Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Titelbild
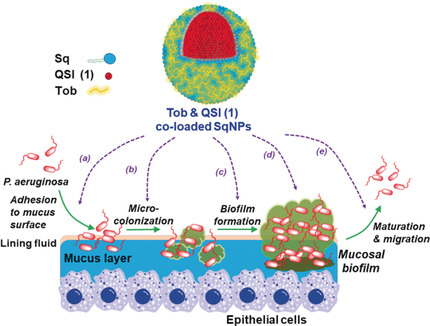
Titelbild: Squalenyl Hydrogen Sulfate Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Delivery of Tobramycin and an Alkylquinolone Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Enable the Eradication of P. aeruginosa Biofilm Infections (Angew. Chem. 26/2020)
- Page: 10285
- First Published: 28 April 2020

Der simultane Transport von Tobramycin- und Alkylchinolon-Inhibitoren durch ein selbstorganisiertes Nanopartikelsystem basierend auf Squalenylhydrogensulfat (SqNPs) stellt eine optimale therapeutische Maßnahme gegen Biofilminfektionen mit P. aeruginosa dar. Wie C.-M. Lehr et al. in ihrer Zuschrift auf S. 10378 beschreiben, zeigt das wirkstoffbeladene SqNPs verbesserte Biofilmpenetration und verstärkte Wirksamkeit in relevanten biologischen Barrieren, was zu einer vollständigen Eradikation von P. aeruginosa-Biofilmen bei 16-fach geringerer Tobramycinkonzentration als mit Tobramycin allein führt.
Innentitelbild: Structural Elucidation of Selective Solvatochromism in a Responsive-at-Metal Cyclometalated Platinum(II) Complex (Angew. Chem. 26/2020)
- Page: 10286
- First Published: 28 April 2020

Platin gehört die Welt! Ein responsiver Platin(II)-Emitter kann supramolekulare und redoxchemische Transformationen “auf Abruf” eingehen, wie M. J. MacLachlan et al. in ihrer Zuschrift aufS. 10434 demonstrieren. PtII wird selektiv zu PtIII oder PtIV oxidiert, wodurch sich die strukturellen und photophysikalischen Eigenschaften des Emitters diversifizieren lassen. Die feine Modulation der Pt⋅⋅⋅Pt-Wechselwirkungen durch Lösungsmittelmoleküle führt zu starken vapochromen und solvatochromen Effekten.
Innenrücktitelbild: High-Pressure Synthesis of Metal–Inorganic Frameworks Hf4N20⋅N2, WN8⋅N2, and Os5N28⋅3 N2 with Polymeric Nitrogen Linkers (Angew. Chem. 26/2020)
- Page: 10753
- First Published: 28 April 2020

Metall-anorganische Gerüstverbindungen Hf4N20⋅N2, WN8⋅N2 und Os5N28⋅N2, die aus Übergangsmetallen und polymeren Stickstofflinkern aufgebaut sind, wurden von M. Bykov et al. in einer einstufigen Synthese aus den Elementen unter Hochdruckbedingungen hergestellt (siehe die Zuschrift auf S. 10407). In den kanalartigen Poren dieser anorganischen Polymere befinden sich eindimensionale, π-konjugierte Anordnungen von Stickstoffmolekülen, die ihnen leitfähige Eigenschaften verleihen.
Rücktitelbild: Droplet Precise Self-Splitting on Patterned Adhesive Surfaces for Simultaneous Multidetection (Angew. Chem. 26/2020)
- Page: 10754
- First Published: 28 April 2020

Die präzise Trennung und Lokalisierung von Mikrotröpfchen sind grundlegende Arbeitsgänge in verschiedenen Forschungsbereichen, z. B. beim biologischen Screening, der kombinatorischen Analyse und bei der Erkennung komplexer Proben. In ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 10622 demonstrieren M. Li, Q. Li, Y. Song et al. eine Strategie zur Selbstaufspaltung von Tröpfchen, um unabhängige Mikrotröpfchen mit wohldefinierter Morphologie und Anordnung zu generieren und simultane Nachweise komplexer Analyte in einzelnen Probetröpfchen zu realisieren.
Frontispiz
Frontispiz: Construction of Helically Stacked π-Electron Systems in Poly(quinolylene-2,3-methylene) Stabilized by Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds
- First Published: 15 June 2020
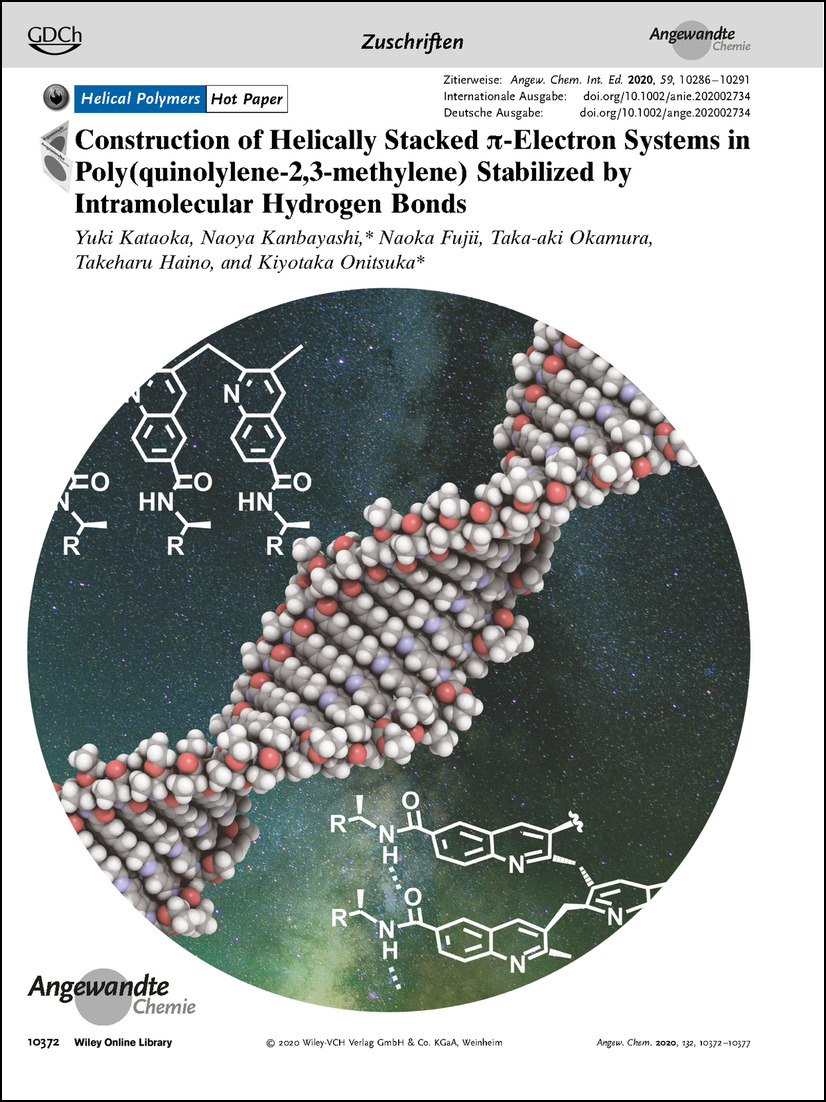
Helikale Polymere Die Synthese eines neuartigen Typs π-gestapelter Polymere wird von N. Kanbayashi, K. Onitsuka et al. in der Zuschrift auf S. 10372 beschrieben. Die Struktur wird durch spektroskopische Analysen und AFM-Messungen bestätigt.
Frontispiz: Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to Acetic Acid by a Molecular Manganese Corrole Complex
- First Published: 15 June 2020

CO2-Verwertung Im Forschungsartikel auf S. 10614 ff. beschreiben S. Roy, W. Schöfberger et al. die elektrokatalytische Reduktion von CO2 zu Essigsäure durch einen molekulare Mangan-Corrolkomplex. Die Bildung und Reduktion einer Oxalat-Zwischenstufe wird vorgeschlagen.
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis: Angew. Chem. 26/2020
- Pages: 10289-10309
- First Published: 15 June 2020
Autoren-Profil
Liming Dai
- Pages: 10312-10313
- First Published: 03 February 2020

Mein erstes Experiment war meine Doktorarbeit über lösliche konjugierte leitfähige Polymere unter Anleitung von John W. White nach einem Studium der chemischen Verfahrenstechnik. Meine größte Inspiration ist die Apollo-Mission der NASA in den 1960er Jahren …“ Dies und mehr von und über Liming Dai finden Sie in seinem Autoren-Profil.
