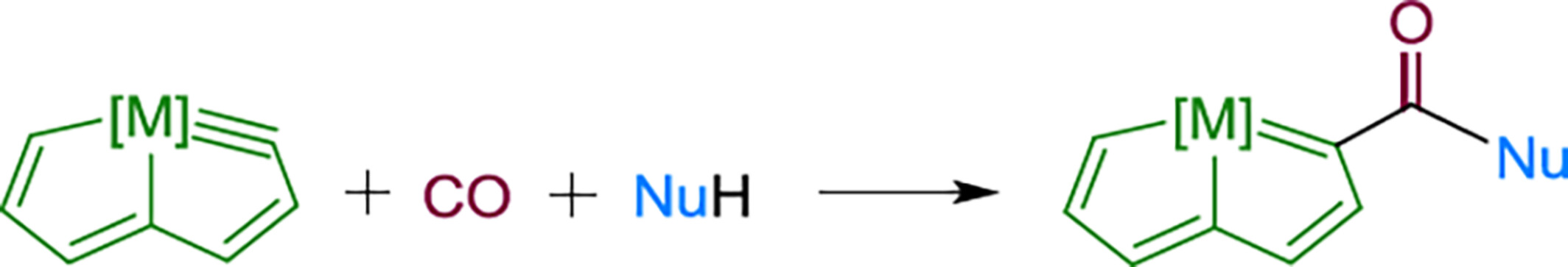Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 2685
- First Published: 15 October 2024
The syntheses of poly[2]catenane gels reported to date all rely on the polymer as the backbone. We reported poly[2]catenane gels prepared by entirely sequential self-assembly of small molecules via noncovalent and dynamic covalent bonds. Due to the presence of hydrogen bonds in the poly[2]catenane gels, the gels also possessed stimulus responsiveness and self-healing properties. More details are discussed in the article by Ji et al. on pages 2699—2704.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 2686
- First Published: 15 October 2024

Practical CO2 and CO electroreduction are often operated at elevated temperatures, yet the correlation between the temperature increase and catalytic activity and selectivity has not been well-defined. This study uncovers that higher temperatures enhance *CO coverages, but in CO2 reduction, they also promote *CO desorption to vapor-phase CO, lowering C2H4 selectivity. In CO reduction, elevated temperatures facilitate CO diffusion to overcome the unfavorable *CO adsorption thermodynamics, which promotes C—C coupling. More details are discussed in the article by Wang et al. on pages 2705—2711.
Contents
Concise Report
Poly[2]catenane Gels Based on Sequential Assembly of Small Molecules
- Pages: 2699-2704
- First Published: 09 July 2024
![Poly[2]catenane Gels Based on Sequential Assembly of Small Molecules†](/cms/asset/a75a7ad4-2e76-49df-935e-fc9922ff9394/cjoc202400435-toc-0001-m.jpg)
We reported poly[2]catenane gels prepared by entirely sequential self-assembly of small molecules via noncovalent and dynamic covalent bonds. First, monomer M1 self-assembled into linear supramolecular polymers through hydrogen bonding and π-π interactions. Upon the addition of M2 and M3, dynamic covalent bonds were generated to transform supramolecular polymers into poly[2]catenane gels.
Understanding the Temperature Effect on Carbon-Carbon Coupling during CO2 and CO Electroreduction in Zero-Gap Electrolyzers
- Pages: 2705-2711
- First Published: 09 July 2024
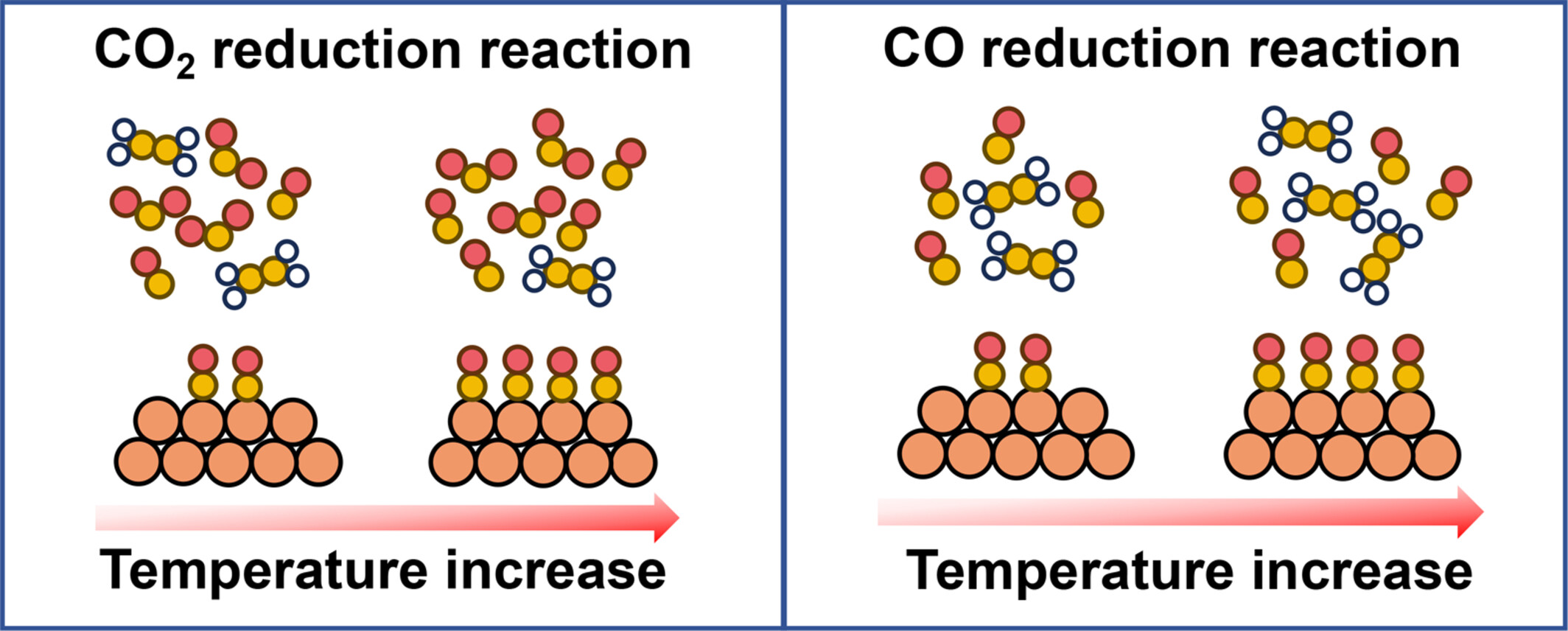
This study focuses on the effect of temperature on the kinetics and product selectivity of CO2 and CO electroreduction. Although the elevated temperature increases *CO coverages in both reactions, it promotes *CO desorption in CO2 reduction but increases C—C coupling activity in CO reduction, causing the observed differences in selectivities.
