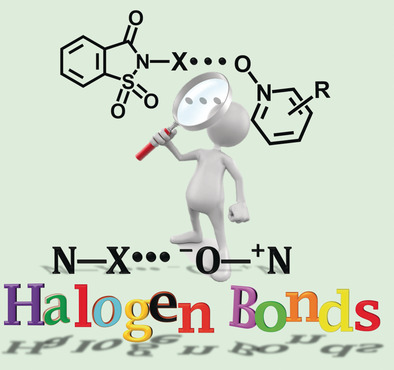
Strong N−X⋅⋅⋅−O−N+ (X=I, Br) halogen bonds, by using oxygen as halogen bond acceptor, are obtained from N-halosaccharins and aromatic N-oxides. The donor–acceptor-dependent tunable X⋅⋅⋅O distances are investigated by using computational methods, solution NMR spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analysis.
Photocatalysis
Geometric E→Z Isomerisation of Alkenyl Silanes by Selective Energy Transfer Catalysis: Stereodivergent Synthesis of Triarylethylenes via a Formal anti-Metallometallation
- Pages: 18619-18626
- First Published: 21 September 2019
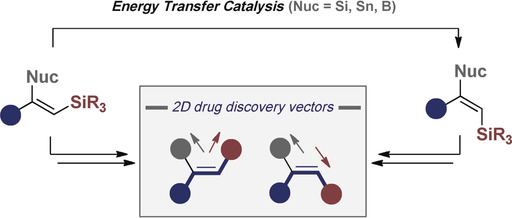
A geometrical E→Z isomerisation of alkenyl silanes proceeding through selective energy transfer is enabled by an organic sensitiser and displays high selectivity for trisubstituted systems. Mixed bis-nucleophiles (Si, Sn, B) also undergo facile isomerisation, thereby enabling a formal anti-metallometallation.
Electrochemistry
In Situ Observation of Dynamic Galvanic Replacement Reactions in Twinned Metallic Nanowires by Liquid Cell Transmission Electron Microscopy
- Pages: 18627-18633
- First Published: 17 October 2019
Polymer Actuators
Fabrication of Large Single Crystals for Platinum-Based Linear Polymers with Controlled-Release and Photoactuator Performance
- Pages: 18634-18640
- First Published: 15 October 2019
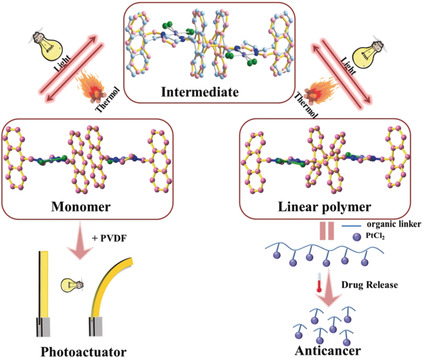
Strong enough to bend: A coordination driven self-assembly strategy secures the appropriate head-to-tail alignment of anthracene moieties gave large Pt-based linear polymer crystals through a [4+4] cycloaddition of anthracene in a single-crystal to single-crystal fashion. The reversible contraction of unit-cell volume upon irradiation or heating gave a photoactuator.
Photothermal Therapy | Very Important Paper
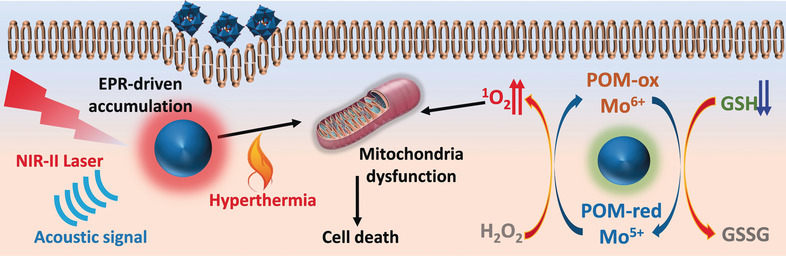
Mo2C-Derived Polyoxometalate for NIR-II Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Chemodynamic/Photothermal Synergistic Therapy
- Pages: 18641-18646
- First Published: 11 October 2019
Solid-State Batteries
Anisotropically Electrochemical–Mechanical Evolution in Solid-State Batteries and Interfacial Tailored Strategy
- Pages: 18647-18653
- First Published: 14 October 2019

Solid as a rock: The unsatisfactory electrochemical performance in solid-state batteries originates from internal strain-induced contact loss, heterogeneous phase transformation, and the augmentation of metallic surface passivation layers. With in situ growth of solid sulfide electrolyte into 3D FeS2 microstructure, these issues can be significantly inhibited and superior electrochemical performance can be achieved.