Nachrichten
CNRS-Silbermedaillen:D. Farrusseng, E. Collet undP. Poulin / CNRS-Bronzemedaillen:J. Wencel-Delord und D. Voiry
- Page: 10314
- First Published: 28 April 2020
Highlights
Naturstoffsynthese
Taxan trifft Propellan: Erste Totalsynthese des hochkomplexen Diterpens Canataxpropellan
- Pages: 10316-10318
- First Published: 16 April 2020
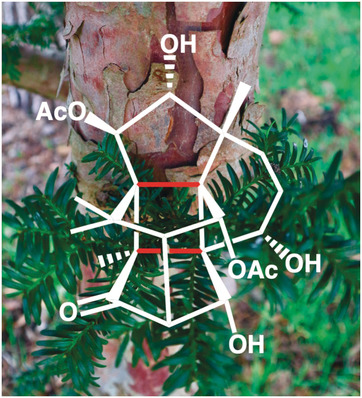
Die Merkmale zweier ikonischer Stoffklassen vereinen sich in der Struktur des hochkomplexen Diterpens Canataxpropellan und bilden eine beträchtliche Herausforderung, welche von Gaich und Mitarbeitern gemeistert wurde. Ihre wagemutige Strategie und der resultierende Nutzen für das Gebiet der Terpenchemie werden in diesem Highlight vorgestellt.
Standpunkt
Electrocatalysis
Does a Thermoneutral Electrocatalyst Correspond to the Apex of a Volcano Plot for a Simple Two-Electron Process?
- Pages: 10320-10324
- First Published: 17 March 2020
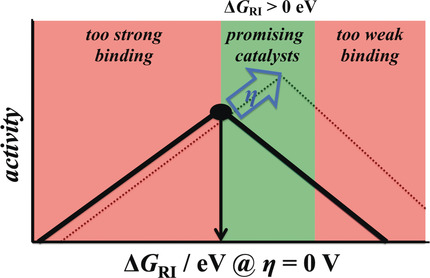
Tip of the volcano: Electrode materials are classically assessed by their location on a volcano curve, using the binding strength of a reaction intermediate (RI) as a descriptor. For a two-electron process, the apex of the volcano corresponds to thermoneutral binding of the reaction intermediate at zero overpotential. This Viewpoint addresses the definition of an optimum catalyst when kinetic effects and applied overpotential are factored in, illustrating a right shift of the volcano's top with increasing driving force.
Kurzaufsätze
Asymmetrische Katalyse
Chiral N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands Enable Asymmetric C−H Bond Functionalization
- Pages: 10326-10335
- First Published: 09 December 2019
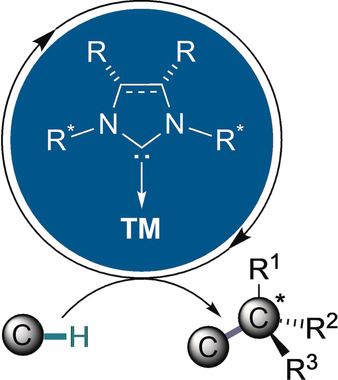
Chirale NHC-Liganden sind in der enantioselektiven Übergangsmetallkatalyse allgegenwärtig, in der metallkatalysierten asymmetrischen C-H-Funktionalisierung ist ihre Verwendung aber noch in einem frühen Stadium. Dieser Kurzaufsatz beleuchtet die Entwicklungen und Fortschritte in diesem sich rasch entwickelnden Forschungsbereich.
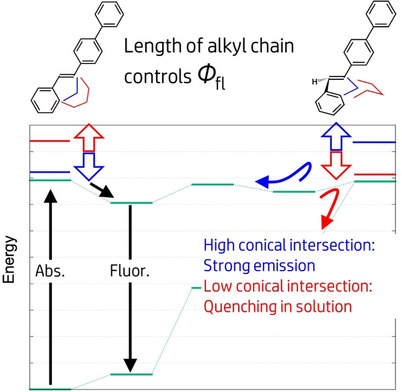
Photon Upconversion
Stimuli-Responsive Molecular Photon Upconversion
- Pages: 10336-10348
- First Published: 24 February 2020
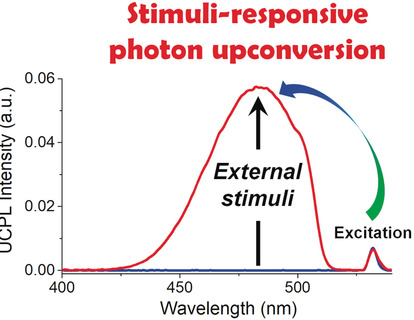
Up and up: This Minireview summarizes recent developments in the switching of triplet–triplet-annihilation-based photon upconversion (TTA-UC) by various external stimuli. The stimuli-responsive TTA-UC systems are categorized into four types based on their switching mechanisms. TTA-UC has the potential to achieve biosensing and chemosensing with unprecedented sensitivity and selectivity.
Aufsätze
Photokatalyse
Multiphotonen-Anregung in der Photoredoxkatalyse: Konzepte, Anwendungen und Methoden
- Pages: 10350-10370
- First Published: 16 January 2020
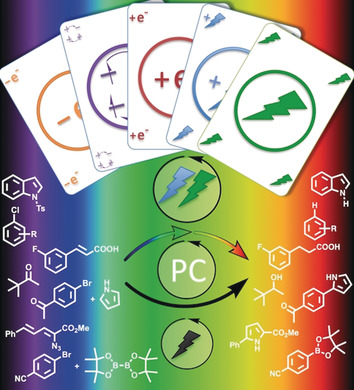
Durch Kombination zweier energiearmer Photonen können thermodynamisch anspruchsvolle Reaktionen angetrieben werden. Das Zusammenspiel von empirischen Fortschritten und mechanistischen Einblicken aus der Spektroskopie machte Multiphotonen-Anregungsprozesse zugänglich für die präparative Photoredoxchemie. Ein Blick auf entwickelte Konzepte und Reaktionen identifiziert Herausforderungen, Sackgassen und zukünftige Möglichkeiten für diesen Forschungszweig.
Zuschriften
Helical Polymers | Hot Paper
Construction of Helically Stacked π-Electron Systems in Poly(quinolylene-2,3-methylene) Stabilized by Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds
- Pages: 10372-10377
- First Published: 08 April 2020
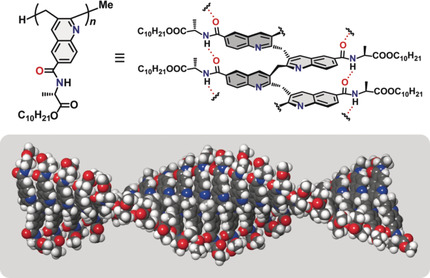
Stack it up: A novel type of π-stacked polymer was synthesized via cyclo-copolymerization of an o-allenylaryl isocyanide. In the poly(quinolylene-2,3-methylene) bearing alanine derivatives as the side chain, the quinoline backbone forms a layered structure with π–π interactions stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonds. The structure was established based on spectroscopy and calculations, and confirmed by AFM measurements.
Drug Delivery | Hot Paper
Squalenyl Hydrogen Sulfate Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Delivery of Tobramycin and an Alkylquinolone Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Enable the Eradication of P. aeruginosa Biofilm Infections
- Pages: 10378-10382
- First Published: 03 April 2020
NMR Spectroscopy
Accelerated Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy with Deep Learning
- Pages: 10383-10386
- First Published: 06 September 2019
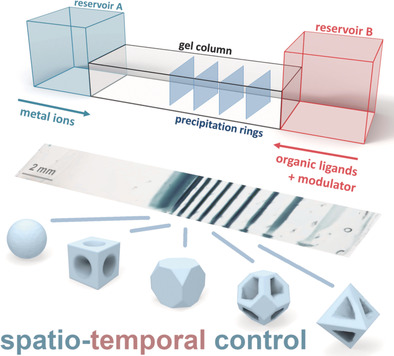
Reaction–Diffusion
Shaping Microcrystals of Metal–Organic Frameworks by Reaction–Diffusion
- Pages: 10387-10391
- First Published: 20 February 2020
Magnetische Eigenschaften
Access to Heteroleptic Fluorido-Cyanido Complexes with a Large Magnetic Anisotropy by Fluoride Abstraction
- Pages: 10392-10396
- First Published: 21 February 2020
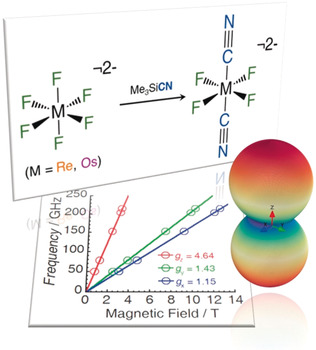
Zwei Übergangsmetallkomplexe mit Fluorid- und Cyanidoliganden, trans-[MIVF4(CN)2]2− (M=Re, Os), wurden durch siliziumvermittelte Fluoridabstraktion hergestellt. Hochfeld-EPR-Spektroskopie und Magnetisierungsdaten belegen eine erhöhte magnetische Anisotropie des ReIV-Komplexes im Vergleich zum [ReF6]2−-Vorläufer.