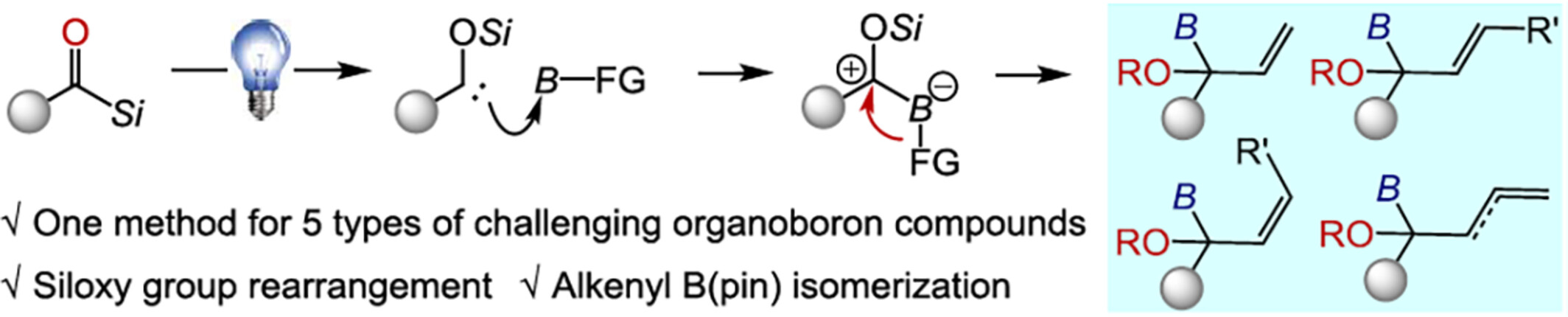
Versatile Synthesis of α-Oxygen Organoboron Compounds via Photo-Induced Siloxycarbene
- Pages: 2712-2716
- First Published: 09 July 2024
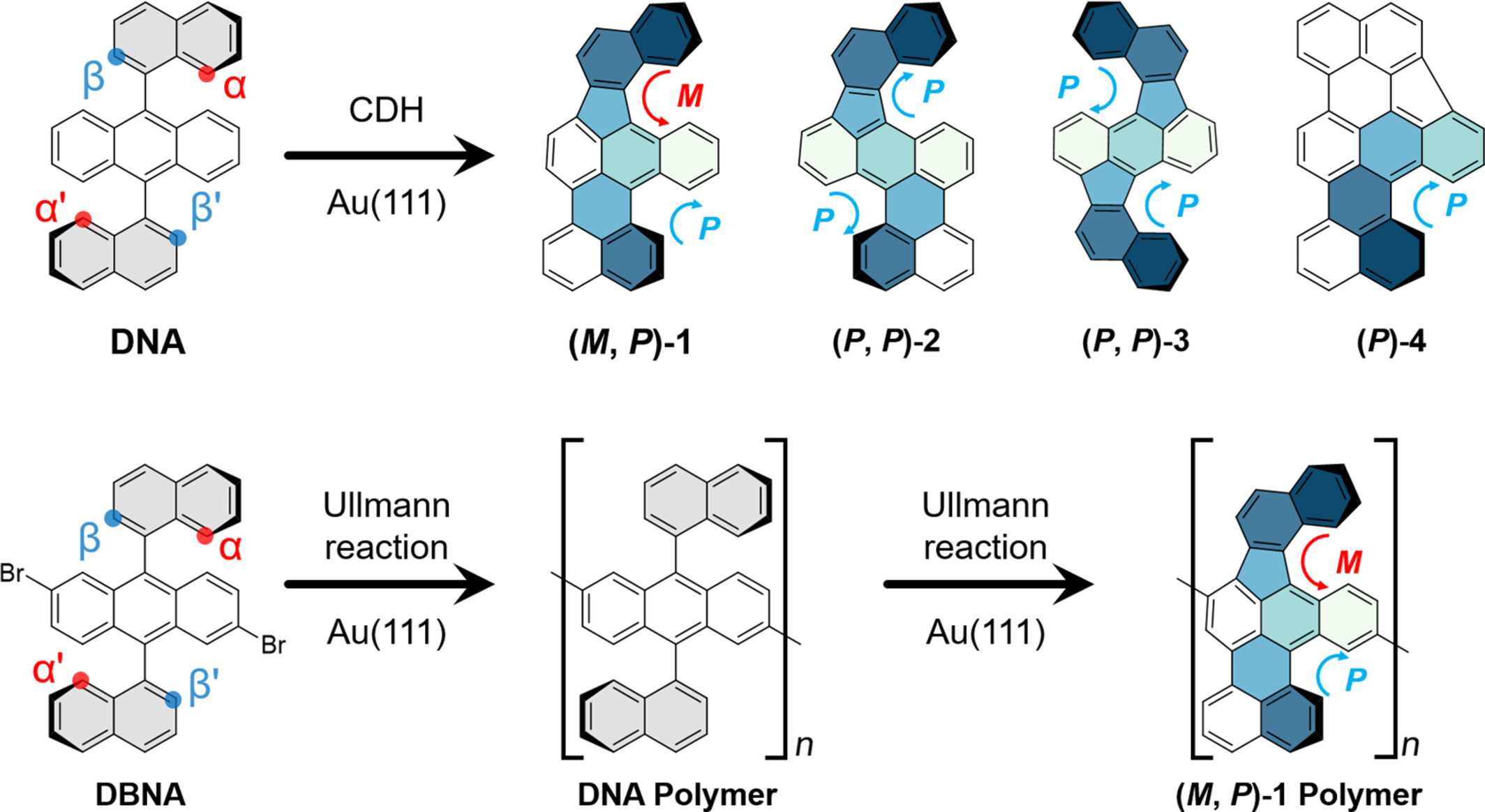
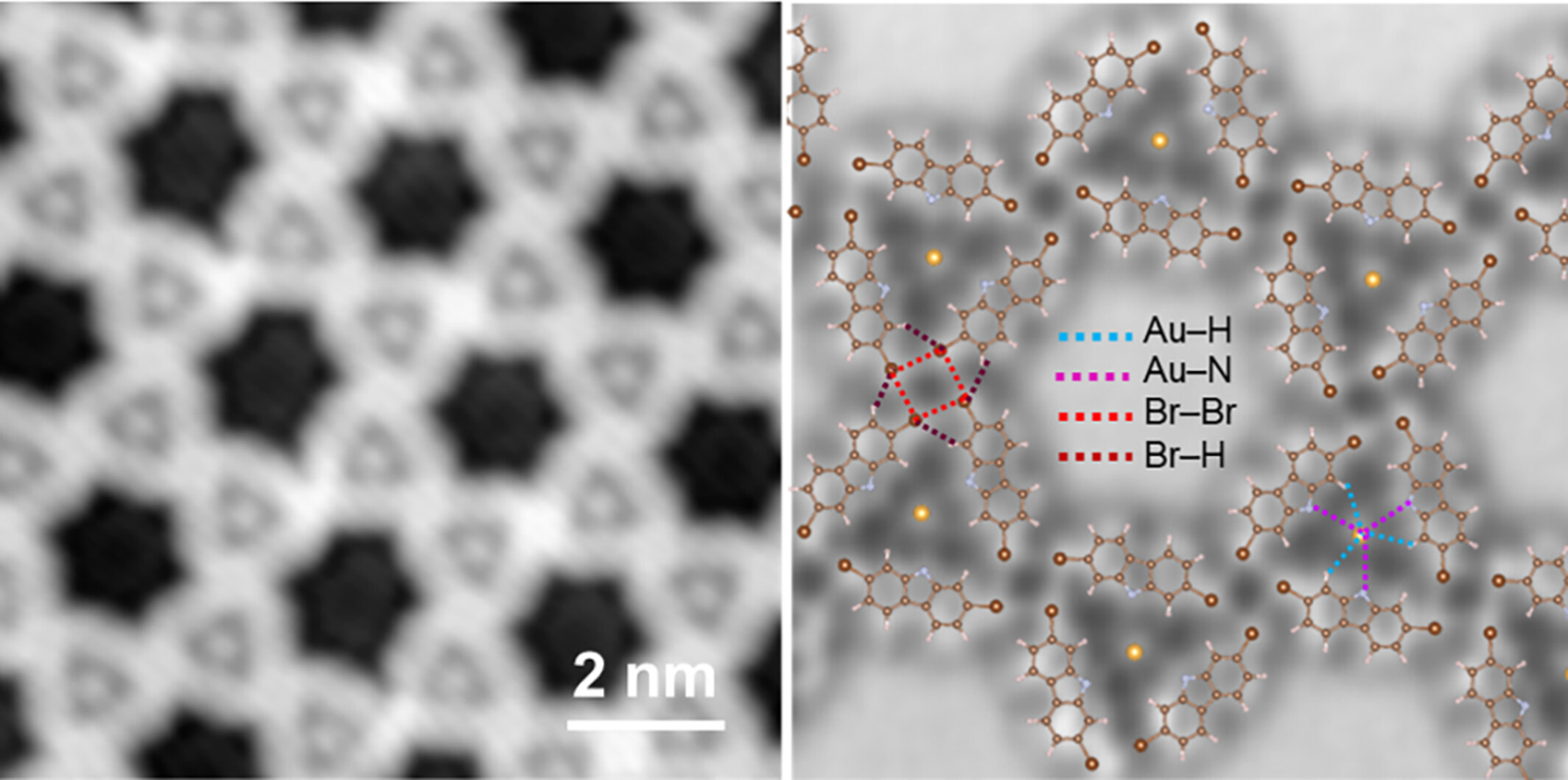
Multiple Interaction Forces Construct Two-Dimensional Self-assembly Kagome Lattices on Au(111)
- Pages: 2717-2722
- First Published: 09 July 2024
Vinylogous Fluorine Stabilizing Effect Enables Rational Design of a Novel Donor-Acceptor Cyclopropane and Its Applications in [3+2] Cycloaddition Reaction and Ring-Opening Polymerization
- Pages: 2723-2727
- First Published: 12 July 2024
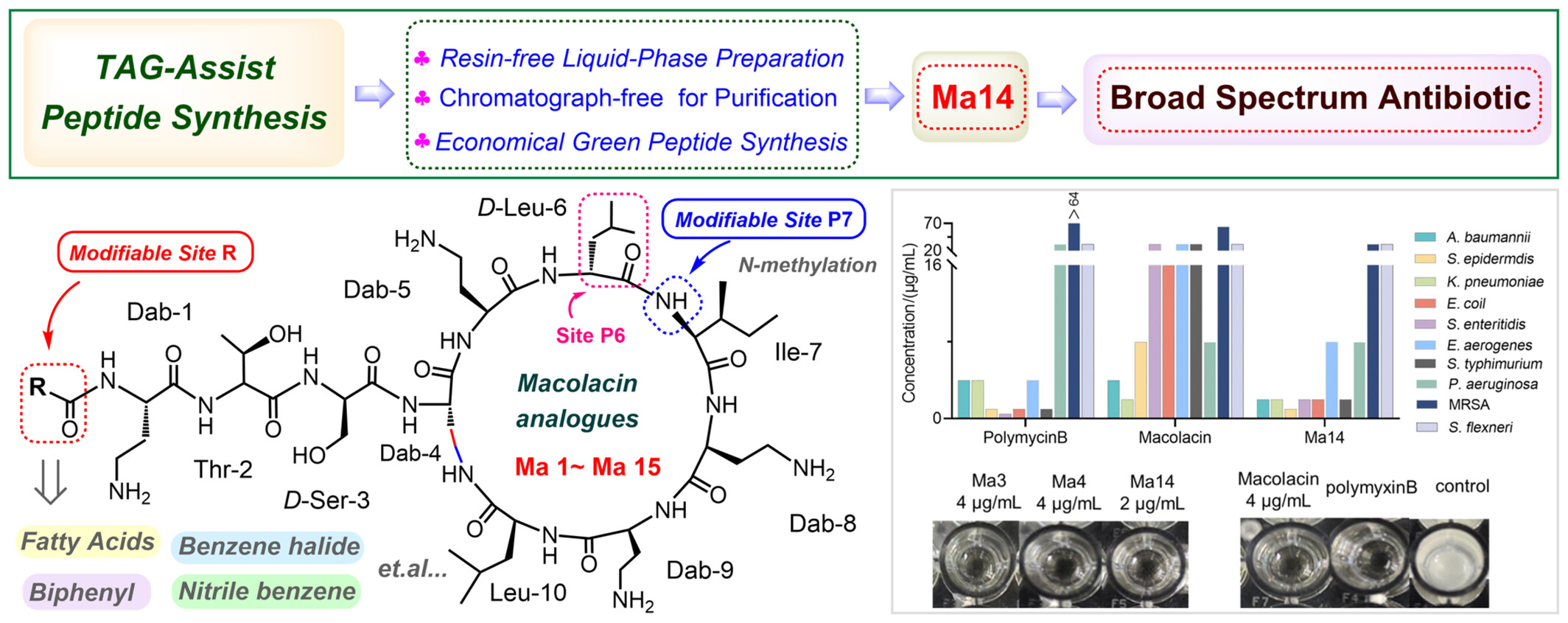
TAG-Assisted Liquid-Phase Synthesis and Structure Activity Relationship of Macolacin-Based Side-to-Tail Cyclopeptides Antibiotic
- Pages: 2728-2742
- First Published: 12 July 2024
Assembling 2D Ni-Co nanosheets onto Mo2C Nanorod towards Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution†
- Pages: 2743-2750
- First Published: 11 July 2024
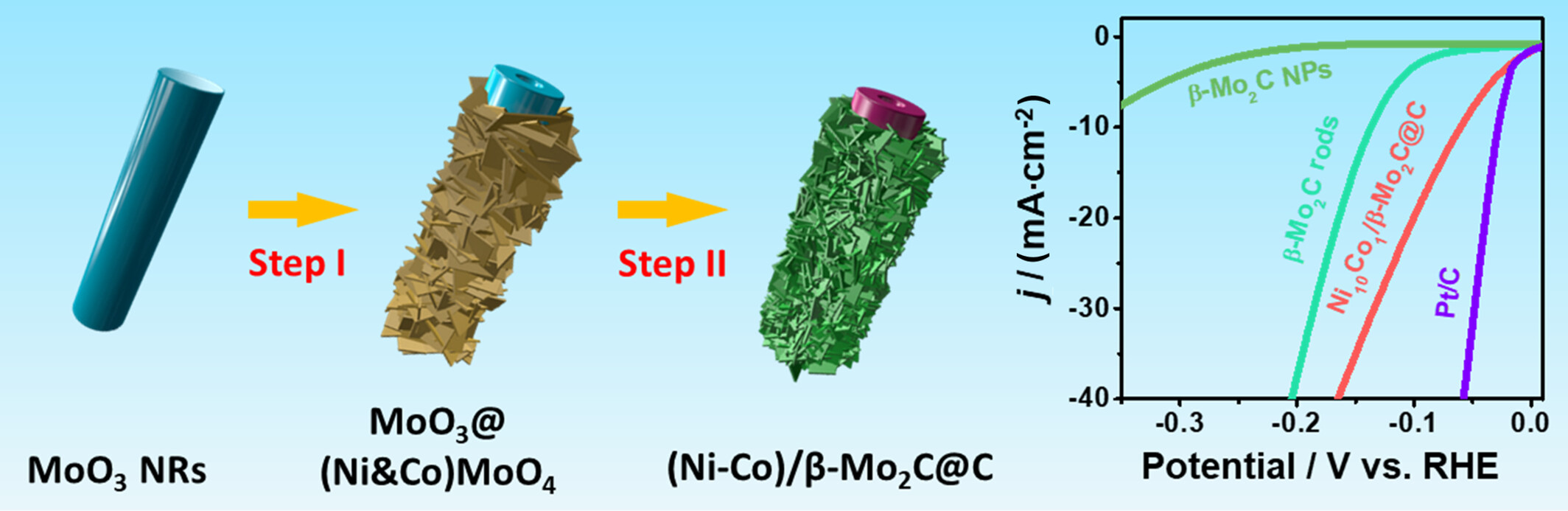
A novel electrocatalyst, Ni-Co/β-Mo2C@C, was rationally engineered to enhance the efficiency of the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). An innovative template-engaged strategy was employed to synthesize hierarchical nanosheet-based MoO3@(Ni&Co)MoO4 nanorods, which were subsequently transformed into