Membranes
An Hetero-Epitaxially Grown Zeolite Membrane
- Pages: 18654-18662
- First Published: 07 October 2019

Planting a seed: The hetero-epitaxial growth of a SSZ-13 (CHA-type) zeolite seed layer with the ZSM-58 (DDR-type) precursor is reported. The resulting membranes show excellent CO2 perm-selectivities, having maximum CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 separation factors (SFs) as high as about 17 and 279, respectively, at 30 °C. In the presence of water vapor, a CO2/N2 SF of about 14 and CO2/CH4 SF of about 78 at 50 °C were recorded.
Cell Adhesion
Phosphorylation Reduces the Mechanical Stability of the α-Catenin/ β-Catenin Complex
- Pages: 18663-18669
- First Published: 18 October 2019
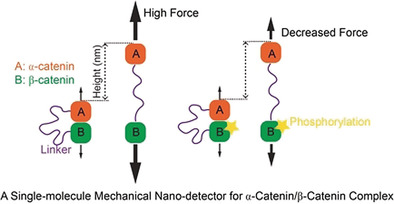
Reach new heights: A single-molecule construct was designed and used to determine the effects of phosphorylation on the mechanical stability of the α-catenin/β-catenin complex, which is a component of cell–cell adherens junctions. Phosphorylation reduces the mechanical stability of the α-catenin/β-catenin complex.
Light-Emitting Diodes
Hybrid Metal Halides with Multiple Photoluminescence Centers
- Pages: 18670-18675
- First Published: 10 October 2019

Luminescent metal halide: A novel 0D metal halide material (C9NH20)9[Pb3Br11](MnBr4)2 has two distinct emitting centers, self-trapped excitons (STE) residing on [Pb3Br11]5− clusters and 4T1-to-6A1 transitions of Mn2+ ions in [MnBr4]2− tetrahedral units. This is the first example of Mn2+ emission and STE emissioncoexisting in a single crystalline material and allows white light-emitting diodes (WLEDs) to be fabricated.
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction | Very Important Paper
Atomic Arrangement in Metal-Doped NiS2 Boosts the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Media
- Pages: 18676-18682
- First Published: 14 October 2019
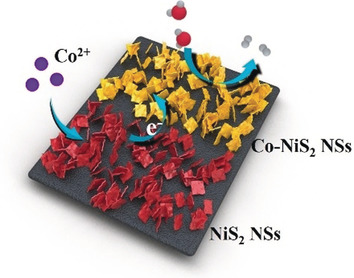
Co doped: Cobalt-doped NiS2 nanosheets (NSs) with optimal eg1 electron configurations and enhanced Ni3+ content exhibit excellent activity and stability for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in alkaline media. DFT results reveal that a Co-NiS2 NSs surface abnormally sensitizes Ni-3d bands towards higher electron-transfer.