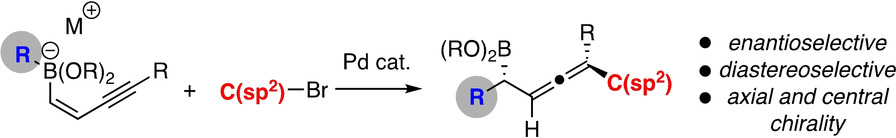
Homogeneous Catalysis
Diastereo- and Enantioselective 1,4-Difunctionalization of Borylenynes by Catalytic Conjunctive Cross-Coupling
- Pages: 10397-10401
- First Published: 25 March 2020
Synthetic Methods
Visible-Light-Induced Palladium-Catalyzed Generation of Aryl Radicals from Aryl Triflates
- Pages: 10402-10406
- First Published: 10 March 2020
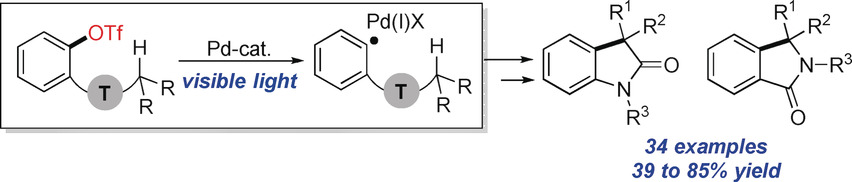
CO fragmentation: Mild visible-light-induced Pd-catalyzed intramolecular C−H arylation of amides is reported. The method features cleavage of C(sp2)−O bonds, leading to hybrid aryl Pd-radical intermediates. The following 1,5-hydrogen atom translocation, intramolecular cyclization, and rearomatization steps lead to valuable N-containing heterocyclic cores. Notably, this method provides access to products with readily enolizable functional groups that are incompatible with traditional Pd-catalyzed conditions. T=Tether.
Metal–Inorganic Frameworks | Hot Paper
High-Pressure Synthesis of Metal–Inorganic Frameworks Hf4N20⋅N2, WN8⋅N2, and Os5N28⋅3 N2 with Polymeric Nitrogen Linkers
- Pages: 10407-10412
- First Published: 24 March 2020
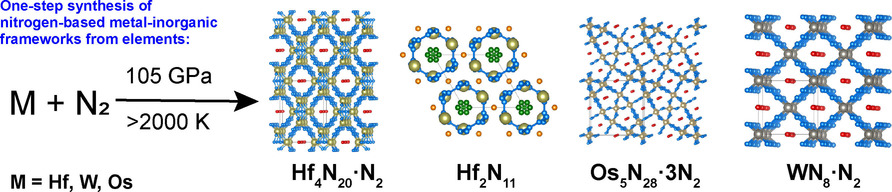
A one-step high-pressure synthetic route is used to complex metal–inorganicframeworks built of transition metals(Hf, Os, and W) that are connected via polymeric nitrogen linkers. The pores are filled with ordered one-dimensional arrays of nitrogen molecules. Owing to the conjugated π-systems, these inorganic polymers are conductive materials.
Fluorescent Probes
A Small-Molecule AIE Chromosome Periphery Probe for Cytogenetic Studies
- Pages: 10413-10417
- First Published: 12 March 2020
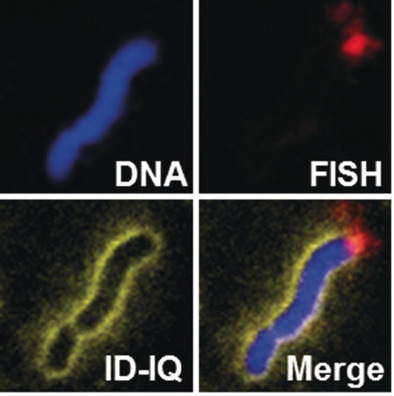
Peripheral vision: A small-molecule fluorescent probe with aggregation-induced emission was developed for chromosome periphery imaging, which facilitates the segmentation of touching or overlapping chromosome clusters, identification of the centromere, and visualization of chromosome morphology. Its compatibility with FISH assays makes it a practical cytogenetic tool in assisting the precise location of a gene in designated chromosomes.
Protein Modification
Chemoselective and Site-Selective Lysine-Directed Lysine Modification Enables Single-Site Labeling of Native Proteins
- Pages: 10418-10422
- First Published: 14 March 2020

A chemical methodology finally addresses the undefeated challenge of modular and precision engineering of a Lys residue in a native protein. The remarkable control over selectivity provides the first-ever approach to target Lys beyond the protein-defined reactivity hotspot. This technology unfolds new gateways and renders analytically pure protein bioconjugates and homogeneous antibody-drug conjugates.
Molecular Machines
Light-Driven Crawling of Molecular Crystals by Phase-Dependent Transient Elastic Lattice Deformation
- Pages: 10423-10428
- First Published: 18 March 2020
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
In Situ Raman Monitoring and Manipulating of Interfacial Hydrogen Spillover by Precise Fabrication of Au/TiO2/Pt Sandwich Structures
- Pages: 10429-10433
- First Published: 24 March 2020
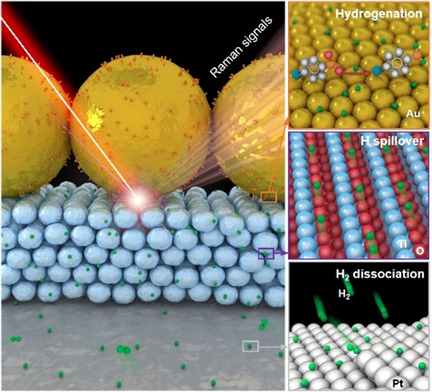
Spillover of hydrogen species at Pt-TiO2-Au interfaces has been investigated in situ using SERS with nanoscale spatial resolution through the precise fabrication of Au/TiO2/Pt sandwich nanostructures. The fundamental mechanism of hydrogen spillover and its influence on selective hydrogenation are revealed.
Platinum Complexes | Hot Paper
Structural Elucidation of Selective Solvatochromism in a Responsive-at-Metal Cyclometalated Platinum(II) Complex
- Pages: 10434-10438
- First Published: 27 March 2020
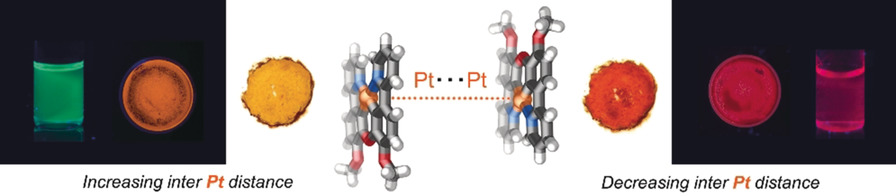
Platinum is king! A responsive-at-metal PtII emitter undergoes controlled supramolecular and redox transformations. PtII selectively oxidizes into PtIII or PtIV, thus diversifying the structural and photophysical properties of the system. Delicate modulation of Pt⋅⋅⋅Pt interactions by solvent molecules results in strong solvatochromism for the PtII complex.
Metal–Organic Frameworks
Formation of a Single-Crystal Aluminum-Based MOF Nanowire with Graphene Oxide Nanoscrolls as Structure-Directing Agents
- Pages: 10439-10444
- First Published: 18 March 2020
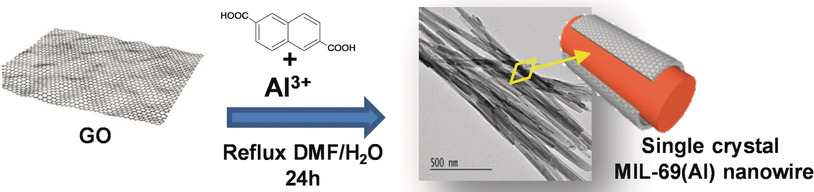
Single-crystal nanowires (NWs) of the Al3+ dicarboxylate MIL-69(Al) MOF were synthesized by using graphene oxide nanoscrolls as structure-directing agents. The interplay between multimodal characterization techniques and molecular modeling unravels their mechanism of formation involving size-confinement and specific interactions.
Biocatalysis
CYP505E3: A Novel Self-Sufficient ω-7 In-Chain Hydroxylase
- Pages: 10445-10448
- First Published: 08 March 2020

Put it there! CYP505E3, a self-sufficient cytochrome P450 monooxygenase from the fungus Aspergillus terreus, catalyzes the regioselective in-chain hydroxylation of alkanes, fatty alcohols, and fatty acids at the ω-7 position. It can thus be used for the biocatalytic production of δ-dodecalactone from dodecanoic acid and1-dodecanol.
Hydrogen Evolution
Consecutive Charging of a Perylene Bisimide Dye by Multistep Low-Energy Solar-Light-Induced Electron Transfer Towards H2 Evolution
- Pages: 10449-10453
- First Published: 24 March 2020
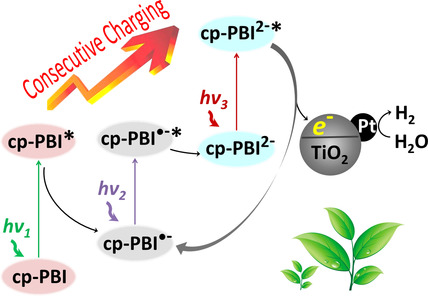
The charge of the light brigade: By a sequence of absorption and photo-induced electron-transfer processes electron-poor perylene bisimides (cp-BPI) are transformed into their electron-richdianions which upon another photoexcitation exhibit sufficient reductive power to drive hydrogen evolution at Pt/TiO2 nanoparticles.