hierarchical Ni-Co/β-Mo2C@C through direct carburization at high temperature. Benefitting from several structural advantages including large exposed surface, fast charge transfer, Ni-Co dual-doping, and unique hierarchical structure, the prepared Ni-Co/β-Mo2C@C exhibited exceptional electrocatalytic performance for HER in acidic conditions, characterized by a low overpotential and remarkable stability.
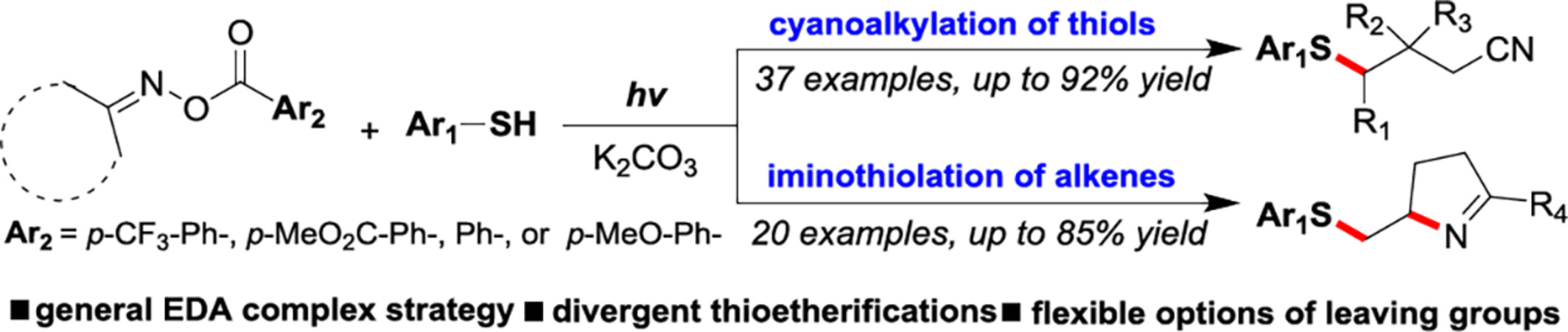
A General Electron Donor-Acceptor Photoactivation Using Oxime Esters Enabled Divergent Thioetherifications
- Pages: 2751-2756
- First Published: 12 July 2024
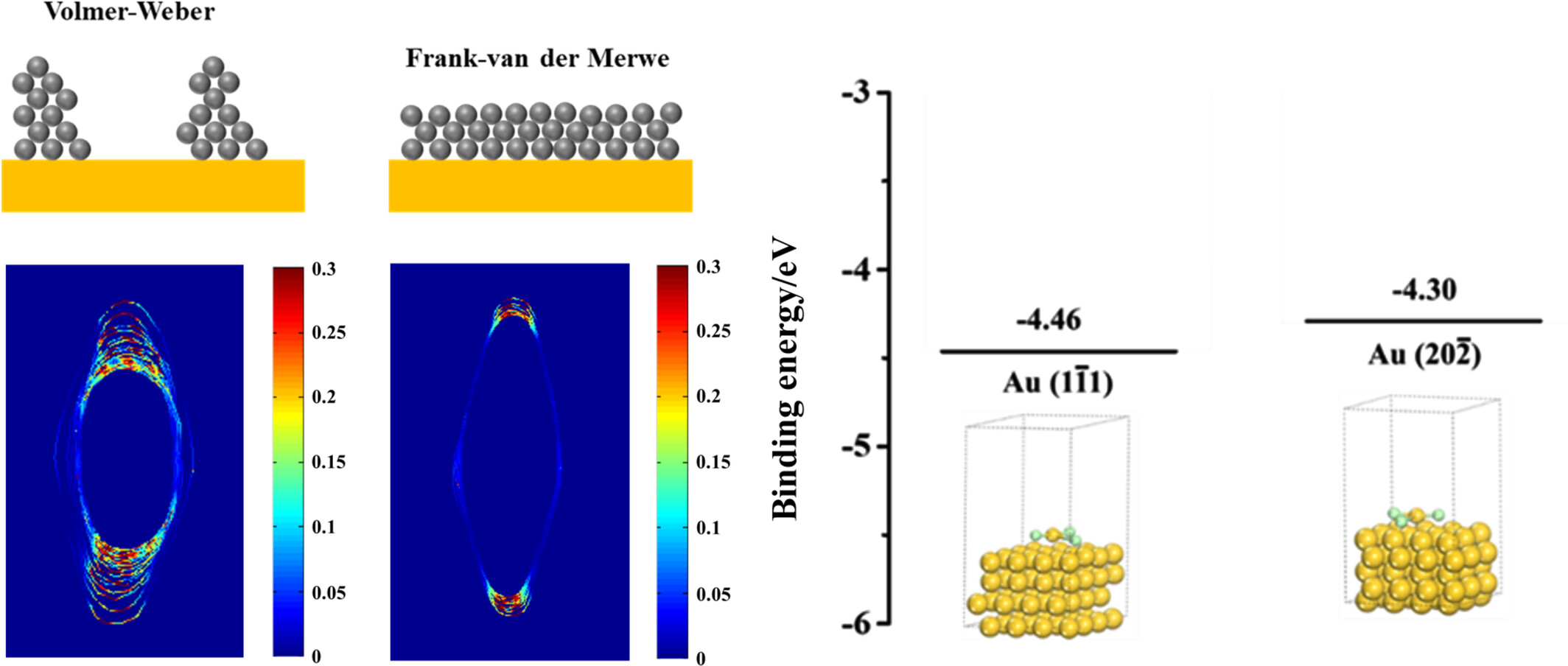
In Situ Liquid Cell Transmission Electron Microscopy Observations of Growth and Anticorrosion Behaviors of AuCl3 Shell on Au Nanobipyramids
- Pages: 2757-2764
- First Published: 11 July 2024
Carbonylation Reactions of a Metallapentalyne: Synthesis of Its Ester and Amide Derivatives
- Pages: 2765-2772
- First Published: 14 July 2024
Structurally Divergent Synthesis of Azetidines, 5,6-Dihydro-1,3-oxazines and 2,3-Dihydro-1,4-oxazines through Palladium-Catalyzed Tandem Allylic Substitution Reaction
- Pages: 2773-2778
- First Published: 16 July 2024
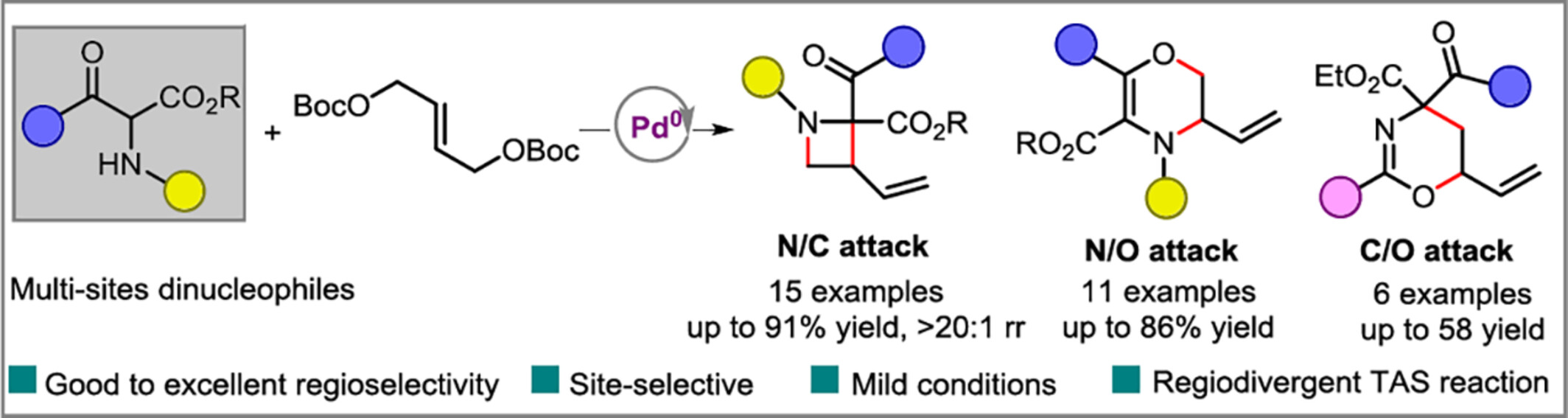