Systems Chemistry
Barcoding Biological Reactions with DNA-Functionalized Vesicles
- Pages: 18683-18690
- First Published: 09 October 2019
Prebiotic Chemistry | Hot Paper
Proto-Urea-RNA (Wöhler RNA) Containing Unusually Stable Urea Nucleosides
- Pages: 18691-18696
- First Published: 01 October 2019
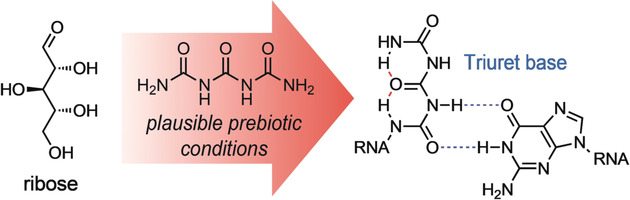
The prebiotic starting molecules bis-urea (biuret) and tris-urea (triuret) directly react with ribose. The urea-ribosides are remarkably stable because of a network of intramolecular, bifurcated hydrogen bonds, which even allowed the synthesis of phosphoramidite building blocks and incorporation of the units into RNA. Urea-containing RNA bases are therefore good candidates for a proto-RNA world.
Glycoconjugates
The Core Fucose on an IgG Antibody is an Endogenous Ligand of Dectin-1
- Pages: 18697-18702
- First Published: 18 October 2019
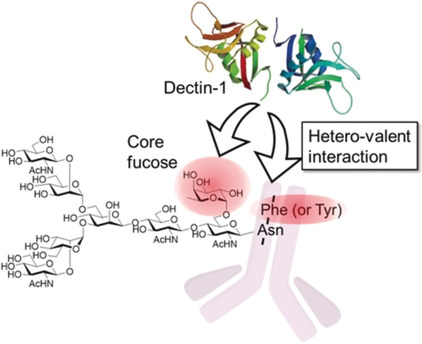
A long-standing secret unveiled: The mammalian lectin responsible for the recognition of the core fucose on N-glycans is Dectin-1, a known anti-β-glucan lectin. Dectin-1 recognizes aromatic amino acids adjacent to the N-terminal asparagine at the glycosylation site as well as a core fucose. This heterovalent interaction is the origin of the efficacy and unique recognition pattern of Dectin-1.
Alzheimer's disease | Very Important Paper
Significant Upregulation of Alzheimer's β-Amyloid Levels in a Living System Induced by Extracellular Elastin Polypeptides
- Pages: 18703-18709
- First Published: 14 October 2019
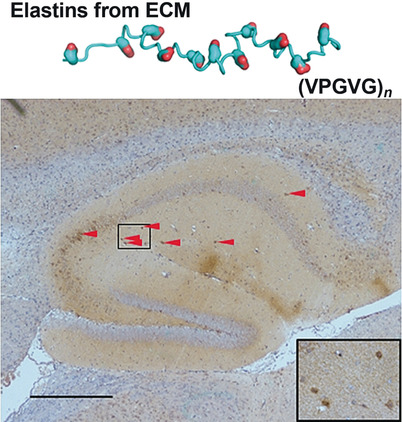
Treatment with elastin polypeptides, a component of the brain extracellular matrix (ECM), increases levels of β-amyloid, associated with Alzheimer's disease, both in vitro and in vivo. This is associated with the occurrence of early-stage cognitive impairment in animals. This provides a new insight into Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.
Biocatalysis
X-ray Crystallography and Vibrational Spectroscopy Reveal the Key Determinants of Biocatalytic Dihydrogen Cycling by [NiFe] Hydrogenases
- Pages: 18710-18714
- First Published: 07 October 2019
![X-ray Crystallography and Vibrational Spectroscopy Reveal the Key Determinants of Biocatalytic Dihydrogen Cycling by [NiFe] Hydrogenases](/cms/asset/ef664c2b-e75a-495c-91b9-e149dd72f3b3/anie201908258-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Where does the H2 go? Using an F420-reducing [NiFe]-hydrogenase from Methanosarcina barkeri as a model enzyme, it is shown that the protein backbone provides a strained chelating scaffold that tunes the [NiFe] active site for efficient H2 binding and conversion. The protein matrix also directs H2 diffusion to the [NiFe] site via two gas channels and allows the distribution of electrons between functional protomers through a subunit-bridging FeS cluster.