Energy Conversion
Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting from a Ferroelectric Hybrid Salt [Ph3MeP]4[Ni(NCS)6] Embedded in a Polymer Matrix
- Pages: 10454-10459
- First Published: 23 March 2020
Biocatalysis
Enantiocomplementary Epoxidation Reactions Catalyzed by an Engineered Cofactor-Independent Non-natural Peroxygenase
- Pages: 10460-10464
- First Published: 11 March 2020
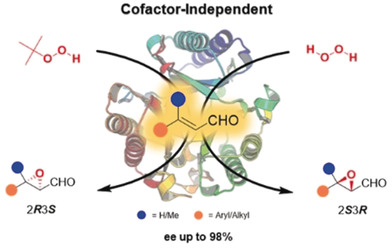
No cofactor needed! An uncommon cofactor-independent peroxygenase was engineered based on a promiscuous tautomerase that uses different hydroperoxides (t-BuOOH and H2O2) to achieve enantiocomplementary epoxidations of various α,β-unsaturated aldehydes, giving access to both enantiomers of the corresponding α,β-epoxy-aldehydes with high enantiopurity (up to 98 % ee).
Single-Chain Magnets | Hot Paper
Enhanced Single-Chain Magnet Behavior via Anisotropic Exchange in a Cyano-Bridged MoIII–MnII Chain
- Pages: 10465-10470
- First Published: 23 March 2020
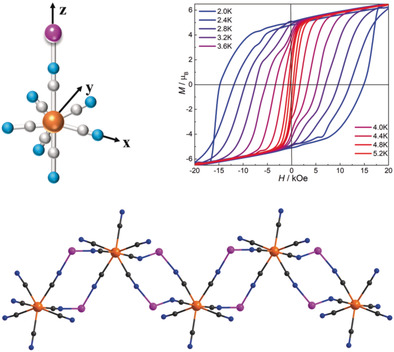
Magnetic chain: A novel [Mo(CN)7]4− based single-chain magnet with a high relaxation barrier of 178(4) K is reported. The compound exhibits open magnetic hysteresis loops below 5.2 K, with a large coercive field of 1.5 T at 2 K. These exceptional properties are attributed to the strong anisotropic MoIII–MnII exchange coupling.
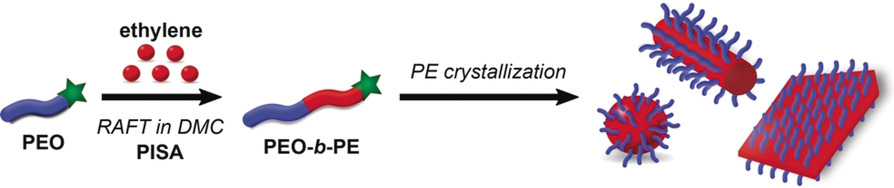
Block Copolymers | Hot Paper
Ethylene Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly (PISA) of Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-polyethylene Copolymers via RAFT
- Pages: 10471-10476
- First Published: 20 March 2020
Heterogene Katalyse
Silver-Triggered Activity of a Heterogeneous Palladium Catalyst in Oxidative Carbonylation Reactions
- Pages: 10477-10481
- First Published: 24 February 2020
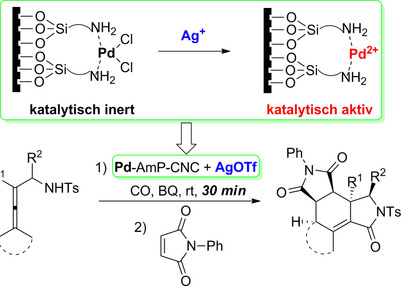
Silberpfeil: Eine durch Silber ausgelöste, heterogene, Pd-katalysierte oxidative Carbonylierung von Allenamiden ermöglicht den Aufbau von Pyrrolidonen und polycyclischen Verbindungen mit mehreren Stereozentren. Der Katalysator (Pd-AmP-CNC) kann mindestens 9-mal ohne Aktivitätsverlust verwendet werden. Das Ag-Salz entfernt Cl von Pd-AmP-CNC und erzeugt dabei hoch aktives PdII, was zu der hohen Effizienz führt.
Gold Catalysis
Gold(I)-Catalyzed Highly Diastereo- and Enantioselective Cyclization–[4+3] Annulation Cascades between 2-(1-Alkynyl)-2-alken-1-ones and Anthranils
- Pages: 10482-10486
- First Published: 25 March 2020
![Gold(I)-Catalyzed Highly Diastereo- and Enantioselective Cyclization–[4+3] Annulation Cascades between 2-(1-Alkynyl)-2-alken-1-ones and Anthranils](/cms/asset/9907e52c-c833-44a2-97f5-3012caee1876/ange202001854-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Gold-catalyzed [4+3]-annulations of 2-(1-alkynyl)-2-alken-1-ones with anthranils to yield epoxybezoazepine products with excellent exo-diastereoselectivity (dr>25:1) are reported. More importantly, enantioselective versions of these [4+3]-cycloadditions have been developed with chiral gold catalysts under ambient conditions (DCM, 0 °C), with ee levels of 88.0–99.9 %, further highlighting their synthetic values.
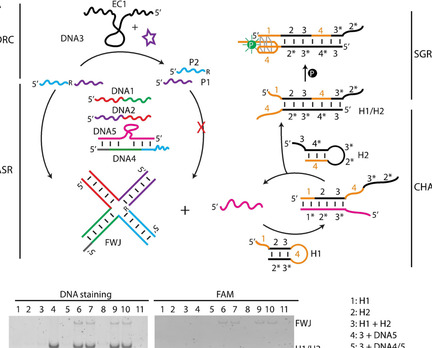
DNA Nanotechnology | Hot Paper
A Multi-component All-DNA Biosensing System Controlled by a DNAzyme
- Pages: 10487-10491
- First Published: 24 March 2020
Topological Engineering
DNA Framework-Based Topological Cell Sorters
- Pages: 10492-10496
- First Published: 18 March 2020
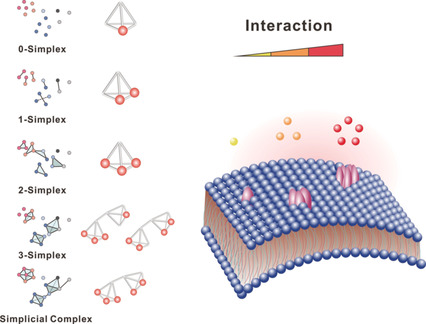
Topologically controlled ligands with a family of tetrahedral DNA frameworks (TDFs) were generated through the formation of 0-simplex to 3-simplex, and to simplicial complex. The multiple ligands are stoichiometrically and topologically arranged to allow the tuning of the binding strength between ligands and receptors as validated with cell sorting.
NMR Spectroscopy | Hot Paper
Sensitivity-Enhanced 13C-NMR Spectroscopy for Monitoring Multisite Phosphorylation at Physiological Temperature and pH
- Pages: 10497-10501
- First Published: 17 March 2020
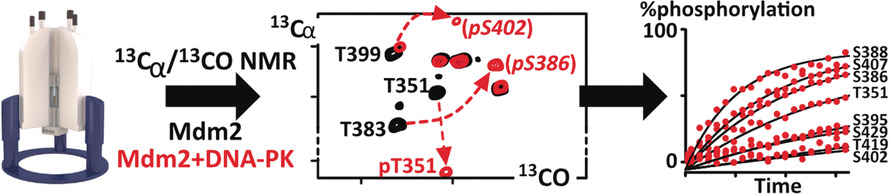
An NMR spectroscopy method has been developed to monitor site-specific phosphorylation at high pH and temperature, both of which are necessary for kinase activity but have previously prevented the thorough characterization of disordered proteins. This approach uses sensitivity-enhanced 13Cα-13CO experiments and is demonstrated using Mdm2, BRCA2, and Oct4. Using this approach, many more phosphorylation cases can now beinvestigated using NMR spectroscopy.
Electroanalysis | Hot Paper
Intracellular Wireless Analysis of Single Cells by Bipolar Electrochemiluminescence Confined in a Nanopipette
- Pages: 10502-10506
- First Published: 25 March 2020
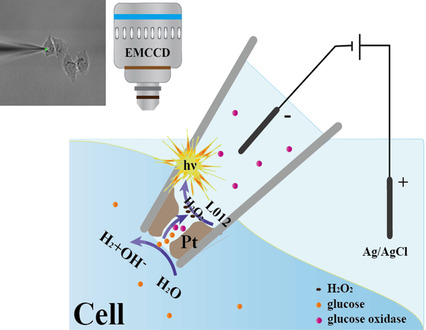
A nanopipette tip decorated with a Pt deposit is used as an open bipolar electrochemiluminescence device to achieve intracellular wireless electroanalysis. The porous structure of Pt deposit permits electrochemical transport of intracellular molecules into the nanopipette. Intracellular concentrations of H2O2 or glucose are measured in vivo as well as the intracellular sphingomyelinase activity.
Homogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
Iridium-Catalyzed Selective Cross-Coupling of Ethylene Glycol and Methanol to Lactic Acid
- Pages: 10507-10511
- First Published: 18 March 2020
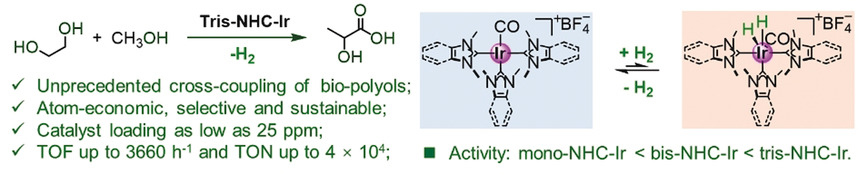
Good things come in threes: An unprecedented dehydrogenative C−C cross-coupling with inexpensive bulk ethylene glycol and methanol has been developed by using a novel iridium catalyst bearing three N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs). This procedure represents a highly selective and atom-economic approach for the synthesis of lactic acid (TOF up to 3660 h−1). TOF=turnover frequency; TON=turnover number.
Analytical Methods
An Electrochemophysiological Microarray for Real-Time Monitoring and Quantification of Multiple Ions in the Brain of a Freely Moving Rat
- Pages: 10512-10516
- First Published: 19 March 2020
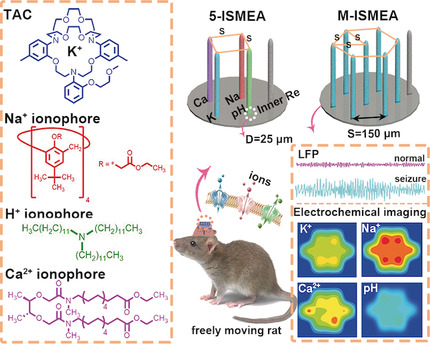
Mapping the brain: In this work, an electrochemophysiological microarray was created for real-time mapping and simultaneous quantification of chemical signals for K+, Ca2+, Na+, and pH in the live brain of a freely moving rat, combined with recording the electrical signals using electrophysiology. This powerful tool could open a new vista in fundamental research on brains.
RAFT Polymerization
Peripheral RAFT Polymerization on a Covalent Organic Polymer with Enhanced Aqueous Compatibility for Controlled Generation of Singlet Oxygen
- Pages: 10517-10521
- First Published: 20 March 2020
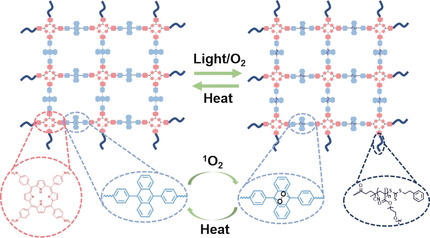
A fair COP: A covalent organic polymer is prepared by crosslinking the photosensitizer 4,4′,4′′,4′′′-(porphyrin-5,10,15,20-tetrayl)tetraaniline (TAPP) with 4,4′- (anthracene-9,10-diyl)dibenzoic acid (ADDA). Simultaneous generation of singlet oxygen by two mechanisms is achieved, which is promising in treating hypoxic tumors.
Vibrational Strong Coupling | Hot Paper
On the Role of Symmetry in Vibrational Strong Coupling: The Case of Charge-Transfer Complexation
- Pages: 10522-10526
- First Published: 27 March 2020
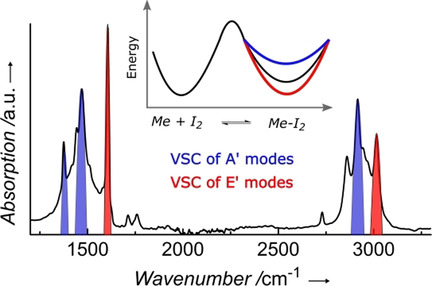
We built this CT: By studying the mesitylene–I2 charge transfer (CT) complex, it is shown that vibrational strong coupling induces large changes in the equilibrium constant KDA of the CT complex, which can be either enhanced or suppressed depending only on the symmetry of the vibration coupled to the vacuum electromagnetic field.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Dramatic Enhancement of Binding Affinities Between Foldamer-Based Receptors and Anions by Intra-Receptor π-Stacking
- Pages: 10527-10531
- First Published: 10 March 2020
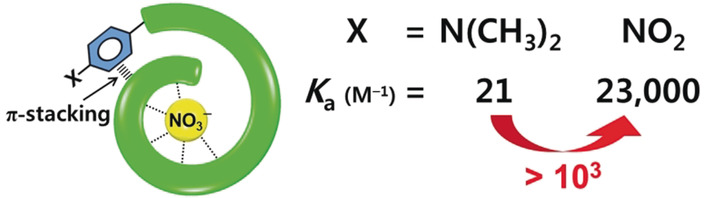
Send reinforcements: Binding affinities between foldamer-based receptors and anions are greatly reinforced by π-stacking within the receptors. The association constant increases by more than three orders of magnitude when N(CH3)2 is replaced with NO2, despite both complexes forming five identical hydrogen bonds.
Metal–Organic Frameworks | Very Important Paper
Electroactive Metal–Organic Frameworks as Emitters for Self-Enhanced Electrochemiluminescence in Aqueous Medium
- Pages: 10532-10536
- First Published: 20 March 2020
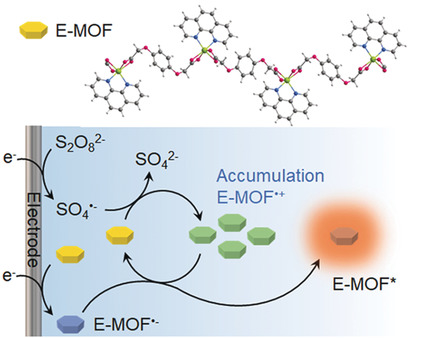
Electroactive MOFs: An electroactive metal–organic framework was designed as an electrochemiluminescence (ECL) emitter. It demonstrated a surface state mechanism in both co-reactant and annihilation ECL in aqueous medium. The self-enhanced cathodic ECL emission was realized via the accumulation of cation radicals.
Copper Catalysis
Copper-Catalyzed Regioselective Borocarbonylative Coupling of Unactivated Alkenes with Alkyl Halides: Synthesis of β-Boryl Ketones
- Pages: 10537-10541
- First Published: 25 March 2020
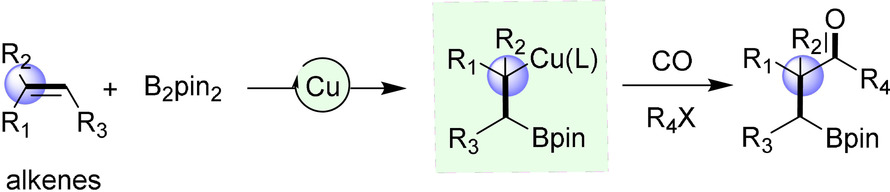
The borocarbonylative coupling of unactivated alkenes with alkyl halides remains a challenge. In this communication, a Cu-catalyzed borocarbonylative coupling of unactivated alkenes with alkyl halides for the synthesis of β-boryl ketones has been developed. A broad range of β-boryl ketone derivatives was prepared in moderate to excellent yields with complete regioselectivity.
Nanostructures
Cellular AND Gates: Synergistic Recognition to Boost Selective Uptake of Polymeric Nanoassemblies
- Pages: 10542-10546
- First Published: 09 March 2020
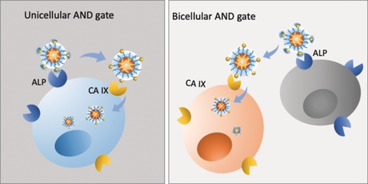
It′s logical: A cellular AND gate ensures the specific uptake of a polymeric nanoassembly only when two proteins (alkaline phosphatase, ALP, and carbonic anhydrase, CA XI) are present on the cell surface. ALP removes a protecting group from the nanoassembly, exposing the ligand of CA XI, enabling uptake. These proteins can be present on the surface of the same cell (a unicellular AND gate) or on the surfaces of different cells (a bicellular AND gate).
Enzyme Inhibition | Hot Paper
A Biomimetic Nanoparticle to “Lure and Kill” Phospholipase A2
- Pages: 10547-10551
- First Published: 23 March 2020
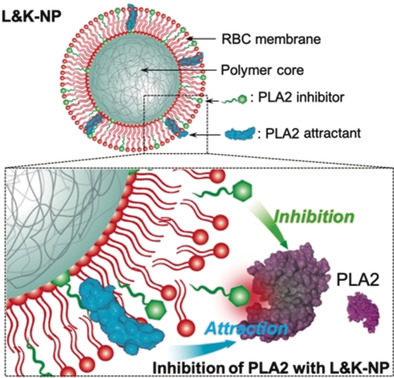
Modified red blood cell membrane is used to fabricate a cell-like nanoparticle for safe and effective inhibition of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) based on a „lure and kill“ working mechanism. The resulting nanoparticle can attract the PLA2 enzyme and subsequently inhibit its bioactivity. As a result, the nanoparticle can effectively inhibit PLA2-induced hemolysis and protect animals from PLA2-induced lethality.