A regiodivergent synthesis of azetidines, 5,6-dihydro-1,3-oxazines and 2,3-dihydro-1,4-oxazines has been achieved through palladium-catalyzed tandem allylic substitution reaction. This protocol provides a variety of heterocycles in satisfactory yields with good to excellent regioselectivities under mild reaction conditions.
In-situ Post-Synthetic Treatment of CsPbBr3 Perovskite Nanocrystals in Nanoporous Silica Microspheres
- Pages: 2779-2787
- First Published: 17 July 2024
One-Dimensional Metal-Organic Framework for High-Efficiency Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to CO
- Pages: 2788-2794
- First Published: 16 July 2024
Self-assembling Monolayer-Assisted Perovskite Growth Enables High-Performance Solar Cells
- Pages: 2795-2803
- First Published: 14 July 2024

Self-assembled monolayers (MeO-2PACz, MPA-CPA, 4PADCB) were employed as HTL to contrastively investigate the effects on the crystallization and growth of the top perovskite. 4PADCB was identified as the optimal template, enabling the preparation of vertically growing perovskite film with larger grain size, lower defect density and more excellent mechanical properties. Benefitting from the above properties, 4PADCB-based device achieved a PCE of 24.80% without any additional processing.
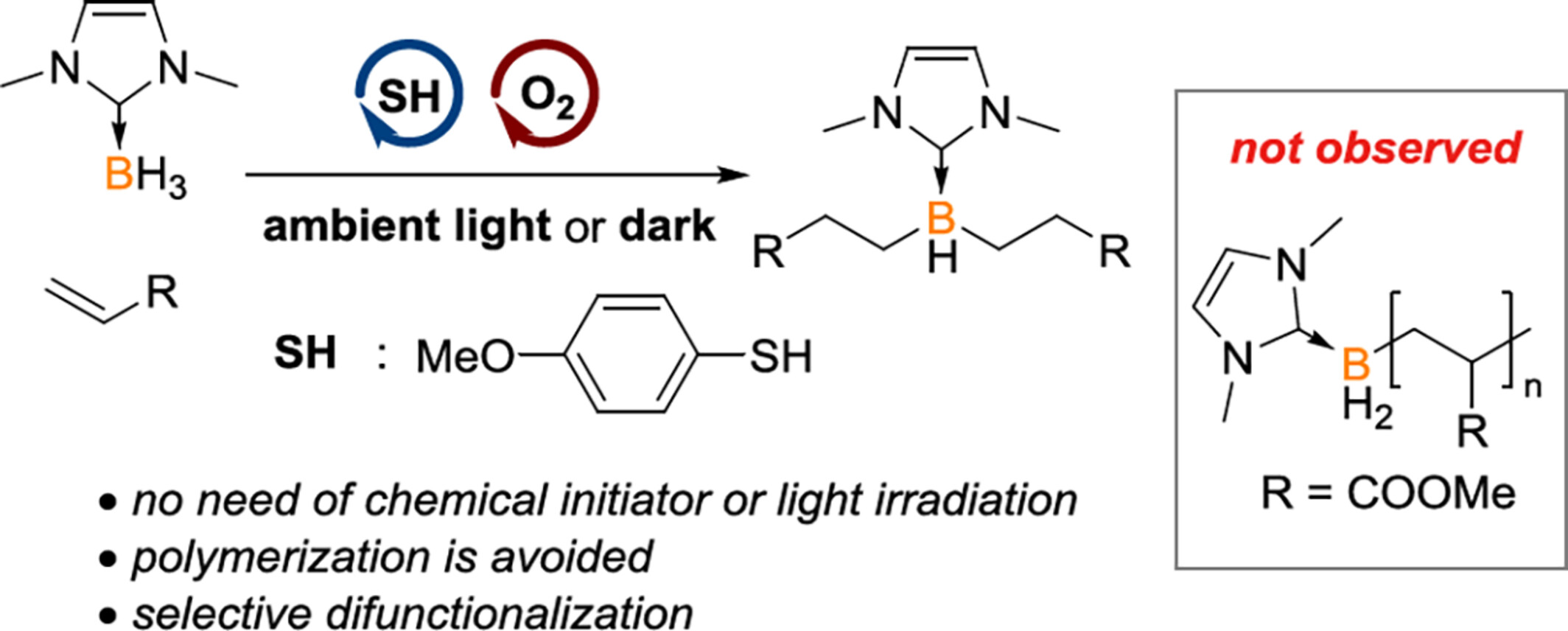
Functionalization of Boranes through Thiol/Oxygen Catalysis
- Pages: 2804-2810
- First Published: 17 July 2024
On-surface Synthesis of Multiple Non-benzenoid Carbohelicenes Fused with Fluorene Unit(s)
- Pages: 2811-2817
- First Published: 17 July 2024