Enzymes
Imino- and Azasugar Protonation Inside Human Acid β-Glucosidase, the Enzyme that is Defective in Gaucher Disease
- Pages: 10552-10555
- First Published: 19 March 2020
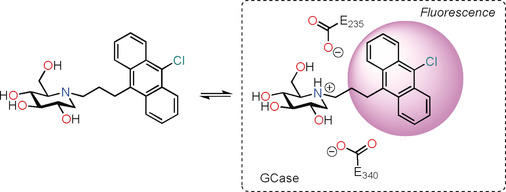
P-P-Pick up a proton: Inhibitor protonation inside human acid β-glucosidase or glucocerebrosidase (GCase), the enzyme involved in Gauchers disease, was directly observed using fluorescence. The results show that that derivatives of the inhibitors 1-deoxynojirimycin and isofagomine are protonated by GCase when bound, even if they are completely unprotonated outside the enzyme.
C−H Functionalization
Iridium-Catalyzed β-Alkynylation of Aliphatic Oximes as Masked Carbonyl Compounds and Alcohols
- Pages: 10556-10559
- First Published: 20 March 2020
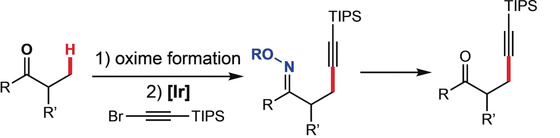
An Ir-catalyzed C(sp3)−H alkynylation of aliphatic ketones, aldehydes, and alcohols was achieved by using the corresponding oxime derivatives and a IrIII catalyst. This general reaction is selective towards primary C(sp3)−H bonds and can be used for the late-stage C−H alkynylation of complex molecules.
C−H Activation
Iridium(III) Catalysts with an Amide-Pendant Cyclopentadienyl Ligand: Double Aromatic Homologation Reactions of Benzamides by Fourfold C−H Activation
- Pages: 10560-10564
- First Published: 30 March 2020
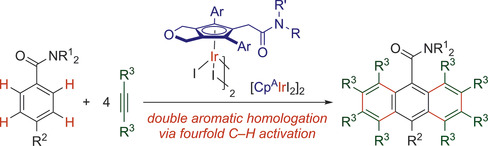
Iridium(III) catalysts that bear an amide-pendant cyclopentadienyl ligand ([CpAIrI2]2) were synthesized and characterized. Double aromatic homologation reactions of benzamides with alkynes by fourfold C−H activation proceeded in good to high yields when these [CpAIrI2]2 catalysts were used, demonstrating their superior catalytic performance in this challenging transformation.
Nitrogen Reduction | Very Important Paper
A Spectroscopic Study of Electrochemical Nitrogen and Nitrate Reduction on Rhodium Surfaces
- Pages: 10565-10569
- First Published: 23 March 2020
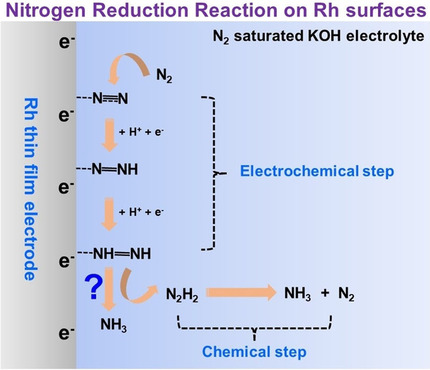
Two on the same path: On Rh surfaces, the electrochemical reductions of nitrogen and nitrate share the same reaction intermediate N2Hx (0≤x≤2) in alkaline electrolytes. The intermediate was detected by both surface-enhanced infrared-absorption spectroscopy (SEIRAS) and differential electrochemical mass spectrometry (DEMS). Possible reaction pathways are also proposed.
Biocatalysis
Photoenzymatic Hydrogenation of Heteroaromatic Olefins Using ‘Ene’-Reductases with Photoredox Catalysts
- Pages: 10570-10574
- First Published: 17 March 2020
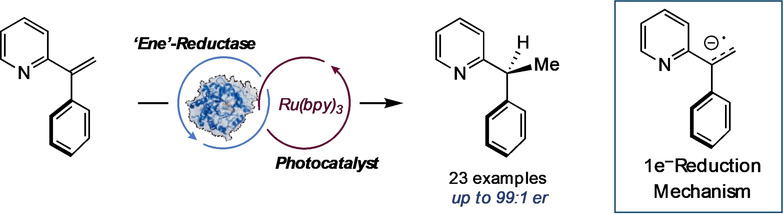
HAT-trick: Flavin-dependent ‘ene'-reductases can reduce vinyl pyridines when irradiated with visible light in the presence of a photoredox catalyst. The reaction proceeds via a radical mechanism where the vinyl pyridine is reduced to a neutral benzylic radical in solution. Calculations reveal this radical to be „dynamically stable“ and therefore sufficiently long-lived to diffuse into the enzyme active site for stereoselective hydrogen atom transfer (HAT).
Artificial Receptors | Hot Paper
Recognition and Stabilization of Unsaturated Fatty Acids by a Polyaromatic Receptor
- Pages: 10575-10578
- First Published: 20 March 2020
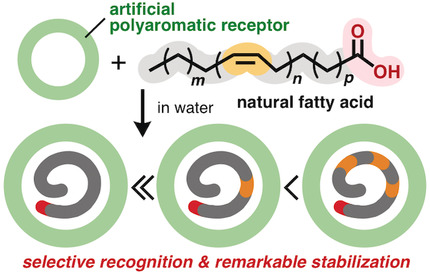
A polyaromatic cavity: The exclusive binding of a monounsaturated fatty acid from a mixture with the corresponding saturated substrate was demonstrated by an artificial polyaromatic receptor in water. Competitive binding experiments revealed higher binding affinity of the receptor for oligo- and polyunsaturated fatty acids (see picture). Within the receptor, the biosubstrates were stabilized against air, light, and heat owing to the polyaromatic shielding effect.
Imaging
An Efficient Near-Infrared Emissive Artificial Supramolecular Light-Harvesting System for Imaging in the Golgi Apparatus
- Pages: 10579-10583
- First Published: 20 March 2020
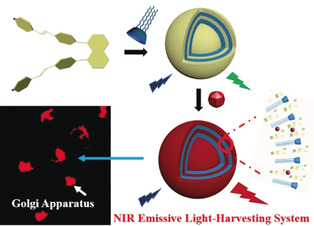
Combined harvester: Supramolecular co-assembly of lower-rim dodecyl-modified sulfonatocalix[4]arene (SC4AD) and naphthyl-1,8-diphenyl pyridinium derivative (NPS) gives a light-harvesting platform showing significant aggregation induced emission enhancement (AIEE). By using these near-infrared (NIR) emissive nanoparticles imaging in the Golgi apparatus is possible.
Potassium Superoxide Batteries
From K-O2 to K-Air Batteries: Realizing Superoxide Batteries on the Basis of Dry Ambient Air
- Pages: 10584-10587
- First Published: 30 March 2020
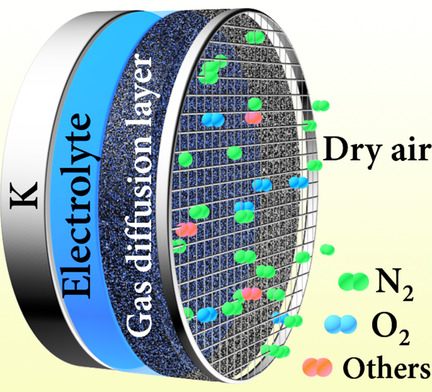
Getting rid of O2 cylinders: Dry ambient air is utilized for a K-air (dry) battery, which sheds light on the reversible potassium superoxide electrochemistry. This motivates the development of high-efficiency superoxide battery technology and is an important step towards the direct use of air in metal–air batteries.
Electrocatalysis
Distance Synergy of MoS2-Confined Rhodium Atoms for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution
- Pages: 10588-10593
- First Published: 29 March 2020
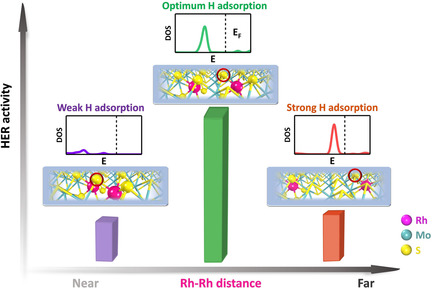
Single atoms of rhodium are confined in MoS2, leading to an ultra-high HER activity. By optimizing the distance between the confined Rh atoms, a low overpotential of only 67 mV is achieved at a current density of 10 mA cm−2, which surpasses the activity of most reported MoS2-based catalysts in acidic solution.
Cyanid-Aggregate
Salze von HCN-Cyanid-Aggregaten: [CN(HCN)2]− und [CN(HCN)3]−
- Pages: 10594-10599
- First Published: 06 February 2020
Einzelatomkatalysatoren | Hot Paper
Zusammenwirken elektronischer und sterischer Effekte bei der Tieftemperatur-CO-Oxidation an Einzelatom-Metallzentren in defekt-manipuliertem HKUST-1
- Pages: 10600-10604
- First Published: 20 March 2020
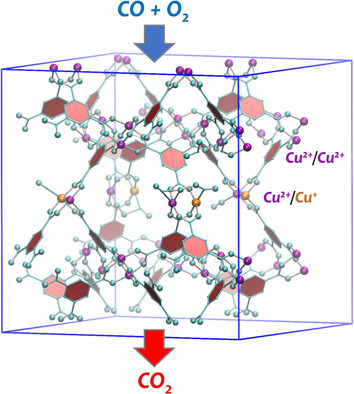
Ein komplexes Zusammenwirken: Eine umfangreiche Studie verbindet fortgeschrittene Spektroskopie und Theorie und zeigt das Auftreten elektronischer und sterischer Effekte bei reduzierten einzelnen Cu+/Cu2+ Dimeren in defektmanipulierten HKUST-1-SURMOFs zur Erzielung einer hohen katalytischen Aktivität für die Tieftemperatur-CO-Oxidation. Es wird ein neuer Reaktionsmechanismus mit einer ungeladenen O2-Spezies als wichtigstem Zwischenprodukt vorgestellt.