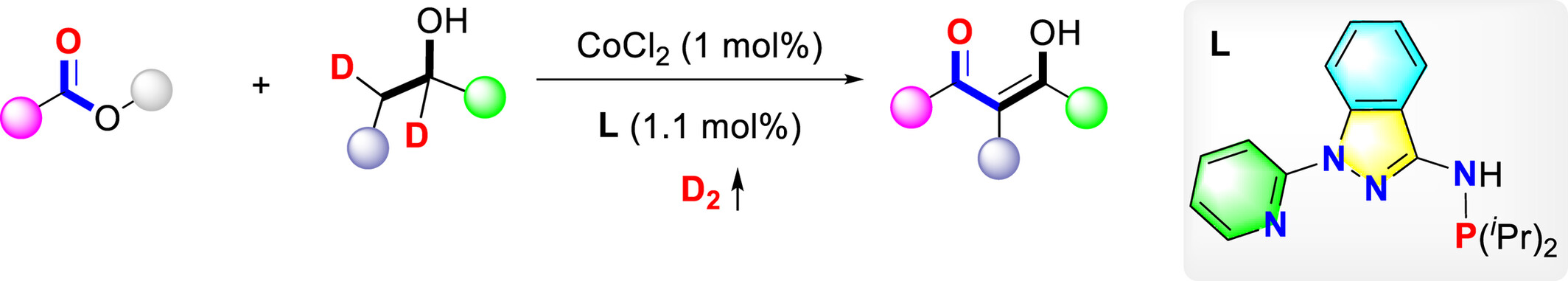
Co-Catalyzed Dehydrogenation Claisen Condensation of Secondary Alcohols with Esters
- Pages: 2818-2824
- First Published: 17 July 2024
Secondary Aggregation Induced by Volatile Additive for Improved Exciton Diffusion and Charge Separation in High Efficiency Organic Photovoltaic Devices
- Pages: 2825-2832
- First Published: 17 July 2024
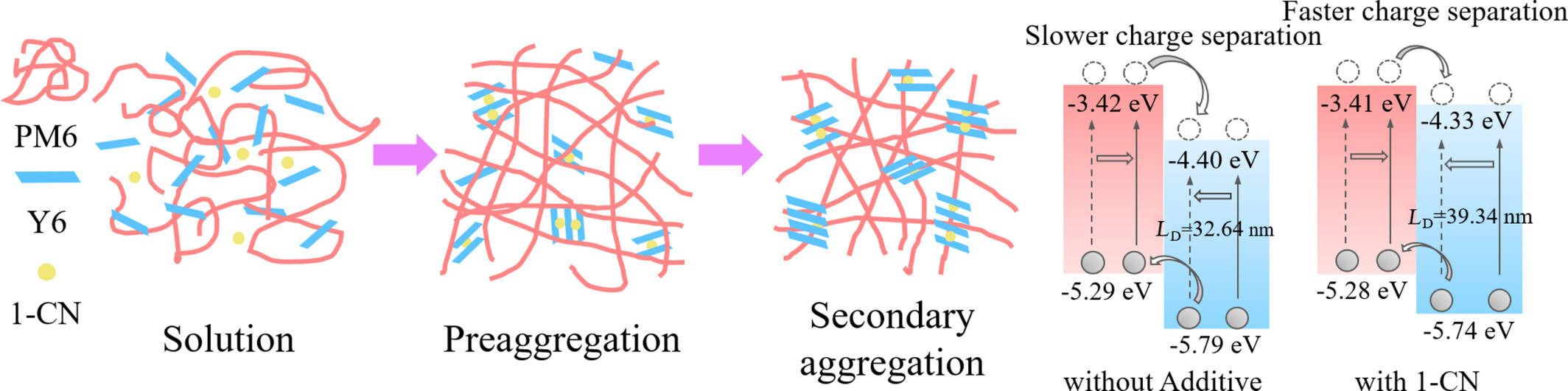
This study conducted a comprehensive exploration of the mechanism of the classic volatile additive 1-CN in the PM6:Y6 system and innovatively discovered the secondary aggregation effect. Additionally, the study established the connection from film formation kinetics to morphology control to exciton dynamics.
Enantioselective Total Synthesis of (+)-Propolisbenzofuran B
- Pages: 2833-2839
- First Published: 22 July 2024
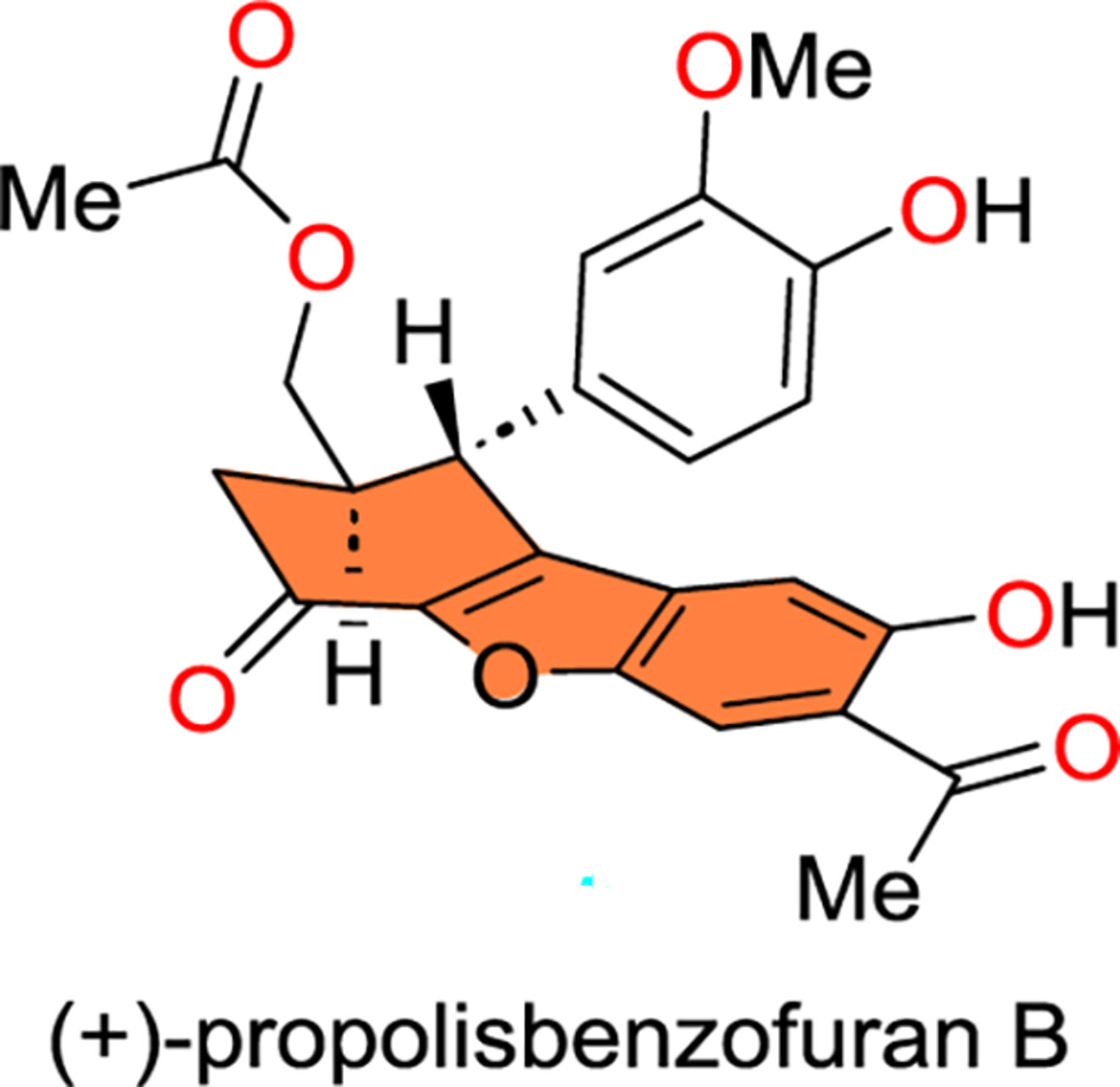
The first catalytic asymmetric total synthesis of (+)-propolisbenzofuran B was reported. This achievement was made possible by a highly enantioselective rhodium-catalyzed hydrogenation of a tetrasubstituted olefin. Other features include the construction of the central tetrahydrodibenzo[b,d]furan core via a sequence of Zn(II)-mediated regioselective benzofuran formation and Dieckmann cyclization, and C-H oxidations involving a visible light-induced Fe(III)-catalyzed benzylic C(sp3)-H oxidation.