Cyanometallate
Isolierung und strukturelle Charakterisierung der achtfach protonierten Octacyanometallate [M(CNH)8]4+ (M=MoIV,WIV) aus Supersäuren
- Pages: 10605-10608
- First Published: 24 March 2020
![Isolierung und strukturelle Charakterisierung der achtfach protonierten Octacyanometallate [M(CNH)8]4+ (M=MoIV,WIV) aus Supersäuren](/cms/asset/65321410-9c6e-4142-958e-8d6423f82f05/ange202002366-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Gib Acht! Alle acht Cyanid-Liganden der Octacyanometallate Mo(CN)84− und W(CN)84− werden unter supersauren Bedingungen protoniert, ohne dass Blausäure (HCN) gebildet wird. Stattdessen bilden sich homoleptische Komplexe von Mo4+ und W4+ mit acht Isoblausäure-Liganden, welche vollständig charakterisiert werden konnten.
Lewis-Säuren | Very Important Paper
Synthese eines gegenanionstabilisierten Bis(silylium)ions
- Pages: 10609-10613
- First Published: 26 March 2020
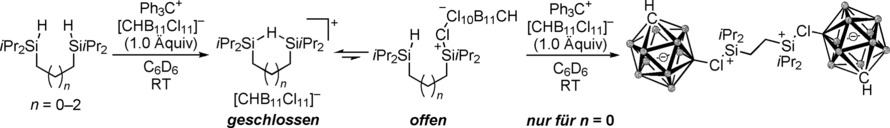
Endlich mal was Positives. Ein Silyliumion ist schon alleine schwer handhabbar, aber was, wenn zwei dieser Superelektrophile in einem Molekül nah beieinander sind? In Abhängigkeit vom Abstand zwischen diesen Lewis-sauren Zentren wird eine solche, vormals kaum zu fassende zweizähnige Lewis-Säure greifbar, charakterisierbar und bei Raumtemperatur lagerfähig.
Forschungsartikel
CO2 Reduction
Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to Acetic Acid by a Molecular Manganese Corrole Complex
- Pages: 10614-10621
- First Published: 13 April 2020
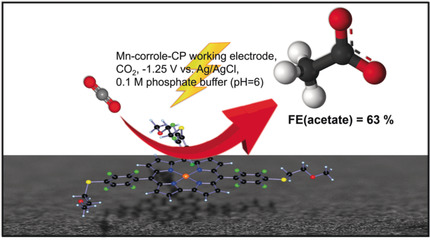
Electrochemical reduction of CO2 to acetic acid is achieved with a molecular MnIII-corrole complex. Electroreduction of MnIII leads to the electroactive MnII species, which binds CO2 and stabilizes the reduced intermediates to allow the reduction of CO2 to acetic acid in a moderately acidic aqueous medium (pH 6) with a selectivity of 63 % and a turn over frequency of 8.25 h−1, when immobilized on a carbon paper (CP) electrode.
Microarrays | Hot Paper
Droplet Precise Self-Splitting on Patterned Adhesive Surfaces for Simultaneous Multidetection
- Pages: 10622-10626
- First Published: 09 April 2020
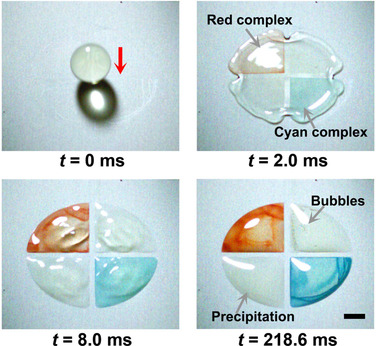
Dropping into place: A droplet self-splitting strategy was developed to divide a droplet into microdroplets and deposit them in a well-defined array. Matter exchange between the generated microdroplets was fully prohibited in the self-splitting process, thus enabling simultaneous arrayed reactions (see picture) and the detection of multiple analytes using only one droplet of sample.
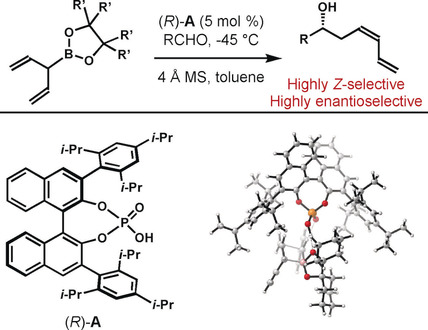
Asymmetric Catalysis
Chiral Phosphoric Acid Dual-Function Catalysis: Asymmetric Allylation with α-Vinyl Allylboron Reagents
- Pages: 10627-10635
- First Published: 15 March 2020
Antibiotics
The Kalimantacin Polyketide Antibiotics Inhibit Fatty Acid Biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus by Targeting the Enoyl-Acyl Carrier Protein Binding Site of FabI
- Pages: 10636-10643
- First Published: 24 March 2020
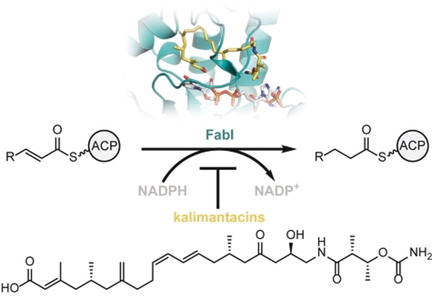
Combating MRSA: The kalimantacin antibiotics mimic the conformation of the natural fatty acyl substrate to inhibit the activity of the essential enoyl-ACP reductase enzyme FabI in Staphylococcus aureus. The findings of this study provide insights into the mode of action of this novel class of FabI inhibitors.
Ionic Liquid Crystals | Hot Paper
Self-Assembly of Aminocyclopropenium Salts: En Route to Deltic Ionic Liquid Crystals
- Pages: 10644-10652
- First Published: 02 March 2020
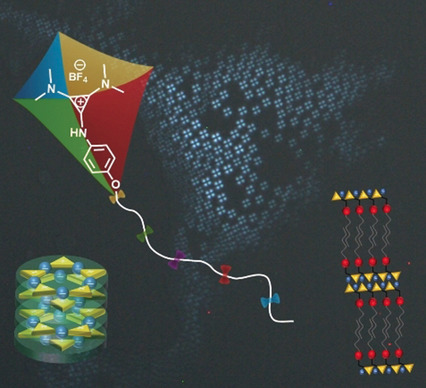
Cyclopropenium-based liquid crystals form lamellar or columnar mesophases, depending on the substitution of head group and the number of peripheral chains. The effective volume of headgroup versus hydrophobic part determines the mesophase type. These compounds bridge the gap between low molecular weight organocatalysts and polymeric electrolytes based on cyclopropenium.
Luminogens
Bridged Stilbenes: AIEgens Designed via a Simple Strategy to Control the Non-radiative Decay Pathway
- Pages: 10653-10660
- First Published: 02 March 2020
Nanostructures
Strain-Enhanced Metallic Intermixing in Shape-Controlled Multilayered Core–Shell Nanostructures: Toward Shaped Intermetallics
- Pages: 10661-10667
- First Published: 20 March 2020

Pd-Ni-Pt in the mix: A method for studying the intermixing process in a shaped nanoparticle was devised. It uses multilayered Pd-Ni-Pt core–shell nanocubes as precursors. Under mild conditions, the intermixing between Ni and Pt could be tuned by changing layer thickness and number, triggering intermixing while preserving nanoparticle shape.
Metal–Oxo Complexes | Hot Paper
Synthesis, Structure, and Bonding of d3 Molybdenum–Oxo Complexes
- Pages: 10668-10673
- First Published: 14 March 2020
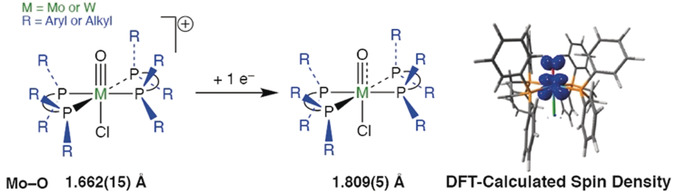
Rare examples of low-oxidation-state molybdenum- and tungsten–oxo compounds (d3) have been prepared. They are found to possess long M−O bonds, owing to the oxo-radical character of their electronic structures. The stability of these compounds is strongly modulated via the steric bulk of the equatorial ligands, providing a design motif for controlling oxo-centered reactivity.