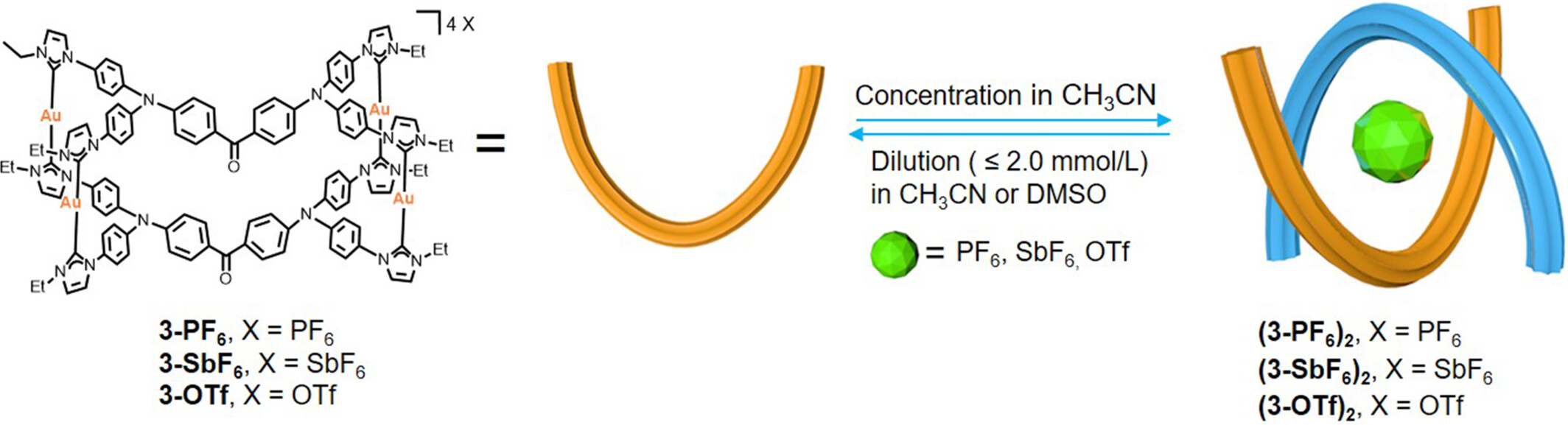
Stimuli-Responsive Interconversion between Poly-NHC-Based Organometallic Assemblies and Their Self-Aggregated Dimers
- Pages: 2840-2844
- First Published: 22 July 2024
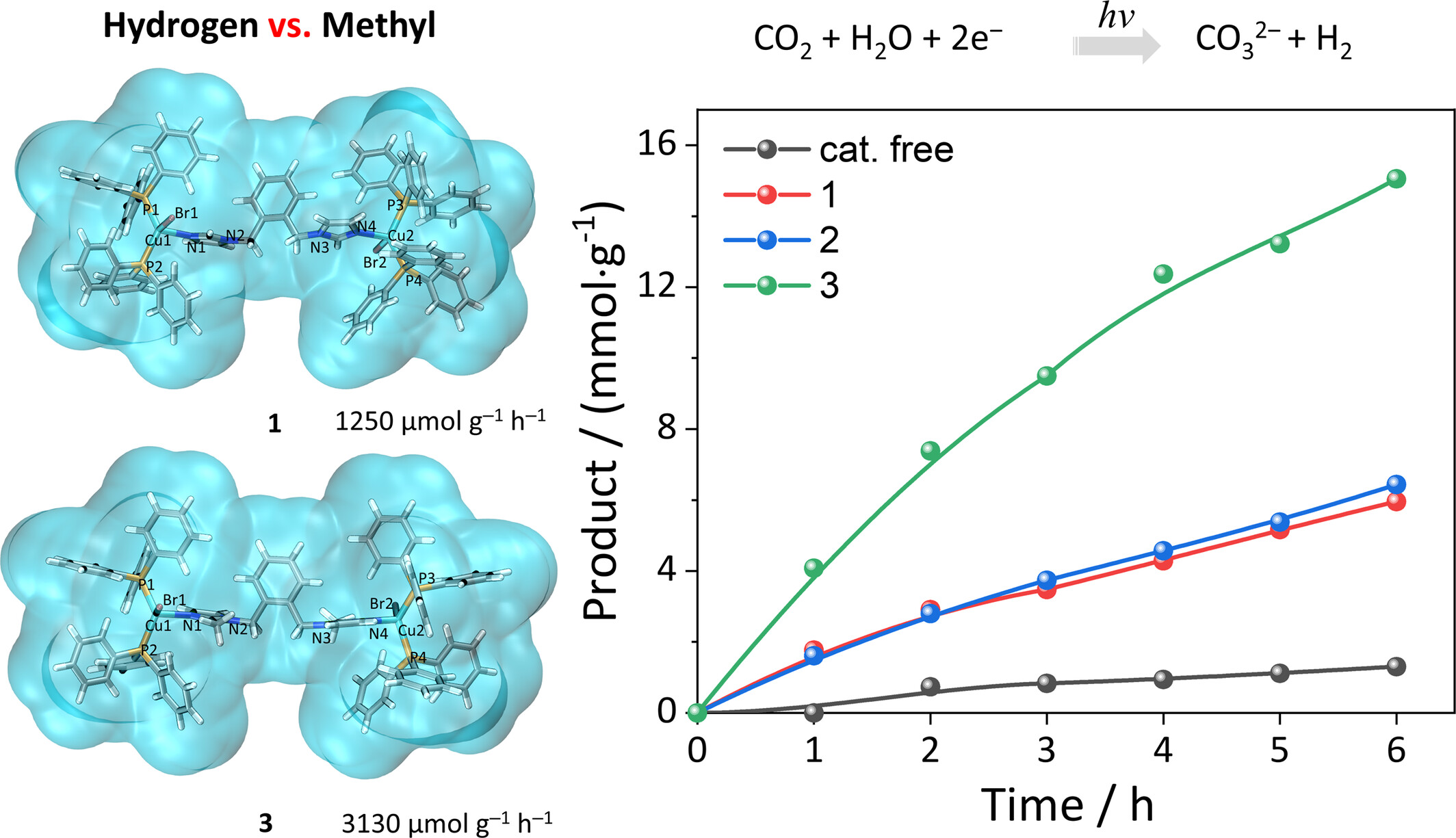
Substituent Modulated Electronic Properties of Cu(I) Active Site in Metal–Organic Halides for Boosting Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 2845-2852
- First Published: 22 July 2024
Chemistry Authors Up Close
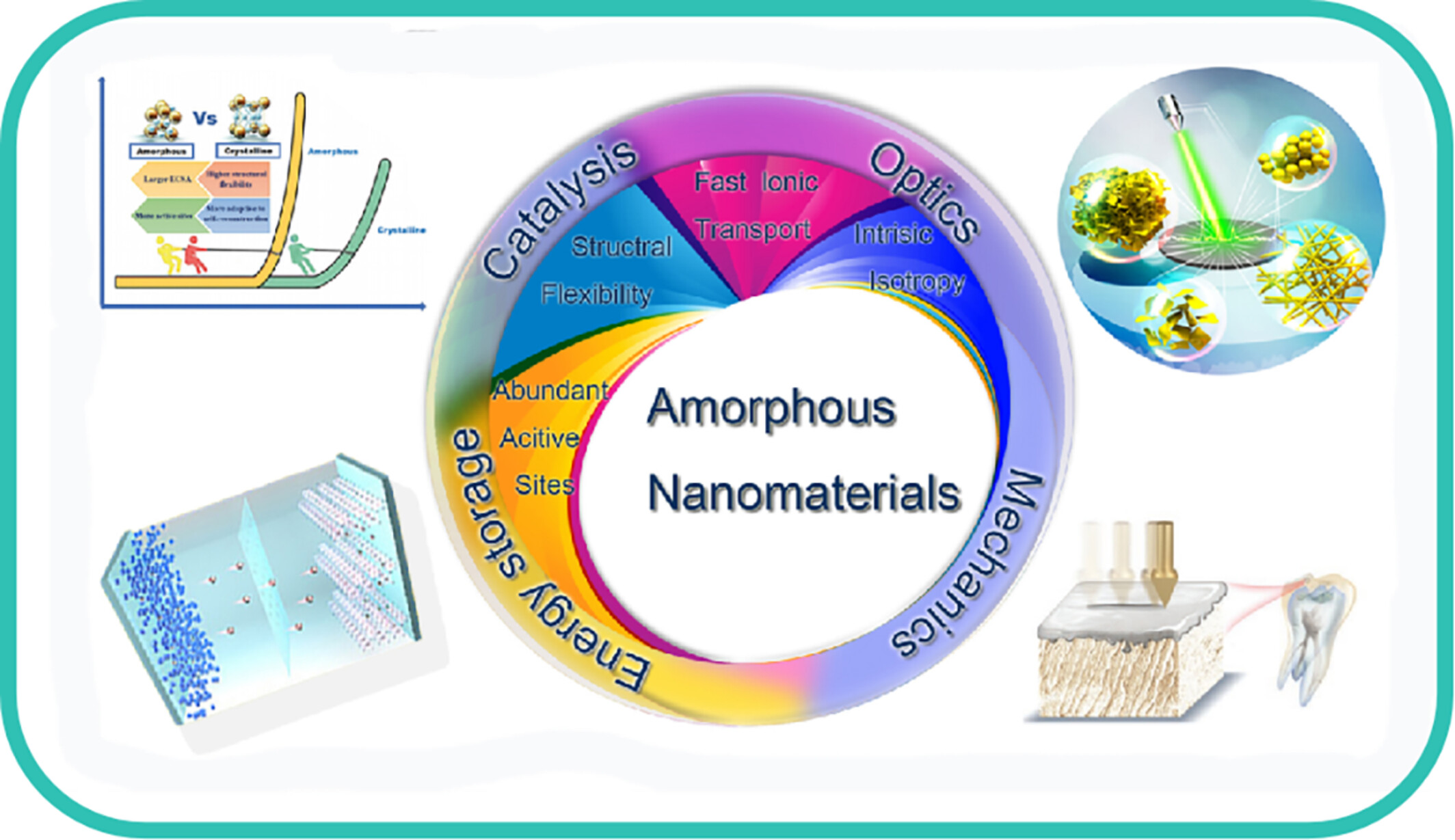
Recent Advances of Amorphous Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications
- Pages: 2853-2876
- First Published: 22 July 2024
Recent Advances
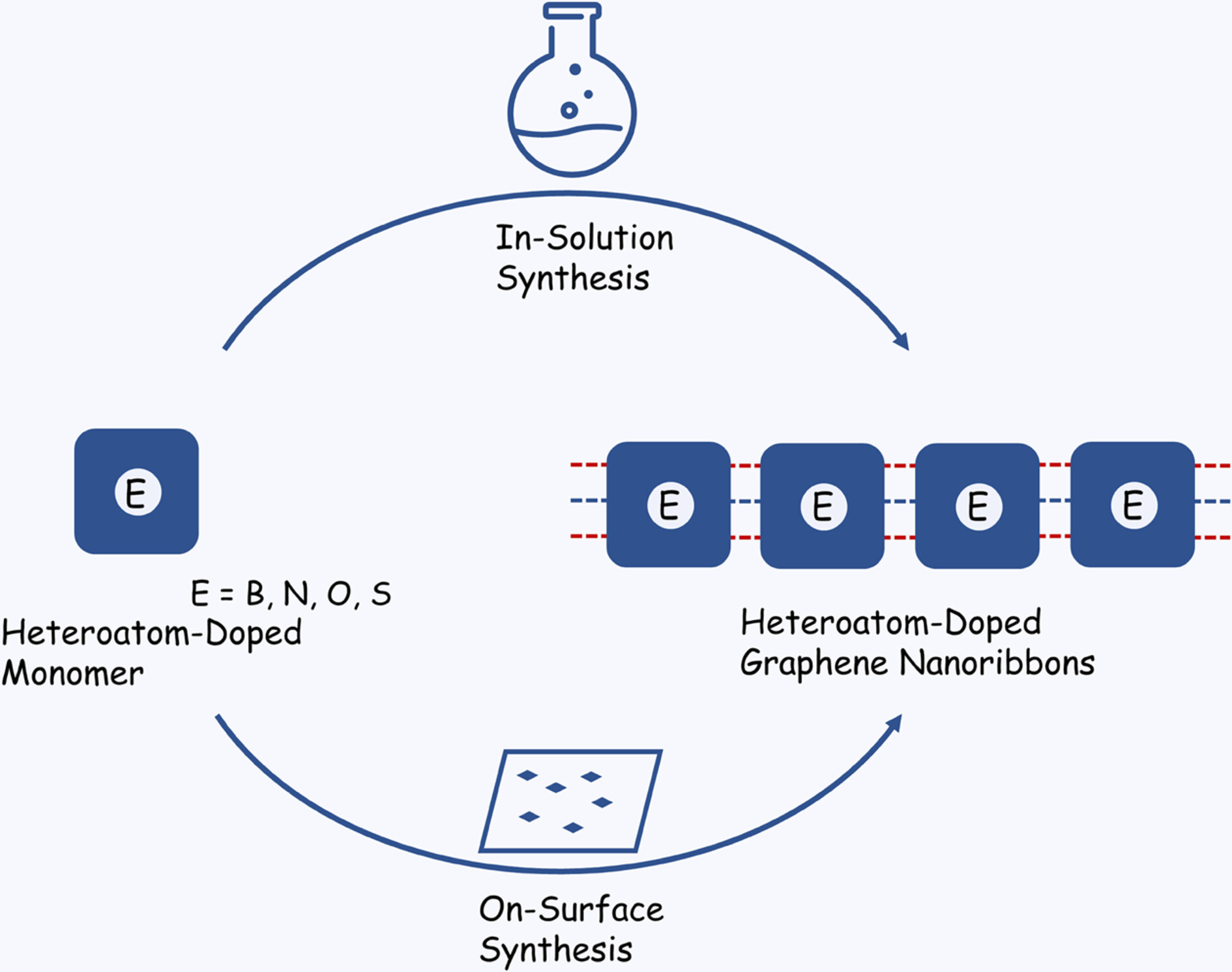
Heteroatom-Doped Graphene Nanoribbons: Precision Synthesis and Emerging Properties
- Pages: 2877-2894
- First Published: 30 July 2024
Emerging Topic
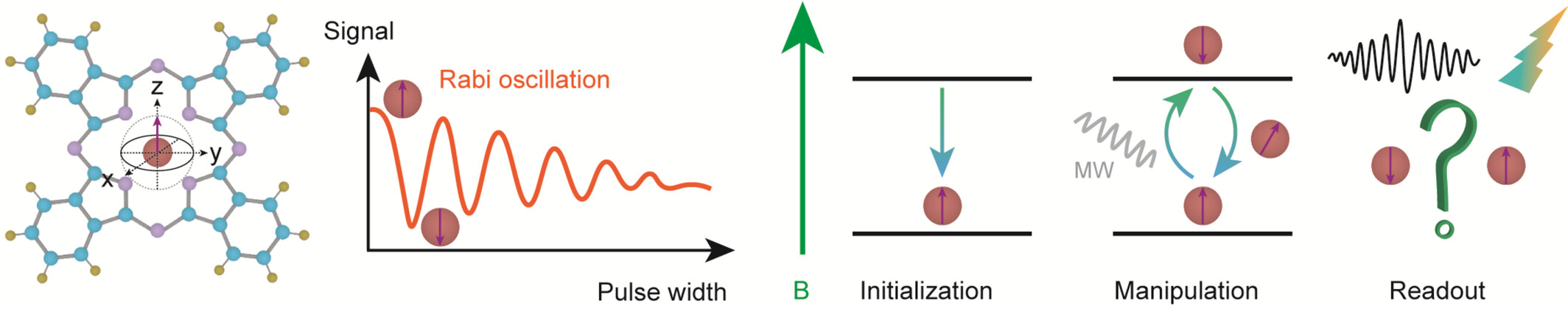
Coherent Addressing of Single Molecular Electron Spin Qubits
- Pages: 2895-2901
- First Published: 30 July 2024
Critical Review
Metal-Decorated Porous Organic Polymers: Bridged the Gap between Organic and Inorganic Scaffolds
- Pages: 2902-2934
- First Published: 08 August 2024