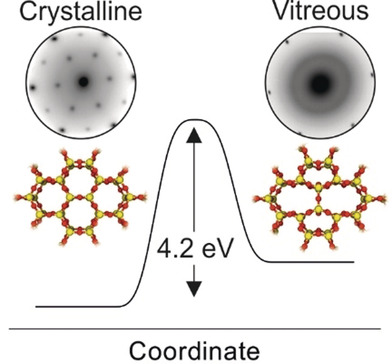
Phase Transitions
A Silica Bilayer Supported on Ru(0001): Following the Crystalline-to Vitreous Transformation in Real Time with Spectro-microscopy
- Pages: 10674-10680
- First Published: 15 March 2020
Battery Electrodes | Very Important Paper
A Long Cycle-Life High-Voltage Spinel Lithium-Ion Battery Electrode Achieved by Site-Selective Doping
- Pages: 10681-10689
- First Published: 23 March 2020
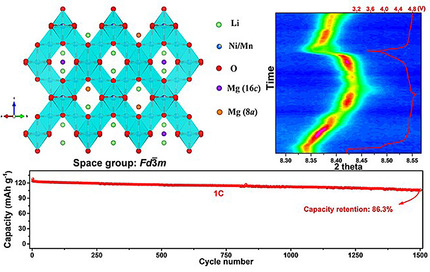
Magnesium is selectively doped onto both tetrahedral (8a) and octahedral (16c) sites in Fd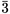 m LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. The Mg stabilizes the structure against structural deformation and suppresses unfavorable two-phase reactions during cycling process, thus contributing to an excellent extended-long-term electrochemical performance.
m LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. The Mg stabilizes the structure against structural deformation and suppresses unfavorable two-phase reactions during cycling process, thus contributing to an excellent extended-long-term electrochemical performance.
Structure Elucidation | Hot Paper
Side-On Bonded Beryllium Dinitrogen Complexes
- Pages: 10690-10696
- First Published: 20 March 2020
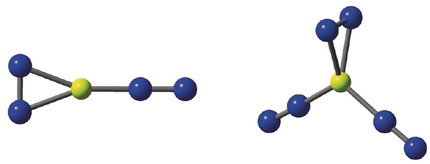
The good side: The preparation and spectroscopic identification of the complexes NNBe(η2-N2) and (NN)2Be(η2-N2) and the energetically higher lying isomers Be(NN)2 and Be(NN)3 are reported. NNBe(η2-N2) and (NN)2Be(η2-N2) are the first examples of covalently side-on bonded N2 adducts of a main-group element. The analysis of the electronic structure using modern methods of quantum chemistry suggests that NNBe(η2-N2) and (NN)2Be(η2-N2) should be classified as π complexes rather than metalladiazirines.
Molecular Magnetism
Coercive Fields Above 6 T in Two Cobalt(II)–Radical Chain Compounds
- Pages: 10697-10705
- First Published: 14 April 2020
Silicon Nanowire Arrays
Constant Electricity Generation in Nanostructured Silicon by Evaporation-Driven Water Flow
- Pages: 10706-10712
- First Published: 18 March 2020

A novel hydrovoltaic device for efficiently utilizing water flow in silicon nanowire arrays to generate constant electricity depending on natural water evaporation is demonstrated. Through changing ion concentration in water, as well as the length and surface charge of SiNWs, it was discovered that the mechanism of electricity generation is mainly ascribed to streaming potential.
Heterocycles | Hot Paper
Electrophotocatalytic Decarboxylative C−H Functionalization of Heteroarenes
- Pages: 10713-10719
- First Published: 30 March 2020
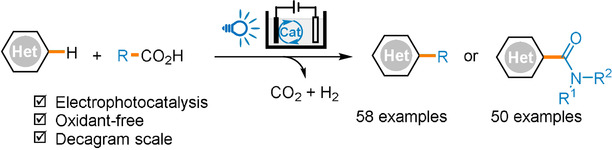
A broadly applicable electrophotocatalytic method for the direct decarboxylative C−H alkylation and carbamoylation of heteroarenes has been developed. This method combines the advantages of photocatalysis and electrochemistry to enable the functionalization of a broad range of substrates and to allow the decarboxylative C−H functionalization reactions to proceed by H2 evolution, obviating the need for oxidizing reagents and proton acceptors.
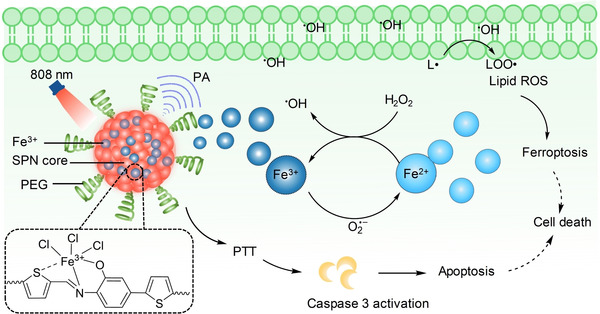
Nanotheranostics | Very Important Paper
Semiconducting Polycomplex Nanoparticles for Photothermal Ferrotherapy of Cancer
- Pages: 10720-10725
- First Published: 24 March 2020
Synthetic Methods
Sila- and Germacarboxylic Acids: Precursors for the Corresponding Silyl and Germyl Radicals
- Pages: 10726-10731
- First Published: 26 March 2020
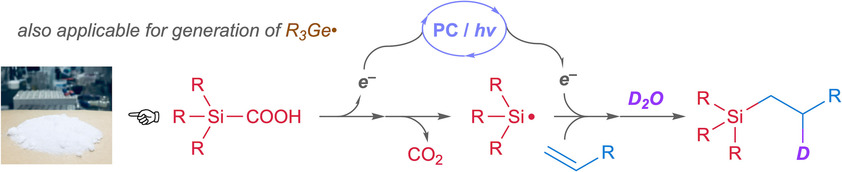
Generation of silyl radicals by photoinduced decarboxylation of silacarboxylic acids is described. The reaction proceeds smoothly in the presence of a commercially available photocatalyst with broad functional-group compatibility. This reaction could also be performed in the presence of water, enabling the use of D2O as the deuteration reagent. Germyl radicals were similarly obtained.
RNA Modifications
Chemical Deprenylation of N6-Isopentenyladenosine (i6A) RNA
- Pages: 10732-10737
- First Published: 20 March 2020
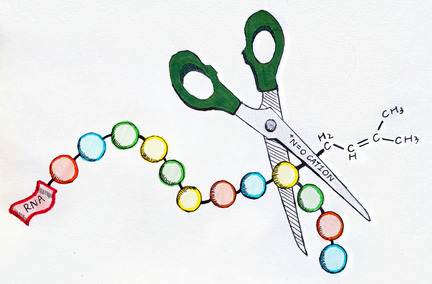
Artificial Deprenylase: An oxoammonium cation has been identified as a unique chemical motif that targets prenylated i6A RNA and exhibits remarkable selectivity and efficiency in both live cells and plants. This demonstrates that small organic molecules as artificial enzyme mimics can be powerful tools to modulate RNA epigenetic modification for the precise control of biological events.
Nanocatalysis
Rare-Earth Single Erbium Atoms for Enhanced Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- Pages: 10738-10744
- First Published: 18 March 2020
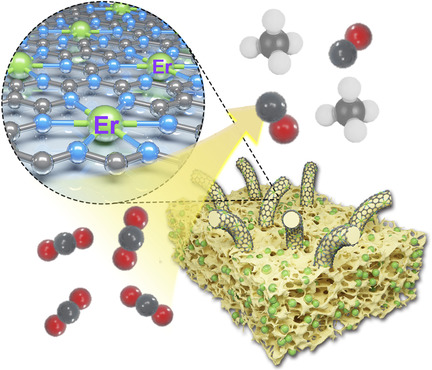
A catalyst with a high density of rare-earth single Er atoms supported on a carbon nitride nanotube (HD-Er1/CN-NT) is synthesized by an atom-confinement and coordination strategy (ACC). Experimental results and DFT calculations reveal that the single Er atoms play a key role in the photocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction in a pure-water system. The ACC strategy also extends to the synthesis of other rare-earth single-atom catalysts.
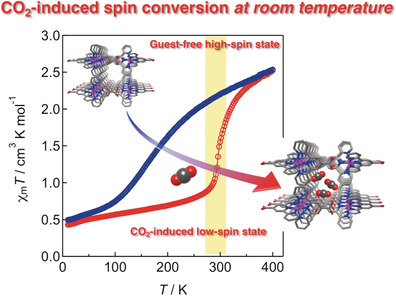
Solid-State Structures | Hot Paper
CO2-Induced Spin-State Switching at Room Temperature in a Monomeric Cobalt(II) Complex with the Porous Nature
- Pages: 10745-10752
- First Published: 18 March 2020







![Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting from a Ferroelectric Hybrid Salt [Ph3MeP]4[Ni(NCS)6] Embedded in a Polymer Matrix](/cms/asset/f1056917-b831-4b4f-85a3-42a01857bda4/ange202001250-toc-0001-m.jpg)
![Salze von HCN-Cyanid-Aggregaten: [CN(HCN)2]− und [CN(HCN)3]−](/cms/asset/7da7424f-b465-4037-b29d-7315886e381e/ange201915206-toc-0001-m.jpg)