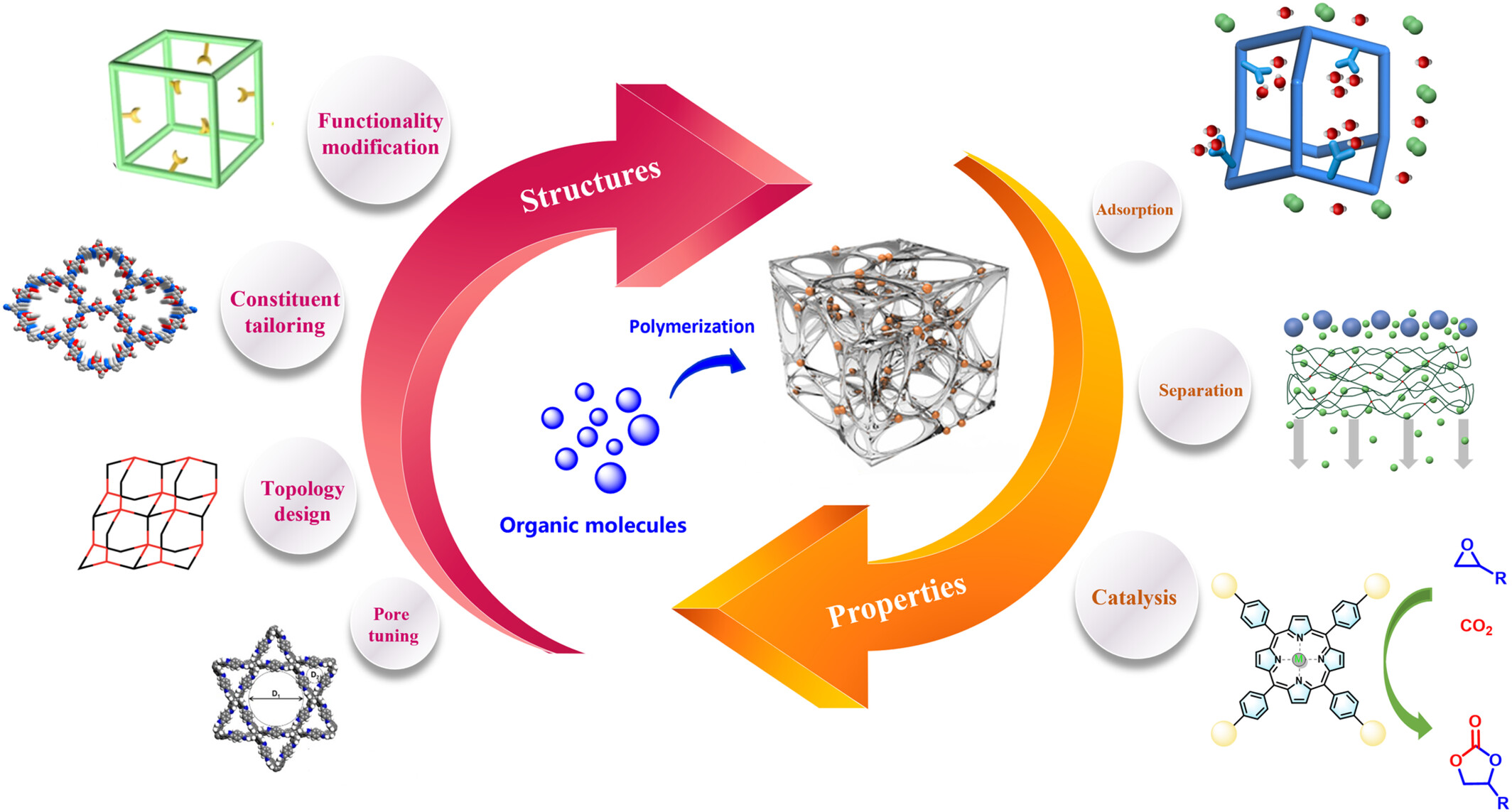
The inherent organic nature, tailored pore structures, and adjustable chemical components of POPs offer a versatile platform for the incorporation of various metal active sites. Meticulously designed molecular building blocks can serve as organic ligands uniformly distributed throughout POPs, leading to the effective isolation of inorganic metal active sites at the molecular level. In this manner, POPs containing active metal centers bridge the gap between organic and inorganic scaffolds. This review aims to provide an overview of recent research progress on metal-decorated POPs, focusing on strategies for incorporating metal active sites into POPs and their applications in adsorption, separation, catalysis, and photoelectrochemistry.
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 2939
- First Published: 15 October 2024

Simple reaction, useful chemistry. The electron donor-acceptor complex (EDA) photochemistry provides a simple and efficient platform for organic synthesis. A general EDA complex strategy formed by readily accessible thiophenolate anion and oxime ester successfully realizes the diverse synthesis of thioethers under visible light irradiation. Such a strategy could also enable a thiol-catalysis for the synthesis of phenanthridines. More details are discussed in the article by Zhong et al. on pages 2751—2756.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 2940
- First Published: 15 October 2024

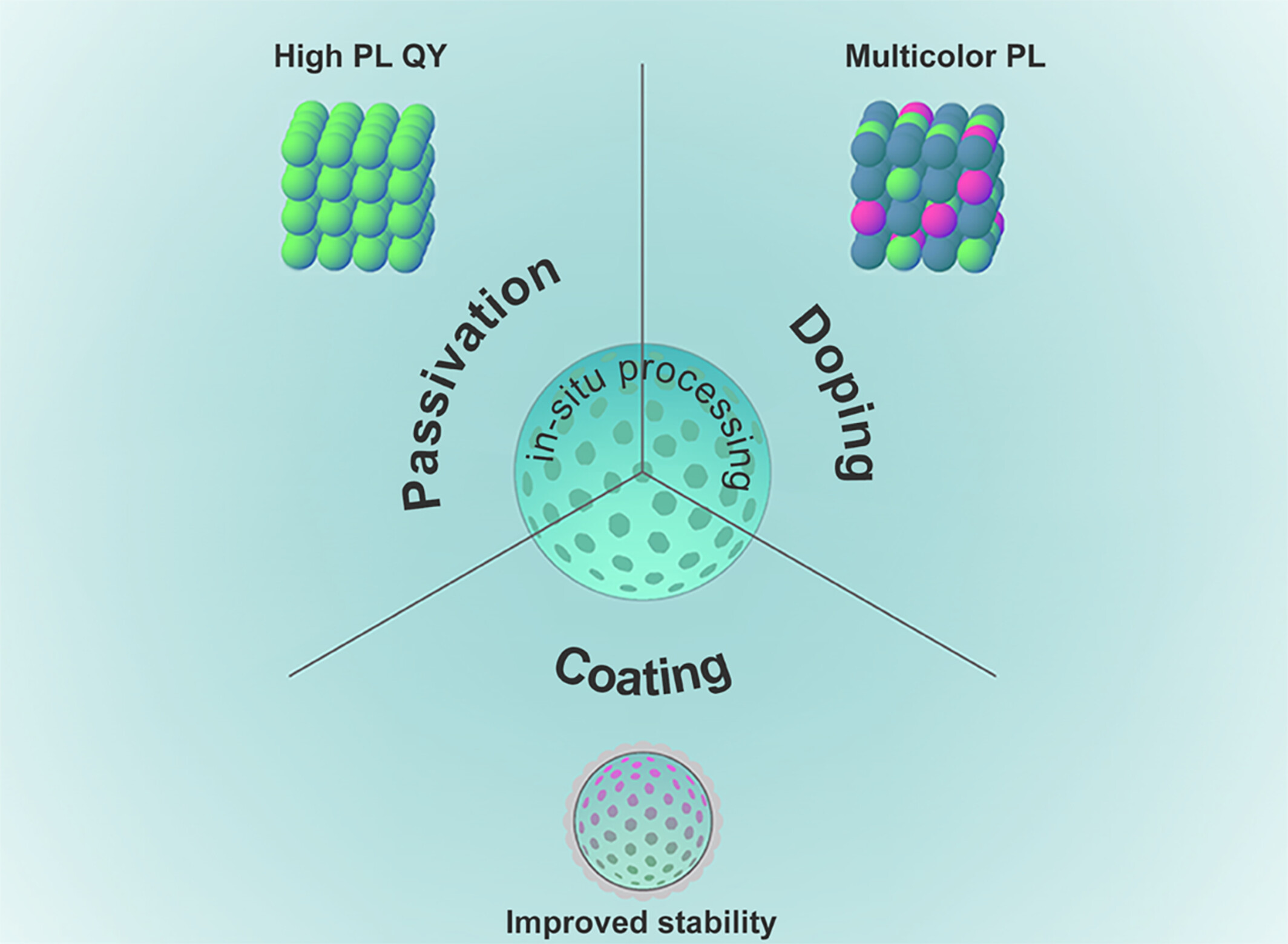
The in-situ post-synthetic treatment of CsPbBr₃ nanocrystals confined within nanoporous silica microspheres enhances their optical properties, addressing key challenges in lead halide perovskites. Surface passivation with Br⁻ ions boosts photoluminescence quantum yield, while Mn²⁺ doping introduces a new emission band, enabling precise control of optical properties. Coating with a SiO₂ shell further enhances the stability of the nanocrystals in polar solvents, expanding their potential for diverse applications. More details are discussed in the article by Huang et al. on pages 2779—2787.





![Vinylogous Fluorine Stabilizing Effect Enables Rational Design of a Novel Donor-Acceptor Cyclopropane and Its Applications in [3+2] Cycloaddition Reaction and Ring-Opening Polymerization†](/cms/asset/289c1638-71aa-4f04-a6f3-1ac7267c8eb9/cjoc202400348-toc-0001-m.jpg)